The Association between CAG Repeat Length and Age of Onset of Juvenile-Onset Huntington’s Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of Data
2.2. Statistical Analysis
2.3. Institutional Ethical Approval
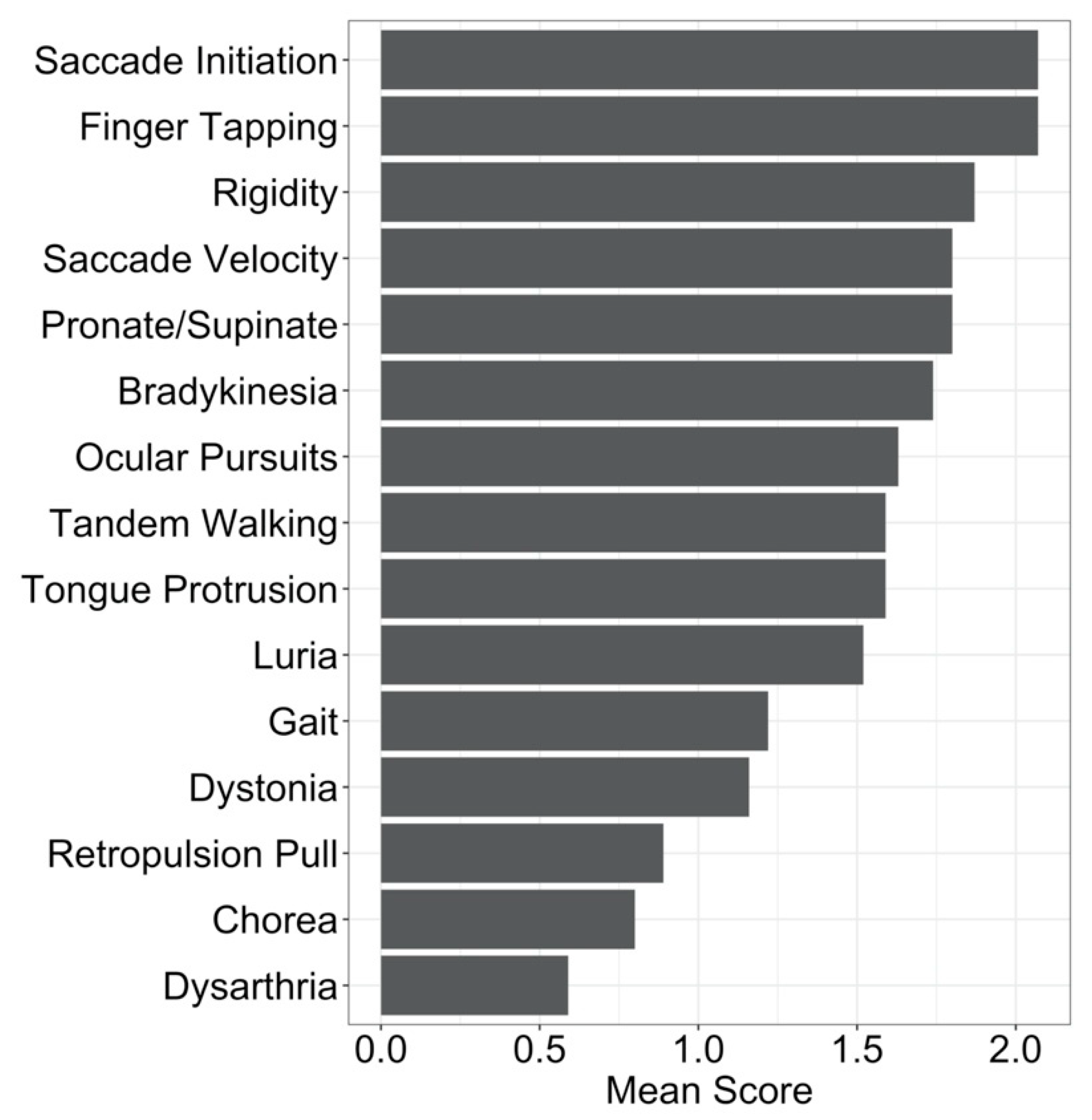
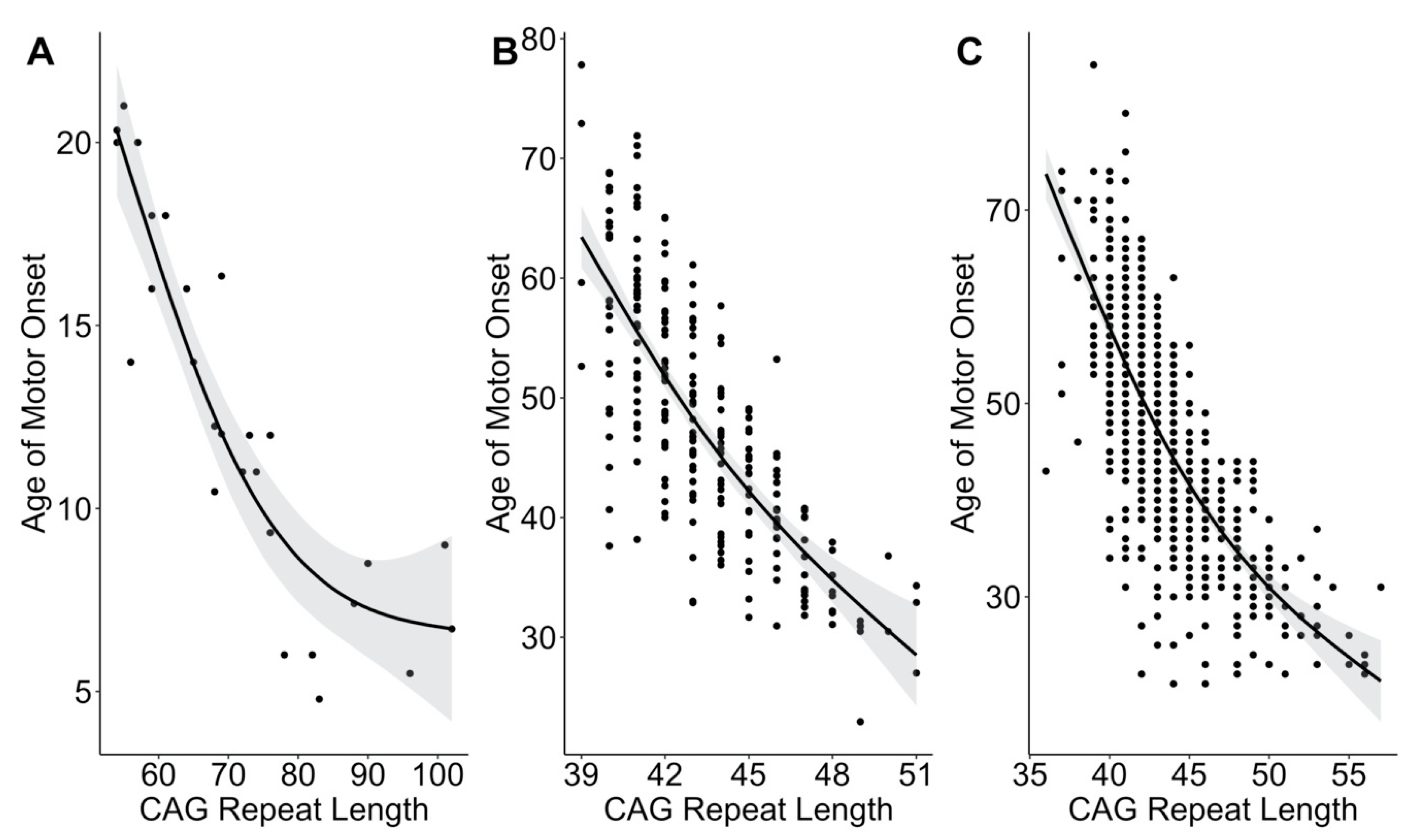
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Macdonald, M.E.; Ambrose, C.M.; Duyao, M.P.; Myers, R.H.; Lin, C.; Srinidhi, L.; Barnes, G.; Taylor, S.A.; James, M.; Groot, N.; et al. A novel gene containing a trinucleotide repeat that is expanded and unstable on Huntington’s disease chromosomes. Cell 1993, 72, 971–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langbehn, D.R.; Brinkman, R.; Falush, D.; Paulsen, J.S.; Hayden, M.R. A new model for prediction of the age of onset and penetrance for Huntington’s disease based on CAG length. Clin. Genet. 2004, 65, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stine, O.; Pleasant, N.; Franz, M.L.; Abbott, M.H.; Folstein, S.E.; Ross, C.A. Correlation between the onset age of Huntington’s disease and length of the trinucleotide repeat in IT-15. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1993, 2, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucotte, G.; Turpin, J.; Riess, O.; Epplen, J.T.; Siedlaczk, I.; Loirat, F.; Hazout, S. Confidence intervals for predicted age of onset, given the size of (CAG) n repeat, in Huntington’s disease. Qual. Life Res. 1995, 95, 231–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew, S.E.; Goldberg, Y.P.; Kremer, B.; Telenius, H.; Theilmann, J.; Adam, S.; Starr, E.; Squitieri, F.; Lin, B.; Kalchman, M.A.; et al. The relationship between trinucleotide (CAG) repeat length and clinical features of Huntington’s disease. Nat. Genet. 1993, 4, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squitieri, F.; Sabbadini, G.; Mandich, P.; Gellera, C.; Di Maria, E.; Bellone, E.; Castellotti, B.; Nargi, E.; De Grazia, U.; Frontali, M.; et al. Family and molecular data for a fine analysis of age at onset in Huntington disease. Am. J. Med Genet. 2000, 95, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, S.; Rong, J.; Nguyen, H.H.P.; Cape, A.; Tomiuk, J.; Soehn, A.S.; Freudenberg-Hua, Y.; Propping, P.; Freudenberg, J.; Tong, L.; et al. Huntingtin-associated protein-1 is a modifier of the age-at-onset of Huntington’s disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2008, 17, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.-M.; Zhang, Y.-B.; Wu, Z.-Y. Huntington’s Disease: Relationship Between Phenotype and Genotype. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 54, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, T.-K.; Hu, J.; Pringsheim, T. Risk factors for the onset and progression of Huntington disease. NeuroToxicology 2017, 61, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squitieri, F.; Frati, L.; Ciarmiello, A.; Lastoria, S.; Quarrell, O. Juvenile Huntington’s disease: Does a dosage-effect pathogenic mechanism differ from the classical adult disease? Mech. Ageing Dev. 2006, 127, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronin, T.; Rosser, A.; Massey, T.H. Clinical Presentation and Features of Juvenile-Onset Huntington’s Disease: A Systematic Review. J. Huntington’s Dis. 2019, 8, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kieburtz, K.; Penney, J.B.; Corno, P.; Ranen, N.; Shoulson, I.; Feigin, A.; Abwender, D.; Greenarnyre, J.T.; Higgins, D.; Marshall, F.J.; et al. Unified Huntington’s disease rating scale: Reliability and consistency. Mov. Disord. 1996, 11, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulsen, J.S.; Long, J.D.; Rosser, A.E.; Harrington, D.L.; Erwin, C.J.; Williams, J.K.; Westervelt, H.J.; Johnson, H.J.; Aylward, E.H.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Prediction of manifest Huntington’s disease with clinical and imaging measures: A prospective observational study. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 1193–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landwehrmeyer, G.B.; Fitzer-Attas, C.J.; Giuliano, J.D.; Gonçalves, N.; Anderson, K.E.; Cardoso, F.; Ferreira, J.J.; Mestre, T.A.; Stout, J.C.; Sampaio, C. Data Analytics from Enroll-HD, a Global Clinical Research Platform for Huntington’s Disease. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pr. 2016, 4, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Plas, E.; Langbehn, D.R.; Conrad, A.L.; Koscik, T.R.; Tereshchenko, A.; Epping, E.; Magnotta, V.; Nopoulos, P. Abnormal brain development in child and adolescent carriers of mutant huntingtin. Neurol. 2019, 93, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saudou, F.; Humbert, S. The Biology of Huntingtin. Neuron 2016, 89, 910–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, J.; Kamholz, J.A.; Moser, D.J.; Feely, S.M.; Paulsen, J.S.; Nopoulos, P. Substance abuse may hasten motor onset of Huntington disease. Neurol. 2017, 88, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, J.L.; Nopoulos, P.C.; Killoran, A.; Kamholz, J.A. Statin use and delayed onset of Huntington’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2018, 34, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, J.; Harshman, L.A.; Langbehn, D.R.; Nopoulos, P.C. Hypertension Is Associated with an Earlier Age of Onset of Huntington’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-M.; Wheeler, V.C.; Chao, M.J.; Vonsattel, J.P.G.; Pinto, R.M.; Lucente, D.; Abu-Elneel, K.; Ramos, E.M.; Mysore, J.S.; Gillis, T.; et al. Identification of Genetic Factors that Modify Clinical Onset of Huntington’s Disease. Cell 2015, 162, 516–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-M.; Correia, K.; Loupe, J.; Kim, K.-H.; Barker, D.; Hong, E.P.; Chao, M.J.; Long, J.D.; Lucente, D.; Vonsattel, J.P.G.; et al. CAG Repeat Not Polyglutamine Length Determines Timing of Huntington’s Disease Onset. Cell 2019, 178, 887–900.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Squitieri, F.; Berardelli, A.; Nargi, E.; Castellotti, B.; Mariotti, C.; Cannella, M.; Lavitrano, M.L.; De Grazia, U.; Gellera, C.; Ruggieri, S. Atypical movement disorders in the early stages of Huntington’s disease: Clinical and genetic analysis. Clin. Genet. 2000, 58, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langbehn, D.R.; Hayden, M.R.; Paulsen, J.S.; The PREDICT-HD Investigators of the Huntington Study Group. CAG-repeat length and the age of onset in Huntington disease (HD): A review and validation study of statistical approaches. Am. J. Med Genet. Part B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2009, 153B, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schultz, J.L.; Moser, A.D.; Nopoulos, P.C. The Association between CAG Repeat Length and Age of Onset of Juvenile-Onset Huntington’s Disease. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 575. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10090575
Schultz JL, Moser AD, Nopoulos PC. The Association between CAG Repeat Length and Age of Onset of Juvenile-Onset Huntington’s Disease. Brain Sciences. 2020; 10(9):575. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10090575
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchultz, Jordan L., Amelia D. Moser, and Peg C. Nopoulos. 2020. "The Association between CAG Repeat Length and Age of Onset of Juvenile-Onset Huntington’s Disease" Brain Sciences 10, no. 9: 575. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10090575
APA StyleSchultz, J. L., Moser, A. D., & Nopoulos, P. C. (2020). The Association between CAG Repeat Length and Age of Onset of Juvenile-Onset Huntington’s Disease. Brain Sciences, 10(9), 575. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10090575




