Personality Traits Modulate the Effect of tDCS on Reading Speed of Social Sentences
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Non-invasive Brain Stimulation (NIBS)
1.2. Moderation of tDCS Effect by Approach and Avoidance Personality Traits
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Stimuli
2.4. Affective Tests
2.5. Procedure
2.5.1. Experimental Task
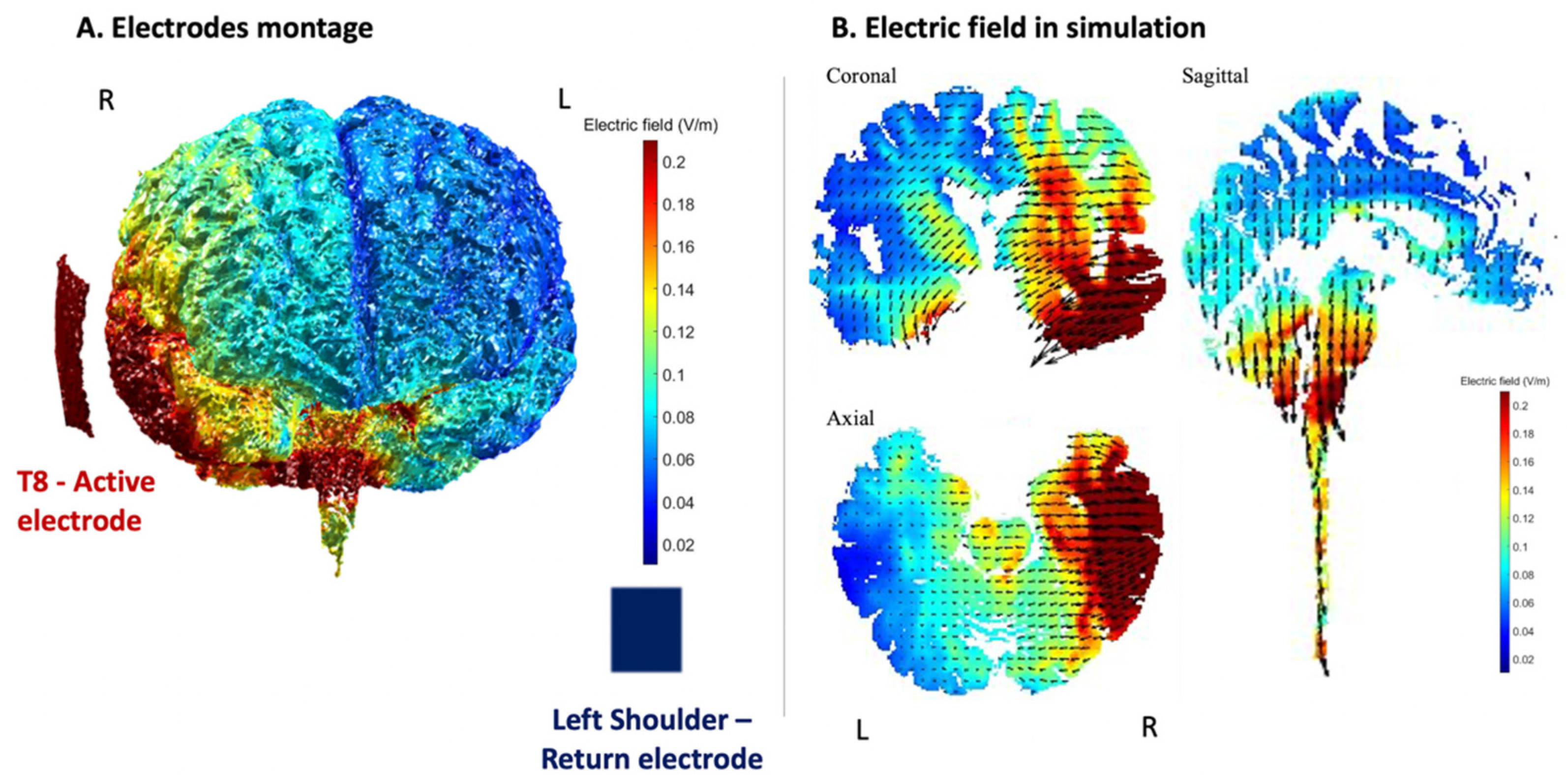
2.5.2. Protocol for tDCS Application
2.5.3. tDCS Procedure
3. Results
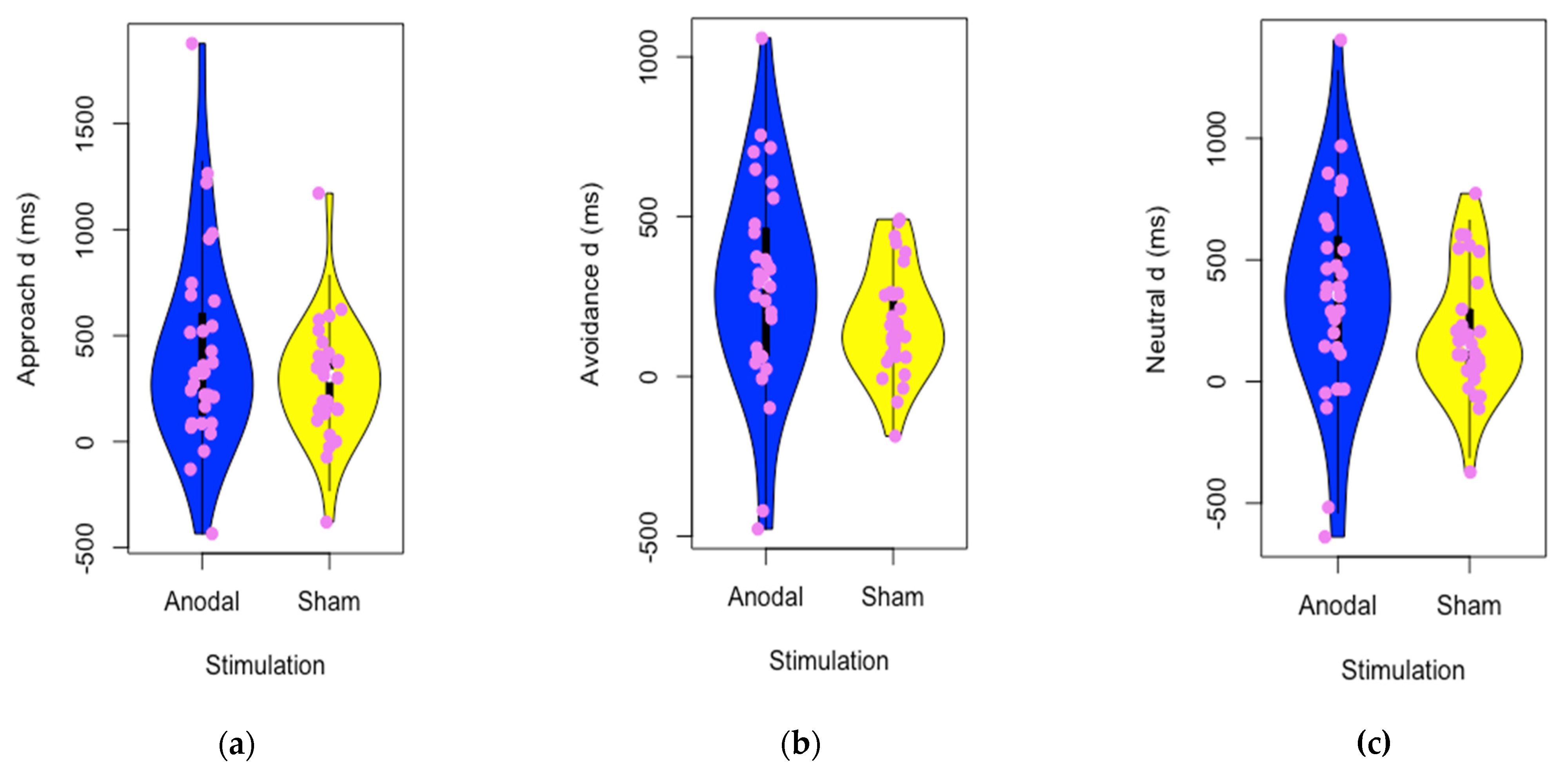
3.1. Moderation of tDCS by Affective Traits
3.2. Behavioral Approach System (BAS)
3.3. Behavioral Inhibition System (BIS)
4. Discussion
4.1. tDCS Effect on Reading Speed Improvement Is Modulated by Approach/Avoidance Trait
4.2. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dodell-Feder, D.; Koster-Hale, J.; Bedny, M.; Saxe, R. FMRI Item Analysis in a Theory of Mind Task. NeuroImage 2011, 55, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, D.P.; Adolphs, R. The Social Brain in Psychiatric and Neurological Disorders. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2012, 16, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spunt, R.P.; Falk, E.B.; Lieberman, M.D. Dissociable Neural Systems Support Retrieval of How and Why Action Knowledge. Psychol. Sci. 2010, 21, 1593–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobbini, M.I.; Koralek, A.C.; Bryan, R.E.; Montgomery, K.J.; Haxby, J.V. Two Takes on the Social Brain: A Comparison of Theory of Mind Tasks. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2007, 19, 1803–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofalo, S.; Timmermann, C.; Battaglia, S.; Maier, M.E.; di Pellegrino, G. Mediofrontal Negativity Signals Unexpected Timing of Salient Outcomes. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2017, 29, 718–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battaglia, S.; Garofalo, S.; di Pellegrino, G.; Starita, F. Revaluing the Role of VmPFC in the Acquisition of Pavlovian Threat Conditioning in Humans. J. Neurosci. 2020, 40, 8491–8500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battaglia, S.; Serio, G.; Scarpazza, C.; D’Ausilio, A.; Borgomaneri, S. Frozen in (e)Motion: How Reactive Motor Inhibition Is Influenced by the Emotional Content of Stimuli in Healthy and Psychiatric Populations. Behav. Res. Ther. 2021, 146, 103963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, R.; Latinus, M.; Charest, I.; Crabbe, F.; Belin, P. People-Selectivity, Audiovisual Integration and Heteromodality in the Superior Temporal Sulcus. Cortex 2014, 50, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.; Gallate, J. The function of the anterior temporal lobe: A review of the empirical evidence. Brain Res. 2012, 1449, 94–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellena, G.; Starita, F.; Haggard, P.; Làdavas, E. The Spatial Logic of Fear. Cognition 2020, 203, 104336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candini, M.; Battaglia, S.; Benassi, M.; di Pellegrino, G.; Frassinetti, F. The Physiological Correlates of Interpersonal Space. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.H.; Senju, A.; Tomalski, P. The Two-Process Theory of Face Processing: Modifications Based on Two Decades of Data from Infants and Adults. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2015, 50, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pelphrey, K.A.; Morris, J.P. Brain Mechanisms for Interpreting the Actions of Others from Biological-Motion Cues. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 2006, 15, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pelphrey, K.A.; Carter, E.J. Brain Mechanisms for Social Perception. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1145, 283–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saitovitch, A.; Bargiacchi, A.; Chabane, N.; Brunelle, F.; Samson, Y.; Boddaert, N.; Zilbovicius, M. Social Cognition and the Superior Temporal Sulcus: Implications in Autism. Rev. Neurol. (Paris) 2012, 168, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.Y.J.; Rosenblau, G.; Keifer, C.; Pelphrey, K.A. An Integrative Neural Model of Social Perception, Action Observation, and Theory of Mind. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2015, 51, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flores, L.E.; Eckstrand, K.L.; Silk, J.S.; Allen, N.B.; Ambrosia, M.; Healey, K.L.; Forbes, E.E. Adolescents’ Neural Response to Social Reward and Real-World Emotional Closeness and Positive Affect. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2018, 18, 705–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelphrey, K.A.; Viola, R.J.; McCarthy, G. When Strangers Pass: Processing of Mutual and Averted Social Gaze in the Superior Temporal Sulcus. Psychol. Sci. 2004, 15, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, L.A.; Olson, I.R. Social Cognition and the Anterior Temporal Lobes. NeuroImage 2010, 49, 3452–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tavares, P.; Lawrence, A.D.; Barnard, P.J. Paying Attention to Social Meaning: An FMRI Study. Cereb. Cortex 2008, 18, 1876–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marrero, H.; Urrutia, M.; Beltrán, D.; Gámez, E.; Díaz, J.M. Understanding Approach and Avoidance in Verbal Descriptions of Everyday Actions: An ERP Study. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2017, 17, 612–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrero, H.; Gámez, E.; Diaz, J.M.; Urrutia, M.; de Vega, M. Carefully encoding approach and avoidance body locomotion with interpersonal conduct in narrated interactions. Can. J. Exp. Psychol. 2015, 69, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yavari, F.; Jamil, A.; Mosayebi Samani, M.; Vidor, L.P.; Nitsche, M.A. Basic and Functional Effects of Transcranial Electrical Stimulation (TES)—An Introduction. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2018, 85, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, A.T.; Jalinous, R.; Freeston, I.L. Non-invasive magnetic stimulation of human motor cortex. Lancet 1985, 325, 1106–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, M.S.; Aston-Jones, G. Noninvasive Techniques for Probing Neurocircuitry and Treating Illness: Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS), Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) and Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (TDCS). Neuropsychopharmacology 2010, 35, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitsche, M.A.; Cohen, L.G.; Wassermann, E.M.; Priori, A.; Lang, N.; Antal, A.; Paulus, W.; Hummel, F.; Boggio, P.S.; Fregni, F.; et al. Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation: State of the Art 2008. Brain Stimulat. 2008, 1, 206–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgomaneri, S.; Battaglia, S.; Garofalo, S.; Tortora, F.; Avenanti, A.; di Pellegrino, G. State-Dependent TMS over Prefrontal Cortex Disrupts Fear-Memory Reconsolidation and Prevents the Return of Fear. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, 3672–3679.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunelin, J.; Mondino, M.; Gassab, L.; Haesebaert, F.; Gaha, L.; Suaud-Chagny, M.-F.; Saoud, M.; Mechri, A.; Poulet, E. Examining Transcranial Direct-Current Stimulation (TDCS) as a Treatment for Hallucinations in Schizophrenia. Am. J. Psychiatry 2012, 169, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, M.-F.; Paulus, W.; Nitsche, M.A. Therapeutic Effects of Non-Invasive Brain Stimulation with Direct Currents (TDCS) in Neuropsychiatric Diseases. NeuroImage 2014, 85, 948–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loo, C.K.; Alonzo, A.; Martin, D.; Mitchell, P.B.; Galvez, V.; Sachdev, P. Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation for Depression: 3-Week, Randomised, Sham-Controlled Trial. Br. J. Psychiatry 2012, 200, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marrero, H.; Yagual, S.N.; García-Marco, E.; Gámez, E.; Beltrán, D.; Díaz, J.M.; Urrutia, M. Enhancing Memory for Relationship Actions by Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation of the Superior Temporal Sulcus. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer, A.; Antonietti, A. TDCS Modulatory Effect on Reading Processes: A Review of Studies on Typical Readers and Individuals with Dyslexia. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thomson, J.M.; Doruk, D.; Mascio, B.; Fregni, F.; Cerruti, C. Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Modulates Efficiency of Reading Processes. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsalou, L.W. Simulation, Situated Conceptualization, and Prediction. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 1281–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwaan, R.A. The immersed experiencer: Toward an embodied theory of language comprehension. In The Psychology of Learning and Motivation; Ross, B.H., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2004; Volume 44, pp. 35–62. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, J.A.A. A critique of Eysenck’s theory of personality. In A Model for Personality; Eysenck, H.J., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1981; pp. 246–276. [Google Scholar]
- Metuki, N.; Sela, T.; Lavidor, M. Enhancing Cognitive Control Components of Insight Problems Solving by Anodal TDCS of the Left Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex. Brain Stimulat. 2012, 5, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blumenthal, T.D. Extraversion, Attention, and Startle Response Reactivity. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2001, 31, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sela, T.; Ivry, R.B.; Lavidor, M. Prefrontal Control during a Semantic Decision Task That Involves Idiom Comprehension: A Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Study. Neuropsychologia 2012, 50, 2271–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giakoumaki, S.G.; Roussos, P.; Tsapakis, E.M.; Koiliari, E.; Pasparakis, E.; Zouraraki, C.; Bitsios, P. Cognitive and Personality Analysis of Startle Reactivity in a Large Cohort of Healthy Males. Biol. Psychol. 2013, 94, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaRowe, S.D.; Patrick, C.J.; Curtin, J.J.; Kline, J.P. Personality Correlates of Startle Habituation. Biol. Psychol. 2006, 72, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eysenck, M.W.; Derakshan, N.; Santos, R.; Calvo, M.G. Anxiety and cognitive performance: Attentional control theory. Emotion 2007, 7, 336–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.G.; Buchner, A. G*Power 3: A Flexible Statistical Power Analysis Program for the Social, Behavioral, and Biomedical Sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldfield, R.C. The assessment and analysis of handedness: The Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia 1971, 9, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carver, C.S.; White, T.L. Behavioral Inhibition, Behavioral Activation, and Affective Responses to Impending Reward and Punishment: The BIS/BAS Scales. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1994, 67, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitsche, M.A.; Doemkes, S.; Karaköse, T.; Antal, A.; Liebetanz, D.; Lang, N.; Tergau, F.; Paulus, W. Shaping the Effects of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation of the Human Motor Cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 2007, 97, 3109–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.; Datta, A.; Bikson, M.; Parra, L.C. Realistic Volumetric-Approach to Simulate Transcranial Electric Stimulation—ROAST—A Fully Automated Open-Source Pipeline. J. Neural Eng. 2019, 16, 056006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez, E.; Gómez-Ariza, C.J.; Díez-Álamo, A.M.; Alonso, M.A.; Fernandez, A. The Processing of Semantic Relatedness in the Brain: Evidence from Associative and Categorical False Recognition Effects Following Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation of the Left Anterior Temporal Lobe. Cortex 2017, 93, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwissler, B.; Sperber, C.; Aigeldinger, S.; Schindler, S.; Kissler, J.; Plewnia, C. Shaping Memory Accuracy by Left Prefrontal Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 4022–4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paulus, W. Transcranial electrical stimulation (tES-tDCS; tRNS, tACS) methods. Neuropsychol. Rehabil. 2011, 21, 602–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunoni, A.R.; Amadera, J.; Berbel, B.; Volz, M.S.; Rizzerio, B.G.; Fregni, F. A Systematic Review on Reporting and Assessment of Adverse Effects Associated with Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2011, 14, 1133–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauschke, C.; Bahn, D.; Vesker, M.; Schwarzer, G. The Role of Emotional Valence for the Processing of Facial and Verbal Stimuli—Positivity or Negativity Bias? Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaup, B.; Lüdtke, J.; Zwaan, R.A. Processing Negated Sentences with Contradictory Predicates: Is a Door That Is Not Open Mentally Closed? J. Pragmat. 2006, 38, 1033–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sentence | Direction | Question Example | Correct Answer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pedro/aceptó a Rosa/en Whatshapp (Pedro/accepted Rosa/in Whatsapp) | Approach | ¿Dice que Pedro aceptó a Rosa en Whatshapp? (Is it stated that Pedro accepted Rosa in Whatshapp?) | Yes |
| Pedro/bloqueó a Rosa/en Whatshapp (Pedro/blocked Rosa/in Whatshapp | Avoidance | ¿Dice que Pedro aceptó a Rosa en Whatshapp? (Is it stated that Pedro accepted Rosa in Whatshapp?) | No |
| Verónica/dedujo el precio/del abrigo (Verónica/deduced the price/of the coat) | Neutral | ¿Dice que Verónica dedujo el precio del abrigo? (Is it stated that Verónica deduced the price of the coat?) | Yes |
| Type of Effect | Severity | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Tingling | Mild | 27.14% |
| Itching | Mild | 67.14% |
| Warm | Mild | 4.28% |
| Direction | Stimulation | Mean | SD | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approach | Anodal | 425.81 | 465.06 | 31 |
| Sham | 288.82 | 280.42 | 29 | |
| Avoid. | Anodal | 284.83 | 327.73 | 31 |
| Sham | 171.56 | 170.30 | 29 | |
| Neutral | Anodal | 363.5 | 418.53 | 31 |
| Sham | 196.49 | 255.64 | 29 |
| Direction | Stimulation | Mean | SD | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approach | Anodal | 490.37 | 412.64 | 11 |
| Sham | 206.099 | 309.16 | 10 | |
| Avoid. | Anodal | 334.41 | 217.85 | 11 |
| Sham | 87.13 | 166.84 | 10 | |
| Neutral | Anodal | 411.12 | 420.50 | 11 |
| Sham | 81.03 | 228.46 | 10 |
| Direction | Stimulation | Mean | SD | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approach | Anodal | 583.70 | 412.52 | 11 |
| Sham | 280.76 | 417.18 | 10 | |
| Avoid. | Anodal | 366.82 | 263.08 | 11 |
| Sham | 169.39 | 188.28 | 10 | |
| Neutral | Anodal | 562.93 | 418.99 | 11 |
| Sham | 130.92 | 280.96 | 10 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reyes, C.; Padrón, I.; Nila Yagual, S.; Marrero, H. Personality Traits Modulate the Effect of tDCS on Reading Speed of Social Sentences. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1464. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111464
Reyes C, Padrón I, Nila Yagual S, Marrero H. Personality Traits Modulate the Effect of tDCS on Reading Speed of Social Sentences. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(11):1464. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111464
Chicago/Turabian StyleReyes, Cristian, Iván Padrón, Sara Nila Yagual, and Hipólito Marrero. 2021. "Personality Traits Modulate the Effect of tDCS on Reading Speed of Social Sentences" Brain Sciences 11, no. 11: 1464. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111464
APA StyleReyes, C., Padrón, I., Nila Yagual, S., & Marrero, H. (2021). Personality Traits Modulate the Effect of tDCS on Reading Speed of Social Sentences. Brain Sciences, 11(11), 1464. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111464







