The Light Cupula Phenomenon: A Scoping Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
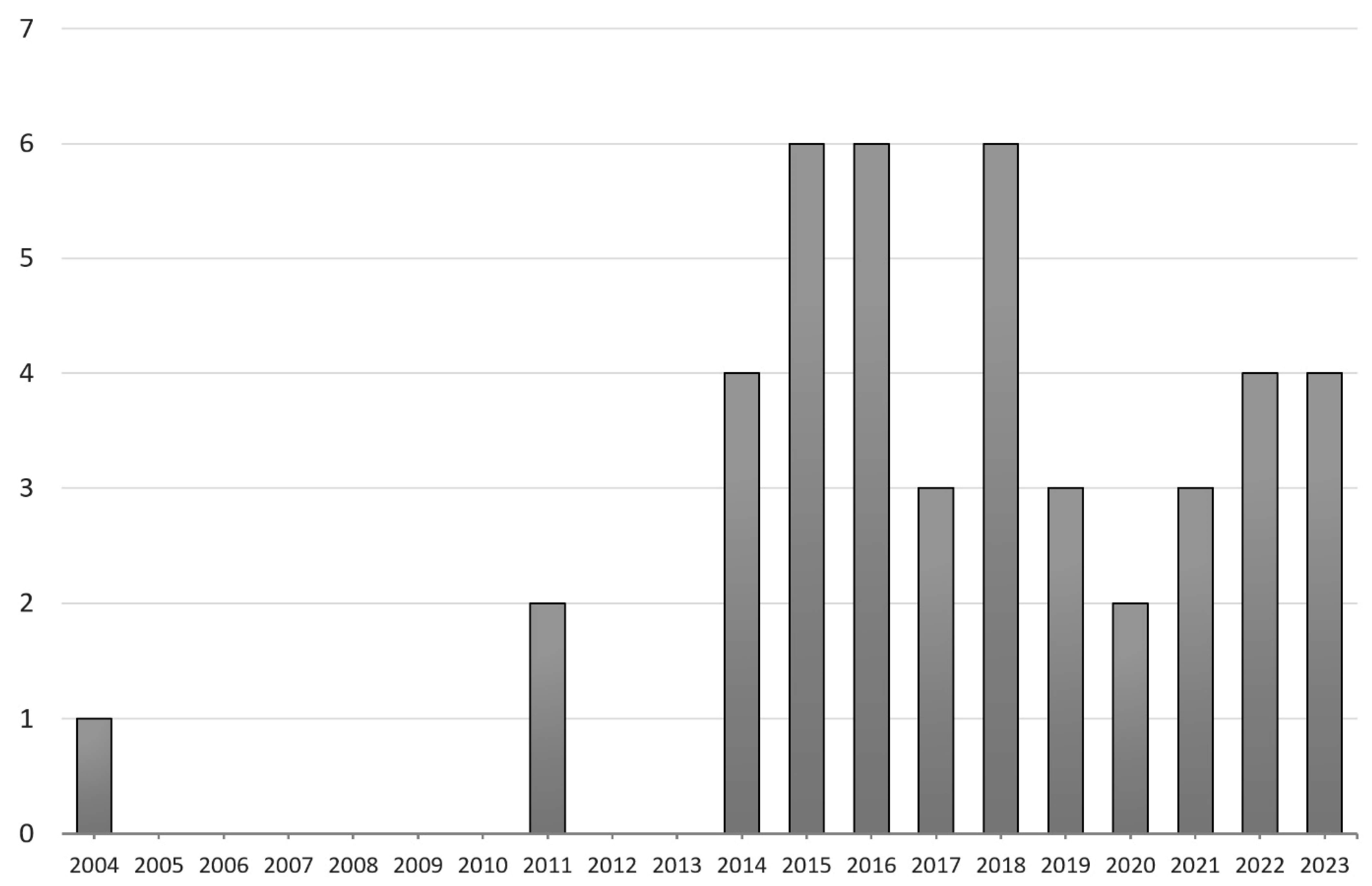
2. Methods
3. History of the Concept of Light Cupula
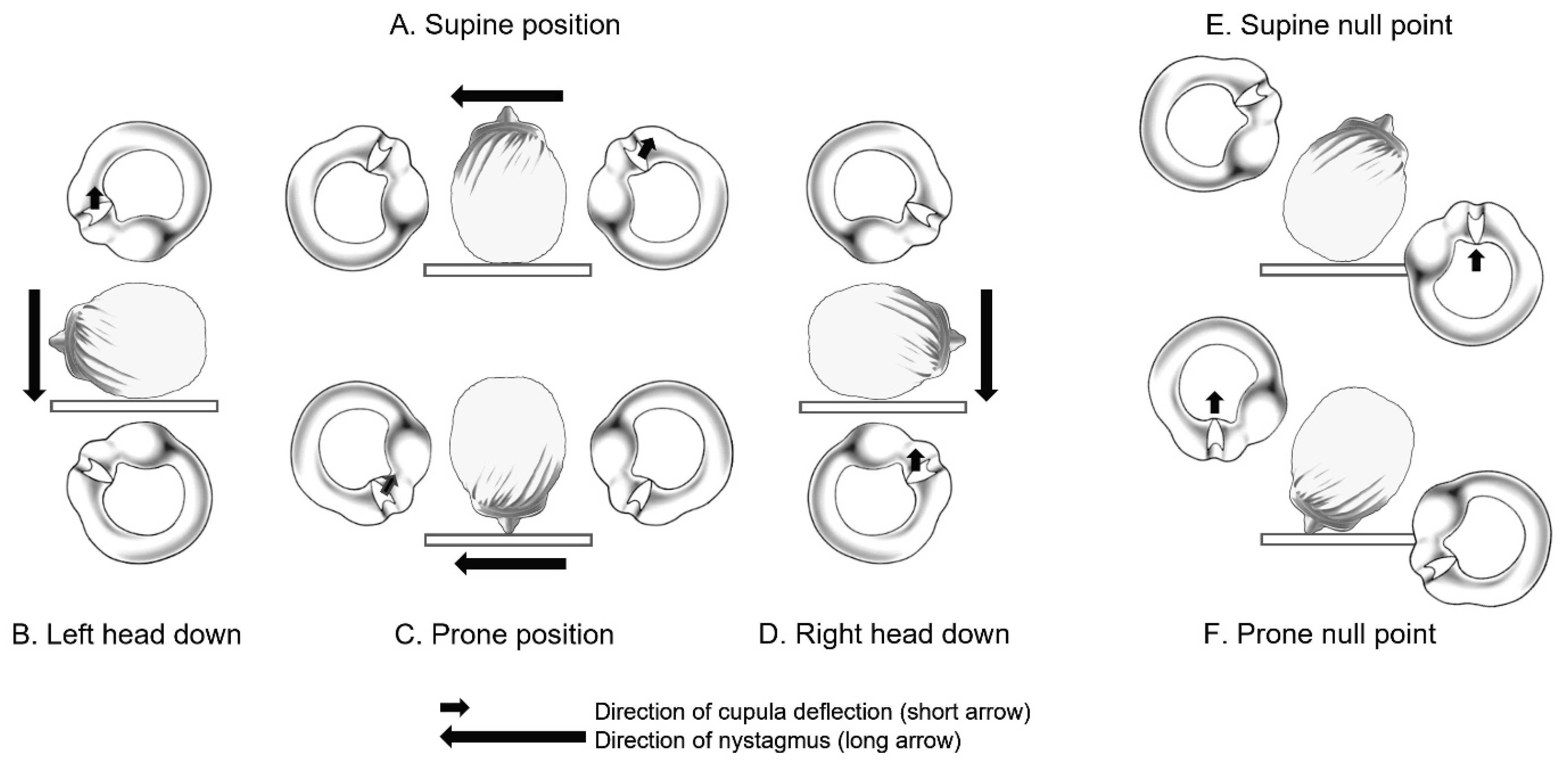
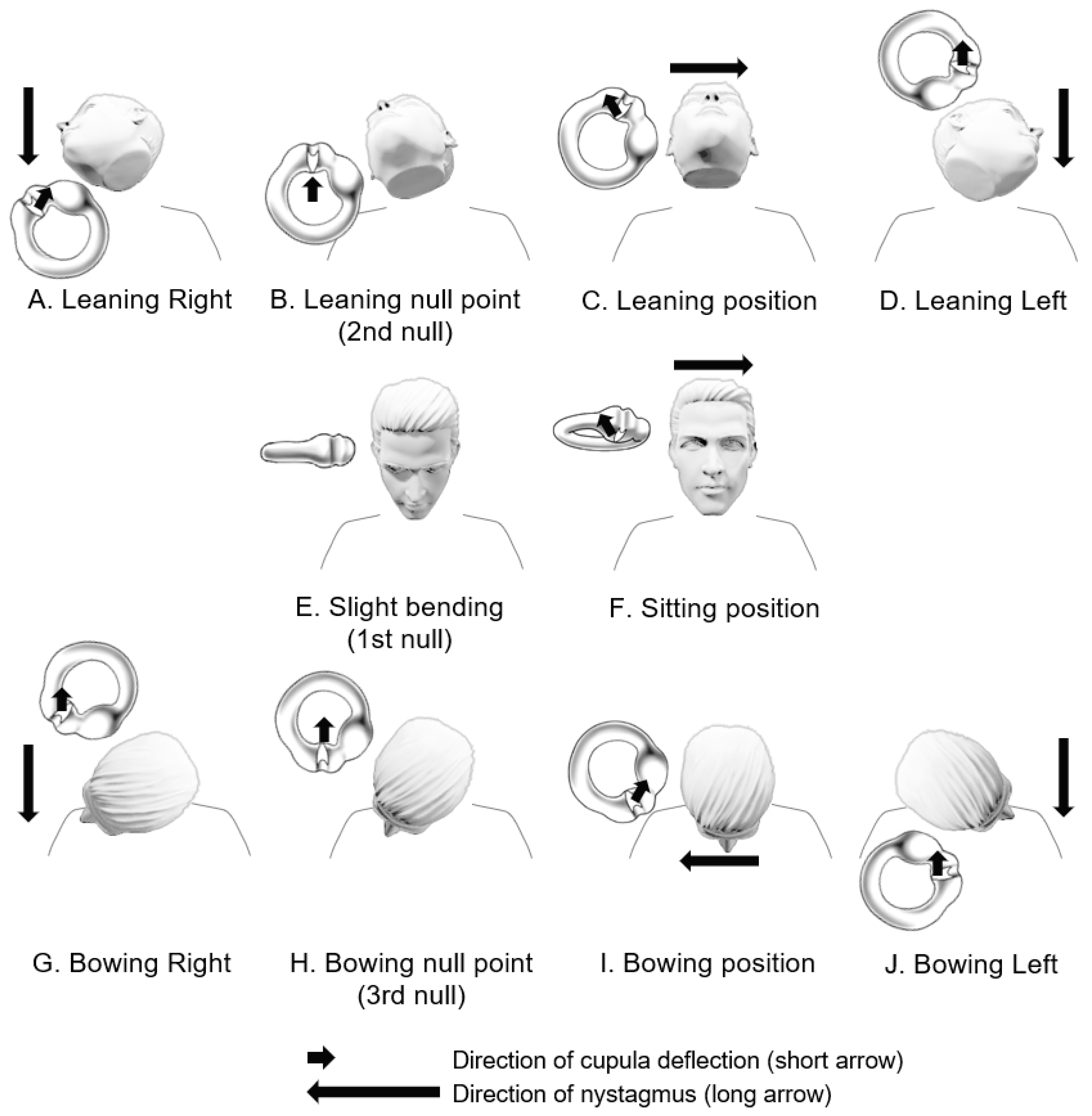
4. Clinical Features and Diagnosis of Patients with Light Cupula
5. Mechanisms
5.1. Lighter Cupula Theory
5.2. Heavier Endolymph Theory
5.3. Light Debris Theory
5.4. Utricular Macula Theory
5.5. Density Difference between Perilymph and Endolymph
6. Etiologies and Differential Diagnosis
6.1. Vestibular Migraine and Light Cupula
6.2. Central Lesions and Light Cupula
6.3. Other Inner Ear Disorders and Light Cupula
7. Treatments
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, C.H.; Kim, M.B.; Ban, J.H. Persistent geotropic direction-changing positional nystagmus with a null plane: The light cupula. Laryngoscope 2014, 124, E15–E19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Oh, S.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Kang, J.H.; Kim, D.U.; Jeong, S.H.; Choi, K.D.; Moon, I.S.; Kim, B.K.; Oh, H.J.; et al. Randomized clinical trial for apogeotropic horizontal canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Neurology 2012, 78, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschan, G.; Bergstedt, M.; Goldberg, L.; Laurell, L. Positional nystagmus in man during and after alcohol intoxication. Q. J. Stud. Alcohol 1956, 17, 381–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Money, K.E.; Johnson, W.H.; Corlett, B.M. Role of Semicircular Canals in Positional Alcohol Nystagmus. Am. J. Physiol. 1965, 208, 1065–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Money, K.E.; Myles, W.S. Heavy water nystagmus and effects of alcohol. Nature 1974, 247, 404–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigeno, K.; Oku, R.; Takahashi, H.; Kumagami, H.; Nakashima, S. Static direction-changing horizontal positional nystagmus of peripheral origin. J. Vestib. Res. Equilib. Orientat. 2001, 11, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hiruma, K.; Numata, T. Positional nystagmus showing neutral points. ORL J. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. Relat. Spec. 2004, 66, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H.; Shin, J.E.; Kim, Y.W. A new method for evaluating lateral semicircular canal cupulopathy. Laryngoscope 2015, 125, 1921–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichijo, H. Neutral position of persistent direction-changing positional nystagmus. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2016, 273, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Wang, L.; Song, H.; Gao, B.; Yang, Y.; Lyu, F. Clinical Characteristics of persistent geotropic horizontal direction-changing positional nystagmus: Experience in 189 participants. J. Vestib. Res. Equilib. Orientat. 2023, 33, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergenius, J.; Tomanovic, T. Persistent geotropic nystagmus--a different kind of cupular pathology and its localizing signs. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2006, 126, 698–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomanovic, T.; Bergenius, J. Can the nystagmus pattern in patients with a ‘light cupula’ be reproduced in hemi-labyrinthectomized subjects during positional alcohol nystagmus 1? Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2011, 131, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curthoys, I.S.; Oman, C.M. Dimensions of the horizontal semicircular duct, ampulla and utricle in the human. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 1987, 103, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiruma, K.; Numata, T.; Mitsuhashi, T.; Tomemori, T.; Watanabe, R.; Okamoto, Y. Two types of direction-changing positional nystagmus with neutral points. Auris Nasus Larynx 2011, 38, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, M.B. Effect of intratympanic steroid injection in light cupula. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2018, 138, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, J.H.; Kim, M.B.; Hong, S.M. Immediate and Short-Term Therapeutic Results Between Direction-Changing Positional Nystagmus with Short- and Long-Duration Groups. Ear Hear. 2016, 37, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H.; Hong, S.M. Is the modified cupulolith repositioning maneuver effective for treatment of persistent geotropic direction-changing positional nystagmus? Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2018, 275, 1731–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, D.B.; Ko, K.M.; Lee, J.H.; Park, H.J.; Song, M.H. Natural history of horizontal canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo is truly short. J. Neurol. 2015, 262, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.M.; Kim, S.K.; Park, I.S.; Shim, M.G. Pseudo-spontaneous nystagmus in patients with geotropic direction-changing positional nystagmus. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, N.; Gubbels, S.P.; Schwartz, S.R.; Edlow, J.A.; El-Kashlan, H.; Fife, T.; Holmberg, J.M.; Mahoney, K.; Hollingsworth, D.B.; Roberts, R.; et al. Clinical Practice Guideline: Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (Update). Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2017, 156, S1–S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogun, O.A.; Büki, B.; Cohn, E.S.; Janky, K.L.; Lundberg, Y.W. Menopause and benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Menopause 2014, 21, 886–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, T.; Matsuda, K.; Takeda, N.; Uno, A.; Kitahara, T.; Horii, A.; Nishiike, S.; Inohara, H. Light cupula: The pathophysiological basis of persistent geotropic positional nystagmus. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e006607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Huang, Q.; Chen, L.; Liu, P.; Feng, T.; Ou, Y.; Zheng, Y. Clinical Findings in Patients With Persistent Positional Nystagmus: The Designation of “Heavy and Light Cupula”. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigeno, K.; Egami, T.; Sasano, T. Experimental study of nystagmus induced by injecting various solutions into the middle ear cavity. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 1989, 108, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, T.; Saito, K.; Doi, K. Intractable persistent direction-changing geotropic nystagmus improved by lateral semicircular canal plugging. Case Rep. Otolaryngol. 2015, 2015, 192764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H.; Choi, J.M.; Jung, H.V.; Park, H.J.; Shin, J.E. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss with simultaneous positional vertigo showing persistent geotropic direction-changing positional nystagmus. Otol. Neurotol. 2014, 35, 1626–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H.; Shin, J.E.; Yang, Y.S.; Im, D. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss with positional vertigo: Initial findings of positional nystagmus and hearing outcomes. Int. J. Audiol. 2016, 55, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.W.; Shin, J.E.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, C.H. Persistent Positional Vertigo in a Patient with Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: A Case Report. J. Audiol. Otol. 2015, 19, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.E.; Jeong, K.H.; Ahn, S.H.; Kim, C.H. Conversion between geotropic and apogeotropic persistent direction-changing positional nystagmus. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2015, 135, 1238–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.Y.; Lee, E.S.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.S. Persistent geotropic positional nystagmus after meningitis: Evidence for light cupula. J. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 379, 279–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H.; Shin, J.E.; Shin, D.H.; Kim, Y.W.; Ban, J.H. “Light cupula” involving all three semicircular canals: A frequently misdiagnosed disorder. Med. Hypotheses 2014, 83, 541–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schubert, M.C.; Dunlap, P.M.; Whitney, S.L. A Case Study of High-Velocity, Persistent Geotropic Nystagmus: Is This BPPV? J. Neurol. Phys. Ther. 2017, 41, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichijo, H. Persistent direction-changing geotropic positional nystagmus. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2012, 269, 747–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichijo, H. Persistent Type of Geotropic Direction-changing Positional Nystagmus. Equilib. Res. 2006, 65, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tomanovic, T.; Bergenius, J. Vestibular findings in patients with persistent geotropic positional nystagmus: The ‘light cupula’ phenomenon. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2014, 134, 904–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichijo, H.; Teramoto, H. Eye Movements Induced by Stimulation to the Otolith Organs. Int. J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2023, 12, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H.; Pham, N.C. Density difference between perilymph and endolymph: A new hypothesis for light cupula phenomenon. Med. Hypotheses 2019, 123, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Brevern, M.; Radtke, A.; Clarke, A.H.; Lempert, T. Migrainous vertigo presenting as episodic positional vertigo. Neurology 2004, 62, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polensek, S.H.; Tusa, R.J. Nystagmus during attacks of vestibular migraine: An aid in diagnosis. Audiol. Neuro-Otol. 2010, 15, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechner, C.; Taylor, R.L.; Todd, C.; Macdougall, H.; Yavor, R.; Halmagyi, G.M.; Welgampola, M.S. Causes and characteristics of horizontal positional nystagmus. J. Neurol. 2014, 261, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radtke, A.; von Brevern, M.; Neuhauser, H.; Hottenrott, T.; Lempert, T. Vestibular migraine: Long-term follow-up of clinical symptoms and vestibulo-cochlear findings. Neurology 2012, 79, 1607–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, E.; Li, F.; Liu, D.; Wang, J.; Guo, Z.; Chen, J.; Guo, J.; Zhang, S. Dispelling Mist That Obscures Positional Vertigo in Vestibular Migraine. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.L.; Tian, E.; Xu, W.C.; Zhu, Y.T.; Kong, W.J. Light Cupula: To Be Or Not to Be? Curr. Med. Sci. 2020, 40, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Kim, E.S.; Kim, M.; Chu, H.; Ma, H.I.; Lee, J.S.; Koo, J.W.; Kim, H.J.; Hong, S.K. Isolated horizontal positional nystagmus from a posterior fossa lesion. Ann. Neurol. 2014, 76, 905–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.H.; Oh, S.Y. Geotropic central paroxysmal positional nystagmus in a patient with human immunodeficiency virus encephalopathy. J. Neuro-Ophthalmol. 2014, 34, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.Y.; Jang, J.Y.; Oh, E.H.; Choi, J.H.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Choi, K.D. Persistent geotropic positional nystagmus in unilateral cerebellar lesions. Neurology 2018, 91, e1053–e1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschan, G.; Stahle, J. Nystagmus in Menière’s disease during attacks; a nystagmographical study. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 1957, 47, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H.; Yang, Y.S.; Im, D.; Shin, J.E. Nystagmus in patients with unilateral acute otitis media complicated by serous labyrinthitis. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2016, 136, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H.; Choi, J.W.; Han, K.J.; Lee, Y.S.; Shin, J.E. Direction-fixed and Direction-changing Positional Nystagmus in Ramsay Hunt Syndrome. Otol. Neurotol. 2018, 39, e209–e213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Jo, S.W.; Chung, W.K.; Byeon, H.K.; Lee, W.S. A cupulolith repositioning maneuver in the treatment of horizontal canal cupulolithiasis. Auris Nasus Larynx 2012, 39, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, W.W.; Song, K.; Lee, H.Y. Persistent Geotropic Direction-Changing Positional Nystagmus Treated With Transcutaneous Vagus Nerve Stimulation. Brain Stimul. 2016, 9, 469–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| HC Canalolithiasis (Posterior Arm) | HC Canalolithiasis (Anterior Arm) | HC Cupulolithiasis (Heavy Cupula) | Light Cupula | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DCPN | Geotropic | Apogeotropic | Apogeotropic | Geotropic |
| Duration | Transient | Transient | Persistent | Persistent |
| Latency | + | + | - | - |
| Fatigability | + | + | - | - |
| Null plane | - | - | + | + |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, D.-H.; Kim, T.H.; Jang, M.; Kim, C.-H. The Light Cupula Phenomenon: A Scoping Review. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14010015
Lee D-H, Kim TH, Jang M, Kim C-H. The Light Cupula Phenomenon: A Scoping Review. Brain Sciences. 2024; 14(1):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14010015
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Dong-Han, Tae Hee Kim, Minho Jang, and Chang-Hee Kim. 2024. "The Light Cupula Phenomenon: A Scoping Review" Brain Sciences 14, no. 1: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14010015
APA StyleLee, D.-H., Kim, T. H., Jang, M., & Kim, C.-H. (2024). The Light Cupula Phenomenon: A Scoping Review. Brain Sciences, 14(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14010015





