A Joint Modelling Approach to Analyze Risky Decisions by Means of Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Behavioural Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The BART Data
2.2. The Cognitive Model
2.3. The Neural Model
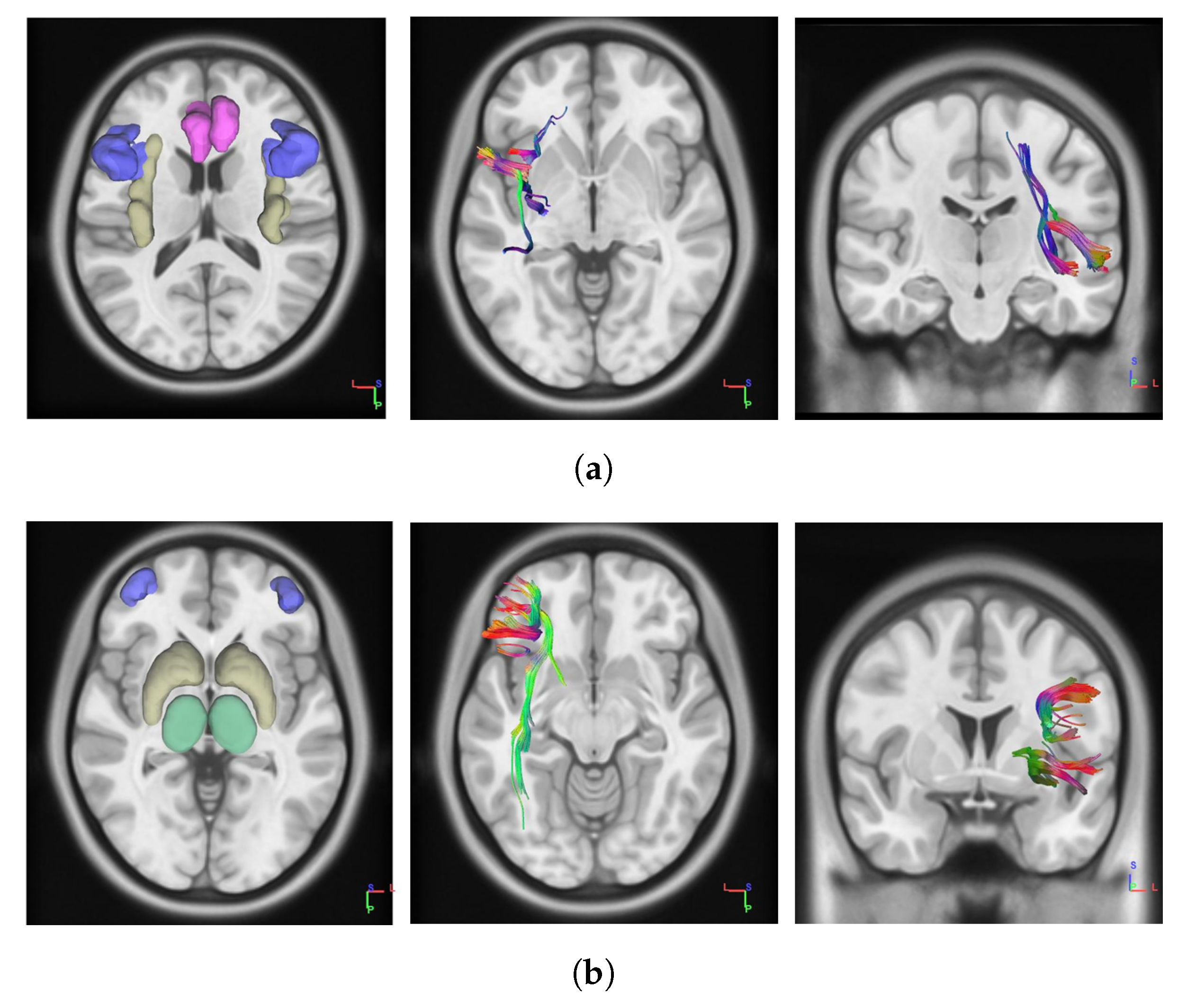
2.4. DTI Data Processing
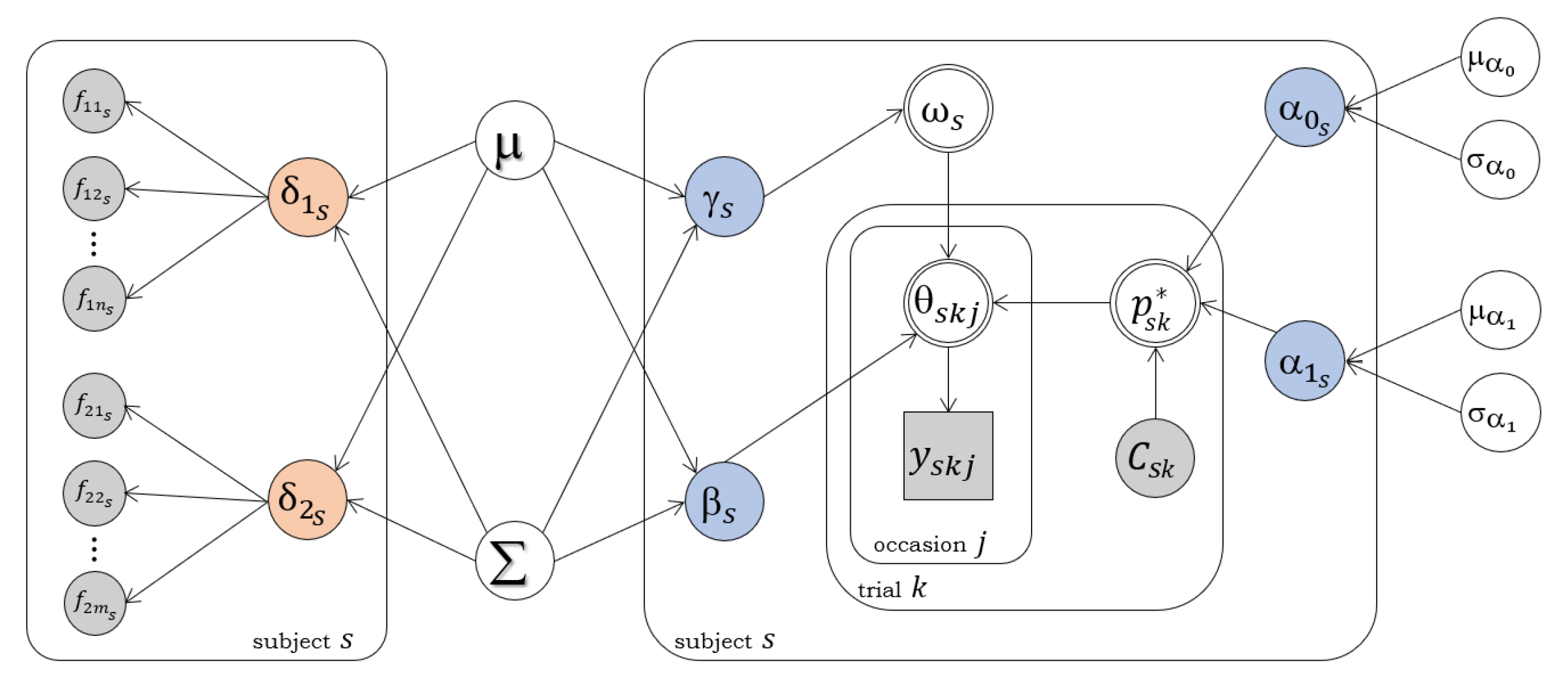
2.5. Joint Modelling
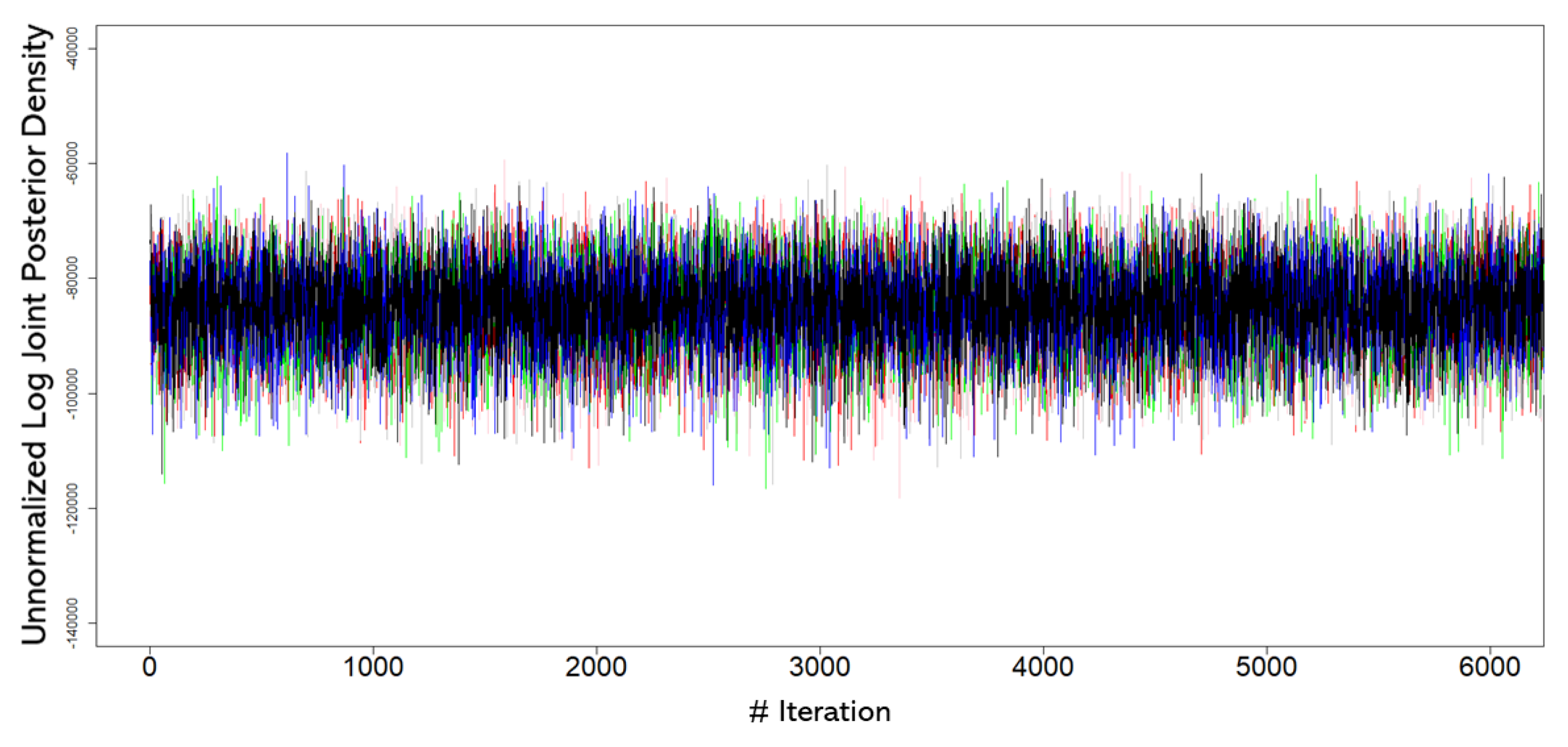
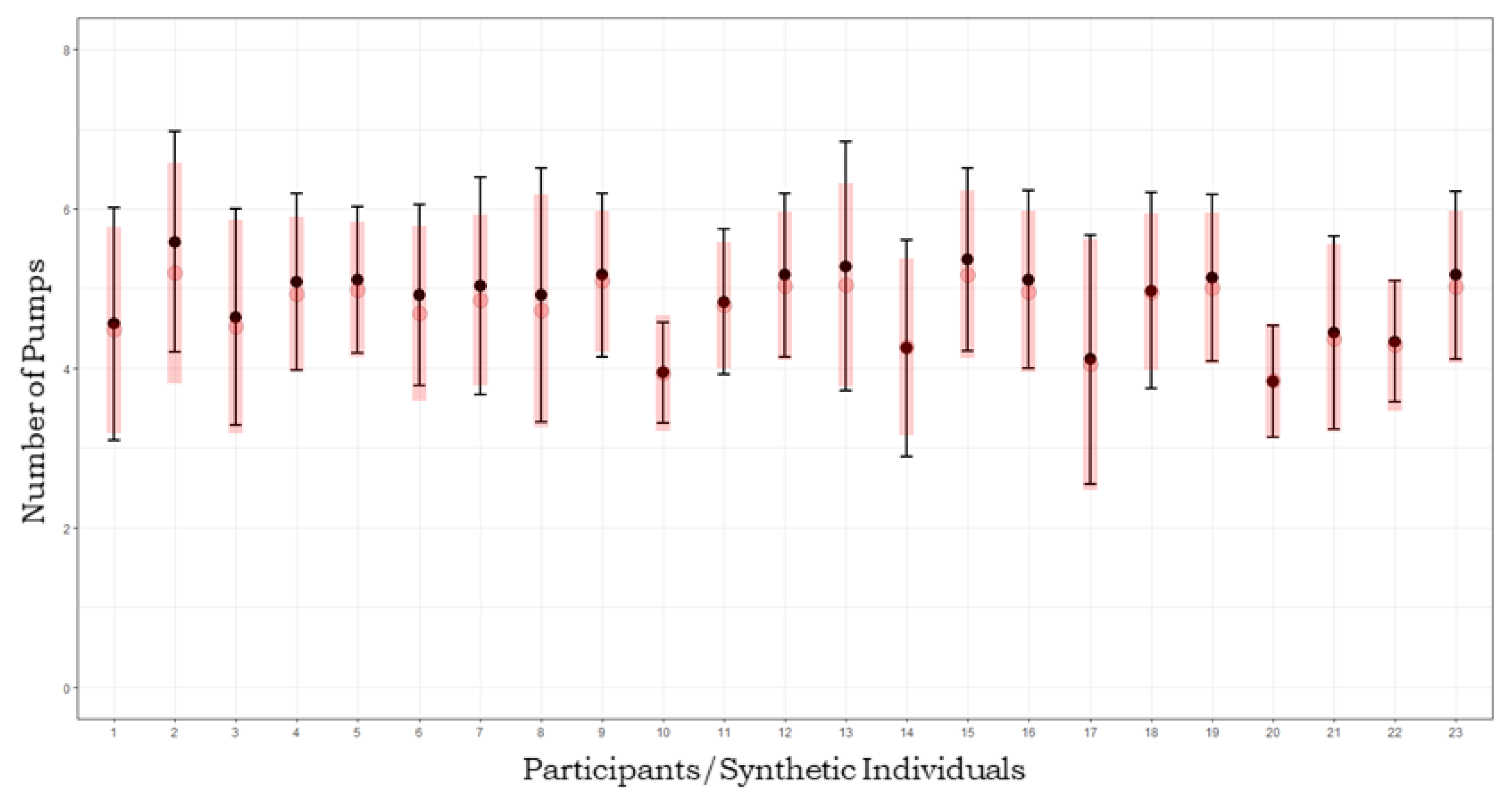
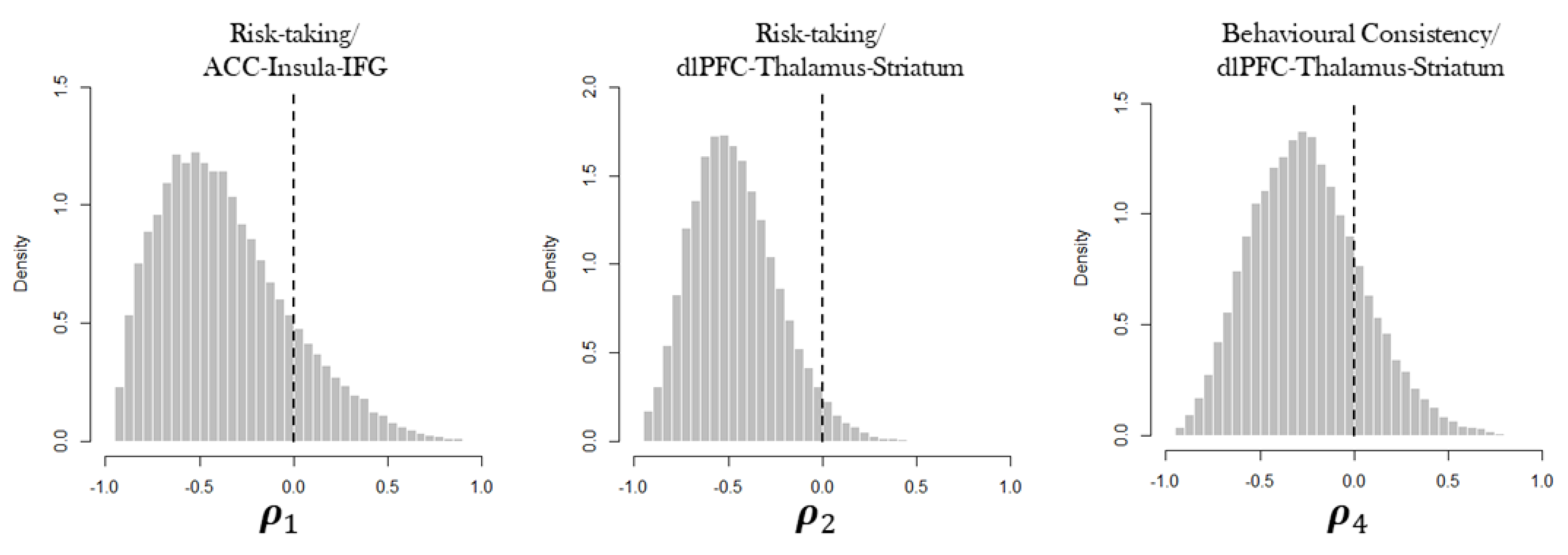
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DTI | Diffusion Tensor Imaging |
| BART | Balloon Analogue Risk task |
| MNI | Montreal Neurological Institute |
Appendix A
References
- Turner, B.M.; Forstmann, B.U.; Wagenmakers, E.J.; Brown, S.D.; Sederberg, P.B.; Steyvers, M. A Bayesian framework for simultaneously modeling neural and behavioral data. NeuroImage 2013, 72, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, G.E.; Mittner, M.; Forstmann, B.U.; Heathcote, A. On the efficiency of neurally-informed cognitive models to identify latent cognitive states. J. Math. Psychol. 2017, 76, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridwell, D.A.; Cavanagh, J.F.; Collins, A.G.; Nunez, M.D.; Srinivasan, R.; Stober, S.; Calhoun, V.D. Moving beyond ERP components: A selective review of approaches to integrate EEG and behavior. Front. Human Neurosci. 2018, 12, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.D.; Wagenmakers, E.J. Bayesian Cognitive Modeling: A practical Course; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lewandowsky, S.; Farrell, S. Computational Modeling in Cognition: Principles and Practice; SAGE Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M. Special issue on hierarchical Bayesian models. J. Math. Psychol. 2011, 55, 1–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, D. Bayesian Reasoning and Machine Learning; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Forstmann, B.U.; Wagenmakers, E.J.; Eichele, T.; Brown, S.; Serences, J.T. Reciprocal relations between cognitive neuroscience and formal cognitive models: opposites attract? Trends Cogn. Sci. 2011, 15, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunez, M.D.; Vandekerckhove, J.; Srinivasan, R. How attention influences perceptual decision making: Single-trial EEG correlates of drift-diffusion model parameters. J. Math. Psychol. 2017, 76, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, B.M.; Rodriguez, C.A.; Norcia, T.M.; McClure, S.M.; Steyvers, M. Why more is better: Simultaneous modeling of EEG, fMRI, and behavioral data. NeuroImage 2016, 128, 96–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palestro, J.J.; Bahg, G.; Sederberg, P.B.; Lu, Z.L.; Steyvers, M.; Turner, B.M. A tutorial on joint models of neural and behavioral measures of cognition. J. Math. Psychol. 2018, 84, 20–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, G.J.; Heeger, D.J. Cross-orientation suppression in human visual cortex. J. Neurophys. 2011, 106, 2108–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.L.; Li, X.; Tjan, B.S.; Dosher, B.A.; Chu, W. Attention extracts signal in external noise: A BOLD fMRI study. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2011, 23, 1148–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kragel, J.E.; Morton, N.W.; Polyn, S.M. Neural activity in the medial temporal lobe reveals the fidelity of mental time travel. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 2914–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mack, M.L.; Preston, A.R.; Love, B.C. Decoding the brain’s algorithm for categorization from its neural implementation. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, 2023–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Ravenzwaaij, D.; Provost, A.; Brown, S.D. A confirmatory approach for integrating neural and behavioral data into a single model. J. Math. Psychol. 2017, 76, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejuez, C.W.; Read, J.P.; Kahler, C.W.; Richards, J.B.; Ramsey, S.E.; Stuart, G.L.; Strong, D.R.; Brown, R.A. Evaluation of a behavioral measure of risk taking: The balloon analogue risk task (BART). J. Exp. Psychol. Appl. 2002, 8, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aklin, W.M.; Lejuez, C.; Zvolensky, M.J.; Kahler, C.W.; Gwadz, M. Evaluation of behavioral measures of risk taking propensity with inner city adolescents. Behav. Res. Ther. 2005, 43, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldenberg, D.; Telzer, E.H.; Lieberman, M.D.; Fuligni, A.J.; Galván, A. Greater response variability in adolescents is associated with increased white matter development. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2017, 12, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cazzell, M.; Li, L.; Lin, Z.J.; Patel, S.J.; Liu, H. Comparison of neural correlates of risk decision making between genders: An exploratory fNIRS study of the Balloon Analogue Risk Task (BART). Neuroimage 2012, 62, 1896–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bornovalova, M.A.; Daughters, S.B.; Hernandez, G.D.; Richards, J.B.; Lejuez, C. Differences in impulsivity and risk-taking propensity between primary users of crack cocaine and primary users of heroin in a residential substance-use program. Exp. Clin. Psychopharm. 2005, 13, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejuez, C.; Aklin, W.M.; Jones, H.A.; Richards, J.B.; Strong, D.R.; Kahler, C.W.; Read, J.P. The balloon analogue risk task (BART) differentiates smokers and nonsmokers. Exp. Clin. Psychopharm. 2003, 11, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ravenzwaaij, D.; Dutilh, G.; Wagenmakers, E.J. Cognitive model decomposition of the BART: Assessment and application. J. Math. Psychol. 2011, 55, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poldrack, R.A.; Barch, D.M.; Mitchell, J.; Wager, T.; Wagner, A.D.; Devlin, J.T.; Cumba, C.; Koyejo, O.; Milham, M. Toward open sharing of task-based fMRI data: the OpenfMRI project. Front. Neuroinf. 2013, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J.R.; Poldrack, R.A. Materials and Methods for OpenfMRI ds009: The Generality of Self Control. 2014. Available online: https://www.openfmri.org/media/ds000009/ds009_methods_0_CchSZHn.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2019).
- Wallsten, T.S.; Pleskac, T.J.; Lejuez, C.W. Modeling behavior in a clinically diagnostic sequential risk-taking task. Psychol. Rev. 2005, 112, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, S.; Cribari-Neto, F. Beta regression for modelling rates and proportions. J. Appl. Stat. 2004, 31, 799–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierpaoli, C.; Basser, P.J. Toward a quantitative assessment of diffusion anisotropy. Magn. Reson. Med. 1996, 36, 893–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beppu, T.; Inoue, T.; Shibata, Y.; Kurose, A.; Arai, H.; Ogasawara, K.; Ogawa, A.; Nakamura, S.; Kabasawa, H. Measurement of fractional anisotropy using diffusion tensor MRI in supratentorial astrocytic tumors. J. Neurooncol. 2003, 63, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, M.S.; Vorobyev, V.; Moe, D.; Parkkola, R.; Hämäläinen, H. Brain structural correlates of risk-taking behavior and effects of peer influence in adolescents. PloS ONE 2014, 9, e112780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, S.D.; Steinberg, J.L.; Ma, L.; Hasan, K.M.; Kramer, L.A.; Zuniga, E.A.; Narayana, P.A.; Moeller, F.G. Diffusion tensor imaging and decision making in cocaine dependence. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohno, M.; Morales, A.M.; Guttman, Z.; London, E.D. A neural network that links brain function, white-matter structure and risky behavior. Neuroimage 2017, 149, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukunaga, R.; Brown, J.W.; Bogg, T. Decision making in the Balloon Analogue Risk Task (BART): anterior cingulate cortex signals loss aversion but not the infrequency of risky choices. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2012, 12, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krain, A.L.; Wilson, A.M.; Arbuckle, R.; Castellanos, F.X.; Milham, M.P. Distinct neural mechanisms of risk and ambiguity: A meta-analysis of decision-making. Neuroimage 2006, 32, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawitz, A.; Fukunaga, R.; Brown, J.W. Anterior insula activity predicts the influence of positively framed messages on decision making. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2010, 10, 392–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Christopoulos, G.I.; Tobler, P.N.; Bossaerts, P.; Dolan, R.J.; Schultz, W. Neural correlates of value, risk, and risk aversion contributing to decision making under risk. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 12574–12583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhnen, C.M.; Knutson, B. The neural basis of financial risk taking. Neuron 2005, 47, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furman, D.J.; Hamilton, J.P.; Gotlib, I.H. Frontostriatal functional connectivity in major depressive disorder. Biol. Mood Anxiety Disord. 2011, 1, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basser, P.J.; Pierpaoli, C. Microstructural and physiological features of tissues elucidated by quantitative-diffusion-tensor MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Ser. B 1996, 111, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, F.C.; Verstynen, T.D.; Wang, Y.; Fernández-Miranda, J.C.; Tseng, W.Y.I. Deterministic diffusion fiber tracking improved by quantitative anisotropy. PloS ONE 2013, 8, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christidi, F.; Karavasilis, E.; Samiotis, K.; Bisdas, S.; Papanikolaou, N. Fiber tracking: A qualitative and quantitative comparison between four different software tools on the reconstruction of major white matter tracts. Eur. J. Radiol. Open 2016, 3, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolls, E.T.; Joliot, M.; Tzourio-Mazoyer, N. Implementation of a new parcellation of the orbitofrontal cortex in the automated anatomical labeling atlas. Neuroimage 2015, 122, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desikan, R.S.; Ségonne, F.; Fischl, B.; Quinn, B.T.; Dickerson, B.C.; Blacker, D.; Buckner, R.L.; Dale, A.M.; Maguire, R.P.; Hyman, B.T.; et al. An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest. Neuroimage 2006, 31, 968–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, F.C.; Panesar, S.; Fernandes, D.; Meola, A.; Yoshino, M.; Fernandez-Miranda, J.C.; Vettel, J.M.; Verstynen, T. A population-based atlas of the macroscale structural connectome in the human brain. bioRxiv 2017, 2017, 136473. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, B.M.; Forstmann, B.U.; Love, B.C.; Palmeri, T.J.; Van Maanen, L. Approaches to analysis in model-based cognitive neuroscience. J. Math. Psychol. 2017, 76, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsh, A.; Richardson, A. Approaches to the Robust Estimation of Mixed Models Handbook of Statistics; Elsevier Science BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Pinheiro, J.C.; Liu, C.; Wu, Y.N. Efficient Algorithms for Robust Estimation in Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using the Multivariate t Distribution. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 2001, 10, 249–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilks, W.R.; Richardson, S.; Spiegelhalter, D. Markov Chain Monte Carlo in Practice; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Team, R.C. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; Tea, R Core: Vienna, Austria, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Plummer, M. JAGS: A program for analysis of Bayesian graphical models using Gibbs sampling. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Workshop on Distributed Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria, 20–22 March 2003; Volume 124, pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.S.; Yajima, M.; Su, M.Y.S. Package ‘R2jags’. R Package Version 0.03-08. 2015. Available online: http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=R2jags (accessed on 1 December 2019).
- Casella, G.; George, E.I. Explaining the Gibbs sampler. Am. Stat. 1992, 46, 167–174. [Google Scholar]
- Gelman, A.; Rubin, D.B. Inference from iterative simulation using multiple sequences. Stat. Sci. 1992, 7, 457–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelman, A.; Shalizi, C.R. Philosophy and the practice of Bayesian statistics. Br. J. Math. Stat. Psychol. 2013, 66, 8–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.D. How cognitive modeling can benefit from hierarchical Bayesian models. J. Math. Psychol. 2011, 55, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, A.C.; Sugar, C.A.; Hellemann, G.; London, E.D. Is all risk bad? Young adult cigarette smokers fail to take adaptive risk in a laboratory decision-making test. Psychopharmacology 2011, 215, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphries, M.D.; Khamassi, M.; Gurney, K. Dopaminergic control of the exploration-exploitation trade-off via the basal ganglia. Front. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen-Adad, J.; Descoteaux, M.; Rossignol, S.; Hoge, R.D.; Deriche, R.; Benali, H. Detection of multiple pathways in the spinal cord using q-ball imaging. Neuroimage 2008, 42, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, L.; Leow, A.D.; Jahanshad, N.; Chiang, M.C.; Barysheva, M.; Lee, A.D.; Toga, A.W.; McMahon, K.L.; De Zubicaray, G.I.; Wright, M.J.; et al. How does angular resolution affect diffusion imaging measures? Neuroimage 2010, 49, 1357–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.012 | ||||
| 1.013 | ||||
| 1.001 | ||||
| 1.001 | ||||
| 1.019 | ||||
| 1.010 | ||||
| 1.013 | ||||
| 1.008 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
D’Alessandro, M.; Gallitto, G.; Greco, A.; Lombardi, L. A Joint Modelling Approach to Analyze Risky Decisions by Means of Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Behavioural Data. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10030138
D’Alessandro M, Gallitto G, Greco A, Lombardi L. A Joint Modelling Approach to Analyze Risky Decisions by Means of Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Behavioural Data. Brain Sciences. 2020; 10(3):138. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10030138
Chicago/Turabian StyleD’Alessandro, Marco, Giuseppe Gallitto, Antonino Greco, and Luigi Lombardi. 2020. "A Joint Modelling Approach to Analyze Risky Decisions by Means of Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Behavioural Data" Brain Sciences 10, no. 3: 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10030138
APA StyleD’Alessandro, M., Gallitto, G., Greco, A., & Lombardi, L. (2020). A Joint Modelling Approach to Analyze Risky Decisions by Means of Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Behavioural Data. Brain Sciences, 10(3), 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10030138





