Abstract
Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) was initially described as important for dopaminergic neuronal survival and is involved in many other essential functions in the central nervous system. Characterization of GDNF phenotype in mammals is well described; however, studies in non-mammalian vertebrate models are scarce. Here, we characterized the anatomical distribution of gdnf-expressing cells in adult zebrafish brain by means of combined in situ hybridization (ISH) and immunohistochemistry. Our results revealed that gdnf was widely dispersed in the brain. gdnf transcripts were co-localized with radial glial cells along the ventricular area of the telencephalon and in the hypothalamus. Interestingly, Sox2 positive cells expressed gdnf in the neuronal layer but not in the ventricular zone of the telencephalon. A subset of GABAergic precursor cells labeled with dlx6a-1.4kbdlx5a/6a: green fluorescence protein (GFP) in the pallium, parvocellular preoptic nucleus, and the anterior and dorsal zones of the periventricular hypothalamus also showed expression with gdnf mRNA. In addition, gdnf signals were detected in subsets of dopaminergic neurons, including those in the ventral diencephalon, similar to what is seen in mammalian brain. Our work extends our knowledge of gdnf action sites and suggests a potential role for gdnf in adult brain neurogenesis and regeneration.
1. Introduction
Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) is the most studied member of the GDNF family of ligands (GFLs), which also consists of neurturin, artemin, and persephin. GDNF has a high affinity toward the GDNF family receptors (GFR)α1, which then activates the intracellular signaling cascades such as MAP kinases and Akt through the receptor tyrosine kinase RET and/or the neural cell adhesion molecule [1,2,3]. GDNF was first identified from conditioned media of striatal astrocytes, and in vitro studies showed GDNF could prevent apoptosis and enhance differentiation of embryonic mesencephalic-derived dopaminergic neurons [4]. Extensive preclinical research carried out on GDNF for its restorative function in Parkinson’s Disease (PD) [5,6,7,8] and its crucial role for the maintenance of adult catecholaminergic neurons in the nigrostriatal system [9] have shown promise and generated great interest in using GDNF as a therapeutic agent for intervention in neurodegenerative diseases such as PD.
GDNF is widely expressed in the central and peripheral nervous systems such as motor neurons [10] as well as in the enteric nervous system [11]. The presence of GDNF in these neurons is correlated with its significant role in neuroprotection. Study of tissue-specific GDNF expression in the developing human fetal brain suggests critical importance in the development and maintenance of various types of neuronal and non-neuronal cells [12]. During mouse development, gdnf transcripts first appear in the ventral forebrain at E7.5, with expression peaking at E.9.5, then decreasing from E10.5. At E.13.5, gdnf expression increases but only in the ventral midbrain. Interestingly, gdnf expression re-emerges throughout the brain at 18.5 and persists into adulthood [13,14].
Due to the sheer complexity of the mammalian brain, there is still no consensus on the endogenous functions of GDNF on dopaminergic neuron development and maintenance [9,15,16,17,18], and a recent clinical study showed contrasting results [19]. The zebrafish (Danio rerio) has been recognized as an alternative model for studying molecular and cell biology in neuroscience and translational research [20]. Given that the zebrafish has simpler neuroanatomy and smaller brain size without compromising its homology of neural circuit function, this model may contribute some clarity of the mode of action of gdnf on the neurophysiology of the brain [21]. For instance, fewer neurons in the zebrafish brain allow for qualitative analyses of neuronal activity patterns in order to reconstruct the dynamic brain network into neuronal computation information to decipher mechanistic insights underlying higher-level vertebrate brain functions. These properties contribute to the use of the zebrafish in examining the reparative capability of the brain.
Shepherd et al. were the first to characterize gdnf in zebrafish. Whole-mount in situ hybridization showed that gdnf was expressed in the central nervous system (CNS) of zebrafish larvae as well as in the enteric neurons and pronephric ducts [22]. As reported for rodent Gdnf, zebrafish gdnf was shown to be critical in enteric nervous system development and peripheral axons of sensory neurons [22,23]. Moreover, neuroprotection against neuronal death induced by a mutated human Tau protein was seen in zebrafish overexpressing gdnf [24]. Nevertheless, limited gdnf functional studies have been carried out in the zebrafish central nervous system, particularly in the brain itself at both larval and adult stages. Expression of gdnf and its receptor has been documented in the adult zebrafish brain, however, the types of cells expressing gdnf have not yet been reported. This information is essential to add further knowledge on the potential functions or underlying mechanisms of gdnf action in the CNS of zebrafish. Here, we characterize the neuroanatomical expression of gdnf and identify the gdnf-positive cells in the adult zebrafish brain.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Care and Handling
All zebrafish used in this study were housed under standard conditions with 14-hours light and 10-hours dark of photoperiod, and water temperature set at 28 °C. The experiment handling and euthanasia procedures were approved by the University of Ottawa Animal Care Committee following guidelines of the Canadian Council on Animal Care, under the ethics number: BL-2081. Zebrafish did not receive any drug treatment prior to the experiment. Wild-type and transgenic Tg (dlx6a-1.4kbdlx5a/6a:GFP) [25] were used in this study.
2.2. Brain Dissection and Tissue Processing
Sexually mature adult zebrafish were euthanized with an overdose of tricaine methanesulfonate (Sigma-Aldrich). Brains from at least two adult zebrafish were used for the analysis of each neuronal protein maker in this study. The skull was then opened to expose the brain and fixed overnight in 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) at 4 °C. The brain was dissected and washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) followed by overnight cryopreservation in 30% sucrose at 4 °C. The brain was embedded in optimal cutting temperature (OCT) compound and flash frozen in liquid nitrogen. The tissue was cryosectioned into ~12–14 µm thick sections that were adhered to the Superfrost PlusTM coated slides (Thermo Scientific). The slides were stored at −20 °C until further use.
2.3. In Situ Hybridization
RNA template was isolated from 7 dpf larvae for gdnf probe synthesis. Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) amplification of the targeted gdnf coding region used the following primers: 5’-TGTCCACACGTCCCCTTTTC–3’ (forward) and reverse primer 5’–CTCCAAGCTGTCGTCCAGAA–3’ (reverse). The PCR products were TA-cloned into pDRIVE vector (Qiagen) and the sequencing analysis was carried out to confirm the product sequence. The plasmid was linearized by HindIII or BamHI and digoxigenin (DIG)-labeled gdnf sense and antisense probes were generated, respectively, by in vitro transcription using DIG RNA labeling mix (Roche) contained T7 or SP6 RNA polymerase (Roche).
In situ hybridization was performed according to Reference [26] with slight modifications. To minimize the possibility of RNA degradation, all buffers used before the probe hybridization step were prepared in diethylpyrocarbonate (DPEC)-treated water or PBS. Briefly, the sections were washed with 0.3% Triton-X and PBS. The tissues were permeabilized with proteinase K (5 µg/mL) (0.1 M Tris-HCl PH 8, 50 mM EDTA) for 15 min at room temperature. After re-fixation in 4% PFA, the tissues underwent an acetylation step to reduce the background. The tissues were then incubated with hybridization buffer (50% deionized formamide, 10% dextran sulfate, 1 mg/mL yeast tRNA, 1X Denhardt’s, 1X salt) containing DIG-labeled gdnf probe overnight at 70 °C in a humidified chamber. On the following day, the slides were washed in solution A (1X SSC, 50% formamide, 0.1% Triton-X) at 70 °C for twice, and twice again with TBST (0.14 M NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 25 mM Tris HCl PH 7.5, 0.1% Triton-X) at room temperature. The tissues were incubated in the blocking solution (10% FBS/TBST) for 1 hour at room temperature. The anti-digoxigenin alkaline phosphatase Fab fragments (1:2000, Roche) were diluted in blocking solution and incubated with the sections overnight at 4 °C. On the next day, the tissues were washed with TBST and NTMT (100 mM NaCl, 100 mM Tris-HCl, 50 mM MgCl2, 0.1% Triton-X) before it stained with substrate solution (NBT/BCIP, Roche) to reveal the hybridization signal. The signal was closely monitored to avoid overstaining. The tissues were stained overnight at room temperature if the staining was still weak after 3–4 h incubation in substrate solution.
2.4. Combined Fluorescence in Situ Hybridization and Immunohistochemistry
The protocol for fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) was slightly modified from the colorimetric in situ hybridization (ISH) procedure. The tissue permeabilization step using proteinase K was replaced with incubation in 10 mM sodium citrate (0.05% Tween-20) for 20 min at 85 °C and the hybridization temperature was adjusted to 63 °C. Endogenous horseradish peroxidase was inhibited by incubating in 2% H2O2/TNT (0.1 M Tris-HCl pH 7.5, 0.15 M NaCl, 0.5% Triton-X) for 10 min. The sections were then incubated overnight with anti-DIG-POD (ROCHE) in blocking solution (0.1 M Tris-HCl pH 7.5, 0.15 M NaCl, 0.5% Tween-20, 0.5% Perkin Elmer block powder) at room temperature. On the following day, the sections were washed several times in TNT buffer and the fluorescent in situ signal was amplified using the Tyramide Signal Amplification (TSA) Cyanine 3 system (PerkinElmer, NEL753001KT) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Cy3 fluorophore was diluted (1:100) in amplification solution and the tissues were stained for 20 min in the dark.
Immunohistochemistry was carried out immediately after FISH. To stop the FISH reaction, sections were washed in PBS and re-fixed for 5 min in 4% PFA/PBS. After rinsing with 0.5% PBST (PBS/0.5% Triton-X), the tissues were treated with 5% FBS/PBST for 1–2 h at room temperature and incubated overnight at room temperature with different primary antibodies (diluted in 5% FBS/PBST) as listed in Table 1. Sections were washed in PBST and incubated overnight at 4 °C with either goat anti-rabbit or anti-mouse Alexa Fluor 488 (1:400, Invitrogen). After secondary antibody incubation, the sections were washed with PBST and then counterstained with Vectashield mounting medium with DAPI (Vector Laboratories). A sense probe was used as a specificity control.

Table 1.
Antibodies utilized for immunohistochemistry.
2.5. Microscopy
At least 5 sections per region with gdnf signal were examined and the most representative images were captured. There was no obvious difference in the staining patterns between the samples. All sections were imaged under the Nikon A1 confocal microscope with 25× water-dipping objective and with digital zoom for close-up analysis. Z-stacks of 1–2 µm were captured and the low magnification images were constructed from the maximum intensity projection of z-stacks of the section using NIS-Elements software (version 4.5, Praha, Czech Republic. Higher magnification images were used for co-localization analysis; they were constructed from selected z-stacks. Co-localization analysis was carried out in a qualitative format. The images were post-processed to adjust for light and contrast using the NIS-Elements software (version 4.5) or Image J. All nomenclature and graphical illustrations images of coronal and sagittal sections of the adult zebrafish brain are adapted from “Neuroanatomy of The Zebrafish Brain” [27] unless stated otherwise.
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of gdnf Expression Patterns in the Adult Zebrafish Brain
To analyze the spatial distribution of gdnf mRNA, in situ hybridization (ISH) was performed on a series of sagittal or transverse sections of the whole adult zebrafish brain. The results revealed that gdnf expression is widely distributed in the adult brain (Figure 1A). In the forebrain, strong gdnf signals were detected in the olfactory bulb (OB) (Figure 1B), dorsal (Dd and Dm), and ventral (Vd and Vv) telencephalic area (Figure 1C–E). In the midbrain, there was relatively weaker gdnf expression in the optic tectum (TeO) and more intense expression in the periventricular gray zone (PGZ), torus longitudinalis (TL), and periventricular hypothalamus (Figure 1A, F–G). The cerebellum (CCe) in the hindbrain also showed gdnf expression (Figure 1H–I).
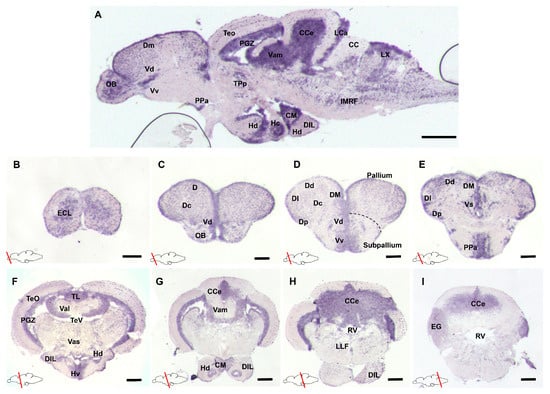
Figure 1.
Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (gdnf) expression pattern in the adult zebrafish brain (A) Sagittal section of the adult zebrafish brain showing distribution of gdnf mRNA by in situ hybridization in, (B–E) telencephalon, (F–H) mesencephalon, and (I) rhombencephalon. Scale bars: (A) 200 µm (B–I) 50 µm. Abbreviations: CC: Crista cerebellaris; CCe: Corpus cerebelli; CM: Corpus mamillare; D: Dorsal telencephalic area; DI: later zone of dorsal telencephalic area; DIL: Diffuse nucleus of the inferior lobe; Dm: Medial zone of dorsal telencephalic area; Dc: Central zone of dorsal telencephalic area; Dd: Dorsal zone of dorsal telencephalic area; Dp: Posterior zone of dorsal telencephalic area; ECL: External cellular layer of olfactory bulb including mitral cells; EG: Eminentia granularis; Hc: Caudal zone of periventricular hypothalamus; Hd: Dorsal zone of periventricular hypothalamus; IMRF: Intermediate reticular formation; LCa: Lobus caudalis cerebelli DIL; LLF: Lateral longitudinal fascicle; LX: Vagal love; OB: Olfactory bulb; PGZ: Periventricular gray zone of optic tectum; PPa: Parvocellular preoptic nucleus, anterior part; RV: Rhombencephalic ventricle; TeO: Tectum opticum; TeV: Tectal ventricle; TL: Torus longitudinalis; TPp: Periventricular nucleus of posterior tuberculum; Val: Lateral division of valvular cerebelli; Vam: Medial division of valvular cerebelli; Vas: Vascular lacuna of area postrema; Vd: Dorsal nucleus of ventral telencephalic area; VM: ventromedial thalami nuclei; Vs: Supracommissural nucleus of ventral telencephalic area; Vv: Ventral nucleus of ventral telencephalic area.
3.2. Characterization of gdnf Expression in Stem/Progenitor Cells
Next, we aimed to identify the cell types that were expressing gdnf by performing FISH in combination with immunohistochemistry. Firstly, we investigated whether radial glial cells expressed gdnf. Here, we used glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and brain lipid-binding protein (BLBP) antibodies as markers for radial glial cells. As shown in Figure 2A–G, radial glial cells reside along the ventricular cavities in the telencephalon and co-expressed gdnf. However, there were only a few BLBP+/gdnf+ cells observed in the lateral margin of the periventricular gray zone of the optic tectum (PGZ), which is recognized as having quiescent radial glial cells (Figure 2H–N). In addition, BLBP+ cells in the caudal zone of the periventricular hypothalamus (Hc), a region of active proliferation, and neurogenesis were found to express gdnf transcripts (Figure 2P–S).
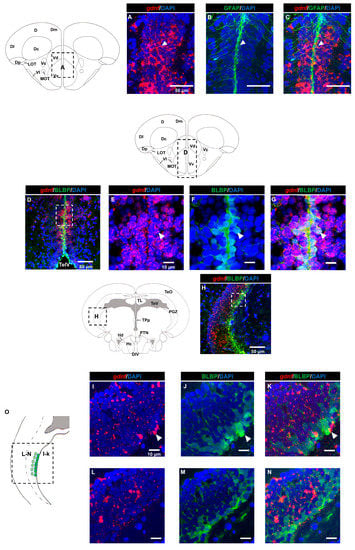
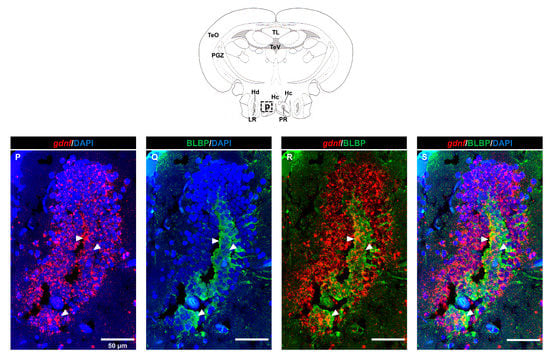
Figure 2.
Co-expression of gdnf and radial glial cell markers using FISH/immunohistochemistry. (A–C) gdnf is expressed with glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and (D–G) brain lipid-binding protein (BLBP) along the ventral telencephalic area, as indicated by the white arrowheads, (H) but only few cells with BLBP in the lateral margin of the periventricular gray zone (PGZ) of the optic tectum in the mesencephalon. Enlarged regions of PGZ with different layers of selected z-stacks that consist of BLBP-positive cells in the (I–K) outer layer and (L–N) inner layer and that are depicted in the (O) schematic diagram. (P–S) gdnf mRNA-positive cells are also BLBP immunoreactive in the caudal zone of periventricular hypothalamus (Hc) (the images were constructed from the selected z-stacks). Black dashes in the graphical illustrations outline the regions of interest. The white dashes outline the regions of higher magnification that were constructed from the selected z-stacks. Abbreviations: D: Dorsal telencephalic area; Dc: Central zone of dorsal telencephalic area; DI: later zone of dorsal telencephalic area; Dm: Medial zone of dorsal telencephalic area; Dp: Posterior zone of dorsal telencephalic area; LR: Lateral recess of diencephalic ventricle; LOT: Lateral olfactory tract; MOT: Medial olfactory tract; PR: posterior recess of diencephalic ventricle; Vc: Central nucleus of ventral telencephalic area; Vd: Dorsal nucleus of ventral telencephalic area; VI: Lateral nucleus of ventral telencephalic area; Vv: Ventral nucleus of ventral telencephalic area; DIV: Diencephalic ventricle; Hc: Caudal zone of periventricular hypothalamus; Hd: Dorsal zone of periventricular hypothalamus; PGZ: Periventricular gray zone of optic tectum; PTN: Posterior tuberal nucleus; TeO: Tectum opticum; TeV: Tectal ventricle; TL: Torus longitudinalis; TPp: Periventricular nucleus of posterior tuberculum.
As we observed strong expression of gdnf in the ventricular region and its co-expression with BLBP in the telencephalon where stem cells are positioned, we attempted to ascertain whether the gdnf-expressing cells could be Sox2-positive stem cells. Strong Sox2 signals were observed in the ventricular zone (vz), ventral nucleus (Vv), dorsal nucleus (Vd) of the ventral telencephalon, and medial zone of dorsal telencephalon (Dm), with relatively weaker Sox2 signals in the neuronal layer (nl) (Figure 3A–H). Expression of gdnf was not detected in Sox2-expressing cells in the vz within the rostral subpallium (Figure 3A–D). Interestingly, gdnf expression was not co-localized with that of Sox2 in the vz but was seen in the neuronal layer (nl) in the telencephalon (Figure 3E–H). In the Hc, where gdnf+/BLBP+ cells reside, gdnf was also present in Sox2 immunoreactive cells (Figure 3I–L).
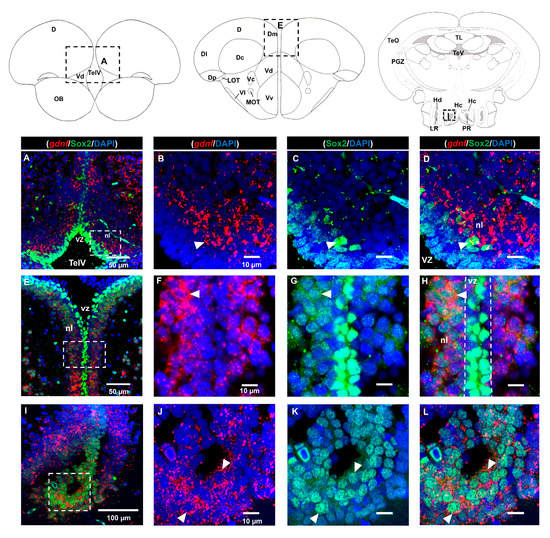
Figure 3.
Co-localization of gdnf with Sox2. gdnf transcripts are found in Sox2-positive cells in the neuronal layer (nl) of (A–D) the dorsal nucleus of the ventral telencephalic area (Vd), (E–H) nl along the ventricular zone (vz)of the telencephalon and (I–L) the caudal zone of the periventricular hypothalamus (Hc). Black dashes in the graphical illustrations outline the regions of interest. White dashes outline the respective magnified regions that were constructed from the selected z-stacks. The white arrowheads indicate co-expression of gdnf with Sox2 immunoreactive cells. Abbreviations: D: Dorsal telencephalic area; Dc: Central zone of dorsal telencephalic area; DI: later zone of dorsal telencephalic area; Dm: Medial zone of dorsal telencephalic area; Dp: Posterior zone of dorsal telencephalic area; Hc: Caudal zone of periventricular hypothalamus; Hd: Dorsal zone of periventricular hypothalamus; LOT: Lateral olfactory tract; LR: Lateral recess of diencephalic ventricle; MOT: Medial olfactory tract; nl: neuronal layer; OB: Olfactory bulb; PGZ: Periventricular gray zone of optic tectum; PR: posterior recess of diencephalic ventricle; TelV: Telencephalic ventricle; TeO: Tectum opticum; TeV: Tectal ventricle; TL: Torus longitudinalis; Vc: Central nucleus of ventral telencephalic area; Vd: Dorsal nucleus of ventral telencephalic area; VI: Lateral nucleus of ventral telencephalic area; Vv: Ventral nucleus of ventral telencephalic area; vz: ventricular zone.
GDNF was shown to be produced by GABAergic neurons in the rodent striatum [28], but it is not known if GDNF is expressed in GABAergic progenitor cells. Here, we used adult transgenic Tg (dlx6a-1.4kbdlx5a/6a:GFP) zebrafish for immunostaining with GFP and FISH for gdnf transcripts. Analysis of sagittal sections (Figure 4A–C) demonstrated that co-expression of gdnf with GFP was detected in the dorsal telencephalic area (Figure 4D–F), in the anterior part of the parvocellular preoptic nucleus (PPa) (Figure 4G–J), and in the Hc (Figure 4K–N).
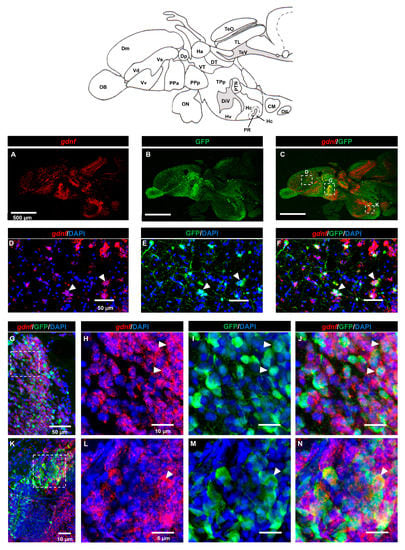
Figure 4.
Expression of gdnf in GABAergic precursor cells of Tg (dlx6a-1.4kbdlx5a/6a: green fluorescence protein (GFP) fish. (A–C) An overview of gdnf transcripts (red) and GFP on a sagittal view of the adult zebrafish brain. The images depict co-localization of gdnf with subpopulation of GFP-positive cells in (D–F) pallium (G–J) parvocellular preoptic nucleus, anterior part (PPa), and (K–N) caudal zone of periventricular hypothalamus (Hc) as indicated with white arrowhead. The white dashes outline the enlarged regions that were constructed from selected z-stacks. Abbreviations: CM: Corpus mamillare; Dm: medial zone of dorsal telencephalic area; DIL: Diffuse nucleus of the inferior lobe; Dp: Posterior zone of dorsal telencephalic area; DiV: Diencephalic ventricle; Ha: Habenula; DT: Dorsal thalamus; Hc: Caudal zone of periventricular hypothalamus; Hv: Ventral zone of periventricular hypothalamus OB: Olfactory bulb; ON: Optic nerve; PPa: Parvocellular preoptic nucleus, anterior part; PPp: Parvocellular preoptic nucleus, posterior part; PR: Posterior recess of diencephalic ventricle; PTN: Posterior tuberal nucleus; TeO: Tectum opticum; TeV: Tectal ventricle; TPp: Periventricular nucleus of posterior tuberculum; V: ventral telencephalic area; Vd: dorsal nucleus of V; Vv: Ventral nucleus of V; Vs: Supracommissural nucleus of V; VT: Ventral thalamus.
3.3. gdnf is Synthesized in Both Early Differentiated Neurons and Mature Neurons
Analysis of the brain regions in the dorsal telencephalon (Figure 5A–D) and PGZ (Figure 5E–H) that labeled with the HuC/D marker suggested that most of the gdnf-positive cells were committed toward neuronal linage. This evidence was confirmed by co-labeling of gdnf mRNA in mature neuronal cells with anti-acetylated α-tubulin antibody in the OB (Figure 6A–D), dorsal telencephalon (Figure 6E–H), and PGZ (Figure 6I–L).
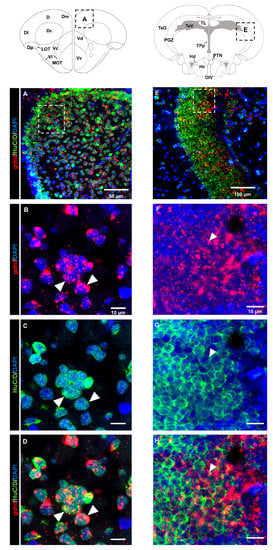
Figure 5.
Coronal sections of adult brain revealing early-differentiated neuronal marker (HuC/D) immunoreactivity co-localized with gdnf mRNA. gdnf mRNA is co-expressed with HuC/D as indicated with white arrowheads in (A–D) dorsal telencephalic area, and (E–H) periventricular gray zone (PGZ) of the optic tectum. Black dashes in the graphical illustrations outline the regions of interest. The white dashes outline the enlarged regions that were constructed from selected z-stacks. Abbreviations: D: Dorsal telencephalic area; Dc: Central zone of dorsal telencephalic area; DI: later zone of dorsal telencephalic area; Dm: Medial zone of dorsal telencephalic area; Dp: Posterior zone of dorsal telencephalic area; LOT: Lateral olfactory tract; MOT: Medial olfactory tract ; Vc: Central nucleus of ventral telencephalic area; Vd: Dorsal nucleus of ventral telencephalic area; VI: Lateral nucleus of ventral telencephalic area; Vv: Ventral nucleus of ventral telencephalic area; DIV: Diencephalic ventricle; Hc: Caudal zone of periventricular hypothalamus; Hd: Dorsal zone of periventricular hypothalamus; PGZ: Periventricular gray zone of optic tectum; PTN: Posterior tuberal nucleus; TeO: Tectum opticum; TeV: Tectal ventricle; TL: Torus longitudinalis; TPp: Periventricular nucleus of posterior tuberculum.
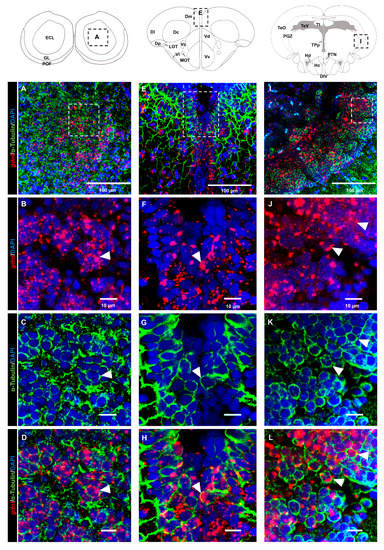
Figure 6.
The mature neuronal marker acetylated α-tubulin is co-expressed with gdnf transcripts. Co-expression of gdnf and acetylated tubulin is detected in (A–D) olfactory bulb (OB), (E–H) medial zone of the dorsal telencephalon area (Dm), and (I–L) periventricular gray zone (PGZ) of optic tectum. Black dashes in the graphical illustrations outline the regions of interest. White dashes outline the respective magnified regions that were constructed from selected z-stacks. The white arrowheads indicate the co-expression of gdnf and acetylated α-tubulin. Abbreviations: ECL: External cellular layer of olfactory bulb including mitral cells; GL: Glomerular layer of olfactory bulb; POF: Primary olfactory fiber layer; D: Dorsal telencephalic area; Dc: Central zone of dorsal telencephalic area; DI: later zone of dorsal telencephalic area; Dm: Medial zone of dorsal telencephalic area; Dp: Posterior zone of dorsal telencephalic area; LOT: Lateral olfactory tract; MOT: Medial olfactory tract; Vc: Central nucleus of ventral telencephalic area; Vd: Dorsal nucleus of ventral telencephalic area; VI: Lateral nucleus of ventral telencephalic area; Vv: Ventral nucleus of ventral telencephalic area; DIV: Diencephalic ventricle; Hc: Caudal zone of periventricular hypothalamus; Hd: Dorsal zone of periventricular hypothalamus; PGZ: Periventricular gray zone of optic tectum; PTN: Posterior tuberal nucleus; TeO: Tectum opticum; TeV: Tectal ventricle; TL: Torus longitudinalis; TPp: Periventricular nucleus of posterior tuberculum.
3.4. gdnf is Co-Expressed in the Subpopulation of Tyrosine Hydroxylase Immunoreactive Neurons
A tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) antibody was used as a marker for dopaminergic neurons. In the OB (cluster 1) (Figure 7A–D) and the subpallium area of the telencephalon (cluster 2) (Figure 7E–H), a few cells expressing gdnf transcripts also expressed TH. In the diencephalon, we did not see co-localization in cluster 3 (preoptic area). Co-expression of gdnf with TH-positive neurons was observed in cluster 7 of the periventricular pretectal nucleus (PPr) (Figure 7I–L) and in cluster 4 in the anterior part of the parvocellular preoptic nucleus (PPa) (Figure 7M–S). Only a few cells of cluster 5 in the posterior part of parvocellular preoptic nucleus (PPp) co-expressed gdnf and TH (Figure 8A–D), whereas a more occasional co-expression was seen in cluster 11 (Figure 8E–H), cluster 6 (Figure 8I–M) in the prethalamic region, cluster 8 in the anterior part of the paraventricular organ (PVOa) (Figure 9A–D), and cluster 13 of the posterior tuberal nucleus (PTN) (Figure 9E–K). Transcripts of gdnf were not detected in clusters 9 and 12. Table 2 summarizes the results.
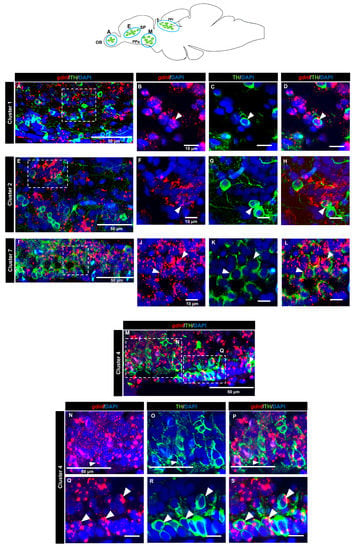
Figure 7.
gdnf is expressed in catecholaminergic subpopulations in the telencephalon and pretectum region. Sagittal section of adult zebrafish brain showing some co-expression of gdnf in TH-positive neurons of (A–D) cluster 1 in olfactory bulbs (OB), and (E–H) cluster 2 in subpallium (SP). Clear co-expression is observed in (I–L) cluster 7 in periventricular pretectal nucleus (PPr) and (M–S) cluster 4 in parvocellular preoptic nucleus, anterior part (PPa). The white arrowheads represent the co-expression of gdnf and TH. Blue outlines in the graphical illustration represent the regions of the respective TH subpopulation neurons. White dashes outline the respective magnified regions that were constructed from selected z-stacks.
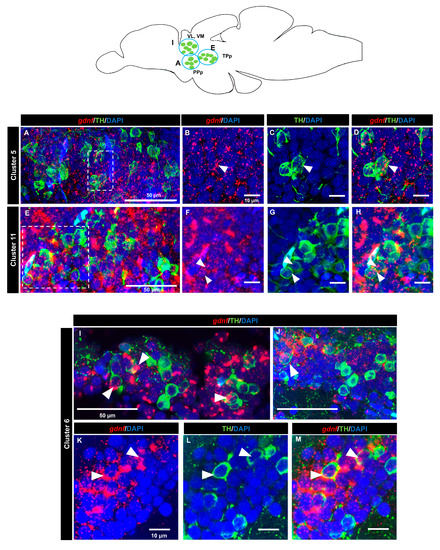
Figure 8.
Co-expression of gdnf mRNA with catecholaminergic subpopulations in the diencephalon. FISH/immunohistochemistry for gdnf (red) and TH (green) on sagittal sections of (A–D) cluster 5 in parvocellular preoptic nucleus, posterior part (PPp), (E–H) cluster 11 in periventricular nucleus of posterior tuberculum (TPp), and (I–M) cluster 6 in anterior, intermediate, ventrolateral, and ventromedial thalami nuclei (A, I, VL, and VM). Blue circles in the schematic sagittal view of the adult zebrafish brain represent the regions of the respective TH neuron subpopulations. White dashes outline the respective magnified regions that are constructed from selected z-stacks. The white arrowheads indicate the co-localization of gdnf and TH.
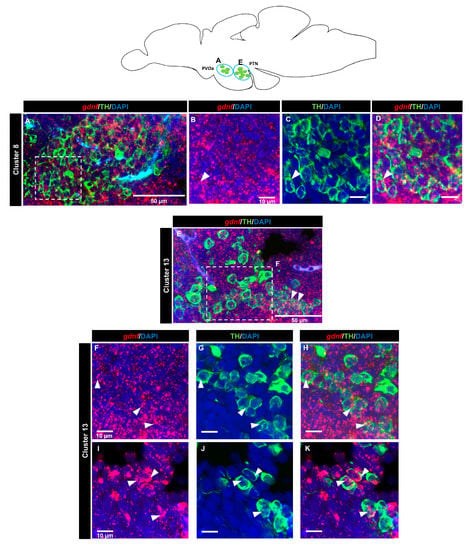
Figure 9.
gdnf mRNA is detected in catecholaminergic subpopulations in the ventral diencephalon. Distribution of neuronal clusters expressing gdnf (red) and TH (green) of (A–D) cluster 8 in the paraventricular organ, anterior part (PVOa) and (E–K) cluster 13 in the periventricular hypothalamus and posterior tuberal nucleus (PTN). Blue circles in the schematic sagittal view of the adult zebrafish brain represent the regions of the respective TH subpopulation neurons. White dashes outline the magnified regions that were constructed from selected z-stacks. The white arrowheads indicate the co-expression of gdnf and TH.

Table 2.
Qualitative analysis of gdnf expression in TH immunoreactive neurons in the adult zebrafish brain.
4. Discussion
The present study describes the expression pattern of gdnf transcripts at the cellular level in the adult zebrafish brain. In the absence of a specific antibody to zebrafish gdnf, we used in situ hybridization in combination with immunohistostaining to further identify sub-population of neurons that express gdnf. Our results demonstrated that gdnf transcripts were not only localized in progenitor/radial glial cells but also in neurons, such as dopaminergic neurons.
Our results concur with a previous study that demonstrated that gdnf expression persists into adulthood and is not restricted to developmental stages [29]. Likewise, GDNF expression has been reported in rodents at adult stages [30,31,32]. The wide expression of gdnf in the zebrafish brain suggests a role for gdnf in maintaining neuron survival and in other physiological functions in the central nervous system.
Heterogenous stem/progenitor cells reside in the ventricular zone of the telencephalon and are known to be responsible for adult neurogenesis and regeneration in zebrafish [33,34]. Our in situ hybridization results revealed there was intense gdnf expression along the periventricular zone, leading us to look into the localization of gdnf in neuronal progenitor cells (NPCs) and radial glial cells.
Sox2 is present in stem cells/progenitor cells of the central nervous system (CNS) and is required for maintaining neural stemness (pluripotency and self-renewal capacities) and mending neural injuries [35,36,37]. It is interesting to note that gdnf is only expressed in the Sox2 immunoreactive cells located in the neuronal layer, adjacent to the periventricular zone of the telencephalon. Prior to neuronal differentiation, Sox2 expression is suppressed in order to activate the proneural transcription program. Our results showed that cells that are gdnf-positive express an apparently much lower Sox2 signal compared to that seen in the ventricular zone (Figure 3E–H). This would indicate that these cells were early committed neurons. GDNF is a protein that is mainly secreted by neurons in the mammalian CNS [30,38]. We have similarly observed in this study that gdnf expression was mostly localized with early differentiated neurons and mature neurons, further supporting the notion that gdnf enhances neuronal differentiation [39,40,41]. It could also be involved in early neuronal fate specification during adult brain neurogenesis.
It is unclear whether rodents express GDNF in radial glial cells despite some studies suggesting this possibility [12,42,43,44]. Some groups showed that there was low expression of GDNF by glial cells [28,30,45]. In the zebrafish brain, we observed gdnf co-localized with radial glial cells (in GFAP and BLBP positive cells) in the ventricular telencephalic area (Vd/Vv) (Figure 2A–G). The zebrafish telencephalon, particularly along the ventricular zone, is a well-studied neurogenic niche. The telencephalon has tremendous neuro-regenerative capacity that could functionally help its recovery from lesions, with the ventricular radial glial cell being a key player in the process [46,47]. Increases in GDNF have been reported in synthesizing glial cells following brain lesions or in neuroinflammation animal models [38,48]. Based on these observations, it could be alluded that neuronal progenitor niche cells require gdnf for homeostatic maintenance in the telencephalon. In our study, it was unclear whether gdnf+/BLBP+ cells were state I (quiescent) or state II (dividing) radial glial cells, as state II cells are intermingled throughout the ventricular zone and it has been reported that less than 20% of the radial glial cells are expressing the proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) protein [49,50]. Notch activity and its receptors are present in quiescent radial glial cells and notch signaling appears to be highly associated with regulating the equilibrium between proliferative and quiescence stages of radial glial cells [49,50]. A recent study in rats showed that GDNF could counteract spinal cord injury-induced Notch activation and promote transplanted neuronal progenitor cell differentiation toward neuronal linage rather than into astrocytes [51]. A mechanistic study on the relationship of gdnf and Notch signaling in radial glial cells fate in the zebrafish brain would be of interest. Likewise, the radial glial cells in the periventricular gray zone (PGZ) are characterized as quiescent and injury-inducible to become active proliferative cells [52,53,54]. However, in our hands, we detected few BLBL+/gdnf+ cells occasionally in the lateral margin of the PGZ. In the hypothalamus, particularly in the caudal zone of the periventricular hypothalamus (Hc), gdnf is co-localized with BLBP immunoreactive cells and Sox2. Diversity of gdnf expression pattern in the brain suggested it has multiple roles in maintaining radial glial cells.
The Dlx family of homeobox transcription factors are expressed in progenitor cells that give rise to GABAergic neurons in vertebrates, including zebrafish [55,56,57]. Expression of dlx5a partially overlaps with that of gad1, a GABAergic neurons marker. Hence, the co-localization of gdnf in dlx5a-positive neurons of Tg (dlx5a/dlx6a:EGFP) transgenic fish supports our hypothesis that gdnf is present in GABAergic precursor cells. This is also consistent with the evidence in rodent that GABAergic interneurons are a major source of GDNF [28,58].
Bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) pulse-chase assays revealed that ventricular progenitor cells not only give rise to GABAergic interneurons but also to tyrosine hydroxylase-positive neurons that migrate a short distance into the parenchyma (neuronal zone) [59]. It is known that GDNF is expressed in tyrosine hydroxylase-positive neurons in rodents [30,60] as well as in the human substantia nigra [61]. We wanted to investigate if a similar phenomenon occurs in the zebrafish dopaminergic system. Groups of dopaminergic neurons have been identified and are distributed rostral to caudal in the zebrafish brain [62,63,64,65,66]. We provide the first evidence that gdnf is co-expressed with TH-immunoreactive neurons in subsets dopaminergic neuron clusters, including group 13 in the ventral diencephalon, similar to what was previously documented in the adult rat brain [67]. Loss of dopaminergic neurons in ventral diencephalon was shown to result in locomotor defects after neurotoxin insult [68,69,70,71,72,73] or after genetic disruption [74,75,76,77].
Homology between zebrafish and mammals prompted the question of whether gdnf was involved in dopaminergic neuron function. GDNF is an important molecule for in vitro induction of dopaminergic neuron differentiation [78,79], and overexpression of GDNF in stem cell-based therapy improved dopaminergic neuron commitment after transplantation [41,80,81]. Although exogenously applied GDNF was shown to be neuroprotective or restorative in PD models [58], the endogenous function of GDNF in dopaminergic neurons development and survival remains controversial [11,16]. Nonetheless, a recent study using a novel transgenic model approach provided evidence of GDNF as indispensable for catecholaminergic neuron maintenance [9]. Our laboratory had also explored gdnf function in zebrafish crispants. Impaired gdnf function in zebrafish crispants led to a decrease in dopaminergic neurons in clusters 8 and 13 during development [73]. Whether there would be any spatial or temporal differences in gdnf expression patterns in dopaminergic progenitor cells after damage would be an interesting question to address and could provide clues on gdnf regulation of dopaminergic neuron regeneration in zebrafish.
5. Conclusions
This study provided insight into the anatomical distribution of GDNF in the adult zebrafish brain, wherein the gdnf gene was mainly expressed in early committing and mature neurons, partly in radial glial cells, but not in Sox2-positive neuronal stem cells in the ventral zone of the telencephalon. Our results may shed some light on the potential role of GDNF in adult neurogenesis and regeneration. Importantly, we demonstrated a link between gdnf expression and GABAergic precursor cells and dopaminergic neurons.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.E.D.W., K.H., S.M.N., and M.E.; Methodology, C.E.D.W., K.H., and S.M.; Formal analysis, C.E.D.W.; Resources, M.E.; Writing—original draft preparation, C.E.D.W.; Writing—review and editing, K.H., S.M.N., A.N., and M.E.; Supervision, S.M.N., A.N., and M.E.; Funding acquisition, S.M.N. and M.E. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Malaysian Ministry of Higher Education Fundamental Research Grant Scheme (FP027-2014A), Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada grant (121795), University of Malaya Postgraduate Research grant (PG246-2015B), Special Research Assistance grant (BKS064-2017), and Research University Grant (Faculty of Medicine RU) (GPF014C-2018). Chee Ern David Wong was sponsored by the Malaysian Ministry of Higher Education MyPhD program and the Malaysian Society of Neurosciences Education Grant (ID: 02246).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Vishal Saxena and the staff of the zebrafish lab facility for taking care of the fish.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Paratcha, G.; Ledda, F.; Ibáñez, C.F. The Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule NCAM Is an Alternative Signaling Receptor for GDNF Family Ligands. Cell 2003, 113, 867–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibáñez, C.F. Structure and Physiology of the RET Receptor Tyrosine Kinase. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, 009134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibáñez, C.F.; Andressoo, J.-O. Biology of GDNF and Its Receptors—Relevance for Disorders of the Central Nervous System. Neurobiol. Dis. 2017, 97, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.F.; Doherty, D.H.; Lile, J.D.; Bektesh, S.; Collins, F. GDNF: A Glial Cell Line-Derived Neurotrophic Factor for Midbrain Dopaminergic Neurons. Science 1993, 260, 1130–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintino, L.; Avallone, M.; Brännstrom, E.; Kavanagh, P.; Lockowandt, M.; Garcia Jareño, P.; Breger, L.S.; Lundberg, C. GDNF-Mediated Rescue of the Nigrostriatal System Depends on the Degree of Degeneration. Gene Ther. 2019, 26, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Li, X.; Ge, G.; Liu, J.; Biju, K.C.; Laing, S.D.; Qian, Y.; Ballard, C.; He, Z.; Masliah, E.; et al. GDNF-Expressing Macrophages Mitigate Loss of Dopamine Neurons and Improve Parkinsonian Symptoms in MitoPark Mice. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gash, D.M.; Zhang, Z.; Ovadia, A.; Cass, W.A.; Yi, A.; Simmerman, L.; Russell, D.; Martin, D.; Lapchak, P.A.; Collins, F.; et al. Functional Recovery in Parkinsonian Monkeys Treated with GDNF. Nature 1996, 380, 252–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oiwa, Y.; Nakai, K.; Itakura, T. Histological Effects of Intraputaminal Infusion of Glial Cell Line-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Parkinson Disease Model Macaque Monkeys. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2006, 46, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enterría-Morales, D.; López-López, I.; López-Barneo, J.; d’Anglemont de Tassigny, X. Role of Glial Cell Line-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in the Maintenance of Adult Mesencephalic Catecholaminergic Neurons. Mov. Disord. 2020, 35, 565–576. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson, C.E.; Phillips, H.S.; Pollock, R.A.; Davies, A.M.; Lemeulle, C.; Armanini, M.; Simmons, L.; Moffet, B.; Vandlen, R.A.; to Simmons, L.; et al. GDNF: A Potent Survival Factor for Motoneurons Present in Peripheral Nerve and Muscle. Science 1994, 266, 1062–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.W.; Klein, R.D.; Fariñas, I.; Sauer, H.; Armanini, M.; Phillips, H.; Reichardt, L.F.; Ryan, A.M.; Carver-Moore, K.; Rosenthal, A. Renal and Neuronal Abnormalities in Mice Lacking GDNF. Nature 1996, 382, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, H.; Choi, B.H. Expression of Glial Cell Line-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (GDNF) in the Developing Human Fetal Brain. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2001, 19, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellmich, H.L.; Kos, L.; Cho, E.S.; Mahon, K.A.; Zimmer, A. Embryonic Expression of Glial Cell-Line Derived Neurotrophic Factor (GDNF) Suggests Multiple Developmental Roles in Neural Differentiation and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Interactions. Mech. Dev. 1996, 54, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés, D.; Carballo-Molina, O.A.; Castellanos-Montiel, M.J.; Velasco, I. The Non-Survival Effects of Glial Cell Line-Derived Neurotrophic Factor on Neural Cells. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascual, A.; López-Barneo, J. Reply to “GDNF Is Not Required for Catecholaminergic Neuron Survival in Vivo”. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopra, J.; Vilenius, C.; Grealish, S.; Härma, M.-A.; Varendi, K.; Lindholm, J.; Castrén, E.; Võikar, V.; Björklund, A.; Piepponen, T.P.; et al. GDNF Is Not Required for Catecholaminergic Neuron Survival in Vivo. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, A.; Hidalgo-Figueroa, M.; Piruat, J.I.; Pintado, C.O.; Gómez-Díaz, R.; López-Barneo, J. Absolute Requirement of GDNF for Adult Catecholaminergic Neuron Survival. Nat. Neurosci. 2008, 11, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kopra, J.; Varendi, K.; Porokuokka, L.L.; Panhelainen, A.; Kuure, S.; Marshall, P.; Karalija, N.; Härma, M.-A.; Vilenius, C.; et al. GDNF Overexpression from the Native Locus Reveals Its Role in the Nigrostriatal Dopaminergic System Function. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, 1005710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whone, A.; Luz, M.; Boca, M.; Woolley, M.; Mooney, L.; Dharia, S.; Broadfoot, J.; Cronin, D.; Schroers, C.; Barua, N.U.; et al. Randomized Trial of Intermittent Intraputamenal Glial Cell Line-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Parkinson’s Disease. Brain 2019, 142, 512–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitchai, A.; Rajaretinam, R.K.; Freeman, J.L. Zebrafish as an Emerging Model for Bioassay-Guided Natural Product Drug Discovery for Neurological Disorders. Medicines 2019, 6, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, R.; Genoud, C.; Wanner, A. Analyzing the Structure and Function of Neuronal Circuits in Zebrafish. Front. Neural Circuits 2013, 7, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepherd, I.T.; Beattie, C.E.; Raible, D.W. Functional Analysis of Zebrafish GDNF. Dev. Biol. 2001, 231, 420–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, K.; Dambly-Chaudière, C.; Ghysen, A. Glial Cell Line-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Defines the Path of Developing and Regenerating Axons in the Lateral Line System of Zebrafish. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 19531–19536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.-K.; Yuan, R.-Y.; Lien, H.-W.; Hung, C.-C.; Hwang, P.-P.; Chen, R.P.-Y.; Chang, C.-C.; Liao, Y.-F.; Huang, C.-J. Multiple Signaling Factors and Drugs Alleviate Neuronal Death Induced by Expression of Human and Zebrafish Tau Proteins in Vivo. J. Biomed. Sci. 2016, 23, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerucha, T.; Stühmer, T.; Hatch, G.; Park, B.K.; Long, Q.; Yu, G.; Gambarotta, A.; Schultz, J.R.; Rubenstein, J.L.R.; Ekker, M. A Highly Conserved Enhancer in the Dlx5/Dlx6Intergenic Region Is the Site of Cross-Regulatory Interactions BetweenDlx Genes in the Embryonic Forebrain. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 709–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacialli, P.; Gueguen, M.-M.; Coumailleau, P.; D’Angelo, L.; Kah, O.; Lucini, C.; Pellegrini, E. BDNF Expression in Larval and Adult Zebrafish Brain: Distribution and Cell Identification. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wullimann, M.F.; Rupp, B.; Reichert, H. Neuroanatomy of the Zebrafish Brain. A Topological Atlas; Birkhauser: Basel, Switzerland, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo-Figueroa, M.; Bonilla, S.; Gutiérrez, F.; Pascual, A.; López-Barneo, J. GDNF Is Predominantly Expressed in the PV+ Neostriatal Interneuronal Ensemble in Normal Mouse and after Injury of the Nigrostriatal Pathway. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 864–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucini, C.; Maruccio, L.; Patruno, M.; Tafuri, S.; Staiano, N.; Mascarello, F.; Castaldo, L. Glial Cell Line-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Expression in the Brain of Adult Zebrafish (Danio Rerio). Histol. Histopathol. 2008, 23, 251–261. [Google Scholar]
- Pochon, N.A.-M.; Menoud, A.; Tseng, J.L.; Zurn, A.D.; Aebischer, P. Neuronal GDNF Expression in the Adult Rat Nervous System Identified By In Situ Hybridization. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1997, 9, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-de San Luis, C.; Pascual, A. Simultaneous Detection of Both GDNF and GFRα1 Expression Patterns in the Mouse Central Nervous System. Front. Neuroanat. 2016, 10, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trupp, M.; Belluardo, N.; Funakoshi, H.; Ibáñez, C.F. Complementary and Overlapping Expression of Glial Cell Line-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (GDNF), c-Ret Proto-Oncogene, and GDNF Receptor-α Indicates Multiple Mechanisms of Trophic Actions in the Adult Rat CNS. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 3554–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- März, M.; Chapouton, P.; Diotel, N.; Vaillant, C.; Hesl, B.; Takamiya, M.; Lam, C.S.; Kah, O.; Bally-Cuif, L.; Strähle, U. Heterogeneity in Progenitor Cell Subtypes in the Ventricular Zone of the Zebrafish Adult Telencephalon. Glia 2010, 58, 870–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kizil, C.; Kaslin, J.; Kroehne, V.; Brand, M. Adult Neurogenesis and Brain Regeneration in Zebrafish. Dev. Neurobiol. 2012, 72, 429–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GermanÀ, A.; Montalbano, G.; Guerrera, M.C.; Amato, V.; LaurÀ, R.; Magnoli, D.; Campo, S.; Suarez-Fernandez, E.; Ciriaco, E.; Vega, J.A. Developmental Changes in the Expression of Sox2 in the Zebrafish Brain. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2011, 74, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri, A.L.M.; Cavallaro, M.; Braida, D.; Di Cristofano, A.; Canta, A.; Vezzani, A.; Ottolenghi, S.; Pandolfi, P.P.; Sala, M.; Debiasi, S.; et al. Sox2 Deficiency Causes Neurodegeneration and Impaired Neurogenesis in the Adult Mouse Brain. Dev. Dis. 2004, 131, 3805–3819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaslin, J.; Ganz, J.; Geffarth, M.; Grandel, H.; Hans, S.; Brand, M. Stem Cells in the Adult Zebrafish Cerebellum: Initiation and Maintenance of a Novel Stem Cell Niche. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 6142–6153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte Azevedo, M.; Sander, S.; Tenenbaum, L. GDNF, A Neuron-Derived Factor Upregulated in Glial Cells during Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakshi, A.; Shimizu, S.; Keck, C.A.; Cho, S.; LeBold, D.G.; Morales, D.; Arenas, E.; Snyder, E.Y.; Watson, D.J.; McIntosh, T.K. Neural Progenitor Cells Engineered to Secrete GDNF Show Enhanced Survival, Neuronal Differentiation and Improve Cognitive Function Following Traumatic Brain Injury. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2006, 23, 2119–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Deng, L.; Wang, Y.; Yin, L.; Yang, C.; Du, J.; Yuan, Q. GDNF Enhances Therapeutic Efficiency of Neural Stem Cells-Based Therapy in Chronic Experimental Allergic Encephalomyelitis in Rat. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 1431349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Liang, Y.; Lu, H.; Yang, Z.; Liu, R.; Wang, J.; Song, X.; Long, J.; Li, Y.; Lei, D.; et al. Co-Transplantation of GDNF-Overexpressing Neural Stem Cells and Fetal Dopaminergic Neurons Mitigates Motor Symptoms in a Rat Model of Parkinson’s Disease. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appel, E.; Kolman, O.; Kazimirsky, G.; Blumberg, P.M.; Brodie, C. Regulation of GDNF Expression in Cultured Astrocytes by Inflammatory Stimuli. Neuroreport 1997, 8, 3309–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moretto, G.; Walker, D.G.; Lanteri, P.; Taioli, F.; Zaffagnini, S.; Xu, R.Y.; Rizzuto, N. Expression and Regulation of Glial-Cell-Line-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (GDNF) MRNA in Human Astrocytes in Vitro. Cell Tissue Res. 1996, 286, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicole, O.; Ali, C.; Docagne, F.; Plawinski, L.; MacKenzie, E.T.; Vivien, D.; Buisson, A. Neuroprotection Mediated by Glial Cell Line-Derived Neurotrophic Factor: Involvement of a Reduction of NMDA-Induced Calcium Influx by the Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathway. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 3024–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ubhi, K.; Rockenstein, E.; Mante, M.; Inglis, C.; Adame, A.; Patrick, C.; Whitney, K.; Masliah, E. Neurodegeneration in a Transgenic Mouse Model of Multiple System Atrophy Is Associated with Altered Expression of Oligodendroglial-Derived Neurotrophic Factors. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 6236–6246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- März, M.; Schmidt, R.; Rastegar, S.; Strähle, U. Regenerative Response Following Stab Injury in the Adult Zebrafish Telencephalon. Dev. Dyn. 2011, 240, 2221–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroehne, V.; Freudenreich, D.; Hans, S.; Kaslin, J.; Brand, M. Regeneration of the Adult Zebrafish Brain from Neurogenic Radial Glia-Type Progenitors. Development 2011, 138, 4831–4841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresjanac, M.; Antauer, G. Reactive Astrocytes of the Quinolinic Acid-Lesioned Rat Striatum Express GFRα1 as Well as GDNF in Vivo. Exp. Neurol. 2000, 164, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapouton, P.; Skupien, P.; Hesl, B.; Coolen, M.; Moore, J.C.; Madelaine, R.; Kremmer, E.; Faus-Kessler, T.; Blader, P.; Lawson, N.D.; et al. Notch Activity Levels Control the Balance between Quiescence and Recruitment of Adult Neural Stem Cells. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 7961–7974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira-Carlos, V.; Ganz, J.; Hans, S.; Kaslin, J.; Brand, M. Notch Receptor Expression in Neurogenic Regions of the Adult Zebrafish Brain. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 73384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazaei, M.; Ahuja, C.S.; Nakashima, H.; Nagoshi, N.; Li, L.; Wang, J.; Chio, J.; Badner, A.; Seligman, D.; Ichise, A.; et al. GDNF Rescues the Fate of Neural Progenitor Grafts by Attenuating Notch Signals in the Injured Spinal Cord in Rodents. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, 3538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Okamoto, H.; Ohshima, T. Characterization of Neural Stem Cells and Their Progeny in the Adult Zebrafish Optic Tectum. Dev. Biol. 2010, 342, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, Y.; Ueda, Y.; Ohshima, T. Wnt Signaling Regulates Proliferation and Differentiation of Radial Glia in Regenerative Processes after Stab Injury in the Optic Tectum of Adult Zebrafish. Glia 2018, 66, 1382–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindsey, B.W.; Aitken, G.E.; Tang, J.K.; Khabooshan, M.; Douek, A.M.; Vandestadt, C.; Kaslin, J. Midbrain Tectal Stem Cells Display Diverse Regenerative Capacities in Zebrafish. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, R.B.; Debiais-Thibaud, M.; Talbot, J.C.; Ekker, M. The Relationship between Dlx and Gad1 Expression Indicates Highly Conserved Genetic Pathways in the Zebrafish Forebrain. Dev. Dyn. 2010, 239, 2298–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Xi, Y.; Pollack, J.; Debiais-Thibaud, M.; MacDonald, R.B.; Ekker, M. Activity of Dlx5a/Dlx6a Regulatory Elements during Zebrafish GABAergic Neuron Development. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2011, 29, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solek, C.M.; Feng, S.; Perin, S.; Weinschutz Mendes, H.; Ekker, M. Lineage Tracing of Dlx1a/2a and Dlx5a/6a Expressing Cells in the Developing Zebrafish Brain. Dev. Biol. 2017, 427, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Anglemont de Tassigny, X.; Pascual, A.; López-Barneo, J. GDNF-Based Therapies, GDNF-Producing Interneurons, and Trophic Support of the Dopaminergic Nigrostriatal Pathway. Implications for Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Neuroanat. 2015, 9, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Adolf, B.; Chapouton, P.; Lam, C.S.; Topp, S.; Tannhäuser, B.; Strähle, U.; Götz, M.; Bally-Cuif, L. Conserved and Acquired Features of Adult Neurogenesis in the Zebrafish Telencephalon. Dev. Biol. 2006, 295, 278–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandini, F.; Cova, L.; Armentero, M.-T.; Zennaro, E.; Levandis, G.; Bossolasco, P.; Calzarossa, C.; Mellone, M.; Giuseppe, B.; Deliliers, G.L.; et al. Transplantation of Undifferentiated Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Protects against 6-Hydroxydopamine Neurotoxicity in the Rat. Cell Transplant. 2010, 19, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, N.B.; Siegel, G.J.; Lee, J.M. Depletion of Glial Cell Line-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Substantia Nigra Neurons of Parkinson’s Disease Brain. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2001, 21, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, T.L.; Ronneberger, O.; Ryu, S.; Nitschke, R.; Driever, W. Comprehensive Catecholaminergic Projectome Analysis Reveals Single-Neuron Integration of Zebrafish Ascending and Descending Dopaminergic Systems. Nat Commun 2011, 2, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaslin, J.; Panula, P. Comparative Anatomy of the Histaminergic and Other Aminergic Systems in Zebrafish (Danio Rerio). J. Comp. Neurol. 2001, 440, 342–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rink, E.; Wullimann, M.F. The Teleostean (Zebrafish) Dopaminergic System Ascending to the Subpallium (Striatum) Is Located in the Basal Diencephalon (Posterior Tuberculum). Brain Res. 2001, 889, 316–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallinen, V.; Torkko, V.; Sundvik, M.; Reenilä, I.; Khrustalyov, D.; Kaslin, J.; Panula, P. MPTP and MPP+ Target Specific Aminergic Cell Populations in Larval Zebrafish. J. Neurochem. 2009, 108, 719–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panula, P.; Chen, Y.-C.; Priyadarshini, M.; Kudo, H.; Semenova, S.; Sundvik, M.; Sallinen, V. The Comparative Neuroanatomy and Neurochemistry of Zebrafish CNS Systems of Relevance to Human Neuropsychiatric Diseases. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 40, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso-Chinea, P.; Cruz-Muros, I.; Aymerich, M.S.; Rodríguez-Díaz, M.; Afonso-Oramas, D.; Lanciego, J.L.; González-Hernández, T. Striatal Expression of GDNF and Differential Vulnerability of Midbrain Dopaminergic Cells. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2005, 21, 1815–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretaud, S.; Lee, S.; Guo, S. Sensitivity of Zebrafish to Environmental Toxins Implicated in Parkinson’s Disease. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2004, 26, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, C.S.; Korzh, V.; Strahle, U. Zebrafish Embryos Are Susceptible to the Dopaminergic Neurotoxin MPTP. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2005, 21, 1758–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinley, E.T.; Baranowski, T.C.; Blavo, D.O.; Cato, C.; Doan, T.N.; Rubinstein, A.L. Neuroprotection of MPTP-Induced Toxicity in Zebrafish Dopaminergic Neurons. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2005, 141, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stednitz, S.J.; Freshner, B.; Shelton, S.; Shen, T.; Black, D.; Gahtan, E. Selective Toxicity of L-DOPA to Dopamine Transporter-Expressing Neurons and Locomotor Behavior in Zebrafish Larvae. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2015, 52, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Wei, W.; Gu, W.; Huang, P.; Ren, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Lin, S.; Zhang, B. Visualization of Monoaminergic Neurons and Neurotoxicity of MPTP in Live Transgenic Zebrafish. Dev. Biol. 2008, 314, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyn, M.; Hua, K.; Mohd Noor, S.; Wong, C.E.D.; Ekker, M. Comprehensive Analysis of Neurotoxin-Induced Ablation of Dopaminergic Neurons in Zebrafish Larvae. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Zondervan-van der Linde, H.; Severijnen, L.-A.; Oostra, B.A.; Willemsen, R.; Bonifati, V. Dopaminergic Neuronal Loss and Dopamine-Dependent Locomotor Defects in Fbxo7-Deficient Zebrafish. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, 48911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, D.; Qu, D.; Kwok, K.H.H.; Ng, S.S.; Lim, A.Y.M.; Aw, S.S.; Lee, C.W.H.; Sung, W.K.; Tan, E.K.; Lufkin, T.; et al. Deletion of the WD40 Domain of LRRK2 in Zebrafish Causes Parkinsonism-Like Loss of Neurons and Locomotive Defect. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6, 1000914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soman, S.; Keatinge, M.; Moein, M.; Da Costa, M.; Mortiboys, H.; Skupin, A.; Sugunan, S.; Bazala, M.; Kuznicki, J.; Bandmann, O. Inhibition of the Mitochondrial Calcium Uniporter Rescues Dopaminergic Neurons in Pink1(-/-) Zebrafish. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2017, 45, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anichtchik, O.; Diekmann, H.; Fleming, A.; Roach, A.; Goldsmith, P.; Rubinsztein, D.C. Loss of PINK1 Function Affects Development and Results in Neurodegeneration in Zebrafish. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 8199–8207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, A.; Assey, K.S.; Sturkie, C.D.; West, F.D.; Machacek, D.W.; Stice, S.L. Glial Cell Line-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Enhances in Vitro Differentiation of Mid-/Hindbrain Neural Progenitor Cells to Dopaminergic-like Neurons. J. Neurosci. Res. 2010, 88, 3222–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, J.; Xiao, Y.; Sun, A.X.; Cukuroglu, E.; Tran, H.-D.; Göke, J.; Tan, Z.Y.; Saw, T.Y.; Tan, C.-P.; Lokman, H.; et al. Midbrain-like Organoids from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells Contain Functional Dopaminergic and Neuromelanin-Producing Neurons. Cell Stem Cell 2016, 19, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Luan, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, C. Human Neural Stem Cells with GDNF Site-Specific Integration at AAVS1 by Using AAV Vectors Retained Their Stemness. Neurochem. Res. 2018, 43, 930–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zou, C.; Fu, L.; Wang, B.; An, J.; Song, G.; Wu, J.; Tang, X.; Li, M.; Zhang, J.; et al. Autologous IPSC-Derived Dopamine Neuron Transplantation in a Nonhuman Primate Parkinson’s Disease Model. Cell Discov. 2015, 1, 15012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).