Abstract
Tinnitus is a subjective phantom sound perceived only by the affected person and a symptom of various auditory and non-auditory conditions. The majority of methods used in clinical and basic research for tinnitus diagnosis are subjective. To better understand tinnitus-associated changes in the auditory system, an objective technique measuring auditory sensitivity—the auditory brainstem responses (ABR)—has been suggested. Therefore, the present review aimed to summarize ABR’s features in a rat model during experimentally induced tinnitus. PubMed, Web of Science, Science Direct, and Scopus databanks were searched using Medical Subject Heading (MeSH) terms: auditory brainstem response, tinnitus, rat. The search identified 344 articles, and 36 of them were selected for the full-text analyses. The experimental protocols and results were evaluated, and the gained knowledge was synthesized. A high level of heterogeneity between the studies was found regarding all assessed areas. The most consistent finding of all studies was a reduction in the ABR wave I amplitude following exposure to noise and salicylate. Simultaneously, animals with salicylate-induced but not noise-induced tinnitus had an increased amplitude of wave IV. Furthermore, the present study identified a need to develop a consensus experimental ABR protocol applied in future tinnitus studies using the rat model.
1. Introduction
Tinnitus is an auditory phantom perception despite the absence of external sound. Subjective, chronic tinnitus is diagnosed in humans of all ages, affecting about 16% of the adult population [1,2] and significantly decreasing the life quality of 1–3% of subjects with severe form [3,4,5]. Tinnitus may be a symptom of numerous conditions such as Meniere’s disease, diabetes, arterial hypertension, intracranial hypertension, or hearing loss. The latter, causative reasons, include exposure to noise or ototoxic drugs (i.e., salicylate, cisplatin, quinine) [6,7,8] and have been adapted to induce experimental tinnitus in animals.
A significant challenge during the tinnitus assessment in patients and animal models is the lack of objective diagnostic methods. To date, the clinical evaluation of tinnitus-induced distress is based on the psychometric scores or visual analog scales (VAS) dedicated to measuring various domains. The audiometric assessment of tinnitus (loudness, pitch, residual inhibition) uses the patient’s subjective statement. Similarly, audiometric properties of tinnitus in animals are tested using behavioral paradigms.
There are two established tinnitus induction methods used in animal models: overdose of salicylate and noise exposure [9,10]. Salicylate is known to cause reversible hearing loss and tinnitus in humans [11]. The pioneering work of Jastreboff et al., demonstrating that high doses of salicylate induce tinnitus in animals [10,12], introduced the salicylate-induced tinnitus animal model to basic research. All animals exposed to salicylate develop reversible and dose-dependent pantonal hearing loss co-occurring with tinnitus measured at roughly 16 kHz [9,13]. In contrast to salicylate, noise exposure does not always induce tinnitus. The induction rate varies from 30 to 80%, and the tinnitus frequency depends on the injured part of the auditory periphery [14]. Despite many differences between the salicylate- and noise-induced tinnitus, it is supposed that they share a common mechanistic pathway, converging at the inner hair cell-spiral ganglion neuron synapse [15].
The past decades brought progress in defining the objective, neural correlates of tinnitus. Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and electroencephalography (EEG) implicated the association of tinnitus with increased neural synchrony, reorganization of tonotopic maps, and increased spontaneous firing rates (SFR) [9,16]. Clinical studies also demonstrated changes in the auditory brainstem responses (ABR), which are possibly associated with tinnitus [17]. ABR is an early-response auditory evoked potential (AEP). During ABR, the electrical potentials consisting of five waves are isolated from the brainstem’s entire activity response to a calibrated sound. As a result of its objective nature, ABR is used clinically to estimate hearing thresholds of infants, young children, or adult patients who cannot undergo behavioral testing [18,19] and is an essential clinical tool for identifying retrocochlear lesions and vestibular schwannomas [20].
Moreover, ABR is applied in basic animal research to study age-related auditory changes, investigate the effect of therapeutic drugs on auditory potentials, and determine the mechanisms of diseases affecting the auditory system [21,22]. In rats, wave I of ABR associates with the activity of the peripheral auditory nerve. In contrast, waves II–V are thought to originate from the ventral cochlear nucleus, superior olivary complex, lateral lemniscus, inferior colliculus, and medial geniculate body [23]. The first ABR response was demonstrated in two-weeks old rats, whereas the mature ABR response consisting of five waves was observed in five-week-old rats [24].
The ABR amplitudes (II, III, and V wave) provide information about the ABR signal’s natural generators or modulators [25], whereas ABR latency (waves I–V) offers evidence about brainstem function [26]. It is supposed that the reduced amplitude of wave I and an increased hearing threshold might reflect the reduced sensory input found in tinnitus. In agreement with that, salicylate administration and acoustic trauma were found to reduce the ABR amplitude in experimental rats [27]. Nevertheless, the reduced amplitude could also reflect both signal reduction and desynchronization [28]. Therefore, the remaining necessary effort is to determine the ABR features that would indicate the presence of tinnitus independent of hearing loss. In agreement with that, ABR is frequently used in animal studies of tinnitus [29].
The present literature review attempted to extract and synthesize the knowledge about ABR assessment in rats with experimentally induced tinnitus (salicylate administration, noise, and blast exposures). The main goal was to determine whether there is a consistent impact of salicylate, noise, and blast-induced tinnitus on ABR features such as thresholds, latencies, and amplitudes. In addition, changes in the ABR profile of animals with tinnitus were scrutinized in the context of tinnitus-induction methods.
Our work focused on a rat model, and there were several reasons for this decision. The cochlear physiology and anatomy of humans and rats share similarities (e.g., two and a half cochlear turns) compared to guinea pigs (three and a half turns) [30]. Although the highest audible frequencies at 60 dB SPL of humans are 17.6 kHz and of rats 58 to 70 kHz, the lowest audible frequencies are similar (0.03 kHz for humans and 0.52 kHz for rats) [31]. In contrast to mice, early onset of age-related hearing loss (ARHL) has not been reported for rats. Rats can better tolerate noise exposure and rarely exhibit non-inner ear-related symptoms [32,33]. Auditory afferent periphery, believed to be involved during the process of tinnitus generation, has been much studied in rats more extensively than in any other animal model [34]. Importantly, unlike mice, rats do not develop aggressive behavior following noise exposure or salicylate administration [35]; however, they provide an acknowledged model for noise-induced hearing loss [36] and cochlear synaptopathy, which is consistent with hidden hearing loss [37]. Since 1988, rat remains the most prominent species used in tinnitus studies at the behavioral level [38,39]. Moreover, in the pharmacological studies dedicated to developing new tinnitus treatments, rats are a standard animal model [40]. Finally, our laboratory has a long-standing research interest in the effect of stress on the auditory system of rats [25,41,42].
2. Materials and Methods
For this study, a literature review was performed in August 2020. A search of the following databanks identified the articles:
- Science Direct
- The Search Engine Tool for Scientific (Scopus)
- US National Library of Medicine National Institutes of Health (PubMed)
- Web of Science
The keywords included the following combination of mesh terms:
- “auditory evoked potential” AND “tinnitus” AND “rat”
- “auditory brainstem response” AND “tinnitus” AND “rat”
- “ototoxicity” AND “tinnitus” AND “rat”
Full-text articles were downloaded when the title, abstract, or keywords suggested that the study is eligible for this review. The cardinal eligibility criterion was the publications in the English language. The further procedure of article selection followed the inclusion and exclusion criteria provided below:
Inclusion criteria:
- Articles published between January 2000 and August 2020
- Research dedicated to an animal model of tinnitus induced by salicylate administration (When in addition to salicylate, other drugs were applied, only the data related to salicylate were acquired), blast or noise exposure, when the authors used the ABR to measure auditory abilities of animals
- Using rats
- Original research
Exclusion criteria
- Literature review, editorials
- Full text not available
- Articles not published in English.
The search identified 344 studies. After applying the selection criteria, 36 publications were included in the analysis (Figure 1).
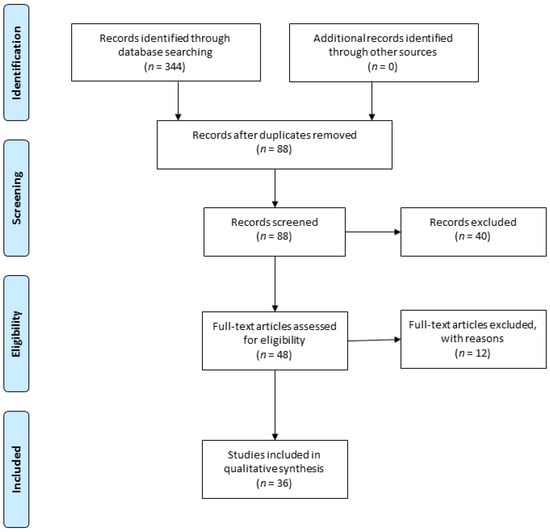
Figure 1.
PRISMA diagram of the study selection process [43]. “n” signifies the number of publications.
Detailed data extracted from the selected publications are summarized in the Supplementary Tables S1 and S2. The following information was collected:
- Aim of the article
- Age, sex, and strain of rats
- Sample size
- Methods used to induce tinnitus (salicylate, noise, blast)
- Methods used to determine the presence of tinnitus
- Stimulus and acquisition characteristics of ABR
- The system used to measure ABR
- Signal intensity
- Rate of signal
- Polarity of signal
- The placement of the electrodes
- Filters
- ABR protocols
- ABR outcome.
The extracted information was analyzed, and the knowledge was synthesized and presented in the Results section.
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection
Thirty-six studies published between January 2000 and August 2020 met the inclusion criteria. The publication date indicated that during the first decade of the 21st century, the research on that topic was published only sporadically (Figure 2), but the number of publications increased in the second decade.
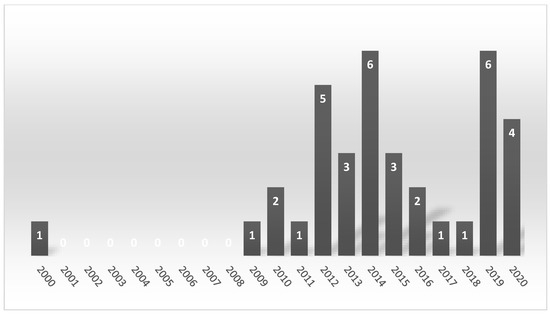
Figure 2.
The number of publications regarding auditory brainstem responses (ABR) and rat model of tinnitus per year.
3.2. Strain, Gender, and Age
In the articles selected for this review, Sprague–Dawley rats (both genders) were used in seventeen studies [13,28,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57]. Wistar rats were used in thirteen [15,27,29,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65], Long–Evans rats were used in four [66,67,68,69], and Fischer rats (FBN) were used in three studies [49,70,71]. One research group used Fischer 344 and Sprague–Dawley rats [49], two studies used both female and male Wistar rats [29,60], and one article did not provide information about the age of rats [45]. All rats were tested during the first few months of their life. No strain-related differences in the hearing thresholds were found [72,73]. However, compared to Sprague–Dawley rats, Wistar rats develop more aggressive behavior after noise exposure and salicylate administration [74]. Summarized data are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Rat strain, gender, and age.
In the studies using substance-induced tinnitus, the sample size varied from 4 to 69 animals. Remarkably, only seven of fourteen studies used a control group of animals [27,50,51,58,59,60,66]. In studies using blast- and noise-induced tinnitus, the number of analyzed animals varied from three to 137. Fourteen of the twenty-two studies had a control group [45,48,54,61,62,63,64,65,67,68,69,70,71]. Two articles did not provide information about the experimental and control group [15,45]. In three publications, there was missing data [45,62,63].
3.3. Methods Used for Tinnitus Induction
For the induction of tinnitus, three methods were used (Figure 3). In 14 articles, tinnitus was induced with salicylate [13,27,28,29,49,50,51,52,53,58,59,60,66]. Nineteen reports analyzed tinnitus after noise exposure [15,44,45,54,55,56,57,61,62,63,64,65,67,68,69,70,71] and three analyzed tinnitus after blast injury [46,47,48]. These publications were analyzed in one group because of the similarity in the blast- and noise-induced tinnitus mechanisms. They will be referred to as “noise-induced” throughout the rest of this review [75].
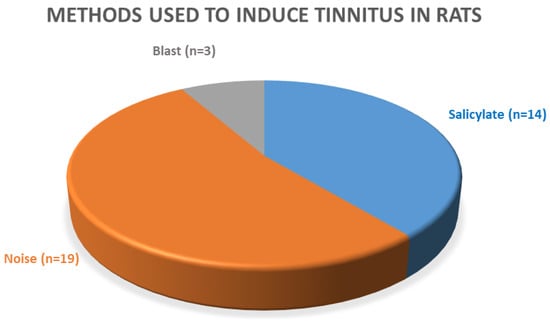
Figure 3.
Methods used to induce tinnitus in the selected articles (n = 36).
3.4. Methods Used to Determine the Presence of Tinnitus
The tinnitus-induction rate in rats exposed to salicylate was 100%, whereas the noise exposure resulted in a tinnitus-induction rate that varied from 30 to 80% [14].
Different methods were used to determine if animals have tinnitus. In studies with substance-induced tinnitus, the primary tinnitus-detection method was the gap-prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle (GPIAS) [13,27,51,52,58,59,60]. GPIAS is based on a hypothesis that assumes that the animals experiencing tinnitus have a fundamental deficit in hearing the silence. Therefore, unlike tinnitus-free animals, animals with tinnitus will not get startled when a sound is played after a short period of silence [44]. In comparison to an operant conditioned procedure, GPIAS does not require training [70]. The operant conditioned procedures require training, e.g., pressing a lever. That type of operant was successfully applied by one study to detect tinnitus [28]. However, six other studies could not determine tinnitus in rats using that method [29,49,50,51,53,66]. Another operant conditioned procedure was “conditioned lick suppression”. During the conditioned leak suppression, the animals choose between the drinking water source: one is a standard bottle, and the other is a spout. Rats are trained to drink from a spout during silence and suppress drinking from a spout during the sound presentation. A light electric shock is used to train the suppressive behavior of rats. If the rats develop tinnitus, they show suppressive behavior and do not use a spout for drinking. This method was used in six studies about noise-induced tinnitus [61,62,63,64,67,68]. In ten further studies, GPIAS was used [44,45,46,47,48,54,55,56,57,69,70]. The last operant-conditioned procedure used to determine tinnitus was a motor task (foraging behavior for sugar water) that was used in three studies [15,65], where animals with tinnitus actively execute the motor task even in the absence of external sound. Rats were trained 3–4 months before the noise exposure [65]. The ratio of activity during an external sound and during periods of silence was used to quantify the motor task [65].
3.5. Salicylate-Induced Tinnitus
Salicylate is commonly used to induce tinnitus in rats [38]. In addition to salicylate, quinine or cisplatin were used to study tinnitus in animals [76]. Despite the similarity in inducing tinnitus-like behavior in rats, the mechanisms behind salicylate- and quinine-induced salicylate are different [13]. Salicylate acts by changing the membrane potential and membrane properties [77]. It is a competitive antagonist for the chloride anion-binding site of prestin [78]—a motor protein of outer hair cells [79]. Additionally, salicylate may impact cochlear fast synaptic transmission via the activation of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) glutamate receptors, accounting for the occurrence of tinnitus [80] and, when administered systemically, it can directly affect the auditory cortex by reversibly depressing the inhibitory, γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-ergic neurons [81]. In contrast, quinine acts by altering the cochlear blood flow and the interaction with calcium channels and calcium-dependent potassium channels [77].
Nevertheless, the most commonly used substance in animal studies is a salicylate [38]. A high dose of sodium salicylate induces short-term, reversible tinnitus in rats, as demonstrated by Jastreboff [8,10]. The minimum dose needed to cause tinnitus in rats is 150 mg/kg [12]. Salicylate evokes changes in the peripheral and central auditory system [13,49,52,58]. In the auditory periphery, high doses of salicylate suppress the electromotility of the auditory outher hair cells (OHC) [78]. However, salicylate’s long-term administration increases the prestin expression in the OHCs [49].
In addition, salicylate reduces the amplitude of compound action potentials (CAP) and impacts ABR modulators [82]. The reduced CAP amplitudes in the rats following chronic salicylate treatment indicate long-term functional or structural damage to spiral ganglion neurons (SGN) [49]. The changes are also reflected by the ABR response (reduced amplitude). Nevertheless, the full mechanism of salicylate-induced tinnitus is still unclear.
In the selected studies, both acute and chronic treatments were used (Table 2). Of 14 selected studies, four used ABRs to determine the presence of tinnitus [28,29,50,60]. Two of them focused on developing a diagnostic method by joining ABR with a forward masker of tinnitus. Forward masking results from one stimulus producing temporal inhibition, thus suppressing the subsequent stimulus [28]. Forward masking can create an unmasking effect that results in a recovery of the suppressed ABR and could potentially be used as an objective indicator of tinnitus [29,60]. The method’s usefulness was demonstrated after a single injection of salicylate (300 mg/kg). In four other studies, a correlation between acoustic startle response (ASR) and ABR was examined in rats injected with a single dose of salicylate, 150 mg/kg [50]. In the last study, electrophysiological changes in auditory evoked potentials were analyzed after a 3-day treatment with 350 mg/kg/day [28].

Table 2.
Features of experiments with salicylate-induced tinnitus.
The mechanism of salicylate-induced tinnitus was studied in rats exposed to 200 mg of salicylate/kg/day for three weeks (5 days a week) [49]. The effect of salicylate on ribbon synapses was assessed in rats treated with 200 mg of salicylate/kg/day for ten consecutive days [27]. Changes in the II wave of ABR (representing ventral cochlear nucleus VCN) were examined after four and eight days of salicylate injection at 300 mg/kg/day [58].
3.6. Noise-Induced Tinnitus
The degree of noise-induced hearing loss depends on the noise intensity, exposure duration, distance from the noise source, spectrum, and interval length [83]. Only about half of noise-exposed animals developed tinnitus in the research selected for this review [54,64,65]. Despite that, only five of the 22 publications divided the rats into groups with and without tinnitus [15,48,65,67,69]. The effect of noise can be mechanical or metabolic [32]. The mechanical effects of noise include loss of either tip links between hair cells or disruption of actin organization in stereocilia. The metabolic impact involves the generation of oxidative stress that may interfere with hair cell function and neurotransmitter release [32].
The Noise Characteristics
The parameters of noise in the animal model are variable. Typically, rats are subjected to high-level noise for 1 to 2 h, binaural or unilateral (when plugged contralateral ear). Mainly, noise characteristics involved 16 kHz, 110–120 dB SPL [45,54,55,56,57,61,62,63,64,67,68]. In three studies, narrow-band noise consisted of 10 kHz and sound level (80–120 dB SPL), and a duration between 1 and 2 h [15,65]. Two researchers’ groups subjected rats for one hour to 116–120 dB SPL and 12 or 17 kHz [44,71].
Binaural exposure to a 10 kHz for 1–2 h led to tinnitus when the sound level was 120 dB SPL but not 80–110 dB SPL [65]. The characteristics of noise used to induce tinnitus are summarized in Table 3.

Table 3.
Features of experiments with noise-induced tinnitus.
The frequency used for acoustic exposure impacts the distribution of noise-induced effects along the cochlea and within the brain [84]. The most significant influence of narrow-band noise was often observed above the noise used [32]. The hearing loss accompanying tinnitus was located in the high-frequency range. The hearing loss, hair cell loss, and changes in the central auditory system are less predictable when using broad-band noise than narrow-band noise [38]. Occurred changes also depend on the sound pressure level (SPL) and the experiment duration [85]. It was demonstrated that only rats subjected to 122 dB SPL for two hours demonstrated elevated hearing thresholds (tested: 0.5 to 2 h, 110, 116, and 122 dB SPL, 16 kHz octave band noise (OBN)) [70].
Unlike the others, one research group used more than one unilateral acoustic trauma, the first being 10 kHz, 118–120 dB peak SPL for two hours, and the second (5 weeks later) of identical characteristics, but applied for three hours [69]. In the research regarding blast-induced tinnitus, a single or three consecutive blasts exposures (194 dB), unilateral and bilateral, were used [46,47,48]
ABR in the selected studies was used to assess hearing loss after noise trauma, determine short- and long-term changes in ABR after the noise, and study the efficacy of drugs for hearing loss.
During most studies using noise and blast exposure, rats were anesthetized. However, there were two exceptions [45,69]. In the first work, rats were held in a slowly rotating hardware cloth cage [45,69]. In the second study, rats were subjected to two noise exposures (51). To avoid the protective effect of isoflurane against hearing loss [86], rats were awake during the second exposure (51). Two articles did not provide information about anesthesia during noise exposure [55,68].
3.7. Methods of ABR Measurement
3.7.1. ABR Recording Systems
Two commercially available systems—Tucker Davis Technologies (TDT) and Intelligent Hearing Systems (IHS)—were used to record ABR. The majority of the groups used the TDT system [13,27,29,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,58,59,60,62,66,69,70]. Three research groups used the system [28,51,89], whereas two other groups used both systems [67,68]. Ten articles provided no information about the system used [15,56,57,61,62,63,64,65].
3.7.2. The Stimulus Signal
ABR responses were elicited by click [15,46,47,48,54,65,66,68,69,71] and tone burst stimuli [13,15,27,28,29,44,45,46,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,57,58,60,61,62,63,64,65,67,68,69,70,71]. The majority of the research teams used a 3–5 ms tone burst [13,15,28,29,44,45,49,51,53,54,55,57,58,59,60,61,62,64,65,66,67,69,70,71]; five groups applied tone bursts of longer duration, 6–10 ms [46,50,54,68,69]. Fives articles did not provide information about signal [27,48,51,53]. Acoustic stimuli were delivered at <4 kHz [47,65]; 1–45/50 kHz [15,65]; 2.5–40 kHz [45]; 6–16 kHz [29,50]; 8–16 kHz [51]; 4–20 kHz [53]; 4–30 kHz [54]; 2–24 kHz [59]; 4–32 kHz [28,49,66]; 6–20 [44]; 6–32 [28,49,52]; 8–20 kHz or 8–32 kHz [51,55,58,62,63,64,67,70,71]; and 10–32 kHz [56,57]. Sound stimuli were presented at a rate of 10–11 [13,55,65,66], 17–19 [50,53], 20–21 [13,28,44,49,51,55,58,59,63], 29–30 [45,70], or 50 [47,51,56,57,61,62,64,69,71] bursts/s. Eight articles did not provide information about repetition rate [15,27,29,46,48,54,60,68]. Sound stimuli were presented directly to the ear canal [28,44,45,46,48,49,50,51,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,67,69,70] or in free field [13,29,52,53,65,68]. The distance between the speaker and ear were 1 to 10 cm [13,29,52,53,65,68]. Eleven articles provided no information about signal delivering [15,27,47,50,54,55,62,63,64,66,71].
3.7.3. Signal to Noise Ratio and Thresholds
Original data were averaged to achieve an increase of the signal to noise ratio. To estimate thresholds, the number of averageness was 512 [51,58,66] or 1000–1024 [13,28,52]. When the amplitude and latency were analyzed, it was 64–256 [15,65], 200 [60], 300–400 [45,46,47,48,54,69], 512 [53,55,68,70], 600 [49], or 1000–1024 [28,56,57,71]. The sound intensity levels gradually decreased from 110 dB SPL in 5–10 decrements. Five reports did not provide this information to estimate hearing thresholds [44,61,62,63,64]. Click (100 μs) was also used to estimate recovery after noise exposure to calculate the correlation factor (corF) [15,65]. The corF reflects changes in waveform and amplitude before and after noise exposure. High values (around 1) of corF reflect the similarity in a waveform, whereas low values (around 0) indicate loss of both waveform similarity and amplitude [15,65].
3.7.4. Electrode Placement
In the majority of the studies, three stainless-steel recording electrodes were inserted subcutaneously: one on the mastoid of the tested ear (reference electrode), one on the vertex (active), and one on the contralateral mastoid (ground) [13,27,46,47,48,51,52,59,65,69]. Some research groups placed the ground electrode on the back of animals [15,50,62,65,71], on the occiput [61,62,63,64], on the leg [45,67,68,70], or on the nose [29]. One research group placed electrodes on the vertex and ipsi- and contralateral mastoids [54]. In two studies, four electrodes were located at the vertex (active), mastoids (references), and the ground electrode was located on the nose tip [60] or on the back [28]. In four papers, electrodes were placed atypically [53,56,57,58]. Two studies have not provided information regarding electrode placement [44,51].
3.7.5. Filters and Polarity
Only a few publications provided information about filters, polarity, and electrode impedance. Averaged ABR waveforms were bandpass-filtered between 30 Hz and 3 kHz [28]; 100 Hz and 1.5 kHz [51]; 100–3 kHz [13,44,51,52,53,68,70,71]; 10–3 kHz [49]; 300–3 kHz [29,45,46,47,48,54,56,57,60,69,71]; 200 Hz and 5 kHz [65]; or 300–10 kHz [66]. The notch filter was 50 Hz or 60 Hz [29,46,47,48,49,53,60]. The polarity was alternating [49,53,65,66].
3.8. Protocols Used for ABR Recordings
3.8.1. Anesthesia
Before the ABR measurement, the rats were anesthetized. The majority of the groups used a mixture of ketamine–HCl and xylazine (ratio: 5:1; 9:1; 1:2:21:1; 6:1; 16:1) [15,27,28,45,48,50,56,57,58,65,66,69,70,71]. In eight publications, isoflurane (4%, 1.5%) was used [13,44,46,48,49,54,67,68]. In addition, chloral hydrate was applied in three cases (0.6 mL/100 g or 400 mg/kg) [29,59,60]. In five studies, instead of xylazine, medetomidine HCl was injected [61,62,63,64]. In one study, a mixture of Zoletil 50 and Rompun 2% or Zoletil (40 mg/kg) + xylazine (10 mg/kg) were used [51,55]. One research group used only ketamine [52], whereas two groups provided no information about the anesthesia [51,68]. In one study, instead of anesthesia, restraint was used [53].
3.8.2. Additional Information
During ABR measurement, animals’ body temperature (37.5 ± 1 °C) was maintained by either a non-heating pad or a warm blanket [28,45,46,47,48,49]. In one study, the body temperature was controlled by maintaining the temperature of 25 °C in a sound-proof room [58]. Even though changes in body temperature modulate brainstem functions [90], most articles have not provided information about maintaining body temperature during measurement [13,15,27,29,44,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71]. Electrode impedance ranged between 1–3 kΩ [29,49,51,53,60].
Detailed information extracted from each publication is presented in Table S2 in the Supplementary Materials.
3.9. ABR Evaluation after Salicylate Treatment
The ABR was used to study whether salicylate induces long-term changes in the auditory system [13,28,50,51,52,59,66], to assess the brainstem function following salicylate administration [28,29,50], and to analyze the effect on ABR modulators [27,28,29,49,53,58,60].
3.9.1. Hearing Thresholds after Salicylate Treatment
Exposure to salicylate at 400 mg/kg for seven consecutive days increased hearing thresholds at two tested frequencies (8 and 16 kHz) (on the seventh and eighth day of the experiment). Ten day-long exposure of rats to salicylate at 200 mg/kg/day has not altered the thresholds measured between 2 and 24 kHz compared to the control group [51]. In addition, no changes in hearing thresholds between 6 and 32 kHz were recorded two weeks after the rats’ exposure to salicylate (300 mg/kg) for four consecutive days [52]. The thresholds between 8 and 32 kHz were not affected by a single injection of 350 mg/kg, two hours after drug administration [51]. Studies comparing hearing thresholds during (1–3 days) and after exposure (4–6 days) demonstrated restoring hearing abilities after salicylate cessation. During and two days after the exposure, hearing thresholds were elevated at 4–32 kHz. On the 6th day of the experiment, the threshold shift recovered (elevation at 16 kHz) [28].
Four weeks of exposure to 8 mg of salicylate/mL in water influenced the hearing abilities. A higher mean threshold (at 4–32 dB) was detected in the treated animals compared to the control group, 38 vs. 35 dB, after salicylate cessation [66].
Duron et al. examined changes occurring in auditory function 30–90 min after a single injection of 150 mg/mL in Sprague–Dawley rats (43). Already 1–1.5 h after injection, thresholds were elevated (6–16 kHz). The shift was more remarkable at higher frequencies, increasing by about +8.5 dB at 6 kHz to +17.5 dB at 16 kHz [50].
3.9.2. Effects of Salicylate on ABR Amplitudes and Latencies
The administration of salicylate (300 mg/kg) for eight consecutive days has reduced the ABR amplitudes in all tested frequencies (8–32 kHz, 70 dB) when measured eight days after salicylate cessation. One week later, the reduction of amplitudes lessened [58]. A lower concentration of salicylate (200 mg/kg) applied for ten days has not changed the thresholds, but the reduced amplitude wave I at 2–24 kHz was observed [27]. With a higher concentration of salicylate (350 mg/kg) applied over three days, the amplitude of wave I was reduced, whereas the changes in amplitudes of waves II and IV were seen only on the first day. Wave V was not affected by salicylate [28].
In contrast, wave V’s amplitude was reduced at 12 kHz after a single salicylate injection (250 mg/kg) for at least three days after injection. The amplitude of wave II was also reduced in a broader range (4, 16, and 20 kHz) [53]. Waves IV and I were reduced at 16 kHz 90 min after a single dose (150 mg/kg) [50]. The reduced amplitude of wave III after prolonged exposure to salicylate (3 weeks, five days a week) persisted from 3 days to 4 weeks after cessation [49].
In conclusion, wave I’s amplitude decreased, whereas wave IV’s amplitude increased after salicylate exposure [28,49,50,53,58]. The amplitude of wave III was not affected by a short treatment (1–3 days), but prolonged exposure to salicylate caused the amplitude reduction [28,49,50,58]. The decrease of ABR amplitude was seen even though the threshold was not affected [27]. There was a correlation between the presence of tinnitus and decreased amplitude observed in male Wistar rats. In agreement with that, the return of amplitude to the baseline level correlated with subsidence of tinnitus (based on GPIAS) [58].
A single dose of salicylate (150 mg/kg) affected the latency of wave I and IV. Ninety minutes after salicylate administration, wave I was prolonged at 6, 10, and 12 kHz, whereas the latency of wave IV was reduced (only if measured at 10 kHz) [50]. Intervals III–IV decreased at 6 kHz 60 min after salicylate injection. The changes in latency of wave I were not observed after ten days of exposure to salicylate at the concentration of (200 mg/kg) [27]. The reduced latencies of waves I–IV at 6, 16, and 28 kHz (tested between 4 and 32 kHz) were observed during treatment and one day after salicylate cessation (350 mg/kg/day for three days). On days 2–4th after cessation, only latency II–IV at 32 kHz was prolonged [28]. Changes in latencies were dose-dependent [27,28,50]. Assessment of individual ABR waves revealed alternations dependent on the stimulus frequencies (Table 4).

Table 4.
Salicylate-induced changes in ABR amplitude and latency.
3.10. ABR Evaluation after Noise Exposure
ABR was used to assess the capacity of noise injury to induce the auditory threshold shift [15,44,54,55,56,57,61,62,63,64,65,68,69,70,89]. To estimate the recovery after noise trauma, ABR Waveform Correlation was used [15,65]. Following blast exposure, hearing thresholds and wave I amplitude were analyzed [46,47,48].
3.10.1. Hearing Thresholds after Noise Exposure
Rats subjected to acoustic trauma had elevated hearing thresholds, and the unilateral noise exposure injured only one side. Observed elevated thresholds depended on the noise parameters. Immediately after unilateral noise exposure (16 kHz, 115 dB SPL for 1.5 h), the hearing thresholds in exposed ears (threshold: 70–90 dB peSPL) were higher than in control. Six weeks later, the thresholds were still elevated (70–90 dB peSPL) [56,57]. Four to six weeks after noise exposure, all rats (n = 11) presented behavior consistent with tinnitus perception (measured by GPIAS) [57]. Unilateral exposure to noise for one hour (16 kHz, 110 dB) evoked a significant increase in the hearing thresholds at 8–20 kHz in the affected ears (immediately after noise) [61,62]. Simultaneously, five of eight animals tested positive for tinnitus (based on lick suppression task) [62]. Immediately after noise exposure (16 kHz, 116 dB, 1 h), rats had elevated mean threshold (+30–50 dB at 8–32 kHz) [68].
Following noise exposure (8–16 kHz, 115 dB for two hours), the thresholds remained higher for one month in the stimulated ears (threshold: 50–60 dB peSPL), which was not observed in the contralateral ears (thresholds: 20–40 dB peSPL) [54]. After acoustic trauma, four of six rats developed tinnitus (as per GAP detection) [54]. Shorter acoustic exposure (16 kHz, 115 dB, 1 h) induced tinnitus in about 50% of rats (14 animals of 30) tested with a conditioned lick suppression task [64]. The thresholds shift recovered six months after the exposure to noise [63,64].
Long-term hearing loss was observed after a single, unilateral exposure to 120 dB, 16 kHz for one hour. The elevated threshold persisted for 14 months [67]. Although the hearing loss was demonstrated in all rats, not all of them developed tinnitus. Nine months after noise exposure, no differences in thresholds were observed between the noise-exposed rats without tinnitus and the control animals [67]. Restoration to baseline levels after single, unilateral noise (17 kHz, 116 dB for one hour) was observed 16 weeks after noise exposure [71]. At the same time, 10 of 14 noise-exposed rats developed tinnitus at the frequencies between 24 and 32 kHz, as assessed by GAP detection [91].
Rats exposed to 10 kHz, 120 dB for two hours had elevated hearing thresholds at frequencies higher than 8 kHz in exposed ears for at least 15 days following noise exposure (frequencies tested: 1–50 kHz) [15]. While there were no differences in hearing thresholds between tinnitus-positive and -negative animals, rats with lesser tinnitus had a slighter reduction in the number of synapses on inner hair cells [15]. The difference in hearing thresholds in rats with and without tinnitus was described by Rüttiger et al. [65]. Rats with noise-induced tinnitus (binaural exposure for one hour, or one and a half hours, 10 kHz, 120 dB SPL) had a significantly larger hearing loss than rats without tinnitus. Six days after one-hour noise exposure, the hearing loss in frequencies above 11.3 kHz was considerably higher than the tinnitus-free group. Thirty days after 1.5 h noise exposure, an elevated hearing threshold in animals with tinnitus was also significantly greater at low frequencies (tested: 1–45 kHz). Tinnitus was determined in five of 15 and five of 17 rats, respectively (the motor task) [65]. The lower intensity of the above noise (<120 dB, 10 kHz, 1–2 h) did not evoke elevation in hearing thresholds in Wistar rats [65].
The selected studies detected different patterns of audiometric changes following noise exposure. Two hours after single unilateral noise exposure (12 kHz,120 dB, one-hour exposure), ABR thresholds increased by about 30–45 dB at 12 kHz (tested range: 6–20 kHz). While some rats developed permanent hearing loss (>2 weeks), other animals’ hearing abilities recovered within three consecutive days. The changes were absent in contralateral ears [44]. The observed differences might be related to the used outbred rat strain (Sprague–Dawley). A different pattern was observed in other studies when acoustic exposure of 16 kHz, 116 dB for two hours, was used [45]. After one week, an increase in hearing thresholds between 2.5 and 40 kHz was observed between SPL 10 and 40 dB [45].
Turner et al. demonstrated that noise with an intensity below 122 dB SPL (16 kHz, 0.5–2 h) did not evoke changes in the hearing thresholds two hours after exposure (8–32 kHz) [70]. That observation was confirmed by the study of Kim et al. Despite extended noise exposure time (four hours), the next day, no elevated hearing thresholds (8–32 kHz) were determined in the experimental animals [55].
The effect of two exposures on behavior consistent with tinnitus perception was demonstrated in Long–Evans rats. Following 1 to 8 weeks after two noise exposures (10 kHz, 118–120 dB, 2 and 3 h), rats with tinnitus had broader hearing loss than rats without tinnitus (8–28 kHz vs. 12–28 kHz, respectively). Tinnitus was demonstrated in 12 of 18 rats (GPIAS) [69].
Bilateral blast (194 dB for 10 ms) produced an immediate elevation in hearing thresholds from 39 to about 62 dB peSPL at frequencies less than 4 kHz [47]. On days 14, 28, and 90, after the blast, thresholds recovered to 37.86 dB SPL, 30.71 dB SPL, and 27.86 dB SPL, respectively [47].
In another study, 14 days after a single unilateral blast, the hearing level of animals returned to baseline [47]. In contrast, Sprague–Dawley rats, following a unilateral blast, had elevated hearing thresholds between eight and 28 kHz in both ears one day after blast exposure. Three to six weeks later, threshold elevation was still observed but only in the frequencies between 16 and 28 kHz and only in the blast-exposed ears [46].
In the selected studies, not all animals developed tinnitus. Unfortunately, only a few studies performed audiometric analyses of the animals with positive behavioral tests indicative of tinnitus [65,67]. These analyses demonstrated differences in the hearing thresholds between the animals with and without tinnitus. After the noise exposure, rats with tinnitus had increased hearing thresholds [65] and a broader hearing loss than the noise-exposed animals without tinnitus [69]. Rats with tinnitus had elevated thresholds at 8–28 kHz, whereas rats without tinnitus had elevated thresholds at 12–28 kHz (following two noise exposures). Nevertheless, there was no correlation between threshold shift and GPIAS results [69]. In disagreement with the above results, Brozoski et al. [67] observed no differences in hearing thresholds between rats with and without tinnitus.
3.10.2. Effects of Noise on ABR Amplitudes and Latencies
The influence of noise exposure on the alternation and recovery of the ABR waveform was analyzed by calculating the click-induced ABR waveform correlation factor (CorF) [15,65]. The CorF reflects changes in waveform and amplitude [65] before and after noise exposure. High values (around 1) of corF are indicative of similarities in waveforms, whereas low values (about 0) indicate loss of both waveform similarity and amplitude [15,65]. Fifteen days after single noise exposure (10 kHz,120 dB, two hours, unilateral), the overall ABR amplitude was reduced. Simultaneously, the ABR threshold was elevated at frequencies higher than 8 kHz (assessment of 1–50 kHz) [15]. Moreover, a negative relationship between tinnitus and a number of synaptic contacts on the inner hair cells was observed (tinnitus test: the motor task), as reflected by the ABR wave I [15].
While the ABR waveform of rats exposed to noise (10 kHz, 110 dB for two hours) was restored within two weeks, rats exposed to higher noise intensity (120 dB) had distorted ABR waveforms and reduced amplitude two weeks after noise trauma [65]. The overall amplitude reduction was observed in rats 6–30 days after bilateral noise exposure (10 kHz, 120 dB, 1 or 1.5 h) [65]. Compared to tinnitus-free rats, rats with tinnitus had a reduced hearing recovery 6 and 30 days after noise trauma [65]
After the unilateral blast, the threshold recovered fully within five weeks (8–28 kHz), whereas the amplitude of wave I at 28 kHz was still reduced [48]. Tinnitus was determined in eight of 13 animals (GPIAS). There were no differences in ABR between tinnitus and tinnitus-free rats, and the ABR amplitudes were reduced in all exposed rats [48]. In summary, noise exposure induces ABR amplitude reduction. Table 5 summarizes the observed changes.

Table 5.
Changes in amplitude in rats after noise exposure.
Some common similarities determined in ABR amplitudes after salicylate and noise exposure are presented in Figure 4.
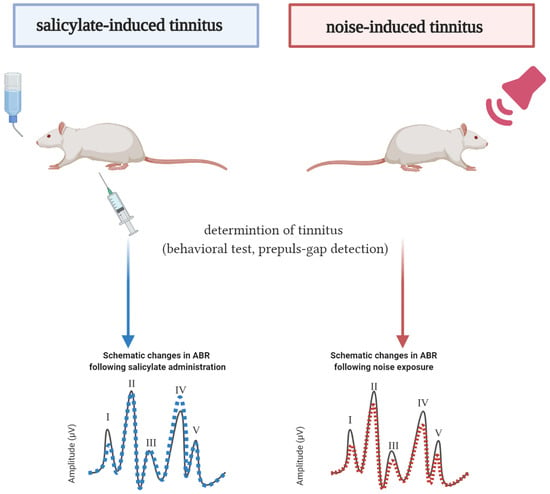
Figure 4.
Schematic representation of the ABR profile’s similarities and differences between the control rats and animals with tinnitus (created with BioRender.com). Of 36 publications included in this review, four publications regarding noise-induced tinnitus and six publications regarding salicylate-induced tinnitus qualified for the quantitative ABR analyses. The solid black line represents the ABR of the control animals. The dashed blue line represents the ABR of rats with salicylate-induced tinnitus [27,28,49,53,58,59]. The red dashed line represents the ABR of rats with noise-induced tinnitus [15,65]. Only the changes consistently reported by two or more studies were taken into account. The changes in latencies are not presented due to inconsistencies between the studies.
4. Discussion
This review aimed to evaluate the auditory brainstem response changes occurring in rats’ auditory systems after experimentally induced-tinnitus. Thirty-six studies published between January 2000 and August 2020 and dedicated to the rat model met the inclusion criteria. Based on the selected studies, we summarize the knowledge of audiometric changes occurring in tinnitus using ABR.
In the selected articles, the principal inducers of tinnitus (noise and salicylate) were used. Rats exposed to salicylate had changes in hearing thresholds and ABR waveforms in specific frequencies [49,50,51,53,59]. Despite considerable differences between the studies, two consistent parallels were identified. The first similar finding was a consistent reduction in wave I and increased wave IV (Figure 4). The reduction of the wave’s I amplitude reflects changes in sensory input. Although there was no significant hair cell loss, a decrease in ribbon synapses was observed [27,59]. In addition, abnormalities in both presynaptic elements and postsynaptic nerve fibers were observed [27]. Reduced sensory input could have lead to the enhanced auditory midbrain responses such as the increased amplitude of wave IV, reflecting changes in the inferior colliculus [65]. In contrast to the salicylate treatment, the noise has induced a reduction in the amplitude of wave IV [15]. The imbalance in excitation and inhibition occurring on the level of inferior colliculus might contribute to tinnitus development [92].
The relation between behavior consistent with tinnitus and the ABR changes was investigated using the female Sprague–Dawley rats exposed to salicylate (350 mg/kg/day for three days, gavage administration) [28]. There was a correlation between tinnitus behavior and changes in ABR amplitude (waves II–V) and latency (waves II and III) [28]. Such association was observed only for specific frequencies (4, 8, 16, and 32 kHz). Nevertheless, upon the return of amplitudes to the baseline level, tinnitus behavior disappeared. There was no association between the amplitude and latency of wave I and hearing thresholds [28]. Fang et al. observed that ABR amplitude was reduced when cochlear sensitivity improved (increased amplitude of the distortion product otoacoustic emissions—DPOAE) [58].
While salicylate evoked tinnitus in all rats, only half of them demonstrated tinnitus after noise exposure [14]. A higher hearing threshold and amplitude reduction were observed in rats subjected to acoustic trauma. After single noise exposure (16 kHz, 120 dB, 1.5 h, bilateral) and two noise exposures (10 kHz, 118–120 dB peSPL, two hours; then five weeks later for three hours, unilateral), rats with tinnitus had higher hearing thresholds than tinnitus-free animals [65,69]. This difference was not observed in rats exposed to 16 kHz, 120 dB for one hour [67]. The variance seems to be an effect of different noise parameters and various times of ABR assessment.
Some differences were also observed regarding the auditory inner hair cells (IHC) synaptic contacts in rats with and without tinnitus [15]. After noise exposure (10 kHz, 120 dB for 1 or 1.5 h), a greater reduction of ribbon synapses in basal and mid-basal turn was observed in rats with tinnitus [65]. No loss of ribbon synapses was seen in the cochlear apical turn after salicylate treatment or noise trauma [60,65]. Cochlear deafferentation depends on the degree of inner hair cell synaptopathy. Two of the studies included in the present review confirmed the notion about the loss of IHCs ribbon synapses (deafferentation), leading to tinnitus when the ABR was reduced. Upon the restoration of ABR, tinnitus was no longer observed [65], indicating that the degree of IHC ribbon loss might be a crucial factor for the recovery of ABR after acoustic trauma and tinnitus generation [65].
In one article, restraint was used during ABR measurement [53]. Restraint applied for four hours was previously shown to impact animals’ hearing abilities by inducing stress and the hypothalamus–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis, thus increasing the systemic levels of corticosterone, which protected animals from the acoustic trauma [89]. Rats subjected to restraint demonstrated abnormalities in CAP and DPOAE. Interestingly, another type of stress—social stress—induced an increase in IHC ribbon synapses [65]. Furthermore, repeated injections might also be a source of anxiety for animals [93]. In the process of data evaluation, we compared hearing thresholds at baseline between mock-injected and non-injected animals and found that the injected rats had higher hearing thresholds by about 10–20 dB [61,62,63,64], which has so far not been reported.
It has been suggested that tinnitus can internally mask the ABR [94]. Therefore, ABR with a forward masker is supposed to be an objective indicator of tinnitus and was used after salicylate treatment in female and male Wistar rats. The forward masker and the probe were presented to both ears. After the above stimulation, rats had a reduction in ABR amplitude and prolonged latencies (I–V). This was not observed in rats treated with salicylate [29,60]. Additional experiments with a larger sample size should be performed to address this exciting issue.
The data extracted and analyzed in the present review suggest that a loss of cochlear inner hair cell ribbon synapses could contribute to the development of tinnitus reflected by reducing the amplitude of wave I, which was also observed in human studies [17]. Some studies suggest measuring abnormalities in wave V’s latency to indicate cochlear synaptopathy in humans after noise exposure [95]. The term “cochlear synaptopathy” was proposed to describe damage at the cochlear synapse without any loss of hair cells, resulting in “hidden hearing loss” [96].
The eardrum perforation is one of the most frequent injuries after blast exposure [91]. Despite the middle ear’s known impact on ABR response, none of the articles dedicated to the blast injury provided information about the middle ear status after blast [46,47,48].
The factors that could affect ABR are summarized in Table 6. It is our recommendation to use this summary as a template for the experimental outlines.

Table 6.
Factors possibly influencing ABR response.
Several limitations were identified in the data collected. The first limitation was a lack of precise information about the experimental protocol during ABR measurements such as animals’ body temperature or anesthesia. Both of these factors could influence the ABR recordings. Each decrement at 0.5 °C of the body temperature may significantly alter ABR latencies and amplitudes [105,106]. What is more, rats anaesthetized with isoflurane (1.5–2%; 4%) have higher hearing thresholds in comparison to thresholds after an administration of ketamine + xylazine (50 mg/kg + 9 mg/kg) [101,103]. One study reported a lack of amplitude differences after blast exposure between the rats anesthetized with isoflurane (4%) or ketamine. However, other researchers observed poorer ABR responses after isoflurane (dose not known) [48,70]. What is more, there are no studies on the impact of anesthesia on substance-induced tinnitus.
The second limitation was a variation in the frequencies tested by ABR. While the standard testing range includes <4 to 24/32 kHz, some selected papers provide information only for single frequencies [97].
The third pitfall is various techniques used for ABR recording, such as signal delivery. Acoustic stimuli were delivered directly to the ear or in the free field. These different conditions may also contribute to the differences in latencies and amplitudes reported.
The fourth limitation was a high sample size variation, which might have impacted the results (e.g., reduction, improvement vs. no changes in amplitude of wave II, III, and V) in rats following salicylate [28,49,50,53,58]. Nevertheless, the sample size was not used as an exclusion criterion because of our review’s character.
The fifth limitation is not reporting whether the gender differences influenced rats’ hearing abilities [29,60]. Older male rats (8–24 months old) had higher ABR thresholds and overall smaller amplitude than female rats. Despite the lack of ABR differences between young female and male rats, adult female rats had shorter latencies (I–IV) than the male rats [100,107]. Various studies also demonstrated a link between hearing thresholds and the menstrual cycle [111,112], suggesting that the estrous cycle phase should be considered when using female rats.
The sixth limitation is the variety of methods used to determine the presence of tinnitus in rats.
The studies using ABR for the evaluation of experimentally induced tinnitus in the rat model demonstrated differences in hearing abilities after tinnitus induction. Observed changes depended on the drug dose, noise intensity, time point of audiometric measurement, and frequency used during ABR measurement. Differences in results were also observed even if the experiments were conducted by the same research group [27,59].
All the above limitations indicate a great need to create a universal protocol, at least for each research group, if not for all of them. Nevertheless, the most consistent finding across all studies was a general reduction of ABR amplitudes in the animals experiencing noise-induced tinnitus. In contrast, In rats with salicylate-induced tinnitus, the amplitude of wave I was also reduced, but the amplitude of wave IV increased.
Clinical studies in tinnitus patients with normal hearing (frequency 0.25–8 kHz) demonstrated reduced amplitude of wave I at high intensities (80–90 dB SPL). The amplitude of wave V was not affected compared to the control group [113]. Despite the reduction of wave I, a normal wave V, might be an effect of increased neural responsiveness in the central auditory system to compensate for the reduced activity of the auditory nerve [113]. No differences in the amplitude of wave V in tinnitus patients and an average hearing threshold were also described in the study of Kehrle et al. [114]. In contrast, Gu et al. observed a higher amplitude of wave V in patients with tinnitus [115]. The authors suggested that wave’s V higher amplitude is an artifact induced by a lower frequency filter cutoff [115]. To sum up, ABR amplitude changes were determined in patients with tinnitus and normal hearing thresholds (based on pure tone audiometry). Reduction in the amplitude of wave I likely indicates a cochlear synaptopathy, whereas the unchanged or elevated amplitude of wave V could reflect central regions’ compensated responses [17].
Studies in patients with tinnitus and high-frequency hearing loss demonstrated greater amplitude of wave III than in the control group without tinnitus (threshold-, sex-, and age-matched) [116]. Interestingly, such differences were not observed in a previous study published by the same group. Nevertheless, the mean ABR amplitudes tended to be reduced [117].
In 2017, a review dedicated to studying changes in the ABR of patients with tinnitus was published [17]. The results indicated a high level of heterogeneity between the clinical studies. This heterogeneity was attributed to different etiologies of tinnitus, gender, age, and various protocols used for ABR recording. Similar diverseness was observed in our review. Interestingly, similar to ABR’s study in individuals with tinnitus, animal studies’ most consistent finding was a reduced amplitude of wave I. Despite the similar methods for tinnitus induction in animal studies, there is still a considerable heterogeneity of results suggesting a possible intrinsic heterogeneity of tinnitus and the importance of using a standardized universal protocol to perform the experiments.
5. Future Directions
For future studies, we acknowledge using the rat model as offering three significant advantages: (i) the presence of similarities in the phantom character of tinnitus between rats and humans; (ii) the ability to perform the audiometric measurements before and after tinnitus onset; and (iii) the possibility to control and modify experimental factors influencing tinnitus. However, in future investigations, sufficient details regarding the tinnitus induction and ABR protocols (factors listed in Table 6) should ensure the data reproducibility and facilitate future work.
6. Conclusions
The publications included in the present review provided audiometric characteristics of hearing loss and contributed to a better understanding of tinnitus in the rat model. In animals with salicylate-induced tinnitus, ABR waves had a shorter latency as in the control animals, reduced amplitude of wave I, and increased amplitude of wave IV. In contrast, in animals with noise-induced tinnitus, all ABR waves had reduced amplitudes, implicating that salicylate and noise induce different changes in the auditory brainstem which still result in the tinnitus percept. Contrasting changes in the amplitude of wave IV could reflect fluctuations in the auditory processing that are not related to tinnitus but might be associated with the cause of tinnitus. The overall evidence collected in the present work urges to establish a universal protocol for electrophysiological recording and animal handling in future animal studies on tinnitus.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3425/10/12/901/s1, Table S1: Extracted data regarding tinnitus characteristics and tinnitus-relevant changes in ABR, Table S2: Extracted data regarding ABR setups.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.D. and A.J.S.; methodology, E.D. and A.J.S.; validation, E.D. and A.J.S.; formal analysis, E.D. and A.J.S.; investigation, E.D.; resources, A.J.S.; data curation, E.D. and A.J.S.; writing—original draft preparation E.D.; writing—review and editing, E.D., H.O. and A.J.S.; visualization, E.D. and A.J.S.; supervision, H.O. and A.J.S.; project administration, A.J.S.; funding acquisition, A.J.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by European Commission Action HORIZON 2020, TIN-ACT (Research School for TINnitus Assessment, Causes and Treatments) grant number 764604/ESR11.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dawes, P.; Fortnum, H.; Moore, D.R.; Emsley, R.; Norman, P.; Cruickshanks, K.; Davis, A.; Edmondson-Jones, M.; McCormack, A.; Lutman, M.; et al. Hearing in middle age: A population snapshot of 40- to 69-year olds in the United Kingdom. Ear Hear. 2014, 35, e44–e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCormack, A.; Edmondson-Jones, M.; Fortnum, H.; Dawes, P.D.; Middleton, H.; Munro, K.J.; Moore, D.R. Investigating the association between tinnitus severity and symptoms of depression and anxiety, while controlling for neuroticism, in a large middle-aged UK population. Int. J. Audiol. 2015, 54, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makar, S.K.; Mukundan, G.; Gore, G. Treatment of Tinnitus: A Scoping Review. Int. Tinnitus J. 2017, 21, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, J.A.; Dennis, K.C.; Schechter, M.A. General review of tinnitus: Prevalence, mechanisms, effects, and management. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2005, 48, 1204–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nondahl, D.M.; Cruickshanks, K.J.; Dalton, D.S.; Klein, B.E.; Klein, R.; Schubert, C.R.; Tweed, T.S.; Wiley, T.L. The impact of tinnitus on quality of life in older adults. J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2007, 18, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Møller, A.R. Pathophysiology of tinnitus. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2003, 36, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurek, B.; Olze, H.; Haupt, H.; Szczepek, A.J. The more the worse: The grade of noise-induced hearing loss associates with the severity of tinnitus. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 3071–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jastreboff, P.J. Tinnitus retraining therapy. In Progress in Brain Research; Langguth, B., Hajak, G., Kleinjung, T., Cacace, A., Møller, A.R., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2007; Volume 166, pp. 415–423. [Google Scholar]
- Eggermont, J.J. Can Animal Models Contribute to Understanding Tinnitus Heterogeneity in Humans? Front. Aging Neurosci. 2016, 8, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jastreboff, P.J.; Brennan, J.F.; Coleman, J.K.; Sasaki, C.T. Phantom auditory sensation in rats: An animal model for tinnitus. Behav. Neurosci. 1988, 102, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puel, J.L.; Guitton, M.J. Salicylate-induced tinnitus: Molecular mechanisms and modulation by anxiety. Prog. Brain Res. 2007, 166, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jastreboff, P.J.; Sasaki, C.T. An animal model of tinnitus: A decade of development. Am. J. Otol. 1994, 15, 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- Ralli, M.; Lobarinas, E.; Fetoni, A.R.; Stolzberg, D.; Paludetti, G.; Salvi, R. Comparison of salicylate- and quinine-induced tinnitus in rats: Development, time course, and evaluation of audiologic correlates. Otol. Neurotol. 2010, 31, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knipper, M.; Van Dijk, P.; Nunes, I.; Rüttiger, L.; Zimmermann, U. Advances in the neurobiology of hearing disorders: Recent developments regarding the basis of tinnitus and hyperacusis. Prog. Neurobiol. 2013, 111, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bing, D.; Lee, S.C.; Campanelli, D.; Xiong, H.; Matsumoto, M.; Panford-Walsh, R.; Wolpert, S.; Praetorius, M.; Zimmermann, U.; Chu, H.; et al. Cochlear NMDA receptors as a therapeutic target of noise-induced tinnitus. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 35, 1905–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eggermont, J.J.; Roberts, L.E. The neuroscience of tinnitus. Trends Neurosci. 2004, 27, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milloy, V.; Fournier, P.; Benoit, D.; Noreña, A.; Koravand, A. Auditory Brainstem Responses in Tinnitus: A Review of Who, How, and What? Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciorba, A.; Hatzopoulos, S.; Corazzi, V.; Cogliandolo, C.; Aimoni, C.; Bianchini, C.; Stomeo, F.; Pelucchi, S. Newborn hearing screening at the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit and Auditory Brainstem Maturation in preterm infants. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 123, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markand, O.N. Brainstem auditory evoked potentials. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1994, 11, 319–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupa, V.; Job, A.; George, M.; Rajshekhar, V. Cost-effective initial screening for vestibular schwannoma: Auditory brainstem response or magnetic resonance imaging? Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2003, 128, 823–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, M.S.; Gordon, D.G.; Levin, V.A. Evaluation of desmethylmisonidazole-induced neurotoxicity in the rat using brainstem auditory evoked potentials. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1984, 10, 1377–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, R.; Montgomery, S.C.; Graves, K.A.; Caspary, D.M.; Cox, B.C. The FBN rat model of aging: Investigation of ABR waveforms and ribbon synapse changes. Neurobiol. Aging 2018, 62, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarado, J.C.; Fuentes-Santamaría, V.; Jareño-Flores, T.; Blanco, J.L.; Juiz, J.M. Normal variations in the morphology of auditory brainstem response (ABR) waveforms: A study in Wistar rats. Neurosci. Res. 2012, 73, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blatchley, B.J.; Cooper, W.A.; Coleman, J.R. Development of auditory brainstem response to tone pip stimuli in the rat. Brain Res. 1987, 429, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepek, A.J.; Dietz, G.P.H.; Reich, U.; Hegend, O.; Olze, H.; Mazurek, B. Differences in Stress-Induced Modulation of the Auditory System Between Wistar and Lewis Rats. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabiani, M.; Sohmer, H.; Tait, C.; Gafni, M.; Kinarti, R. A functional measure of brain activity: Brain stem transmission time. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1979, 47, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Peng, Z.; Yu, S.K.; Song, Q.L.; Qu, T.F.; He, L.; Liu, K.; Gong, S.S. Loss of Cochlear Ribbon Synapse Is a Critical Contributor to Chronic Salicylate Sodium Treatment-Induced Tinnitus without Change Hearing Threshold. Neural Plast. 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castañeda, R.; Natarajan, S.; Jeong, S.Y.; Hong, B.N.; Kang, T.H. Electrophysiological changes in auditory evoked potentials in rats with salicylate-induced tinnitus. Brain Res. 2019, 1715, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.P.; Chen, L. Auditory brainstem response as a possible objective indicator for salicylate-induced tinnitus in rats. Brain Res. 2012, 1485, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, A.A.S.; Rossato, M.; de Oliveira, J.A.A.; Hyppolito, M.A. Understanding the anatomy of ears from guinea pigs and rats and its use in basic otologic research. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2009, 75, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heffner, H.E.; Heffner, R.S. Hearing ranges of laboratory animals. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2007, 46, 20–22. [Google Scholar]
- Holt, A.G.; Kühl, A.; Braun, R.D.; Altschuler, R. The rat as a model for studying noise injury and otoprotection. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2019, 146, 3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willott, J.F. Factors affecting hearing in mice, rats, and other laboratory animals. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2007, 46, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reijntjes, D.O.J.; Pyott, S.J. The afferent signaling complex: Regulation of type I spiral ganglion neuron responses in the auditory periphery. Hear. Res. 2016, 336, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guitton, M.J. Tinnitus-provoking salicylate treatment triggers social impairments in mice. J. Psychosom. Res. 2009, 67, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escabi, C.D.; Frye, M.D.; Trevino, M.; Lobarinas, E. The rat animal model for noise-induced hearing loss. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2019, 146, 3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobarinas, E.; Spankovich, C.; Le Prell, C.G. Evidence of “hidden hearing loss” following noise exposures that produce robust TTS and ABR wave-I amplitude reductions. Hear. Res. 2017, 349, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von der Behrens, W. Animal models of subjective tinnitus. Neural Plast. 2014, 2014, 741452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.G.; Parrish, J.L.; Hughes, L.F.; Toth, L.A.; Caspary, D.M. Hearing in laboratory animals: Strain differences and nonauditory effects of noise. Comp. Med. 2005, 55, 12–23. [Google Scholar]
- Cederroth, C.R.; Dyhrfjeld-Johnsen, J.; Langguth, B. An update: Emerging drugs for tinnitus. Expert Opin. Emerg. Drugs 2018, 23, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurek, B.; Haupt, H.; Joachim, R.; Klapp, B.F.; Stöver, T.; Szczepek, A.J. Stress induces transient auditory hypersensitivity in rats. Hear. Res. 2010, 259, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurek, B.; Haupt, H.; Klapp, B.F.; Szczepek, A.J.; Olze, H. Exposure of Wistar rats to 24-h psycho-social stress alters gene expression in the inferior colliculus. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 527, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; The, P.G. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laundrie, E.; Sun, W. Acoustic trauma-induced auditory cortex enhancement and tinnitus. J. Otol. 2014, 9, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ropp, T.J.; Tiedemann, K.L.; Young, E.D.; May, B.J. Effects of unilateral acoustic trauma on tinnitus-related spontaneous activity in the inferior colliculus. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2014, 15, 1007–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, G.; Mei, Z.; Hojjat, H.; Pace, E.; Kallakuri, S.; Zhang, J.S. Therapeutic effect of sildenafil on blast-induced tinnitus and auditory impairment. Neuroscience 2014, 269, 367–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.C.; Pace, E.; Pierozynski, P.; Kou, Z.; Shen, Y.; VandeVord, P.; Haacke, E.M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J. Blast-induced tinnitus and hearing loss in rats: Behavioral and imaging assays. J. Neurotrauma 2012, 29, 430–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Pace, E.; Lepczyk, L.; Kaufman, M.; Zhang, J.; Perrine, S.A.; Zhang, J. Blast-Induced Tinnitus and Elevated Central Auditory and Limbic Activity in Rats: A Manganese-Enhanced MRI and Behavioral Study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.D.; Kermany, M.H.; D’Elia, A.; Ralli, M.; Tanaka, C.; Bielefeld, E.C.; Ding, D.; Henderson, D.; Salvi, R. Too much of a good thing: Long-term treatment with salicylate strengthens outer hair cell function but impairs auditory neural activity. Hear. Res. 2010, 265, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duron, J.; Monconduit, L.; Avan, P. Auditory Brainstem Changes in Timing may Underlie Hyperacusis in a Salicylate-induced Acute Rat Model. Neuroscience 2020, 426, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, C.H.; Lee, S.; Park, I.Y.; Song, A.; Moon, C.; Cho, G.W. Memantine Attenuates Salicylate-induced Tinnitus Possibly by Reducing NR2B Expression in Auditory Cortex of Rat. Exp. Neurobiol. 2019, 28, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralli, M.; Troiani, D.; Podda, M.V.; Paciello, F.; Eramo, S.L.; de Corso, E.; Salvi, R.; Paludetti, G.; Fetoni, A.R. The effect of the NMDA channel blocker memantine on salicylate-induced tinnitus in rats. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2014, 34, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sawka, B.; Wei, S. The Effects of Salicylate on Auditory Evoked Potential Amplitwde from the Auditory Cortex and Auditory Brainstem. J. Otol. 2014, 9, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, S.F.; Luo, H.; Zhang, J.; Kim, E.; Xu, Y. An animal model of deep brain stimulation for treating tinnitus: A proof of concept study. Laryngoscope 2018, 128, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.C.; Kim, H.; Kim, Y.S.; Jung, S.K.; Park, I.Y.; Choung, Y.H.; Jang, J.H. Objective Verification of Acute Tinnitus and Validation of Efficacy of Systemic Steroids in Rats. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2020, 35, e81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zwieten, G.; Jahanshahi, A.; van Erp, M.L.; Temel, Y.; Stokroos, R.J.; Janssen, M.L.F.; Smit, J.V. Alleviation of Tinnitus With High-Frequency Stimulation of the Dorsal Cochlear Nucleus: A Rodent Study. Trends Hear. 2019, 23, 2331216519835080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zwieten, G.; Janssen, M.L.F.; Smit, J.V.; Janssen, A.M.L.; Roet, M.; Jahanshahi, A.; Stokroos, R.J.; Temel, Y. Inhibition of Experimental Tinnitus With High Frequency Stimulation of the Rat Medial Geniculate Body. Neuromodulation 2019, 22, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, T.Y. Salicylate-Induced Hearing Loss Trigger Structural Synaptic Modifications in the Ventral Cochlear Nucleus of Rats via Medial Olivocochlear (MOC) Feedback Circuit. Neurochem. Res. 2016, 41, 1343–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Peng, Z.; Yu, S.; Song, Q.L.; Qu, T.F.; Liu, K.; Gong, S.S. Exposure to sodium salicylate disrupts VGLUT3 expression in cochlear inner hair cells and contributes to tinnitus. Physiol. Res. 2020, 69, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.P.; Chen, L. Forward acoustic masking enhances the auditory brainstem response in a diotic, but not dichotic, paradigm in salicylate-induced tinnitus. Hear. Res. 2015, 323, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Hamilton, E.; Begum, S.; Smith, P.F.; Darlington, C.L. The effects of acoustic trauma that can cause tinnitus on spatial performance in rats. Neuroscience 2011, 186, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; McNamara, E.; Stiles, L.; Darlington, C.L.; Smith, P.F. Evidence that Memantine Reduces Chronic Tinnitus Caused by Acoustic Trauma in Rats. Front. Neurol. 2012, 3, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; McPherson, K.; Smith, P.F. Effects of early and late treatment with L-baclofen on the development and maintenance of tinnitus caused by acoustic trauma in rats. Neuroscience 2014, 258, 410–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Reid, P.; Smith, P.F. Cannabinoid CB1 Receptor Agonists Do Not Decrease, but may Increase Acoustic Trauma-Induced Tinnitus in Rats. Front. Neurol. 2015, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, W.; Zuccotti, A.; Jaumann, M.; Lee, S.C.; Panford-Walsh, R.; Xiong, H.; Zimmermann, U.; Franz, C.; Geisler, H.S.; Köpschall, I.; et al. Noise-induced inner hair cell ribbon loss disturbs central arc mobilization: A novel molecular paradigm for understanding tinnitus. Mol. Neurobiol. 2013, 47, 261–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, C.A.; Brozoski, T.J.; Holder, T.M.; Caspary, D.M. Effects of chronic salicylate on GABAergic activity in rat inferior colliculus. Hear. Res. 2000, 147, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brozoski, T.; Wisner, K.; Randall, M.; Caspary, D. Chronic Sound-induced Tinnitus and Auditory Attention in Animals. Neuroscience 2019, 407, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brozoski, T.J.; Wisner, K.W.; Sybert, L.T.; Bauer, C.A. Bilateral dorsal cochlear nucleus lesions prevent acoustic-trauma induced tinnitus in an animal model. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2012, 13, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, E.; Zhang, J. Noise-induced tinnitus using individualized gap detection analysis and its relationship with hyperacusis, anxiety, and spatial cognition. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.G.; Larsen, D. Effects of noise exposure on development of tinnitus and hyperacusis: Prevalence rates 12 months after exposure in middle-aged rats. Hear. Res. 2016, 334, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Brozoski, T.J.; Turner, J.G.; Ling, L.; Parrish, J.L.; Hughes, L.F.; Caspary, D.M. Plasticity at glycinergic synapses in dorsal cochlear nucleus of rats with behavioral evidence of tinnitus. Neuroscience 2009, 164, 747–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlemiller, K.K.; Jones, S.M.; Johnson, K.R. Application of Mouse Models to Research in Hearing and Balance. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2016, 17, 493–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamesdaniel, S.; Ding, D.; Kermany, M.H.; Jiang, H.; Salvi, R.; Coling, D. Analysis of cochlear protein profiles of Wistar, Sprague-Dawley, and Fischer 344 rats with normal hearing function. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 3520–3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Hamilton, E.; McNamara, E.; Smith, P.F.; Darlington, C.L. The effects of chronic tinnitus caused by acoustic trauma on social behaviour and anxiety in rats. Neuroscience 2011, 193, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J. Blast-induced tinnitus: Animal models. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2019, 146, 3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaltenbach, J.A.; Rachel, J.D.; Mathog, T.A.; Zhang, J.; Falzarano, P.R.; Lewandowski, M. Cisplatin-induced hyperactivity in the dorsal cochlear nucleus and its relation to outer hair cell loss: Relevance to tinnitus. J. Neurophysiol. 2002, 88, 699–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jastreboff, P.J.; Brennan, J.F.; Sasaki, C.T. Quinine-induced tinnitus in rats. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1991, 117, 1162–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos-Sacchi, J.; Song, L.; Zheng, J.; Nuttall, A.L. Control of mammalian cochlear amplification by chloride anions. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 3992–3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, D.; He, D.Z.; Klöcker, N.; Ludwig, J.; Schulte, U.; Waldegger, S.; Ruppersberg, J.P.; Dallos, P.; Fakler, B. Intracellular anions as the voltage sensor of prestin, the outer hair cell motor protein. Science 2001, 292, 2340–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guitton, M.J.; Caston, J.; Ruel, J.; Johnson, R.M.; Pujol, R.; Puel, J.L. Salicylate induces tinnitus through activation of cochlear NMDA receptors. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 3944–3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.Y.; Luo, B.; Wang, H.T.; Chen, L. Differential effects of sodium salicylate on current-evoked firing of pyramidal neurons and fast-spiking interneurons in slices of rat auditory cortex. Hear. Res. 2009, 253, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolzberg, D.; Salvi, R.J.; Allman, B.L. Salicylate toxicity model of tinnitus. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, W.W.; Bohne, B.A.; Boettcher, F.A. Effect of periodic rest on hearing loss and cochlear damage following exposure to noise. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1987, 82, 1253–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredelius, L.; Johansson, B.; Bagger-Sjöbäck, D.; Wersäll, J. Qualitative and quantitative changes in the guinea pig organ of Corti after pure tone acoustic overstimulation. Hear. Res. 1987, 30, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, W.W. Recent studies of temporary threshold shift (TTS) and permanent threshold shift (PTS) in animals. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1991, 90, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.W.; Ahn, J.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Kang, H.H.; Lee, Y.K.; Kim, J.U.; Koo, S.W. The effect of isoflurane, halothane and pentobarbital on noise-induced hearing loss in mice. Anesth. Analg. 2007, 104, 1404–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüttiger, L.; Singer, W.; Panford-Walsh, R.; Matsumoto, M.; Lee, S.C.; Zuccotti, A.; Zimmermann, U.; Jaumann, M.; Rohbock, K.; Xiong, H.; et al. The reduced cochlear output and the failure to adapt the central auditory response causes tinnitus in noise exposed rats. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggermont, J.J.; Spoor, A. Cochlear adaptation in guinea pigs. A quantitative description. Audiology 1973, 12, 193–220. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liberman, M.C. Restraint stress and protection from acoustic injury in mice. Hear. Res. 2002, 165, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, S.; Cahani, M.; Sohmer, H.; Horowitz, M.; Shahar, A. Effects of body temperature elevation on auditory nerve-brain-stem evoked responses and EEGs in rats. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1985, 60, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Urioste, R.T.; Wei, Y.; Wilder, D.M.; Arun, P.; Sajja, V.; Gist, I.D.; Fitzgerald, T.S.; Chang, W.; Kelley, M.W.; et al. Blast-induced hearing impairment in rats is associated with structural and molecular changes of the inner ear. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.I.; Coomber, B. Tinnitus-related changes in the inferior colliculus. Front. Neurol. 2015, 6, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Valenzuela, C.; Gárate-Pérez, M.F.; Sotomayor-Zárate, R.; Delano, P.H.; Dagnino-Subiabre, A. Reboxetine Improves Auditory Attention and Increases Norepinephrine Levels in the Auditory Cortex of Chronically Stressed Rats. Front. Neural Circuits 2016, 10, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, H.J.; An, Y.H.; Kim, D.H.; Yoon, J.E.; Yoon, J.H. Comparisons of auditory brainstem response and sound level tolerance in tinnitus ears and non-tinnitus ears in unilateral tinnitus patients with normal audiograms. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehraei, G.; Hickox, A.E.; Bharadwaj, H.M.; Goldberg, H.; Verhulst, S.; Liberman, M.C.; Shinn-Cunningham, B.G. Auditory Brainstem Response Latency in Noise as a Marker of Cochlear Synaptopathy. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 3755–3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liberman, M.C.; Kujawa, S.G. Cochlear synaptopathy in acquired sensorineural hearing loss: Manifestations and mechanisms. Hear. Res. 2017, 349, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ABR User Guide. 2020. Available online: https://www.tdt.com/files/manuals/ABRGuide.pdf (accessed on 20 October 2020).
- Gärtner, K.; Büttner, D.; Döhler, K.; Friedel, R.; Lindena, J.; Trautschold, I. Stress response of rats to handling and experimental procedures. Lab. Anim. 1980, 14, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Backoff, P.M.; Caspary, D.M. Age-related changes in auditory brainstem responses in Fischer 344 rats: Effects of rate and intensity. Hear. Res. 1994, 73, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, M.W.; Williams, H.L.; Holloway, J.A. Brain-stem auditory evoked potentials in the rat: Effects of gender, stimulus characteristics and ethanol sedation. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1984, 59, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruebhausen, M.R.; Brozoski, T.J.; Bauer, C.A. A comparison of the effects of isoflurane and ketamine anesthesia on auditory brainstem response (ABR) thresholds in rats. Hear. Res. 2012, 287, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheppard, A.M.; Zhao, D.L.; Salvi, R. Isoflurane anesthesia suppresses distortion product otoacoustic emissions in rats. J. Otol. 2018, 13, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzopoulos, S.; Petruccelli, J.; Laurell, G.; Finesso, M.; Martini, A. Evaluation of anesthesia effects in a rat animal model using otoacoustic emission protocols. Hear. Res. 2002, 170, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maria, P.L.S.; Redmond, S.L.; Atlas, M.D.; Ghassemifar, R. Histology of the healing tympanic membrane following perforation in rats. Laryngoscope 2010, 120, 2061–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, G.T.; Britt, R.H. Effects of hypothermia on the cat brain-stem auditory evoked response. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1984, 57, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, T.A.; Stockard, J.J.; Weidner, W.J. The effects of temperature and acute alcohol intoxication on brain stem auditory evoked potentials in the cat. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1980, 49, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogová, Z.; Popelář, J.; Chiumenti, F.; Chumak, T.; Burianová, J.S.; Rybalko, N.; Syka, J. Age-Related Differences in Hearing Function and Cochlear Morphology between Male and Female Fischer 344 Rats. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcondes, F.K.; Bianchi, F.J.; Tanno, A.P. Determination of the estrous cycle phases of rats: Some helpful considerations. Braz. J. Biol. 2002, 62, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, M.W.; Williams, H.L.; Holloway, J.A. Postnatal development of the brainstem auditory evoked potential and far-field cochlear microphonic in non-sedated rat pups. Brain Res. 1984, 316, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meltser, I.; Canlon, B. Protecting the auditory system with glucocorticoids. Hear. Res. 2011, 281, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, A.; Maiolino, L.; Agnello, C.; Messina, A.; Caruso, S. Auditory brain stem response throughout the menstrual cycle. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2003, 112, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, N.; Sidhu, R.S.; Babbar, R. Brainstem auditory evoked responses in different phases of menstrual cycle. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. JCDR 2012, 6, 1640–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaette, R.; McAlpine, D. Tinnitus with a normal audiogram: Physiological evidence for hidden hearing loss and computational model. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 13452–13457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kehrle, H.M.; Granjeiro, R.C.; Sampaio, A.L.; Bezerra, R.; Almeida, V.F.; Oliveira, C.A. Comparison of auditory brainstem response results in normal-hearing patients with and without tinnitus. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2008, 134, 647–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.W.; Herrmann, B.S.; Levine, R.A.; Melcher, J.R. Brainstem auditory evoked potentials suggest a role for the ventral cochlear nucleus in tinnitus. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2012, 13, 819–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attias, J.; Pratt, H.; Reshef, I.; Bresloff, I.; Horowitz, G.; Polyakov, A.; Shemesh, Z. Detailed analysis of auditory brainstem responses in patients with noise-induced tinnitus. Audiology 1996, 35, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attias, J.; Urbach, D.; Gold, S.; Shemesh, Z. Auditory event related potentials in chronic tinnitus patients with noise induced hearing loss. Hear. Res. 1993, 71, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).