Superhydrophobic/Flame Retardant/EMI Shielding Fabrics: Manufacturing Techniques and Property Evaluations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
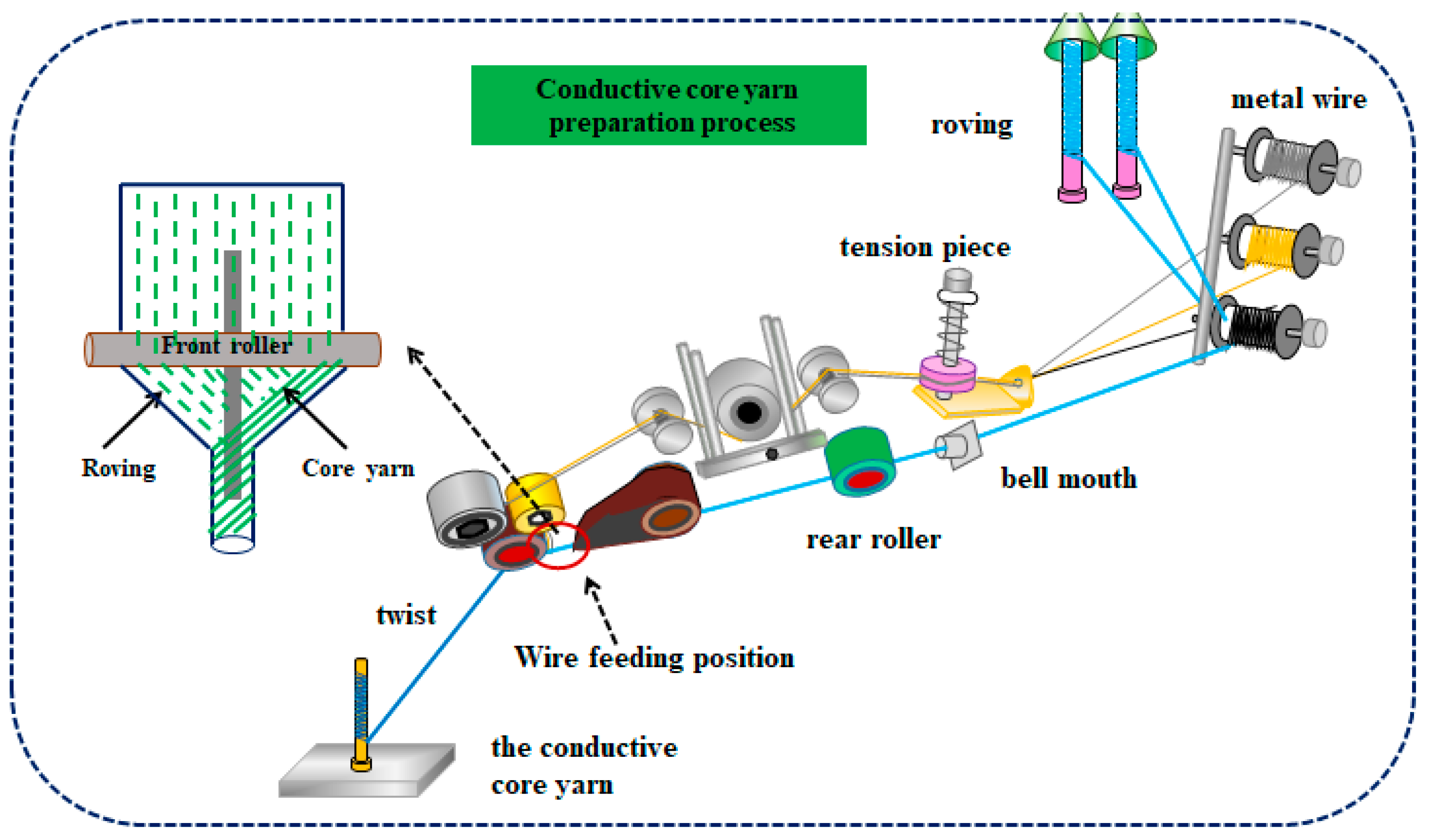
2.2. Preparation of Conductive Wrapped Yarns
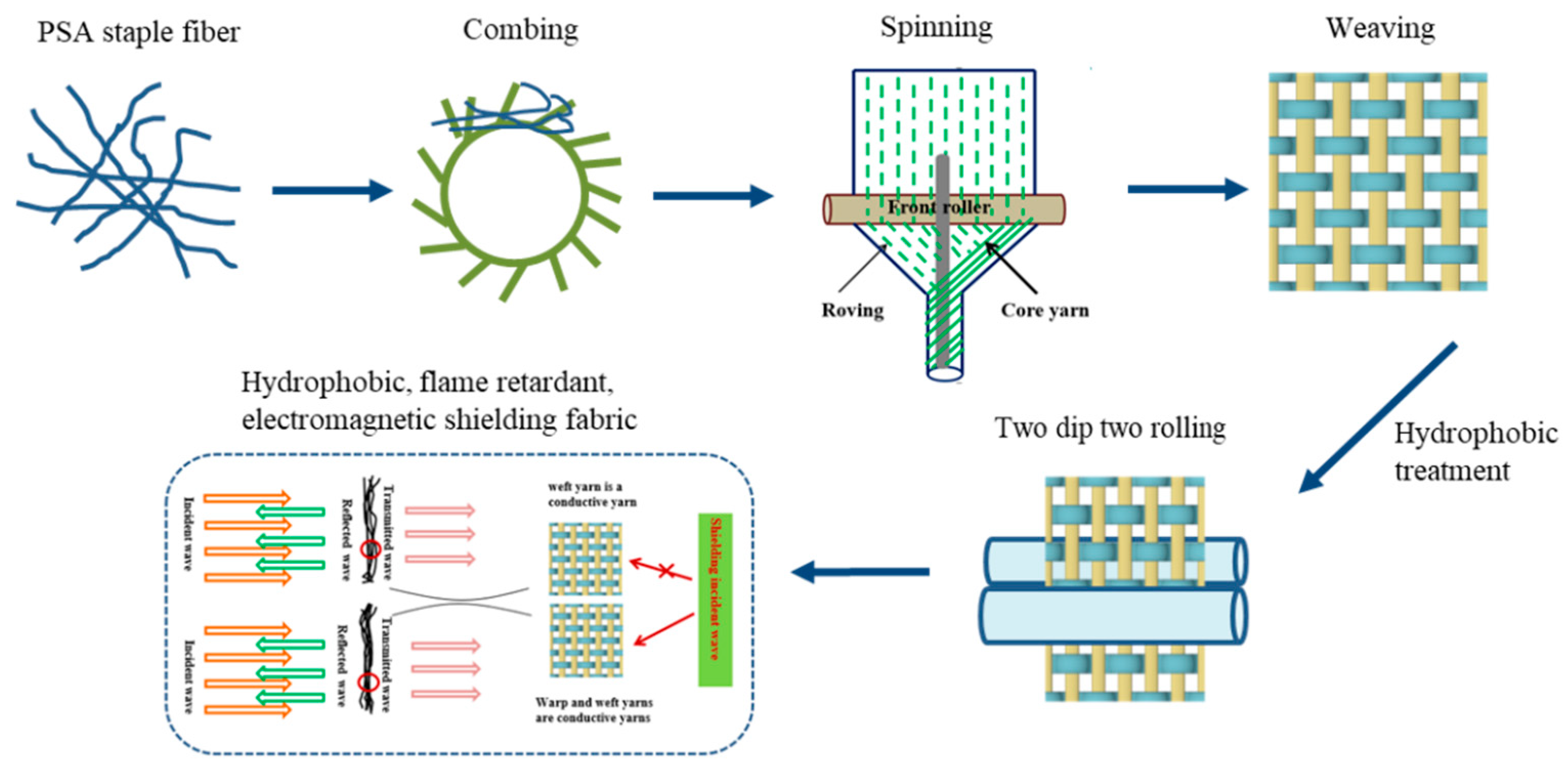
2.3. Preparation of EMI Shielding Fabrics
2.4. Preparation of Superhydrophobic/Flame Retardant/EMI Shielding Fabrics
2.5. Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
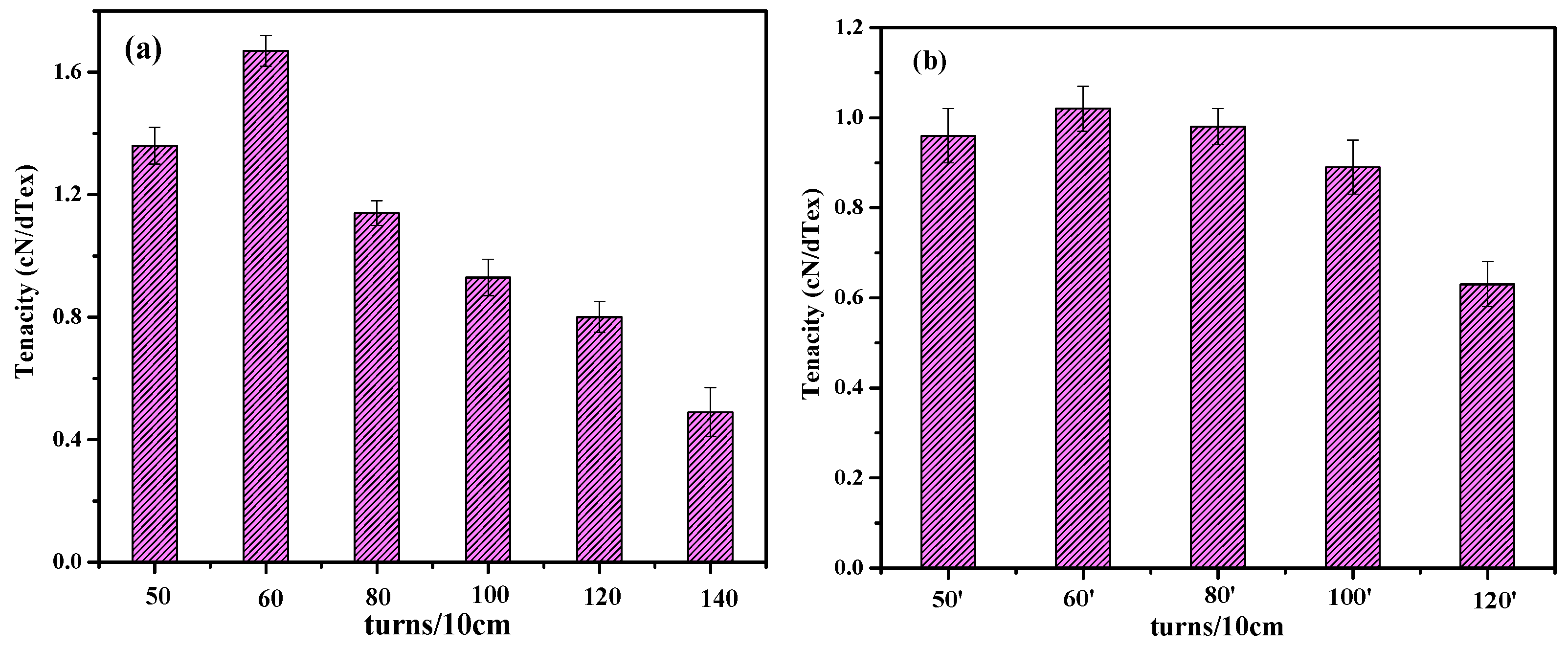
3.1. Breaking Strength of Conductive Wrapped Yarns
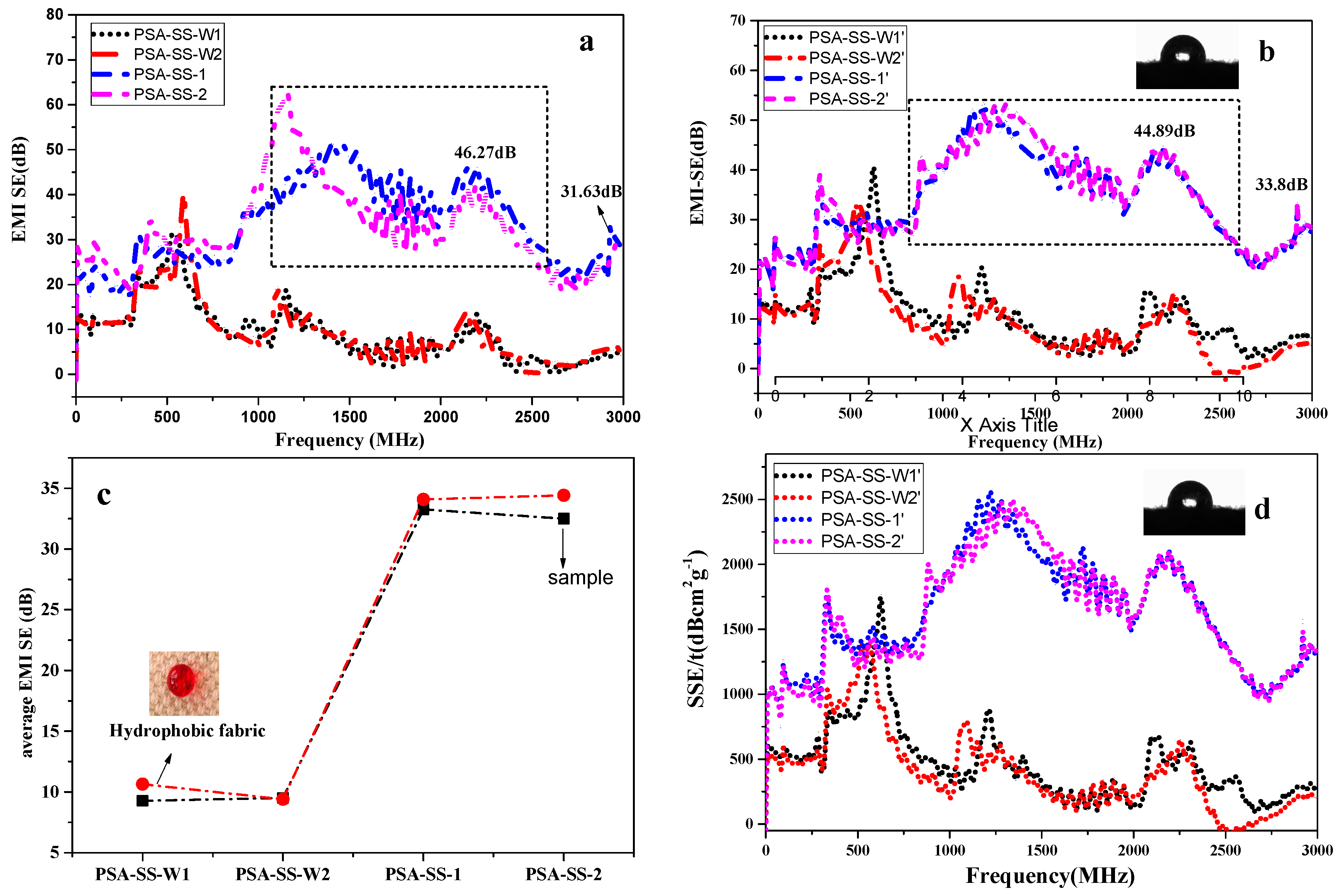
3.2. EMI Shielding Effectiveness of Conductive Fabrics
3.3. The Permittivity of Conductive Fabrics
3.4. The Effects of Superhydrophobic Treatment on TG, DSC and Fabric Burnt Length
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shahzad, F.; Alhabeb, M.; Hatter, C.B.; Anasori, B.; Man Hong, S.; Koo, C.M. Electromagnetic interference shielding with 2d transition metal carbides (mxenes). Science 2016, 353, 1137–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eddib, A.A.; Chung, D.D.L. The importance of the electrical contact between specimen and testing fixture in evaluating the electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness of carbon materials. Carbon 2017, 117, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.L.; Lou, C.W.; Liu, C.F.; Huang, C.H.; Song, X.M.; Lin, J.H. Polypropylene/graphene and polypropylene/carbon fiber conductive composites&58; mechanical, crystallization and electromagnetic properties. Appl. Sci. 2015, 5, 1196–1210. [Google Scholar]
- Drakakis, E.; Kymakis, E.; Tzagkarakis, G.; Louloudakis, D.; Katharakis, M.; Kenanakis, G.; Suchea, M.; Tudose, V.; Koudoumas, E. A study of the electromagnetic shielding mechanisms in the GHz frequency range of graphene based composite layers. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 398, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tana, Y.J.; Lia, J.; Gao, Y.; Li, J.; Guo, S.Y.; Wang, M. A facile approach to fabricating silver-coated cotton fiber non-woven fabrics for ultrahigh electromagnetic interference shielding. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 458, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.C.; Ma, C.C.M.; Hsiao, S.T.; Wang, Y.S.; Yang, C.Y.; Liao, W.H. Electromagnetic interference shielding performance of waterborne polyurethane composites filled with silver nanoparticles deposited on functionalized graphene. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 385, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Lee, H.; Ha, I.; Cho, H.; Kim, K.K.; Kwon, J. Highly Stretchable and Transparent Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Film Based on Silver Nanowire Percolation Network for Wearable Electronics Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 44609–44616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomassin, J.M.; Jérôme, C.; Pardoen, T. Polymer/carbon based composites as electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 2013, 74, 211–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.T.; Chen, F.F.; Zhu, Y.J. Binary Strengthening and Toughening of MXene/Cellulose Nanofiber Composite Paper with Nacre-Inspired Structure and Superior Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Properties. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 4583–4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.H.; Theilmann, P.T.; Asbeck, P.M.; Bandaru, P.R. Enhanced Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Through the Use of Functionalized Carbon-Nanotube-Reactive Polymer Composites. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2010, 9, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.W.; Lee, S.E.; Jeong, Y.G. Carbon nanotube/cellulose papers with high performance in electric heating and electromagnetic interference shielding. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2016, 131, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.B.; Lee, M.L.; Ramakrishna, S. Electromagnetic Shielding Effectiveness of Stainless Steel/Polyester Woven Fabrics. Text. Res. J. 2001, 71, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, J.S.; Chi, Y.S.; Kang, T.J. Electromagnetic Shielding Effectiveness of Multifunctional Metal Composite Fabrics. Text. Res. J. 2008, 78, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdumlu, N.; Saricam, C. Electromagnetic shielding effectiveness of woven fabrics containing cotton/metal-wrapped hybrid yarns. J. Ind. Text. 2016, 46, 1084–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, C.W.; Lin, T.A.; Chen, A.P. Stainless steel/polyester woven fabrics and copper/polyester woven fabrics: Manufacturing techniques and electromagnetic shielding effectiveness. J. Ind. Text. 2015, 46, 214–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.C.; Lee, K.C.; Lin, J.H.; Koch, M. Fabrication of conductive woven fabric and analysis of electromagnetic shielding via measurement and empirical equation. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2007, 1, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.D.; Kung, C.L.; Hsieh, W.C.; Hsu, C.M.; Chen, C.Y. Study on cleaning the surface of stainless steel 316 using plasma electrolysis technology. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Dai, B.; Ren, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhu, P. Preparation and Study of Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Materials Comprised of Ni-Co Coated on Web-Like Biocarbon Nanofibers via Electroless Deposition. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Zhai, W.; Tao, M.; Ling, J.; Zheng, W. Lightweight, Multifunctional Polyetherimide/Graphene@Fe3O4 Composite Foams for Shielding of Electromagnetic Pollution. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 11383–11391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Lan, C.; Qiu, Y.; Ying, M. Nanocomposites: Step-by-step strategy for constructing multilayer structured coatings toward high-efficiency electromagnetic interference shielding. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 3, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, Y.; Xue, Y.; Song, J.; Sun, Y.; Huang, L.; Liu, X.; Sun, J. Superhydrophobic coatings on wood substrate for self-cleaning and EMI shielding. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 436, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Y.W.; Sun, Z.; Wang, X.H. Microstructure and friction performance of copper film fabricated by ion implantation assisted electroless plating on PTFE. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2011, 27, 1680–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.C.; Lee, K.C.; Lin, J.H.; Koch, M. Comparison of electromagnetic shielding effectiveness properties of diverse conductive textiles via various measurement techniques. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2007, 192–193, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Li, Y.; An, N.; Sun, J. Applied Voltage and Near-Infrared Light Enable Healing of Superhydrophobicity Loss Caused by Severe Scratches in Conductive Superhydrophobic Films. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 6777–6784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rung, S.; Schwarz, S.; Götzendorfer, B.; Esen, C.; Hellmann, R. Time dependence of wetting behavior upon applying hierarchic nano-micro periodic surface structures on brass using ultra short laser pulses. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baliga, S.; Wong, W.T. Depolymerization of poly(ethylene terephthalate) recycled from post-consumer soft-drink bottles. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Chem. 1989, 27, 2071–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandola, B.K.; Horrocks, A.R.; Myler, P.; Blair, D. Mechanical performance of heat/fire damaged novel flame retardant glass-reinforced epoxy composites. Compos. Part A-Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2003, 34, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Araby, S.; Wang, C.H.; Wu, H.; Meng, Q.; Kuan, H.C.; Kim, N.K. Development of flame-retarding elastomeric composites with high mechanical performance. Compos. Part A-Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2018, 109, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiarong, R. Thermal treated analysis of PSA fiber. Melliand China 2007, 1, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Wang, X.; Qiu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Hu, P.A. Infrared-transparent films based on conductive graphenenetwork fabrics for electromagnetic shielding. Carbon 2015, 87, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, D.; Lu, L.; Teh, K.S.; Wan, Z.; Xie, Y.; Tang, Y. Highly flexible and ultra-thin Ni-plated carbon-fabric/polycarbonate film for enhanced electromagnetic interference shielding. Carbon 2018, 132, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yi, D.; Shen, B.; Zhang, L.; Ma, X.; Pang, Y.; Liu, L.; Wei, X.; Zheng, W. Semi-transparent biomass-derived macroscopic carbon grids for efficient and tunable electromagnetic shielding. Carbon 2018, 139, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Xiao, T. Preparation of polypyrrole coated cotton conductive fabrics. J. Text. Inst. 2016, 108, 829–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, X. The research of EM wave absorbing properties of ferrite/silicon carbide double coated polyester woven fabric. J. Text. Inst. 2017, 109, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjmand, M.; Apperley, T.; Okoniewski, M.; Sundararaj, U. Comparative study ofelectromagnetic interference shielding properties of injection molded versus compression molded multi-walled carbon nanotube/polystyrene composites. Carbon 2012, 50, 5126–5134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saleh, M.H.; Saadeh, W.H.; Sundararaj, U. EMI shielding effectiveness of carbon based nanostructured polymeric materials: A comparative study. Carbon 2013, 60, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Li, G.; Yu, Y.; Sui, G.; Yang, X. Ablation and thermal properties of ethylene-propylene-diene elastomer composites reinforced with polysulfonamide short fibers. J. Appl.Polym. Sci. 2009, 113, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulier, J.; Chabert, B.; Chauchard, J. Synthesis and properties of some polyamides and polysulfonamides. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 18, 2435–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Fabric Code | Warp Yarn | Weft Yarn | Fabric Weight (g/m2) | Thickness (mm) | Number of Warp Yarns (ends/10 cm) | Number of Weft Yarns (picks/10 cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSA-SS-1 | PSA/SS-60 | PSA/SS-60 | 228.74 | 0.41 | 120 | 110 |
| PSA-SS-2 | PSA/SS-60′ | PSA/SS-60′ | 233.64 | 0.41 | 120 | 110 |
| PSA-SS-W1 | PSA | PSA/SS-60 | 210.92 | 0.38 | 120 | 110 |
| PSA-SS-W2 | PSA | PSA/SS-60′ | 214.36 | 0.38 | 120 | 110 |
| Fabric Type | Thickness (mm) | Density (g/cm3) | EMI SE (dB) | SE/t (dB/mm) | SSE (dB cm3g−1) | SSE/t (dB cm2g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSA-SS-W1′ | 0.41 | 0.56 | 10.64 | 25.95 | 19 | 463.43 |
| PSA-SS-W2′ | 0.41 | 0.57 | 9.38 | 22.87 | 16.46 | 401.33 |
| PSA-SS-1′ | 0.38 | 0.55 | 34.08 | 89.68 | 61.96 | 1623.98 |
| PSA-SS-2′ | 0.38 | 0.56 | 34.42 | 90.57 | 61.46 | 1617.38 |
| Sample | T 5wt% (°C) | Tmax1 (°C) | Tmax2 (°C) | Residue at 800 °C(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSA-SS-W1 | 435.4 | 450.8 | 519.4 | 50.67 |
| PSA-SS-W1′ | 210.6 | 454.0 | 510.9 | 29.74 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, H.-K.; Wang, Y.; Li, T.-T.; Lou, C.-W.; He, Q.; Lin, J.-H. Superhydrophobic/Flame Retardant/EMI Shielding Fabrics: Manufacturing Techniques and Property Evaluations. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1914. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9091914
Peng H-K, Wang Y, Li T-T, Lou C-W, He Q, Lin J-H. Superhydrophobic/Flame Retardant/EMI Shielding Fabrics: Manufacturing Techniques and Property Evaluations. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(9):1914. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9091914
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Hao-Kai, Yanting Wang, Ting-Ting Li, Ching-Wen Lou, Qi He, and Jia-Horng Lin. 2019. "Superhydrophobic/Flame Retardant/EMI Shielding Fabrics: Manufacturing Techniques and Property Evaluations" Applied Sciences 9, no. 9: 1914. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9091914
APA StylePeng, H.-K., Wang, Y., Li, T.-T., Lou, C.-W., He, Q., & Lin, J.-H. (2019). Superhydrophobic/Flame Retardant/EMI Shielding Fabrics: Manufacturing Techniques and Property Evaluations. Applied Sciences, 9(9), 1914. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9091914







