Preliminary Evaluation of the Clinical Benefit of a Novel Visual Rehabilitation Program in Patients Implanted with Trifocal Diffractive Intraocular Lenses: A Blinded Randomized Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
- (a)
- Patients who had undergone refractive lens exchange surgery for the correction of presbyopia at least 1 week before the evaluation visit.
- (b)
- Patients implanted with trifocal diffractive IOLs.
- (c)
- Availability and motivation to perform the assigned visual training.
- (d)
- Availability to attend all follow-up visits.
- (a)
- Patients implanted with monofocal, extended depth of focus (EDOF), or refractive multifocal IOLs.
- (b)
- Intraoperative complications leading to significant visual sequelae.
- (c)
- Neurological disorders.
- (d)
- Any active ocular disease.
- (e)
- Other previous ocular surgeries, including laser corneal refractive surgery.
- (f)
- Irregular cornea.
- (g)
- Illiteracy.
- (h)
- Any type of psychological disorder.
2.2. Surgical Intervention
2.3. Clinical Protocol
2.3.1. Clinical Examination
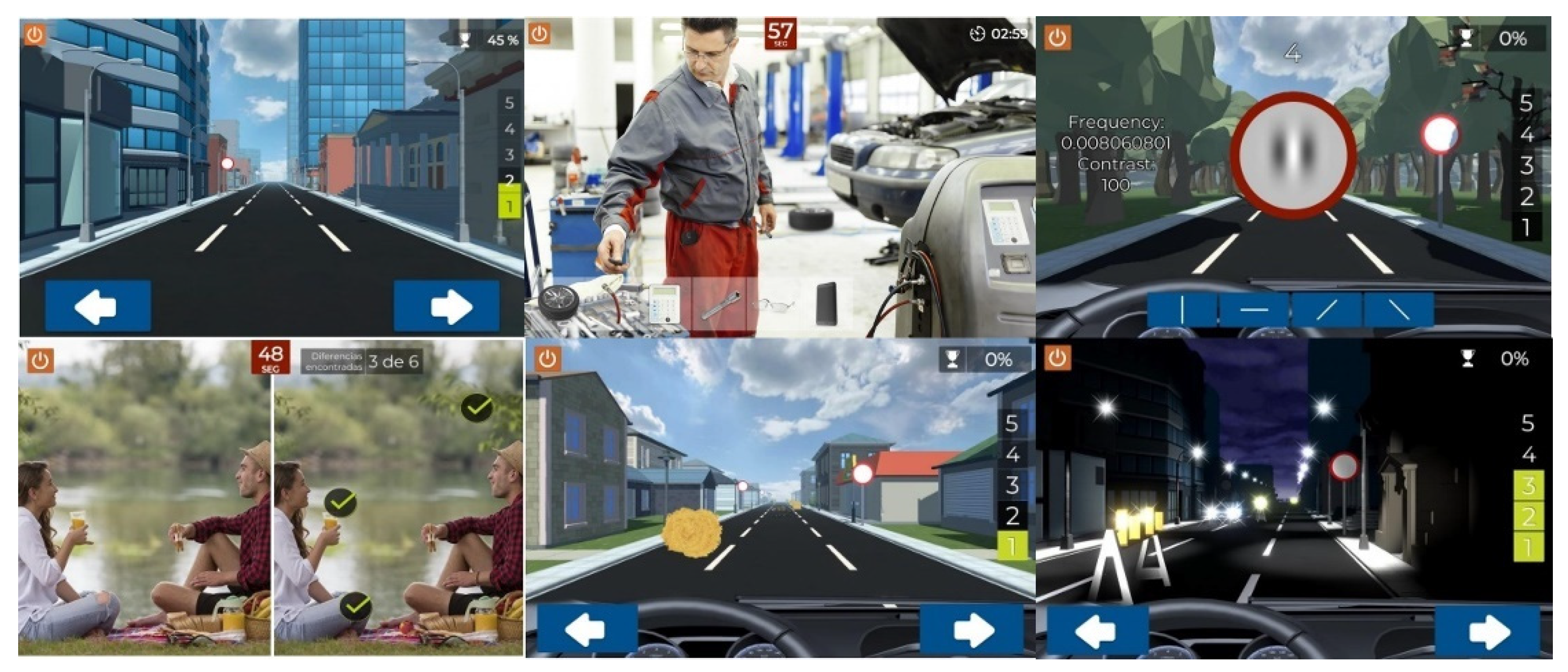
2.3.2. Visual Training Programs
Study Software
Gabor Stimuli
Placebo Software
Installation an Indications
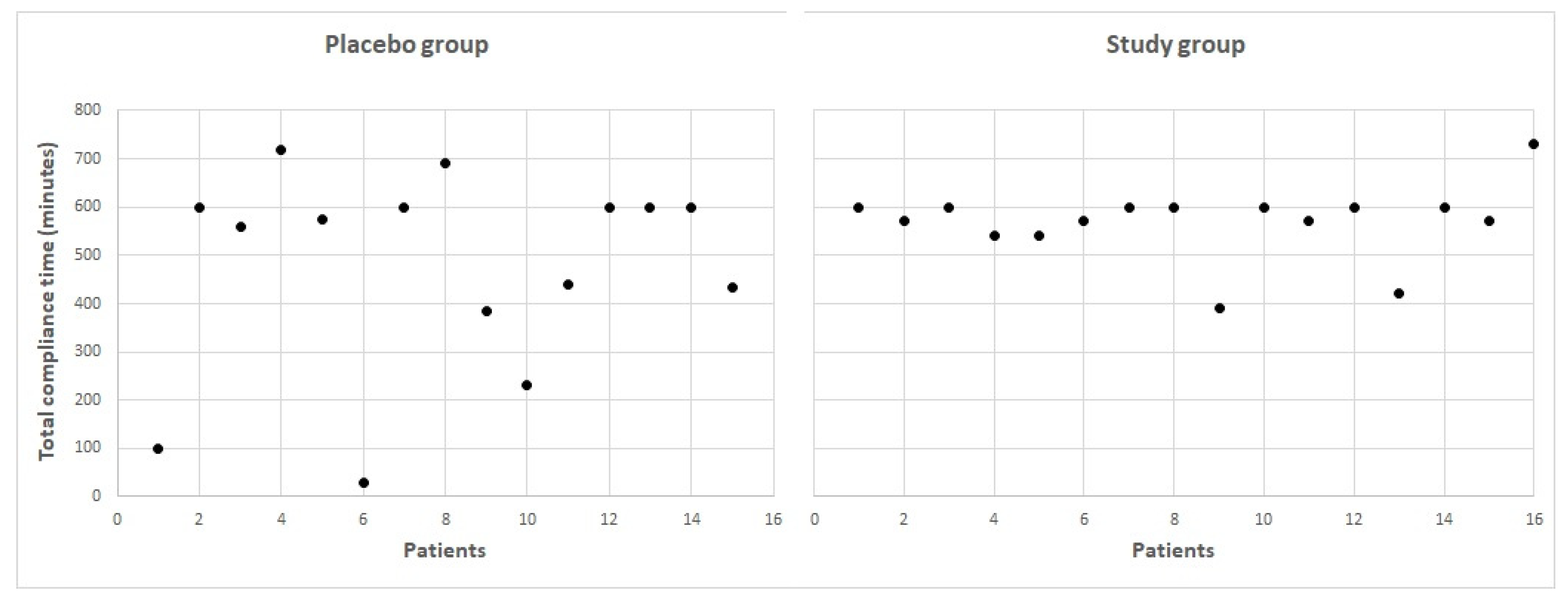
2.3.3. Compliance
2.3.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. General Description of the Samples and Groups
3.2. Compliance
3.3. Refractive Changes
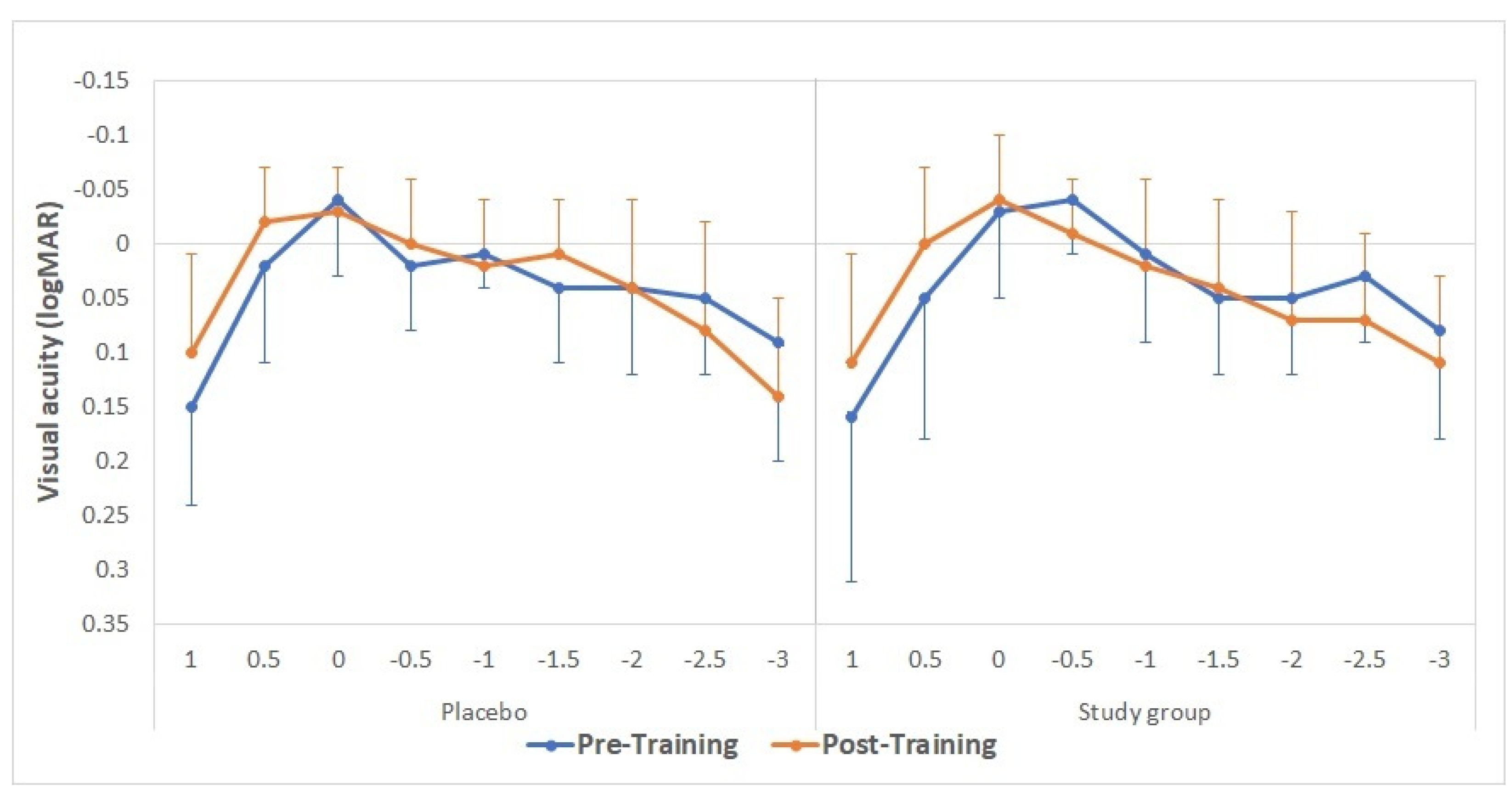
3.4. Visual Acuity Changes
3.5. Contrast Sensitivity Changes
3.6. Evaluation of the Effect for Both Types of IOLs
3.7. Data Re-Analysis with Those Cases with Compliance Time of 300 Min or More
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khandelwal, S.S.; Jun, J.J.; Mak, S.; Booth, M.S.; Shekelle, P.G. Effectiveness of multifocal and monofocal intraocular lenses for cataract surgery and lens replacement: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2019, 257, 863–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palomino-Bautista, C.; Sánchez-Jean, R.; Carmona-Gonzalez, D.; Piñero, D.P.; Molina-Martín, A. Depth of field measures in pseudophakic eyes implanted with different type of presbyopia-correcting IOLs. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomino-Bautista, C.; Sánchez-Jean, R.; Carmona-González, D.; Piñero, D.P.; Molina-Martín, A. Subjective and objective depth of field measures in pseudophakic eyes: Comparison between extended depth of focus, trifocal and bifocal intraocular lenses. Int. Ophthalmol. 2020, 40, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamora-de La Cruz, D.; Zúñiga-Posselt, K.; Bartlett, J.; Gutierrez, M.; Abariga, S.A. Trifocal intraocular lenses versus bifocal intraocular lenses after cataract extraction among participants with presbyopia. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 6, CD012648. [Google Scholar]
- Modi, S.; Lehmann, R.; Maxwell, A.; Solomon, K.; Cionni, R.; Thompson, V.; Horn, J.; Caplan, M.; Fisher, B.; Hu, J.G.; et al. Visual and patient-reported outcomes of a diffractive trifocal intraocular lens compared with those of a monofocal intraocular lens. Ophthalmology 2021, 128, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaza-Puche, A.B.; Alio, J.L.; Sala, E.; Mojzis, P. Impact of low mesopic contrast sensitivity outcomes in different types of modern multifocal intraocular lenses. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 26, 612–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, J.; Rodríguez-Vallejo, M.; Martínez, J.; Burguera, N.; Piñero, D.P. What we have learnt from 30 years living with positive dysphotopsia after intraocular lens implantation?: A review. Exp. Rev. Ophthalmol. 2021, 16, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiler, T.G.; Wegner, A.; Senfft, T.; Seiler, T. Dissatisfaction after trifocal IOL implantation and its improvement by selective wavefront-guided LASIK. J. Refract. Surg. 2019, 35, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiya, K.; Hayashi, K.; Shimizu, K.; Negishi, K.; Sato, M.; Bissen-Miyajima, H.; Survey Working Group of the Japanese Society of Cataract and Refractive Surgery. Multifocal intraocular lens explantation: A case series of 50 eyes. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 158, 215–220.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, A.; Ali, T.K.; Waren, D.P.; Donaldson, K.E. Causes and correction of dissatisfaction after implantation of presbyopia-correcting intraocular lenses. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2016, 10, 1965–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, M.A.; Randleman, J.B.; Doyle Stulting, R. Dissatisfaction after multifocal intraocular lens implantation. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2009, 35, 992–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coco-Martin, M.B.; Valenzuela, P.L.; Maldonado-López, M.J.; Santos-Lozano, A.; Molina-Martín, A.; Piñero, D.P. Potential of video games for the promotion of neuroadaptation to multifocal intraocular lenses: A narrative review. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 12, 1782–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, A.M.; Miranda, A.C.; Patricio, M.; McAlinden, C.; Silva, F.L.; Murta, J.N.; Castelo-Branco, M. Functional magnetic resonance imaging to assess the neurobehavioral impact of dysphotopsia with multifocal intraocular lenses. Ophthalmology 2017, 124, 1280–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, A.M.; Miranda, Â.C.; Patrício, M.M.; McAlinden, C.; Silva, F.L.; Castelo-Branco, M.; Murta, J.N. Functional magnetic resonance imaging to assess neuroadaptation to multifocal intraocular lenses. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2017, 43, 1287–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaymak, H.; Fahle, M.; Ott, G.; Mester, U. Intraindividual comparison of the effect of training on visual performance with ReSTOR and Tecnis diffractive multifocal IOLs. J. Refract. Surg. 2008, 24, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mester, U.; Fahle, M.; Ott, G.; Kaymak, H. Functional vision training after MIOL implantation. Ophthalmologe 2008, 105, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Rodríguez, C.J.; Fukumitsu, H.; Ruiz-Fortes, P.; Soto-Negro, R.; Merino-Suárez, M.; Piñero, D.P. Efficacy of perceptual learning-based vision training as an adjuvant to occlusion therapy in the management of amblyopia: A pilot study. Vision 2021, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coco-Martin, M.B.; Piñero, D.P.; Leal-Vega, L.; Hernández-Rodríguez, C.J.; Adiego, J.; Molina-Martín, A.; de Fez, D.; Arenillas, J.F. The potential of virtual reality for inducing neuroplasticity in children with amblyopia. J. Ophthalmol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halicka, J.; Bittsansky, M.; Sivak, S.; Piñero, D.P.; Ziak, P. Virtual reality visual training in an adult patient with anisometropic amblyopia: Visual and functional magnetic resonance outcomes. Vision 2021, 5, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Zhang, J.Y. Dichoptic training in adults with amblyopia: Additional stereoacuity gains over monocular training. Vis. Res. 2018, 152, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žiak, P.; Holm, A.; Halička, J.; Mojžiš, P.; Piñero, D.P. Amblyopia treatment of adults with dichoptic training using the virtual reality oculus rift head mounted display: Preliminary results. BMC Ophthalmol. 2017, 17, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedamurthy, I.; Nahum, M.; Bavelier, D.; Levi, D.M. Mechanisms of recovery of visual function in adult amblyopia through a tailored action video game. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, R.F.; Babu, R.J.; Clavagnier, S.; Black, J.; Bobier, W.; Thompson, B. The iPod binocular home-based treatment for amblyopia in adults: Efficacy and compliance. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2014, 97, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yalcin, E.; Balci, O. Efficacy of perceptual vision therapy in enhancing visual acuity and contrast sensitivity function in adult hypermetropic anisometropic amblyopia. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2014, 8, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tan, D.T.; Fong, A. Efficacy of neural vision therapy to enhance contrast sensitivity function and visual acuity in low myopia. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2008, 34, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Rodríguez, C.J.; Piñero, D.P.; Molina-Martín, A.; Morales-Quezada, L.; de Fez, D.; Leal-Vega, L.; Arenillas, J.F.; Coco-Martín, M.B. Stimuli characteristics and psychophysical requirements for visual training in amblyopia: A narrative review. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten Brinke, L.F.; Davis, J.C.; Barha, C.K.; Liu-Ambrose, T. Effects of computerized cognitive training on neuroimaging outcomes in older adults: A systematic review. BMC Geriatr. 2017, 17, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaus, M.; Marron, E.M.; Viejo-Sobera, R.; Redolar-Ripoll, D. Neural basis of video gaming: A systematic review. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAnanya, J.J.; Alexander, K.R. Contrast sensitivity for letter optotypes vs. gratings under conditions biased toward parvocellular and magnocellular pathways. Vis. Res. 2006, 46, 1574–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Fez, D.; Luque, M.J.; García-Domene, M.C.; Camps, V.; Piñero, D. Colorimetric characterization of mobile devices for vision applications. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2016, 93, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrhel, M.J.; Trussell, H.J. Color device calibration: A mathematical formulation. IEEE. Trans. Image Process. 1999, 8, 1796–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberman, H.R.; Pentland, A.P. Microcomputer-based estimation of psychophysical thresholds: The Best PEST. Behav. Res. Method. Instrum. 1982, 14, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tootell, R.; Hadjikhani, N.; Vanduffel, W.; Liu, A.K.; Mendola, J.D.; Sereno, M.I.; Dale, A.M. Functional analysis of primary visual cortex (V1) in humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgeson, M. Visual altereffects: Cortical neurons change their tune. Curr. Biol. 2004, 14, 751–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hienert, J.; Stjepanek, K.; Hirnschall, N.; Ruiss, M.; Zwickl, H.; Findl, O. Visual performance of two diffractive trifocal intraocular lenses: A randomized trial. J. Refract. Surg. 2021, 37, 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, F.; Ferreira, T.B. Comparison of clinical outcomes of 3 trifocal IOLs. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2020, 46, 1247–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poyales, F.; Garzon, N. Comparison of 3-month visual outcomes of a spherical and a toric trifocal intraocular lens. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2019, 45, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bar, M. Visual objects in context. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2004, 5, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michael, R.; van Rijn, L.J.; van den Berg, T.J.T.P.; Barraquer, R.I.; Grabner, G.; Wilhelm, H.; Coeckelbergh, T.; Emesz, M.; Marvan, P.; Nischler, C. Association of lens opacities, intraocular straylight, contrast sensitivity and visual acuity in European drivers. Acta Ophthalmol. 2009, 87, 666–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Fez, M.D.; Luque, M.J.; Viqueira, V. Enhancement of contrast sensitivity and losses of chromatic discrimination with tinted lenses. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2002, 79, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque, M.J.; Capilla, P.; de Fez, M.D.; García-Domene, M.C. Images perceived after chromatic or achromatic contrast sensitivity losses. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2010, 87, E313–E322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Placebo Group | Study Group | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LogMAR Uncorrected Visual Acuity | Distance (4 m) | Right | 0.03 ± 0.09 (−0.08–0.30) | 0.05 ± 0.07 (−0.08–0.15) | 0.21 |
| Left | 0.07 ± 0.12 (−0.08–0.40) | 0.05 ± 0.10 (−0.08–0.22) | 0.51 | ||
| Intermediate (1 m) | Right | 0.04 ± 0.05 (0.00–0.15) | 0.10 ± 0.13 (0.00–0.40) | 0.35 | |
| Left | 0.06 ± 0.10 (0.00–0.30) | 0.11 ± 0.12 (0.00–0.40) | 0.17 | ||
| Near (40 cm) | Right | 0.10 ± 0.10 (0.00–0.30) | 0.10 ± 0.11 (0.00–0.30) | 0.88 | |
| Left | 0.15 ± 0.13 (0.00–0.40) | 0.09 ± 0.11 (0.00–0.30) | 0.24 | ||
| LogMAR Distance-Corrected Visual Acuity | Distance (4 m) | Right | −0.01 ± 0.04 (−0.08–0.02) | −0.01 ± 0.03 (−0.08–0.05) | 0.86 |
| Left | −0.01 ± 0.05 (−0.08–0.10) | −0.00 ± 0.04 (−0.08–0.10) | 0.82 | ||
| Intermediate (1 m) | Right | 0.05 ± 0.05 (0.00–0.15) | 0.09 ± 0.13 (0.00–0.40) | 0.65 | |
| Left | 0.05 ± 0.07 (0.00–0.22) | 0.13 ± 0.15 (0.00–0.54) | 0.15 | ||
| Near (40 cm) | Right | 0.08 ± 0.09 (0.00–0.30) | 0.08 ± 0.08 (0.00–0.30) | 0.68 | |
| Left | 0.09 ± 0.09 (0.00–0.22) | 0.09 ± 0.12 (0.00–0.30) | 0.83 |
| Placebo Group | Study Group | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before Training | Distance (4 m) | −0.01 ± 0.04 (−0.08–0.05) | −0.01 ± 0.07 (−0.08–0.10) | 0.64 |
| Intermediate (1 m) | 0.00 ± 0.03 (−0.08–0.05) | 0.03 ± 0.08 (−0.08–0.15) | 0.25 | |
| Near (40 cm) | 0.05 ± 0.09 (0.00–0.30) | 0.05 ± 0.08 (0.00–0.22) | 0.92 | |
| After Training | Distance (4 m) | −0.04 ± 0.05 (−0.11–0.05) | −0.03 ± 0.06 (−0.08–0.10) | 0.76 |
| Intermediate (1 m) | 0.01 ± 0.06 (−0.08–0.15) | 0.01 ± 0.08 (−0.08–0.15) | 0.67 | |
| Near (40 cm) | 0.08 ± 0.12 (0.00–0.30) | 0.06 ± 0.08 (0.00–0.22) | 0.83 |
| Optopad Contrast Sensitivity Test | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo Group | Study Group | p-Value | ||
| Before Training | 1.5 cpd | 3.45 ± 0.11 (3.30–3.65) | 3.46 ± 0.09 (3.37–3.58) | 0.80 |
| 3.0 cpd | 3.71 ± 0.19 (3.38–4.11) | 3.74 ± 0.13 (3.50–3.99) | 0.51 | |
| 6.0 cpd | 3.45 ± 0.24 (3.05–3.86) | 3.47 ± 0.19 (3.26–3.86) | 0.81 | |
| 12.0 cpd | 2.94 ± 0.29 (2.53–3.40) | 2.97 ± 0.23 (2.53–3.32) | 0.77 | |
| 24.0 cpd | 2.21 ± 0.31 (1.76–2.78) | 2.13 ± 0.17 (1.76–2.51) | 0.57 | |
| After Training | 1.5 cpd | 3.47 ± 0.16 (3.05–3.72) | 3.62 ± 0.24 (3.37–4.13) | 0.13 |
| 3.0 cpd | 3.76 ± 0.20 (3.50–4.11) | 3.92 ± 0.27 (3.38–4.23) | 0.08 | |
| 6.0 cpd | 3.44 ± 0.28 (3.05–3.99) | 3.53 ± 0.25 (3.05–3.99) | 0.27 | |
| 12.0 cpd | 2.99 ± 0.55 (1.64–3.82) | 2.88 ± 0.34 (2.27–3.24) | 0.33 | |
| 24.0 cpd | 2.11 ± 0.23 (1.76–2.51) | 2.13 ± 0.19 (1.76–2.37) | 0.85 | |
| Optictrain-CS Contrast Sensitivity Test | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo Group | Study Group | p-Value | ||
| Before Training | 0.5 cpd | 1.88 ± 0.24 (1.54–2.30) | 2.02 ± 0.20 (1.78–2.30) | 0.13 |
| 1.0 cpd | 2.22 ± 0.14 (2.01–2.30) | 2.17 ± 0.19 (1.78–2.30) | 0.54 | |
| 1.5 cpd | 2.20 ± 0.15 (2.01–2.30) | 2.19 ± 0.17 (1.85–2.30) | 0.89 | |
| 3.0 cpd | 2.10 ± 0.19 (1.78–2.30) | 2.10 ± 0.23 (1.66–2.30) | 0.86 | |
| 4.5 cpd | 2.10 ± 0.29 (1.32–2.30) | 1.99 ± 0.28 (1.32–2.30) | 0.18 | |
| 6.0 cpd | 1.92 ± 0.32 (1.19–2.30) | 1.95 ± 0.31 (1.19–2.30) | 0.78 | |
| After Training | 0.5 cpd | 1.98 ± 0.22 (1.52–2.30) | 1.96 ± 0.31 (1.51–2.30) | 0.94 |
| 1.0 cpd | 2.15 ± 0.23 (1.58–2.30) | 2.11 ± 0.18 (1.78–2.30) | 0.39 | |
| 1.5 cpd | 2.13 ± 0.15 (2.01–2.30) | 2.26 ± 0.11 (2.01–2.30) | 0.02 * | |
| 3.0 cpd | 2.05 ± 0.20 (1.58–2.30) | 2.18 ± 0.30 (1.58–2.91) | 0.20 | |
| 4.5 cpd | 1.85 ± 0.25 (1.54–2.30) | 1.94 ± 0.28 (1.58–2.30) | 0.35 | |
| 6.0 cpd | 1.76 ± 0.24 (1.52–2.30) | 1.86 ± 0.30 (1.40–2.30) | 0.32 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piñero, D.P.; Molina-Martin, A.; Ramón, M.L.; Rincón, J.L.; Fernández, C.; de Fez, D.; Arenillas, J.F.; Leal-Vega, L.; Coco-Martín, M.B.; Maldonado, M.J. Preliminary Evaluation of the Clinical Benefit of a Novel Visual Rehabilitation Program in Patients Implanted with Trifocal Diffractive Intraocular Lenses: A Blinded Randomized Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11091181
Piñero DP, Molina-Martin A, Ramón ML, Rincón JL, Fernández C, de Fez D, Arenillas JF, Leal-Vega L, Coco-Martín MB, Maldonado MJ. Preliminary Evaluation of the Clinical Benefit of a Novel Visual Rehabilitation Program in Patients Implanted with Trifocal Diffractive Intraocular Lenses: A Blinded Randomized Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(9):1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11091181
Chicago/Turabian StylePiñero, David P., Ainhoa Molina-Martin, María L. Ramón, José L. Rincón, Cristian Fernández, Dolores de Fez, Juan F. Arenillas, Luis Leal-Vega, María Begoña Coco-Martín, and Miguel J. Maldonado. 2021. "Preliminary Evaluation of the Clinical Benefit of a Novel Visual Rehabilitation Program in Patients Implanted with Trifocal Diffractive Intraocular Lenses: A Blinded Randomized Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial" Brain Sciences 11, no. 9: 1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11091181
APA StylePiñero, D. P., Molina-Martin, A., Ramón, M. L., Rincón, J. L., Fernández, C., de Fez, D., Arenillas, J. F., Leal-Vega, L., Coco-Martín, M. B., & Maldonado, M. J. (2021). Preliminary Evaluation of the Clinical Benefit of a Novel Visual Rehabilitation Program in Patients Implanted with Trifocal Diffractive Intraocular Lenses: A Blinded Randomized Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Brain Sciences, 11(9), 1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11091181








