GIS-Based Solar Radiation Mapping, Site Evaluation, and Potential Assessment: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Solar Radiation Mapping Using GISs
2.1. Overview
2.2. Solar Radiation Map as a Spatial DB
2.3. Spatial Solar Radiation Mapping Using Interpolation Methods
2.4. Solar Radiation Estimation for Stations with No Solar Radiation Records
2.5. Solar Radiation Model
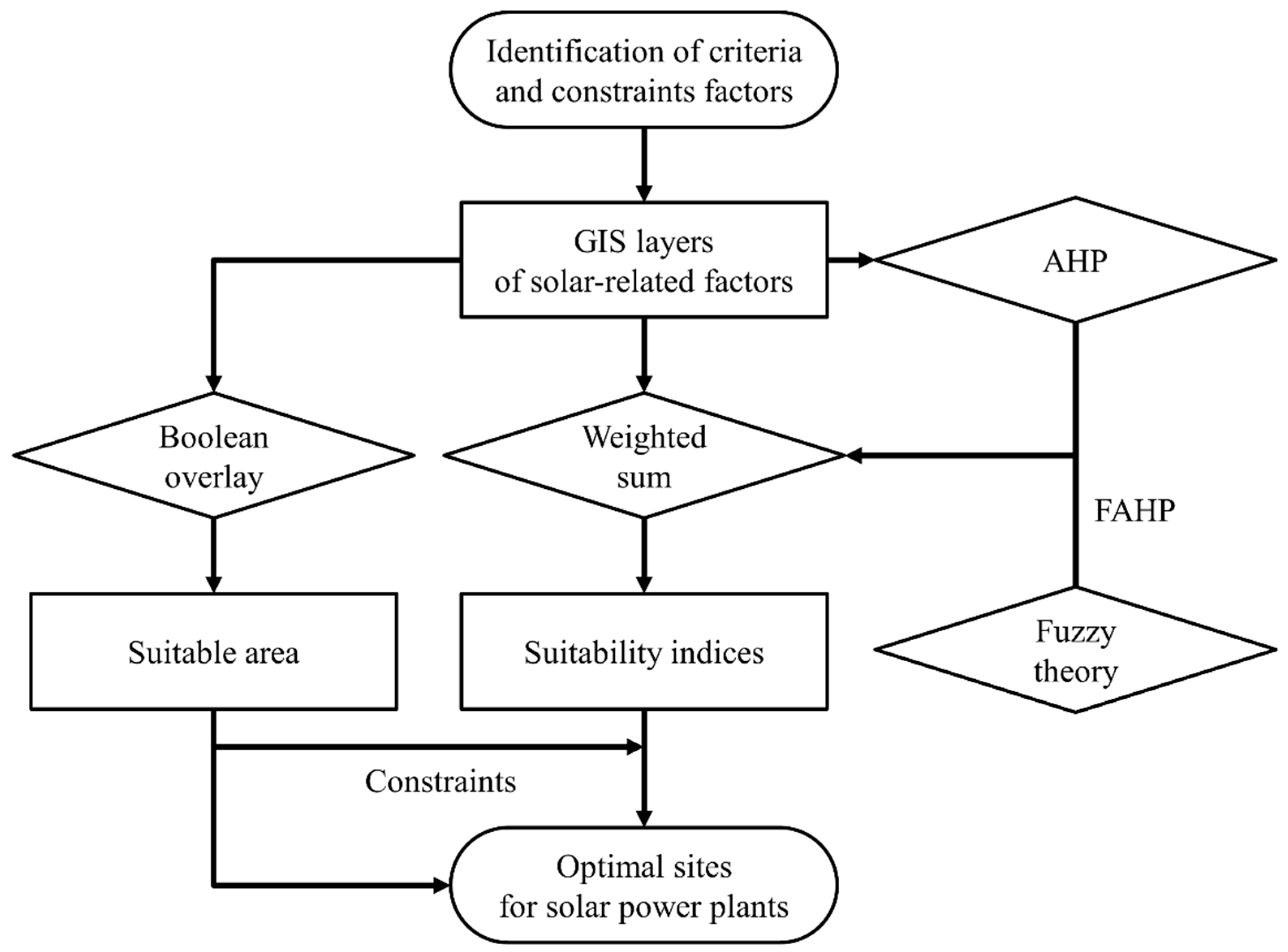
3. Solar Site Evaluation Using GISs
3.1. Overview
3.2. Boolean Overlay
3.3. Weighted Sum
3.4. Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP)
3.5. Fuzzy AHP (FAHP)
3.6. Other Approaches
3.7. Solar Site Evaluation for Specific Objects
4. Solar Potential Assessment Using GISs
4.1. Overview
4.2. DB and Visualization Tools
4.3. Rooftop Extraction Tool
4.4. Radiation Modeling Tool
4.5. Shading Analysis Tool
4.6. Spatial Analysis Tool
5. Discussion and Conclusions
- (1)
- Solar radiation maps can be useful spatial DBs in spatial and temporal analyses of solar resources. Interpolation methods can be employed for solar radiation mapping in areas with sufficient measured data. The results are presented as solar maps over large areas in pixels. In the absence of sufficient measured solar radiation data, other weather information can be used to predict solar radiation. This method is performed for a specific point, such as a station, by predicting the solar radiation relatively accurately based on various parameters. In recent years, machine learning techniques such as ANNs have been used. After accurately estimating the solar radiation for additional stations, more accurate solar radiation mapping can be achieved via interpolation. Solar radiation models using topography were also developed to predict solar radiation where there is no measured data. Various algorithms and shadow analysis based on GISs are mainly utilized in these models. The solar radiation maps produced using these methods can facilitate the identification of solar resources in specific areas and the determination of suitable areas for solar power plants. Validation using measured data is necessary to verify the accuracy of such maps.
- (2)
- GISs are useful for site evaluation when installing solar power plants for PV or CSP. While diffuse radiation is also an important factor in PV suitability analysis, only direct radiation is considered in CSP suitability analysis. In most site evaluation studies, solar radiation is the primary consideration and is obtained in various ways depending on the presence or absence of data. In particular, site evaluation by employing a GIS is useful for supporting decision making on the regional scale, and it is necessary to consider economic, environmental, technical, social, and risk factors in addition to solar radiation. These factors can be used to exclude unsuitable regions through Boolean overlay. They can also be employed in various MCDA methods to estimate suitability indices. Some researchers have performed suitability analysis for buildings, mines, and reservoirs.
- (3)
- The assessment of solar PV potential is critical in the development of planning policies and financing schemes for successful PV system deployment. Most of the reviewed literature focused on assessing the technical potential in the region of interest among the three types of solar potential. GISs are effective for assessing physical potential (total solar radiation on the surface/rooftop) and geographic potential (available surface/rooftop area considering the shadow), serving various purposes such as DB and visualization, rooftop extraction, radiation modeling, shading analysis, and spatial analysis tools. In addition, GISs can be utilized to visualize and interpret solar energy-based power output or economic values in the geospatial context in technical potential assessment.
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations and Symbols
| AHP | analytic hierarchy process |
| ANN | artificial neural network |
| ATM | atmospheric and topographic model |
| CAES | compressed air energy storage |
| CBR | case based reasoning |
| CSP | concentrated solar power |
| DB | database |
| DEM | digital elevation model |
| DHI | diffuse horizontal irradiance |
| DNI | direct normal irradiance |
| DSM | digital surface model |
| ESMAP | energy sector management assistance program |
| FAHP | fuzzy analytic hierarchy process |
| FEM | finite element method |
| FLOWA | fuzzy logic ordered weight averaging |
| GHI | global horizontal irradiance |
| GIS | geographic information system |
| IODC | Indian Ocean Data Coverage |
| IRIS | Interactive robustness analysis and parameters’ inference for multicriteria sorting problems |
| LiDAR | Light Detection and Ranging |
| MADSR | monthly average daily solar radiation |
| MCDA | multi-criteria decision analysis |
| MCDM | multi-criteria decision making |
| NREL | National Renewable Energy Laboratory |
| OR-SAGE | Oak ridge siting analysis for power generation expansion |
| PV | photovoltaics |
| SAM | system advisor model |
| SHWS | solar hot water systems |
| SWARA | step-wise weight assessment ratio analysis |
| TOPSIS | technique for order preference by similarity to ideal solution |
| TRNSYS | transient systems simulation |
| US | United States |
| WASPAS | weighted aggregates Sum Product Assessment |
References
- Choi, Y.; Rayl, J.; Tammineedi, C.; Brownson, J.R.S. PV Analyst: Coupling ArcGIS with TRNSYS to assess distributed photovoltaic potential in urban areas. Sol. Energy 2011, 85, 2924–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zekai, S. Solar energy in progress and future research trends. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2014, 30, 367–416. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Kleissl, J.; Gueymard, C.A.; Pedro, H.T.C.; Coimbra, C.F.M. History and trends in solar irradiance and PV power forecasting: A preliminary assessment and review using text mining. Sol. Energy 2018, 168, 60–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, S.; Catita, C.; Redweik, P.; Brito, M.C. Modelling solar potential in the urban environment: State-of-the-art review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 41, 915–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrami, M.; Abbaszadeh, P. An overview of renewable energies in Iran. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 24, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, Z.R.; Asim, M. Surface measured solar radiation data and solar energy resource assessment of Pakistan: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 2839–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawilska, E.; Brooks, M.J. An assessment of the solar resource for Durban, South Africa. Renew. Energy 2011, 36, 3433–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Choi, Y.; Yoon, S. Analysis of photovoltaic potential at abandoned mine promotion districts in Korea. Geosyst. Eng. 2015, 18, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, D.; Barbour, E.; Harrison, G.P. The UK solar energy resource and the impact of climate change. Renew. Energy 2014, 71, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šúri, M.; Huld, T.A.; Dunlop, E.D. PV-GIS: A web-based solar radiation database for the calculation of PV potential in Europe. Int. J. Sust. Energy 2005, 24, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandra, T.; Shruthi, B. Spatial mapping of renewable energy potential. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2007, 11, 1460–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nematollahi, O.; Kim, K.C. A feasibility study of solar energy in South Korea. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 77, 566–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamdari, P.; Nematollahi, O.; Alemrajabi, A.A. Solar energy potentials in Iran: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 21, 778–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stökler, S.; Schillings, C.; Kraas, B. Solar resource assessment study for Pakistan. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 58, 1184–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumbayan, M.; Abudureyimu, A.; Nagasaka, K. Mapping of solar energy potential in Indonesia using artificial neural network and geographical information system. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 1437–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, C.; Hong, T.; Lee, M.; Park, H.S. Estimation of the Monthly Average Daily Solar Radiation using Geographic Information System and Advanced Case-Based Reasoning. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 4829–4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Koo, C.; Hong, T.; Park, H.S. Framework for the Mapping of the Monthly Average Daily Solar Radiation Using an Advanced Case-Based Reasoning and a Geostatistical Technique. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 4604–4612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, C.; Hong, T.; Jeong, K.; Kim, J. Development of the monthly average daily solar radiation map using a-CBR, FEM, and Kriging method. Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. 2018, 24, 489–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofierka, J.; Šúri, M. The solar radiation model for Open source GIS: Implementation and applications. In Proceedings of the Open Source GIS—GRASS Users Conference 2002, Trento, Italy, 11–13 September 2002; pp. 51–70. [Google Scholar]
- Šúri, M.; Hofierka, J. A New GIS-based Solar Radiation Model and Its Application to Photovoltaic Assessments. Trans. GIS 2004, 8, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubayah, R.; Rich, P.M. Topographic solar radiation models for GIS. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 1995, 9, 405–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corripio, J.G. Vectorial algebra algorithms for calculating terrain parameters from dems and solar radiation modelling in mountainous terrain. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2003, 17, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redweik, P.; Catita, C.; Brito, M. Solar energy potential on roofs and facades in an urban landscape. Sol. Energy 2013, 97, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fluri, T.P. The potential of concentrating solar power in South Africa. Energy Policy 2009, 37, 5075–5080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrouni, A.A.; Mezrhab, A.; Mezrhab, A. CSP sites suitability analysis in the Eastern region of Morocco. Energy Procedia 2014, 49, 2270–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Merrouni, A.A.; Mezrhab, A.; Mezrhab, A. PV sites suitability analysis in the Eastern region of Morocco. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2016, 18, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Fu, D.; Lu, X.; Wua, T.; Tong, Q. Selecting photovoltaic generation sites in Tibet using remote sensing and geographic analysis. Sol. Energy 2016, 133, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hott, R.; Santini, R.; Brownson, J.R.S. GIS-based Spatial Analysis for Large-Scale Solar Power and Transmission Line Issues: Case Study of Wyoming, U.S. In Proceedings of the 41st American Solar Energy Society Meeting, Denver, CO, USA, 13–17 May 2012; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Jahangiri, M.; Ghaderi, R.; Haghani, A.; Nematollahi, O. Finding the best locations for establishment of solar-wind power stations in Middle-East using GIS: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 66, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwarzai, M.A.; Nagasaka, K. Utility-scale implementable potential of wind and solar energies for Afghanistan using GIS multi-criteria decision analysis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 71, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherboudj, I.; Ghedira, H. Assessment of solar energy potential over the United Arab Emirates using remote sensing and weather forecast data. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 55, 1210–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, C.P.; Silva, F.B.E.; Lavalle, C. An assessment of the regional potential for solar power generation in EU-28. Energy Policy 2016, 88, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janke, J.R. Multicriteria GIS modeling of wind and solar farms in Colorado. Renew. Energy 2010, 35, 2228–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevallos-Sierra, J.; Ramos-Martin, J. Spatial assessment of the potential of renewable energy: The case of Ecuador. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 1154–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, Y.N.; Kentel, E.; Duzgun, H.S. GIS-based site selection methodology for hybrid renewable energy systems: A case study from western Turkey. Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 70, 90–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, J.; Ames, D.P.; Solan, D.; Lee, R.; Carlisle, J. Using GIS analytics and social preference data to evaluate utility-scale solar power site suitability. Renew. Energy 2015, 81, 825–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vafaeipour, M.; Zolfani, H.S.; Mohammad, H.M.V.; Derakhti, A.; Eshkalag, M.K. Assessment of regions priority for implementation of solar projects in Iran: New application of a hybrid multi-criteria decision-making approach. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 86, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziuku, S.; Seyitini, L.; Mapurisa, B.; Chikodzi, D.; Kuijk, K. Potential of Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) in Zimbabwe. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2014, 23, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Garni, H.Z.; Awasthi, A. Solar PV power plant site selection using a GIS-AHP based approach with application in Saudi Arabia. Appl. Energy 2017, 206, 1225–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyan, M. GIS-based solar farms site selection using analytic hierarchy process (AHP) in Karapinar region, Konya/Turkey. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 28, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yushchenko, A.; de Bono, A.; Chatenoux, B.; Patel, M.K.; Ray, N. GIS-based assessment of photovoltaic (PV) and concentrated solar power (CSP) generation potential in West Africa. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 2088–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrouni, A.A.; Elalaoui, F.E.; Mezrhab, A.; Mezrhab, A.; Ghennioui, A. Large scale PV sites selection by combining GIS and Analytical Hierarchy Process. Case study: Eastern Morocco. Renew. Energy 2018, 119, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, A.; Jensen, S.S.; Pedersen, A.B. Solar power potential of Tanzania: Identifying CSP and PV hot spots through a GIS multicriteria decision making analysis. Renew. Energy 2017, 113, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahri, M.; Hakdaoui, M.; Maanan, M. The evaluation of solar farm locations applying Geographic Information System and Multi-Criteria Decision-Making methods: Case study in southern Morocco. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 51, 1354–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, J.J.W.; Hudson, M.D. Regional Scale wind farm and solar farm suitability assessment using GIS-assisted multi-criteria evaluation. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 138, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asakereh, A.; Omid, M.; Alimardani, R.; Sarmadian, F. Developing a GIS-based Fuzzy AHP Model for Selecting Solar Energy Sites in Shodirwan Region in Iran. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Technol. 2014, 68, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noorollahi, E.; Fadai, D.; Shirazi, M.A.; Ghodsipour, S.H. Land Suitability Analysis for Solar Farms Exploitation Using GIS and Fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy Process (FAHP)-A Case Study of Iran. Energies 2016, 9, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charabi, Y.; Gastli, A. PV site suitability analysis using GIS-based spatial fuzzy multi-criteria evaluation. Renew. Energy 2011, 36, 2554–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, J.; Brownson, J.R.S. Solar farm suitability using geographic information system fuzzy sets and analytic hierarchy processes: Case study of Ulleung Island, Korea. Energies 2016, 9, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Lozano, J.M.; Teruel-Solano, J.; Soto-Elvira, P.L.; García-Cascales, M.S. Geographical Information Systems (GIS) and Multi-Criteria Decision Making (MCDM) methods for the evaluation of solar farms locations: Case study in south-eastern Spain. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 24, 544–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Lozano, J.M.; Antunes, H.C.; García-cascales, M.S.; Dias, L.C. GIS-based photovoltaic solar farms site selection using ELECTRE-TRI: Evaluating the case for Torre Pacheco, Murcia, Southeast of Spain. Renew. Energy 2014, 66, 478–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondino, E.B.; Fabrizio, E.; Chiabrando, R. Site Selection of Large Ground-Mounted Photovoltaic Plants: A GIS Decision Support System and an Application to Italy. Int. J. Green Energy 2015, 12, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omitaomu, O.A.; Blevins, B.R.; Jochem, W.C.; Mays, G.T.; Belles, R.; Hadley, S.W.; Harrison, T.J.; Bhaduri, B.L.; Neish, B.S.; Rose, A.N. Adapting a GIS-based multicriteria decision analysis approach for evaluating new power generating sites. Appl. Energy 2012, 96, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Song, J. Assessment of Photovoltaic Potentials at Abandoned Mine Reclamation Sites in Korea using Renewable Energy Resource Maps. New Renew. Energy 2016, 12, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Oh, M.; Park, H.D. Analysis and Prioritization of the Floating Photovoltaic System Potential for Reservoirs in Korea. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukac, N.; Žlaus, D.; Seme, S.; Žalik, B.; Štumberger, G. Rating of roofs’ surfaces regarding their solar potential and suitability for PV systems, based on LiDAR data. Appl. Energy 2013, 102, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Hong, T.; Jeong, J.; Jeong, K. Development of a rooftop solar photovoltaic rating system considering the technical and economic suitability criteria at the building level. Energy 2018, 160, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Choi, Y.; Jang, M.; Yoon, S. A Comparison of Wind Power and Photovoltaic Potentials at Yeongok, Mulno and Booyoung Abandoned Mines in Kangwon Province, Korea. J. Korean Soc. Miner. Energy Resour. Eng. 2014, 51, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarigan, E.; Djuwari; Purba, L. Assessment of PV Power Generation for Household in Surabaya Using SolarGIS—PvPlanner Simulation. Energy Procedia 2014, 47, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Besarati, S.M.; Padilla, R.V.; Goswami, D.Y.; Stefanakos, E. The potential of harnessing solar radiation in Iran: Generating solar maps and viability study of PV power plants. Renew. Energy 2013, 53, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichter, T.; Soria, R.; Szklo, A.; Schaeffer, R.; Lucena, A.F.P. Assessing the potential role of concentrated solar power (CSP) for the northeast power system of Brazil using a detailed power system model. Energy 2017, 121, 695–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukač, N.; Seme, S.; Žlaus, D.; Štumberger, G.; Žalik, B. Buildings roofs photovoltaic potential assessment based on LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) data. Energy 2014, 66, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamasco, L.; Asinari, P. Scalable methodology for the photovoltaic solar energy potential assessment based on available roof surface area: Application to Piedmont Region (Italy). Sol. Energy 2011, 85, 1041–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malagueta, D.; Szklo, A.; Borba, B.S.M.C.; Soria, R.; Aragão, R.; Schaeffer, R.; Dutra, R. Assessing incentive policies for integrating centralized solar power generation in the Brazilian electric power system. Energy Policy 2013, 59, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-pomares, L.; Martínez, D.; Polo, J.; Perez-astudillo, D.; Bachour, D.; San, A. Analysis of the long-term solar potential for electricity generation in Qatar. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 73, 1231–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milbrandt, A.R.; Heimiller, D.M.; Perry, A.D.; Field, C.B. Renewable energy potential on marginal lands in the United States. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 29, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, J.; Arsalan, M.H. Estimation of rooftop solar photovoltaic potential using geo-spatial techniques: A perspective from planned neighborhood of Karachi Pakistan. Renew. Energy 2016, 90, 188–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo, S.; Montanẽś, C.; Dopazo, C.; Fueyo, N. Roof-top solar energy potential under performance-based building energy codes: The case of Spain. Sol. Energy 2011, 85, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charabi, Y.; Gastli, A. GIS assessment of large CSP plant in Duqum, Oman. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastli, A.; Charabi, Y.; Zekri, S. GIS-based assessment of combined CSP electric power and seawater desalination plant for Duqum—Oman. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofierka, J.; Kaňuk, J. Assessment of photovoltaic potential in urban areas using open-source solar radiation tools. Renew. Energy 2009, 34, 2206–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catita, C.; Redweik, P.; Pereira, J.; Brito, M.C. Extending solar potential analysis in buildings to vertical facades. Comput. Geosci. 2014, 66, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo, S.; Rodrigues, M.; Fueyo, N. A method for estimating the geographical distribution of the available roof surface area for large-scale photovoltaic energy-potential evaluations. Sol. Energy 2008, 82, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polo, J.; Bernardos, A.; Navarro, A.A.; Fernandez-Peruchena, C.M.; Ramírez, L.; Guisado, M.V.; Martínez, S. Solar resources and power potential mapping in Vietnam using satellite-derived and GIS-based information. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 98, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, L.; Wang, J.; Chen, C.; Tsai, H. Evaluation of the development potential of rooftop solar photovoltaic in Taiwan. Renew. Energy 2015, 76, 582–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Hong, T.; Jeong, K.; Kim, J. A bottom-up approach for estimating the economic potential of the rooftop solar photovoltaic system considering the spatial and temporal diversity. Appl. Energy 2018, 232, 640–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.; Lee, M.; Koo, C.; Jeong, K.; Kim, J. Development of a method for estimating the rooftop solar photovoltaic (PV) potential by analyzing the available rooftop area using Hillshade analysis. Appl. Energy 2017, 194, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Choi, Y. Evaluation of rooftop photovoltaic electricity generation systems for establishing a green campus. Geosyst. Eng. 2015, 18, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Song, J. Sustainable development of abandoned mine areas using renewable energy systems: A case study of the photovoltaic potential assessment at the tailings dam of abandoned Sangdong mine, Korea. Sustainability 2016, 8, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Choi, Y. Analysis of the Potential for Use of Floating Photovoltaic Systems on Mine Pit Lakes: Case Study at the Ssangyong Open-Pit Limestone Mine in Korea. Energies 2016, 9, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifton, J.; Boruff, B.J. Assessing the potential for concentrated solar power development in rural Australia. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 5272–5280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.S.; Zhu, R.; Liu, Z.; Lu, L.; Peng, J.; Tang, Z.; Lo, C.H.; Chan, W.K. Estimation of Hong Kong’ s solar energy potential using GIS and remote sensing technologies. Renew. Energy 2016, 99, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massimo, A.; Dell’Isola, M.; Frattolillo, A.; Ficco, G. Development of a Geographical Information System (GIS) for the Integration of Solar Energy in the Energy Planning of a Wide Area. Sustainability 2014, 6, 5730–5744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Hof, A.; Wang, R.; Liu, J.; Lin, Y.; Yang, D. GIS-based approach for potential analysis of solar PV generation at the regional scale: A case study of Fujian Province. Energy Policy 2013, 58, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayrakci, M.; Choi, Y.; Brownson, J.R.S. Temperature dependent power modeling of photovoltaics. Energy Procedia 2014, 57, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahtta, R.; Joshi, P.K.; Jindal, A.K. Solar power potential mapping in India using remote sensing inputs and environmental parameters. Renew. Energy 2014, 71, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, A.; Roberts, B.; Heimiller, D.; Blair, N.; Porro, G.; Lopez, A.; Roberts, B.; Blair, N.; Porro, G.U.S. Renewable Energy Technical Potentials A GIS-Based Analysis. Available online: https://www.nrel.gov/docs/fy12osti/51946.pdf (accessed on 24 December 2018).
- Monforti, F.; Huld, T.; Bódis, K.; Vitali, L.; D’Isidoro, M.; Lacal-arántegui, R. Assessing complementarity of wind and solar resources for energy production in Italy. A Monte Carlo approach. Renew. Energy 2014, 63, 576–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niblick, B.; Landis, A.E. Assessing renewable energy potential on United States marginal and contaminated sites. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 60, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Choi, Y.; Suh, J.; Park, H.; Jang, M.; Go, W.R. Assessment of Photovoltaic Potentials at Buguk, Sungsan and Younggwang Abandoned Mines in Jeollanam-do, Korea. J. Korean Soc. Miner. Energy Resour. Eng. 2013, 50, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffat, R.; Grassi, S.; Raubal, M. A scalable method for estimating rooftop solar irradiation potential over large regions. Appl. Energy 2018, 216, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastli, A.; Charabi, Y. Solar electricity prospects in Oman using GIS-based solar radiation maps. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 790–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Kammen, D.M. Where, when and how much solar is available? A provincial-scale solar resource assessment for China. Renew. Energy 2016, 85, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köberle, A.C.; Gernaat, D.E.H.J.; van Vuuren, D.P. Assessing current and future techno-economic potential of concentrated solar power and photovoltaic electricity generation. Energy 2015, 89, 739–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterseim, J.H.; Herr, A.; Miller, S.; White, S.; O’Connell, D.A. Concentrating solar power/alternative fuel hybrid plants: Annual electricity potential and ideal areas in Australia. Energy 2014, 68, 698–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
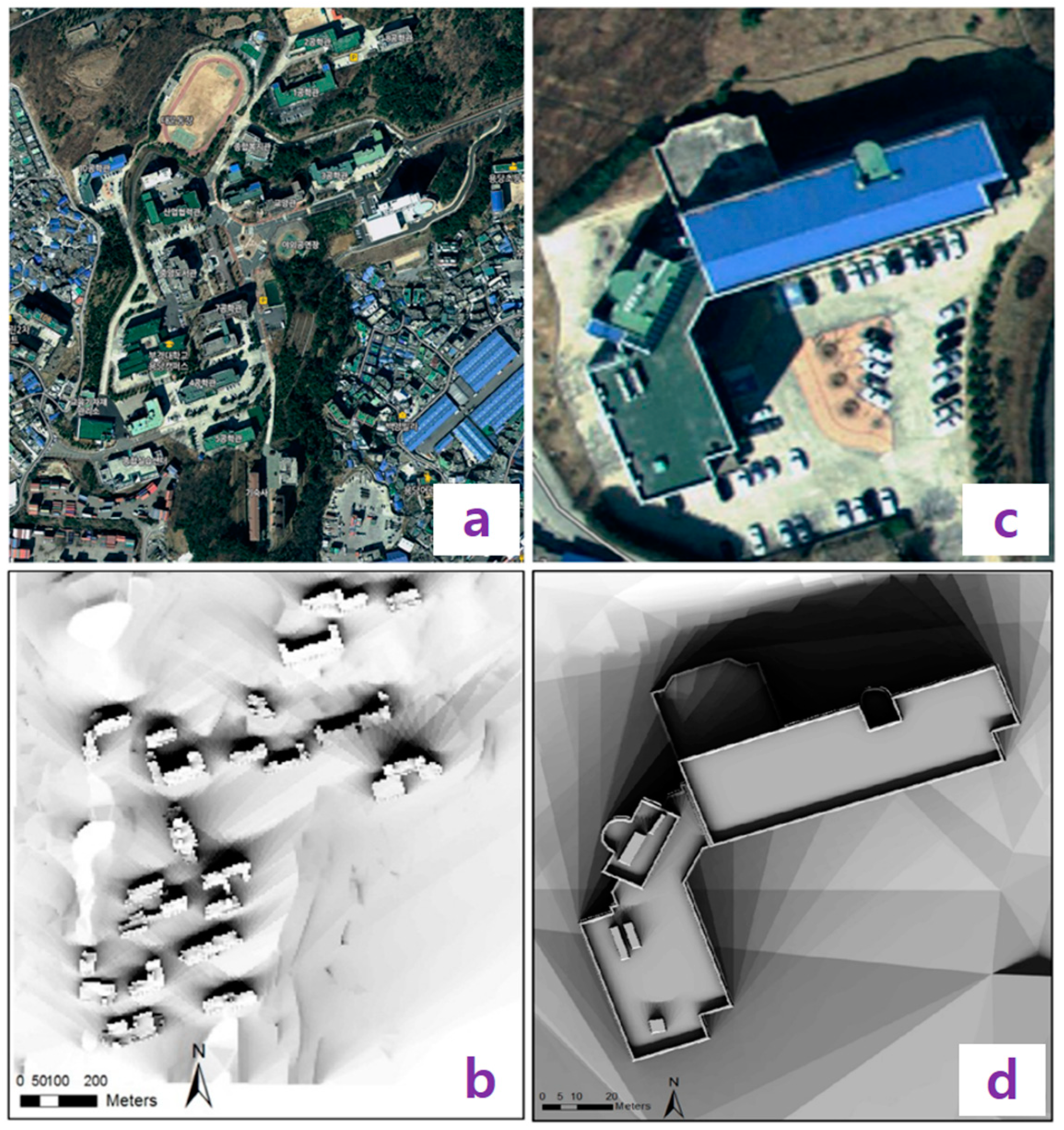
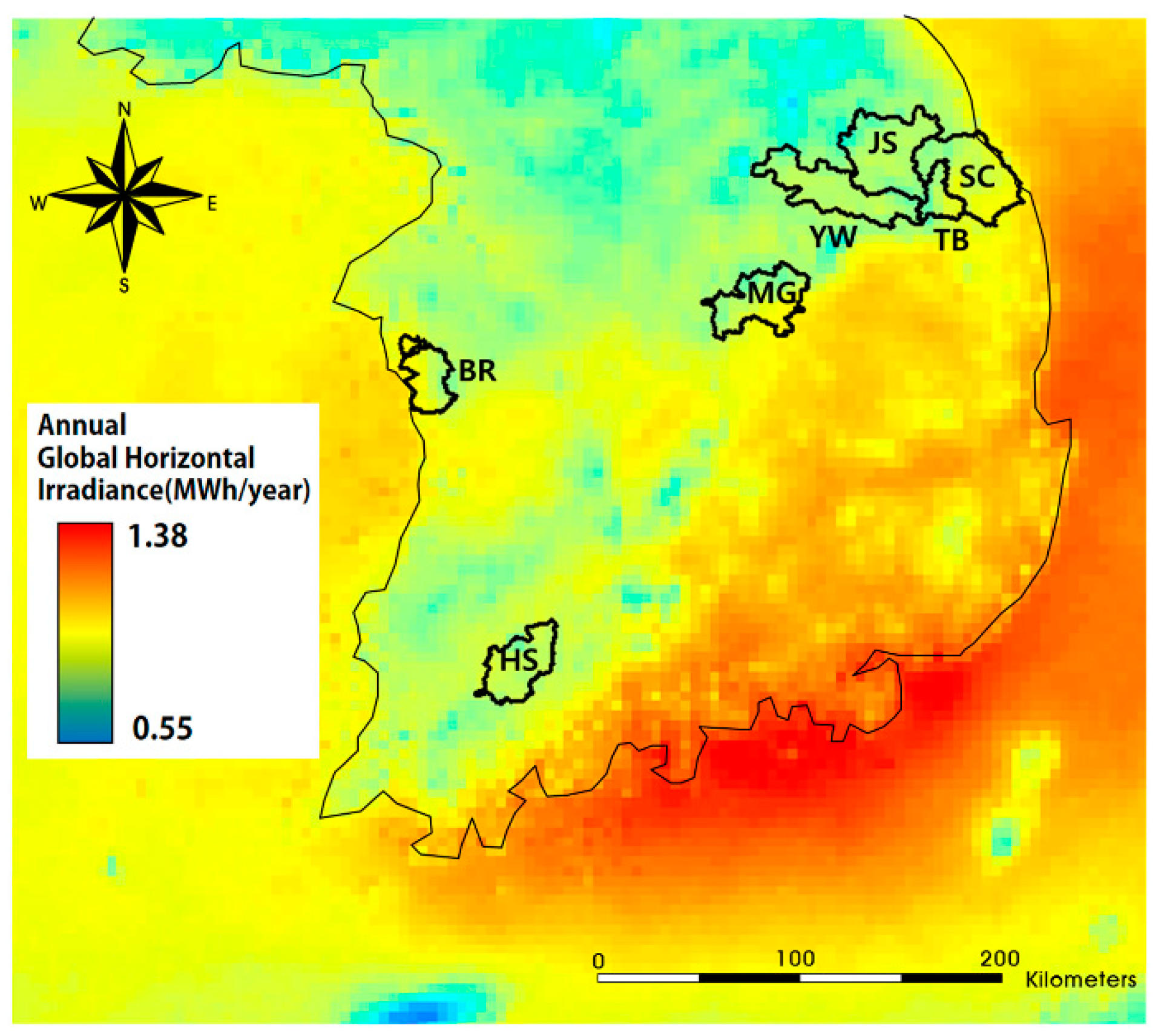
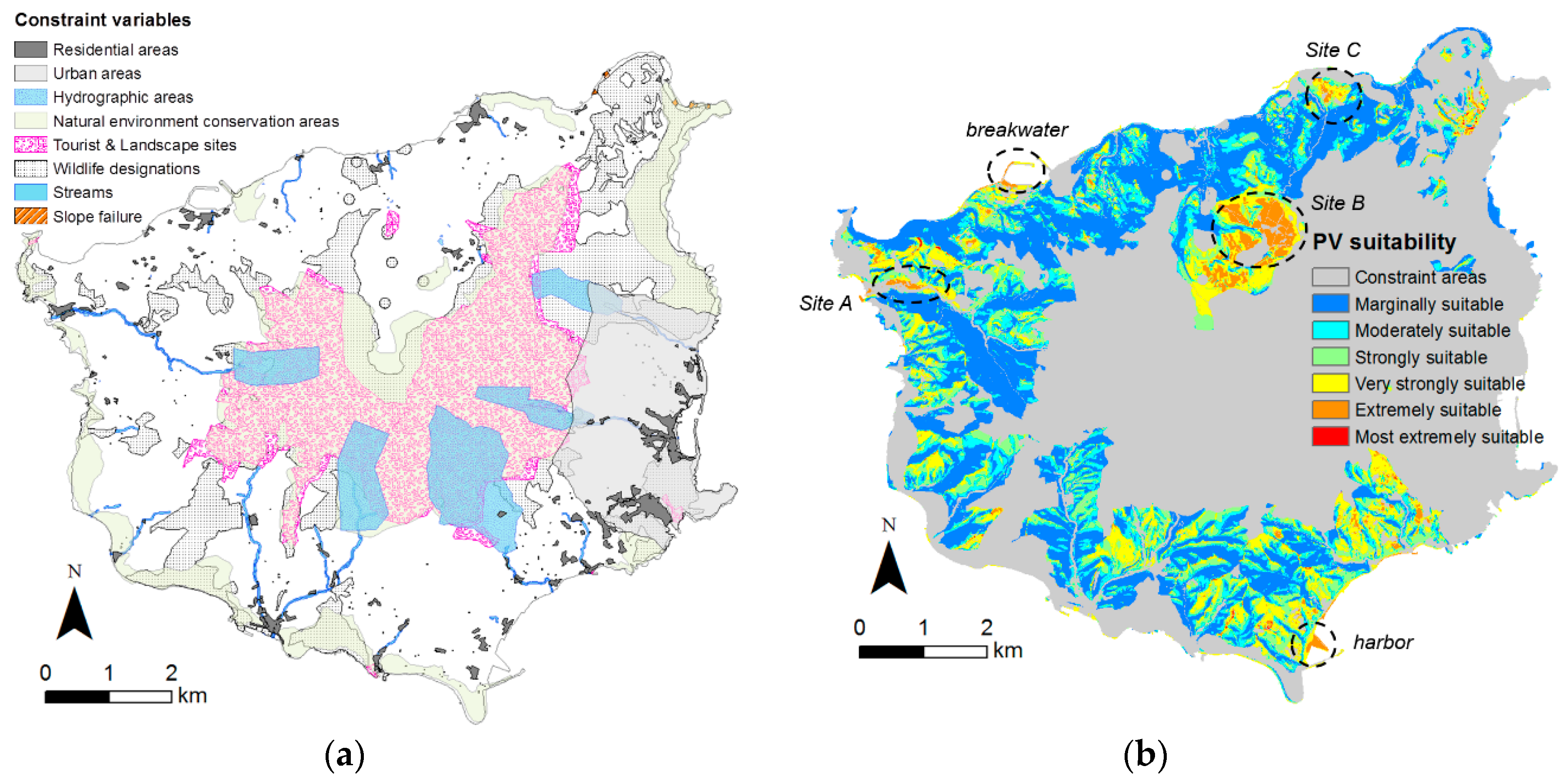

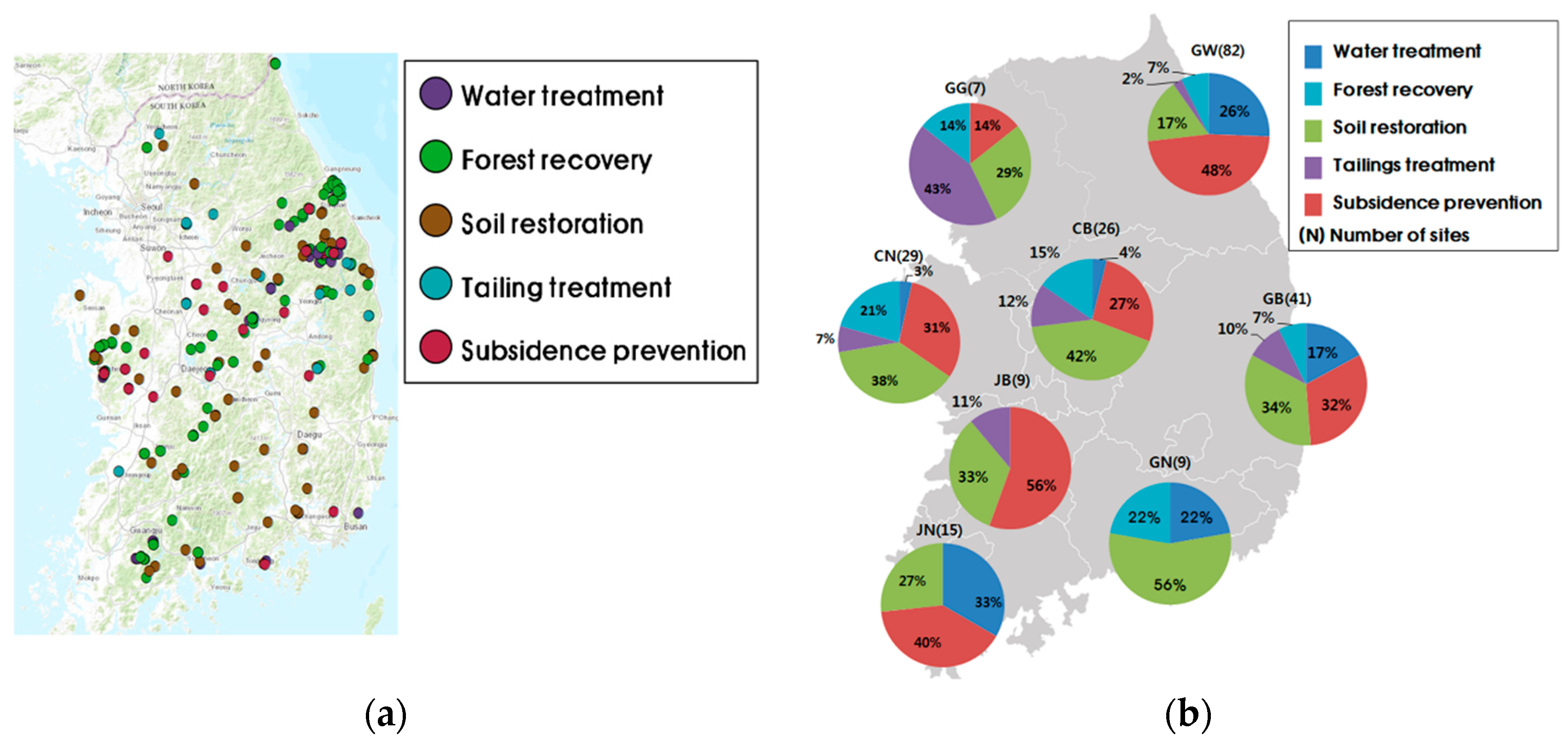
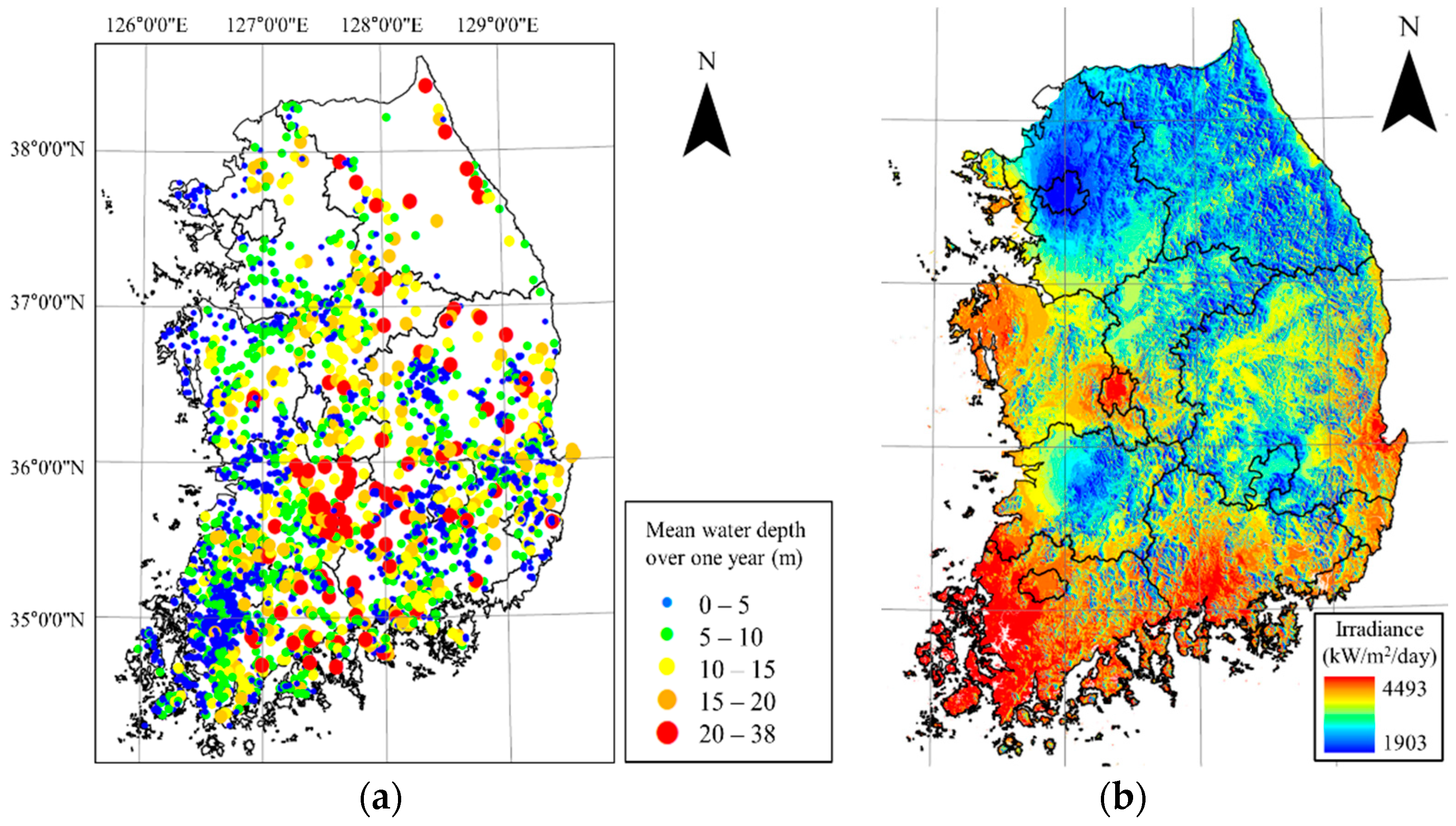
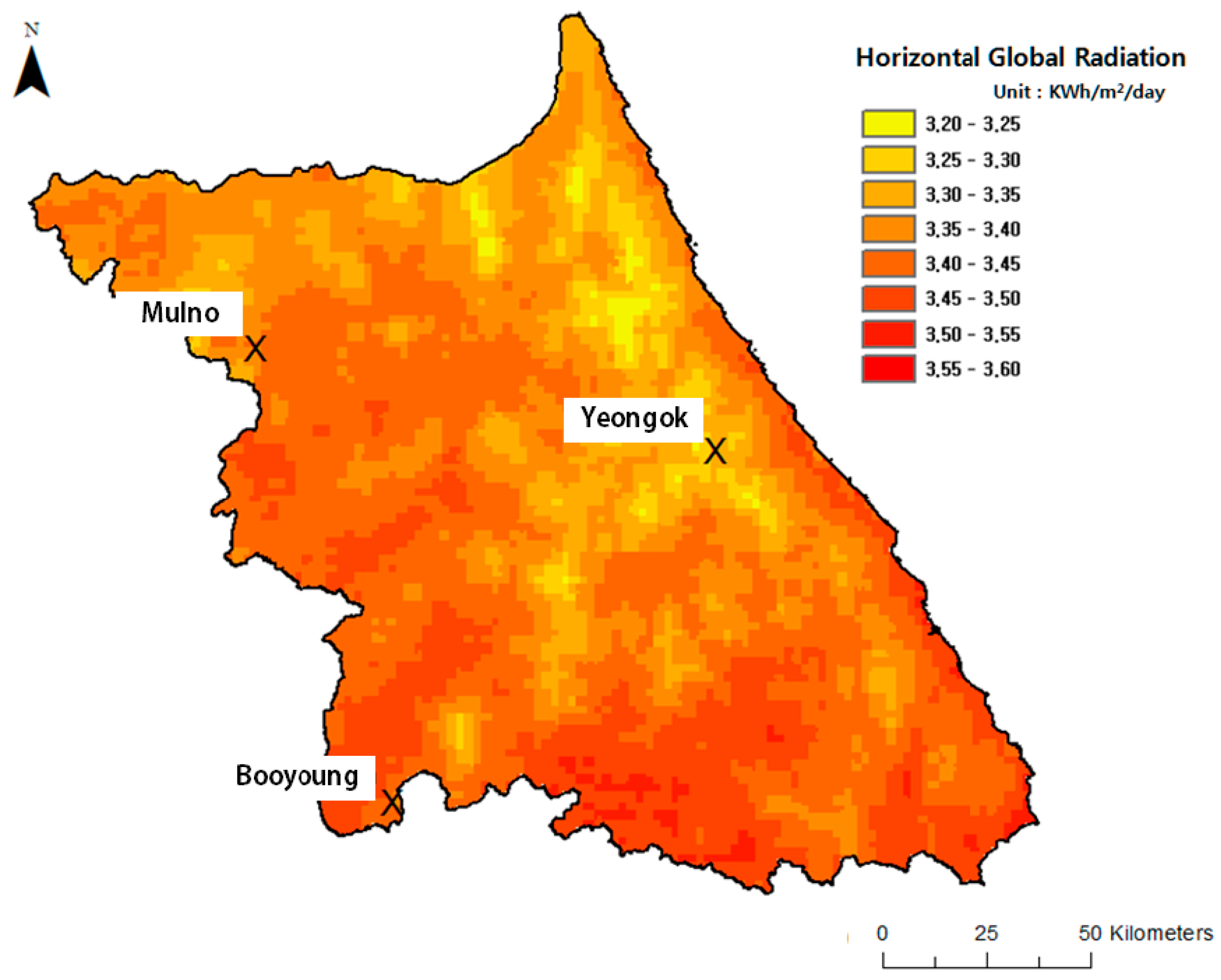


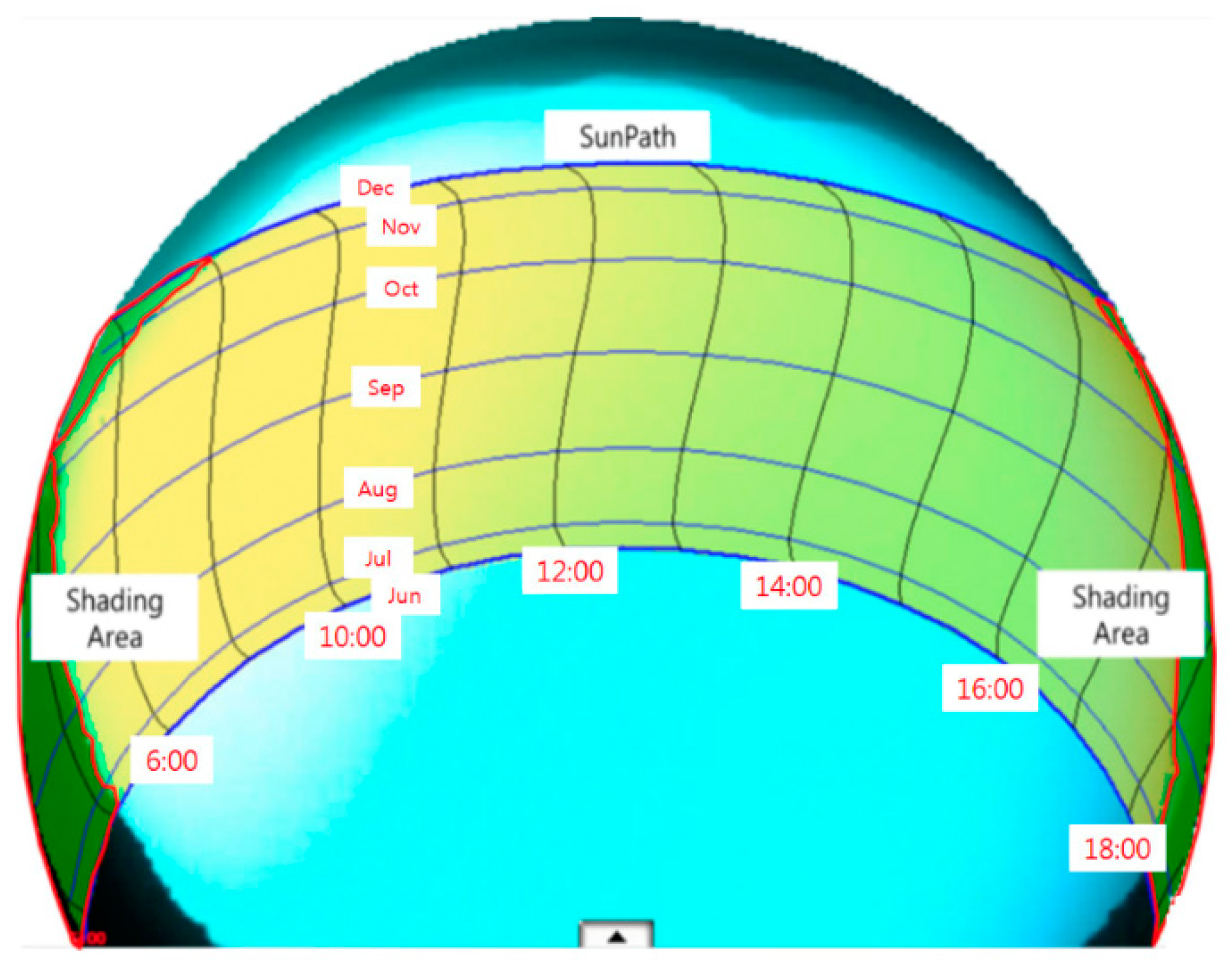
| References | Usage or Method | Scale | Location | Used Data Type | Spatial Unit | Temporal Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bahrami and Abbaszadeh [5] | DB | National | Iran | Solar map | - | - |
| Tahir and Asim [6] | DB | National | Pakistan | Solar map | - | - |
| Zawilska and Brooks [7] | DB | Regional | Durban, South Africa | Solar map | - | - |
| Song et al. [8] | DB | Regional | Korea (mines) | Solar map | - | - |
| Burnett et al. [9] | DB | National | United Kingdom | Solar map | - | - |
| Šúri et al. [10] | DB | Continental | Europe | Solar map | - | - |
| Ramachandra and Shruthi [11] | Multivariate relationship | Regional | Karnataka, India | Station measurement | Administrative district | Seasonal |
| Nematollahi and Kim [12] | Interpolation | National | Korea | Station measurement | Pixel | Monthly, Annual |
| Alamdari et al. [13] | Interpolation | National | Iran | Station measurement | Pixel | Monthly, Annual |
| Stökler et al. [14] | Model validation | National | Pakistan | Satellite image, Station measurement | Pixel | Annual |
| Rumbayan et al. [15] | ANN 1 | National | Indonesia | Station measurement | Administrative district | Monthly |
| Koo et al. [16] | Advanced CBR 2 | National | Korea | Station measurement | Point | Monthly |
| Lee et al. [17] | Advanced CBR, Interpolation | National | Korea | Station measurement | Point, Pixel | Monthly |
| Koo et al. [18] | Advanced CBR, FEM 3, Interpolation | National | Korea | Station measurement | Point, Pixel | Monthly |
| Hofierka and Šúri [19] | r.sun | Continental, National | Central and Eastern Europe, Slovakia | DEM 4, Various parameters | Pixel | Daily, Monthly, Annual |
| Šúri and Hofierka [20] | r.sun | Continental | Central and Eastern Europe | DEM, Various parameters | Pixel | Monthly |
| Dubayah and Rich [21] | SOLARFLUX, ATM 5 | Regional | Tiefort Mountains and Grand Canyon, US | DEM, Plant canopies | Pixel | Monthly |
| Corripio [22] | Shadow analysis | Regional | Mont Blanc Massif, France | DEM | Pixel | 15 min intervals |
| Redweik et al. [23] | Shadow analysis | Local | The University of Lisbon, Portugal (buildings) | DSM 6, Station measurement | Pixel | Hourly, Seasonal, Annual |
| References | Methods | Scale | Location | Solar Map | Result | Energy Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fluri [24] | Boolean overlay | National | South Africa | Institution | Suitable area | CSP |
| Merrouni et al. [25] | Boolean overlay | Regional | Eastern Morocco | Analyst tool | Suitable area | CSP |
| Merrouni et al. [26] | Boolean overlay | Regional | Eastern Morocco | Interpolation | Suitable area | CSP |
| Wang et al. [27] | Boolean overlay | National | Tibet, China | Satellite image | Suitable area | PV |
| Hott et al. [28] | Boolean overlay | Regional | Wyoming, US | Institution | Suitable area | PV, CSP |
| Jahangiri et al. [29] | Boolean overlay | Continental | Middle-East | Interpolation | Suitable area | Solar, Wind |
| Anwarzai and Nagasaka [30] | Boolean overlay | National | Afghanistan | Institution | Suitable area | PV, CSP, Wind |
| Gherboudj and Ghedira [31] | Weighted sum | National | United Arab Emirates | Satellite image | Suitability map | PV, CSP |
| Castillo et al. [32] | Weighted sum | Continental | Europe | Institution | Suitability map | PV |
| Janke [33] | Weighted sum | Regional | Colorado | Institution | Suitability map | Solar, Wind |
| Cevallos-Sierra and Ramos-Martin [34] | Weighted sum | National | Ecuador | Institution | Suitability map | PV, CSP, Wind |
| Aydin et al. [35] | Weighted sum, Fuzzy | Regional | Western Turkey | Institution | Suitability map | PV |
| Brewer et al. [36] | Weighted sum, PVMapper | Regional | Southwestern US | Institution | Suitability map | PV |
| Vafaeipour et al. [37] | SWARA 1, WASPAS 2 | National | Iran | Institution | Suitability for cities | PV |
| Ziuku et al. [38] | AHP 3 | National | Zimbabwe | Interpolation | Suitability map | CSP |
| Al Garni and Awasthi [39] | AHP | National | Saudi Arabia | Analyst tool | Suitability map | PV |
| Uyan [40] | AHP | Regional | Karapinar, Turkey | Institution | Suitability map | Solar |
| Yushchenko et al. [41] | AHP | Continental | West Africa | Institution | Suitability map | PV, CSP |
| Merrouni et al. [42] | AHP | Regional | Eastern Morocco | Institution | Suitability map | PV |
| Aly et al. [43] | AHP | National | Tanzania | Institution | Suitability map | PV, CSP |
| Tahri et al. [44] | AHP | Regional | Southern Morocco | Analyst tool | Suitability map | PV |
| Watson and Hudson [45] | AHP | Regional | Southern England | Analyst tool | Suitability map | Solar, Wind |
| Asakereh et al. [46] | FAHP 4 | Regional | Shodirwan, Iran | Interpolation | Suitability map | PV |
| Noorollahi et al. [47] | FAHP | National | Iran | Institution | Suitability map | PV |
| Charabi and Gastli [48] | FLOWA 5 | National | Oman | Analyst tool | Suitability map | PV, CSP |
| Suh and Brownson [49] | FAHP | Regional | Ulleung Island, Korea | Analyst tool | Suitability map | PV |
| Sánchez-Lozano et al. [50] | AHP, TOPSIS 6 | Regional | Cartagena, Spain | Analyst tool | Suitability map | PV |
| Sánchez-Lozano et al. [51] | ELECTRE-TRI, IRIS 7 | Regional | Torre Pacheco, Spain | Analyst tool | Suitability map | PV |
| Mondino et al. [52] | ANN | Regional | Piedmont, Italy | Analyst tool | Suitability map | PV |
| Omitaomu et al. [53] | OR-SAGE 8 | Regional | Western US | Institution | Suitable area for each energy | CSP, Nuclear, Advanced coal, CAES 9 |
| Choi and Song [54] | Overlay | National | Korea (Mines) | Institution | Suitable mines | PV |
| Kim et al. [55] | Shadow analysis | National | Korea (Reservoirs) | Interpolation | Suitable reservoirs | Floating PV |
| Lukac et al. [56] | Shadow analysis | Local | Maribor, Slovenia (Buildings) | Measurement | Rooftop suitability | PV |
| Lee et al. [57] | Shadow analysis, Cluster analysis | Local | Gangnam, Korea (Buildings) | Institution | Rooftop suitability | PV |
| Role of GIS | No. | Solar Type | No. | Analysis Scale | No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DB & Visualization tools | 9 | PV | 23 | Global | 1 |
| Rooftop extraction tool | 2 | CSP | 6 | National | 16 |
| Radiation modeling tool | 6 | General | 1 | Region | 20 |
| Shading analysis tool | 7 | PV & CSP | 9 | Object | 2 |
| Spatial analysis tool | 15 | ||||
| Sum | 39 | Sum | 39 | Sum | 39 |
| Month | Time | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | |
| January | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.02 | 0.63 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.96 | 0.72 | 0.02 | 0 | 0 |
| February | 0 | 0 | 0.04 | 0.64 | 0.99 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.99 | 0.44 | 0.06 | 0 |
| March | 0 | 0.10 | 0.56 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.84 | 0 | 0 |
| April | 0 | 0.09 | 0.83 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.92 | 0.03 | 0 |
| May | 0 | 0.24 | 0.92 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.33 | 0 |
| June | 0 | 0.25 | 0.92 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.65 | 0 |
| July | 0 | 0.15 | 0.89 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.69 | 0 |
| August | 0 | 0.10 | 0.84 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.99 | 0.21 | 0 |
| September | 0 | 0.17 | 0.84 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.73 | 0 | 0 |
| October | 0 | 0.04 | 0.64 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.26 | 0 | 0 |
| November | 0 | 0 | 0.02 | 0.54 | 0.98 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.97 | 0.60. | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| December | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.01 | 0.61 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.89 | 0.42 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, Y.; Suh, J.; Kim, S.-M. GIS-Based Solar Radiation Mapping, Site Evaluation, and Potential Assessment: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1960. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9091960
Choi Y, Suh J, Kim S-M. GIS-Based Solar Radiation Mapping, Site Evaluation, and Potential Assessment: A Review. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(9):1960. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9091960
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Yosoon, Jangwon Suh, and Sung-Min Kim. 2019. "GIS-Based Solar Radiation Mapping, Site Evaluation, and Potential Assessment: A Review" Applied Sciences 9, no. 9: 1960. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9091960
APA StyleChoi, Y., Suh, J., & Kim, S.-M. (2019). GIS-Based Solar Radiation Mapping, Site Evaluation, and Potential Assessment: A Review. Applied Sciences, 9(9), 1960. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9091960







