Acute Effects of Aerobic Exercise on Somatosensory-Evoked Potentials in Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Method
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Experimental Intervention
2.3. Control Intervention
2.4. Recordings
2.5. Stimulations
2.6. Data Analysis
2.6.1. Pre-Processing
2.6.2. Extraction of Somatosensory-Evoked Potential (SEP) Parameters
2.6.3. Statistics
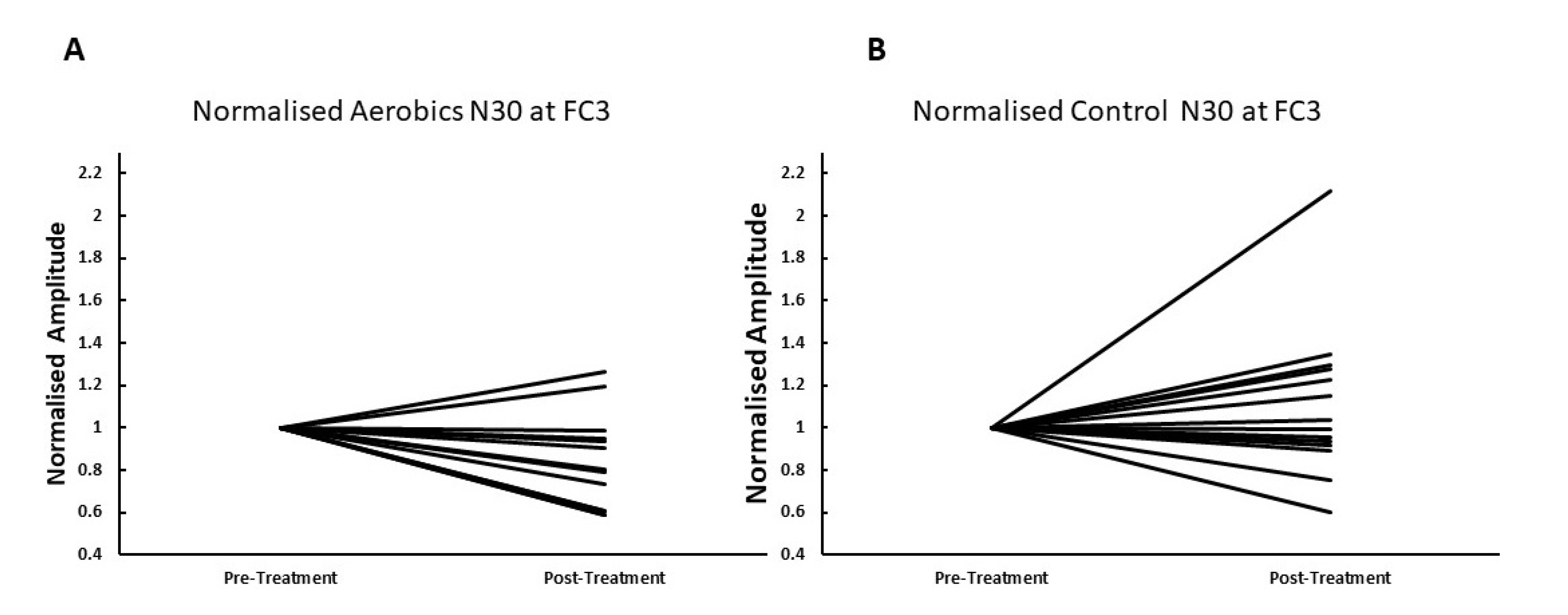
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bloom, D.E. 7 billion and counting. Science 2011, 333, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A. A problem for our age. Nature 2011, 475, S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Deyn, P.; Goeman, J.; Vervaet, A.; Dourcy-Belle-Rose, B.; Van Dam, D.; Geerts, E. Prevalence and incidence of dementia among 75–80-year-old community-dwelling elderly in different districts of Antwerp, Belgium: The Antwerp Cognition (ANCOG) Study. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2011, 113, 736–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferri, C.P.; Prince, M.; Brayne, C.; Brodaty, H.; Fratiglioni, L.; Ganguli, M.; Hall, K.; Hasegawa, K.; Hendrie, H.; Huang, Y. Global prevalence of dementia: A Delphi consensus study. Lancet 2005, 366, 2112–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokin, G.B.; Goldstein, L.S. Axonal transport and Alzheimer’s disease. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2006, 75, 607–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klafki, H.W.; Staufenbiel, M.; Kornhuber, J.; Wiltfang, J. Therapeutic approaches to Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2006, 129, 2840–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.; Lah, J.; Goldstein, F.; Steenland, K.; Bliwise, D. Mild cognitive impairment: An opportunity to identify patients at high risk for progression to Alzheimer’s disease. Clin. Ther. 2006, 28, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, S. Alzheimer’s disease: The benefits of early treatment. Eur. J. Neurol. 2005, 12, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suva, D.; Favre, I.; Kraftsik, R.; Esteban, M.; Lobrinus, A.; Miklossy, J. Primary motor cortex involvement in Alzheimer disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1999, 58, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geula, C.; Mesulam, M.M. Systematic regional variations in the loss of cortical cholinergic fibers in Alzheimer’s disease. Cerebral Cortex 1996, 6, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teipel, S.J.; Stahl, R.; Dietrich, O.; Schoenberg, S.O.; Perneczky, R.; Bokde, A.L.; Reiser, M.F.; Möller, H.J.; Hampel, H. Multivariate network analysis of fiber tract integrity in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroimage 2007, 34, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uylings, H.B.; De Brabander, J. Neuronal changes in normal human aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Cogn. 2002, 49, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovach, C.R. Sensoristasis and imbalance in persons with dementia. J. Nurs. Scholarsh. 2000, 32, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen-Mansfield, J.; Dakheel-Ali, M.; Marx, M.S.; Thein, K.; Regier, N.G. Which unmet needs contribute to behavior problems in persons with advanced dementia? Psychiatry Res. 2015, 228, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Allison, T.; McCarthy, G.; Wood, C.C. The relationship between human long-latency somatosensory evoked potentials recorded from the cortical surface and from the scalp. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1992, 84, 301–314. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, S.; della Volpe, R.; Ginanneschi, F.; Ulivelli, M.; Bartalini, S.; Spidalieri, R.; Rossi, A. Early somatosensory processing during tonic muscle pain in humans: Relation to loss of proprioception and motor ‘defensive’strategies. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2003, 114, 1351–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulut, S.; Özmerdivenli, R.; Bayer, H. Effects of exercise on somatosensory-evoked potentials. Int. J. Neurosci. 2003, 113, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakata, H.; Oshiro, M.; Namba, M.; Shibasaki, M. Effects of aerobic exercise under different thermal conditions on human somatosensory processing. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2016, 311, R629–R636. [Google Scholar]
- Walsh, P.; Kane, N.; Butler, S. The clinical role of evoked potentials. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2005, 76 (Suppl. 2), ii16–ii22. [Google Scholar]
- Allison, T.; McCarthy, G.; Wood, C.C.; Darcey, T.M.; Spencer, D.D.; Williamson, P.D. Human cortical potentials evoked by stimulation of the median nerve. II. Cytoarchitectonic areas generating short-latency activity. J. Neurophysiol. 1989, 62, 694–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, T.; McCarthy, G.; Wood, C.C.; Williamson, P.D.; Spencer, D.D. Human cortical potentials evoked by stimulation of the median nerve. II. Cytoarchitectonic areas generating long-latency activity. J. Neurophysiol. 1989, 62, 711–722. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Inui, K.; Wang, X.; Tamura, Y.; Kaneoke, Y.; Kakigi, R. Serial processing in the human somatosensory system. Cereb. Cortex 2004, 14, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chéron, G.; Borenstein, S. Specific gating of the early somatosensory evoked potentials during active movement. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1987, 67, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chéron, G.; Borenstein, S. Gating of the early components of the frontal and parietal somatosensory evoked potentials in different sensory-motor interference modalities. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. Evoked Potentials Sect. 1991, 80, 522–530. [Google Scholar]
- Kida, T.; Wasaka, T.; Nakata, H.; Kakigi, R. Centrifugal regulation of task-relevant somatosensory signals to trigger a voluntary movement. Exp. Brain Res. 2006, 169, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebolla, A.M.; Palmero-Soler, E.; Dan, B.; Cheron, G. Frontal phasic and oscillatory generators of the N30 somatosensory evoked potential. NeuroImage 2011, 54, 1297–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauguiere, F.; Desmedt, J.; Courjon, J. Astereognosis and dissociated loss of frontal or parietal components of somatosensory evoked potentials in hemispheric lesions: Detailed correlations with clinical signs and computerized tomographic scanning. Brain 1983, 106, 271–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urushihara, R.; Murase, N.; Rothwell, J.C.; Harada, M.; Hosono, Y.; Asanuma, K.; Shimazu, H.; Nakamura, K.; Chikahisa, S.; Kitaoka, K. Effect of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation applied over the premotor cortex on somatosensory-evoked potentials and regional cerebral blood flow. Neuroimage 2006, 31, 699–709. [Google Scholar]
- Kaňovský, P.; Bareš, M.; Rektor, I. The selective gating of the N30 cortical component of the somatosensory evoked potentials of median nerve is different in the mesial and dorsolateral frontal cortex: Evidence from intracerebral recordings. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2003, 114, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossini, P.; Gigli, G.; Marciani, M.; Zarola, F.; Caramia, M. Non-invasive evaluation of input-output characteristics of sensorimotor cerebral areas in healthy humans. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. Evoked Potentials Sect. 1987, 68, 88–100. [Google Scholar]
- Allison, T.; McCarthy, G.; Wood, C.C.; Jones, S.J. Potentials evoked in human and monkey cerebral cortex by stimulation of the median nerve: A review of scalp and intracranial recordings. Brain 1991, 114, 2465–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmedt, J.E.; Huy, N.T.; Bourguet, M. The cognitive P40, N60 and P100 components of somatosensory evoked potentials and the earliest electrical signs of sensory processing in man. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1983, 56, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbruzzese, G.; Reni, L.; Cocito, L.; Ratto, S.; Abbruzzese, M.; Favale, E. Short-latency somatosensory evoked potentials in degenerative and vascular dementia. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1984, 47, 1034–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen-Dahm, C.; Madsen, C.S.; Waldemar, G.; Ballegaard, M.; Hejl, A.M.; Johnsen, B.; Jensen, T.S. Contact heat evoked potentials (CHEPs) in patients with mild-moderate Alzheimer’s disease and matched control—A pilot study. Pain Med. 2015, 17, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ferri, R.; Del Gracco, S.; Elia, M.; Musumeci, S.; Spada, R.; Stefanini, M. Scalp topographic mapping of middle-latency somatosensory evoked potentials in normal aging and dementia. Neurophysiol. Clin./Clin. Neurophysiol. 1996, 26, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen, J.M.; Montaño, R.; Donahue, C.H.; Adair, J.C.; Knoefel, J.K.; Qualls, C.; Hart, B.; Ranken, D.; Aine, C.J. Somatosensory responses in normal aging, mild cognitive impairment, and Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neural Transm. 2010, 117, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachibana, H.; Takeda, M.; Okuda, B.; Kawabata, K.; Nishimura, H.; Kodama, N.; Iwamoto, Y.; Sugita, M. Multimodal evoked potentials in Alzheimer’s disease and Binswanger’s disease. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry Neurol. 1996, 9, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, J. Somatosensory event-related potentials (ERPs) in patients with different types of dementia. J. Neurol. Sci. 1994, 121, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, K.C.; Pontifex, M.B.; Scudder, M.R.; Brown, M.L.; Hillman, C.H. The effects of single bouts of aerobic exercise, exergaming, and videogame play on cognitive control. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2011, 122, 1518–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.K.; Labban, J.; Gapin, J.; Etnier, J.L. The effects of acute exercise on cognitive performance: A meta-analysis. Brain Res. 2012, 1453, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiffer, R.; Darby, L.A.; Fullenkamp, A.; Morgan, A.L. Effects of acute aerobic exercise on executive function in older women. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2015, 14, 574. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perciavalle, V.; Alagona, G.; De Maria, G.; Rapisarda, G.; Costanzo, E.; Perciavalle, V.; Coco, M. Somatosensory evoked potentials and blood lactate levels. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 36, 1597–1601. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nasreddine, Z.S.; Phillips, N.A.; Bédirian, V.; Charbonneau, S.; Whitehead, V.; Collin, I.; Cummings, J.L.; Chertkow, H. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment, MoCA: A brief screening tool for mild cognitive impairment. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2005, 53, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nasreddine, Z.S.; Phillips, N.A.; Bédirian, V.; Charbonneau, S.; Whitehead, V.; Collin, I.; Cummings, J.L.; Chertkow, H. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment, MoCA: A Brief Screening Tool for Mild Cognitive Impairment. 2019. Available online: https://www.mocatest.org/ (accessed on 22 September 2020).
- She, J.; Nakamura, H.; Makino, K.; Ohyama, Y.; Hashimoto, H. Selection of suitable maximum-heart-rate formulas for use with Karvonen formula to calculate exercise intensity. Int. J. Autom. Comput. 2015, 12, 62–69. [Google Scholar]
- Kamijo, K.; Hayashi, Y.; Sakai, T.; Yahiro, T.; Tanaka, K.; Nishihira, Y. Acute effects of aerobic exercise on cognitive function in older adults. J. Gerontol. Ser. B 2009, 64, 356–363. [Google Scholar]
- Nakata, H.; Oshiro, M.; Namba, M.; Shibasaki, M. Effects of passive heat stress on human somatosensory processing. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2015, 309, R1387–R1396. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, L.D.; Frank, L.L.; Foster-Schubert, K.; Green, P.S.; Wilkinson, C.W.; McTiernan, A.; Cholerton, B.A.; Plymate, S.R.; Fishel, M.A.; Watson, G. Aerobic exercise improves cognition for older adults with glucose intolerance, a risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2010, 22, 569–579. [Google Scholar]
- Amjad, I.; Toor, H.; Niazi, I.K.; Afzal, H.; Jochumsen, M.; Shafique, M.; Allen, K.; Haavik, H.; Ahmed, T. Therapeutic effects of aerobic exercise on EEG parameters and higher cognitive functions in mild cognitive impairment patients. Int. J. Neurosci. 2019, 129, 551–562. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Q.; Chastan, N.; Bair, W.N.; Resnick, S.M.; Ferrucci, L.; Studenski, S.A. The brain map of gait variability in aging, cognitive impairment and dementia—A systematic review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 74, 149–162. [Google Scholar]
- Nuwer, M.R. Fundamentals of evoked potentials and common clinical applications today. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1998, 106, 142–148. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, S. An ‘interference’approach to the study of somatosensory evoked potentials in man. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1981, 52, 517–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakigi, R.; Jones, S. Effects on median nerve SEPs of tactile stimulation applied to adjacent and remote areas of the body surface. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. Evoked Potentials Sect. 1985, 62, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kida, T.; Wasaka, T.; Nakata, H.; Akatsuka, K.; Kakigi, R. Centrifugal regulation of a task-relevant somatosensory signal triggering voluntary movement without a preceding warning signal. Exp. Brain Res. 2006, 173, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakata, H.; Inui, K.; Wasaka, T.; Nishihira, Y.; Kakigi, R. Mechanisms of differences in gating effects on short-and long-latency somatosensory evoked potentials relating to movement. Brain Topogr. 2003, 15, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, D.; Yamashiro, K.; Onishi, H.; Shimoyama, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Maruyama, A. The effect of water immersion on short-latency somatosensory evoked potentials in human. BMC Neurosci. 2012, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodges, P.W.; Moseley, G.L. Pain and motor control of the lumbopelvic region: Effect and possible mechanisms. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2003, 13, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluger, A.; Gianutsos, J.G.; Golomb, J.; Ferris, S.H.; George, A.E.; Franssen, E.; Reisberg, B. Patterns of motor impairment in normal aging, mild cognitive decline, and early Alzheimer’Disease. J. Gerontol. Ser. B Psychol. Sci. Soc. Sci. 1997, 52, P28–P39. [Google Scholar]
- Schröter, A.; Mergl, R.; Bürger, K.; Hampel, H.; Möller, H.J.; Hegerl, U. Kinematic analysis of handwriting movements in patients with Alzheimer’s disease, mild cognitive impairment, depression and healthy subjects. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2003, 15, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzumura, S.; Osawa, A.; Maeda, N.; Sano, Y.; Kandori, A.; Mizuguchi, T.; Yin, Y.; Kondo, I. Differences among patients with Alzheimer’s disease, older adults with mild cognitive impairment and healthy older adults in finger dexterity. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2018, 18, 907–914. [Google Scholar]
- Mustroph, M.L.; Chen, S.; Desai, S.C.; Cay, E.B.; DeYoung, E.K.; Rhodes, J.S. Aerobic exercise is the critical variable in an enriched environment that increases hippocampal neurogenesis and water maze learning in male C57BL/6J mice. Neuroscience 2012, 219, 62–71. [Google Scholar]
- Lelic, D.; Niazi, I.K.; Holt, K.; Jochumsen, M.; Dremstrup, K.; Yielder, P.; Murphy, B.; Drewes, A.M.; Haavik, H. Manipulation of dysfunctional spinal joints affects sensorimotor integration in the prefrontal cortex: A brain source localization study. Neural Plast. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, H.H.; Murphy, B. Altered sensorimotor integration with cervical spine manipulation. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2008, 31, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, P.; Murphy, B. The Effect of Sacroiliac Joint Manipulation on Feed-Forward Activation Times of the Deep Abdominal Musculature. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2006, 29, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desmedt, J.E.; Cheron, G. Somatosensory evoked potentials to finger stimulation in healthy octogenarians and in young adults: Wave forms, scalp topography and transit times of pariental and frontal components. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1980, 50, 404–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakigi, R.; Shibasaki, H. Effects of age, gender, and stimulus side on scalp topography of somatosensory evoked potentials following median nerve stimulation. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. Off. Publ. Am. Electroencephalogr. Soc. 1991, 8, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klunk, W.; Panchalingam, K.; Moossy, J.; McClure, R.; Pettegrew, J. N-acetyl-L-aspartate and other amino acid metabolites in Alzheimer’s disease brain: A preliminary proton nuclear magnetic resonance study. Neurology 1992, 42, 1578–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyman, B.T.; Van Hoesen, G.W.; Damasio, A.R.; Barnes, C.L. Alzheimer’s disease: Cell-specific pathology isolates the hippocampal formation. Science 1984, 225, 1168–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitsch, R.; Frotscher, M. Reduction of posttraumatic transneuronal” early gene” activation and dendritic atrophy by the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist MK-801. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 5197–5200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilela, T.C.; Muller, A.P.; Damiani, A.P.; Macan, T.P.; da Silva, S.; Canteiro, P.B.; de Sena Casagrande, A.; dos Santos Pedroso, G.; Nesi, R.T.; de Andrade, V.M. Strength and aerobic exercises improve spatial memory in aging rats through stimulating distinct neuroplasticity mechanisms. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 7928–7937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.M.; Staines, W.R. The effects of acute aerobic exercise on the primary motor cortex. J. Mot. Behav. 2015, 47, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amjad, I.; Niazi, I.K.; Toor, H.G.; Nedergaard, R.B.; Shafique, M.; Holt, K.; Haavik, H.; Ahmed, T. Acute Effects of Aerobic Exercise on Somatosensory-Evoked Potentials in Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 663. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10100663
Amjad I, Niazi IK, Toor HG, Nedergaard RB, Shafique M, Holt K, Haavik H, Ahmed T. Acute Effects of Aerobic Exercise on Somatosensory-Evoked Potentials in Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment. Brain Sciences. 2020; 10(10):663. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10100663
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmjad, Imran, Imran Khan Niazi, Hamza Ghazanfar Toor, Rasmus Bach Nedergaard, Muhammad Shafique, Kelly Holt, Heidi Haavik, and Touqeer Ahmed. 2020. "Acute Effects of Aerobic Exercise on Somatosensory-Evoked Potentials in Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment" Brain Sciences 10, no. 10: 663. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10100663
APA StyleAmjad, I., Niazi, I. K., Toor, H. G., Nedergaard, R. B., Shafique, M., Holt, K., Haavik, H., & Ahmed, T. (2020). Acute Effects of Aerobic Exercise on Somatosensory-Evoked Potentials in Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment. Brain Sciences, 10(10), 663. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10100663









