Hydrogels to Support Transplantation of Human Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Culture of ARPE-19
2.2. Culture of hESC-RPEs
2.3. Synthesis of GelMA
2.4. Synthesis of HAMA
2.5. Synthesis of Modified Alginate
2.6. Compressive Measurements
2.7. Formation of Different Thin-Layer Hydrogels
2.8. Cell Morphology, Proliferation, and Viability in Different Hydrogels
2.9. hESC-RPEs Characterization by Immunostaining
2.10. Secretion Ability of PEDF and VEGF by ELISA
2.11. Subretinal Transplantation of Selected Hydrogel
2.12. In Vivo Degradation of the Selected Hydrogel
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
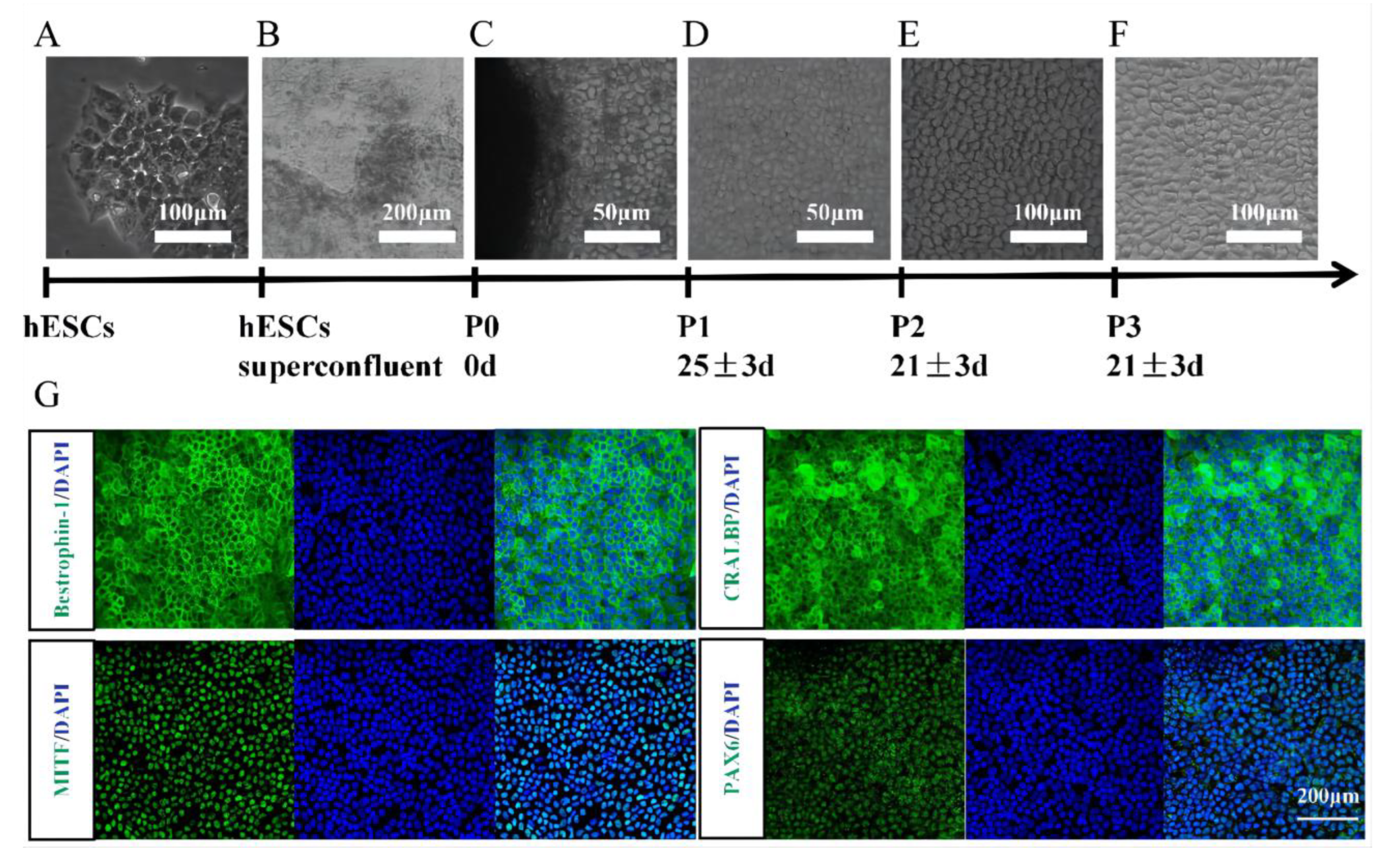
3.1. Identification of hESC-Derived RPE Cells
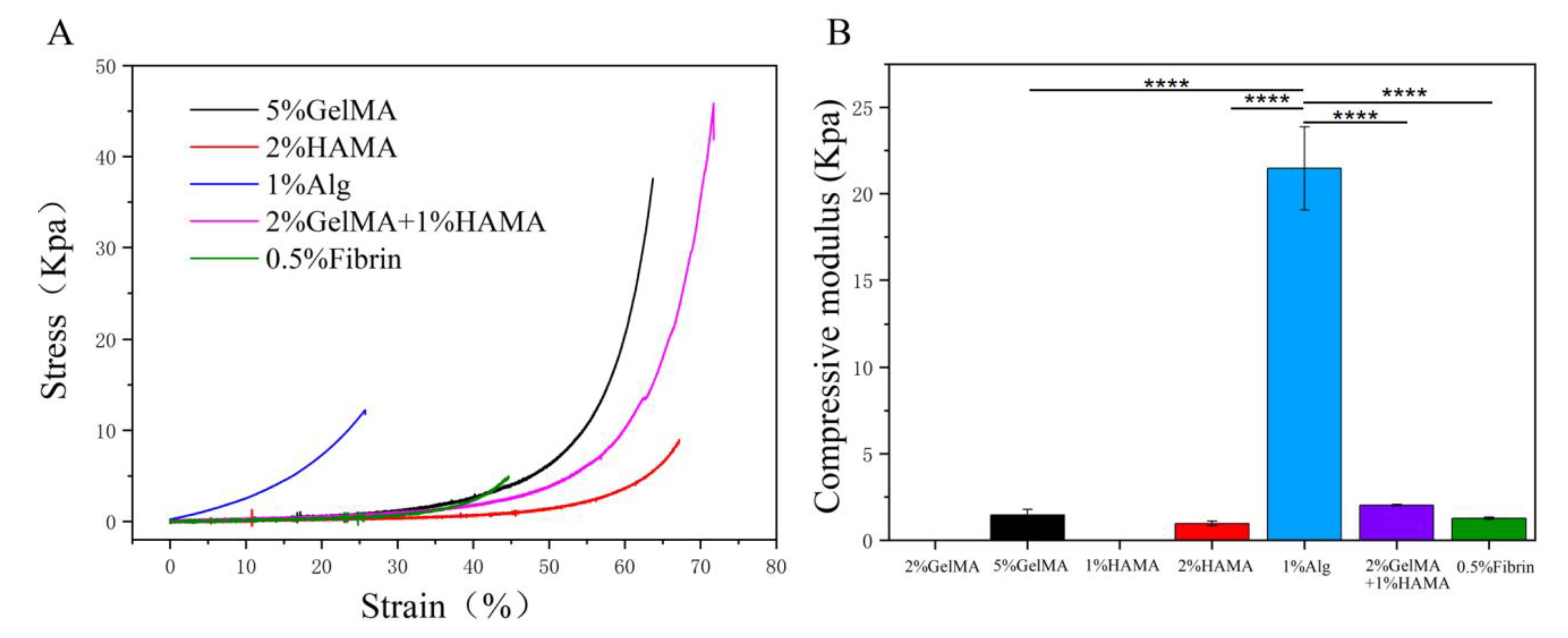
3.2. Evaluate the Mechanical Properties of the Low Concentration Hydrogels
3.3. The Normal Cell Morphology, Proliferation, and Viability of hESC-RPE on Fibrin
3.4. Functional Protein Secretion of hESC-RPE on Fibrin
3.5. In Vivo Immunogenicity and Degradation of Fibrin in the Subretinal Space




4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davidson, A.E.; Millar, I.D.; Urquhart, J.; Burgess-Mullan, R.; Shweikh, Y.; Parry, N.; O’Sullivan, J.; Maher, G.J.; McKibbin, M.; Downes, S.M.; et al. Missense Mutations in a Retinal Pigment Epithelium Protein, Bestrophin-1, Cause Retinitis Pigmentosa. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 85, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanie-Jahromi, F.; Ahmadieh, H.; Soheili, Z.-S.; Davari, M.; Ghaderi, S.; Kanavi, M.R.; Samiei, S.; Deezagi, A.; Pakravesh, J.; Bagheri, A. Enhanced generation of retinal progenitor cells from human retinal pigment epithelial cells induced by amniotic fluid. BMC Res. Notes 2012, 5, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- An, C.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Pang, B.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Liao, H.; Ren, C.; et al. Continuous microfluidic encapsulation of single mesenchymal stem cells using alginate microgels as injectable fillers for bone regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2020, 111, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, F.S.Y.; Tsang, K.K.; Chu, A.M.W.; Chan, B.; Yao, K.M.; Lo, A.C.Y. Injectable cell-encapsulating composite alginate-collagen platform with inducible termination switch for safer ocular drug delivery. Biomaterials 2019, 201, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, S.; Gregory, C.A.; Alge, D.L. Interplay between degradability and integrin signaling on mesenchymal stem cell function within poly(ethylene glycol) based microporous annealed particle hydrogels. Acta Biomater. 2019, 101, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Yue, Z.; Lucarelli, E.; Wallace, G.G. Hybrid Printing Using Cellulose Nanocrystals Reinforced GelMA/HAMA Hydrogels for Improved Structural Integration. Adv. Health Mater. 2020, 9, e2001410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero Aguilar, L.M.; Kapsa, R.M.; O’Connell, C.D.; McArthur, S.L.; Stoddart, P.R.; Moulton, S.E. Controlled Release from PCL-Alginate Microspheres via Secondary Encapsulation Using GelMA/HAMA Hydrogel Scaffolds. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 3779–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.M.; Kim, E.Y.; Hwang, J.H.; Lee, G.Y.; Cho, S.J.; Bae, J.Y.; Song, J.E.; Yoon, K.H.; Joo, C.-K.; Lee, D.; et al. A Study on Proliferation and Behavior of Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells on Purified Alginate Films. Int. J. Stem Cells 2011, 4, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Najafabadi, H.S.; Soheili, Z.-S.; Ganji, S.M. Behavior of a spontaneously arising human retinal pigment epithelial cell line cul-tivated on thin alginate film. J. Ophthal. Vis. Res. 2015, 10, 286–294. [Google Scholar]
- Heidari, R.; Soheili, Z.-S.; Samiei, S.; Ahmadieh, H.; Davari, M.; Nazemroaya, F.; Bagheri, A.; Deezagi, A. Alginate as a Cell Culture Substrate for Growth and Differentiation of Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 175, 2399–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, N.C.; Hallam, D.; Karimi, A.; Mellough, C.B.; Chen, J.; Steel, D.H.; Lako, M. 3D culture of human pluripotent stem cells in RGD-alginate hydrogel improves retinal tissue development. Acta Biomater. 2017, 49, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wikstrom, J.; Elomaa, M.; Syvajarvi, H.; Kuokkanen, J.; Yliperttula, M.; Honkakoski, P.; Urtti, A. Alginate-based microencapsulation of retinal pigment epithelial cell line for cell therapy. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, J.K.; Manzar, Z.; Bachman, L.A.; Andrews-Pfannkoch, C.; Knudsen, T.; Hill, M.; Schmidt, H.; Iezzi, R.; Pulido, J.S.; Marmorstein, A.D. Fibrin hydrogels as a xenofree and rapidly degradable support for transplantation of retinal pigment epithelium monolayers. Acta Biomater. 2018, 67, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandai, M.; Watanabe, A.; Kurimoto, Y.; Hirami, Y.; Morinaga, C.; Daimon, T.; Fujihara, M.; Akimaru, H.; Sakai, N.; Shibata, Y.; et al. Autologous induced stem-cell-derived retinal cells for macular degeneration. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1038–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Cruz, L.; Fynes, K.; Georgiadis, O.; Kerby, J.; Luo, Y.H.; Ahmado, A.; Vernon, A.; Daniels, J.T.; Nommiste, B.; Hasan, S.M.; et al. Phase 1 clinical study of an embryonic stem cell-derived retinal pigment epithelium patch in age-related macular degeneration. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, H.W.; Wang, L.; Li, S.Y.; Zhao, C.J.; Hao, J.; Li, Q.Y.; Zhao, T.T.; Wu, W.; Wang, Y.; et al. Human embryonic stem cell-derived retinal pigment epithelium transplants as a potential treatment for wet age-related macular degeneration. Cell Discov. 2018, 4, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Den Bulcke, A.I.; Bogdanov, B.; De Rooze, N.; Schacht, E.H.; Cornelissen, M.; Berghmans, H. Structural and rheological prop-erties of methacrylamide modified gelatin hydrogels. Biomacromolecules 2000, 1, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowley, J.A.; Madlambayan, G.; Mooney, D.J. Alginate hydrogels as synthetic extracellular matrix materials. Biomaterials 1999, 20, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.Y.; Zou, T.; Gong, Y.; Chen, S.Y.; Zeng, Y.X.; Gao, L.X.; Weng, C.H.; Xu, H.W.; Yin, Z.Q. Functional assessment of cryopreserved clinical grade hESC-RPE cells as a qualified cell source for stem cell therapy of retinal degenerative diseases. Exp. Eye Res. 2021, 202, 108305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Zeng, Y.; Xu, H.; Yin, Z.Q. Subretinal transplantation of retinal pigment epithelium overexpressing fibrinu-lin-5 inhibits laser-induced choroidal neovascularization in Mice. Exp. Eye Res. 2015, 136, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Q.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z.-X.; Zhu, W.-W.; Tan, Y.-Q.; Han, W.-F.; Wu, J.; Feng, C.-J.; Fang, J.-H.; et al. Accreditation of Biosafe Clinical-Grade Human Embryonic Stem Cells According to Chinese Regulations. Stem Cell Rep. 2017, 9, 366–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullins, R.F.; Johnson, M.N.; Faidley, E.A.; Skeie, J.M.; Huang, J. Choriocapillaris Vascular Dropout Related to Density of Drusen in Human Eyes with Early Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 1606–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gullapalli, V.K.; Sugino, I.K.; Van Patten, Y.; Shah, S.; Zarbin, M.A. Retinal pigment epithelium resurfacing of aged submacular human Bruch’s membrane. Trans. Am. Ophthalmol. Soc. 2004, 102, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- da Cruz, L.; Chen, F.K.; Ahmado, A.; Greenwood, J.; Coffey, P. RPE transplantation and its role in retinal disease. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2007, 26, 598–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomita, M.; Lavik, E.; Klassen, H.; Zahir, T.; Langer, R.; Young, M.J. Biodegradable Polymer Composite Grafts Promote the Survival and Differentiation of Retinal Progenitor Cells. Stem Cells 2005, 23, 1579–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Kim, D.; Jeong, Y.W.; Choi, M.J.; Lee, G.W.; Thangavelu, M.; Song, J.E.; Khang, G. Engineering retinal pigment epithelial cells regeneration for transplantation in regenerative medicine using PEG/Gellan gum hydrogels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 130, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kador, K.E.; Goldberg, J.L. Scaffolds and stem cells: Delivery of cell transplants for retinal degenerations. Expert Rev. Ophthalmol. 2012, 7, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mazumder, M.A.J.; Fitzpatrick, S.D.; Muirhead, B.; Sheardown, H. Cell-adhesive thermogelling PNIPAAm/hyaluronic acid cell delivery hydrogels for potential application as minimally invasive retinal therapeutics. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2012, 100A, 1877–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Baranov, P.; Aydin, A.; Abdelgawad, H.; Singh, D.; Niu, W.; Kurisawa, M.; Spector, M.; Young, M.J. In Situ Cross-linking Hydrogel as a Vehicle for Retinal Progenitor Cell Transplantation. Cell Transplant. 2019, 28, 596–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H. Injectable hydrogels delivering therapeutic agents for disease treatment and tissue engineering. Biomater. Res. 2018, 22, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mantha, S.; Pillai, S.; Khayambashi, P.; Upadhyay, A.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, O.; Pham, H.M.; Tran, S.D. Smart Hydrogels in Tissue Engi-neering and Regenerative Medicine. Materials 2019, 12, 3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rim, M.A.; Choi, J.H.; Park, A.; Youn, J.; Lee, S.; Kim, N.E.; Song, J.E.; Khang, G. Characterization of Gelatin/Gellan Gum/Glycol Chi-tosan Ternary Hydrogel for Retinal Pigment Epithelial Tissue Reconstruction Materials. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 6079–6087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, K.T.; Wang, A.; Nguyen, A.B.; Iyer, J.; Tran, S.D. Recent Advances in Hydrogels: Ophthalmic Applications in Cell Delivery, Vitreous Substitutes, and Ocular Adhesives. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, S.; Zhao, T.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Du, J.; Ying, L.; Lin, J.; Zhang, C.; Hu, W.; Wang, L.; et al. Gelatin Methacrylate (GelMA)-Based Hydrogels for Cell Transplantation: An Effective Strategy for Tissue Engineering. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2019, 15, 664–679. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, S.; Yildirimer, L.; Zhao, H.; Ding, R.; Wang, H.; Cui, W.; Weitz, D. Injectable stem cell-laden photocrosslinkable mi-crospheres fabricated using microfluidics for rapid generation of osteogenic tissue constructs. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 2809–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, S.; Li, Q.; Chen, K.; An, C.; Wang, L.; van den Beucken, J.J.; Wang, H. Control of Matrix Stiffness Using Methacrylate-Gelatin Hydrogels for a Macrophage-Mediated Inflammatory Response. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 3091–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suri, S.; Schmidt, C.E. Photopatterned collagen–hyaluronic acid interpenetrating polymer network hydrogels. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 2385–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camci-Unal, G.; Cuttica, D.; Annabi, N.; Demarchi, D.; Khademhosseini, A. Synthesis and Characterization of Hybrid Hyaluronic Acid-Gelatin Hydrogels. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aramant, R.B.; Seiler, M.J. Transplanted Sheets of Human Retina and Retinal Pigment Epithelium Develop Normally in Nude Rats. Exp. Eye Res. 2002, 75, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Davidovich, A.E.; Schloss, J.M.; Chippada, U.; Schloss, R.R.; Langrana, N.A.; Yarmush, M.L. Neural lineage differentiation of embryonic stem cells within alginate microbeads. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 4489–4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schramm, C.; Spitzer, M.S.; Henke-Fahle, S.; Steinmetz, G.; Januschowski, K.; Heiduschka, P.; Geis-Gerstorfer, J.; Biedermann, T.; Bartz-Schmidt, K.U.; Szurman, P. The Cross-linked Biopolymer Hyaluronic Acid as an Artificial Vitreous Substitute. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francke, M.; Uhlmann, S.; Pannicke, T.; Goczalik, I.; Uckermann, O.; Weick, M.; Härtig, W.; Wiedemann, P.; Reichenbach, A.; Bringmann, A. Experimental Dispase-Induced Retinopathy Causes Up-Regulation of P2Y Receptor-Mediated Calcium Responses in Müller Glial Cells. Ophthalmic Res. 2003, 35, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Wang, Z.; Sun, X.; Wang, F.; Xu, X.; Zhang, X. Safety and Efficacy of Dispase and Plasmin in Pharmacologic Vitreolysis. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2004, 45, 3286–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elman, M.J.; Raden, R.Z.; Carrigan, A. Intravitreal Injection of Tissue Plasminogen Activator for Central Retinal Vein Occlusion. Retina 2003, 23, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, J.K.; Mano, F.; Iezzi, R., Jr.; LoBue, S.A.; Holman, B.H.; Fautsch, M.P.; Olsen, T.W.; Pulido, J.S.; Marmorstein, A.D. Fibrin hydrogels are safe, degradable scaffolds for sub-retinal im-plantation. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Malchiodi-Albedi, F.; Feher, J.; Caiazza, S.; Formisano, G.; Perilli, R.; Falchi, M.; Petrucci, T.; Scorcia, G.; Tombran-Tink, J. Pedf (Pigment epithelium-derived Factor) promotes increase and maturation of pigment granules in pigment epithelial cells in neonatal albino rat retinal cultures. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 1998, 16, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ani, A.; Toms, D.; Sunba, S.; Giles, K.; Touahri, Y.; Schuurmans, C.; Ungrin, M. Scaffold-Free Retinal Pigment Epithelium Microtissues Exhibit Increased Release of PEDF. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomson, H.A.; Treharne, A.J.; Backholer, L.S.; Cuda, F.; Grossel, M.C.; Lotery, A.J. Biodegradable poly(α-hydroxy ester) blended microspheres as suitable carriers for retinal pigment epithelium cell transplantation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2010, 95A, 1233–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuriyama, S.; Nakano, T.; Yoshimura, N.; Ohuchi, T.; Moritera, T.; Honda, Y. Mass cultivation of human retinal pigment epithelial cells with microcarrier. Ophthalmologica 1992, 205, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, Y.; Alexandre, U.; Ma, X. Hydrogels to Support Transplantation of Human Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12121620
Wei Y, Alexandre U, Ma X. Hydrogels to Support Transplantation of Human Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells. Brain Sciences. 2022; 12(12):1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12121620
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Ying, Uwimana Alexandre, and Xiang Ma. 2022. "Hydrogels to Support Transplantation of Human Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells" Brain Sciences 12, no. 12: 1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12121620
APA StyleWei, Y., Alexandre, U., & Ma, X. (2022). Hydrogels to Support Transplantation of Human Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells. Brain Sciences, 12(12), 1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12121620






