Unexplained Progressive Neurological Deficits after Corpus Callosotomy May Be Caused by Autoimmune Encephalitis: A Case of Suspected Postoperative Anti-NMDAR Encephalitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Case Presentation
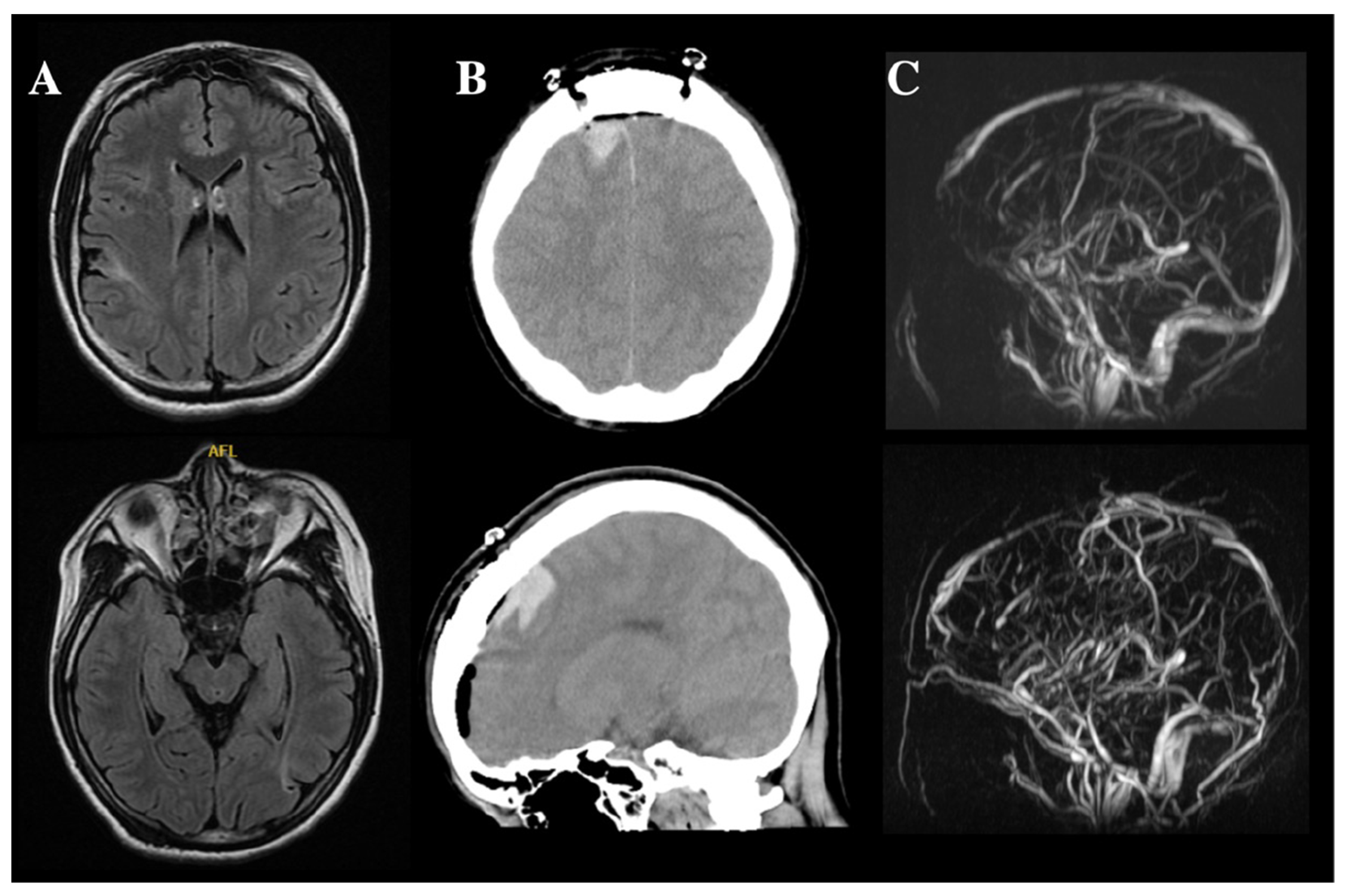
2.1. Cerebral Hemorrhage and CVST
2.2. Progressive Neurological Deficits (Suspected Autoimmune Encephalitis)
2.3. Progressive Neurological Deficits Resolved after Immunotherapy
2.4. Outcome for This Patient
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rugg-Gunn, F.; Miserocchi, A.; McEvoy, A. Epilepsy surgery. Pr. Neurol. 2020, 20, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, S.; Nolan, S.J.; Newton, R. Surgery for epilepsy: A systematic review of current evidence. Epileptic Disord. 2016, 18, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, P.; Brodie, M.J. Early identification of refractory epilepsy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samanta, D.; Ostendorf, A.P.; Willis, E.; Singh, R.; Gedela, S.; Arya, R.; Scott Perry, M. Underutilization of epilepsy surgery: Part I: A scoping review of barriers. Epilepsy Behav. 2021, 117, 107837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaddiparti, A.; Huang, R.; Blihar, D.; Du Plessis, M.; Montalbano, M.J.; Tubbs, R.S.; Loukas, M. The Evolution of Corpus Callosotomy for Epilepsy Management. World Neurosurg. 2021, 145, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uda, T.; Kunihiro, N.; Umaba, R.; Koh, S.; Kawashima, T.; Ikeda, S.; Ishimoto, K.; Goto, T. Surgical Aspects of Corpus Callosotomy. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okanishi, T.; Fujimoto, A. Corpus Callosotomy for Controlling Epileptic Spasms: A Proposal for Surgical Selection. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markosian, C.; Patel, S.; Kosach, S.; Goodman, R.R.; Tomycz, L.D. Corpus Callosotomy in the Modern Era: Origins, Efficacy, Technical Variations, Complications, and Indications. World Neurosurg. 2022, 159, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozaki, T.; Fujimoto, A.; Ichikawa, N.; Baba, S.; Enoki, H.; Okanishi, T. Higher intelligence may be a risk factor for postoperative transient disturbance of consciousness after corpus callosotomy. Epilepsy Behav. 2021, 115, 107617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, A.; Hatano, K.; Nozaki, T.; Sato, K.; Enoki, H.; Okanishi, T. Postoperative Pneumocephalus on Computed Tomography Might Predict Post-Corpus Callosotomy Chemical Meningitis. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmau, J.; Tuzun, E.; Wu, H.Y.; Masjuan, J.; Rossi, J.E.; Voloschin, A.; Baehring, J.M.; Shimazaki, H.; Koide, R.; King, D.; et al. Paraneoplastic anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitis associated with ovarian teratoma. Ann. Neurol. 2007, 61, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalmau, J.; Armangué, T.; Planagumà, J.; Radosevic, M.; Mannara, F.; Leypoldt, F.; Geis, C.; Lancaster, E.; Titulaer, M.J.; Rosenfeld, M.R.; et al. An update on anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis for neurologists and psychiatrists: Mechanisms and models. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 1045–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graus, F.; Titulaer, M.J.; Balu, R.; Benseler, S.; Bien, C.G.; Cellucci, T.; Cortese, I.; Dale, R.C.; Gelfand, J.M.; Geschwind, M.; et al. A clinical approach to diagnosis of autoimmune encephalitis. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iimura, Y.; Sugano, H.; Ueda, T.; Matsuda, S.; Karagiozov, K.; Tsunemi, T.; Takanashi, M.; Shimada, T.; Maruyama, S.; Otsubo, H. Relapse of Herpes Simplex Encephalitis by Epilepsy Surgery 35 Years after the First Infection: A Case Report and Literature Review. NMC Case Rep. J. 2021, 8, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso-Vanegas, M.A.; Quintero-Lopez, E.; Martinez-Albarran, A.A.; Moreira-Holguin, J.C. Recurrent Herpes Simplex Virus Encephalitis After Neurologic Surgery. World Neurosurg. 2016, 89, 731.e1–e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, A.; Shahar, T.; Margalit, N. Herpes Simplex Type 2 Encephalitis After Craniotomy: Case Report and Literature Review. World Neurosurg. 2016, 88, 691.e9–e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldea, S.; Joly, L.M.; Roujeau, T.; Oswald, A.M.; Devaux, B. Postoperative herpes simplex virus encephalitis after neurosurgery: Case report and review of the literature. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2003, 36, e96–e99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorcet, G.; Benaiteau, M.; Bost, C.; Mengelle, C.; Bonneville, F.; Martin-Blondel, G.; Pariente, J. Two Cases of Late-Onset Anti-NMDAr Auto-Immune Encephalitis After Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Encephalitis. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, J.N.; Schwarz, G.; Puttinger, G.; Hengsberger, A.M.; Guggenberger, S.; Weis, S.; Trenkler, J.; Aichholzer, M.; Oertzen, T.J.V. Anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis triggered by epilepsy surgery. J. Neurol. 2018, 265, 1708–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinohara, Y.; Minematsu, K.; Amano, T.; Ohashi, Y. Modified Rankin scale with expanded guidance scheme and interview questionnaire: Interrater agreement and reproducibility of assessment. Cereb. Dis. 2006, 21, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, S.E.; Pargeon, K.; Frechette, E.S.; Hirsch, L.J.; Dalmau, J.; Friedman, D. Extreme delta brush: A unique EEG pattern in adults with anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis. Neurology 2012, 79, 1094–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Yan, B.; Wang, R.; Li, C.; Chen, C.; Zhou, D.; Hong, Z. Seizure outcomes in patients with anti-NMDAR encephalitis: A follow-up study. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 2104–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, X.P.; Vidaurre, J.; Peng, X.L.; Jiang, L.; Zhong, M.; Hu, Y. Seizure Characteristics, Outcome, and Risk of Epilepsy in Pediatric Anti-N-Methyl-d-Aspartate Receptor Encephalitis. Pediatr. Neurol. 2020, 105, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iizuka, T.; Sakai, F.; Ide, T.; Monzen, T.; Yoshii, S.; Iigaya, M.; Suzuki, K.; Lynch, D.R.; Suzuki, N.; Hata, T.; et al. Anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis in Japan: Long-term outcome without tumor removal. Neurology 2008, 70, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surjus, L.T.; Campos, R.T. Interface between intellectual disability and mental health: Hermeneutic review. Rev. Saude Publica 2014, 48, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLennan, J.D. Dual Diagnosis: A Problematic Construct When Applied to Persons with Intellectual Disabilities. Can. J. Psychiatry 2018, 63, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armangue, T.; Leypoldt, F.; Dalmau, J. Autoimmune encephalitis as differential diagnosis of infectious encephalitis. Curr Opin Neurol 2014, 27, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blinder, T.; Lewerenz, J. Cerebrospinal Fluid Findings in Patients With Autoimmune Encephalitis-A Systematic Analysis. Front. Neurol 2019, 10, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, J.; Gros, P.; Lapointe, S.; Amtashar, F.S.; Steriade, C.; Maurice, C.; Wennberg, R.A.; Day, G.S.; Tang-Wai, D.F. Searching for autoimmune encephalitis: Beware of normal CSF. J. Neuroimmunol. 2020, 345, 577285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmau, J.; Gleichman, A.J.; Hughes, E.G.; Rossi, J.E.; Peng, X.; Lai, M.; Dessain, S.K.; Rosenfeld, M.R.; Balice-Gordon, R.; Lynch, D.R. Anti-NMDA-receptor encephalitis: Case series and analysis of the effects of antibodies. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 1091–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titulaer, M.J.; McCracken, L.; Gabilondo, I.; Armangué, T.; Glaser, C.; Iizuka, T.; Honig, L.S.; Benseler, S.M.; Kawachi, I.; Martinez-Hernandez, E.; et al. Treatment and prognostic factors for long-term outcome in patients with anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis: An observational cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacchi, S.; Franke, K.; Wewegama, D.; Needham, E.; Patel, S.; Menon, D. Magnetic resonance imaging and positron emission tomography in anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis: A systematic review. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 52, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Cui, L.; Wang, W.; Jiao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jiao, J. Early identification of anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis presenting cerebral lesions in unconventional locations on magnetic resonance imaging. J. Neuroimmunol. 2018, 320, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalmau, J. NMDA receptor encephalitis and other antibody-mediated disorders of the synapse: The 2016 Cotzias Lecture. Neurology 2016, 87, 2471–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, M.; Martinez-Hernandez, E.; Arino, H.; Armangue, T.; Spatola, M.; Petit-Pedrol, M.; Saiz, A.; Rosenfeld, M.R.; Graus, F.; Dalmau, J. Clinical and pathogenic significance of IgG, IgA, and IgM antibodies against the NMDA receptor. Neurology 2018, 90, e1386–e1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, D.; Alqallaf, A.; Hays, R.; Freeman, M.; Chen, K.; Ding, K.; Agostini, M.; Vernino, S. Neurological Autoantibody Prevalence in Epilepsy of Unknown Etiology. JAMA Neurol. 2017, 74, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekturk, P.; Baykan, B.; Erdag, E.; Peach, S.; Sezgin, M.; Yapici, Z.; Kucukali, C.I.; Vincent, A.; Tuzun, E. Investigation of neuronal auto-antibodies in children diagnosed with epileptic encephalopathy of unknown cause. Brain Dev. 2018, 40, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| POD 10 | POD 61 | POD 74 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pressure | NA * | 17 cmH2O | 31 cm H2O |
| Leukocytes | 4/μL | 3/μl | 1/μL |
| Protein | 65 mg/dl | 115 mg/dl | 99 mg/dl |
| Glucose | 47 mg/dl | 58 mg/dl | 56 mg/dl |
| IgG index (reference range, <0.7) | NA * | 1.239 | 1.03 |
| Other findings | NA * | Oligoclonal band was positive | The antibody against NMDAR was positive. HSV-PCR and other antibodies (LGI1, Caspr2, AMPAR1, AMPAR2, and GABABR) were negative. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hatano, K.; Fujimoto, A.; Sato, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Sakuma, H.; Enoki, H. Unexplained Progressive Neurological Deficits after Corpus Callosotomy May Be Caused by Autoimmune Encephalitis: A Case of Suspected Postoperative Anti-NMDAR Encephalitis. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13010135
Hatano K, Fujimoto A, Sato K, Yamamoto T, Sakuma H, Enoki H. Unexplained Progressive Neurological Deficits after Corpus Callosotomy May Be Caused by Autoimmune Encephalitis: A Case of Suspected Postoperative Anti-NMDAR Encephalitis. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(1):135. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13010135
Chicago/Turabian StyleHatano, Keisuke, Ayataka Fujimoto, Keishiro Sato, Takamichi Yamamoto, Hiroshi Sakuma, and Hideo Enoki. 2023. "Unexplained Progressive Neurological Deficits after Corpus Callosotomy May Be Caused by Autoimmune Encephalitis: A Case of Suspected Postoperative Anti-NMDAR Encephalitis" Brain Sciences 13, no. 1: 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13010135
APA StyleHatano, K., Fujimoto, A., Sato, K., Yamamoto, T., Sakuma, H., & Enoki, H. (2023). Unexplained Progressive Neurological Deficits after Corpus Callosotomy May Be Caused by Autoimmune Encephalitis: A Case of Suspected Postoperative Anti-NMDAR Encephalitis. Brain Sciences, 13(1), 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13010135






