Transfusion with Blood Plasma from Young Mice Affects rTg4510 Transgenic Tau Mice Modeling of Alzheimer’s Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Breeding and Housing
2.2. Donor Animals and Blood Collection
2.3. Blood Plasma
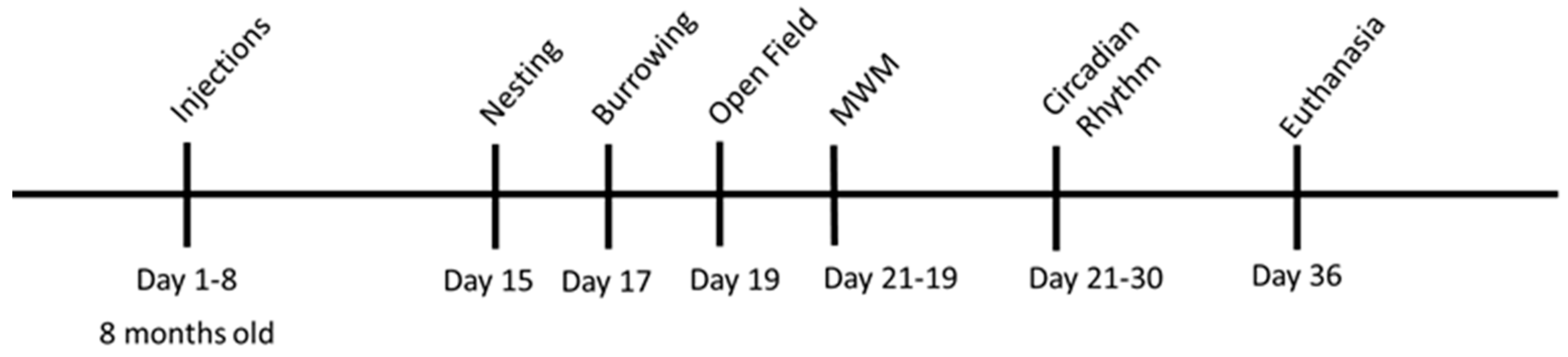
2.4. Experimental Animals
2.5. Behavioral Tests
2.5.1. Nesting
2.5.2. Burrowing
2.5.3. Open Field
2.5.4. Morris Water Maze
2.5.5. Circadian Rhythm
2.6. Brain Analysis
2.6.1. Western Blot Analyses for Protein Expression
2.6.2. Thioflavin-S for Tau Tangle Staining
2.7. Statistical Testing
2.7.1. Morris Water Maze
2.7.2. Circadian Rhythm
2.7.3. Western Blot
2.7.4. Thioflavin-S
3. Results
3.1. Brain Analysis
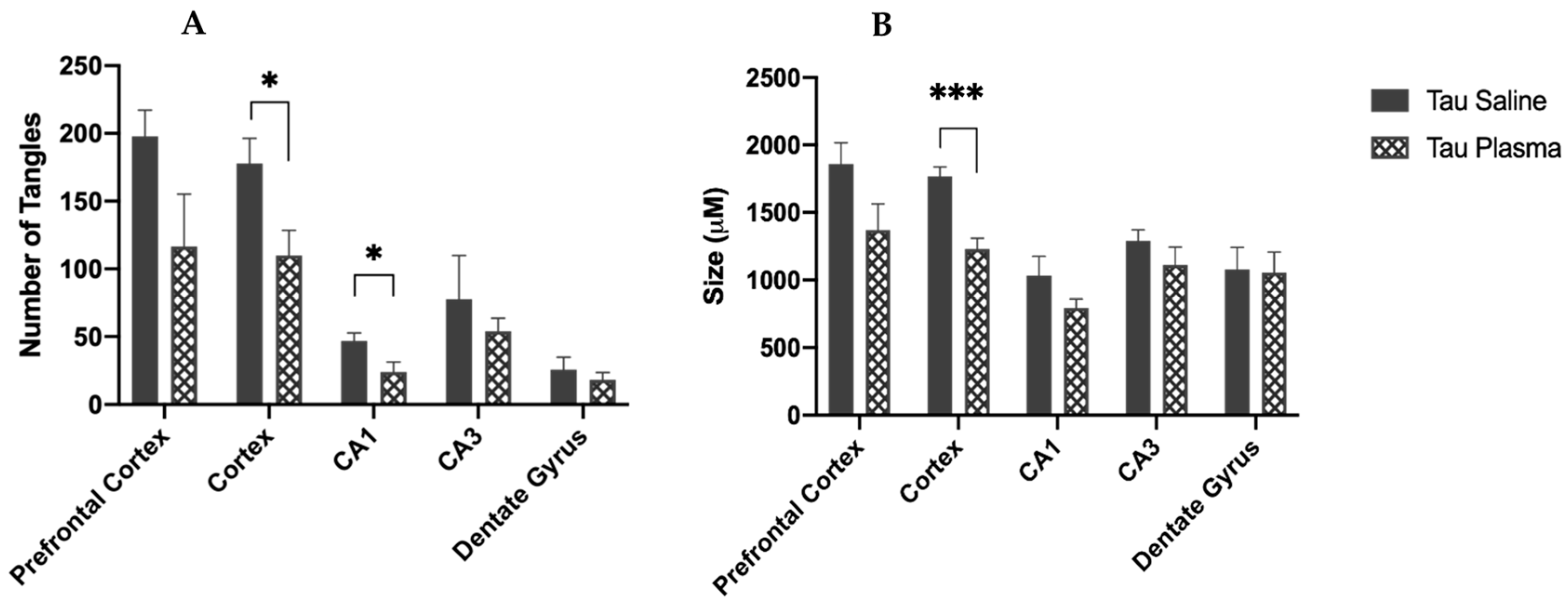
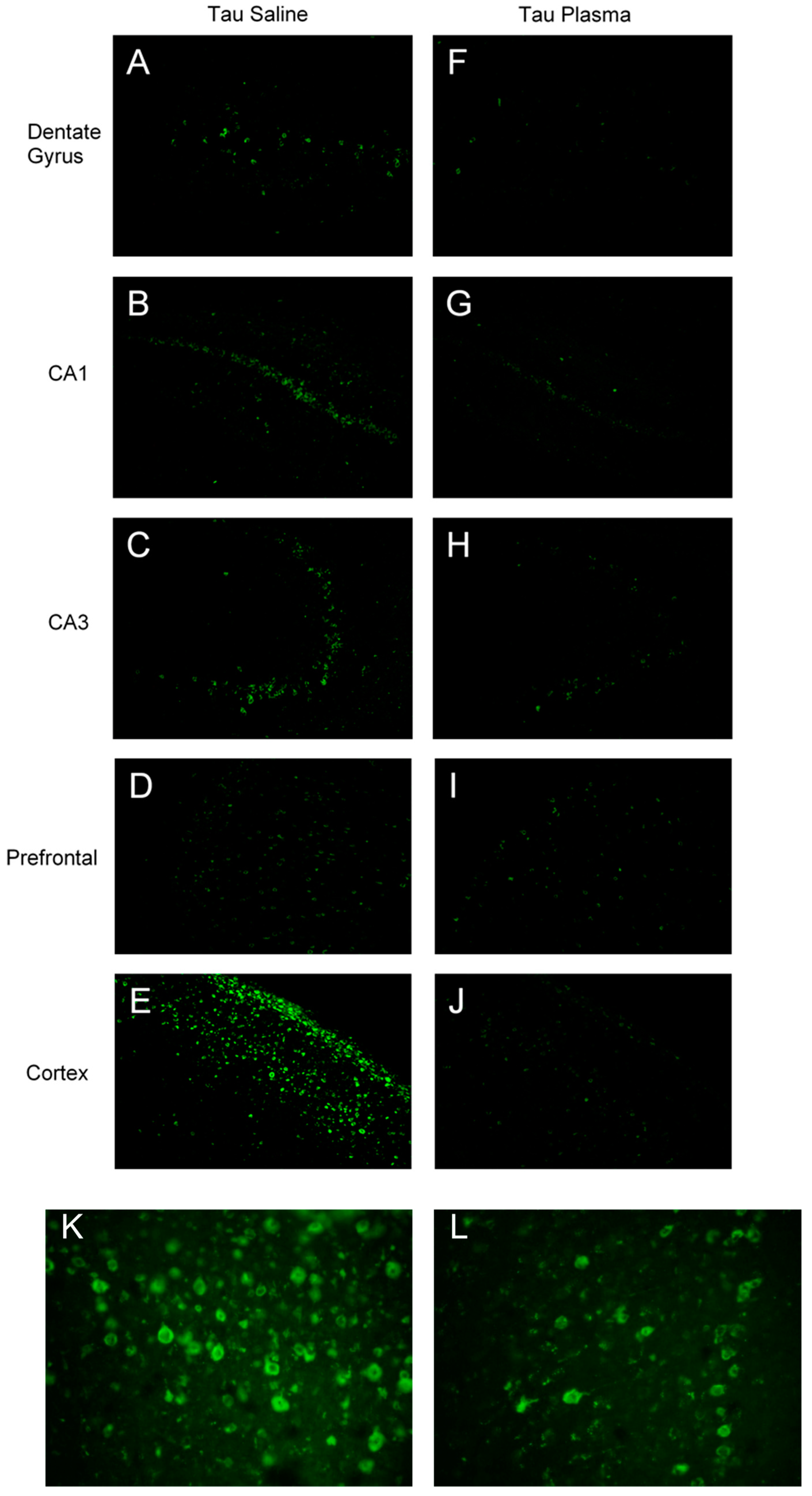
3.1.1. Thioflavin-S in Tangles
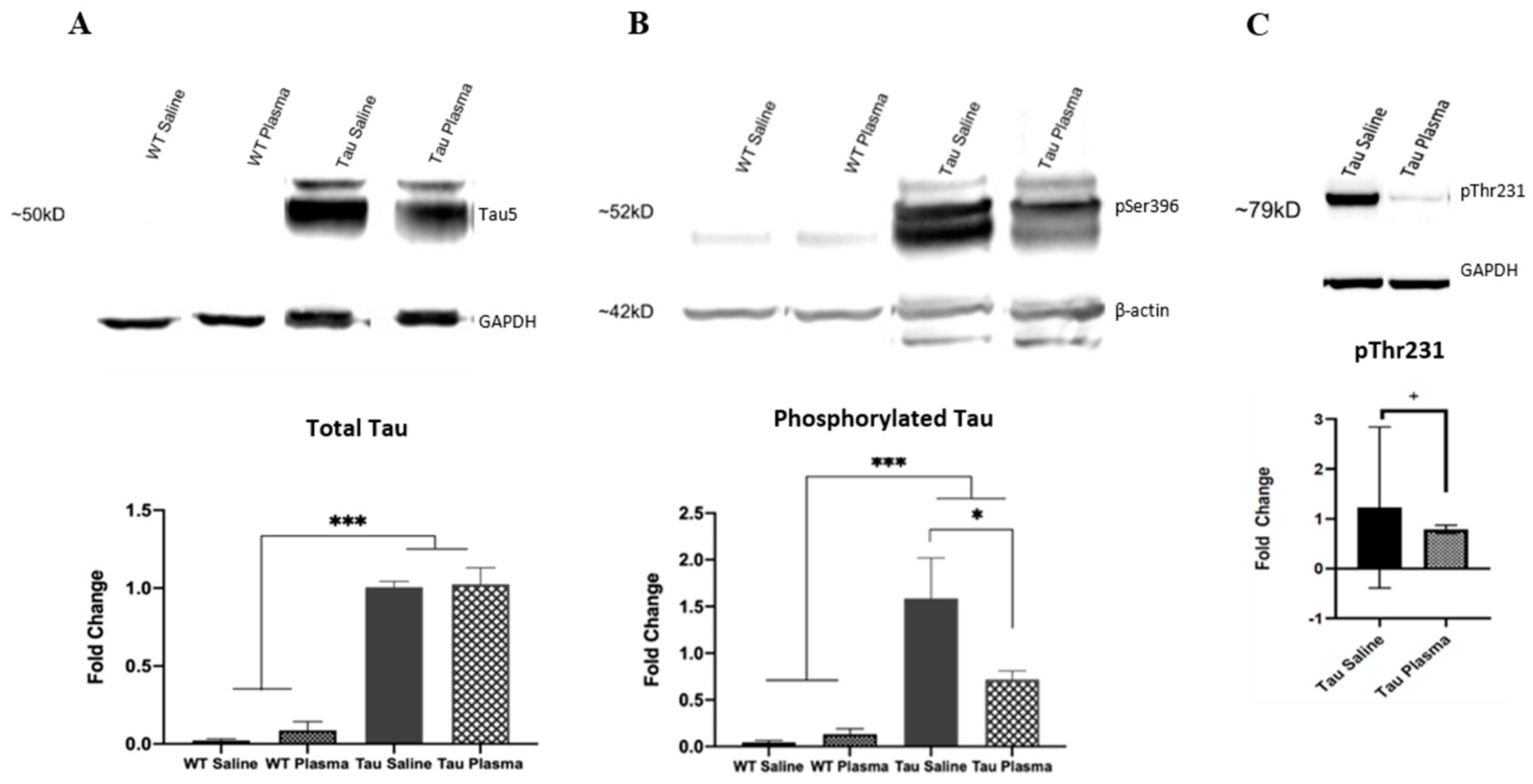
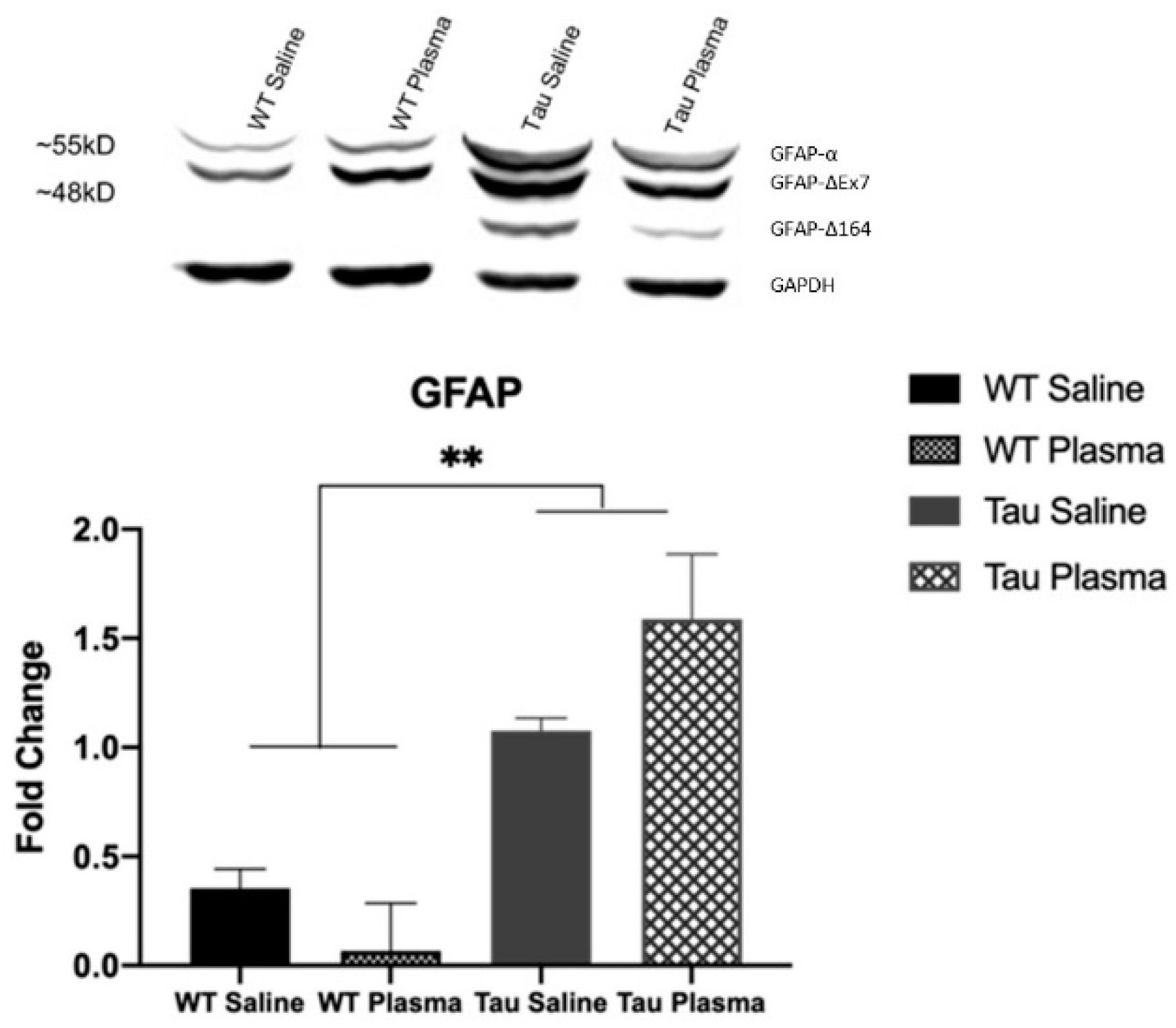
3.1.2. Western Blot
- (i)
- Total Tau
- (ii)
- Phosphorylated Tau
- (iii)
- GFAP
3.2. Behavioral Analysis
3.2.1. Nesting
3.2.2. Burrowing
3.2.3. Open Field
- (i)
- Time spent in the surrounding area
- (ii)
- Distance Traveled
- (iii)
- Velocity
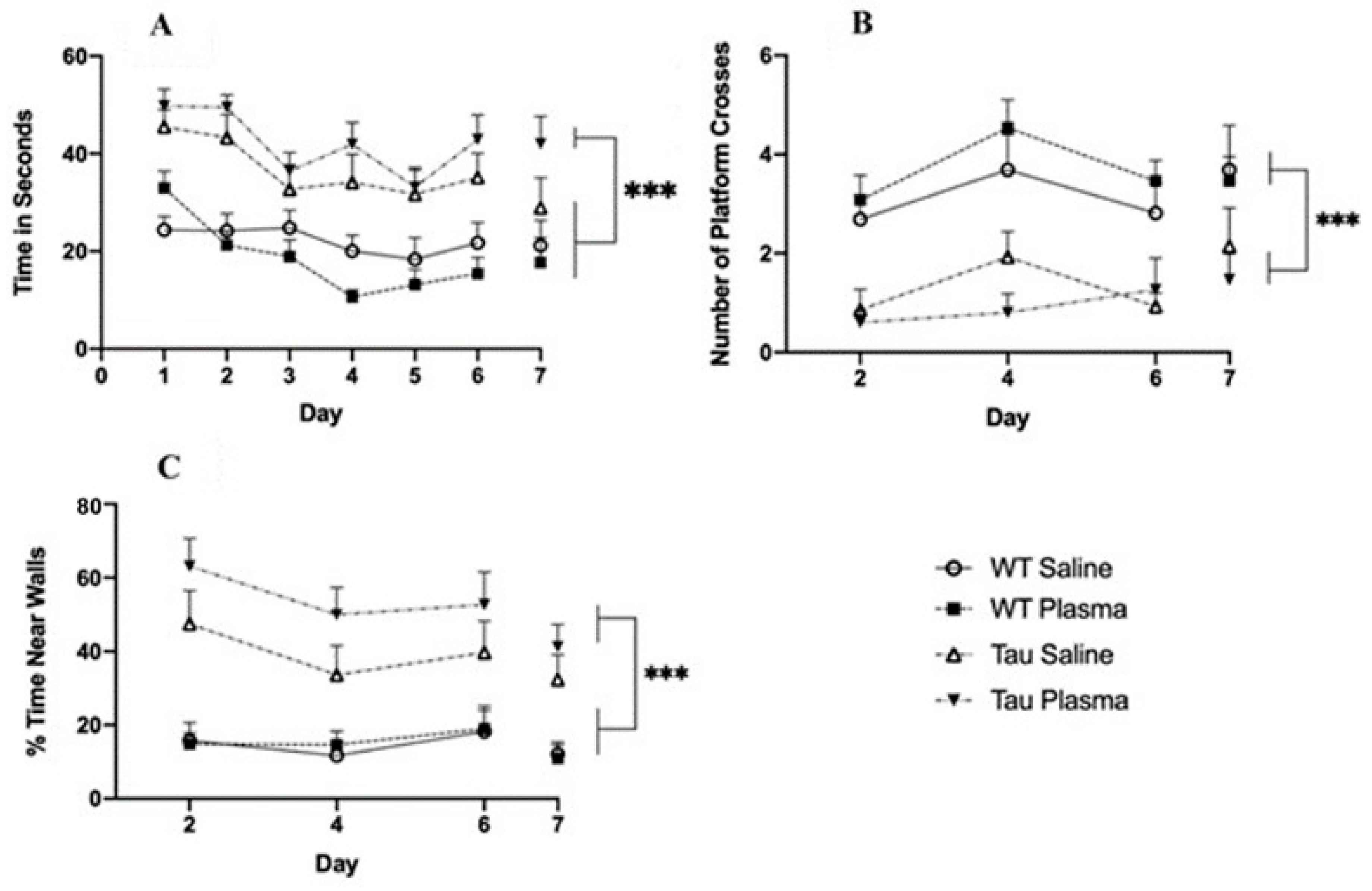
3.2.4. Morris Water Maze
- (i)
- Latency to Platform
- (ii)
- Target Quadrant
- (iii)
- Platform Crosses
- (iv)
- Thigmotaxicity
- (v)
- Swim Speed
3.2.5. Circadian Rhythm
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reddy, P.H.; Reddy, T. Mitochondria as a therapeutic target for aging and neurodegenerative diseases. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2011, 8, 393–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, V.M.; Goedert, M.; Trojanowski, J.Q. Neurodegenarative tauopathies. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 24, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, I.; Iqbal, K.; Tung, Y.; Quinlan, M.; Wisniewski, H.M.; Binder, L.I. Abnormal phosphorylation of the microtubule-associated protein tau in Alzheimer cytoskeleton pathology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 4413–4917. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, S.; Haque, M.; Kim, D.; Kim, D.J.; Kim, Y.K. Cell-based models to investigate tau aggregation. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2014, 12, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinsky, J.; Pichlerova, K.; Hanes, J. Tau protein interaction partners and their roles in Alzheimer’s disease and other tauopathies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Yan, H.; Na Tang, N.; Li, X.; Pang, P.; Li, H.; Chen, W.; Guo, Y.; Shu, S.; Cai, Y.; et al. Impairments of spatial memory in an Alzheimer’s disease model via degeneration of hippocampal cholinergic synapses. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furcila, D.; DeFelipe, J.; Alonso-Nanclares, L. A Study of Amyloid-β and Phosphotau in Plaques and Neurons in the Hippocampus of Alzheimer’s Disease Patients. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 64, 417–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, P.; Sehar, U.; Bisht, J.; Selman, A.; Culberson, J.; Reddy, P.H. Phosphorylated Tau in Alzheimer’s Disease and Other Tauopathies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agatonovic-Kustrin, S.; Kettle, C.; Morton, D.W. A molecular approach in drug development for Alzheimer’s disease. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 553–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyss-Coray, T. Ageing, neurodegeneration and brain rejuvenation. Nature 2016, 539, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villeda, S.; Plambeck, K.; Middeldorp, J. Young blood reverses age-related impairments in cognitive function and synaptic plasticity in mice. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 659–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middeldorp, J.; Lehallier, B.; Villeda, S.A. Preclinical assessment of young blood plasma for Alzheimer’s disease. JAMA Neurol. 2016, 73, 1325–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsden, M.; Kotilinek, L.; Forster, C.; Paulson, J.; McGowan, E.; SantaCruz, K.; Guimaraes, A.; Yue, M.; Lewis, J.; Carlson, G.; et al. Age-dependent neurofibrillary tangle formation, neuron loss, and memory impairment in a mouse model of human tauopathy (P301L). J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 10637–10647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helboe, L.; Egebjerg, J.; Barkholt, P.; Volbracht, C. Early depletion of CA1 neurons and late neurodegeneration in a mouse tauopathy model. Brain Res. 2017, 1665, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santacruz, K.; Lewis, J.; Spires, T.; Paulson, J.; Kotilinek, L.; Ingelsson, M.; Guimaraes, A.; DeTure, M.; Ramsden, M.; McGowan, E.; et al. Tau suppression in a neurodegenerative mouse model improves memory function. Science 2005, 309, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopeikina, K.; Hyman, B.; Spires-Jones, T. Soluble forms of tau are toxic in Alzheimer’s disease. Transl. Neurosci. 2012, 3, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neely, C.L.; Pedemonte, K.A.; Boggs, K.N.; Flinn, J.M. Nest Building Behavior as an Early Indicator of Behavioral Deficits in Mice. J. Vis. Exp. 2019, 152, e60139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craven, K.M.; Kochen, W.R.; Hernandez, C.M.; Flinn, J.M. Zinc exacerbates tau pathology in a tau mouse model. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 64, 617–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippi, S.L.P.; Smith, M.L.; Flinn, J.M. A Novel hAPP/htau Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease: Inclusion of APP with Tau Exacerbates Behavioral Deficits and Zinc Administration Heightens Tangle Pathology. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elie, A.; Prezel, E.; Guérin, C.; Denarier, E.; Ramirez-Rios, S.; Serre, L.; Andrieux, A.; Fourest-Lieuvin, A.; Blanchoin, L.; Arnal, I. Tau co-organizes dynamic microtubule and actin networks. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulga, T.A.; Elson-Schwab, I.; Khurana, V.; Steinhilb, M.L.; Spires-Jones, T.; Hyman, B.T.; Feany, M. Abnormal bundling and accumulation of F-actin mediates tau-induced neuronal degeneration in vivo. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’abramo, C.; Acker, C.M.; Jimenez, H.; Davies, P. Passive Immunization in JNPL3 Transgenic Mice Using an Array of Phospho-Tau Specific Antibodies. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedemonte; Karin, A. The Effects of Young Blood Plasma Transfusions on Older hTau Mice Modeling Alzheimer’s Disease. Ph.D. Dissertation, George Mason University, Fairfax, VA, USA, 2021. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/1920/13223 (accessed on 13 July 2022).
- Musiek, E.S.; Xiong, D.D.; Holtzman, D.M. Sleep, circadian rhythms, and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer disease. Exp. Mol. Med. 2015, 47, e148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Qian, R.; Zhang, J.; Liu, F.; Iqbal, K.; Dai, C.-L.; Gong, C.-X. Young blood plasma reduces Alzheimer’s disease-like brain pathologies and ameliorates cognitive impairment in 3×Tg-AD mice. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2020, 12, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamache, J.; Benzow, K.; Forster, C.; Kemper, L.; Hlynialuk, C.; Furrow, E.; Ashe, K.H.; Koob, M.D. Factors other than hTau overexpression that contribute to tauopathy-like phenotype in rTg4510 mice. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horowitz, A.M.; Villeda, S.A. Therapeutic potential of systemic brain rejuvenation strategies for neurodegenerative disease. F1000Research 2017, 6, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsimpardi, L.; Litterman, N.K.; Schein, P.A.; Miller, C.M.; Loffredo, F.S.; Wojtkiewicz, G.R.; Chen, J.W.; Lee, R.T.; Wagers, A.J.; Rubin, L.L. Vascular and Neurogenic Rejuvenation of the Aging Mouse Brain by Young Systemic Factors. Science 2014, 344, 630–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noël, A.; Poitras, I.; Julien, J.; Petry, F.R.; Morin, F.; Charron, J.; Planel, E. ERK (MAPK) does not phosphorylate tau under physiological conditions in vivo or in vitro. Neurobiol. Aging 2015, 36, 901–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siano, G.; Caiazza, M.C.; Ollà, I.; Varisco, M.; Madaro, G.; Quercioli, V.; Calvello, M.; Cattaneo, A.; Di Primio, C. Identification of an ERK Inhibitor as a Therapeutic Drug Against Tau Aggregation in a New Cell-Based Assay. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finch, C.E. Neurons, glia, and plasticity in normal brain aging. Neurobiol. Aging 2003, 24 (Suppl. 1), S123–S127, discussion S131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofroniew, M.V. Astrogliosis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 7, a020420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamphuis, W.; Mamber, C.; Moeton, M.; Kooijman, L.; Sluijs, J.A.; Jansen, A.H.P.; Verveer, M.; de Groot, L.R.; Smith, V.D.; Rangarajan, S.; et al. GFAP isoforms in adult mouse brain with a focus on neurogenic astrocytes and reactive astrogliosis in mouse models of Alzheimer disease. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hol, E.M.; Roelofs, R.F.; Moraal, E.; Sonnemans, M.A.F.; Sluijs, J.A.; Proper, E.A.; de Graan, P.N.E.; Fischer, D.F.; van Leeuwen, F.W. Neuronal expression of GFAP in patients with Alzheimer pathology and identification of novel GFAP splice forms. Mol. Psychiatry 2003, 8, 786–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Tau | WT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | Male | Female | |
| Plasma | 9 | 6 | 7 | 6 |
| Total | 15 | 13 | ||
| Saline | 7 | 7 | 11 | 5 |
| Total | 14 | 16 | ||
| Day | Number of Trials | Platform Location |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1, 2, 3 | Stationary and submerged * |
| 2 | 1, 2, 3 (Probe) | 1 and 2: Stationary and submerged; 3: Atlantis ** |
| 3 | 1, 2, 3 | Stationary and submerged |
| 4 | 1, 2, 3 (Probe) | 1 and 2: Stationary and submerged; 3: Atlantis |
| 5 | 1, 2, 3 | Stationary and submerged |
| 6 | 1, 2, 3 (Probe) | 1 and 2: Stationary and submerged; 3: Atlantis |
| 7 | 1 (Probe) | Atlantis |
| 8 | 1, 2 | Visible (lighthouse) *** |
| Substance | Manufacturer/Product | Useage |
|---|---|---|
| pSer396 antibody | Abcam (Cambridge, UK): ab109390 | Western blot (1:10,000) phosphorylated tau |
| Tau5 antibody | ThermoFisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA): AHB0042 | Western blot (1:1000) total tau |
| GFAP antibody | ThermoFisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA): MA5-12023 | Western blot (1:10,000) astrocytes |
| β-actin antibody | ThermoFisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA): MA5-15739 | Western blot (1:10,000) loading control |
| GAPDH antibody | ThermoFisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA): MA5-15738 | Western blot (1:10,000) loading control |
| HRP-conjugated secondary antibody | ThermoFisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA): A27036, A28177 | Western blot |
| RIPA buffer | ThermoFisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA): 89901 | Western blot brain homogenate |
| Halt Protease and Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail | ThermoFisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA): 78446 | Western blot brain homogenate |
| NuPAGE 4–12% Bis-Tris gels | Invitrogen (Waltham, MA, USA): NP0321BOX | Western blot |
| NuPAGE MOPS running buffer | Invitrogen (Waltham, MA, USA): NP0001 | Western blot |
| West pico chemiluminescent substrate (SuperSignal) | ThermoFisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA): 34579 | Western blot |
| Potassium permanganate | Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA): 223468 | Thioflavin-S Tau stain |
| Sodium borohydride caplets | Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA): 452890 | Thioflavin-S Tau stain |
| Thioflavine S | Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA): T1892 | Thioflavin-S Tau stain |
| Tau | WT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | Male | Female | |
| Plasma | 4 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| Total | 6 | 6 | ||
| Saline | 3 | 3 | 4 | 2 |
| Total | 6 | 6 | ||
| Tau | WT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | Male | Female | |
| Plasma | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Total | 5 | 2 | ||
| Saline | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| Total | 5 | 2 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hernandez, C.M.; Barkey, R.E.; Craven, K.M.; Pedemonte, K.A.; Alisantosa, B.; Sanchez, J.O.; Flinn, J.M. Transfusion with Blood Plasma from Young Mice Affects rTg4510 Transgenic Tau Mice Modeling of Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 841. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13060841
Hernandez CM, Barkey RE, Craven KM, Pedemonte KA, Alisantosa B, Sanchez JO, Flinn JM. Transfusion with Blood Plasma from Young Mice Affects rTg4510 Transgenic Tau Mice Modeling of Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(6):841. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13060841
Chicago/Turabian StyleHernandez, Carlos M., Rachel E. Barkey, Kristen M. Craven, Karin A. Pedemonte, Bernadette Alisantosa, Jonathan O. Sanchez, and Jane M. Flinn. 2023. "Transfusion with Blood Plasma from Young Mice Affects rTg4510 Transgenic Tau Mice Modeling of Alzheimer’s Disease" Brain Sciences 13, no. 6: 841. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13060841
APA StyleHernandez, C. M., Barkey, R. E., Craven, K. M., Pedemonte, K. A., Alisantosa, B., Sanchez, J. O., & Flinn, J. M. (2023). Transfusion with Blood Plasma from Young Mice Affects rTg4510 Transgenic Tau Mice Modeling of Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain Sciences, 13(6), 841. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13060841






