Metronidazole Encephalopathy EEG Features: A Case Report with Systematic Review of the Literature
Abstract
1. Introduction
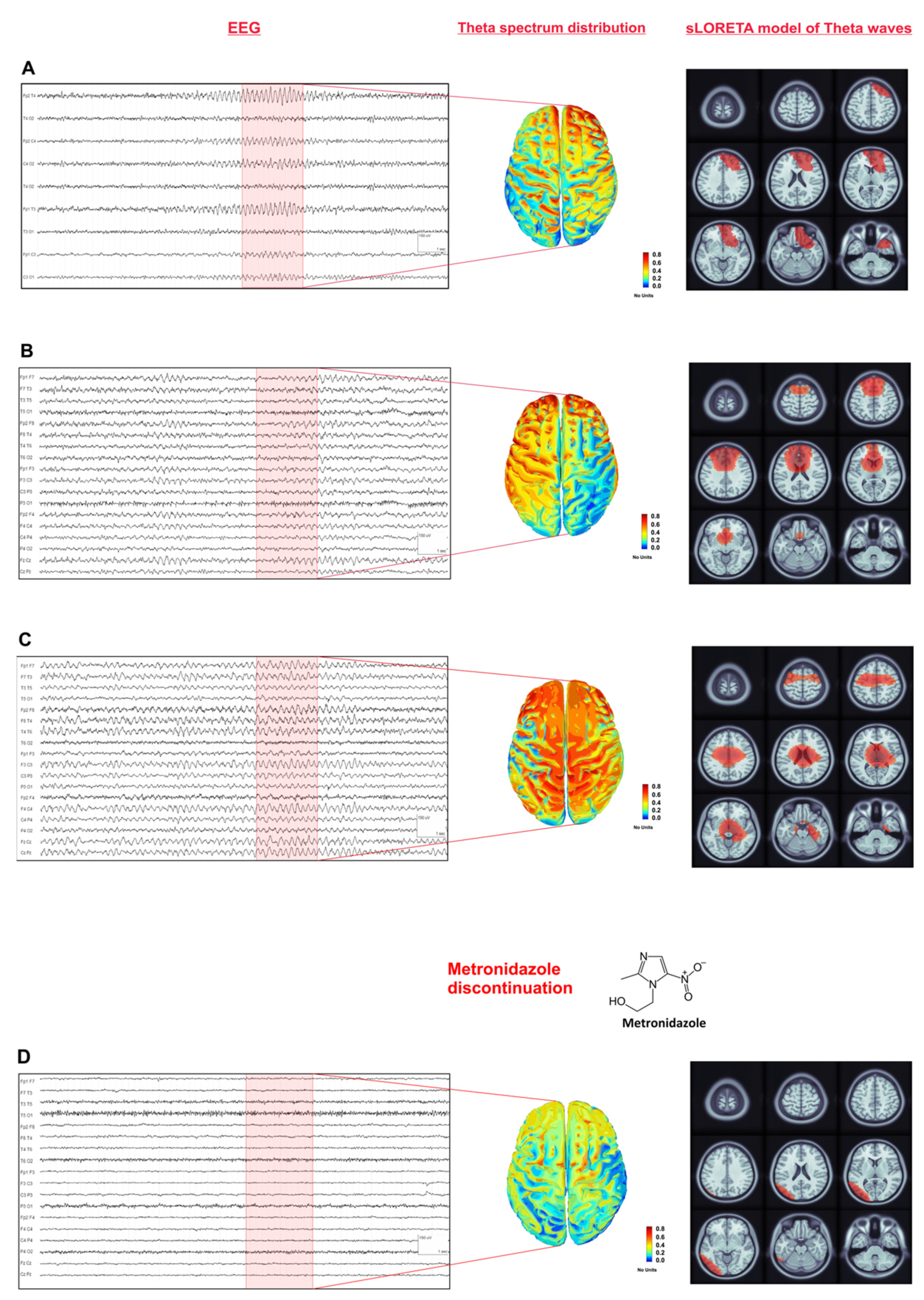
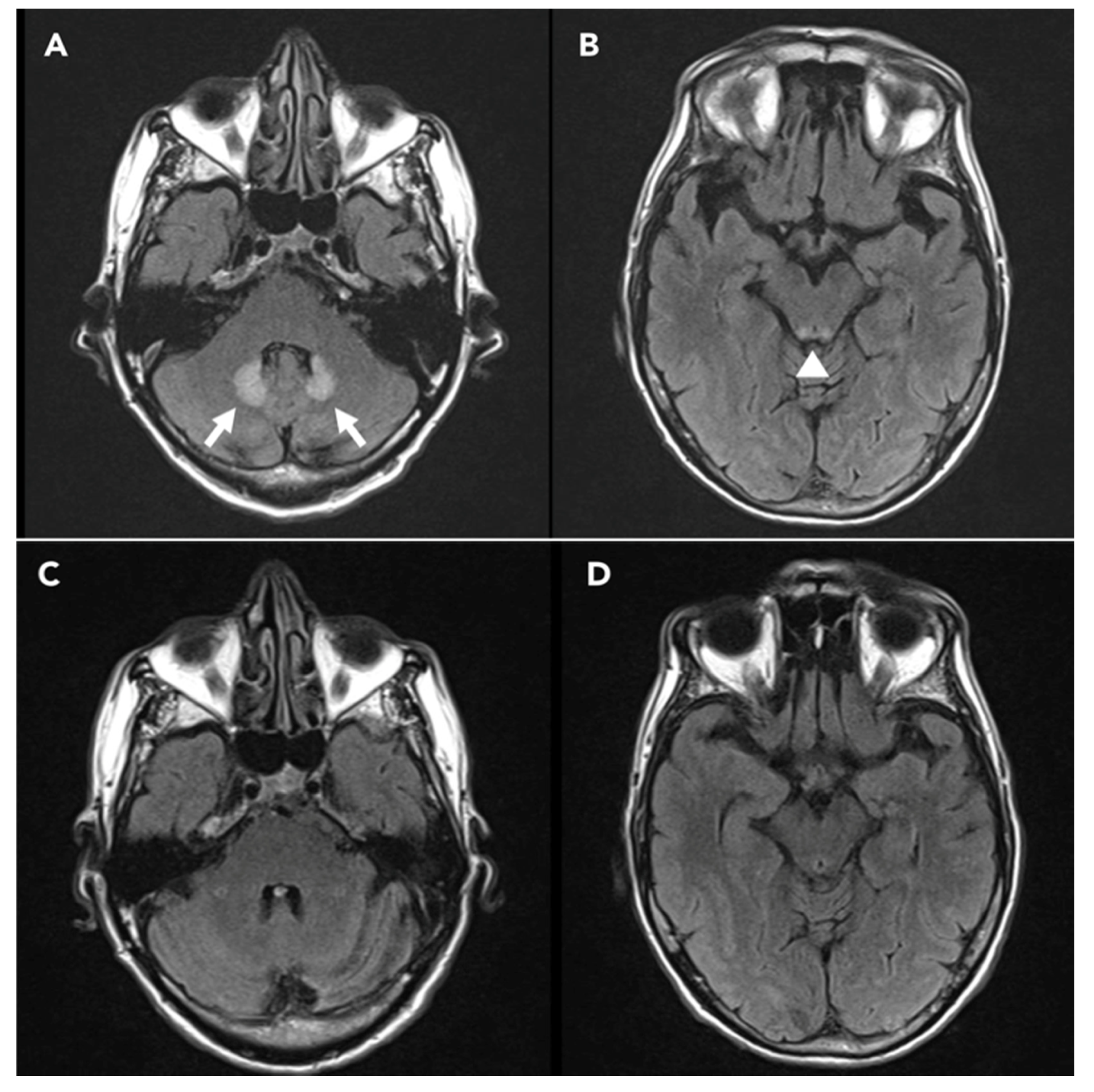
2. Case Presentation
3. Systematic Review
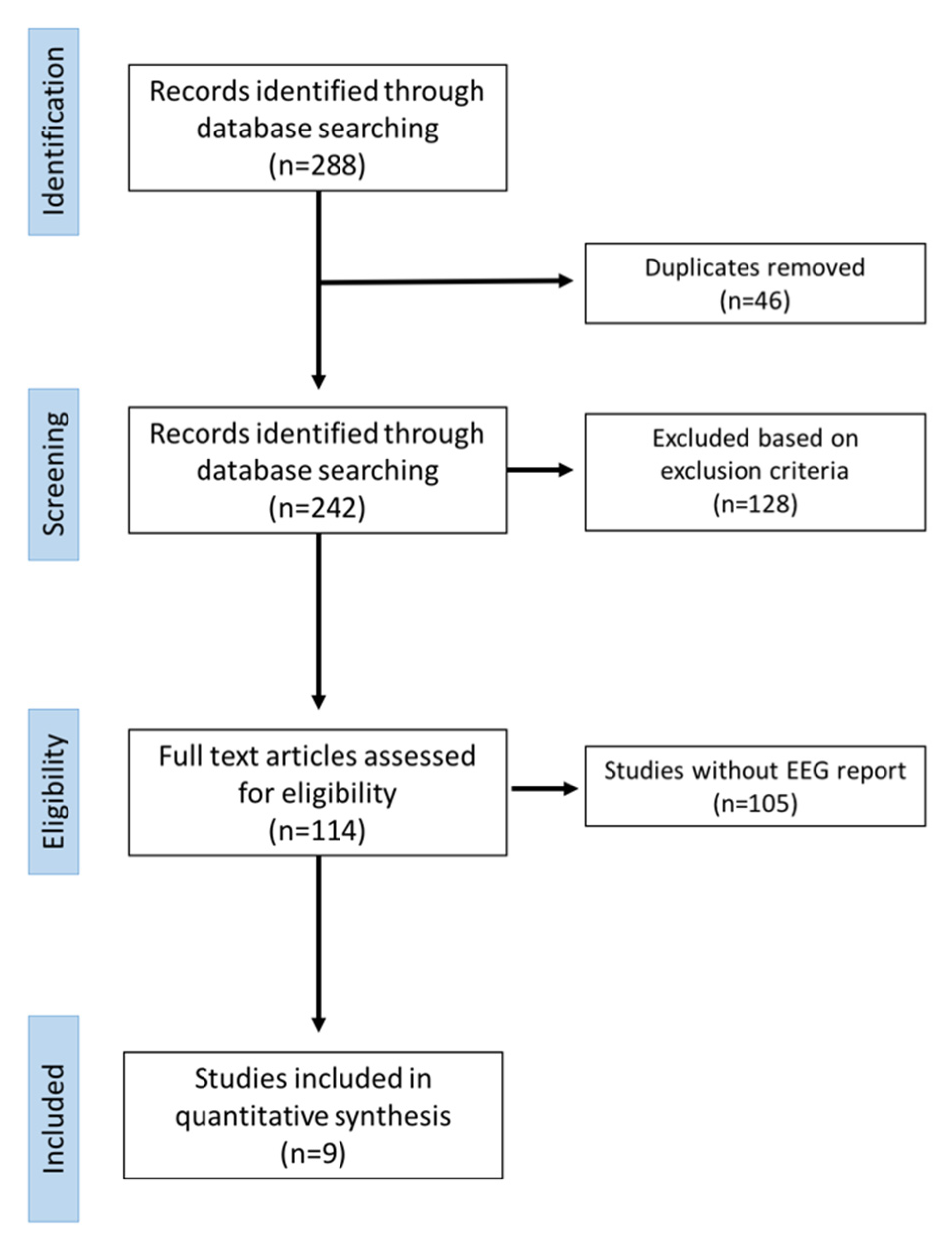
3.1. Data Extraction Process
3.2. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Darby, R.R.; Raibagkar, P.; Castro, L.N.G.; Berkowitz, A.L. Antibiotic-associated encephalopathy. Neurology 2016, 86, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, U.; Panwar, A.; Pandit, A.; Das, S.K.; Joshi, B. Clinical and neuroradiological spectrum of metronidazole induced encephalopathy: Our experience and the review of literature. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. JCDR 2016, 10, OE01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriyama, A.; Jackson, J.L.; Doi, A.; Kamiya, T. Metronidazole-induced central nervous system toxicity: A systematic review. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 2011, 34, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottenberg, M.M.; Hegge, K.A.; Klug Eastman, D.; Kumar, R. Metronidazole-induced encephalopathy: A case report and review of the literature. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2011, 51, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godfrey, M.S.; Finn, A.; Zainah, H.; Dapaah-Afriyie, K. Metronidazole-induced encephalopathy after prolonged metronidazole course for treatment of C. dif ficile colitis. BMJ Case Rep. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.; Na, D.G.; Kim, E.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Son, K.R.; Chang, K.H. MR imaging of metronidazole-induced encephalopathy: Lesion distribution and diffusion-weighted imaging findings. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2007, 28, 1652–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadel, F.; Baillet, S.; Mosher, J.C.; Pantazis, D.; Leahy, R.M. Brainstorm: A user-friendly application for MEG/EEG analysis. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2011, 2011, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitinger, M.; Trinka, E.; Gardella, E.; Rohracher, A.; Kalss, G.; Qerama, E.; Dobesberger, J. Diagnostic accuracy of the Salzburg EEG criteria for non-convulsive status epilepticus: A retrospective study. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Shamseer, L.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst. Rev. 2015, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailes, J.; Willis, J.; Priebe, C.; Strub, R. Encephalopathy With Metronidazole in a Child. Am. J. Dis. Child 1983, 137, 290–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beloosesky, Y.; Grosman, B.; Marmelstein, V.; Grinblat, J. Convulsions induced by metronidazole treatment for Clostridium difficile-associated disease in chronic renal failure. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2000, 319, 338–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferroir, J.P.; Corpechot, C.; Freudenreich, A.; Khalil, A. Metronidazole-related polyneuritis, convulsive seizures, and cerebellar syndrome. Contribution of MRI. Rev. Neurol. (Paris) 2009, 165, 828–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groothoff, M.V.R.; Hofmeijer, J.; Sikma, M.A.; Meulenbelt, J. Irreversible encephalopathy after treatment with high-dose intravenous metronidazole. Clin. Ther. 2010, 32, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantador, A.A.; Meschia, J.F.; Freeman, W.D.; Tatum, W.O. Nonconvulsive status with metronidazole. Neurohospitalist 2013, 3, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, K.; Stern-Nezer, S.; Buckwalter, M.S.; Fischbein, N.; Caulfield, A.F. Metronidazole-induced encephalopathy: Not always a reversible situation. Neurocrit. Care 2015, 22, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onder, H. A case of MRI negative metronidazole-induced encephalopathy and recovery of electroencephalography at follow-up. J. Neurol. Res. 2016, 6, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, H.-H.; Kwan, S.-Y. Electroencephalographic periodic discharges in Metronidazoleinduced encephalopathy: A case report. Acta Neurol. Taiwan 2017, 26, 184–188. [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen, C.G.; Karlsson, W.K.; Amin, F.M.; Lindelof, M. Convulsive seizures as presenting symptom of metronidazole-induced encephalopathy: A case report. Case Rep. Neurol. 2018, 10, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Bitar, M.K.; Boustany, R.-M.N. Common causes of uncommon seizures. Pediatr. Neurol. 2009, 41, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, P.W.; Rossetti, A.O. EEG patterns and imaging correlations in encephalopathy: Encephalopathy part II. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2011, 28, 233–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, S.S.; Neligan, A.; Mullins, G.M.; Daly, S.; McNamara, B.; Galvin, R.J.; Sweeney, B.J. Aetiology and prognosis of encephalopathic patterns on electroencephalogram in a general hospital. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2008, 15, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middleton, F.A.; Strick, P.L. Anatomical evidence for cerebellar and basal ganglia involvement in higher cognitive function. Science 1994, 266, 458–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courchesne, E.; Townsend, J.; Akshoomoff, N.A.; Saitoh, O.; Yeung-Courchesne, R.; Lincoln, A.J.; James, H.E.; Haas, R.H.; Schreibman, L.; Lau, L. Impairment in shifting attention in autistic and cerebellar patients. Behav. Neurosci. 1994, 108, 848–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akshoomoff, N.A.; Courchesne, E. ERP evidence for a shifting attention deficit in patients with damage to the cerebellum. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 1994, 6, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baillieux, H.; De Smet, H.J.; Paquier, P.F.; De Deyn, P.P.; Mariën, P. Cerebellar neurocognition: Insights into the bottom of the brain. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2008, 110, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinker, J. Posterior Fossa Syndrome. Encycl. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2018, 2738–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallez, H.; Vanrumste, B.; Grech, R.; Muscat, J.; De Clercq, W.; Vergult, A.; D’Asseler, Y.; Camilleri, K.P.; Fabri, S.G.; Van Huffel, S.; et al. Review on solving the forward problem in EEG source analysis. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2007, 4, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodbeck, V.; Spinelli, L.; Lascano, A.M.; Wissmeier, M.; Vargas, M.I.; Vulliemoz, S.; Pollo, C.; Schaller, K.; Michel, C.M.; Seeck, M. Electroencephalographic source imaging: A prospective study of 152 operated epileptic patients. Brain 2011, 134, 2887–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lantz, G.; Michel, C.M.; Seeck, M.; Blanke, O.; Spinelli, L.; Thut, G.; Landis, T.; Rosen, I. Space-oriented segmentation and 3-dimensional source reconstruction of ictal EEG patterns. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2001, 112, 688–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzsáki, G.; Draguhn, A. Neuronal oscillations in cortical networks. Science 2004, 304, 1926–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtemanche, R.; Robinson, J.C.; Aponte, D.I. Linking oscillations in cerebellar circuits. Front. Neural Circuits 2013, 7, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cebolla, A.M.; Petieau, M.; Dan, B.; Balazs, L.; McIntyre, J.; Chéron, G. Cerebellar contribution to visuo-attentional alpha rhythm: Insights from weightlessness. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assenza, G.; Capone, F.; di Biase, L.; Ferreri, F.; Florio, L.; Guerra, A.; Marano, M.; Paolucci, M.; Ranieri, F.; Salomone, G.; et al. Oscillatory activities in neurological disorders of elderly: Biomarkers to target for neuromodulation. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’connor, S.M.; Berg, R.W.; Kleinfeld, D. Coherent electrical activity between vibrissa sensory areas of cerebellum and neocortex is enhanced during free whisking. J. Neurophysiol. 2002, 87, 2137–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lazzaro, V.; Restuccia, D.; Molinari, M.; Leggio, M.G.; Nardone, R.; Fogli, D.; Tonali, P. Excitability of the motor cortex to magnetic stimulation in patients with cerebellar lesions. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1994, 57, 108–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kros, L.; Eelkman Rooda, O.H.J.; De Zeeuw, C.I.; Hoebeek, F.E. Controlling Cerebellar Output to Treat Refractory Epilepsy. Trends Neurosci. 2015, 38, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprengers, M.; Vonck, K.; Carrette, E.; Marson, A.G.; Boon, P. Deep brain and cortical stimulation for epilepsy (Review). Summary of findings for the main comparison. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boop, S.; Wheless, J.; Van Poppel, K.; McGregor, A.; Boop, F.A. Cerebellar seizures: Report of 2 cases. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2013, 12, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author, Year | Age (y), Sex | Cumulative dose of Metronidazole (grams) | Neurological Presentation | MRI Findings | EEG Findings | EEG Follow up Findings | Neurological Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bailes et al. 1983 [10] | 12, M | 4 | Focal to bilateral tonic clonic seizures. | Not performed | Diffuse slowing without epileptic discharges (NOT SHOWN) | Normal | Resolution |
| Beloosesky et al. 2000 [11] | 87, F | 18 | Focal to bilateral tonic clonic seizures. | Not performed | Diffuse slowing without epileptic discharges (NOT SHOWN) | Normal | Resolution |
| Ferroir et al. 2009 [12] | 76, M | 45 | Peripheral Neuropathy, Cerebellar syndrome, focal to bilateral tonic clonic seizures. | T2 FLAIR hyperintensity in bilateral dentate nucleus, thalamus, splenium of corpus callosum. | Normal (NOT SHOWN) | Not done | Resolution |
| Groothoff et al. 2010 [13] | 38, F | 132 | Cerebellar syndrome, altered mental status, focal to bilateral tonic clonic seizures. | Abnormal signal in T2 FLAIR in the centrum semiovale and cerebellar peduncles. | Unspecific encephalopathy findings (NOT SHOWN) | Unchanged | Death |
| Cantador et al. 2013 [14] | 56, M | 5 | NCSE † | Hyperintense lesion of the dentate nucleus, middle cerebellar peduncles, olivary nuclei and corpus callosum in FLAIR sequences. | GPDs ‡ | Normalization | Resolution |
| Hobbs et al,.2015 [15] | 65, F | 33 | Confusion and disorientation. | Symmetrical T2 hyperintensity and generally restricted diffusion in bilateral dentate nuclei, corpus callosum, midbrain, superior cerebellar peduncles, internal capsules, and cerebral white matter. | Diffuse slowing, focal left fronto-central slowing, epileptiform sharp waves at left fronto-central (NOT SHOWN) | Unchanged | Coma and Death |
| Önder. 2016 [16] | 68, F | 10.5 | Confusion and disorientation. | MRI showing bilateral globus pallidus T1 hyperintensities. | Diffuse slowing in theta-delta rhythm | Normalization | Resolution |
| Wang et al. 2017 [17] | 58, F | 94.5 | Rapidly progressive consciousness disturbance with vegetative state. | Abnormal high signals in T2 FLAIR at bilateral dentate nuclei of the cerebellum, midbrain and dorsal pons and restricted diffusion in bilateral periventricular white matter, anterior and posterior splenium of corpus callosum. | Generalized high-voltage sharp wave complexes in quasi-periodic patterns with TM **. | Slow background activity at theta range | Unchanged |
| Sørensen et al. 2018 [18] | 66, F | 78 | Cerebellar syndrome, focal to bilateral TC seizures, multifocal myoclonus. | Abnormal T2 FLAIR hyperintense signal changes in the bilateral dentate nuclei. | Normal (NOT SHOWN) | Not done | Resolution |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ricci, L.; Motolese, F.; Tombini, M.; Lanzone, J.; Rea, R.; Di Matteo, F.; Di Lazzaro, V.; Assenza, G. Metronidazole Encephalopathy EEG Features: A Case Report with Systematic Review of the Literature. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10040227
Ricci L, Motolese F, Tombini M, Lanzone J, Rea R, Di Matteo F, Di Lazzaro V, Assenza G. Metronidazole Encephalopathy EEG Features: A Case Report with Systematic Review of the Literature. Brain Sciences. 2020; 10(4):227. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10040227
Chicago/Turabian StyleRicci, Lorenzo, Francesco Motolese, Mario Tombini, Jacopo Lanzone, Roberta Rea, Francesco Di Matteo, Vincenzo Di Lazzaro, and Giovanni Assenza. 2020. "Metronidazole Encephalopathy EEG Features: A Case Report with Systematic Review of the Literature" Brain Sciences 10, no. 4: 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10040227
APA StyleRicci, L., Motolese, F., Tombini, M., Lanzone, J., Rea, R., Di Matteo, F., Di Lazzaro, V., & Assenza, G. (2020). Metronidazole Encephalopathy EEG Features: A Case Report with Systematic Review of the Literature. Brain Sciences, 10(4), 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10040227







