Growing Brains, Nurturing Minds—Neuroscience as an Educational Tool to Support Students’ Development as Life-Long Learners
Abstract
:1. Educational Neuroscience (Teaching for the Brain and Teaching about the Brain)
1.1. Learning and Neuroplasticity
1.1.1. Using Neuroplasticity as Educational Content
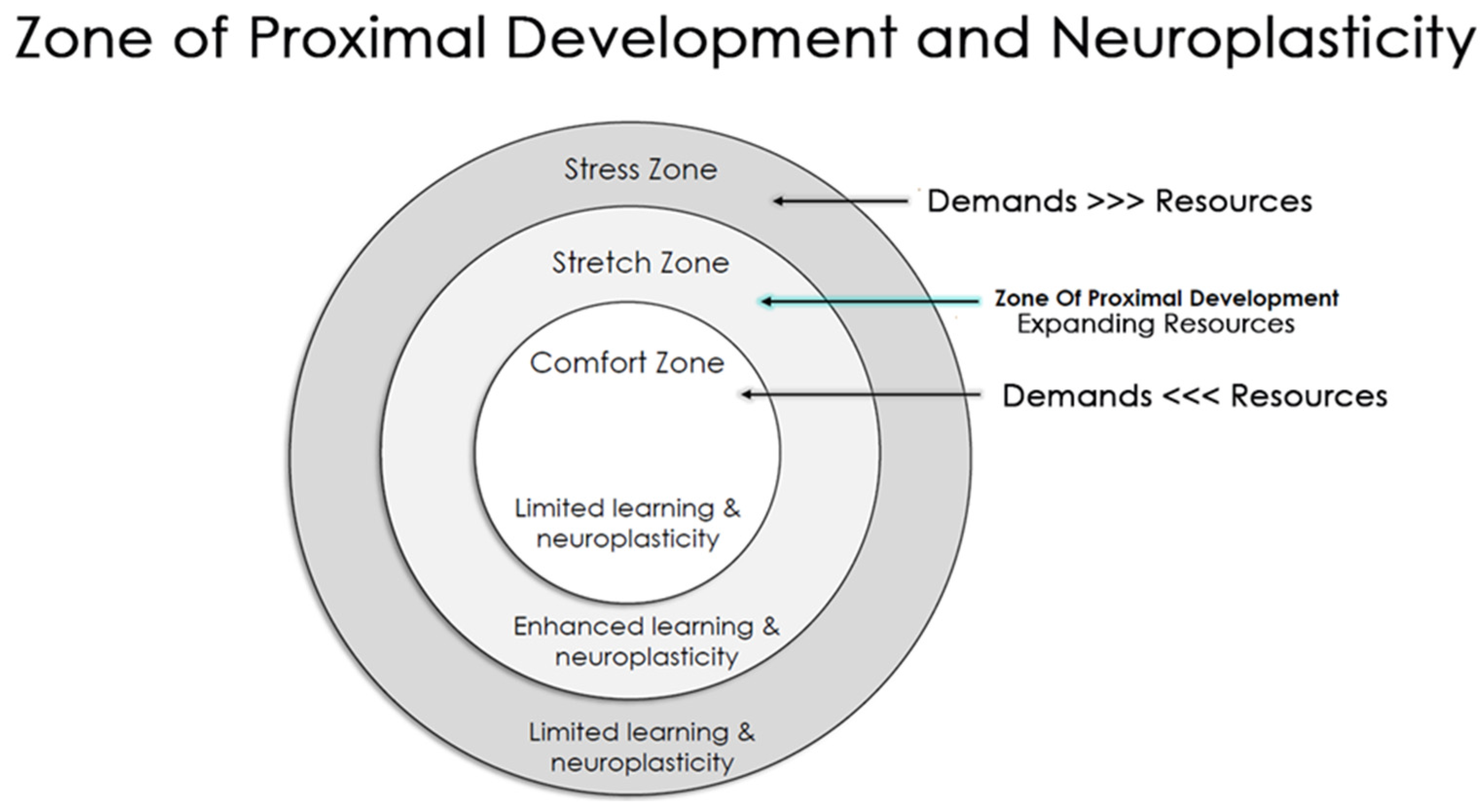
1.1.2. Using Neuroplasticity to Guide Learning Design
1.2. Learning Motivation and Reward
1.2.1. Using Neuroscience (of Reward and Motivation) as Educational Content
1.2.2. Using Neuroscience to Guide Learning Design and Intrinsic Motivation
1.3. Intrinsic and Extrinsic Processing in Learning and Meaning-Making
1.3.1. The Neuroscience of Extrinsic and Intrinsic Processing as Educational Content
1.3.2. Using the Neuroscience of Extrinsic and Intrinsic Processing to Guide Learning Design
2. Discussion
2.1. Teaching Students about Their Developing Brains
2.2. Teaching the Way(s) the Human Brain Learns Best
3. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thomas, M.S.C.; Ansari, D.; Knowland, V.C.P. Annual Research Review: Educational Neuroscience: Progress and Prospects. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2019, 60, 477–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ho, A.J.; Raji, C.A.; Becker, J.T.; Lopez, O.L.; Kuller, L.H.; Hua, X.; Dinov, I.D.; Stein, J.L.; Rosano, C.; Toga, A.W. The Effects of Physical Activity, Education, and Body Mass Index on the Aging Brain. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2011, 32, 1371–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berryhill, M.E.; Jones, K.T. TDCS Selectively Improves Working Memory in Older Adults with More Education. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 521, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneeweis, N.; Skirbekk, V.; Winter-Ebmer, R. Does Education Improve Cognitive Performance Four Decades after School Completion? Demography 2014, 51, 619–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahl, R.E. Adolescent Brain Development: A Period of Vulnerabilities and Opportunities. Keynote Address. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2004, 1021, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, F.S.; Heimer, H.; Giedd, J.N.; Lein, E.S.; Šestan, N.; Weinberger, D.R.; Casey, B.J. Adolescent Mental Health—Opportunity and Obligation. Science 2014, 346, 547–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrmann, D.; Knoll, L.J.; Blakemore, S.-J. Adolescence as a Sensitive Period of Brain Development. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2015, 19, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuchs, E.; Flügge, G. Adult Neuroplasticity: More than 40 Years of Research. Neural Plast. 2014, 2014, 541870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donati, G.; Meaburn, E. What Has Behavioural Genetic Research Told Us About the Origins of Individual Differences in Educational Abilities and Achievements? In Educational Neuroscience; Routledge: London, UK, 2020; pp. 53–87. ISBN 1003016839. [Google Scholar]
- Hackman, D.A.; Kraemer, D.J.M. Socioeconomic Disparities in Achievement: Insights on Neurocognitive Development and Educational Interventions. In Educational Neuroscience; Routledge: London, UK, 2020; pp. 88–119. ISBN 1003016839. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, M.S.C.; Mareschal, D.; Dumontheil, I. Educational Neuroscience: Development across the Life Span; Routledge: London, UK, 2020; ISBN 1000040798. [Google Scholar]
- Weaver, I.C.G. Integrating Early Life Experience, Gene Expression, Brain Development, and Emergent Phenotypes: Unraveling the Thread of Nature via Nurture. Adv. Genet. 2014, 86, 277–307. [Google Scholar]
- Rangaswami, S. Nature, Nurture and the Learning Brain. In Neuro-Systemic Applications in Learning; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 333–368. [Google Scholar]
- Kass, J.; Jain, N. Neural Plasticity; Psychology Press Ltd.: London, UK, 2000; Volume 2, ISBN 0674007433. [Google Scholar]
- Mundkur N Neuroplasticity in Children. Indian J. Pediatr. 2005, 72, 855–857. [CrossRef]
- Cramer, S.C.; Sur, M.; Dobkin, B.H.; O’Brien, C.; Sanger, T.D.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Rumsey, J.M.; Hicks, R.; Cameron, J.; Chen, D. Harnessing Neuroplasticity for Clinical Applications. Brain 2011, 134, 1591–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vygotsky, L.S. Mind in Society: The Development of Higher Psychological Processes; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1980; ISBN 0674076680. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, R.J.; McEwen, B.S. Social Influences on Neuroplasticity: Stress and Interventions to Promote Well-Being. Nat. Neurosci. 2012, 15, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voss, P.; Thomas, M.E.; Cisneros-Franco, J.M.; de Villers-Sidani, É. Dynamic Brains and the Changing Rules of Neuroplasticity: Implications for Learning and Recovery. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carey, L.M. Stroke Rehabilitation: Insights from Neuroscience and Imaging; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012; ISBN 0199797889. [Google Scholar]
- Kleim, J.A.; Jones, T.A. Principles of Experience-Dependent Neural Plasticity: Implications for Rehabilitation after Brain Damage. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2008, 51, S225–S239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kolb, B.; Gibb, R. Brain Plasticity and Behaviour in the Developing Brain. J. Can. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2011, 20, 265. [Google Scholar]
- Petrosini, L.; De Bartolo, P.; Foti, F.; Gelfo, F.; Cutuli, D.; Leggio, M.G.; Mandolesi, L. On Whether the Environmental Enrichment May Provide Cognitive and Brain Reserves. Brain Res. Rev. 2009, 61, 221–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dweck, C.S. Mindset: The New Psychology of Success; Random House Digital, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2008; ISBN 0345472322. [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell, L.S.; Trzesniewski, K.H.; Dweck, C.S. Implicit Theories of Intelligence Predict Achievement across an Adolescent Transition: A Longitudinal Study and an Intervention. Child Dev. 2007, 78, 246–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claro, S.; Paunesku, D.; Dweck, C.S. Growth Mindset Tempers the Effects of Poverty on Academic Achievement. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 8664–8668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Broda, M.; Yun, J.; Schneider, B.; Yeager, D.S.; Walton, G.M.; Diemer, M. Reducing Inequality in Academic Success for Incoming College Students: A Randomized Trial of Growth Mindset and Belonging Interventions. J. Res. Educ. Eff. 2018, 11, 317–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, N.M.; Hamedani, M.G.; Destin, M. Closing the Social-Class Achievement Gap: A Difference-Education Intervention Improves First-Generation Students’ Academic Performance and All Students’ College Transition. Psychol. Sci. 2014, 25, 943–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walton, G.M.; Cohen, G.L. A Brief Social-Belonging Intervention Improves Academic and Health Outcomes of Minority Students. Science 2011, 331, 1447–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zeng, G.; Hou, H.; Peng, K. Effect of Growth Mindset on School Engagement and Psychological Well-Being of Chinese Primary and Middle School Students: The Mediating Role of Resilience. Front. Psychol. 2016, 7, 1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisk, V.F.; Burgoyne, A.P.; Sun, J.; Butler, J.L.; Macnamara, B.N. To What Extent and under Which Circumstances Are Growth Mind-Sets Important to Academic Achievement? Two Meta-Analyses. Psychol. Sci. 2018, 29, 549–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarrasin, J.B.; Nenciovici, L.; Foisy, L.M.B.; Allaire-Duquette, G.; Riopel, M.; Masson, S. Effects of Teaching the Concept of Neuroplasticity to Induce a Growth Mindset on Motivation, Achievement, and Brain Activity: A Meta-Analysis. Trends Neurosci. Educ. 2018, 12, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, R.D.; Pisano, G.P. Neurodiversity as a Competitive Advantage. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2017, 95, 96–103. [Google Scholar]
- Huber, E.; Donnelly, P.M.; Rokem, A.; Yeatman, J.D. Rapid and Widespread White Matter Plasticity during an Intensive Reading Intervention. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, R.R.; Christodoulou, J.A.; Halverson, K.K.; Murtagh, J.; Cyr, A.B.; Schimmel, C.; Chang, P.; Hook, P.E.; Gabrieli, J.D.E. Socioeconomic Status and Reading Disability: Neuroanatomy and Plasticity in Response to Intervention. Cereb. Cortex 2018, 28, 2297–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perdue, M.V.; Mahaffy, K.; Vlahcevic, K.; Wolfman, E.; Erbeli, F.; Richlan, F.; Landi, N. Reading Intervention and Neuroplasticity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Brain Changes Associated with Reading Intervention. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 132, 465–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, K.A.; Sheridan, M.A.; Lambert, H.K. Childhood Adversity and Neural Development: Deprivation and Threat as Distinct Dimensions of Early Experience. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2014, 47, 578–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bryck, R.L.; Fisher, P.A. Training the Brain: Practical Applications of Neural Plasticity from the Intersection of Cognitive Neuroscience, Developmental Psychology, and Prevention Science. Am. Psychol. 2012, 67, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gapp, K.; Bohacek, J.; Grossmann, J.; Brunner, A.M.; Manuella, F.; Nanni, P.; Mansuy, I.M. Potential of Environmental Enrichment to Prevent Transgenerational Effects of Paternal Trauma. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 41, 2749–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weist, M.D.; Eber, L.; Horner, R.; Splett, J.; Putnam, R.; Barrett, S.; Perales, K.; Fairchild, A.J.; Hoover, S. Improving Multitiered Systems of Support for Students With “Internalizing” Emotional/Behavioral Problems. J. Posit. Behav. Interv. 2018, 20, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias-Carrión, O.; Stamelou, M.; Murillo-Rodríguez, E.; Menéndez-González, M.; Pöppel, E. Dopaminergic Reward System: A Short Integrative Review. Int. Arch. Med. 2010, 3, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berridge, K.C.; Robinson, T.E.; Aldridge, J.W. Dissecting Components of Reward: “Liking”, “Wanting”, and Learning. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2009, 9, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ormrod, J.E. Human Learning; Merrill Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1999; ISBN 0138756848. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, R. When No One Can Go to School: Does Online Learning Meet Students’ Basic Learning Needs? Interact. Learn. Environ. 2020, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deci, E.L.; Ryan, R.M. Self-Determination Theory and the Facilitation of Intrinsic Motivation, Social Development, and Well-Being. Am. Psychol. 2000, 55, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandura, A.; Freeman, W.H.; Lightsey, R. Self-Efficacy: The Exercise of Control; Worth Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Krapp, A. Basic Needs and the Development of Interest and Intrinsic Motivational Orientations. Learn. Instr. 2005, 15, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berridge, K.C. Evolving Concepts of Emotion and Motivation. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Degenhardt, L.; Stockings, E.; Patton, G.; Hall, W.D.; Lynskey, M. The Increasing Global Health Priority of Substance Use in Young People. Lancet Psychiatry 2016, 3, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, A.; Gautam, S. Age of Onset of Substance Use and Psychosocial Problems among Individuals with Substance Use Disorders. BMC Psychiatry 2017, 17, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trujillo, C.A.; Obando, D.; Trujillo, A. An Examination of the Association between Early Initiation of Substance Use and Interrelated Multilevel Risk and Protective Factors among Adolescents. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Immordino-yang, M.H. Embodied Brains, Social Minds, Cultural Meaning: Integrating Neuroscientific and Educational Research on Social-Affective Development. Am. Educ. Res. J. 2017, 54, 344–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, P.A.; Greenberg, M.T. The Prosocial Classroom: Teacher Social and Emotional Competence in Relation to Student and Classroom Outcomes. Rev. Educ. Res. 2009, 79, 491–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okonofua, J.A.; Paunesku, D.; Walton, G.M. Brief Intervention to Encourage Empathic Discipline Cuts Suspension Rates in Half among Adolescents. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 5221–5226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Battro, A.M.; Fischer, K.W.; Léna, P.J. Introduction: Mind, Brain, and Education in Theory and Practice. Educ. Brain Essays Neuroeducation 2008, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immordino-Yang, M.H.; Darling-Hammond, L.; Krone, C.R. Nurturing Nature: How Brain Development Is Inherently Social and Emotional, and What This Means for Education. Educ. Psychol. 2019, 54, 185–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberman, M.D. Social Cognitive Neuroscience. Encycl. Soc. Psychol. 2012, 143–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, V.L.; Feldman, R.S. Learning through Tutoring: Low-Achieving Children as Tutors. J. Exp. Educ. 1973, 42, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrbeck, C.A.; Ginsburg-Block, M.D.; Fantuzzo, J.W.; Miller, T.R. Peer-Assisted Learning Interventions with Elementary School Students: A Meta-Analytic Review. J. Educ. Psychol. 2003, 95, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topping, K.J. The Effectiveness of Peer Tutoring in Further and Higher Education: A Typology and Review of the Literature. High. Educ. 1996, 32, 321–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrabian, A. Silent Messages; Wadsworth: Belmont, CA, USA, 1971; Volume 8, ISBN 0534000592. [Google Scholar]
- Richmond, V.P.; Gorham, J.S.; McCroskey, J.C. The Relationship between Selected Immediacy Behaviors and Cognitive Learning. Ann. Int. Commun. Assoc. 1987, 10, 574–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christophel, D.M. The Relationships among Teacher Immediacy Behaviors, Student Motivation, and Learning. Commun. Educ. 1990, 39, 323–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, D.H.; Gorham, J. Effects of Immediacy on Recall of Information. Commun. Educ. 1988, 37, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W. Does Teacher Immediacy Affect Students? A Systematic Review of the Association between Teacher Verbal and Non-Verbal Immediacy and Student Motivation. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frymier, A.B.; Shulman, G.M. “What’s in It for Me?”: Increasing Content Relevance to Enhance Students’ Motivation. Commun. Educ. 1995, 44, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, C.; Bavelier, D. The Role of Selective Attention on Academic Foundations: A Cognitive Neuroscience Perspective. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2012, 2 (Suppl. 1), S30–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markett, S.; Nothdurfter, D.; Focsa, A.; Reuter, M.; Jawinski, P. Attention Networks and the Intrinsic Network Structure of the Human Brain. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2022, 43, 1431–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geva, R.; Zivan, M.; Warsha, A.; Olchik, D. Alerting, Orienting or Executive Attention Networks: Differential Patters of Pupil Dilations. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vossel, S.; Geng, J.J.; Fink, G.R. Dorsal and Ventral Attention Systems: Distinct Neural Circuits but Collaborative Roles. Neuroscientist 2014, 20, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbetta, M.; Shulman, G.L. Control of Goal-Directed and Stimulus-Driven Attention in the Brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2002, 3, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, V.; Uddin, L.Q. Saliency, Switching, Attention and Control: A Network Model of Insula Function. Brain Struct. Funct. 2010, 214, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Onofrj, V.; Chiarelli, A.M.; Wise, R.; Colosimo, C.; Caulo, M. Interaction of the Salience Network, Ventral Attention Network, Dorsal Attention Network and Default Mode Network in Neonates and Early Development of the Bottom-up Attention System. Brain Struct. Funct. 2022, 227, 1843–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sridharan, D.; Levitin, D.J.; Menon, V. A Critical Role for the Right Fronto-Insular Cortex in Switching between Central-Executive and Default-Mode Networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 12569–12574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Immordino-Yang, M.H.; Darling-Hammond, L.; Krone, C. The Brain Basis for Integrated Social, Emotional, and Academic Development: How Emotions and Social Relationships Drive Learning. Natl. Comm. Soc. Emot. Acad. Dev. 2018, 20. [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman, M.D. Education and the Social Brain. Trends Neurosci. Educ. 2012, 1, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.C.; Oathes, D.J.; Chang, C.; Bradley, T.; Zhou, Z.-W.; Williams, L.M.; Glover, G.H.; Deisseroth, K.; Etkin, A. Causal Interactions between Fronto-Parietal Central Executive and Default-Mode Networks in Humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 19944–19949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- D’esposito, M.; Detre, J.A.; Alsop, D.C.; Shin, R.K.; Atlas, S.; Grossman, M. The Neural Basis of the Central Executive System of Working Memory. Nature 1995, 378, 279–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Friston, K.J.; Zeidman, P.; Chen, J.; Li, S.; Razi, A. The Hierarchical Organization of the Default, Dorsal Attention and Salience Networks in Adolescents and Young Adults. Cereb. Cortex 2018, 28, 726–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, L.Q.; Clare Kelly, A.M.; Biswal, B.B.; Xavier Castellanos, F.; Milham, M.P. Functional Connectivity of Default Mode Network Components: Correlation, Anticorrelation, and Causality. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2009, 30, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reineberg, A.E.; Gustavson, D.E.; Benca, C.; Banich, M.T.; Friedman, N.P. The Relationship between Resting State Network Connectivity and Individual Differences in Executive Functions. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manoliu, A.; Meng, C.; Brandl, F.; Doll, A.; Tahmasian, M.; Scherr, M.; Schwerthöffer, D.; Zimmer, C.; Förstl, H.; Bäuml, J. Insular Dysfunction within the Salience Network Is Associated with Severity of Symptoms and Aberrant Inter-Network Connectivity in Major Depressive Disorder. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 7, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.F.; Pavarini, G.; Schnall, S.; Immordino-Yang, M.H. Looking up to Virtue: Averting Gaze Facilitates Moral Construals via Posteromedial Activations. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2018, 13, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Immordino-yang, M.H.; Knecht, D.R. Building Meaning Builds Teens’ Brains. Educ. Leadersh. 2020, 77, 36–43. [Google Scholar]
- Kuzawa, C.W.; Chugani, H.T.; Grossman, L.I.; Lipovich, L.; Muzik, O.; Hof, P.R.; Wildman, D.E.; Sherwood, C.C.; Leonard, W.R.; Lange, N. Metabolic Costs and Evolutionary Implications of Human Brain Development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 13010–13015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lebel, C.; Walker, L.; Leemans, A.; Phillips, L.; Beaulieu, C. Microstructural Maturation of the Human Brain from Childhood to Adulthood. Neuroimage 2008, 40, 1044–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Academies of Sciences and Medicine, E. The Integration of the Humanities and Arts with Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine in Higher Education: Branches from the Same Tree; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; ISBN 0309470641. [Google Scholar]
- Cantor, P.; Osher, D.; Berg, J.; Steyer, L.; Rose, T. Malleability, Plasticity, and Individuality: How Children Learn and Develop in Context1. Appl. Dev. Sci. 2019, 23, 307–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zabelina, D.L.; O’Leary, D.; Pornpattananangkul, N.; Nusslock, R.; Beeman, M. Creativity and Sensory Gating Indexed by the P50: Selective versus Leaky Sensory Gating in Divergent Thinkers and Creative Achievers. Neuropsychologia 2015, 69, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Scientific Council on the Developing Child. Understanding Motivation: Building the Brain Architecture That Supports Learning, Health, and Community Participation: Working Paper No 14. Natl. Sci. Counc. Dev. Child 2018, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, K.L.; Goddings, A.L.; Clasen, L.S.; Giedd, J.N.; Blakemore, S.J. The Developmental Mismatch in Structural Brain Maturation during Adolescence. Dev. Neurosci. 2014, 36, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, S.; Babapoor, J.; Fathi, H. The Relationship between Cognitive Emotion Regulation, Occupational Stress and General Health among Nurses Working in Private Hospitals in Tehran. 2011, pp. 45–53. Available online: https://doaj.org/article/1e217f3b4b714991b99997c7a12c2da0 (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- Meltzoff, A.N.; Kuhl, P.K.; Movellan, J.; Sejnowski, T.J. Foundations for a New Science of Learning. Science 2009, 325, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shonkoff, J.P.; Levitt, P. Neuroscience and the Future of Early Childhood Policy: Moving from Why to What and How. Neuron 2010, 67, 689–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, O.; Kalyuga, S. Cognitive Load Theory, Spacing Effect, and Working Memory Resources Depletion: Implications for Instructional Design. In Form, Function, and Style in Instructional Design: Emerging Research and Opportunities; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2020; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goldberg, H. Growing Brains, Nurturing Minds—Neuroscience as an Educational Tool to Support Students’ Development as Life-Long Learners. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1622. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12121622
Goldberg H. Growing Brains, Nurturing Minds—Neuroscience as an Educational Tool to Support Students’ Development as Life-Long Learners. Brain Sciences. 2022; 12(12):1622. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12121622
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoldberg, Hagar. 2022. "Growing Brains, Nurturing Minds—Neuroscience as an Educational Tool to Support Students’ Development as Life-Long Learners" Brain Sciences 12, no. 12: 1622. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12121622
APA StyleGoldberg, H. (2022). Growing Brains, Nurturing Minds—Neuroscience as an Educational Tool to Support Students’ Development as Life-Long Learners. Brain Sciences, 12(12), 1622. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12121622




