Tremor in Multiple Sclerosis—An Overview and Future Perspectives
Abstract
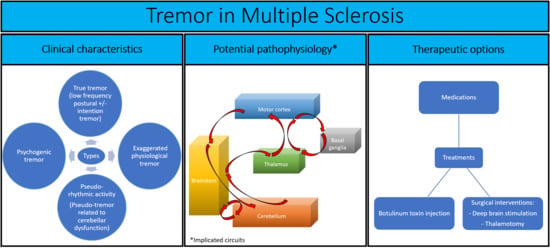
:1. Introduction
2. Epidemiological Background
3. Clinical Manifestations
4. Assessment Modalities
5. Pharmacological and Alternative Treatments
6. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Medication | Studies | Study Design | Main Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Isoniazid | Sabra et al. [46] | Open-label case series (four MS patients) | Improvement in the studied patients |
| Duquette et al. [47] | Open-label trial (13 MS patients) | Mild improvement in 10 patients on at least one of the assessment methods | |
| Morrow et al. [48] | Open-label case series (five MS patients) | Improvement in four patients | |
| Francis et al. [49] | Open-label pilot trial (five MS patients) | No improvement with conventional dose; marginal clinical improvement with dose increase 2–3 fold reduction in tremor on goniometry | |
| Bozek et al. [50] | Double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial (10 MS patients) | Clinical improvement in six out of eight patients who completed the study No significant change on tremograms results Better response in postural vs. intention tremor | |
| Hallet et al. [51] | Double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial (six MS patients) | Improvement in all patients on at least one of the assessment methods | |
| Levetiracetam | Striano et al. [52] | Open-label trial (14 MS patients) | Improvement in 11 patients who completed the study |
| Chitsaz et al. [53] | Open-label trial (22 MS patients) | Transient improvement in 20 patients who completed the study | |
| Solaro et al. [54] | Double-blind, placebo-controlled Crossover trial (eight MS patients) | Significance changes in kinematic but not clinical measures in the six patients who completed the study | |
| Solaro et al. [55] | Double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study (48 MS patients) | Improvement in the subjective but not kinematic measures in patients who received levetiracetam followed by placebo intervention (but not vice versa) | |
| Fey et al. [56] | Double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial (18 MS patients) | No improvement in the 14 patients who completed the study | |
| Topiramate | Schroeder et al. [57] | Case report | Clinical improvement |
| Sechi et al. [58] | Open-label trial (nine patients with cerebellar tremor, of which five had MS) | Clinical and neurophysiological improvement Treatment discontinuation in three patients prior to trial completion | |
| Cannabis | Clifford [59] | Single-blind, placebo-controlled trial (eight MS patients) | Mild subjective but not objective improvement in 5/8 patients; subjective and objective improvement in two patients |
| Meinck et al. [61] | Case report | Clinical and neurophysiological improvement | |
| Wade et al. [62] | Double-blind, placebo-controlled study (160 MS patients) | No subjective changes in tremor (154 patients including 13 patients with tremor as primary symptom) | |
| Zajicek et al. [63] | Multicenter placebo-controlled trial (spasticity as primary outcome) (630 MS patients) | No clinical improvement | |
| Fox et al. [64] | Double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover trial (14 MS patients) | No clinical and neurophysiological improvement | |
| Ondansetron | Rice et al. [68] | Double blind, placebo-controlled crossover study in 20 patients (16 MS patients; three patients with cerebellar degeneration, one patient with lithium intoxication) | Clinical improvement |
| Gbadamosi et al. [69] | Open-label pilot study (14 MS patients) | No clinical improvement | |
| Primidone | Henkin & Herishanu [70] | Case series (two MS patients) | Improvement in two patients |
| Naderi et al. [71] | Open-label pilot study (10 MS patients) | Clinical improvement | |
| 4-aminopyridine | Schniepp et al. [72] | Case report | Clinical improvement |
| Glutethimide | Aisen et al. [73] | Open-label study (six MS patients, two patients with traumatic brain injury) | Functional benefits in six out of eight patients |
| Natalizumab | Rinker et al. [75] | Comparative retrospective trial (natalizumab vs. other disease modifying drugs) (567 MS patients) | Clinical improvement in natalizumab-treated patients |
| Botulinum toxin A injection | Clarke et al. [76] | Open-label pilot study (five MS patients) | No clinical improvement |
| Van der Walt [77] | Double-blind, controlled crossover trial (23 MS patients) | Clinical improvement |
References
- Koch-Henriksen, N.; Sørensen, P.S. The changing demographic pattern of multiple sclerosis epidemiology. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 520–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charcot, J.M. Leçons Sur Les Maladies Du Système Nerveux: Faites à La Salpêtrière; Delahaye et Lecrosnier: Paris, France, 1877. [Google Scholar]
- Feys, P.; Romberg, A.; Ruutiainen, J.; Ketelaer, P. Interference of upper limb tremor on daily life activities in people with multiple sclerosis. Occup. Ther. Health Care 2004, 17, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinker, J.R.; Salter, A.R.; Walker, H.; Amara, A.W.; Meador, W.; Cutter, G.R. Prevalence and characteristics of tremor in the NARCOMS multiple sclerosis registry: A cross-sectional survey. BMJ Open 2015, 5, 006714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alusi, S.H.; Worthington, J.; Glickman, S.; Bain, P.G. A study of tremor in multiple sclerosis. Brain 2001, 124, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koch, M.W.; Mostert, J.; Heersema, D.; De Keyser, J. Tremor in multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. 2007, 254, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lyons, K.E.; Pahwa, R. Deep brain stimulation and tremor. Neurotherapeutics 2008, 5, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deuschl, G.; Bain, P.; Brin, M. Consensus Statement of the Movement Disorder Society on Tremor. Mov. Disord. 2008, 13, 2–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, N.M.; Pasternak, B.; Stenager, E.; Koch-Henriksen, N.; Frisch, M. Multiple sclerosis and risk of Parkinson’s disease: A Danish nationwide cohort study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2014, 21, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayache, S.S.; Chalah, M.A.; Al-Ani, T.; Farhat, W.H.; Zouari, H.; Créange, A.; Lefaucheur, J.-P. Tremor in multiple sclerosis: The intriguing role of the cerebellum. J. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 358, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardocci, N.; Zorzi, G.; Savoldelli, M.; Rumi, V.; Angelini, L. Paroxysmal dystonia and paroxysmal tremor in a young patient with multiple sclerosis. Neurol. Sci. 1995, 16, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alusi, S.H.; Aziz, T.Z.; Glickman, S.; Jahanshahi, M.; Stein, J.F.; Bain, P.G. Stereotactic lesional surgery for the treatment of tremor in multiple sclerosis: A prospective case-controlled study. Brain 2001, 124, 1576–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Proudlock, F.A.; Gottlob, I.; Constantinescu, C. Oscillopsia without Nystagmus Caused by Head Titubation in a Patient with Multiple Sclerosis. J. NeuroOphthalmol. 2002, 22, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartelius, L.; Buder, E.H.; Strand, E.A. Long-Term Phonatory Instability in Individuals With Multiple Sclerosis. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 1997, 40, 1056–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alusi, S.H.; Glickman, S.; Aziz, T.Z.; Bain, P.G. Tremor in multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1999, 66, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sudhakar, P.; Parmar, H.; Cornblath, W.T. Oculopalatal tremor in multiple sclerosis with spontaneous resolution. Neurol. Clin. Pract. 2012, 2, 255–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gresty, M.A.; Ell, J.J.; Findley, L.J. Acquired pendular nystagmus: Its characteristics, localising value and pathophysiology. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1982, 45, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tilikete, C.; Jasse, L.; Pélisson, D.; Vukusic, S.; Durand-Dubief, F.; Urquizar, C.; Vighetto, A. Acquired pendular nystagmus in multiple sclerosis and oculopalatal tremor. Neurology 2011, 76, 1650–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deuschl, G.; Mischke, G.; Schenck, E.; Schulte-Mönting, J.; Lücking, C.H. Symptomatic and Essential Rhythmic Palatal Myoclonus. Brain 1990, 113, 1645–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baizabal-Carvallo, J.F.; Cardoso, F.; Jankovic, J. Myorhythmia: Phenomenology, etiology, and treatment. Mov. Disord. 2014, 30, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohol, M.J.; Orav, E.J.; Weiner, H.L. Disease Steps in multiple sclerosis: A simple approach to evaluate disease progression. Neurology 1995, 45, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittock, S.J.; McClelland, R.L.; Mayr, W.T.; Rodriguez, M.; Matsumoto, J.Y. Prevalence of tremor in multiple sclerosis and associated disability in the Olmsted County population. Mov. Disord. 2004, 19, 1482–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Walt, A.; Buzzard, K.; Sung, S.; Spelman, T.; Kolbe, S.; Marriott, M.; Butzkueven, H.; Evans, A.; Kolbe, S.C. The occurrence of dystonia in upper-limb multiple sclerosis tremor. Mult. Scler. J. 2015, 21, 1847–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coenen, V.A.; Sajonz, B.; Prokop, T.; Reisert, M.; Piroth, T.; Urbach, H.; Jenkner, C.; Reinacher, P.C. The dentato-rubro-thalamic tract as the potential common deep brain stimulation target for tremor of various origin: An observational case series. Acta Neurochir. 2020, 162, 1053–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boonstra, F.; Florescu, G.; Evans, A.; Steward, C.; Mitchell, P.; Desmond, P.; Moffat, B.; Butzkueven, H.; Kolbe, S.; Van Der Walt, A. Tremor in multiple sclerosis is associated with cerebello-thalamic pathology. J. Neural Transm. 2017, 124, 1509–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boonstra, F.; Noffs, G.; Perera, T.; Jokubaitis, V.G.; Vogel, A.P.; Moffat, B.A.; Butzkueven, H.; Evans, A.; Van Der Walt, A.; Kolbe, S.C. Functional neuroplasticity in response to cerebello-thalamic injury underpins the clinical presentation of tremor in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. J. 2019, 26, 696–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karmon, Y.; Morrow, S.; Weinstock, L.; Hojnacki, D.; Weinstock-Guttman, B. Limb Ataxia Originating from Peri-Central Sulcus Demyelinating Lesion in Multiple Sclerosis Patients (P06.176). Neurol. 2012, 78, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feys, P.; Maes, F.; Nuttin, B.; Helsen, W.; Malfait, V.; Nagels, G.; Lavrysen, A.; Liu, X. Relationship between multiple sclerosis intention tremor severity and lesion load in the brainstem. NeuroReport 2005, 16, 1379–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molnar, G.F.; Sailer, A.; Gunraj, C.A.; Lang, A.E.; Lozano, A.M.; Chen, R. Thalamic deep brain stimulation activates the cerebellothalamocortical pathway. Neurology 2004, 63, 907–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayache, S.S.; Ahdab, R.; Neves, D.O.; Nguyen, J.-P.; Lefaucheur, J.-P. Thalamic stimulation restores defective cerebellocortical inhibition in multiple sclerosis tremor. Mov. Disord. 2008, 24, 467–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shale, H.; Fahn, S.; Koller, W.C.; Lang, A.E. What is it? Case 1, 1986. Mov. Disord. 1986, 1, 275–280. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, R.; Kamakura, K.; Tadano, Y.; Hosoda, Y.; Nagata, N.; Tsuchiya, K.; Iwata, M.; Shibasaki, H. MR imaging findings of tremors associated with lesions in cerebellar outflow tracts: Report of two cases. Mov. Disord. 1993, 8, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, M.F.; Miall, R.C.; Bain, P.G.; Liu, X. The onset of voluntary reactive movement is temporally influenced by the central oscillation in action tremor caused by multiple sclerosis. Neurosci. Lett. 2008, 445, 122–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alusi, S.H.; Worthington, J.; Glickman, S.; Findley, L.J.; Bain, P.G. Evaluation of three different ways of assessing tremor in multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2000, 68, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Miall, R.C.; Aziz, T.Z.; Palace, J.A.; Haggard, P.; Stein, J.F. Analysis of action tremor and impaired control of movement velocity in multiple sclerosis during visually guided wrist-tracking tasks. Mov. Disord. 1997, 12, 992–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Miall, R.C.; Aziz, T.Z.; Palace, J.A.; Stein, J.F. Distal versus proximal arm tremor in multiple sclerosis assessed by visually guided tracking tasks. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1999, 66, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Aziz, T.Z.; Miall, R.C.; Rowe, J.; Alusi, S.H.; Bain, P.G.; Stein, J.F. Frequency analysis of involuntary movements during wrist tracking: A way to identify ms patients with tremor who benefit from thalamotomy. Ster. Funct. Neurosurg. 2000, 74, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waubant, E.; Du Montcel, S.T.; Jedynak, C.; Obadia, M.; Hosseini, H.; Damier, P.; Lubetzki, C.; Agid, Y.; Degos, J.-D. Multiple sclerosis tremor and the Stewart-Holmes manoeuvre. Mov. Disord. 2003, 18, 948–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delmastro, H.M.; Ruiz, J.A.; Gromisch, E.S.; Garbalosa, J.C.; Triche, E.W.; Olson, K.M.; Lo, A.C. Quantification characteristics of digital spiral analysis for understanding the relationship among tremor and clinical measures in persons with multiple sclerosis. J. Neurosci. Methods 2018, 307, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feys, P.; Helsen, W.; Prinsmel, A.; Ilsbroukx, S.; Wang, S.; Liu, X. Digitised spirography as an evaluation tool for intention tremor in multiple sclerosis. J. Neurosci. Methods 2007, 160, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrie, R.A.; Goldman, M. Validation of the NARCOMS Registry: Tremor and Coordination Scale. Int. J. MS Care 2011, 13, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hooper, J.; Taylor, R.; Pentland, B.; Whittle, I.R. Rater reliability of Fahn’s tremor rating scale in patients with multiple sclerosis. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1998, 79, 1076–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daudrich, B.; Hurl, D.; Forwell, S. Multidimensional Assessment of Tremor in Multiple Sclerosis. Int. J. MS Care 2010, 12, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpinella, I.; Cattaneo, D.; Ferrarin, M. Hilbert–Huang transform based instrumental assessment of intention tremor in multiple sclerosis. J. Neural Eng. 2015, 12, 046011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayache, S.S.; Al-Ani, T.; Farhat, W.-H.; Zouari, H.; Créange, A.; Lefaucheur, J.-P. Analysis of tremor in multiple sclerosis using Hilbert-Huang Transform. Neurophysiol. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015, 45, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabra, A.F.; Hallett, M.; Sudarsky, L.; Mullally, W. Treatment of action tremor in multiple sclerosis with isoniazid. Neurology 1982, 32, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duquette, P.; Pleines, J.; Du Souich, P. Isoniazid for tremor in multiple sclerosis: A controlled trial. Neurology 1985, 35, 1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, J.; McDowell, H.; Ritchie, C.; Patterson, V. Isoniazid and action tremor in multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1985, 48, 282–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Francis, D.A.; Grundy, D.; Heron, J.R. The response to isoniazid of action tremor in multiple sclerosis and its assessment using polarised light goniometry. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1986, 49, 87–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozek, C.B.; Kastrukoff, L.F.; Wright, J.M.; Perry, T.L.; Larsen, T.A. A controlled trial of isoniazid therapy for action tremor in multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. 1987, 234, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallett, M.; Lindsey, J.W.; Adelstein, B.D.; Riley, P.O. Controlled trial of isoniazid therapy for severe postural cerebellar tremor in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 1985, 35, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Striano, P.; Coppola, A.; Vacca, G.; Zara, F.; Brescia-Morra, V.; Orefice, G.; Striano, S. Levetiracetam for cerebellar tremor in multiple sclerosis: An open-label pilot tolerability and efficacy study. J. Neurol. 2006, 253, 762–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chitsaz, A.; Mehrbod, N.; Etemadifar, M.; Najafi, M. Does levetircetam decrease of the rubral tremor in patients with multiple sclerosis. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2013, 18, S78–S80. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Solaro, C.; Brichetto, G.; Capello, E.; Abuarqub, S.; Sanguineti, V. Activity, tolerability and efficacy of levetiracetam on cerebellar symptoms in multiple sclerosis patients: A pilot kinematic study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2008, 15, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solaro, C.; De Sire, A.; Uccelli, M.M.; Mueller, M.; Bergamaschi, R.; Gasperini, C.; Restivo, D.A.; Stabile, M.R.; Patti, F. Efficacy of levetiracetam on upper limb movement in multiple sclerosis patients with cerebellar signs: A multicenter double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feys, P.; Nagels, G.; Helsen, W.; D’Hooghe, M. The effect of levetiracetam on tremor severity and functionality in patients with multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. J. 2009, 15, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, A.; Linker, R.A.; Lukas, C.; Kraus, P.H.; Gold, R. Successful Treatment of Cerebellar Ataxia and Tremor in Multiple Sclerosis with Topiramate: A case report. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 2010, 33, 317–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sechi, G.; Agnetti, V.; Sulas, F.M.; Sau, G.; Corda, D.; Pitzolu, M.G.; Rosati, G. Effects of topiramate in patients with cerebellar tremor. Prog. NeuroPsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2003, 27, 1023–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifford, D.B. Tetrahydrocannabinol for tremor in multiple sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 1983, 13, 669–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, D.; Pryce, G.; Croxford, J.L.; Brown, P.; Pertwee, R.G.; Huffman, J.W.; Layward, L. Cannabinoids control spasticity and tremor in a multiple sclerosis model. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 404, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinck, H.-M.; Conrad, B. Effect of cannabinoids on spasticity and ataxia in multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. 1989, 236, 120–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, D.T.; Makela, P.; Robson, P.; House, H.; Bateman, C. Do cannabis-based medicinal extracts have general or specific effects on symptoms in multiple sclerosis? A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study on 160 patients. Mult. Scler. J. 2004, 10, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zajicek, J.P.; Fox, P.; Sanders, H.; Wright, D.; Vickery, J.; Nunn, A.; Thompson, A. Cannabinoids for treatment of spasticity and other symptoms related to multiple sclerosis (CAMS study): Multicentre randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2003, 362, 1517–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, P.; Bain, P.G.; Glickman, S.; Carroll, C.; Zajicek, J. The effect of cannabis on tremor in patients with multiple sclerosis. Neurology 2004, 62, 1105–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, K.; Weizman, A.; Weinstein, A. Positive and Negative Effects of Cannabis and Cannabinoids on Health. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 105, 1139–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grotenhermen, F.; Mueller-Vahl, K.R. The Therapeutic Potential of Cannabis and Cannabinoids. Dtsch. Aerzteblatt Online 2012, 109, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trouillas, P. The Cerebellar Serotoninergic System and its Possible Involvement in Cerebellar Ataxia. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 1993, 20, S78–S82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rice, G.P.; Lesaux, J.; Vandervoort, P.; MacEwan, L.; Ebers, G.C. Ondansetron, a 5-HT3 antagonist, improves cerebellar tremor. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1997, 62, 282–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbadamosi, J.; Buhmann, C.; Moench, A.; Heesen, C. Failure of ondansetron in treating cerebellar tremor in MS patients - an open-label pilot study. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2001, 104, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henkin, Y.; Herishanu, Y.O. Primidone as a treatment for cerebellar tremor in multiple sclerosis—Two case reports. Isr. J. Med Sci. 1989, 25, 720–721. [Google Scholar]
- Naderi, F.; Javadi, A.S.; Motamedi, M.; Sahraian, M.A. The Efficacy of Primidone in Reducing Severe Cerebellar Tremors in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 2012, 35, 224–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schniepp, R.; Jakl, V.; Wuehr, M.; Havla, J.; Kümpfel, T.; Dieterich, M.; Strupp, M.; Jahn, K. Treatment with 4-aminopyridine improves upper limb tremor of a patient with multiple sclerosis: A video case report. Mult. Scler. J. 2012, 19, 506–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aisen, M.L.; Holzer, M.; Rosen, M.; Dietz, M.; McDowell, F. Glutethimide Treatment of Disabling Action Tremor in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis and Traumatic Brain Injury. Arch. Neurol. 1991, 48, 513–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammond, E.R.; Kerr, D.A. Ethanol Responsive Tremor in a Patient with Multiple Sclerosis. Arch. Neurol. 2008, 65, 142–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinker, J.R.; Salter, A.; Cutter, G.R. Improvement of multiple sclerosis-associated tremor as a treatment effect of natalizumab. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2014, 3, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, C.E. Botulinum toxin type A in cerebellar tremor caused by multiple sclerosis. Eur. J. Neurol. 1997, 4, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Walt, A.; Sung, S.; Spelman, T.; Marriott, M.; Kolbe, S.C.; Mitchell, P.; Evans, A.; Butzkueven, H. A double-blind, randomized, controlled study of botulinum toxin type A in MS-related tremor. Neurology 2012, 79, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellows, S.; Jankovic, J. Immunogenicity Associated with Botulinum Toxin Treatment. Toxins 2019, 11, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pedouim, F.; Dashtipour, K. Botulinum Toxin: Preparations for Clinical Use, Immunogenicity, Side Effects, and Safety Profile. Semin. Neurol. 2016, 36, 029–033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, H.; Roberts, D.W.; Roth, R.M.; McDonald, B.C.; Coffey, D.J.; Mamourian, A.C.; Hartley, C.; Flashman, L.; Fadul, C.; Saykin, A.J. Chronic deep brain stimulation for the treatment of tremor in multiple sclerosis: Review and case reports. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2003, 74, 1392–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geny, C.; Nguyen, J.-P.; Pollin, B.; Feve, A.; Ricolfi, F.; Cesaro, P.; Degos, J.-D. Improvement of severe postural cerebellar tremor in multiple sclerosis by chronic thalamic stimulation. Mov. Disord. 1996, 11, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, D.; Aziz, T.Z. Deep brain stimulation in the management of neuropathic pain and multiple sclerosis tremor. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2004, 21, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulder, M.; Sernas, T.J.; Karimi, R. Thalamic stimulation in patients with multiple sclerosis: Long-term follow-up. Ster. Funct. Neurosurg. 2003, 80, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berk, C.; Carr, J.; Sinden, M.; Martzke, J.; Honey, C.R. Thalamic deep brain stimulation for the treatment of tremor due to multiple sclerosis: A prospective study of tremor and quality of life. J. Neurosurg. 2002, 97, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCreary, J.K.; Rogers, J.A.; Forwell, S. Upper Limb Intention Tremor in Multiple Sclerosis: An Evidence-Based Review of Assessment and Treatment. Int. J. MS Care 2018, 20, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Makhoul, K.; Ahdab, R.; Riachi, N.; Chalah, M.A.; Ayache, S.S. Tremor in Multiple Sclerosis—An Overview and Future Perspectives. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 722. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10100722
Makhoul K, Ahdab R, Riachi N, Chalah MA, Ayache SS. Tremor in Multiple Sclerosis—An Overview and Future Perspectives. Brain Sciences. 2020; 10(10):722. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10100722
Chicago/Turabian StyleMakhoul, Karim, Rechdi Ahdab, Naji Riachi, Moussa A. Chalah, and Samar S. Ayache. 2020. "Tremor in Multiple Sclerosis—An Overview and Future Perspectives" Brain Sciences 10, no. 10: 722. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10100722
APA StyleMakhoul, K., Ahdab, R., Riachi, N., Chalah, M. A., & Ayache, S. S. (2020). Tremor in Multiple Sclerosis—An Overview and Future Perspectives. Brain Sciences, 10(10), 722. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10100722