Optimization of SSVEP-BCI Virtual Reality Stereo Stimulation Parameters Based on Knowledge Graph
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subsection
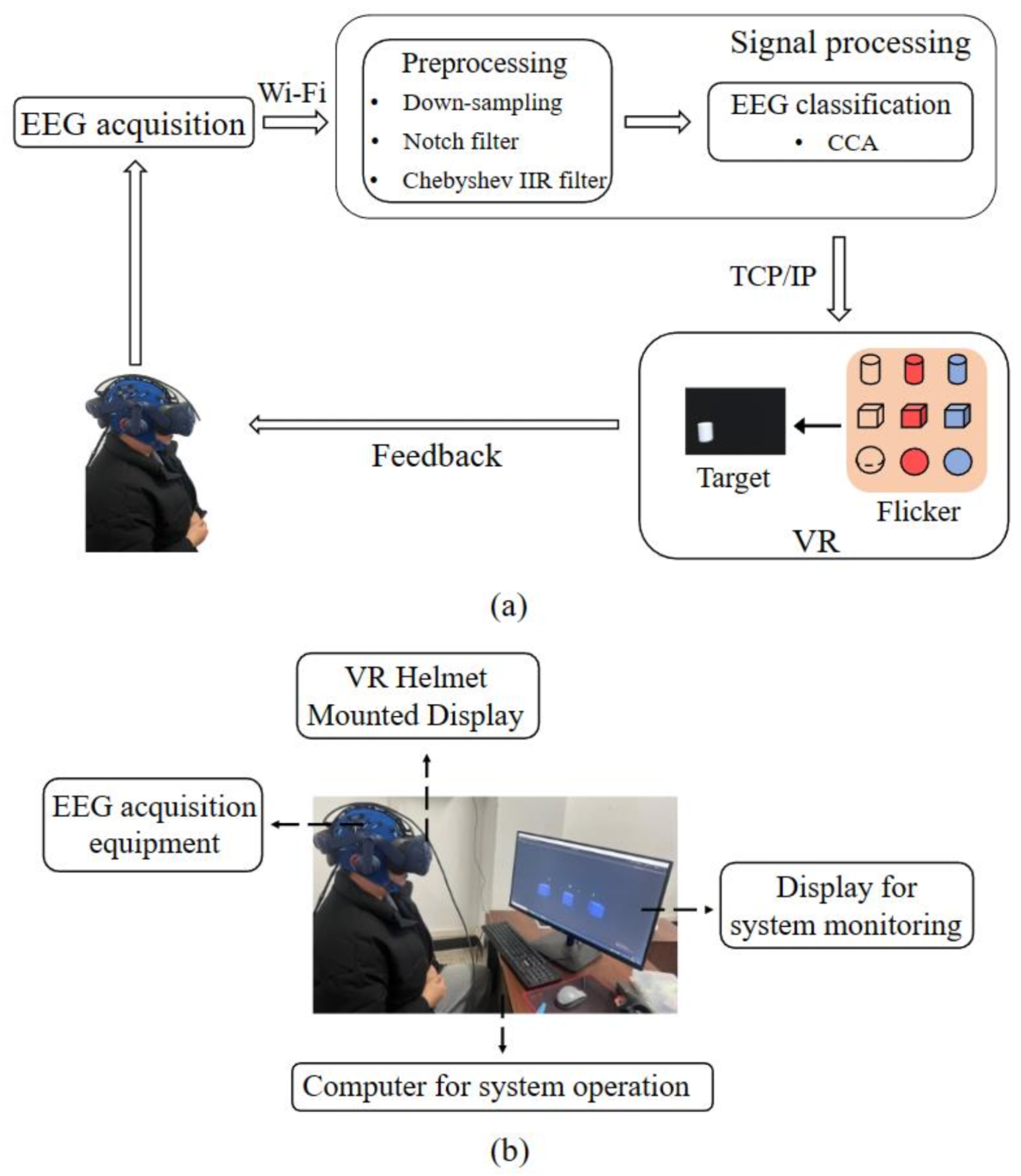
2.2. On-Line VR Stereo Stimulation SSVEP-BCI System Framework
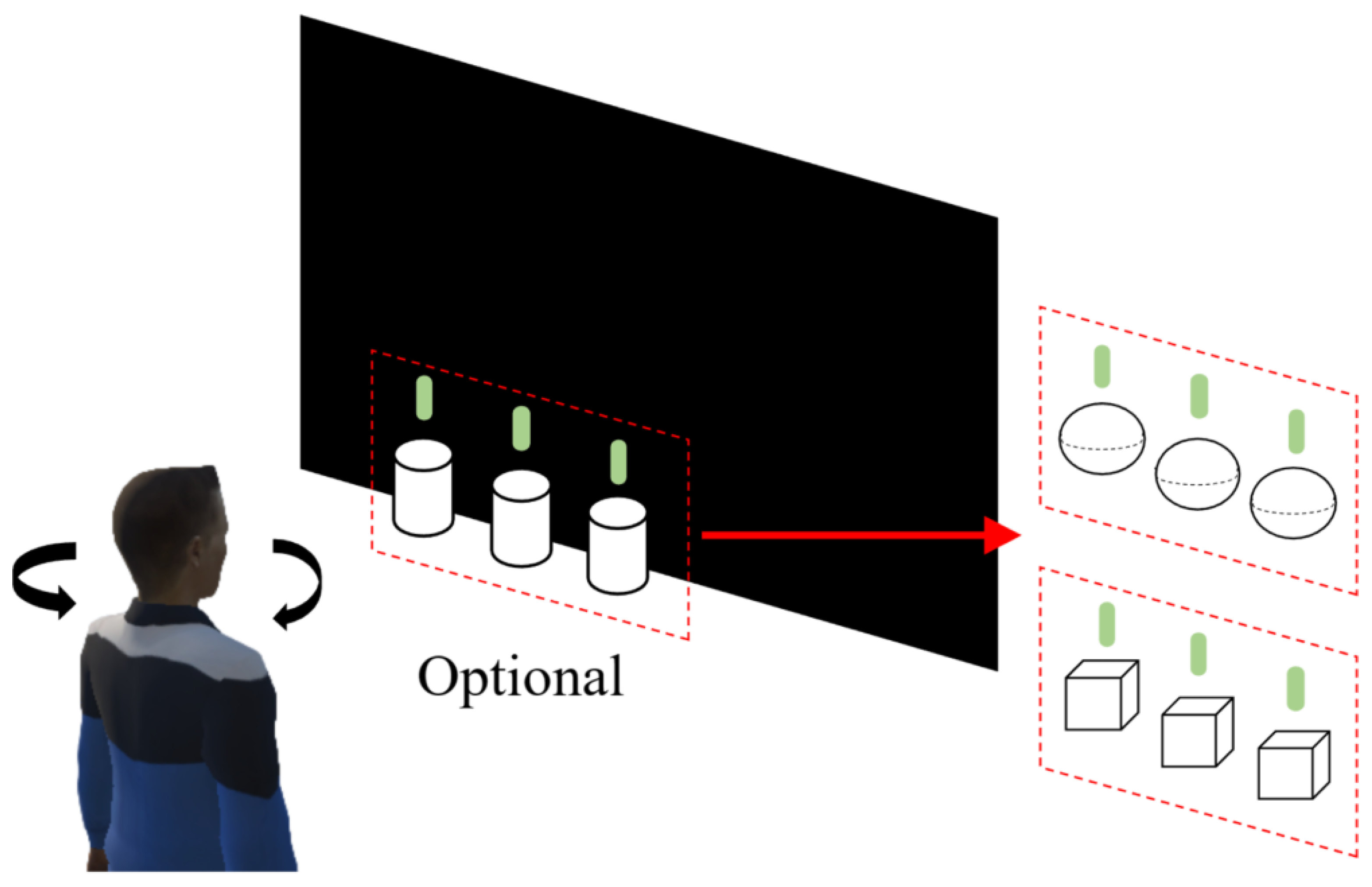
2.3. Constructing VR Stereo Stimulation Targets and Scenes
2.4. Experiment
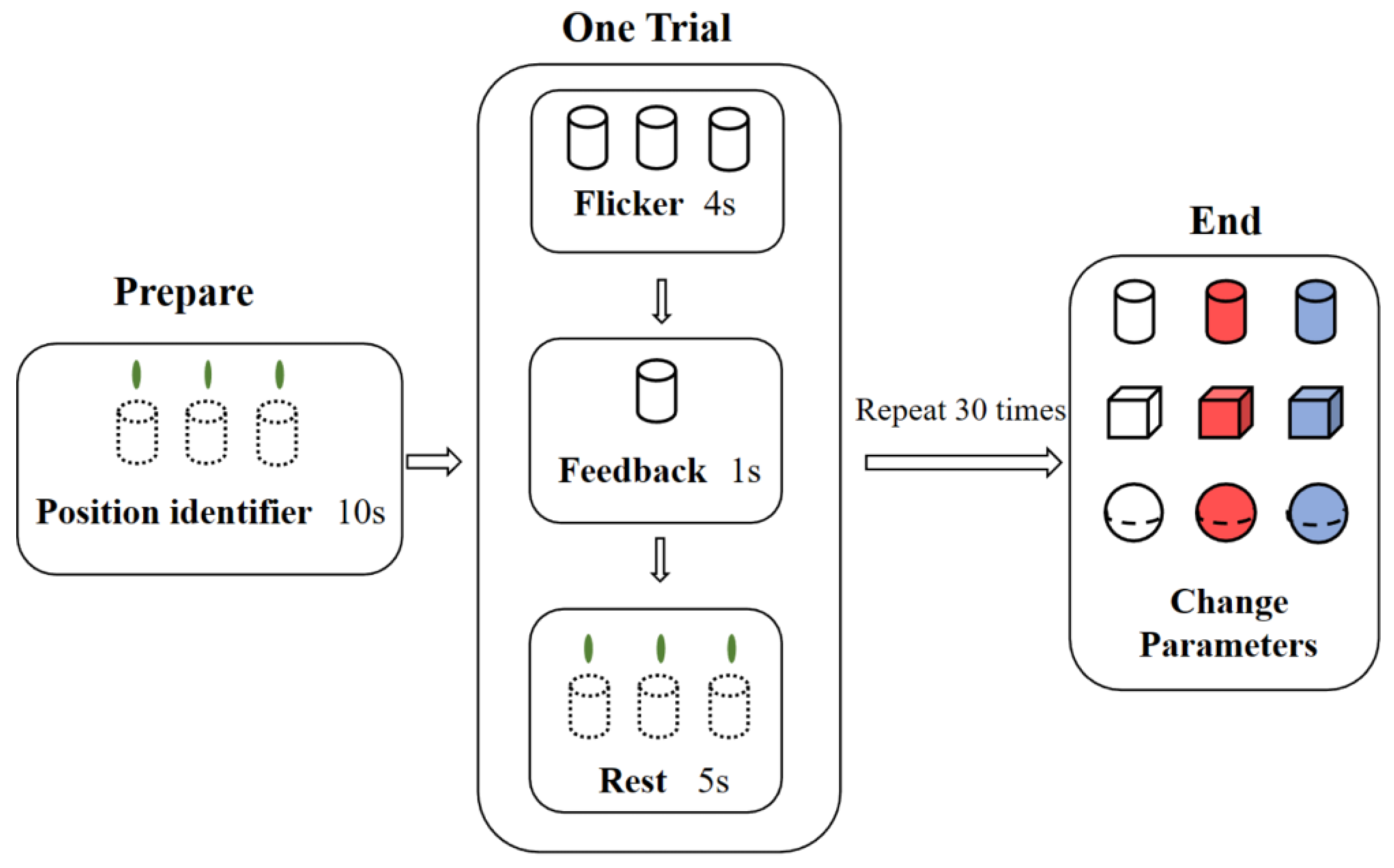
2.4.1. Experimental Process
2.4.2. Data Acquisition Process
2.4.3. Contrast Experiment
2.5. Data Processing Method
2.5.1. Pretreatment
2.5.2. Classification Algorithm
2.5.3. Performance Index
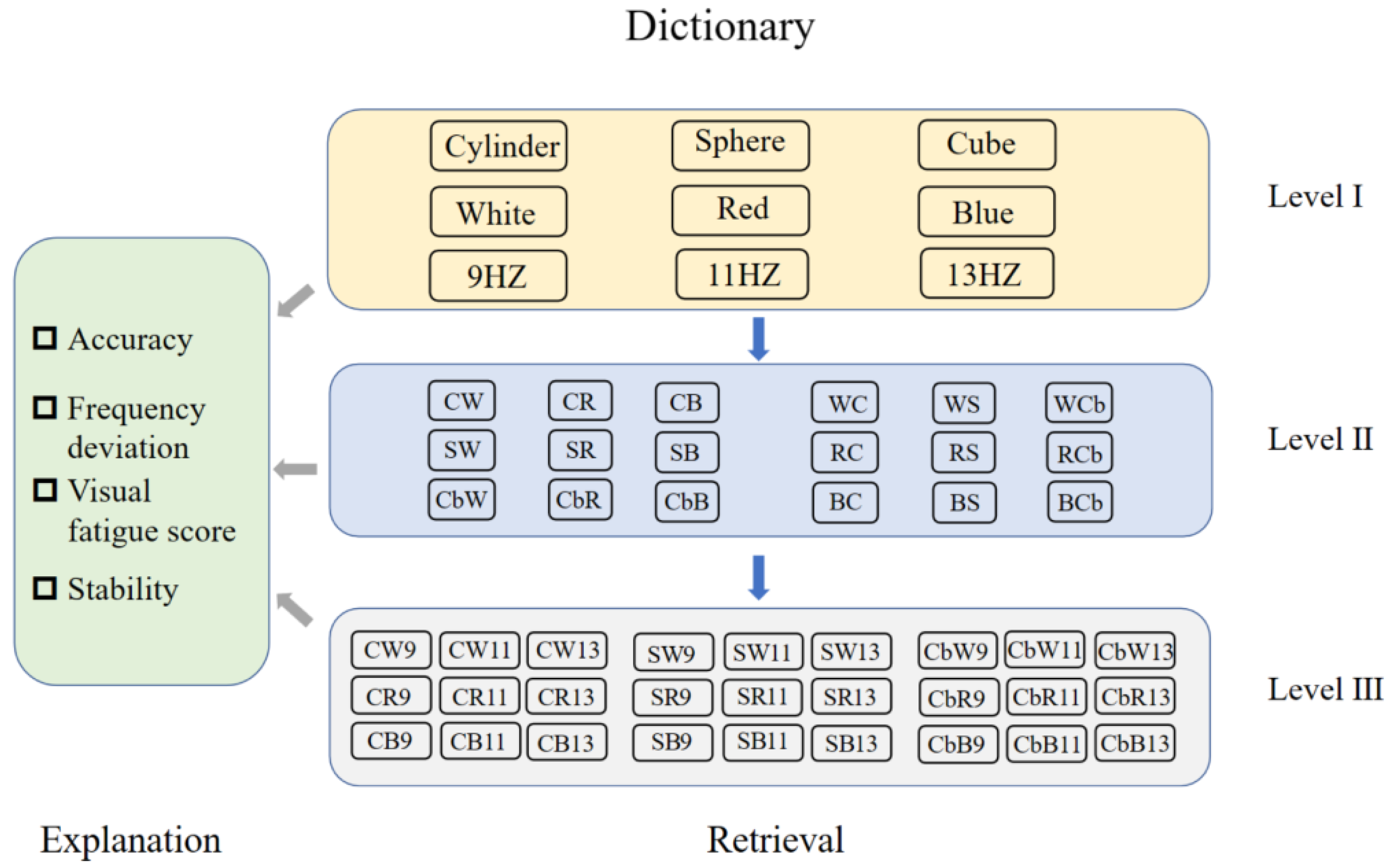
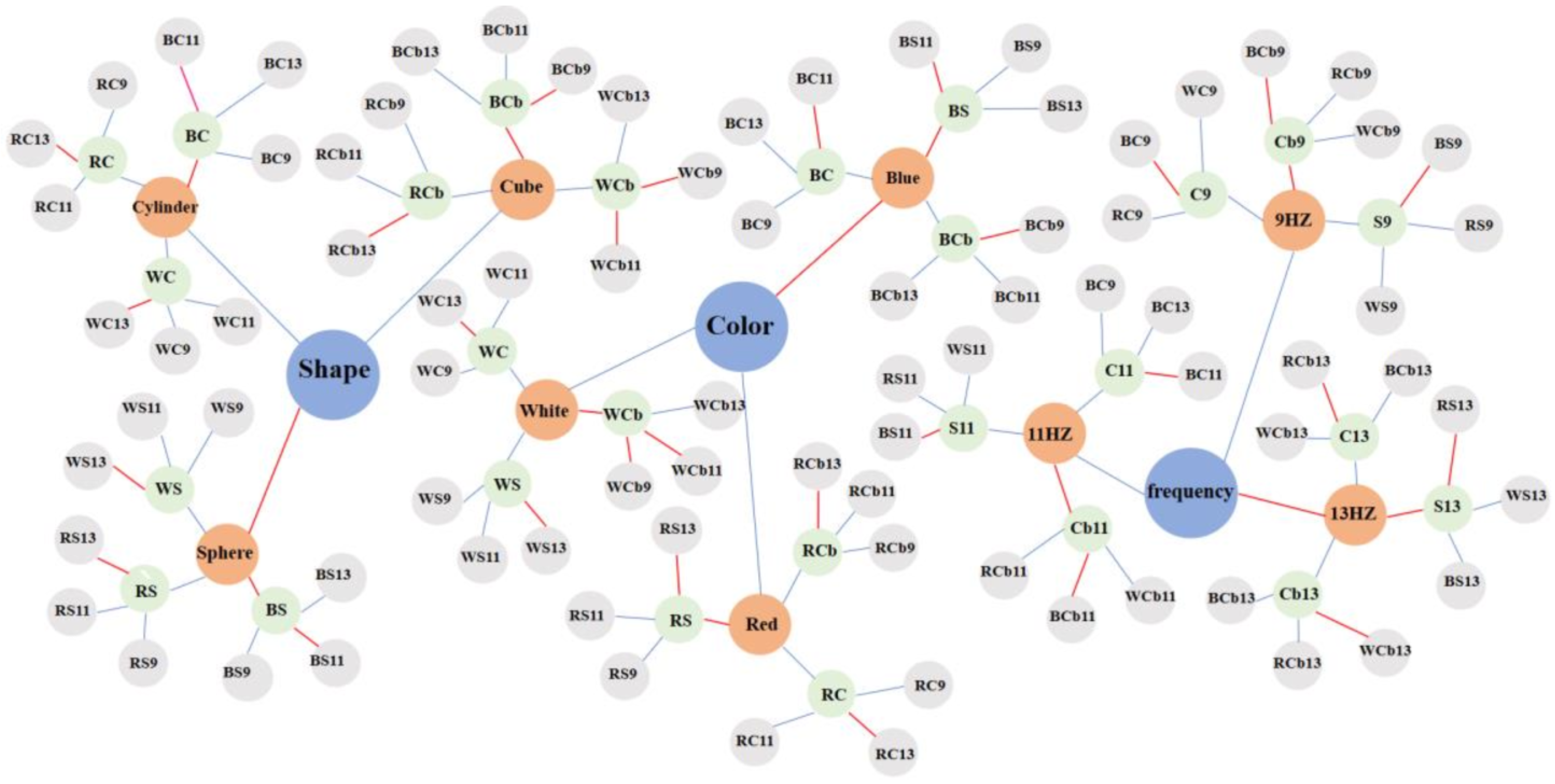
2.6. SSVEP-BCI Virtual Reality SST Parameter Dictionary and Knowledge Graph
3. Results
3.1. Performance Comparison of VR Stereoscopic Stimulation Parameters
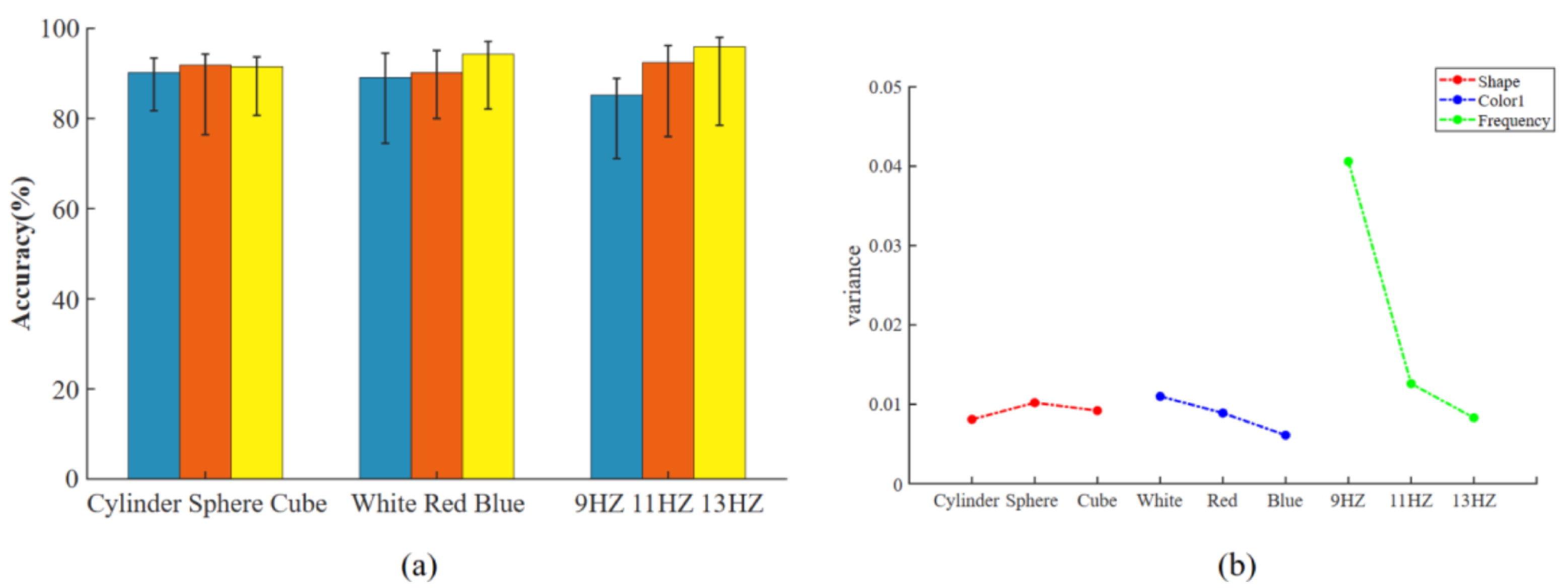
3.1.1. Accuracy
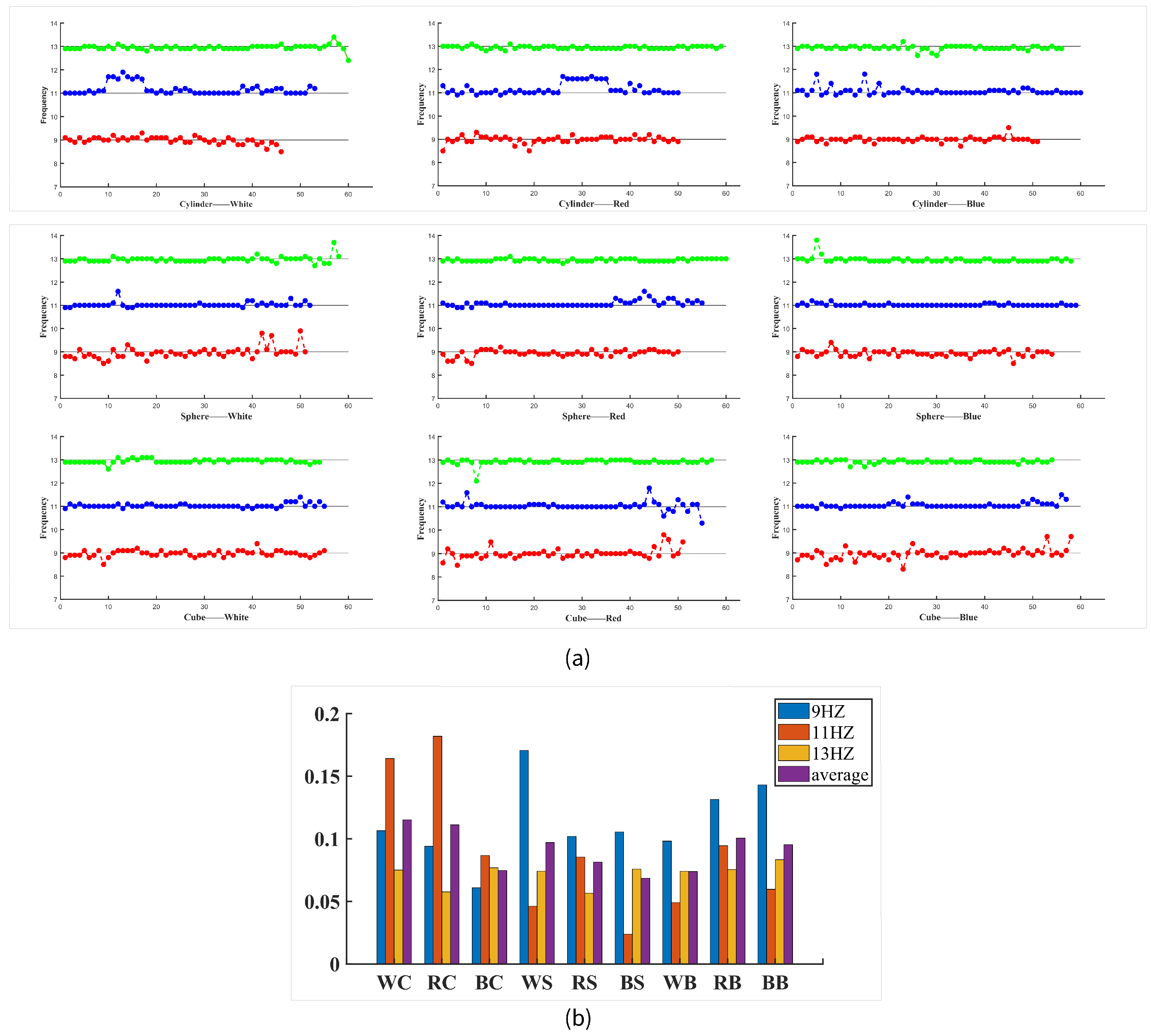
3.1.2. Frequency Deviation
3.1.3. Visual Fatigue
3.2. Knowledge Graph of VR Stereoscopic Stimulation Parameters
3.3. Comparison between SST and PST
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Accuracy (%) | Frequency Deviation (Hz) | |
|---|---|---|
| WC 9 Hz | 76.67 | 0.1065 |
| WC 11 Hz | 88.33 | 0.1642 |
| WC 13 Hz | 100 | 0.075 |
| RC 9 Hz | 83.33 | 0.0940 |
| RC 11 Hz | 83.33 | 0.1820 |
| RC 13 Hz | 98.33 | 0.0576 |
| BC 9 Hz | 85 | 0.0608 |
| BC 11 Hz | 100 | 0.0867 |
| BC 13 Hz | 93.33 | 0.0768 |
| WS 9 Hz | 85 | 0.1706 |
| WS 11 Hz | 86.67 | 0.0461 |
| WS 13 Hz | 96.67 | 0.0741 |
| RS 9 Hz | 83.33 | 0.1020 |
| RS 11 Hz | 91.67 | 0.0855 |
| RS 13 Hz | 100 | 0.0567 |
| BS 9 Hz | 90 | 0.1056 |
| BS 11 Hz | 98.33 | 0.0237 |
| BS 13 Hz | 96.67 | 0.0759 |
| WCb 9 Hz | 91.67 | 0.0982 |
| WCb 11 Hz | 91.67 | 0.0491 |
| WCb 13 Hz | 90 | 0.0741 |
| RCb 9 Hz | 85 | 0.1314 |
| RCb 11 Hz | 91.67 | 0.0945 |
| RCb 13 Hz | 95 | 0.0754 |
| BCb 9 Hz | 96.67 | 0.1431 |
| BCb 11 Hz | 95 | 0.0597 |
| BCb 13 Hz | 90 | 0.0833 |
References
- Rebsamen, B.; Burdet, E.; Guan, C.; Teo, C.L.; Zeng, Q.; Ang, M.; Laugier, C. Controlling a wheelchair using a BCI with low information transfer rate. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE 10th International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 13–15 June 2007; Volumes 1 and 2, pp. 1003–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuo, G.; Wenwen, Z.; Shouyin, L. Asynchronous Brain-computer Interface Intelligent Wheelchair System Based on Alpha Wave and SSVEP EEG Signals. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 4th International Conference on Signal and Image Processing (ICSIP 2019), Wuxi, China, 19–21 July 2019; pp. 611–616. [Google Scholar]
- Latif, M.Y.; Naeem, L.; Hafeez, T.; Raheel, A.; Anwar, S.M. Brain computer interface based robotic arm control. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Smart Cities Conference (ISC2), Wuxi, China, 14–17 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Cantillo-Negrete, J.; Carino-Escobar, R.I.; Carrillo-Mora, P.; Elias-Vinas, D.; Gutierrez-Martinez, J. Motor Imagery-Based Brain-Computer Interface Coupled to a Robotic Hand Orthosis Aimed for Neurorehabilitation of Stroke Patients. J. Healthc. Eng. 2018, 2018, 1624637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Chen, Z.; Gao, S.; Gao, X. A high-itr ssvep-based bci speller. Brain-Comput. Interfaces 2014, 1, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, D.; Wang, Y.K.; Lin, C.T.; Nguyen, H.; Chai, R. Improving EEG-Based Driver Distraction Classification Using Brain Connectivity Estimators. Sensors 2022, 22, 6230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, D.; Liang, B.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, H.; Jung, T.P. The Current Research of Combining Multi-Modal Brain-Computer Interfaces With Virtual Reality. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2021, 25, 3278–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bown, J.; White, E.; Boopalan, A. Looking for the Ultimate Display: A Brief History of Virtual Reality. Bound. Self Real. Online 2017, 239–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pengcheng, C.; Nuo, G. Research of VR-BCI and Its Application in Hand Soft Rehabilitation System. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 7th IEEE International Conference on Virtual Reality (ICVR), Foshan, China, 20–22 May 2021; pp. 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClinton, W.; Caprio, D.; Laesker, D.; Pinto, B.; Garcia, S.; Andujar, M. P300-Based 3D Brain Painting in Virtual Reality. In Proceedings of the CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI), Glasgow, Scotland, 4–9 May 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coogan, C.G.; He, B. Brain-Computer Interface Control in a Virtual Reality Environment and Applications for the Internet of Things. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 10840–10849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achanccaray, D.; Pacheco, K.; Carranza, E.; Hayashibe, M. Immersive Virtual Reality Feedback in a Brain Computer Interface for Upper Limb Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), Miyazaki, Japan, 7–10 October 2018; pp. 1006–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vourvopoulos, A.; Ferreira, A.; Bermudez i Badia, S. NeuRow: An Immersive VR Environment for Motor-Imagery Training with the Use of Brain-Computer Interfaces and Vibrotactile Feedback. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Physiological Computing Systems (PhyCS), Lisbon, Portugal, 27–28 July 2016; pp. 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R. Virtual Reality Games based on Brain Computer Interface. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Human-Computer Interaction (ICHCI), Sanya, China, 4–6 December 2020; pp. 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karácsony, T.; Hansen, J.P.; Iversen, H.K.; Puthusserypady, S. Brain computer interface for neuro-rehabilitation with deep learning classification and virtual reality feedback. In Proceedings of the 10th Augmented Human International Conference 2019, Reims Champagne-Ardenne, France, 11–12 March 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, R.S.; Acharya, J.N.; Baumer, F.M.; French, J.A.; Parisi, P.; Solodar, J.H.; Szaflarski, J.P.; Thio, L.L.; Tolchin, B.; Wilkins, A.J.; et al. Visually sensitive seizures: An updated review by the Epilepsy Foundation. Epilepsia 2022, 63, 739–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wei, S.; Zhang, X.; Mao, L. Development and evaluation of BCI for operating VR flight simulator based on desktop VR equipment. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2022, 51, 101499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Nakanishi, M.; Gao, X.; Jung, T.P.; Gao, S. High-speed spelling with a noninvasive brain-computer interface. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E6058–E6067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Ma, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, M.; Pei, W.; Chen, H. High-Speed Spelling in Virtual Reality with Sequential Hybrid BCIs. IEICE Trans. Inf. Syst. 2018, E101D, 2859–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yang, C.; Pei, W.; Gao, X.; Chen, H. An online brain-computer interface in mobile virtual reality environments. Integr. Comput. Aided Eng. 2019, 26, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grichnik, R.; Benda, M.; Volosyak, I. A VR-Based Hybrid BCI Using SSVEP and Gesture Input. In Advances in Computational Intelligence; Rojas, I., Joya, G., Catala, A., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 11506, pp. 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stawicki, P.; Gembler, F.; Grichnik, R.; Volosyak, I. Remote Steering of a Mobile Robotic Car by Means of VR-Based SSVEP BCI. In Advances in Computational Intelligence; Rojas, I., Joya, G., Catala, A., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 11506, pp. 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, B.; Lee, H.G.; Nam, Y.; Choi, S. Immersive BCI with SSVEP in VR Head-Mounted Display. In Proceedings of the 2015 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE-Engineering-in-Medicine-and-Biology-Society (EMBC), Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Shiosaka, N.; Kanoh, S. A comparison of some frequencies of LED stimulus for steady-state visual evoked potential responses. In Proceedings of the 2017 10th Biomedical Engineering International Conference (BMEiCON), Hokkaido, Japan, 31 August–2 September 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhenghua, W.; Dezhong, Y. Comparison of steady-state visual evoked potentials produced by monochromatic light of different colors. J. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 25, 1021–1024. [Google Scholar]
- Dechwechprasit, P.; Phothisonothai, M.; Tantisatirapong, S. Time-Frequency Analysis of Red-Green Visual Flickers Based on Steady-State Visual Evoked Potential Recording. In Proceedings of the 2016 9th Biomedical Engineering International Conference (BMEiCON), Luang Prabang, Laos, 7–9 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ming, G.; Pei, W.; Gao, X.; Wang, Y. A high-performance SSVEP-based BCI using imperceptible flickers. J. Neural Eng. 2023, 20, 016042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


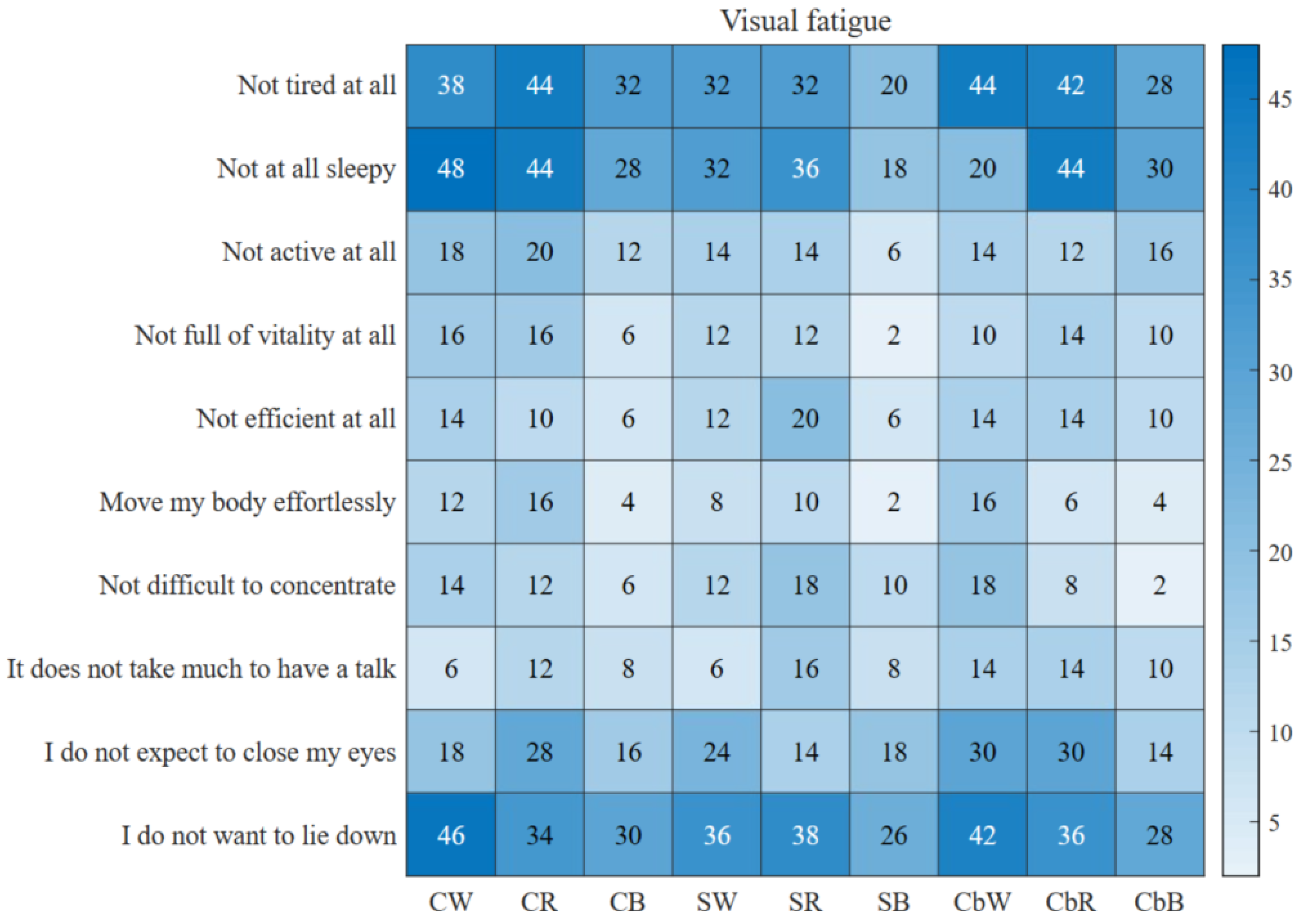
| CW | CR | CB | SW | SR | SB | CbW | CbR | CbB | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Not tired at all | 38 | 44 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 20 | 44 | 42 | 28 |
| Not at all sleepy | 48 | 44 | 28 | 32 | 36 | 18 | 20 | 44 | 30 |
| Not active at all | 18 | 20 | 12 | 14 | 14 | 6 | 14 | 12 | 16 |
| Not full of vitality at all | 16 | 16 | 6 | 12 | 12 | 2 | 10 | 14 | 10 |
| Not efficient at all | 14 | 10 | 6 | 12 | 20 | 6 | 14 | 14 | 10 |
| Move my body effortlessly | 12 | 16 | 4 | 8 | 10 | 2 | 16 | 6 | 4 |
| Not difficult to concentrate | 14 | 12 | 6 | 12 | 18 | 10 | 18 | 8 | 2 |
| It doesn’t take much to have a talk | 6 | 12 | 8 | 6 | 16 | 8 | 14 | 14 | 10 |
| I don’t expect to close my eyes | 18 | 28 | 16 | 24 | 14 | 18 | 30 | 30 | 14 |
| I don’t want to lie down | 46 | 34 | 30 | 36 | 38 | 26 | 42 | 36 | 28 |
| Summary | 230 | 236 | 148 | 188 | 210 | 116 | 222 | 220 | 152 |
| Subject 1 | Subject 2 | Subject 3 | Average | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plane target | Accuracy (%) | 91.67 | 75 | 75 | 80.55 |
| ITR (bit/min) | 18.65 | 8.98 | 8.98 | 12.20 | |
| Feelings (points) | 70 | 60 | 60 | 63.33 | |
| Stereoscopic target | Accuracy (%) | 81.67 | 75 | 90 | 82.22 |
| ITR (bit/min) | 12.25 | 8.98 | 17.42 | 12.88 | |
| Feelings (points) | 80 | 60 | 70 | 70 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, S.; Yang, J.; Ding, P.; Wang, F.; Gong, A.; Fu, Y. Optimization of SSVEP-BCI Virtual Reality Stereo Stimulation Parameters Based on Knowledge Graph. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13050710
Zhu S, Yang J, Ding P, Wang F, Gong A, Fu Y. Optimization of SSVEP-BCI Virtual Reality Stereo Stimulation Parameters Based on Knowledge Graph. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(5):710. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13050710
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Shixuan, Jingcheng Yang, Peng Ding, Fan Wang, Anmin Gong, and Yunfa Fu. 2023. "Optimization of SSVEP-BCI Virtual Reality Stereo Stimulation Parameters Based on Knowledge Graph" Brain Sciences 13, no. 5: 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13050710
APA StyleZhu, S., Yang, J., Ding, P., Wang, F., Gong, A., & Fu, Y. (2023). Optimization of SSVEP-BCI Virtual Reality Stereo Stimulation Parameters Based on Knowledge Graph. Brain Sciences, 13(5), 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13050710






