The Clinical Application of EEG-Signals Recurrence Analysis as a Measure of Functional Connectivity: Comparative Case Study of Patients with Various Neuropsychiatric Disorders
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cases
2.2. EEG Data Recording
2.3. EEG Recurrence Analysis
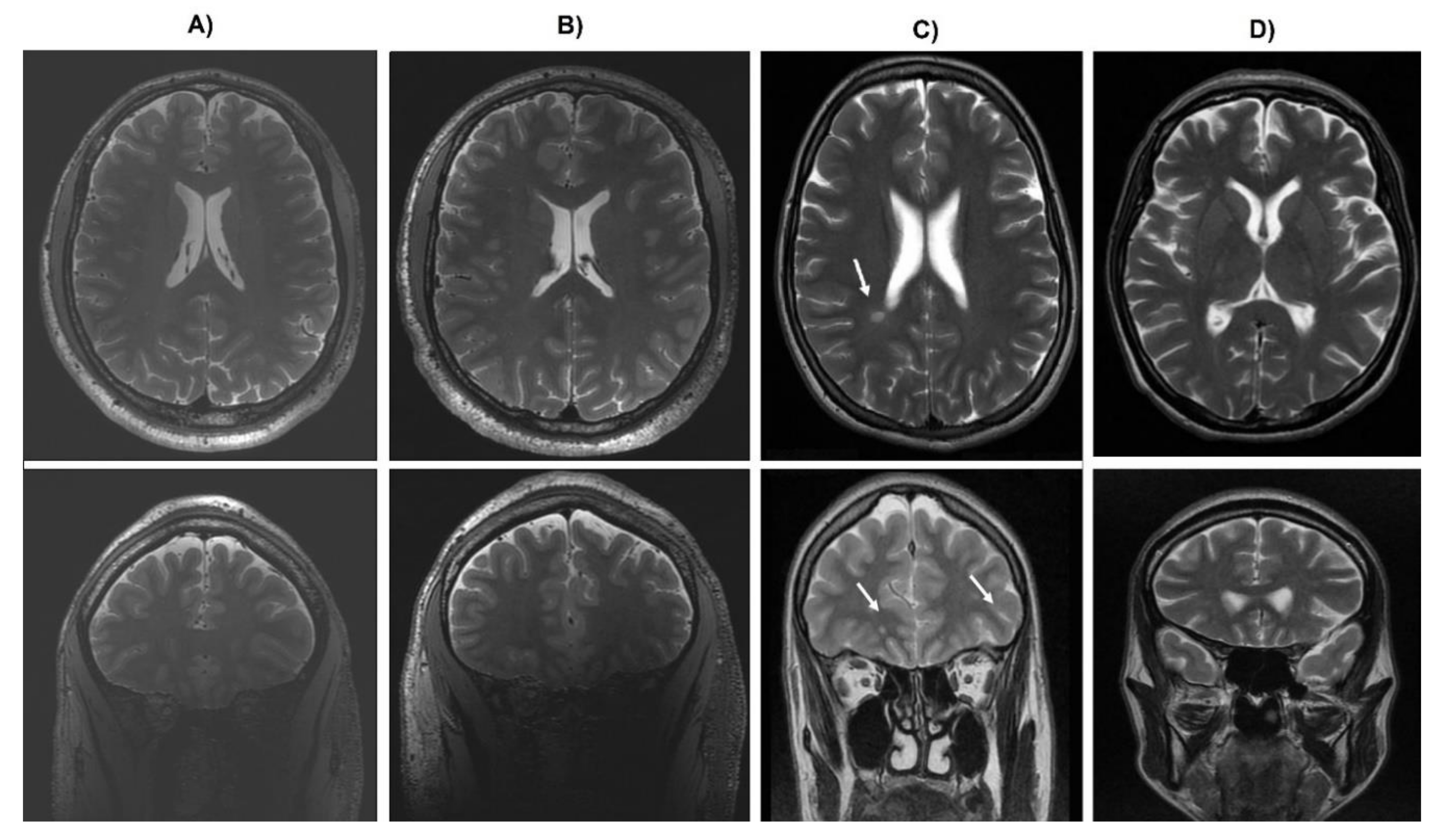
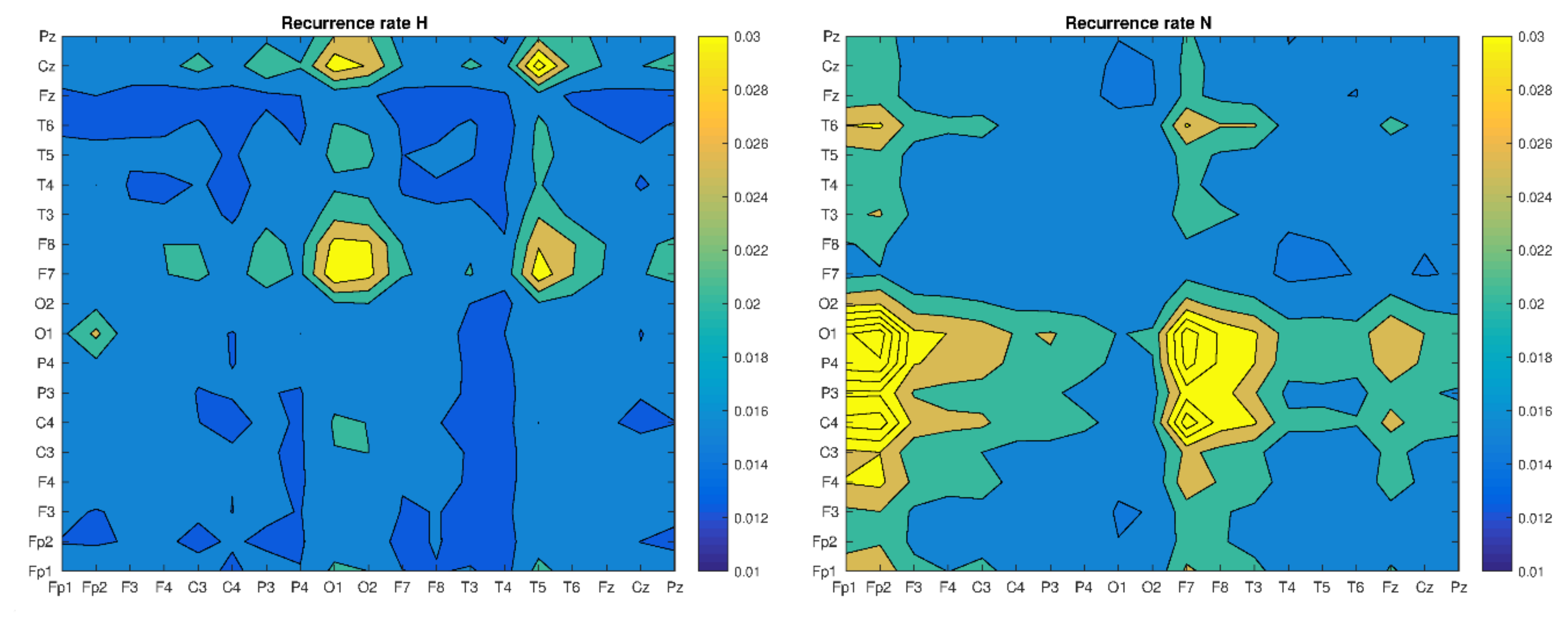
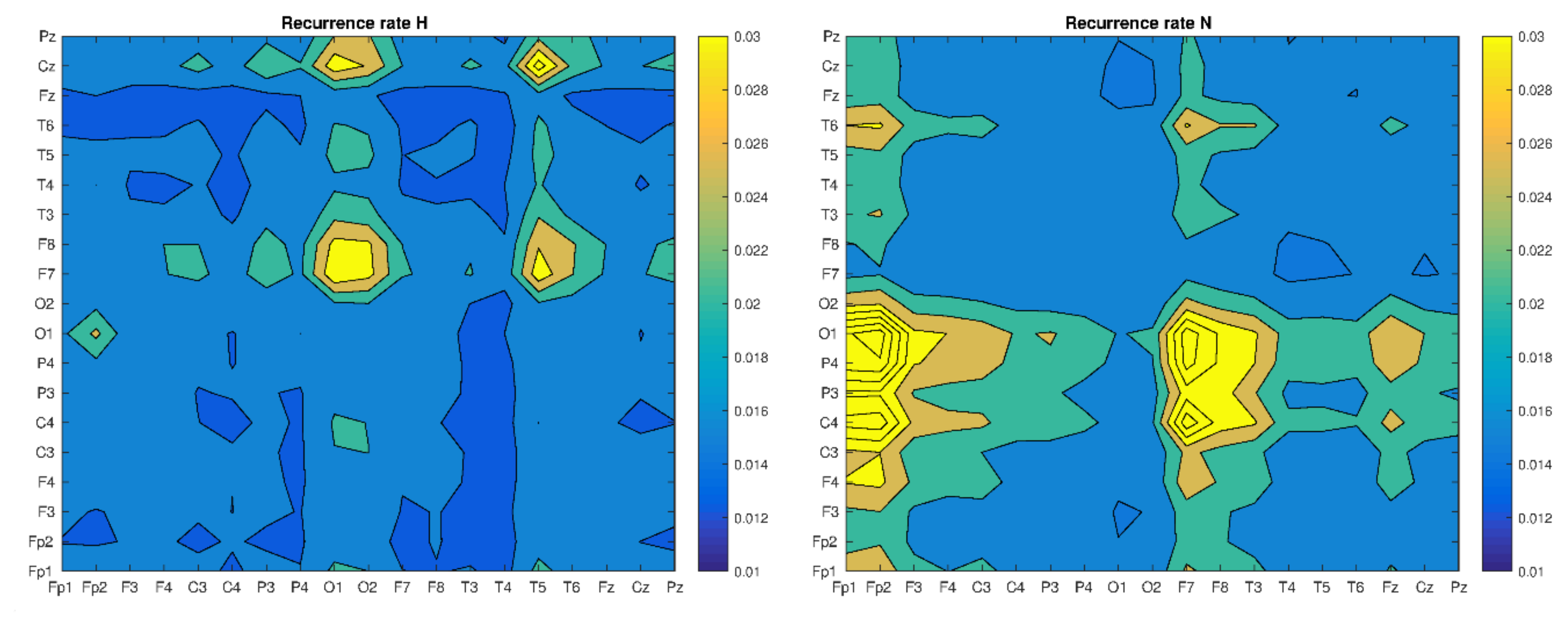
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andreasen, N.C.; Nopoulos, P.; O’Leary, D.S.; Miller, D.D.; Wassink, T.; Flaum, M. Defining the phenotype of schizophrenia: Cognitive dysmetria and its neural mechanisms. Biol. Psychiatry 1999, 46, 908–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friston, K.J. The disconnection hypothesis. Schizophr. Res. 1998, 30, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krukow, P.; Jonak, K.; Karakuła-Juchnowicz, H.; Podkowiński, A.; Jonak, K.; Borys, M.; Harciarek, M. Disrupted functional connectivity within the left prefrontal cortex and sensorimotor areas predicts impaired cognitive speed in patients with first-episode schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2018, 17, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubicki, M.; McCarley, R.; Westin, C.-F.; Park, H.-J.; Maier, S.; Kikinis, R. A review of diffusion tensor imaging studies in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2007, 41, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubl, D.; Koenig, T.; Strik, W.; Federspiel, A.; Kreis, R.; Boesch, C. Pathways that make voices: White matter changes in auditory hallucinations. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2004, 61, 658–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krukow, P.; Jonak, K.; Morylowska-Topolska, J.; Karakuła-Juchnowicz, H. Specific neuropsychological and neurophysiological dysfunctions of a patients with first-episode schizophrenia and comorbid white matter damage. Acta Neuropsychol. 2007, 15, 201–219. [Google Scholar]
- Baleja-Stawicka, I.; Kwiecińska, E.; Kłoszewska, I.A.Ł. Metachromatic leucodystrophy as a cause of dementia and organic delusional syndrome in young adults -a case report. Adv. Psychiatry Neurol. 2008, 17, 237–241. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, C.-Y.; Scarr, S.; Udawela, M.; Everall, I.; Chen, W.J.; Dean, B. Biomarkers in schizophrenia: A focus on blood based diagnostics and theranostics. Word J. Psychiatry 2016, 6, 102–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, W. Neuronal synchrony: A versatile code for the definition of relations? Neuron 1999, 24, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlhass, P.J.; Singer, W. Abnormal neural oscillations and synchrony in schizophrenia. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 11, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonak, K.; Krukow, P.; Karakuła-Juchnowicz, H. Hypercoherence and increased energy of gamma oscillations in patient with first onset of schizophrenia and cerebral white matter damage. Curr. Probl. Psychiatry 2016, 17, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakkalis, V. Review of advanced techniques for the estimation of brain connectivity measured with EEG/MEG. Comput. Biol. Med. 2011, 41, 1110–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litak, G.; Syta, A.; Gajewski, J.; Jonak, J. Detecting and identifying non-stationary courses in the ripping head power consumption by recurrence plots. Meccanica 2010, 45, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syta, A.; Jonak, J.; Jedliski, U.; Litak, G. Failure diagnosis of a gear box by recurrences. J. Vib. Acoust. Trans. ASME 2012, 134, 041006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, U.R.; Faust, O.; Kannathal, N.; Chua, T.; Laxminarayan, S. Non-linear analysis of EEG signals at various sleep stages. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2005, 80, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangaprakash, D.; Pradhan, N. Study of phase synchronization in multichannel seizure EEG using nonlinear recurrence measure. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2014, 11, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, U.R.; Vinitha Sree, S.; Swapna, G.; Martis, R.J.; Suri, J.S. Automated EEG analysis of epilepsy: A review. Knowl. Based Syst. 2013, 45, 147–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngamga, E.J.; Bialonski, S.; Marwan, N.; Kurths, J.; Geier, C.; Lehnertz, K. Evaluation of selected recurrence measures in discriminating pre-ictal and inter-ictal periods from epileptic EEG data. Phys. Lett. Sect. A Gen. At. Solid State Phys. 2016, 380, 1419–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stam, C.J. Nonlinear dynamical analysis of EEG and MEG: Review of an emerging field. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2005, 116, 2266–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, A.; Guccione, P.; Mascolo, L.; Taurisano, P.; Fazio, L.; Nico, G. Combining Graph Analysis and Recurrence Plot on fMRI data. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Symposium on Medical Measurements and Applications (MeMeA) Proceedings, Turin, Italy, 7–9 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Millan, M.J.; Fone, K.; Steckler, T.; Horan, W.P. Negative symptoms of schizophrenia: Clinical characteristics, pathophysiological substrates, experimental models and prospects of improved treatment. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014, 24, 645–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckmann, J.-P.; Kamphorst, S.O.; Ruelle, D. Recurrence Plots of Dynamical Systems. Europhys. Lett. 1987, 4, 973–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takens, F. Detecting Strange Attractors in Turbulence. Lecture Notes in Mathematics Dynamical Systems and Turbulence, Warwick; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1980; pp. 366–381. [Google Scholar]
- Fraser, A.M.; Swinney, H.L. Independent coordinates for strange attractors from mutual information. Phys. Rev. A 1986, 33, 1134–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennel, M.B.; Abarbanel, H.D.I. False neighbors and false strands: A reliable minimum embedding dimension algorithm. Phys. Rev. E 2002, 66, 026209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webber, C.L.; Marwan, N. Recurrence Quantification Analysis–Theory and Best Practices; Springer: Cham/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA; Dordrecht, The Netherlands; London, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Marwan, N.; Carmenromano, M.; Thiel, M.; Kurths, J. Recurrence plots for the analysis of complex systems. Phys. Rep. 2007, 438, 237–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marwan, N.; Donges, J.F.; Zou, Y.; Donner, R.V.; Kurths, J. Complex network approach for recurrence analysis of time series. Phys. Lett. Sect. A Gen. At. Solid State Phys. 2009, 373, 4246–4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webber, C.L.; Zbilut, J.P. Assessing Deterministic Structures in Physiological Systems Using Recurrence Plot Strategies. Bioeng. Approaches Pulm. Physiol. Med. 1994, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
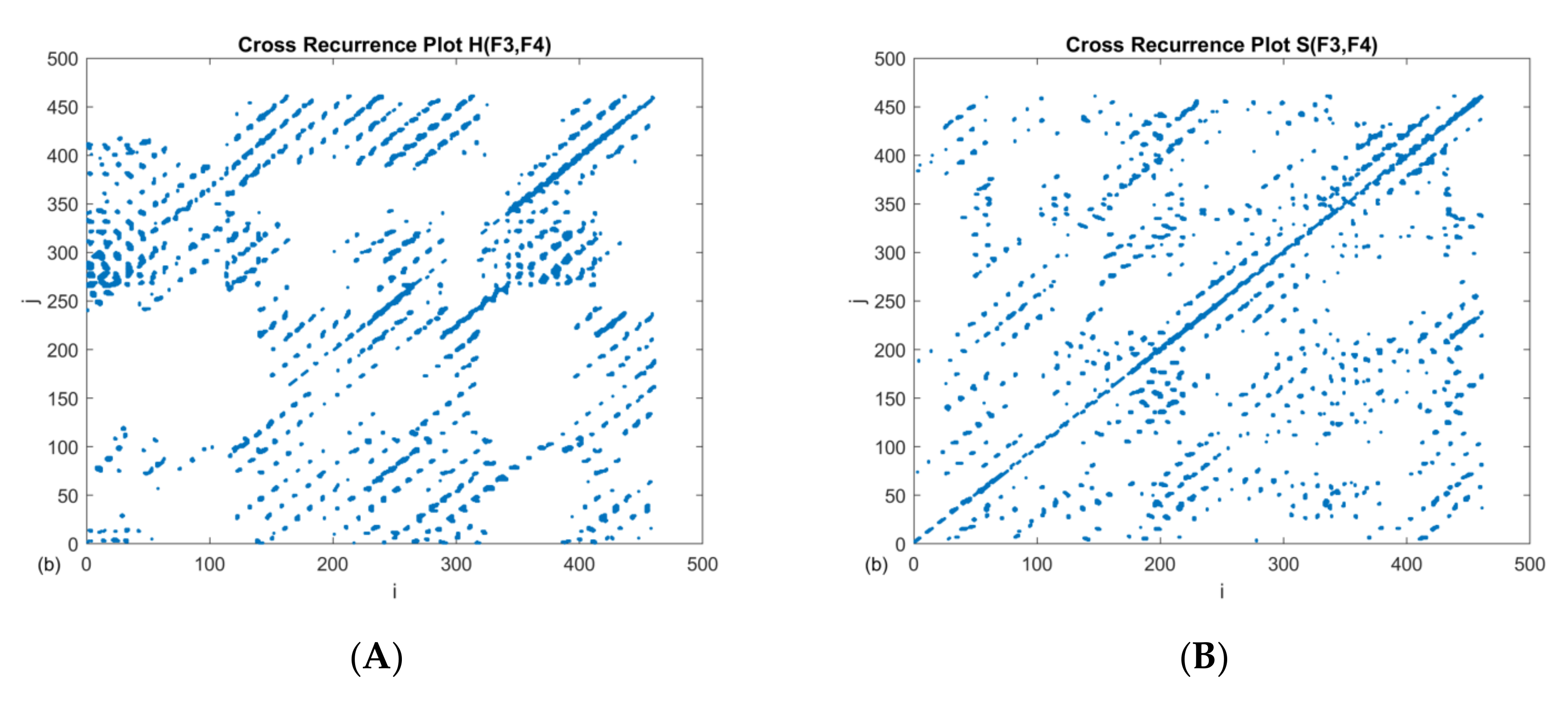

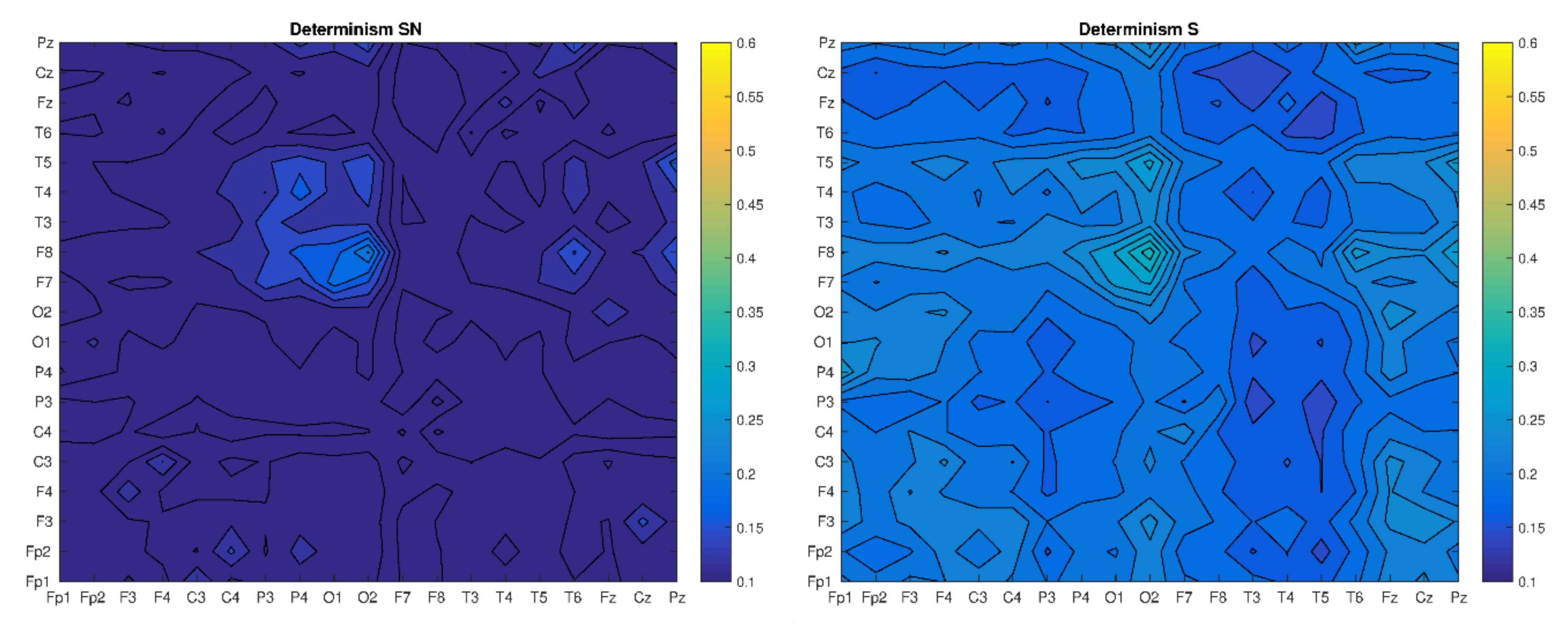
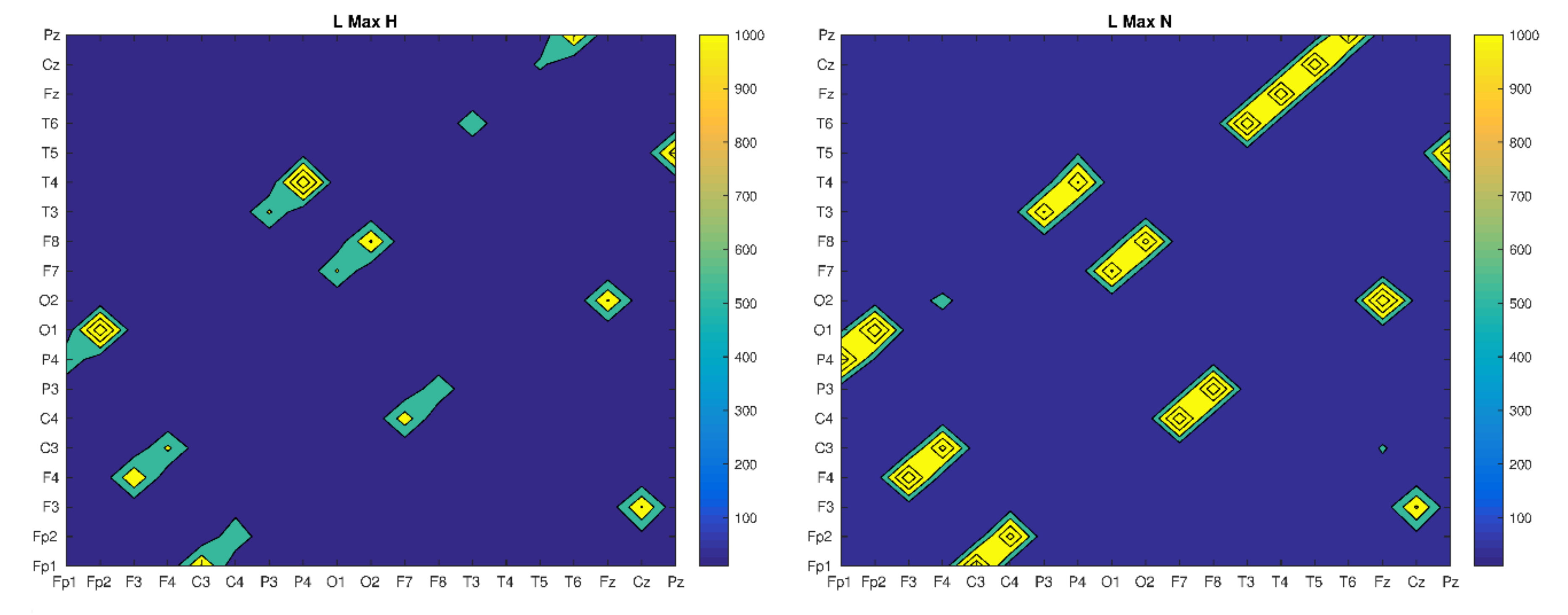

| RR | DET | L | LMAX | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H(F3–F4) | 0.035 | 0.44 | 6.5 | 111 |
| S(F3–F4) | 0.025 | 0.25 | 6.2 | 47 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jonak, K.; Syta, A.; Karakuła-Juchnowicz, H.; Krukow, P. The Clinical Application of EEG-Signals Recurrence Analysis as a Measure of Functional Connectivity: Comparative Case Study of Patients with Various Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10060380
Jonak K, Syta A, Karakuła-Juchnowicz H, Krukow P. The Clinical Application of EEG-Signals Recurrence Analysis as a Measure of Functional Connectivity: Comparative Case Study of Patients with Various Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Brain Sciences. 2020; 10(6):380. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10060380
Chicago/Turabian StyleJonak, Kamil, Arkadiusz Syta, Hanna Karakuła-Juchnowicz, and Paweł Krukow. 2020. "The Clinical Application of EEG-Signals Recurrence Analysis as a Measure of Functional Connectivity: Comparative Case Study of Patients with Various Neuropsychiatric Disorders" Brain Sciences 10, no. 6: 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10060380
APA StyleJonak, K., Syta, A., Karakuła-Juchnowicz, H., & Krukow, P. (2020). The Clinical Application of EEG-Signals Recurrence Analysis as a Measure of Functional Connectivity: Comparative Case Study of Patients with Various Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Brain Sciences, 10(6), 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10060380







