Ictal fMRI: Mapping Seizure Topography with Rhythmic BOLD Oscillations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Case Information
2.2. fMRI Methods
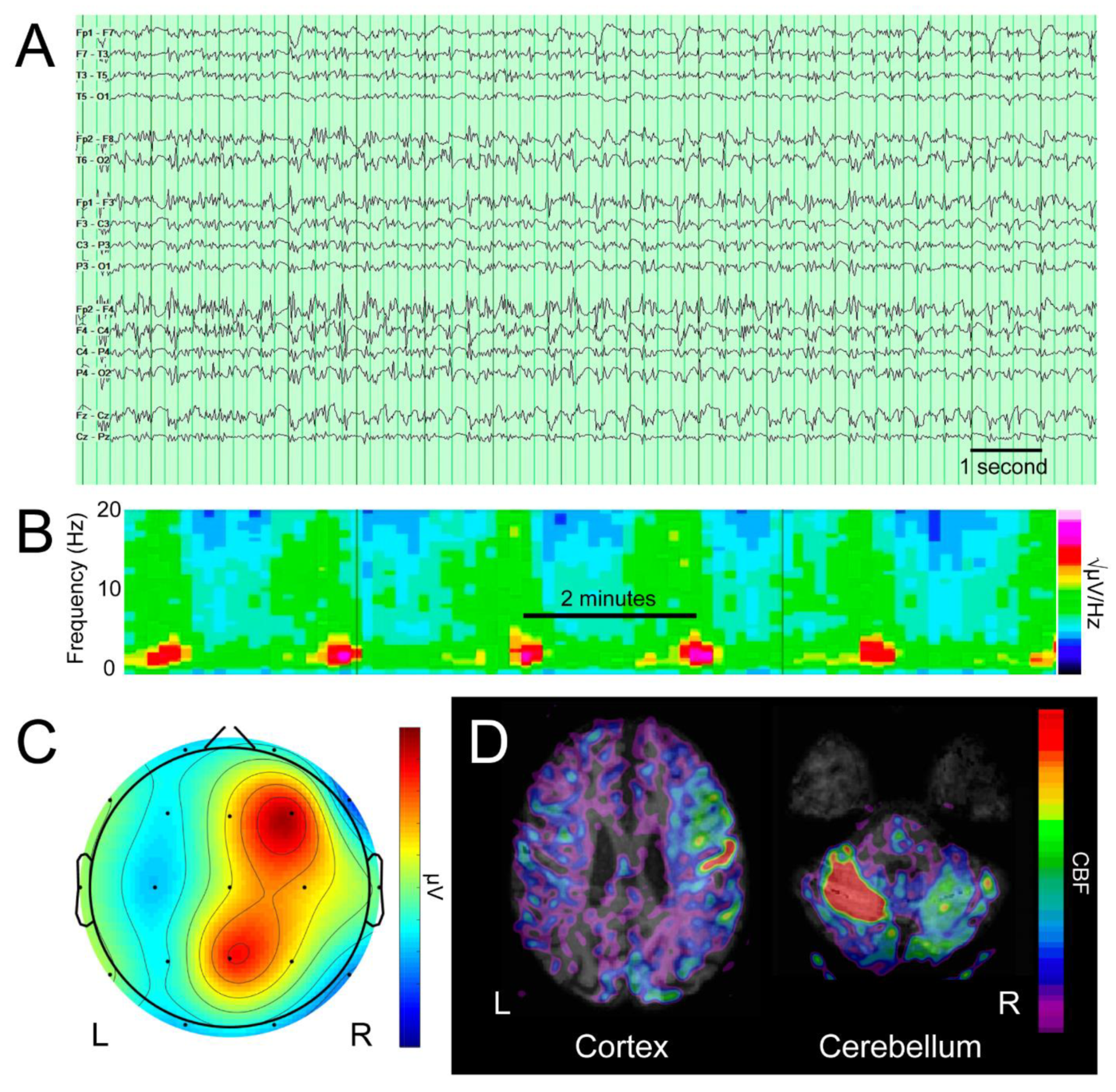
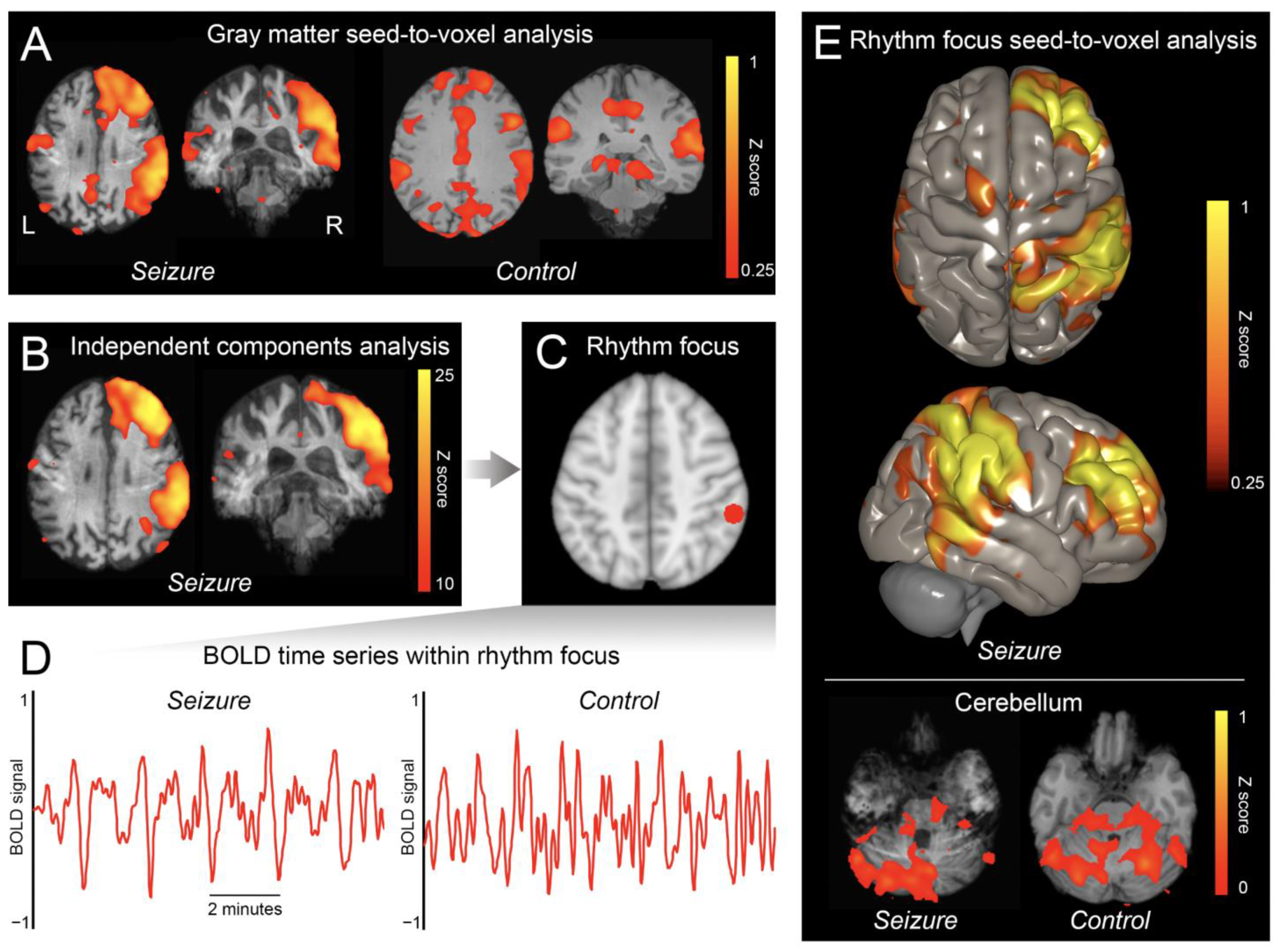
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- San-Juan, D.; Dávila-Rodríguez, D.O.; Jiménez, C.R.; González, M.S.; Carranza, S.M.; Mendoza, J.R.H.; Anschel, D.J. Neuromodulation techniques for status epilepticus: A review. Brain Stimul. 2019, 12, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Nguyen, P.; Pham, N.; Bui, N.; Truong, H.; Ha, S.; Vu, T. Epileptic seizure detection and experimental treatment: A review. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, U.J.; Duncan, J.S.; Lemieux, L. Mapping hemodynamic correlates of seizures using fMRI: A review. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2013, 34, 447–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonmezturk, H.H.; Morgan, V.; Abou-Khalil, B. Focal seizure propagation illustrated by fMRI. Epileptic Disord. 2011, 13, 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salek-Haddadi, A.; Merschhemke, M.; Lemieux, L.; Fish, D.R. Simultaneous EEG-correlated ictal fMRI. Neuroimage 2002, 16, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salek-Haddadi, A.; Mayer, T.; Hamandi, K.; Symms, M.; Josephs, O.; Fluegel, D.; Woermann, F.; Richardson, M.P.; Noppeney, U.; Wolf, P.; et al. Imaging seizure activity: A combined EEG/EMG-fMRI study in reading epilepsy. Epilepsia 2009, 50, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donaire, A.; Bargallo, N.; Falcón, C.; Maestro, I.; Carreno, M.; Setoain, J.; Rumià, J.; Fernández, S.; Pintor, L.; Boget, T. Identifying the structures involved in seizure generation using sequential analysis of ictal-fMRI data. Neuroimage 2009, 47, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szaflarski, J.P.; DiFrancesco, M.; Hirschauer, T.; Banks, C.; Privitera, M.D.; Gotman, J.; Holland, S.K. Cortical and subcortical contributions to absence seizure onset examined with EEG/fMRI. Epilepsy Behav. 2010, 18, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chaudhary, U.J.; Centeno, M.; Thornton, R.C.; Rodionov, R.; Vulliemoz, S.; McEvoy, A.W.; Diehl, B.; Walker, M.C.; Duncan, J.S.; Carmichael, D.W.; et al. Mapping human preictal and ictal haemodynamic networks using simultaneous intracranial EEG-fMRI. NeuroImage Clin. 2016, 11, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sierra-Marcos, A.; Maestro, I.; Falcón, C.; Donaire, A.; Setoain, J.; Aparicio, J.; Rumià, J.; Pintor, L.; Boget, T.; Carreño, M.; et al. Ictal EEG-fMRI in localization of epileptogenic area in patients with refractory neocortical focal epilepsy. Epilepsia 2013, 54, 1688–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tana, M.G.; Bianchi, A.M.; Sclocco, R.; Franchin, T.; Cerutti, S.; Leal, A. Parcel-based connectivity analysis of fMRI data for the study of epileptic seizure propagation. Brain Topogr. 2012, 25, 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalczyk, M.A.; Omidvarnia, A.; Dhollander, T.; Jackson, G.D. Dynamic analysis of fMRI activation during epileptic spikes can help identify the seizure origin. Epilepsia 2020, 61, 2558–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murta, T.; Leal, A.; Garrido, M.I.; Figueiredo, P. Dynamic Causal Modelling of epileptic seizure propagation pathways: A combined EEG-fMRI study. Neuroimage 2012, 62, 1634–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vinette, S.A.; Premji, S.; Beers, C.A.; Gaxiola-Valdez, I.; Pittman, D.J.; Slone, E.G.; Goodyear, B.G.; Federico, P. Pre-ictal BOLD alterations: Two cases of patients with focal epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 2016, 127, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Won, J.; Choi, D.S.; Hong, S.J.; Shin, H.S.; Baek, H.J.; Choi, H.C.; Kim, M.; Kim, R.B. Crossed cerebellar hyperperfusion in patients with seizure-related cerebral cortical lesions: An evaluation with arterial spin labelling perfusion MR imaging. Radiol. Med. 2018, 123, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, D.; Threlkeld, Z.D.; Bodien, Y.G.; Kirsch, J.E.; Huang, S.Y.; Schaefer, P.W.; Rapalino, O.; Hochberg, L.R.; Rosen, B.R.; Edlow, B.L. Intact brain network function in an unresponsive patient with COVID-19. Ann Neurol. 2020, 88, 851–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield-Gabrieli, S.; Nieto-Castanon, A. Conn: A functional connectivity toolbox for correlated and anticorrelated brain networks. Brain Connect. 2012, 2, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Threlkeld, Z.D.; Bodien, Y.G.; Rosenthal, E.S.; Giacino, J.T.; Nieto-Castanon, A.; Wu, O.; Whitfield-Gabrieli, S.; Edlow, B.L. Functional networks reemerge during recovery of consciousness after acute severe traumatic brain injury. Cortex 2018, 106, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behzadi, Y.; Restom, K.; Liau, J.; Liu, T.T. A component based noise correction method (CompCor) for BOLD and perfusion based fMRI. Neuroimage 2007, 37, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bohnen, N.I.; O’Brien, T.J.; Mullan, B.P.; So, E.L. Cerebellar changes in partial seizures: Clinical correlations of quantitative SPECT and MRI analysis. Epilepsia 1998, 39, 640–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milligan, T.A.; Zamani, A.; Bromfield, E. Frequency and patterns of MRI abnormalities due to status epilepticus. Seizure 2009, 18, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baumgartner, C.; Koren, J.P. Seizure detection using scalp-EEG. Epilepsia 2018, 59, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demertzi, A.; Tagliazucchi, E.; Dehaene, S.; Deco, G.; Barttfeld, P.; Raimondo, F.; Martial, C.; Fernández-Espejo, D.; Rohaut, B.; Voss, H.U.; et al. Human consciousness is supported by dynamic complex patterns of brain signal coordination. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaat7603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fischer, D.; Rapalino, O.; Fecchio, M.; Edlow, B.L. Ictal fMRI: Mapping Seizure Topography with Rhythmic BOLD Oscillations. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12121710
Fischer D, Rapalino O, Fecchio M, Edlow BL. Ictal fMRI: Mapping Seizure Topography with Rhythmic BOLD Oscillations. Brain Sciences. 2022; 12(12):1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12121710
Chicago/Turabian StyleFischer, David, Otto Rapalino, Matteo Fecchio, and Brian L. Edlow. 2022. "Ictal fMRI: Mapping Seizure Topography with Rhythmic BOLD Oscillations" Brain Sciences 12, no. 12: 1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12121710
APA StyleFischer, D., Rapalino, O., Fecchio, M., & Edlow, B. L. (2022). Ictal fMRI: Mapping Seizure Topography with Rhythmic BOLD Oscillations. Brain Sciences, 12(12), 1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12121710