Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer in Patients with Alcohol Use Disorder
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sample
2.2. Procedures
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Correlation Between Retinal Thickness and Alcohol Consumption
4.2. Correlation Between Retinal Thickness and Cognitive Impairment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Glossary
| AUD | Alcohol use disorders |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| GCL | Ganglion cell layer |
| GLC+ | Retina layer between RNFL/GLC and IPL/INL |
| GLC++ | Retina layer between ILM and IPL/INL |
| ILM | Inner limiting membrane |
| INL | Inner nuclear layer |
| IPL | Inner plexiform layer |
| IQV | Image quality value |
| MMSE | Mini-mental state examination |
| OCT | Optical coherence tomography |
| RNFL | Macular retina layer between ILM and RNFL/GCL |
| SD-OCT | Spectral domain optical coherence tomography |
| SDU | Standard drinking unit |
| TEDCA | Cognitive Impairment in Alcoholic Population Test |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- WHO. Global Status Report on Alcohol and Health 2018; World Health Organisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Erdozain, A.M.; Morentin, B.; Bedford, L.; King, E.; Tooth, D.; Brewer, C.; Wayne, D.; Johnson, L.; Gerdes, H.K.; Wigmore, P.; et al. Alcohol-related brain damage in humans. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soler Gonzalez, C.; Balcells Olivero, M.; Gual Sole, A. Alcohol related brain damage. State of the art and a call for action. Adicciones 2014, 26, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- London, A.; Benhar, I.; Schwartz, M. The retina as a window to the brain-from eye research to, C.N.S disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2013, 9, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gemelli, H.; Fidalgo, T.M.; Gracitelli, C.P.B.; de Andrade, E.P. Retinal nerve fiber layer analysis in cocaine users. Psychiatry Res. 2019, 271, 226–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwitzer, T.; Schwan, R.; Bubl, E.; Lalanne, L.; Angioi-Duprez, K.; Laprevote, V. Looking into the brain through the retinal ganglion cells in psychiatric disorders: A review of evidences. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 76, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Portilla, M.P.; Garcia-Alvarez, L.; de la Fuente-Tomas, L.; Velasco-Iglesias, Á.; Sáiz, P.A.; González-Blanco, L.; Bobes Bascarán, M.T.; Baamonde, B.; Alcalde, I.; Merayo-Lloves, J.; et al. Could structural changes in the retinal layers be a new biomarker of mental disorders? A systematic review and thematic synthesis. Rev. Psiquiatr. Salud Ment. 2019, 12, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado-Barba, R.; Martinez, A.; Sion, A.; Álvarez-Alonso, M.J.; Robles, A.; Quinto-Guillen, R.; Rubio, G. Development of a screening test for cognitive impairment in alcoholic population: TEDCA. Actas Esp. Psiquiatr. 2017, 45, 201–217. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon-Lipkin, E.; Chodkowski, B.; Reich, D.S.; Smith, S.A.; Pulicken, M.; Balcer, L.J.; Frohman, E.M.; Cutter, G.; Calabresi, P.A. Retinal nerve fiber layer is associated with brain atrophy in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 2007, 69, 1603–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, U.; Ikram, M.K.; Roshchupkin, G.V.; Bonnemaijer, P.W.M.; Colijn, J.M.; Vingerling, J.R.; Niessen, W.J.; Ikram, M.A.; Klaver, C.C.W.; Vernooij, M.W. Thinner retinal layers are associated with changes in the visual pathway: A population-based study. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2018, 39, 4290–4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascaso, F.J.; Cruz, N.; Modrego, P.J.; López-Anton, R.; Santabárbara, J.; Pascual, L.F.; Lobo, A.; Cristóbal, J.A. Retinal alterations in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease: An optical coherence tomography study. J. Neurol. 2014, 261, 1522–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, S.; Kumar, P.S.; Kumar, V.P.; Kattimani, S.; Akkilagunta, S. Effect of chronic alcohol and tobacco use on retinal nerve fibre layer thickness: A case-control study. BMJ Open Ophthalmol. 2017, 1, e000003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moura, F.C.; Monteiro, M.L. Evaluation of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measurements using optical coherence tomography in patients with tobacco-alcohol-induced toxic optic neuropathy. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2010, 58, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, E.M.; Kolappan, M.; Barnes, T.R.; Joyce, E.M.; Ron, M.A. A window into the brain: An in vivo study of the retina in schizophrenia using optical coherence tomography. Psychiatry Res. 2012, 203, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.W.; Tajunisah, I.; Sharmilla, K.; Peyman, M.; Subrayan, V. Retinal nerve fiber layer structure abnormalities in schizophrenia and its relationship to disease state: Evidence from optical coherence tomography. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 7785–7792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagne, A.M.; Hebert, M.; Maziade, M. Revisiting visual dysfunctions in schizophrenia from the retina to the cortical cells: A manifestation of defective neurodevelopment. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2015, 62, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celik, M.; Kalenderoglu, A.; Sevgi Karadag, A.; Bekir Egilmez, O.; Han-Almis, B.; Simsek, A. Decreases in ganglion cell layer and inner plexiform layer volumes correlate better with disease severity in schizophrenia patients than retinal nerve fiber layer thickness: Findings from spectral optic coherence tomography. Eur. Psychiatry 2016, 32, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, U.; Kücük, E.; Ülgen, A.; Özköse, A.; Demircan, S.; Ulusoy, D.M.; Zararsız, G. Retinal nerve fiber layer and macular thickness measurement in patients with schizophrenia. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 26, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehraban, A.; Samimi, S.M.; Entezari, M.; Seifi, M.H.; Nazari, M.; Yaseri, M. Peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in bipolar disorder. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2016, 254, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalenderoglu, A.; Sevgi-Karadag, A.; Celik, M.; Egilmez, O.B.; Han-Almis, B.; Ozen, M.E. Can the retinal ganglion cell layer (GCL) volume be a new marker to detect neurodegeneration in bipolar disorder? Compr. Psychiatry 2016, 67, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, J.M.; Buu, A.; Adams, K.M.; Nigg, J.T.; Puttler, L.I.; Jester, J.M.; Zucker, R.A. Effects of alcoholism severity and smoking on executive neurocognitive function. Addiction 2009, 104, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdeva, A.; Chandra, M.; Choudhary, M.; Dayal, P.; Anand, K.S. Alcohol-Related Dementia and Neurocognitive Impairment: A Review Study. Int. J. High Risk Behav. Addict. 2016, 5, e27976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frías-Torres, C.; Moreno-España, J.; Ortega, L.; Barrio, P.; Gual, A.; Teixidor López, L. Remediation therapy in patients with alcohol use disorders and neurocognitive disorders: A Pilot Study. Adicciones 2018, 30, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, J.Y.; Yang, J.H.; Han, J.S.; Kim, D.G. Analysis of the Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness in Alzheimer Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment. Korean J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 31, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppola, G.; Di Renzo, A.; Ziccardi, L.; Martelli, F.; Fadda, A.; Manni, G.; Barboni, P.; Pierelli, F.; Sadun, A.A.; Parisi, V. Optical coherence tomography in Alzheimer’s disease: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomson, K.L.; Yeo, J.M.; Waddell, B.; Cameron, J.R.; Pal, S. A systematic review and meta-analysis of retinal nerve fiber layer change in dementia, using optical coherence tomography. Alzheimers Dement. (Amst.) 2015, 1, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, H.; Zhu, Z.; Peng, Y. Potential Utility of Retinal Imaging for Alzheimer’s Disease: A Review. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Ramos, T.; Benito-Leon, J.; Villarejo, A.; Bermejo-Pareja, F. Retinal nerve fiber layer thinning in dementia associated with Parkinson’s disease, dementia with Lewy bodies, and Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2013, 34, 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iseri, P.K.; Altinas, O.; Tokay, T.; Yuksel, N. Relationship between cognitive impairment and retinal morphological and visual functional abnormalities in Alzheimer disease. J. Neuroophthalmol. 2006, 26, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundogan, F.C.; Demirkaya, S.; Sobaci, G. Is optical coherence tomography really a new biomarker candidate in multiple sclerosis?—A structural and functional evaluation. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2007, 48, 5773–5781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satue, M.; Rodrigo, M.J.; Otin, S.; Bambo, M.P.; Fuertes, M.I.; Ara, J.R.; Martin, J.; Polo, V.; Larrosa, J.M.; Pablo, L.; et al. Relationship between Visual Dysfunction and Retinal Changes in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
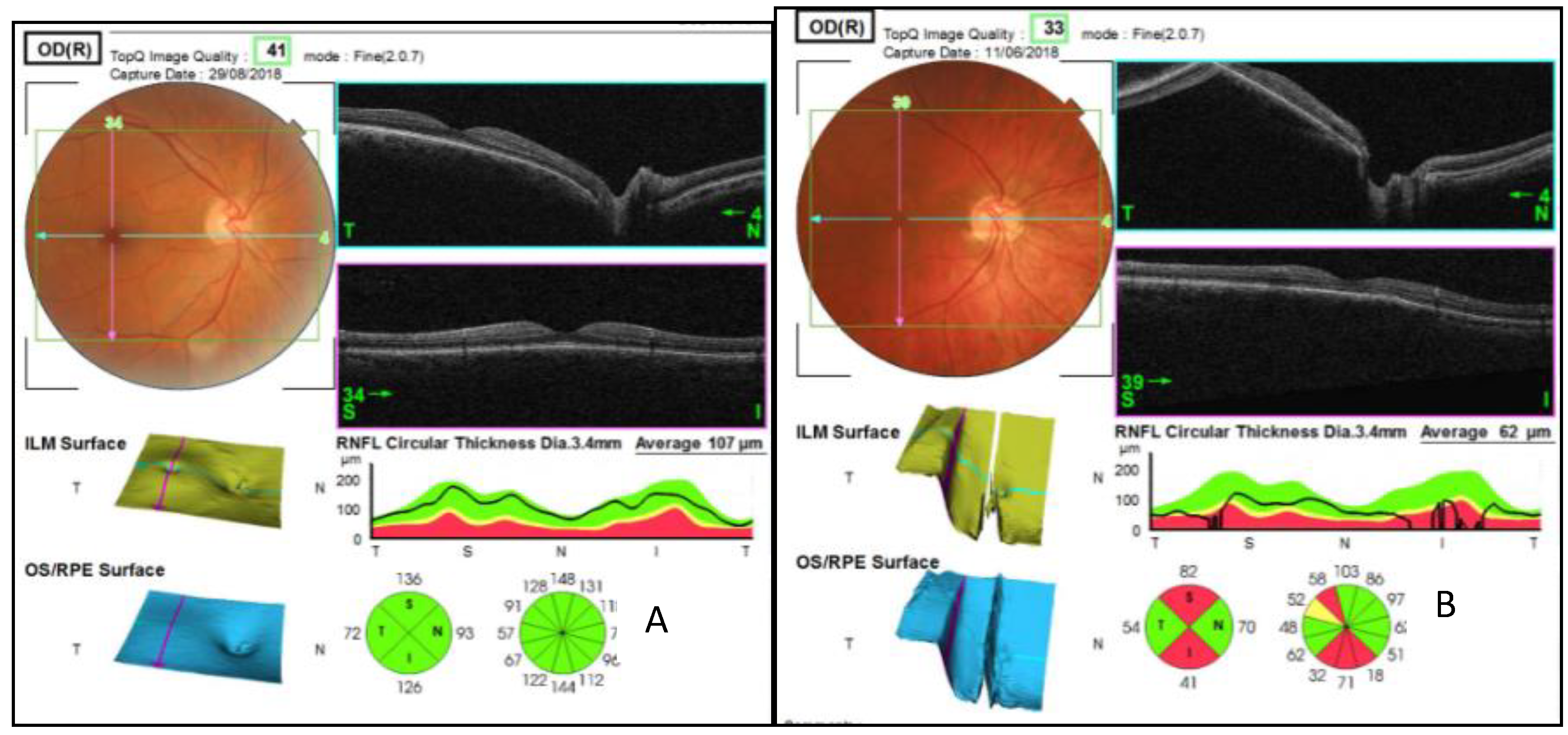
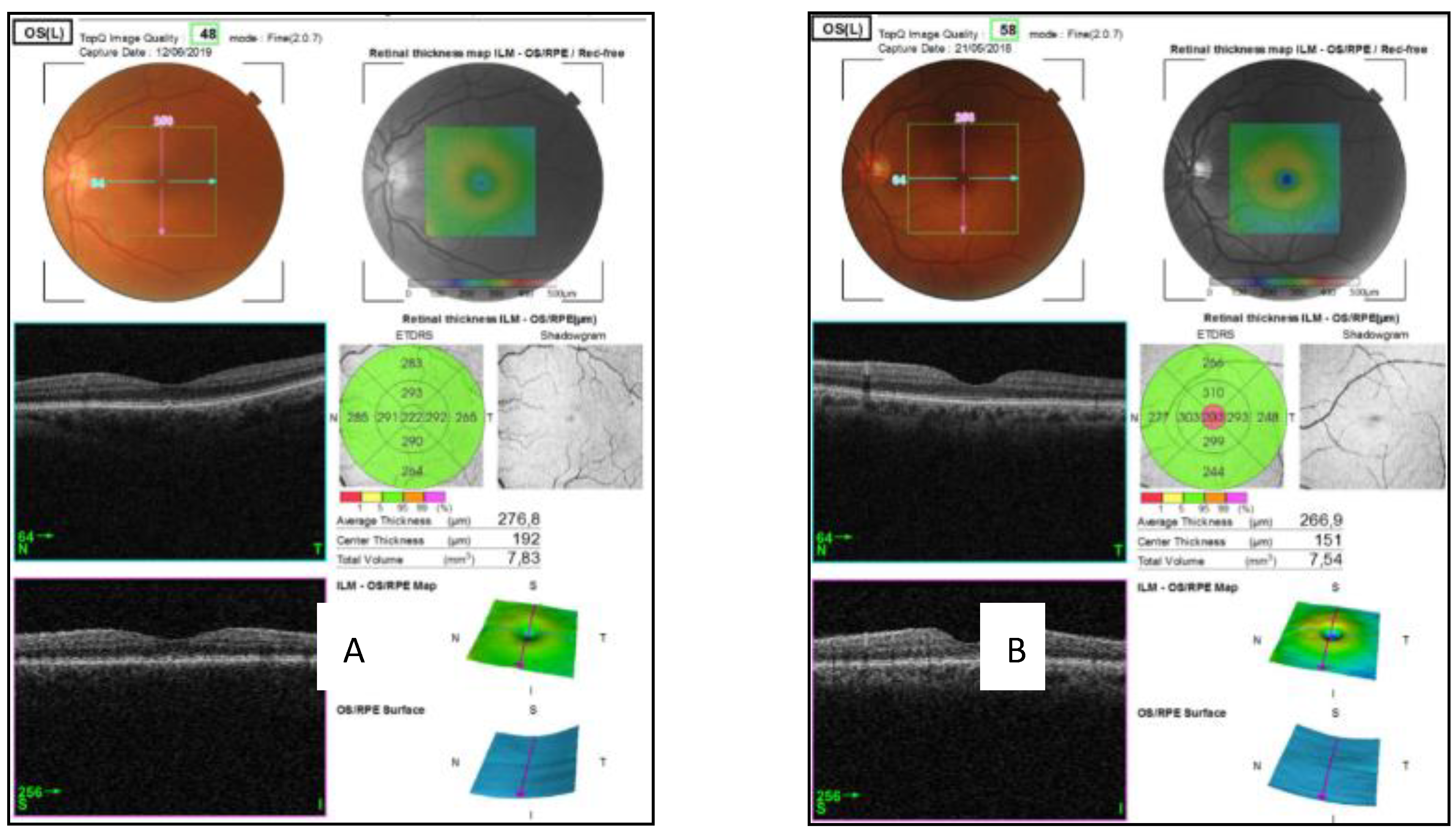
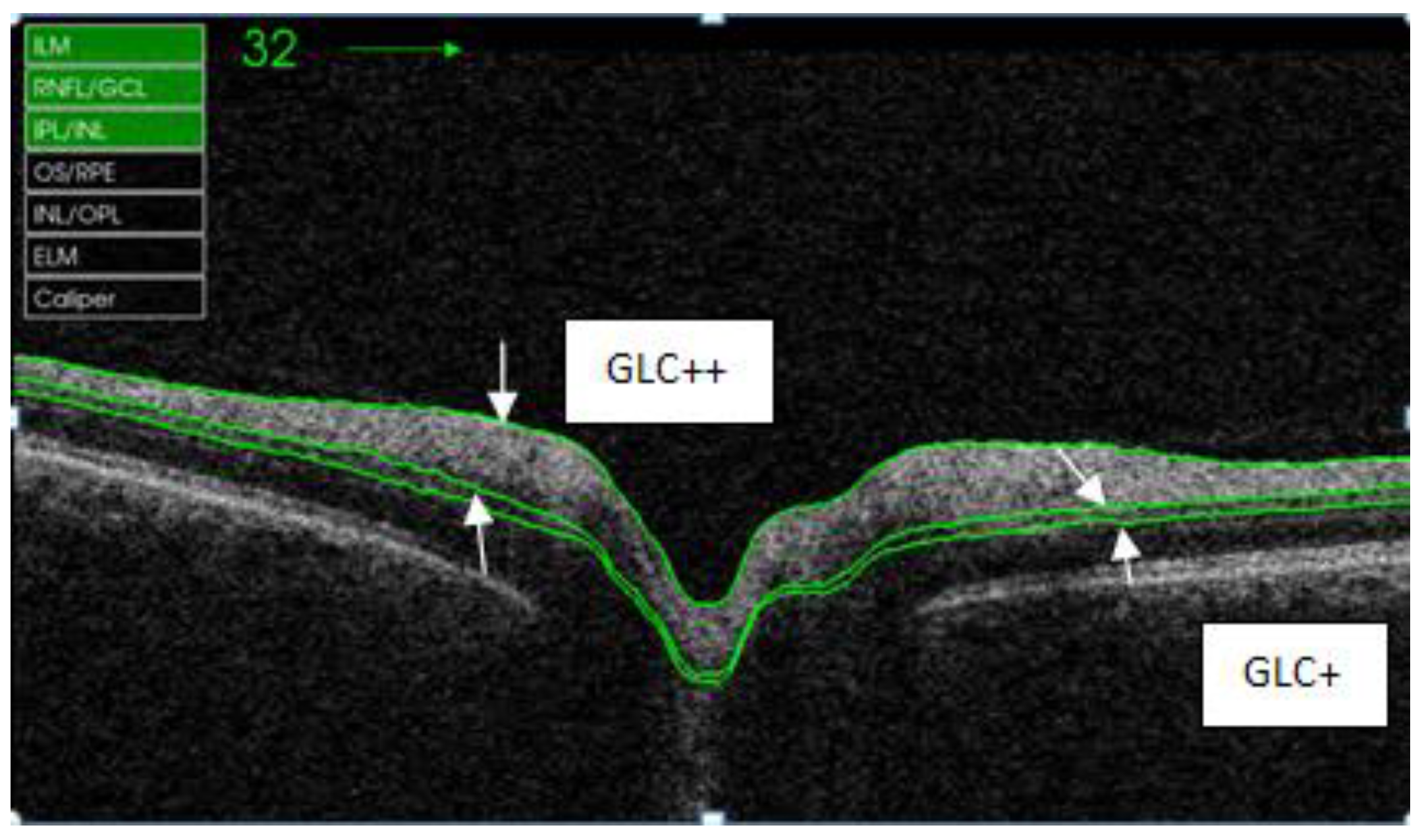
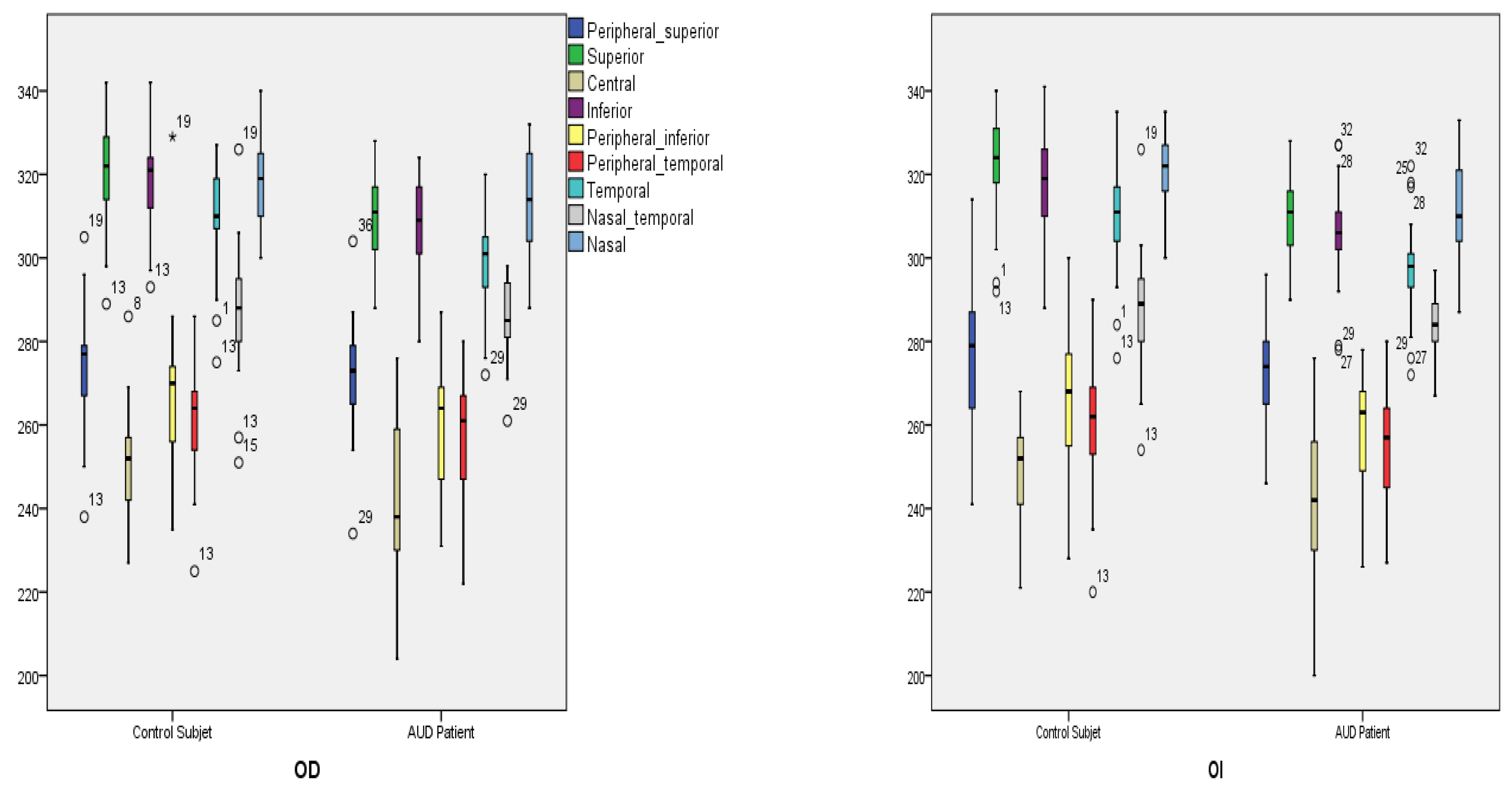
| Quadrants | Control Subjects n = 21 | SD Control (±) | AUD Patients n = 21 | SD Alcohol (±) | Difference CI | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right (µm) | 289.99 | 10.79 | 282.30 | 11.58 | 0.71 to 14.67 | 0.032 * |
| Left (µm) | 289.93 | 10.22 | 281.68 | 10.22 | 1.76 to 14.74 | 0.014 * |
| Quadrants (µm) | Control Subjects n = 21 | SD Control (±) | AUD Patients n = 21 | SD Alcohol (±) | Difference CI | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peripheral superior | ||||||
| Right | 274.86 | 14.57 | 272.29 | 13.71 | −6.25 to 11.40 | 0.559 |
| Left | 276.10 | 16.10 | 272.10 | 12.77 | −5.07 to 11.06 | 0.378 |
| Superior | ||||||
| Right | 320.10 | 13.02 | 309.19 | 11.25 | 3.31 to 18.50 | 0.006 * |
| Left | 321.43 | 13.12 | 309.76 | 11.27 | 4.04 to 19.30 | 0.004 * |
| Central | ||||||
| Right | 250.48 | 13.50 | 237.62 | 34.09 | −3.31 to 29.03 | 0.120 |
| Left | 249.33 | 11.72 | 241.29 | 22.05 | −3.27 to 19.41 | 0.150 |
| Inferior | ||||||
| Right | 318.33 | 12.72 | 307.00 | 13.16 | 3.26 to 19.41 | 0.007 * |
| Left | 317.86 | 12.33 | 305.76 | 12.93 | 4.21 to 19.98 | 0.040 * |
| Peripheral inferior | ||||||
| Right | 267.95 | 18.40 | 260.62 | 13.24 | −2.66 to 17.33 | 0.146 |
| Left | 266.43 | 16.85 | 258.33 | 12.92 | −1.27 to 17.46 | 0.089 |
| Peripheral temporal | ||||||
| Right | 262.29 | 14.33 | 258.00 | 13.34 | −4.35 to 12.92 | 0.320 |
| Left | 261.19 | 15.05 | 255.90 | 13.39 | −3.60 to 14.17 | 0.236 |
| Temporal | ||||||
| Right | 308.14 | 13.35 | 298.48 | 13.72 | −1.22 to 18.11 | 0.026 * |
| Left | 308.10 | 13.22 | 297.10 | 12.95 | 2.84 to 19.16 | 0.010 * |
| Nasal temporal | ||||||
| Right | 288.14 | 16.44 | 285.29 | 9.67 | −5.55 to 11.27 | 0.497 |
| Left | 287.86 | 14.49 | 283.71 | 8.92 | −3.36 to 11.65 | 0.271 |
| Nasal | ||||||
| Right | 319.67 | 11.79 | 312.24 | 12.44 | −0.13 to 1499 | 0.054 |
| Left | 321.10 | 10.25 | 311.19 | 12.77 | 2.67 to 17.13 | 0.008 * |
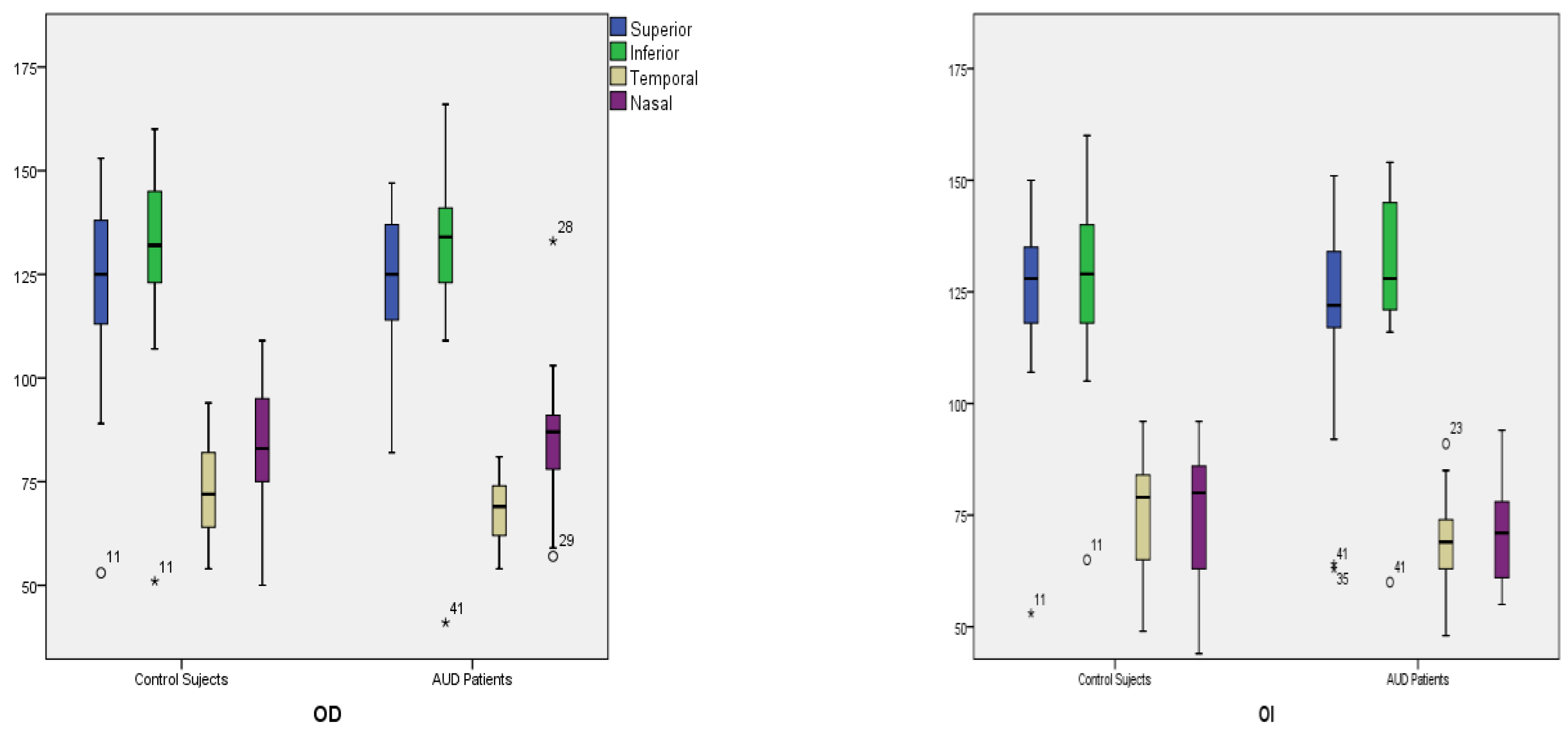
| Quadrants | Control Subjects n = 21 | SD Control (±) | AUD Patients n = 21 | SD Alcohol (±) | Difference CI | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right (µm) | 101.83 | 15.14 | 101.51 | 12.03 | −8.21 to 8.85 | 0.940 |
| Left (µm) | 100.83 | 14.63 | 96.93 | 14.28 | −5.11 to 12.92 | 0.387 |
| Quadrants (µm) | Control Subjects n = 21 | SD Control (±) | AUD Patients n = 21 | SD Alcohol (±) | Difference CI | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Superior | ||||||
| Right | 122.57 | 22.16 | 124.05 | 16.10 | −13.56 to 10.6 | 0.806 |
| Left | 125.14 | 20.18 | 120.76 | 23.31 | −9.22 to 17.98 | 0.519 |
| Inferior | ||||||
| Right | 129.48 | 22.09 | 129.52 | 23.99 | −14.43 to 14.33 | 0.995 |
| Left | 128.62 | 21.09 | 128.86 | 20.18 | −13.11 to 12.64 | 0.970 |
| Temporal | ||||||
| Right | 72.29 | 72.29 | 67.43 | 67.43 | −1.4 to 11.11 | 0.124 |
| Left | 74.71 | 74.71 | 68.43 | 13.53 | −1.95 to 14.52 | 0.131 |
| Nasal | ||||||
| Right | 83.00 | 16.60 | 85.05 | 16.34 | −12.32 to 8.22 | 0.689 |
| Left | 74.86 | 15.13 | 69.67 | 17.00 | −4.84 to 15.23 | 0.302 |
| Quadrants (µm) | Control Subjects n = 21 | SD Control (±) | AUD Patients n = 21 | SD Alcohol (±) | Difference CI | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RNFL macula | ||||||
| Right | 28.97 | 2.20 | 27.77 | 2.13 | −0.16 to 2.54 | 0.081 |
| Left | 28.72 | 2.21 | 27.82 | 2.67 | −0.62 to 2.43 | 0.239 |
| GLC++ 1 | ||||||
| Right | 109.13 | 8.46 | 104.00 | 7.23 | 0.22 to 10.04 | 0.041 * |
| Left | 109.33 | 6.53 | 105.12 | 7.77 | −0.27 to 8.68 | 0.065 |
| GLC+ 2 | ||||||
| Right | 74.75 | 5.95 | 71.52 | 5.14 | −0.24 to 6.70 | 0.670 |
| Left | 74.87 | 5.23 | 70.91 | 5.83 | 0.51 to 7.42 | 0.025 * |
| Inferior Peripheral | TEDCA | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Inferior peripheral | Pearson’s Correlation | 1 | −0.352 * |
| Sig. (bilateral) | 0.035 | ||
| n | 42 | 36 | |
| TEDCA | Pearson’s Correlation | −0.352 * | 1 |
| Sig. (bilateral) | 0.035 | ||
| n | 36 | 36 | |
| Nasal Peripheral | TEDCA | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal peripheral | Pearson’s Correlation | 1 | −0.457 * |
| Sig. (bilateral) | 0.005 | ||
| n | 42 | 36 | |
| TEDCA | Pearson’s Correlation | −0.457 * | 1 |
| Sig. (bilateral) | 0.005 | ||
| n | 36 | 36 | |
| Temporal Peripheral RNFL | TEDCA | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Temporal peripheral RNFL | Pearson’s Correlation | 1 | −0.551 * |
| Sig. (bilateral) | 0.001 | ||
| n | 42 | 36 | |
| TEDCA | Pearson’s Correlation | −0.551 * | 1 |
| Sig. (bilateral) | 0.001 | ||
| n | 36 | 36 | |
| Nasal RNFL | TEDCA | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal RNFL | Pearson’s Correlation | 1 | 0.456 * |
| Sig. (bilateral) | 0.005 | ||
| n | 42 | 36 | |
| TEDCA | Pearson’s Correlation | 0.456 * | 1 |
| Sig. (bilateral) | 0.005 | ||
| n | 36 | 36 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Álvarez-Sesmero, S.; Povedano-Montero, F.J.; Arias-Horcajadas, F.; Marín-Mayor, M.; Navarrete-Chamorro, P.; Raga-Martínez, I.; Rubio, G.; López-Muñoz, F. Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer in Patients with Alcohol Use Disorder. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 5331. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9245331
Álvarez-Sesmero S, Povedano-Montero FJ, Arias-Horcajadas F, Marín-Mayor M, Navarrete-Chamorro P, Raga-Martínez I, Rubio G, López-Muñoz F. Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer in Patients with Alcohol Use Disorder. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(24):5331. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9245331
Chicago/Turabian StyleÁlvarez-Sesmero, Sonia, Francisco J. Povedano-Montero, Francisco Arias-Horcajadas, Marta Marín-Mayor, Patricia Navarrete-Chamorro, Isidoro Raga-Martínez, Gabriel Rubio, and Francisco López-Muñoz. 2019. "Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer in Patients with Alcohol Use Disorder" Applied Sciences 9, no. 24: 5331. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9245331
APA StyleÁlvarez-Sesmero, S., Povedano-Montero, F. J., Arias-Horcajadas, F., Marín-Mayor, M., Navarrete-Chamorro, P., Raga-Martínez, I., Rubio, G., & López-Muñoz, F. (2019). Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer in Patients with Alcohol Use Disorder. Applied Sciences, 9(24), 5331. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9245331







