Exosomes in Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury: Current Perspectives and Future Challenges
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Characteristics of Exosomes
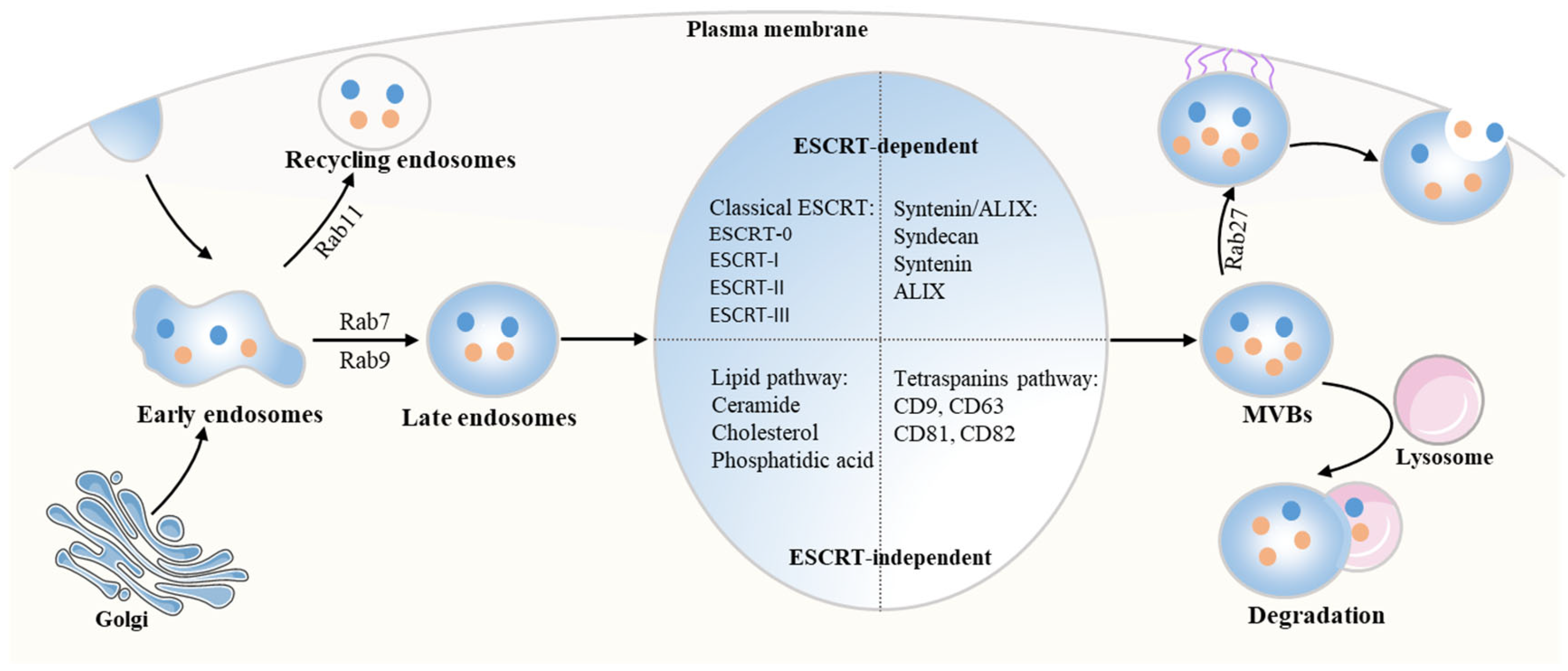
2.1. The Biogenesis of Exosomes
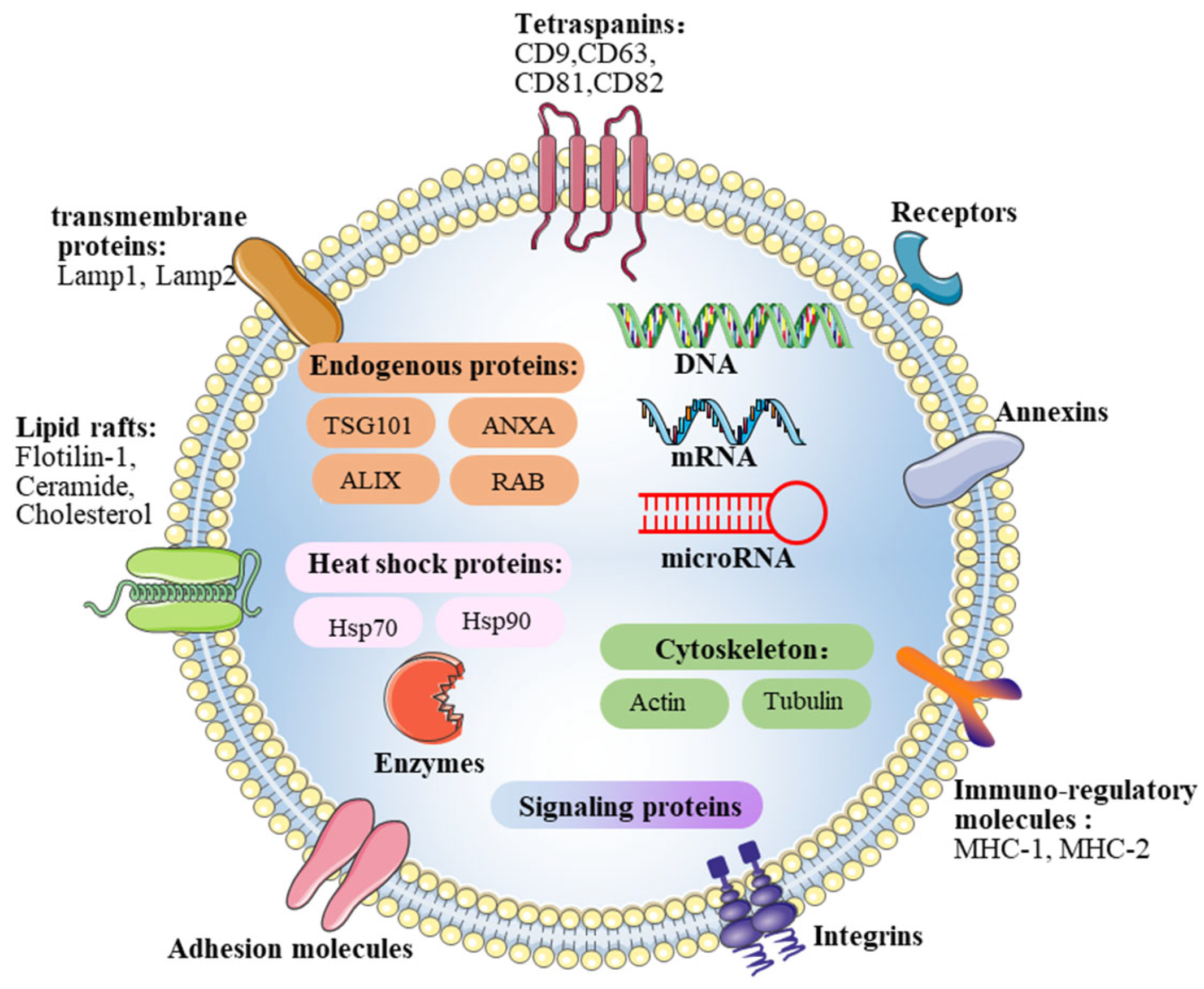
2.2. Contents of Exosomes
2.3. Exosomes Uptake in Recipient Cells during Intercellular Communication
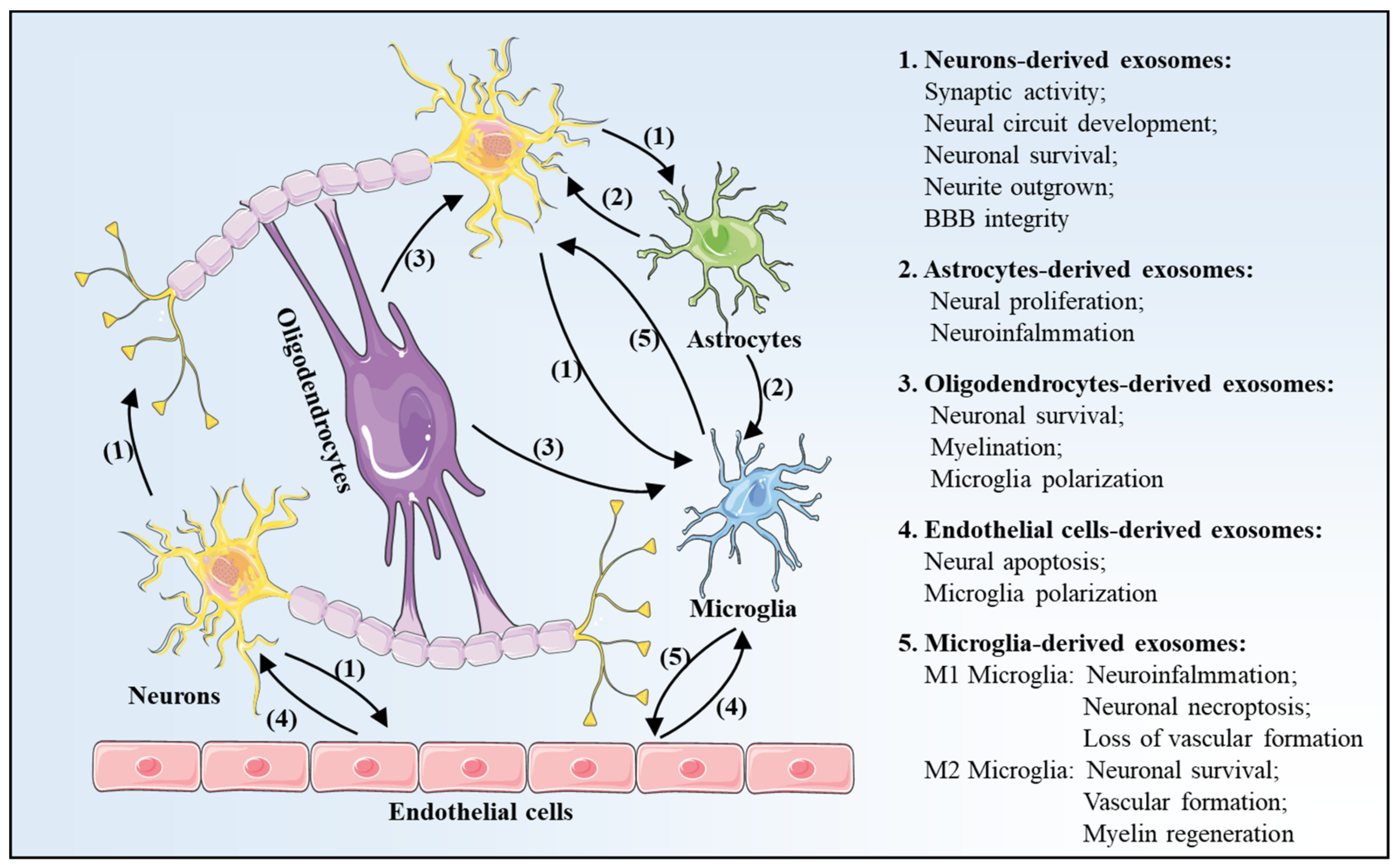
3. Exosomes Profile Changes after Is Chemia-Reperfusion in Brain
3.1. Neurons-Derived Exosomes
3.2. Astrocytes-Derived Exosomes
3.3. Oligodendrocytes-Derived Exosomes
3.4. Endothelial Cells-Derived Exosomes
3.5. Microglia-Derived Exosomes
4. Effects of Exosomes in Cerebral I/R Injury
4.1. Exosomes Effects on Neurogenesis
4.2. Exosomes Effects on Angiogenesis
4.3. Exosomes Effects on Immune Regulation
5. Exosomes-Based Therapy and Application in Cerebral I/R Injury
5.1. MSCs-Derived Exosomes
5.2. NSCs-Derived Exosomes
5.3. IPSCs-Derived Exosomes
| Stem Cells | Contents | Mechanism | Function | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSCs | miR-26b-5p | CH25H | Microglial M1 polarization | [77] |
| miR-133b | N/A | Neurite outgrown | [95,96] | |
| miR-17-92 | PTEN/Akt | Neural plasticity | [97] | |
| N/A | NF-kB | Angiogenesis | [98] | |
| PEDF | Autophagy | neuronal apoptosis | [99] | |
| miR-22-3p | IRF5 | Microglial M1 polarization | [100] | |
| miR-223-3p | CysLT2R | Microglial M2 polarization | [101] | |
| miR-146a-5p | IRAK1/TRAF6 | Neuro-inflammation | [102] | |
| miR-138-5p | lipocalin 2 | Proliferation of astrocytes Inflammation | [103] | |
| miR-221 | ATF3 | Inflammation Neuronal apoptosis | [104] | |
| NSCs | N/A | Bcl-2 | Apoptosis Mitochondrial ultrastructure | [115] |
| N/A | IL-10, TGF-β1 | Inflammation | [117] | |
| iPSCs | N/A | STAT3 | Angiogenesis | [122] |
| N/A | PTEN/Akt | neurite outgrowth | [124] |
5.4. The Limitations of Exosomes-Based Therapy in Cerebral I/R Injury
6. Conclusions and Prospect
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Benesch, C.; Glance, L.G.; Derdeyn, C.P.; Fleisher, L.A.; Holloway, R.G.; Messe, S.R.; Mijalski, C.; Nelson, M.T.; Power, M.; Welch, B.G.; et al. Perioperative Neurological Evaluation and Management to Lower the Risk of Acute Stroke in Patients Undergoing Noncardiac, Nonneurological Surgery: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Circulation 2021, 143, e923–e946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Hu, S.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Xiong, X.; Hu, X.; Chen, J.; Qiu, S. Interleukins and Ischemic Stroke. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 828447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orellana-Urzua, S.; Rojas, I.; Libano, L.; Rodrigo, R. Pathophysiology of Ischemic Stroke: Role of Oxidative Stress. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2020, 26, 4246–4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schellinger, P.D.; Kohrmann, M. 4.5-hour time window for intravenous thrombolysis with recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator is established firmly. Stroke 2014, 45, 912–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balami, J.S.; Sutherland, B.A.; Buchan, A.M. Complications associated with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator therapy for acute ischaemic stroke. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2013, 12, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alia, C.; Cangi, D.; Massa, V.; Salluzzo, M.; Vignozzi, L.; Caleo, M.; Spalletti, C. Cell-to-Cell Interactions Mediating Functional Recovery after Stroke. Cells 2021, 10, 3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, M.; Martin-Jaular, L.; Lavieu, G.; Thery, C. Specificities of secretion and uptake of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles for cell-to-cell communication. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Fu, C.; Wu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y. Central Nervous System Cell-Derived Exosomes in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 9965564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, J.P.; Schulz, A.; Morrison, H. The role of exosomes in intercellular and inter-organ communication of the peripheral nervous system. FEBS Lett. 2022, 596, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Ma, S.; Lv, J.; Wang, X.; Afewerky, H.K.; Li, H.; Lu, Y. The emerging role of exosomes in Alzheimer’s disease. Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 68, 101321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rufino-Ramos, D.; Albuquerque, P.R.; Carmona, V.; Perfeito, R.; Nobre, R.J.; Pereira de Almeida, L. Extracellular vesicles: Novel promising delivery systems for therapy of brain diseases. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2017, 262, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.G.; Buller, B.; Chopp, M. Exosomes—beyond stem cells for restorative therapy in stroke and neurological injury. Nat. Reviews. Neurol. 2019, 15, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Li, J.Y. Exosomes in Parkinson’s Disease: Current Perspectives and Future Challenges. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 964–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijnen, H.F.; Schiel, A.E.; Fijnheer, R.; Geuze, H.J.; Sixma, J.J. Activated platelets release two types of membrane vesicles: Microvesicles by surface shedding and exosomes derived from exocytosis of multivesicular bodies and alpha-granules. Blood 1999, 94, 3791–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, T.; Furthauer, M. Biogenesis and function of ESCRT-dependent extracellular vesicles. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 74, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baietti, M.F.; Zhang, Z.; Mortier, E.; Melchior, A.; Degeest, G.; Geeraerts, A.; Ivarsson, Y.; Depoortere, F.; Coomans, C.; Vermeiren, E.; et al. Syndecan-syntenin-ALIX regulates the biogenesis of exosomes. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 14, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Zhan, W.; Gao, Y.; Huang, L.; Gong, R.; Wang, W.; Zhang, R.; Wu, Y.; Gao, S.; Kang, T. RAB31 marks and controls an ESCRT-independent exosome pathway. Cell Res. 2021, 31, 157–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuffers, S.; Sem Wegner, C.; Stenmark, H.; Brech, A. Multivesicular endosome biogenesis in the absence of ESCRTs. Traffic 2009, 10, 925–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghossoub, R.; Leblanc, R.; David, G.; Zimmermann, P. Tetraspanins and syndecans: Partners in crime for ‘dealing’ exosomes? Med. Sci. 2021, 37, 1101–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anakor, E.; Le Gall, L.; Dumonceaux, J.; Duddy, W.J.; Duguez, S. Exosomes in Ageing and Motor Neurone Disease: Biogenesis, Uptake Mechanisms, Modifications in Disease and Uses in the Development of Biomarkers and Therapeutics. Cells 2021, 10, 2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skotland, T.; Hessvik, N.P.; Sandvig, K.; Llorente, A. Exosomal lipid composition and the role of ether lipids and phosphoinositides in exosome biology. J. Lipid Res. 2019, 60, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.Y.; Li, Q.Q.; Sheng, R. The role and therapeutic potential of exosomes in ischemic stroke. Neurochem. Int. 2021, 151, 105194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, X.; Zuo, Z.; Hong, W.; Tang, H.; Geng, W. Progress of Research on Exosomes in the Protection Against Ischemic Brain Injury. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeppesen, D.K.; Fenix, A.M.; Franklin, J.L.; Higginbotham, J.N.; Zhang, Q.; Zimmerman, L.J.; Liebler, D.C.; Ping, J.; Liu, Q.; Evans, R.; et al. Reassessment of Exosome Composition. Cell 2019, 177, 428–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Escrevente, C.; Keller, S.; Altevogt, P.; Costa, J. Interaction and uptake of exosomes by ovarian cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Wang, Y.; Hsu, C.Y.; Gao, Y.; Meyers, C.A.; Chang, L.; Zhang, L.; Broderick, K.; Ding, C.; Peault, B.; et al. Human perivascular stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles mediate bone repair. eLife 2019, 8, e48191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguchi, S.; Takefuji, M.; Sakaguchi, T.; Ishihama, S.; Mori, Y.; Tsuda, T.; Takikawa, T.; Yoshida, T.; Ohashi, K.; Shimizu, Y.; et al. Cardiomyocytes capture stem cell-derived, anti-apoptotic microRNA-214 via clathrin-mediated endocytosis in acute myocardial infarction. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 11665–11674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.; Du, Z.; Zhang, H.; Feng, Y.; Qi, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, J. Endocytic pathway inhibition attenuates extracellular vesicle-induced reduction of chemosensitivity to bortezomib in multiple myeloma cells. Theranostics 2021, 11, 2364–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, M.; Saheera, S.; Dubey, P.K.; Kahn-Krell, A.; Kumar Govindappa, P.; Singh, S.; Tousif, S.; Zhang, Q.; Lal, H.; Zhang, J.; et al. Novel Mechanisms of Exosome-Mediated Phagocytosis of Dead Cells in Injured Heart. Circ. Res. 2021, 129, 1006–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, K.J.; Christianson, H.C.; Wittrup, A.; Bourseau-Guilmain, E.; Lindqvist, E.; Svensson, L.M.; Morgelin, M.; Belting, M. Exosome uptake depends on ERK1/2-heat shock protein 27 signaling and lipid Raft-mediated endocytosis negatively regulated by caveolin-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 17713–17724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa Verdera, H.; Gitz-Francois, J.J.; Schiffelers, R.M.; Vader, P. Cellular uptake of extracellular vesicles is mediated by clathrin-independent endocytosis and macropinocytosis. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2017, 266, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prada, I.; Meldolesi, J. Binding and Fusion of Extracellular Vesicles to the Plasma Membrane of Their Cell Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hakulinen, J.; Junnikkala, S.; Sorsa, T.; Meri, S. Complement inhibitor membrane cofactor protein (MCP.; CD46) is constitutively shed from cancer cell membranes in vesicles and converted by a metalloproteinase to a functionally active soluble form. Eur. J. Immunol. 2004, 34, 2620–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; He, F.; Li, T.; Chen, J.; Jiang, L.; Ouyang, X.P.; Zuo, L. Role of Exosomes in Brain Diseases. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 743353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.M.; Feng, Y.S.; Tan, Z.X.; Xing, Y.; Dong, F.; Zhang, F. The role of exosomes in stroke. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 6217–6228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.K.T.; Langfelder, P.; Horvath, S.; Palazzolo, M.J. Exosomes and Homeostatic Synaptic Plasticity Are Linked to Each other and to Huntington’s, Parkinson’s, and Other Neurodegenerative Diseases by Database-Enabled Analyses of Comprehensively Curated Datasets. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, C.S.; Fu, S.J.; Hsu, C.L.; Jeng, C.J.; Tang, C.Y.; Huang, Y.S.; Tang, S.C. Neuronal Exosomes Secreted under Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation/Reperfusion Presenting Differentially Expressed miRNAs and Affecting Neuronal Survival and Neurite Outgrowth. Neuromol. Med. 2021, 23, 404–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, Y.; Yelick, J.; Jin, S.; Tian, Y.; Chiang, M.S.R.; Higashimori, H.; Brown, E.; Jarvis, R.; Yang, Y. Exosome reporter mice reveal the involvement of exosomes in mediating neuron to astroglia communication in the CNS. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, H.; Zhang, X.; Chen, R.; Miao, J.; Wang, L.; Cui, L.; Ji, H.; Liu, Y. Cortical Neuron-Derived Exosomal MicroRNA-181c-3p Inhibits Neuroinflammation by Downregulating CXCL1 in Astrocytes of a Rat Model with Ischemic Brain Injury. Neuroimmunomodulation 2019, 26, 217–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Gong, F.; Ge, X.; Lv, C.; Huang, C.; Feng, S.; Zhou, Z.; Rong, Y.; Wang, J.; Ji, C.; et al. Neuron-derived exosomes-transmitted miR-124-3p protect traumatically injured spinal cord by suppressing the activation of neurotoxic microglia and astrocytes. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Li, J.; Zheng, J.; Qin, S. Reactive Astrocytes in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Aging Dis. 2019, 10, 664–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Wang, X.; Ding, Y.; Ren, Z.; Fang, J.; Sun, T.; Guo, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wen, J. CSE-Derived H2S Inhibits Reactive Astrocytes Proliferation and Promotes Neural Functional Recovery after Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Mice Via Inhibition of RhoA/ROCK2 Pathway. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2021, 12, 2580–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Liu, J.; Yang, C.; Xu, Z.; Huang, J.; Lin, J. Astrocyte-derived exosome-transported microRNA-34c is neuroprotective against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via TLR7 and the NF-kappaB/MAPK pathways. Brain Res. Bull. 2020, 163, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, X.; Li, D.; Wang, F.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, Z. Protective Role of Astrocyte-Derived Exosomal microRNA-361 in Cerebral Ischemic-Reperfusion Injury by Regulating the AMPK/mTOR Signaling Pathway and Targeting CTSB. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2020, 16, 1863–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.; Yao, X.; Jiang, Q.; Yang, Y.; He, X.; Tian, W.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, H. Astrocyte-derived exosomes enriched with miR-873a-5p inhibit neuroinflammation via microglia phenotype modulation after traumatic brain injury. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa Gonzalez, M.; Perez-Alvarez, M.J. A 3R-Tau-mediated mechanism in oligodendrocytes: Could it be the key for neuroprotection after stroke? Neural Regen. Res. 2021, 16, 2401–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frohlich, D.; Kuo, W.P.; Fruhbeis, C.; Sun, J.J.; Zehendner, C.M.; Luhmann, H.J.; Pinto, S.; Toedling, J.; Trotter, J.; Kramer-Albers, E.M. Multifaceted effects of oligodendroglial exosomes on neurons: Impact on neuronal firing rate, signal transduction and gene regulation. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruhbeis, C.; Frohlich, D.; Kuo, W.P.; Amphornrat, J.; Thilemann, S.; Saab, A.S.; Kirchhoff, F.; Mobius, W.; Goebbels, S.; Nave, K.A.; et al. Neurotransmitter-triggered transfer of exosomes mediates oligodendrocyte-neuron communication. PLoS Biol. 2013, 11, e1001604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Cesca, F.; Loers, G.; Schweizer, M.; Buck, F.; Benfenati, F.; Schachner, M.; Kleene, R. Synapsin I is an oligomannose-carrying glycoprotein, acts as an oligomannose-binding lectin, and promotes neurite outgrowth and neuronal survival when released via glia-derived exosomes. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 7275–7290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fitzner, D.; Schnaars, M.; van Rossum, D.; Krishnamoorthy, G.; Dibaj, P.; Bakhti, M.; Regen, T.; Hanisch, U.K.; Simons, M. Selective transfer of exosomes from oligodendrocytes to microglia by macropinocytosis. J. Cell. Sci. 2011, 124, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peferoen, L.; Kipp, M.; van der Valk, P.; van Noort, J.M.; Amor, S. Oligodendrocyte-microglia cross-talk in the central nervous system. Immunology 2014, 141, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridder, D.A.; Wenzel, J.; Muller, K.; Tollner, K.; Tong, X.K.; Assmann, J.C.; Stroobants, S.; Weber, T.; Niturad, C.; Fischer, L.; et al. Brain endothelial TAK1 and NEMO safeguard the neurovascular unit. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 1529–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Cao, F.; Takase, H.; Arai, K.; Lo, E.H.; Lok, J. Blood-Brain Barrier Mechanisms in Stroke and Trauma. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2022, 273, 267–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Chai, Y.; Lv, S.; Ye, M.; Wu, M.; Xie, L.; Fan, Y.; Zhu, X.; Gao, Z. Endothelial cell-derived exosomes protect SH-SY5Y nerve cells against ischemia/reperfusion injury. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 40, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, S.; Gao, B.; Sun, C.; Bai, Y.; Cheng, D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, J.; Xu, D. Vascular Endothelial Cell-derived Exosomes Protect Neural Stem Cells Against Ischemia/reperfusion Injury. Neuroscience 2020, 441, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, D.L.; Zuluaga-Ramirez, V.; Gajghate, S.; Reichenbach, N.L.; Polyak, B.; Persidsky, Y.; Rom, S. miR-98 reduces endothelial dysfunction by protecting blood-brain barrier (BBB) and improves neurological outcomes in mouse ischemia/reperfusion stroke model. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. Off. J. Int. Soc. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2020, 40, 1953–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.Y.; Song, J.X.; Cai, H.; Wang, P.P.; Yin, Q.L.; Zhang, Y.D.; Chen, J.; Li, M.; Song, J.J.; Wang, Y.L.; et al. Healthy Serum-Derived Exosomes Improve Neurological Outcomes and Protect Blood-Brain Barrier by Inhibiting Endothelial Cell Apoptosis and Reversing Autophagy-Mediated Tight Junction Protein Reduction in Rat Stroke Model. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 841544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludewig, P.; Winneberger, J.; Magnus, T. The cerebral endothelial cell as a key regulator of inflammatory processes in sterile inflammation. J. Neuroimmunol. 2019, 326, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, H.; Yamaguchi, T.; Yano, H.; Tanaka, J. Microglial metabolic disturbances and neuroinflammation in cerebral infarction. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 145, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanazawa, M.; Ninomiya, I.; Hatakeyama, M.; Takahashi, T.; Shimohata, T. Microglia and Monocytes/Macrophages Polarization Reveal Novel Therapeutic Mechanism against Stroke. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wan, T.; Huang, Y.; Gao, X.; Wu, W.; Guo, W. Microglia Polarization: A Novel Target of Exosome for Stroke Treatment. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 842320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, M.; Li, C.; Yan, Z.; Hu, Z.; Dong, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H. Activated Microglia Exosomes Mediated miR-383-3p Promotes Neuronal Necroptosis Through Inhibiting ATF4 Expression in Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Neurochem. Res. 2021, 46, 1337–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z. Exosomal shuttled miR-424-5p from ischemic preconditioned microglia mediates cerebral endothelial cell injury through negatively regulation of FGF2/STAT3 pathway. Exp. Neurol. 2020, 333, 113411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Li, Z.; He, T.; Qu, M.; Jiang, L.; Li, W.; Shi, X.; Pan, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; et al. M2 microglia-derived exosomes protect the mouse brain from ischemia-reperfusion injury via exosomal miR-124. Theranostics 2019, 9, 2910–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Cai, G.; Liu, K.; Zhuang, Z.; Jia, K.; Pei, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Xu, S.; Cui, C.; et al. Microglia exosomal miRNA-137 attenuates ischemic brain injury through targeting Notch1. Aging 2021, 13, 4079–4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhu, P.; Liu, S.; Jin, Z.; Li, D.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, X.; Shu, C.; Yan, D.; Dong, Z. IL-4-polarized BV2 microglia cells promote angiogenesis by secreting exosomes. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. Off. Organ Wroc. Med. Univ. 2019, 28, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahman, A.A.; Amruta, N.; Pinteaux, E.; Bix, G.J. Neurogenesis After Stroke: A Therapeutic Perspective. Transl. Stroke Res. 2021, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, S.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Y.; Bihl, J.C. Exosomes from miRNA-126-modified endothelial progenitor cells alleviate brain injury and promote functional recovery after stroke. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2020, 26, 1255–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.L.; Zhu, Z.H.; Wang, Y.Z. Neural stem cell transplantation therapy for brain ischemic stroke: Review and perspectives. World J. Stem Cells 2019, 11, 817–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, H.; Yu, Y.; Chen, W.; Waqas, A.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L. Exosomes derived from human neural stem cells stimulated by interferon gamma improve therapeutic ability in ischemic stroke model. J. Adv. Res. 2020, 24, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffo-Romero, A.; Arab, T.; Al-Amri, I.S.; Le Marrec-Croq, F.; Van Camp, C.; Lemaire, Q.; Salzet, M.; Vizioli, J.; Sautiere, P.E.; Lefebvre, C. Medicinal Leech CNS as a Model for Exosome Studies in the Crosstalk between Microglia and Neurons. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tassew, N.G.; Charish, J.; Shabanzadeh, A.P.; Luga, V.; Harada, H.; Farhani, N.; D’Onofrio, P.; Choi, B.; Ellabban, A.; Nickerson, P.E.B.; et al. Exosomes Mediate Mobilization of Autocrine Wnt10b to Promote Axonal Regeneration in the Injured CNS. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Du, X.F.; Li, J.; Zi, H.X.; Bu, J.W.; Yan, Y.; Han, H.; Du, J.L. Neurons secrete miR-132-containing exosomes to regulate brain vascular integrity. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 882–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharghi-Namini, S.; Tan, E.; Ong, L.L.; Ge, R.; Asada, H.H. Dll4-containing exosomes induce capillary sprout retraction in a 3D microenvironment. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Lian, L.; Fu, R.; Liu, J.; Shan, X.; Jin, Y.; Xu, S. Microglia: The Hub of Intercellular Communication in Ischemic Stroke. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 889442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Xiao, L.; Qin, H.; Zhuang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Liu, L.; Di, C.; Zhang, Y. Exosomes-carried microRNA-26b-5p regulates microglia M1 polarization after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Cell Cycle 2020, 19, 1022–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajinejad, M.; Sahab-Negah, S. Neuroinflammation: The next target of exosomal microRNAs derived from mesenchymal stem cells in the context of neurological disorders. J. Cell. Physiol. 2021, 236, 8070–8081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, M.; Liu, H.; Zhu, R.; He, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Liang, D.; Zeng, Q.; et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes attenuate cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury-induced neuroinflammation and pyroptosis by modulating microglia M1/M2 phenotypes. Exp. Neurol. 2021, 341, 113700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; He, R.; Wang, P.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, L.; Liang, J. Exosomes from LPS-stimulated macrophages induce neuroprotection and functional improvement after ischemic stroke by modulating microglial polarization. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 2037–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Tu, Z.; Yang, D.; Hu, M.; Zhou, L.; Li, Q.; Yu, B.; Hou, S. Exosomes from hypoxic pre-treated ADSCs attenuate acute ischemic stroke-induced brain injury via delivery of circ-Rps5 and promote M2 microglia/macrophage polarization. Neurosci. Lett. 2022, 769, 136389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, H.; Sun, G.; Zhang, J.; Edwards, N.J.; Aronowski, J. Neuronal Interleukin-4 as a Modulator of Microglial Pathways and Ischemic Brain Damage. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 11281–11291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sheikh, A.M.; Nagai, A.; Wakabayashi, K.; Narantuya, D.; Kobayashi, S.; Yamaguchi, S.; Kim, S.U. Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation modulates neuroinflammation in focal cerebral ischemia: Contribution of fractalkine and IL-5. Neurobiol. Dis. 2011, 41, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Xiong, Y.; Liu, J. Exosomal miR-199a-5p derived from endothelial cells attenuates apoptosis and inflammation in neural cells by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress. Brain Res. 2020, 1726, 146515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, H.; Pan, J.J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, G.Y. Native and Bioengineered Exosomes for Ischemic Stroke Therapy. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 619565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahjin, F.; Chand, S.; Yelamanchili, S.V. Extracellular Vesicles as Drug Delivery Vehicles to the Central Nervous System. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. Off. J. Soc. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2020, 15, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Jiang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Liang, J.; Zhao, L. Curcumin-laden exosomes target ischemic brain tissue and alleviate cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting ROS-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2020, 117, 111314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fu, N.; Su, J.; Wang, X.; Li, X. Rapid Enkephalin Delivery Using Exosomes to Promote Neurons Recovery in Ischemic Stroke by Inhibiting Neuronal p53/Caspase-3. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 4273290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Cao, L.; He, C.; Ye, Q.; Liang, R.; You, W.; Zhang, H.; Wu, J.; Ye, J.; Tannous, B.A.; et al. Targeted delivery of neural progenitor cell-derived extracellular vesicles for anti-inflammation after cerebral ischemia. Theranostics 2021, 11, 6507–6521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Yang, G. Exosome Mediated Delivery of miR-124 Promotes Neurogenesis after Ischemia. Mol. Therapy. Nucleic Acids 2017, 7, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, S.; Vannberg, F.O.; Dixon, J.B. Lymphatic transport of exosomes as a rapid route of information dissemination to the lymph node. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lai, C.P.; Mardini, O.; Ericsson, M.; Prabhakar, S.; Maguire, C.; Chen, J.W.; Tannous, B.A.; Breakefield, X.O. Dynamic biodistribution of extracellular vesicles in vivo using a multimodal imaging reporter. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.; Peng, Y.; Zeng, H.; Chen, G. Progress in Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Ischemic Stroke. Stem Cells Int. 2021, 2021, 9923566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doeppner, T.R.; Herz, J.; Gorgens, A.; Schlechter, J.; Ludwig, A.K.; Radtke, S.; de Miroschedji, K.; Horn, P.A.; Giebel, B.; Hermann, D.M. Extracellular Vesicles Improve Post-Stroke Neuroregeneration and Prevent Postischemic Immunosuppression. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2015, 4, 1131–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xin, H.; Li, Y.; Buller, B.; Katakowski, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Shang, X.; Zhang, Z.G.; Chopp, M. Exosome-mediated transfer of miR-133b from multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells to neural cells contributes to neurite outgrowth. Stem Cells 2012, 30, 1556–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xin, H.; Wang, F.; Li, Y.; Lu, Q.E.; Cheung, W.L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.G.; Chopp, M. Secondary Release of Exosomes From Astrocytes Contributes to the Increase in Neural Plasticity and Improvement of Functional Recovery After Stroke in Rats Treated With Exosomes Harvested From MicroRNA 133b-Overexpressing Multipotent Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Cell Transplant. 2017, 26, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xin, H.; Katakowski, M.; Wang, F.; Qian, J.Y.; Liu, X.S.; Ali, M.M.; Buller, B.; Zhang, Z.G.; Chopp, M. MicroRNA cluster miR-17-92 Cluster in Exosomes Enhance Neuroplasticity and Functional Recovery After Stroke in Rats. Stroke 2017, 48, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, J.D.; Johansson, H.J.; Graham, C.S.; Vesterlund, M.; Pham, M.T.; Bramlett, C.S.; Montgomery, E.N.; Mellema, M.S.; Bardini, R.L.; Contreras, Z.; et al. Comprehensive Proteomic Analysis of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Exosomes Reveals Modulation of Angiogenesis via Nuclear Factor-KappaB Signaling. Stem Cells 2016, 34, 601–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.; Ding, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Ji, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, X. Exosomes derived from PEDF modified adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by regulation of autophagy and apoptosis. Exp. Cell Res. 2018, 371, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Yang, M.; Pan, Q.; Jin, H.L.; Li, H.F.; Wang, R.R.; Wang, Q.Y.; Zhang, J.P. MicroRNA-22-3p alleviates spinal cord ischemia/reperfusion injury by modulating M2 macrophage polarization via IRF5. J. Neurochem. 2021, 156, 106–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Gan, Y.; Xu, G.; Hua, K.; Liu, D. Exosomes from MSCs overexpressing microRNA-223-3p attenuate cerebral ischemia through inhibiting microglial M1 polarization mediated inflammation. Life Sci. 2020, 260, 118403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zou, X.; Zhang, R.; Xie, Y.; Feng, Z.; Li, F.; Han, J.; Sun, H.; Ouyang, Q.; Hua, S.; et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-146a-5p reduces microglial-mediated neuroinflammation via suppression of the IRAK1/TRAF6 signaling pathway after ischemic stroke. Aging 2021, 13, 3060–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Chen, D.; Gao, F.; Lv, H.; Zhang, G.; Sun, X.; Liu, L.; Mo, D.; Ma, N.; Song, L.; et al. Exosomes derived from microRNA-138-5p-overexpressing bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells confer neuroprotection to astrocytes following ischemic stroke via inhibition of LCN2. J. Biol. Eng. 2019, 13, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, Y.; Hu, J.; Lv, H.; Cui, X.; Di, W. miR-221 Exerts Neuroprotective Effects in Ischemic Stroke by Inhibiting the Proinflammatory Response. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. Off. J. Natl. Stroke Assoc. 2021, 30, 105489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Kim, E.; Choi, S.M.; Kim, D.W.; Kim, K.P.; Lee, I.; Kim, H.S. Microvesicles from brain-extract-treated mesenchymal stem cells improve neurological functions in a rat model of ischemic stroke. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nalamolu, K.R.; Venkatesh, I.; Mohandass, A.; Klopfenstein, J.D.; Pinson, D.M.; Wang, D.Z.; Kunamneni, A.; Veeravalli, K.K. Exosomes Secreted by the Cocultures of Normal and Oxygen-Glucose-Deprived Stem Cells Improve Post-stroke Outcome. Neuromol. Med. 2019, 21, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanpour, M.; Rezaie, J.; Nouri, M.; Panahi, Y. The role of extracellular vesicles in COVID-19 virus infection. Infect. Genet. Evol. J. Mol. Epidemiol. Evol. Genet. Infect. Dis. 2020, 85, 104422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Waqas, A.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, L. Exosomes: Applications in Respiratory Infectious Diseases and Prospects for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2020, 16, 399–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norouzi-Barough, L.; Asgari Khosroshahi, A.; Gorji, A.; Zafari, F.; Shahverdi Shahraki, M.; Shirian, S. COVID-19-Induced Stroke and the Potential of Using Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in the Regulation of Neuroinflammation. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriwastava, S.; Tandon, M.; Podury, S.; Prasad, A.; Wen, S.; Guthrie, G.; Kakara, M.; Jaiswal, S.; Subedi, R.; Elkhooly, M.; et al. COVID-19 and neuroinflammation: A literature review of relevant neuroimaging and CSF markers in central nervous system inflammatory disorders from SARS-COV2. J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 4448–4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, G.; Khan, A.A.; Guo, X.; Gu, Y. Clinical Efficacy and Meta-Analysis of Stem Cell Therapies for Patients with Brain Ischemia. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 6129579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, L.; Wei, Z.Z.; Jiang, M.Q.; Mohamad, O.; Yu, S.P. Stem cell transplantation therapy for multifaceted therapeutic benefits after stroke. Prog. Neurobiol. 2017, 157, 49–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boese, A.C.; Le, Q.E.; Pham, D.; Hamblin, M.H.; Lee, J.P. Neural stem cell therapy for subacute and chronic ischemic stroke. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamblin, M.H.; Lee, J.P. Neural Stem Cells for Early Ischemic Stroke. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, C.; Chen, H.; Li, L.; Ma, S.; Wang, H.; Fu, Y.; Qu, T. Neural Stem Cell-Conditioned Medium Ameliorated Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Rats. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 2018, 4659159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pluchino, S.; Cossetti, C. How stem cells speak with host immune cells in inflammatory brain diseases. Glia 2013, 61, 1379–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Chen, L.; Chen, W.; Li, B.; Yu, Y.; Lin, F.; Guo, X.; Wang, H.; Wu, G.; Gu, B.; et al. Neural Stem Cells Alleviate Inflammation via Neutralization of IFN-gamma Negative Effect in Ischemic Stroke Model. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2018, 14, 1178–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Yamanaka, S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 2006, 126, 663–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ford, E.; Pearlman, J.; Ruan, T.; Manion, J.; Waller, M.; Neely, G.G.; Caron, L. Human Pluripotent Stem Cells-Based Therapies for Neurodegenerative Diseases: Current Status and Challenges. Cells 2020, 9, 2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Nguyen, N.T.P.; Milanese, M.; Bonanno, G. Insights into Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Astrocytes in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasingh, S.; Sigamani, V.; Selvam, V.; Gurusamy, N.; Kirankumar, S.; Vasanthan, J.; Rajasingh, J. Comparative analysis of human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells and umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 8904–8919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Ling, X.; Hu, G.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Li, Q.; Zhao, B.; Wang, Y.; Deng, Z. Small extracellular vesicles secreted by human iPSC-derived MSC enhance angiogenesis through inhibiting STAT3-dependent autophagy in ischemic stroke. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagoshi, N.; Okano, H. iPSC-derived neural precursor cells: Potential for cell transplantation therapy in spinal cord injury. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 989–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.Y.; Zhu, Q.B.; Jin, L.Y.; Yang, Y.; Xu, X.Y.; Hu, X.Y. Exosomes derived from human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neural progenitor cells protect neuronal function under ischemic conditions. Neural Regen. Res. 2021, 16, 2064–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, C.; Zhou, F.; He, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cao, Y. Exosomes in Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury: Current Perspectives and Future Challenges. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1657. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12121657
Zhou C, Zhou F, He Y, Liu Y, Cao Y. Exosomes in Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury: Current Perspectives and Future Challenges. Brain Sciences. 2022; 12(12):1657. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12121657
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Chao, Fating Zhou, Yarong He, Yan Liu, and Yu Cao. 2022. "Exosomes in Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury: Current Perspectives and Future Challenges" Brain Sciences 12, no. 12: 1657. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12121657
APA StyleZhou, C., Zhou, F., He, Y., Liu, Y., & Cao, Y. (2022). Exosomes in Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury: Current Perspectives and Future Challenges. Brain Sciences, 12(12), 1657. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12121657





