Abstract
The objective of this study was to determine the proteolytic activity of bacterial strains from the genus Lactobacillus and their capability in producing peptide inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) in cheese models prepared with their addition. After 5 weeks of ripening, all cheese models studied were characterized by a high ability of angiotensin convertase inhibition which exceeded 80%. The use of the adjunct bacterial cultures from the genus Lactobacillus contributed to lower IC50 values compared with the value determined for the control cheese model. The proteolytic activity of model cheeses varied in their increase through the period of ripening, with changes in values dependent on the adjunct lactic acid bacteria (LAB) strain used for cheesemaking. Starting from the first week of ripening, the lowest proteolytic activity was demonstrated for the control cheese models, whereas the highest activity throughout the ripening period was shown for the cheese models with the addition of Lb. rhamnosus 489.
1. Introduction
Fermented dairy products are often referred to as functional products even though they are not classified in legal regulation under this name as a separate category of food products. Functional products are those which, apart from providing nutrients, contribute to an improvement in a health condition or minimize the risk of incidence of certain diseases, such as circulatory diseases, neoplasms, or osteoporosis, and also offer specified dietetic values for persons with metabolic disorders [1].
Protein fragments, which remain inactive in sequences of precursor proteins, are released upon enzymatic hydrolysis with proteolytic enzymes, and are likely to interact with respective body receptors. The proteins regulating physiological functions are called biologically and functionally active peptides or bioactive peptides, and are produced during the proteolysis of milk proteins, which provide nitrogen compounds to lactic acid bacteria (LABs) and exhibit various activities [2].
The best known currently characterized group of food-derived bioactive peptides is the group of peptides with antihypertensive properties. Most of the representatives of this group are inhibitors of the angiotensin I-converting enzyme—peptidyldipeptide hydrolase (EC.3.4.15.1), also called angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE). ACE hydrolyzes angiotensin I to angiotensin II, which interacts with two receptors and thereby induces the contraction of blood vessels and, consequently, contributes to blood pressure increase. Hence, food products that may block the reaction of angiotensin I conversion to angiotensin II, such as ripening rennet cheeses, may be natural equivalents of hypotensive drugs. Most peptides derived from milk protein possess multi-functional properties [2,3,4].
The literature reports on 420 peptides with ACE-inhibitory activity (expressed as IC50 < 1000 mM) that are derived from eight species and nine proteins of milk, of which 327 are claimed to be unique peptide sequences [5]. Casein is a predominating protein, which represents 77% of all described ACE-inhibiting peptides. This results from the fact that most of the studies addressing this subject are conducted with cheeses, which are composed mainly of casein. Ripening cheeses represents an important source of bioactive peptides, obtained by multiple proteases of LABs, and of other adjunct microflora [5].
The presence of active peptides in cheeses, which are produced with natural methods, depends on the equilibrium between their synthesis and their degradation by the proteolytic system throughout the ripening process of cheeses. Peptidolytic activity is strictly related to the aging of cheese (ripening) and to the type and culture conditions of adjunct starters, as reported by different authors [6,7,8]. Intense proteolytic processes occurring during cheese ripening have been reported to enhance the activity of ACE inhibitors, but only to a certain level over which ACE inhibition will diminish. This may suggest that the bioactive peptides released during cheese ripening upon the activity of proteolytic enzymes of LABs are successively degraded to inactive fragments as a result of further proteolysis [9,10].
Some dairy products (Calpis and Evolus) with documented clinical effects on arterial blood pressure reduction are currently available on the market. In vivo studies are in the process of confirming the functionality of food products containing bioactive peptides in patients [2,11,12].
Some of the literature describes dairy starter cultures used for the manufacture of fermented dairy products (e.g., L. helveticus, L. delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus, L. plantarum, L. rhamnosus, L. acidophilus, Lc. lactis, or S. thermophilus) which are capable of synthesizing bioactive peptides [13,14].
Considering the aforementioned information, a study was undertaken to determine the possibility of synthesis of bioactive peptides with hypotensive properties by selected strains of Lactobacillus spp. in cheese models prepared with their addition.
2. Material and Methods
The experimental material included five model cheeses produced with CHN-19 culture (Lc. lactis ssp. cremoris, L. mesenteroides ssp. cremoris, and Lc. lactis ssp. lactis biovar diacetylactis) used as the basic starter and with Lb. casei 2639, Lb. acidophilus 2499, Lb. rhamnosus 489, and Lb. delbrueckii 490 applied as additional cultures.
2.1. Determination of Proteolytic Activity of Lactobacillus Strains
Both the initial and the overall proteolytic activity of all cultures were determined using the method of Church et al. [15]. The proteolytic activity of each Lactobacillus strain was determined in reconstituted skim milk (RSM) after 6 and 24 h of fermentation at a temperature of 37 °C for determination of the initial and the overall proteolytic activity, respectively. All the organisms were activated from their frozen forms by one transfer into MRS broth (Lactobacillus Broth acc. to DE MAN, ROGOSA and SHARPE, Merck, Poland). The obtained cultures were passaged twice by a transfer 1 mL of inoculum into 100 mL of sterile supplemented (with glucose and yeast extract) reconstituted skim milk (SRSM). Then, 1 mL of the inoculum from the SRSM was transferred into 100 mL of RSM and after 24 h of incubation at 37 °C, and 1 mL of culture was transferred to 100 mL of RSM and incubated for either 6 or 24 h.
For determinations of the proteolytic activity of the analyzed strains, trichloroacetic acid (TCA) filtrates of the samples were prepared by mixing 5 mL of the sample with 1 mL of distilled water and 10 mL of 0.75 N TCA (Avantor Performance Materials, Poland), followed by centrifugation (MPW-352R centrifuge, Poland) at 4000 g and 4 °C for 30 min. The supernatants were filtered through a 0.45 μm syringe membrane filter (MILLEX HV, Milipore, Poland). The proteolytic activity of all cultures was determined by the reaction of 150 μL of the TCA filtrate with 3 mL of o-phthaldialdehyde reagent (OPA, Sigma-Aldrich, Poland). Absorbance was measured after vortexing and 2 min incubation at room temperature at 340 nm (Genesis UV-VIS Spectrophotometer, Thermo Scientific).
2.2. Preparation of Cheese Models
Cheese models were prepared in 500 mL sterile centrifuge bottles (Nalgene centrifuge ware, Thermo Scientific) [16]. 400 mL of commercial, industrially-pasteurized, and microfiltrated (74 ± 1 °C/15 s) milk (3.2% protein and 2% fat) were poured into the bottles (which were autoclaved prior to use) that were then placed in a water bath at a temperature of 35 °C. After this, the basic commercial CHN-19 starter (at a concentration 8.94 log CFU/mL) and, depending on cheese model variant, the adjunct culture (at a concentration 9.14 log CFU/mL), as well as 0.2 mL (4%) of a solution of coagulating enzymes (Fromase 2200 TL Granulate, DSM Food Specielities BV, The Netherlands) were added to the bottles. The bottles were closed and their content was mixed. The bottles were placed in a water bath with a temperature of 35 °C. After coagulation (for ca. 20–30 min), they were kept in a water bath for 20 min in order to achieve the desired consistency of the curd, and then the curd was cut using a narrow knife made of stainless steel. The curd–whey mixture was shaken for 20 min. 160 mL ± 3 mL of whey was discarded and the same volume of water with a temperature of 35 °C was added. Curd washing ended after 10 min of mixing, and afterwards the bottles were centrifuged for 10 min (320 g) at room temperature in order to remove what was likely the greatest amount of the water phase. Once the water had been removed, the bottles were centrifuged again (1400 g) at 30 °C for 1 h. The whey was then decanted and the curd was centrifuged (1400 g) for 30 min. After centrifugation, miniature cheese models were kept in bottles in a water bath (35 °C) until a pH of 5.20 was reached. Next, the cheeses were salted by pouring them in with 35 mL of saturated brine (270 g NaCl/L, Avantor Performance Materials, Poland) with a temperature of 11 °C, in the same vessel. After 5 min, the brine was removed and cheeses were transferred into sterile boxes with a grid, which facilitated whey draining, and were then placed in a cold store at 11 °C for 24 h. The weight of the cheese models were 70 ± 5 g. The prepared experimental models of cheeses (described below) were then taken out from the boxes, vacuum-packed in polyethylene foil (Cryovac packaging), and stored at 11 ± 0.5 °C for 5 weeks.
Five variants of cheese models were prepared in the study and determined as:
- C—a control cheese model consisting of milk, 2% of basic CHN-19 starter, and a coagulant;
- Lba 2499—a cheese model consisting of milk, 2% of CHN-19 starter, 1.5% of Lb. acidophilus 2499 culture, and a coagulant;
- Lbr 489—a cheese model consisting of milk, 2% of CHN-19 starter, 1.5% of Lb. rhamnosus 489 culture, and a coagulant;
- Lbd 490—a cheese model consisting of milk, 2% of CHN-19 starter, 1.5% of Lb. delbrueckii 490 culture, and a coagulant;
- Lbc 2639—a cheese model consisting of milk, 2% of CHN-19 starter, 1.5% of Lb. casei 2639 culture, and a coagulant.
Cheese model variants (C, Lba 2499, Lbr 489, Lbd 490, and Lbc 2639) were obtained in replicates performed three times.
2.3. Measurement of the ACE-Inhibitory Activity of Dutch-Type Cheese Models
The ACE-inhibitory activity of the TCA filtrates of the cheese models was assayed by the methods of Cushman and Cheung [17] and Ramchandran and Shah [18]. The assay mixture contained an hippuryl-L-histidyl-L-leucine (HHL, Sigma–Aldrich, Poland) solution (5 mM HHL in 0.1 M borate buffer containing 0.3 M NaCl, pH 8.3) used as a substrate and an ACE solution (from rabbit lung, 0.1 U mL−1, Sigma Aldrich, Poland). The residue containing hippuric acid was dissolved in deionized water and the absorbance was measured (Genesis UV-VIS spectrophotometer, Thermo Scientific) at 228 nm against deionized water as a blank.
The percentage of inhibition (ACE) was calculated using the following formula:
where:
A is the absorbance in the presence of ACE and without the sample, B is the absorbance without ACE and the sample, C is the absorbance with ACE and the sample, and D is the absorbance with the sample but without ACE.
The ACE inhibition was also expressed in terms of IC50, defined as the concentration of protein in a sample (mg mL−1) required to inhibit 50% of the ACE activity. The IC50 value was predicted by determining protein concentration in a water soluble extract (WSE) of cheese models, followed by the determination of protein concentration which ensured 50% inhibition of ACE activity. The protein concentration in the TCA filtrates was determined with the method of Lowry et al. [19].
2.4. Determination of Proteolysis of Dutch-Type Cheese Models
The reaction mixture used for determinations of the proteolytic activity in WSE of cheese models contained 3 mL of an OPA reagent (o-phthaldialdehyde, Sigma-Aldich, Poland) and 0.15 mL of WSE. The mixture was stirred, left for 2 min at a room temperature, and subjected to absorbance measurement at a wavelength of λ = 340 nm.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
All determinations were performed 2 times. Results obtained were subjected to a statistical analysis using StatGraphics 4.1 software. One-way (ANOVA) analysis of variance was conducted. Tukey’s test was applied to compare the significance of differences between mean values (as honestly significance difference (HSD)) at a significance level of α = 0.05.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Proteolytic Activity of Lactobacillus Strains
Results of determinations of the initial and overall proteolytic activity of the tested LAB strains are presented in Figure 1. The initial proteolytic activity of all tested LAB strains was similar and did not differ significantly from that determined in the control sample. A balance was maintained at the early stage of fermentation between the consumption of free fatty acids and the degradation of peptides and milk proteins by LABs. In contrast, differences were observed in the overall proteolytic activity measured after 24 h. Among all analyzed LAB strains, the lowest activity was exhibited by Lb. delbrueckii 490, while the highest activity was exhibited by the Lb. casei 2639; the values of absorbance—being an indicator of the ongoing proteolysis—accounted for 0.262 and 0.512, respectively (Figure 1). The proteolytic activity of the Lb. casei 2639 strain was ca. twofold higher than that of Lb. delbrueckii 490. Proteolytic activity of the strains used as adjunct by active cultures in cheesemaking that is too high is undesirable, as it may lead to rapid proteolytic transformations during ripening and, consequently, to changes in the organoleptic traits of cheeses (such as a bitter taste and an untypical aroma).
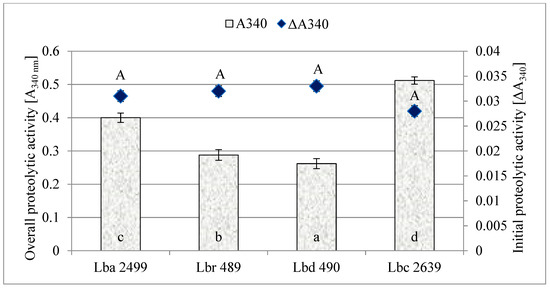
Figure 1.
Initial and overall proteolytic activity of examined Lactobacillus strains (mean values and standard deviations). A: homogenous group initial proteolysis, n = 6; a–d: homogenous groups overall proteolysis, n = 6).
Donkor et al. [20] determined the initial and overall proteolytic activity (after 24 h incubation) of the following probiotic strains: Lb. acidophilus LAFTI L10 and Lb. casei LAFTI L26, as well as Lb. acidophilus 4962 and Lb. casei 279. Likewise, in our study we found no differences in the initial proteolytic activity between the tested strains. The lowest overall proteolytic activity was determined for the strain Lb. casei Lc 279 (0.290). In turn, very high activities accounting for 0.460, 0.670, and 1.90 were found for Lb. acidophilus LAFTI L10, Lb. acidophilus La 4962, and Lb. casei LAFTI L26, respectively. The proteolytic activity of Lb. acidophilus 2499 determined in our study at 0.400 is similar to that reported by Donkor et al. [20] for Lb. acidophilus LAFTI L10 (0.460). In turn, the activity of Lb. casei 2639 determined in our study at 0.512 is considerably higher from the activity assayed by Donkor et al. [20] for Lb. casei Lc 279 (0.290) and over threefold lower from that determined for Lb. casei LAFTI L26 (1.90).
It was concluded that the analyzed bacterial strains from the genus Lactobacillus exhibited various overall proteolytic activities. Thus, large differences in proteolytic activity may result from the various activities of their proteolytic systems, and resultantly, from the various number of amine groups released in RSM during incubation, as well as from their various nutritional needs.
3.2. Proteolytic and ACE-Inhibitory Activity (%) During Ripening of Dutch-Type Cheese Models
Results of determinations of the proteolytic and ACE-inhibitory activities in the studied cheese models during their ripening are presented in Figure 2. After one week of ripening, the highest ACE-inhibitory activity was found in the cheese models with the addition of Lb. acidophilus 2499 (Figure 2). In other cases of cheese models, the ACE-inhibitory activity was slightly higher than in the control cheeses (69%), and ACE inhibition ranged from 74 to 79%. The control cheeses were also characterized by the lowest proteolytic activity (0.270). This slightly higher value, reaching ca. 0.305, was determined for the cheese models containing adjunct cultures Lb. acidophilus 2499 and Lb. delbrueckii 490. In turn, the highest proteolytic activity was determined for the cheese models manufactured with the addition of Lb. rhamnosus 489 and Lb. casei 2639. Similar dependencies, but with higher values, were observed in cheese models after 3 weeks of ripening, with the highest proteolytic activity being demonstrated in the cheese models with adjunct cultures Lb. rhamnosus 489.
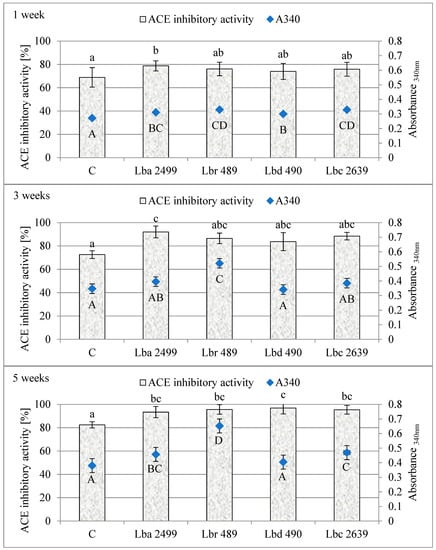
Figure 2.
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activity (%) and proteolysis of water soluble extract (WSE) from Dutch-type cheese models during ripening (mean values and standard deviations). a–c: homogenous groups ACE, n = 6; A–D: homogenous groups proteolysis, n = 6.
One of the main factors affecting the proteolytic activity in cheeses is the water content. Water content of the analyzed cheese models (48–49%, data not shown) was higher than the typical water content of Dutch-type cheeses (42–45%). This was due to two reasons: firstly, the analyzed cheese models were not subjected to pressing and their brining was relatively short, and secondly, the higher water content of the produced models contributed to greater enhancement of proteolysis under model conditions.
After 3 and 5 week storage, a similar ACE-inhibitory activity was observed in the cheeses with adjunct cultures, despite the presence of different homogeneous groups in the Tukey tests (HSD). Cheese models with the addition of Lb. acidophilus 2499 were characterized by the best ACE-inhibitory capability among all cheese variants both after 1 week and 3 weeks of ripening.
After 5 weeks of storage, all analyzed cheese models were characterized by a high capability for ACE inhibition, exceeding beyond 90%. Similar ACE inhibition was noted in the cheese models with adjunct cultures of Lb. acidophilus 2499, Lb. rhamnosus 489, and Lb. casei 2639, however it was considerably higher than in the control cheese models. The addition of strains from the genus Lactobacillus to cheese models influenced the effectiveness of ACE inhibition because the tested strains contributed to a higher ACE inhibition compared to that achieved in the control cheeses at the end of ripening. The adjunct LAB strains also determined the proteolytic activity of the analyzed cheese models after 5 weeks of their ripening. The lowest proteolytic activity was determined in the cheese models with Lb. delbrueckii 490 and in the control models (Figure 2). A significantly higher activity compared to control cheeses was assayed in the cheese models containing adjunct cultures Lb. acidophilus 2499 and Lb. casei 2639 (ca. 0.460). In turn, the highest activity was determined in the cheese models with the addition of Lb. rhamnosus 489, and it was 1.5-fold higher than that determined in the control cheeses. Ong et al. [21] showed an increase in the content of inhibitors within the first 24 weeks of ripening of probiotic and control Cheddar cheeses, which remained at a similar level within the 12 subsequent weeks.
The study results indicate that the proteolytic transformations occurring during cheese model ripening are significantly influenced by the adjunct cultures which intensify casein hydrolysis by releasing peptides responsible for ACE inhibition from its chains. Considering the proteolytic activity of the analyzed LAB strains established in the cheese models by determining the number of free amine groups, being a measure of the degree of proteolysis during ripening, its values were observed to vary and increase throughout the ripening of cheese models depending on the adjunct LAB strain used in cheesemaking. There were no statistically significant differences in the cheese models with the addition of Lb. acidophilus 2499, Lb. rhamnosus 489, and Lb. casei 2639 cultures.
The IC50 values of the studied cheese models determined throughout the ripening period are presented in Table 1. Immediately after cheesemaking, the lowest IC50 value (0.7 mg mL−1) was determined in the cheese models with the addition of Lb. acidophilus 2499 and Lb. rhamnosus 489. The addition of these two adjunct strains during cheesemaking had a significant effect on the produce of ACE inhibitors. An inconsiderably higher IC50 value was determined in the cheese models with the addition of Lb. delbrueckii 490 and Lb. casei 2639. In turn, the highest concentration of peptides needed to obtain 50% inhibition of ACE activity was determined in the control cheese models (0.84 mg mL−1). The lowest IC50 values were noted in the cheese models containing lactobacilli after 5 weeks of ripening. The results above indicate that the lactobacilli produced ACE inhibitors from the beginning of the ripening process. After 5 weeks of ripening, the lowest IC50 value among all cheese models with the addition of LABs from the genus Lactobacillus was determined in those containing Lb. delbrueckii 490 (0.39 mg mL−1), and the highest value was determined in those with Lb. casei 2639 (0.47 mg mL−1) (Table 1). IC50 values were not significantly different between the control cheese model and the other three models with the addition of Lb. acidophilus 2499, Lb. rhamnosus 489, and Lb. casei 2639. Therefore, the low value of IC50 in the control cheese model may indicate a crucial role of the starter cultures in the formation of peptides with antihypertensive properties during the ripening of the examined cheese models. An increase in the ACE-inhibitory activity in cheeses containing various adjunct strains of LAB was reported by Ong and Shah [22]. A comparative analysis of the ACE-inhibitory activity of the same cheese models in our study revealed the IC50 parameter to be a better indicator when comparing enzyme inhibition effectiveness because it takes account of the concentration of peptides and dissolved proteins in a sample.

Table 1.
IC50 values of ACE-inhibitory activity from control cheese models and with adjunct culture (mg mL−1).
The results of investigations reported in the literature point to vast differences in the ACE-inhibitory activity among various cheese species and to the usability of in vitro studies in the identification of cheese samples with a high ACE-inhibitory activity. The ability to identify the stage of cheese ripening at which the concentration of bioactive peptides is the highest may help in establishing the point in the ripening process when the cheeses exhibit the greatest health-promoting properties [23,24].
The literature data indicate that the presence of ACE inhibitors is affected to a greater extent by the cheesemaking technology (including the heat treatment of milk) [10,25], starter culture and adjunct LABs used [21,22,25], and ripening conditions (period and temperature) [1,9,26,27,28], than by cheese species. The shelf-lives of the majority of the Dutch-type cheeses produced and consumed across the globe are not long. The recommended minimal ripening period is 5 weeks or preferably even shorter. For this reason, investigations of cheeses of this type but with a ripening period that is a few or even a dozen times longer concern a relatively low number of cheeses available in retail. In our study, the cheese models were analyzed for 5 weeks and these analyses demonstrated an increasing activity of ACE inhibitors. This confirms that the Dutch-type cheeses should be ripened for the period of 5 weeks at a minimum.
It is difficult to establish a close relationship between the ACE-inhibitory activity in vitro and the hypotensive effect in vivo. This arouses some doubts concerning the use of the ACE-inhibitory activity in vitro as the sole criterion in the identification of substances with a potentially hypotensive effect, owing to the possibility of their physiological transformations in vivo [29]. This has been confirmed in a study conducted by Bernabucci et al. [30], where the authors demonstrated that the in vitro ACE-inhibitory activity of naturally-formed bioactive peptides in Parmigiano Reggiano (PR) and Grana Padano (GP) cheeses caused no hypotensive effect in vivo. Hence, the in vitro ACE-inhibitory activity cannot be used as the sole criterion in the evaluation of potentially hypotensive substances. Therefore, it is necessary to examine the beneficial hypotensive properties of bioactive peptides in vivo considering the possibility of their enzymatic degradation or diminished absorption under these conditions.
4. Conclusions
The use of adjunct strains from the genus Lactobacillus increased contents of peptide inhibitors of ACE in the cheese models with their addition compared to the control cheeses. Contents of these inhibitors were observed to increase throughout 5 weeks of ripening, hence their lower amount was needed to induce 50% inhibition of ACE. Results of our study demonstrate that the adjunct strains used in cheesemaking intensified the synthesis of peptides with hypotensive properties in vitro. However, caution should be exercised regarding the obtained ACE-inhibitory activity in vitro and the speculated hypotensive effect in vivo, given that the hypotensive properties of bioactive peptides need to be confirmed under in vivo conditions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.G. and A.P.; Methodology, M.G.; Formal Analysis, M.G.; Investigation, M.G.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, M.G.; Writing—Review & Editing, M.G., A.P. and A.B.-P.; Supervision, M.G. and A.P.
Funding
This research was funded by Wacław Dąbrowski Institute of Agricultural and Food Biotechnology, statutory subject BST [500-01-GM-01], FBW [510-01-GM-01].
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ryhänen, E.L.; Pihlanto-Leppälä, A.; Pahkala, E. A new type of ripened, low-fat cheese with bioactive properties. Int. Dairy J. 2001, 11, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziuba, B.; Dziuba, M. Milk proteins-derived bioactive peptides in dairy products: Molecular, biological and methodological aspects. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2014, 13, 5–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, M.; Hudson, J.A.; Korpela, R.; de los Reyes-Gavilán, C.G. Impact on human health of microorganisms present in fermented dairy products: An overview. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 412714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Singh, R.; Rana, S. Bioactive peptides: A review. Int. J. Bioautom. 2011, 15, 223–250. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, S.D.; Beverly, R.L.; Qu, Y.; Dallas, D.C. Milk bioactive peptide database: A comprehensive database of milk protein-derived bioactive peptides and novel visualization. Food Chem. 2017, 232, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieber, R.; Bütikofer, U.; Egger, C.; Portmann, R.; Walther, B.; Wechsler, D. ACE-inhibitory activity and ACE-inhibiting peptides in different cheese varieties. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2010, 90, 47–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista, D.P.; Galli, B.D.; Cavalheiro, F.G.; Negrāo, F.; Eberlin, M.N.; Gigante, M.L. Lactobacillus helveticus LH-B02 favours the release of bioactive peptide during Prato cheese ripening. Int. Dairy J. 2018, 87, 75–83. [Google Scholar]
- Reale, A.; Ianniello, R.G.; Ciocia, F.; Di Renzo, T.; Boscaino, F.; Ricciardi, A.; Coppola, R.; Parente, E.; Zotta, T.; McSweeney, P.L.H. Effect of respirative and catalase-positive Lactobacillus casei adjuncts on the production and quality of Cheddar-type cheese. Int. Dairy J. 2016, 63, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addeo, F.; Chianese, L.; Salzano, A.; Sacchi, R.; Cappuccio, U.; Ferranti, P.; Malorni, A. Characterization of the 12% trichloroacetic acid-insoluble oligopeptides of Parmigiano-Reggiano cheese. J. Dairy Res. 1992, 59, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smacchi, E.; Gobbetti, M. Bioactive peptides in dairy products: Synthesis and interaction with proteolytic enzymes. Food Microbiol. 2000, 17, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA. Evolus and reduce arterial stiffness—Scientific substantiation of a health claim related to Lactobacillus helveticus fermented Evolus® low-fat milk products and reduction of arterial stiffness pursuant to article 14 of the regulation (EC) No 1924/2006—Scientific opinion of the panel on dietetic products, nutrition and allergies; question number EFSA-Q-2008-218. EFSA J. 2008, 6, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Korhonen, H.; Pihlanto, A. Bioactive peptides: Production and functionality. Int. Dairy J. 2006, 16, 945–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafeez, Z.; Cakir-Kiefer, C.; Roux, E.; Perrin, C.; Miclo, L.; Dary-Mourot, A. Strategies of producing bioactive peptides from milk proteins to functionalize fermented milk products. Rev. Artic. Food Res. Int. 2014, 63, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajirostamloo, B. Bioactive component in milk and dairy product. Int. Sci. Index Agric. Biosyst. Eng. 2010, 4, 870–874. [Google Scholar]
- Church, F.C.; Swaisgood, H.E.; Porter, D.H.; Catignani, G.L. Spectrophotometric assay using o-phthaldialdehyde for determination of proteolysis in milk and isolated milk proteins. J. Dairy Sci. 1983, 66, 1219–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hynes, E.; Ogier, J.C.; Delacroix-Buchet, A. Protocol for the manufacture of miniature washed-curd cheeses under controlled microbiological conditions. Int. Dairy J. 2000, 10, 733–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushman, D.W.; Cheung, H.S. Spectrophotometric assay and properties of the angiotensin-converting enzyme of rabbit lung. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1971, 20, 1637–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramchandran, L.; Shah, N.P. Influence of addition of Raftiline HP® on the growth, proteolytic, ACE-and α-glucosidase inhibitory activities of selected lactic acid bacteria and Bifidobacterium. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 43, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Donkor, O.N.; Henriksson, A.; Vasiljevic, T.; Shah, N.P. Proteolytic activity of dairy lactic acid bacteria and probiotics as determinant of growth and in vitro angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory activity in fermented milk. Le Lait 2007, 87, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, L.; Henriksson, A.; Shah, N.P. Angiotensin converting enzyme-inhibitory activity in Cheddar cheeses made with the addition of probiotic Lactobacillus casei sp. Le Lait 2007, 87, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, L.; Shah, N.P. Release and identification of angiotensin-converting enzyme-inhibitory peptides as influenced by ripening temperatures and probiotic adjuncts in Cheddar cheeses. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 41, 1555–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pripp, A.H.; Sørensen, R.; Stepaniak, L.; Sørhaug, T. Relationship between proteolysis and angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibition in different cheeses. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 39, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smacchi, E.; Gobbetti, M. Peptides from several Italian cheeses inhibitory to proteolytic enzymes of lactic acid bacteria, Pseudomonas fluorescens ATCC 948 and to the angiotensin I-converting enzyme. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 1998, 22, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meira, S.M.M.; Daroit, D.J.; Helfer, V.E.; Corrêa, A.P.F.; Segalin, J.; Carro, S.; Brandelli, A. Bioactive peptides in water-soluble extracts of ovine cheeses from Southern Brazil and Uruguay. Food Res. Int. 2012, 48, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meisel, H.; Goepfert, A.; Gunther, S. ACE-inhibitory activities in milk products. Milchwissenschaft 1997, 52, 307–311. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, T.; Nakamura, T.; Kitazawa, H.; Kawai, Y.; Itoh, T. Isolation and structural analysis of antihypertensive peptides that exist naturally in Gouda cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 2000, 83, 1434–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, L.; Shah, N.P. Influence of probiotic Lactobacillus acidophilus and L. helveticus on proteolysis, organic acid profiles, and ACE inhibitory activity of Cheddar cheeses ripened at 4, 8, and 12 °C. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, M111–M120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuknytė, M.; Cattaneo, S.; Masotti, F.; De Noni, I. Occurrence and fate of ACE-inhibitor peptides in cheeses and in their digestates following in vitro static gastrointestinal digestion. Food Chem. 2015, 168, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernabucci, U.; Catalani, E.; Basiricò, L.; Morera, P. In vitro ACE-inhibitory activity and in vivo antihypertensive effects of water-soluble extract by Parmigiano Reggiano and Grana Padano cheeses. Int. Dairy J. 2014, 37, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).