Optogenetic Suppression of Lateral Septum Somatostatin Neurons Enhances Hippocampus Cholinergic Theta Oscillations and Local Synchrony
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
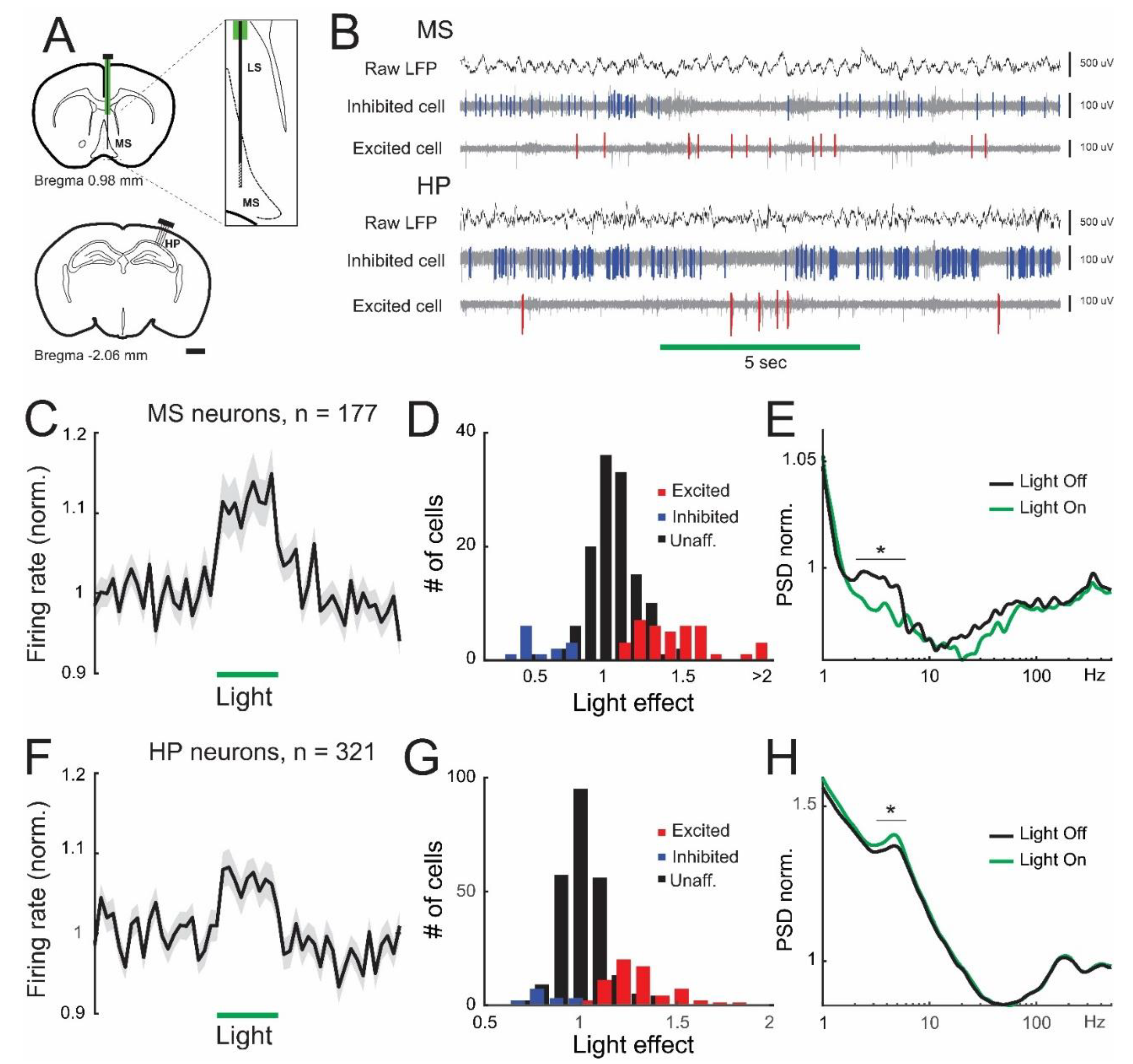
3.1. Lateral Septum Somatostatin Cells Regulate Firing Patterns in the Medial Septum and Dorsal Hippocampus
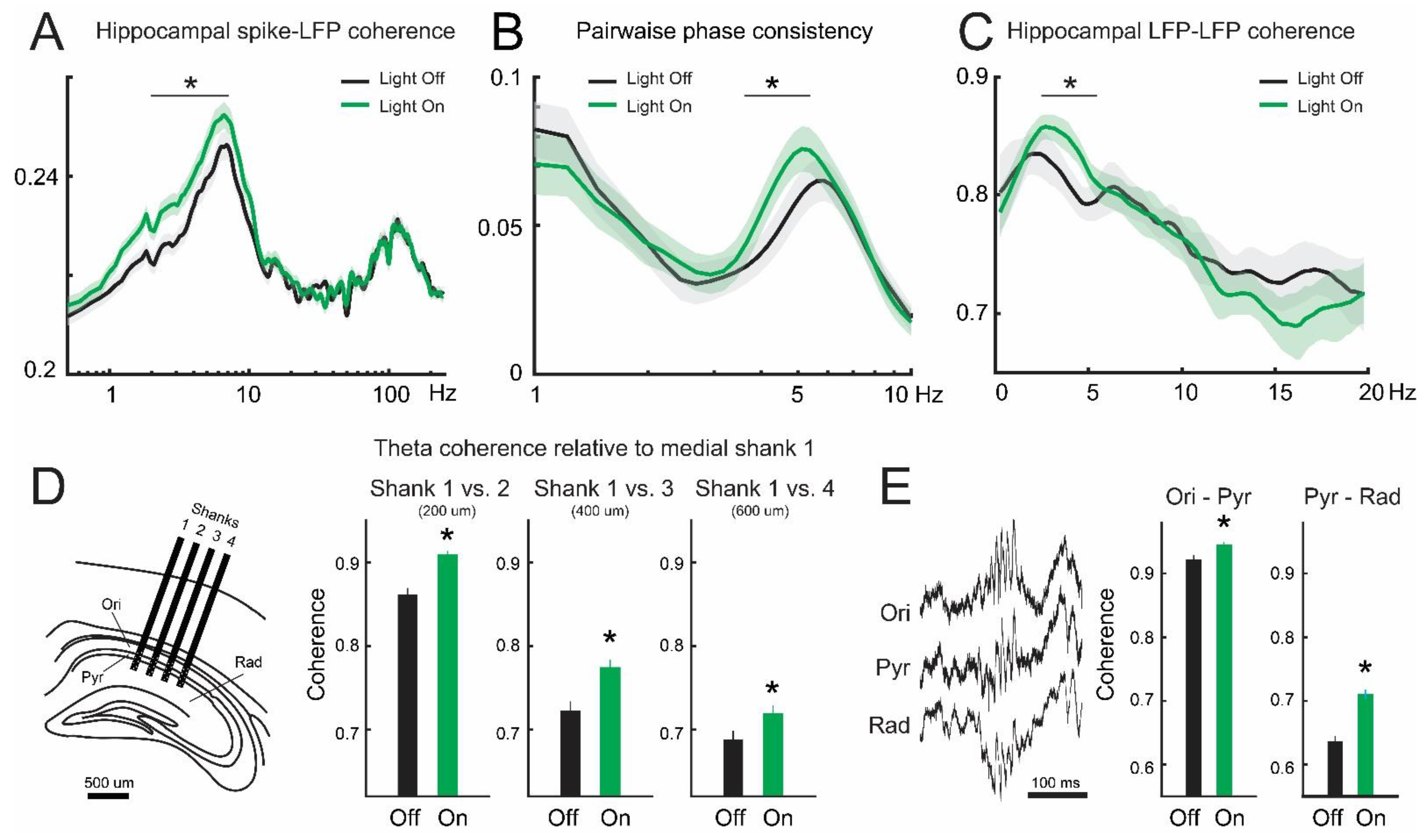
3.2. Inhibition of Lateral Septum Somatostatin Cells Enhances Theta Oscillations in the Dorsal Hippocampus
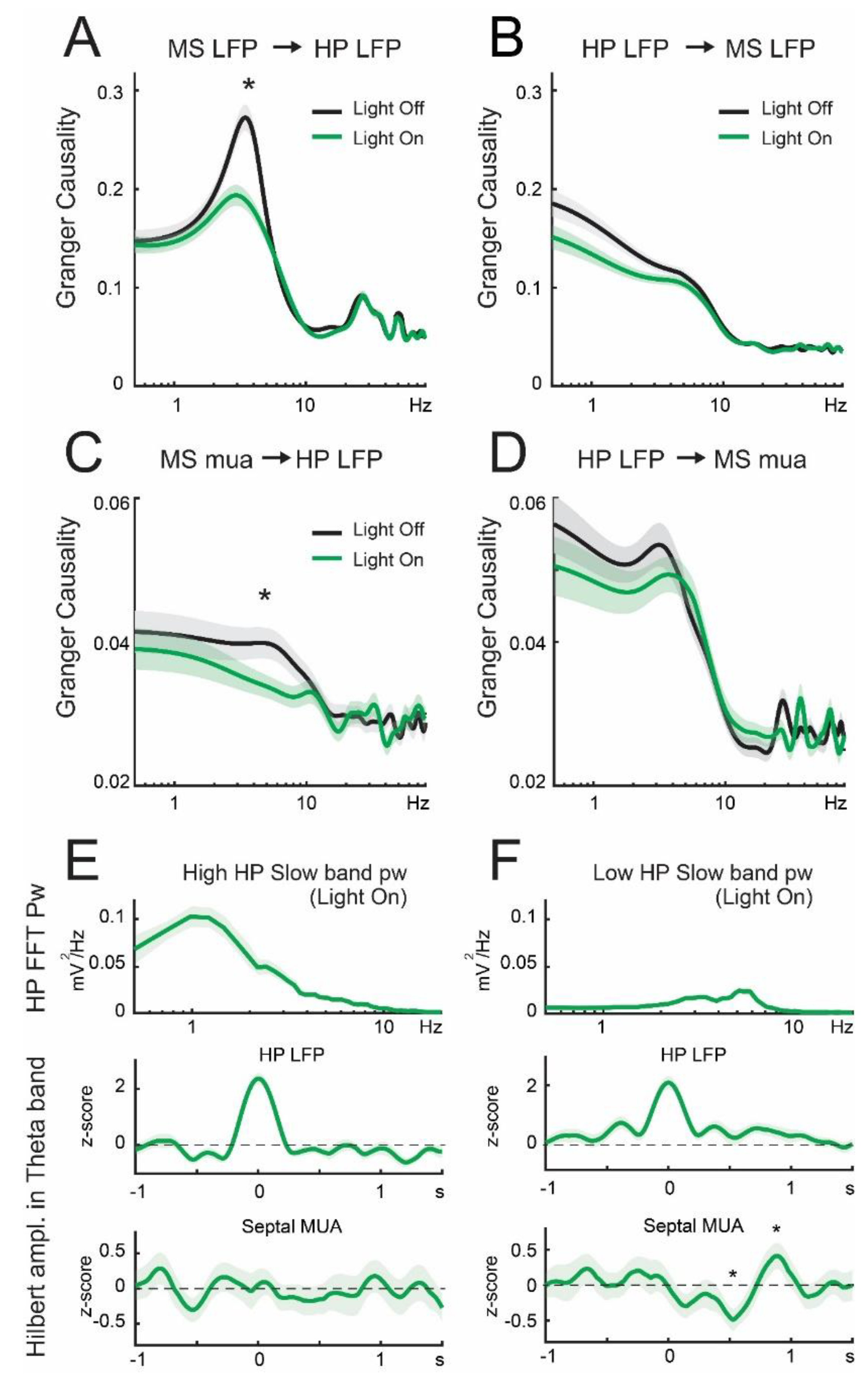
3.3. Lateral Septum Somatostatin Cells Modulate Functional Connectivity between Medial Septum and Dorsal Hippocampus during Theta Oscillations
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vanderwolf, C.H. Hippocampal Electrical Activity and Voluntary Movement in the Rat. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1969, 26, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzsáki, G. Theta Oscillations in the Hippocampus. Neuron 2002, 33, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buzsáki, G.; Moser, E.I. Memory, Navigation and Theta Rhythm in the Hippocampal-Entorhinal System. Nat. Neurosci. 2013, 16, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dunn, S.L.S.; Town, S.M.; Bizley, J.K.; Bendor, D. Behaviourally Modulated Hippocampal Theta Oscillations in the Ferret Persist during Both Locomotion and Immobility. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, T.E. Hippocampal Rhythmic Slow Activity (RSA, Theta): A Critical Analysis of Selected Studies and Discussion of Possible Species-Differences. Brain Res. Rev. 1980, 2, 69–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gray, J.A.; McNaughton, N. The Neuropsychology of Anxiety: An Enquiry into the Function of the Septo-Hippocampal System; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2008; ISBN 9780191712517. [Google Scholar]
- Sainsbury, R.S.; Heynen, A.; Montoya, C.P. Behavioral Correlates of Hippocampal Type 2 Theta in the Rat. Physiol. Behav. 1987, 39, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramis, R.; Vanderwolf, C.H.; Bland, B.H. Two Types of Hippocampal Rhythmical Slow Activity in Both the Rabbit and the Rat: Relations to Behavior and Effects of Atropine, Diethyl Ether, Urethane, and Pentobarbital. Exp. Neurol. 1975, 49, 58–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsanov, M. Speed and Oscillations: Medial Septum Integration of Attention and Navigation. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Unal, G.; Joshi, A.; Viney, T.J.; Kis, V.; Somogyi, P. Synaptic Targets of Medial Septal Projections in the Hippocampus and Extrahippocampal Cortices of the Mouse. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 15812–15826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, N.; Song, H.; Chu, G.; Zhan, X.; Liu, B.; Mu, Y.; Wang, J.-Z.; Lu, Y. Basal Forebrain Cholinergic Innervation Induces Depression-Like Behaviors Through Ventral Subiculum Hyperactivation. Neurosci. Bull. 2022, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Ding, M.; Topchiy, I.; Kocsis, B. Reciprocal Interactions between Medial Septum and Hippocampus in Theta Generation: Granger Causality Decomposition of Mixed Spike-Field Recordings. Front. Neuroanat. 2017, 11, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nita, D.A.; Cissé, Y.; Timofeev, I.; Steriade, M. Waking-Sleep Modulation of Paroxysmal Activities Induced by Partial Cortical Deafferentation. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16495431 (accessed on 22 May 2019).
- Bender, F.; Gorbati, M.; Cadavieco, M.C.; Denisova, N.; Gao, X.; Holman, C.; Korotkova, T.; Ponomarenko, A. Theta Oscillations Regulate the Speed of Locomotion via a Hippocampus to Lateral Septum Pathway. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Freund, T.F.; Antal, M. GABA-Containing Neurons in the Septum Control Inhibitory Interneurons in the Hippocampus. Nature 1988, 336, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frotscher, M.; Léránth, C. Cholinergic Innervation of the Rat Hippocampus as Revealed by Choline Acetyltransferase Immunocytochemistry: A Combined Light and Electron Microscopic Study. J. Comp. Neurol. 1985, 239, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, C.; Chan-Palay, V.; Wu, J.Y. Septal Neurons Containing Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase Immunoreactivity Project to the Hippocampal Region in the Rat Brain. Anat. Embryol. 1984, 169, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jinno, S.; Klausberger, T.; Marton, L.F.; Dalezios, Y.; Roberts, J.D.B.; Fuentealba, P.; Bushong, E.A.; Henze, D.; Buzsaki, G.; Somogyi, P. Neuronal Diversity in GABAergic Long-Range Projections from the Hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 8790–8804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malik, R.; Li, Y.; Schamiloglu, S.; Sohal, V.S. Top-down Control of Hippocampal Signal-to-Noise by Prefrontal Long-Range Inhibition. Cell 2022, 185, 1602–1617.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Chung, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhong, P.; Ma, C.; Chang, W.C.; Weissbourd, B.; Sakai, N.; Luo, L.; Nishino, S.; et al. Basal Forebrain Circuit for Sleep-Wake Control. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 1641–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, N.; Alonso, A.; Morales, C.; Espinosa, P.; Chávez, A.E.; Fuentealba, P. Basal Forebrain Gating by Somatostatin Neurons Drives Prefrontal Cortical Activity. Cereb. Cortex 2019, 29, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vinck, M.; van Wingerden, M.; Womelsdorf, T.; Fries, P.; Pennartz, C.M.A. The Pairwise Phase Consistency: A Bias-Free Measure of Rhythmic Neuronal Synchronization. Neuroimage 2010, 51, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, L.; Seth, A.K. The MVGC Multivariate Granger Causality Toolbox: A New Approach to Granger-Causal Inference. J. Neurosci. Methods 2014, 223, 50–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Espinosa, N.; Alonso, A.; Lara-Vasquez, A.; Fuentealba, P. Basal Forebrain Somatostatin Cells Differentially Regulate Local Gamma Oscillations and Functionally Segregate Motor and Cognitive Circuits. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Csicsvari, J.; Hirase, H.; Czurkó, A.; Mamiya, A.; Buzsáki, G. Oscillatory Coupling of Hippocampal Pyramidal Cells and Interneurons in the Behaving Rat. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 274–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vandecasteele, M.; Varga, V.; Berényi, A.; Papp, E.; Barthó, P.; Venance, L.; Freund, T.F.; Buzsáki, G. Optogenetic Activation of Septal Cholinergic Neurons Suppresses Sharp Wave Ripples and Enhances Theta Oscillations in the Hippocampus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 13535–13540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dannenberg, H.; Pabst, M.; Braganza, O.; Schoch, S.; Niediek, J.; Bayraktar, M.; Mormann, F.; Beck, H. Synergy of Direct and Indirect Cholinergic Septo-Hippocampal Pathways Coordinates Firing in Hippocampal Networks. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 8394–8410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Csicsvari, J.; Hirase, H.; Czurkó, A.; Mamiya, A.; Buzsáki, G. TFast Network Oscillations in the Hippocampal CA1 Region of the Behaving Rat. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, RC20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ikeda, H.; Wright, M.J. Receptive Field Organization of ‘Sustained’ and ‘Transient’ Retinal Ganglion Cells Which Subserve Different Functional Roles. J. Physiol. 1972, 227, 769–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaborszky, L.; Duque, A. Local Synaptic Connections of Basal Forebrain Neurons. Behav. Brain Res. 2000, 115, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, B.H. Anatomical, Physiological, and Pharmacological Properties Underlying Hippocampal Sensorimotor Integration. Available online: https://www.cambridge.org/core/books/abs/information-processing-by-neuronal-populations/anatomical-physiological-and-pharmacological-properties-underlying-hippocampal-sensorimotor-integration/68D9752BFCD76083343AE0DADB143E05 (accessed on 8 September 2020).
- Bland, B.H.; Bird, J.; Jackson, J.; Natsume, K. Medial Septal Modulation of the Ascending Brainstem Hippocampal Synchronizing Pathways in the Freely Moving Rat. Hippocampus 2006, 16, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Zhang, G.W.; Tao, C.; Seo, M.B.; Zhang, N.K.; Huang, J.J.; Zhang, L.I.; Tao, H.W. A Bottom-up Reward Pathway Mediated by Somatostatin Neurons in the Medial Septum Complex Underlying Appetitive Learning. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidenbecher, T.; Laxmi, T.R.; Stork, O.; Pape, H.C. Amygdalar and Hippocampal Theta Rhythm Synchronization during Fear Memory Retrieval. Science 2003, 301, 846–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adhikari, A.; Topiwala, M.A.; Gordon, J.A. Single Units in the Medial Prefrontal Cortex with Anxiety-Related Firing Patterns Are Preferentially Influenced by Ventral Hippocampal Activity. Neuron 2011, 71, 898–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gordon, J.A.; Lacefield, C.O.; Kentros, C.G.; Hen, R. State-Dependent Alterations in Hippocampal Oscillations in Serotonin 1A Receptor-Deficient Mice. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 6509–6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, M.G.; Chrobak, J.J.; Sik, A.; Wiley, R.G.; Buzsáki, G. Hippocampal Theta Activity Following Selective Lesion of the Septal Cholinergic SysteM. Neuroscience 1994, 62, 1033–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Z.; Yakel, J.L. Cholinergic Regulation of Hippocampal Theta Rhythm. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konopacki, J.; Bland, B.H.; Bruce MacIver, M.; Roth, S.H. Cholinergic Theta Rhythm in Transected Hippocampal Slices: Independent CA1 and Dentate Generators. Brain Res. 1987, 436, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, T.; Konopacki, J.; Bocian, R.; Caban, B. Theta-Related Gating Cells in Hippocampal Formation: In Vivo and in Vitro Study. Hippocampus 2013, 23, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, E.A.; Richard, A.; Thwaites, M.; Ailon, J.; Peters, S.; Dickson, C.T. Cyclic and Sleep-like Spontaneous Alternations of Brain State under Urethane Anaesthesia. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrón-Oyarzo, I.; Espinosa, N.; Aguilar, M.; Fuenzalida, M.; Aboitiz, F.; Fuentealba, P. Coordinated Prefrontal–Hippocampal Activity and Navigation Strategy-Related Prefrontal Firing during Spatial Memory Formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 7123–7128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bassant, M.H.; Simon, A.; Poindessous-Jazat, F.; Csaba, Z.; Epelbaum, J.; Dournaud, P. Medial Septal GABAergic Neurons Express the Somatostatin Sst2A Receptor: Functional Consequences on Unit Firing and Hippocampal Theta. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 2032–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montgomery, S.M.; Betancur, M.I.; Buzsáki, G. Behavior-Dependent Coordination of Multiple Theta Dipoles in the Hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 1381–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fuhrmann, F.; Justus, D.; Sosulina, L.; Kaneko, H.; Beutel, T.; Friedrichs, D.; Schoch, S.; Schwarz, M.K.; Fuhrmann, M.; Remy, S. Locomotion, Theta Oscillations, and the Speed-Correlated Firing of Hippocampal Neurons Are Controlled by a Medial Septal Glutamatergic Circuit. Neuron 2015, 86, 1253–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vinck, M.; Batista-Brito, R.; Knoblich, U.; Cardin, J.A. Arousal and Locomotion Make Distinct Contributions to Cortical Activity Patterns and Visual Encoding. Neuron 2015, 86, 740–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deng, K.; Yang, L.; Xie, J.; Tang, H.; Wu, G.S.; Luo, H.R. Whole-Brain Mapping of Projection from Mouse Lateral Septal Nucleus. Biol. Open 2019, 8, bio043554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, C.; Yao, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Cheng, M.; Chen, J.; Zhao, R.; Liao, F.; Shi, R.; Song, S. Somatostatin Neurons in the Basal Forebrain Promote High-Calorie Food Intake. Available online: https://europepmc.org/article/med/28683305 (accessed on 8 September 2020).
- Besnard, A.; Gao, Y.; TaeWoo Kim, M.; Twarkowski, H.; Reed, A.K.; Langberg, T.; Feng, W.; Xu, X.; Saur, D.; Zweifel, L.S.; et al. Dorsolateral Septum Somatostatin Interneurons Gate Mobility to Calibrate Context-Specific Behavioral Fear Responses. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.; Kim, D.W.; Anderson, D.J. Antagonistic Control of Social versus Repetitive Self-Grooming Behaviors by Separable Amygdala Neuronal Subsets. Cell 2014, 158, 1348–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korchynska, S.; Rebernik, P.; Pende, M.; Boi, L.; Alpár, A.; Tasan, R.; Becker, K.; Balueva, K.; Saghafi, S.; Wulff, P.; et al. A Hypothalamic Dopamine Locus for Psychostimulant-Induced Hyperlocomotion in Mice. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, A.Z.; Gordon, J.A. Long-Range Neural Synchrony in Behavior. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 38, 171–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khemka, S.; Barnes, G.; Dolan, R.J.; Bach, D.R. Dissecting the Function of Hippocampal Oscillations in a Human Anxiety Model. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 6869–6876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cornwell, B.R.; Arkin, N.; Overstreet, C.; Carver, F.W.; Grillon, C. Distinct Contributions of Human Hippocampal Theta to Spatial Cognition and Anxiety. Hippocampus 2012, 22, 1848–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, N. Grid Cells and Theta as Oscillatory Interference: Theory and Predictions. Hippocampus 2008, 18, 1157–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wells, C.E.; Amos, D.P.; Jeewajee, A.; Douchamps, V.; Rodgers, J.; O’Keefe, J.; Burgess, N.; Lever, C. Novelty and Anxiolytic Drugs Dissociate Two Components of Hippocampal Theta in Behaving Rats. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 8650–8667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adhikari, A.; Topiwala, M.A.; Gordon, J.A. Synchronized Activity between the Ventral Hippocampus and the Medial Prefrontal Cortex during Anxiety. Neuron 2010, 65, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kalueff, A.V.; Stewart, A.M.; Song, C.; Berridge, K.C.; Graybiel, A.M.; Fentress, J.C. Neurobiology of Rodent Self-Grooming and Its Value for Translational Neuroscience. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2016, 17, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Negrón-Oyarzo, I.; Neira, D.; Espinosa, N.; Fuentealba, P.; Aboitiz, F. Prenatal Stress Produces Persistence of Remote Memory and Disrupts Functional Connectivity in the Hippocampal-Prefrontal Cortex Axis. Cereb. Cortex 2015, 25, 3132–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Frequency Band | Light off | Light on | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Slow band (0.5–3 Hz) | 73.2 ± 3.3 | 71.9 ± 3.4 | 0.531 |
| Theta (4–7 Hz) | 68.3 ± 3.3 | 78.4 ± 4.4 | 7.99 × 10−7 (*) |
| Slow-gamma (20–40 Hz) | 22.5 ± 1.9 | 23.1 ± 1.8 | 0.266 |
| High-gamma (60–140 Hz) | 6.6 ± 0.5 | 6.8 ± 0.5 | 0.158 |
| Frequency Band | Light off | Light on | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Slow band (0.5–3 Hz) | 79.4 ± 7.3 | 81.8 ± 4.3 | 0.63 |
| Theta (4–7 Hz) | 58.8 ± 9.7 | 63.1 ± 10.6 | 0.259 |
| Slow-gamma (20–40 Hz) | 17.7 ± 2.7 | 17.3 ± 2.6 | 0.784 |
| High-gamma (60–140 Hz) | 6.1 ± 1.1 | 6.3 ± 1.0 | 0.605 |
| Frequency Band | Light off | Light on | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Slow band (0.5–3 Hz) | 0.16 ± 0.009 | 0.15 ± 0.008 | 0.97 |
| Theta (3–6 Hz) | 0.18 ± 0.008 | 0.15 ± 0.007 | 2.4 × 10−6 (*) |
| Slow-gamma (20–40 Hz) | 0.08 ± 0.003 | 0.075 ± 0.003 | 0.27 |
| High-gamma (60–140 Hz) | 0.06 ± 0.001 | 0.06 ± 0.001 | 0.74 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Espinosa, N.; Alonso, A.; Caneo, M.; Moran, C.; Fuentealba, P. Optogenetic Suppression of Lateral Septum Somatostatin Neurons Enhances Hippocampus Cholinergic Theta Oscillations and Local Synchrony. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13010001
Espinosa N, Alonso A, Caneo M, Moran C, Fuentealba P. Optogenetic Suppression of Lateral Septum Somatostatin Neurons Enhances Hippocampus Cholinergic Theta Oscillations and Local Synchrony. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleEspinosa, Nelson, Alejandra Alonso, Mauricio Caneo, Constanza Moran, and Pablo Fuentealba. 2023. "Optogenetic Suppression of Lateral Septum Somatostatin Neurons Enhances Hippocampus Cholinergic Theta Oscillations and Local Synchrony" Brain Sciences 13, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13010001
APA StyleEspinosa, N., Alonso, A., Caneo, M., Moran, C., & Fuentealba, P. (2023). Optogenetic Suppression of Lateral Septum Somatostatin Neurons Enhances Hippocampus Cholinergic Theta Oscillations and Local Synchrony. Brain Sciences, 13(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13010001





