Feasibility Study of Using Carbide Slag as In-Bed Desulfurizer in Circulating Fluidized Bed Boiler
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Design
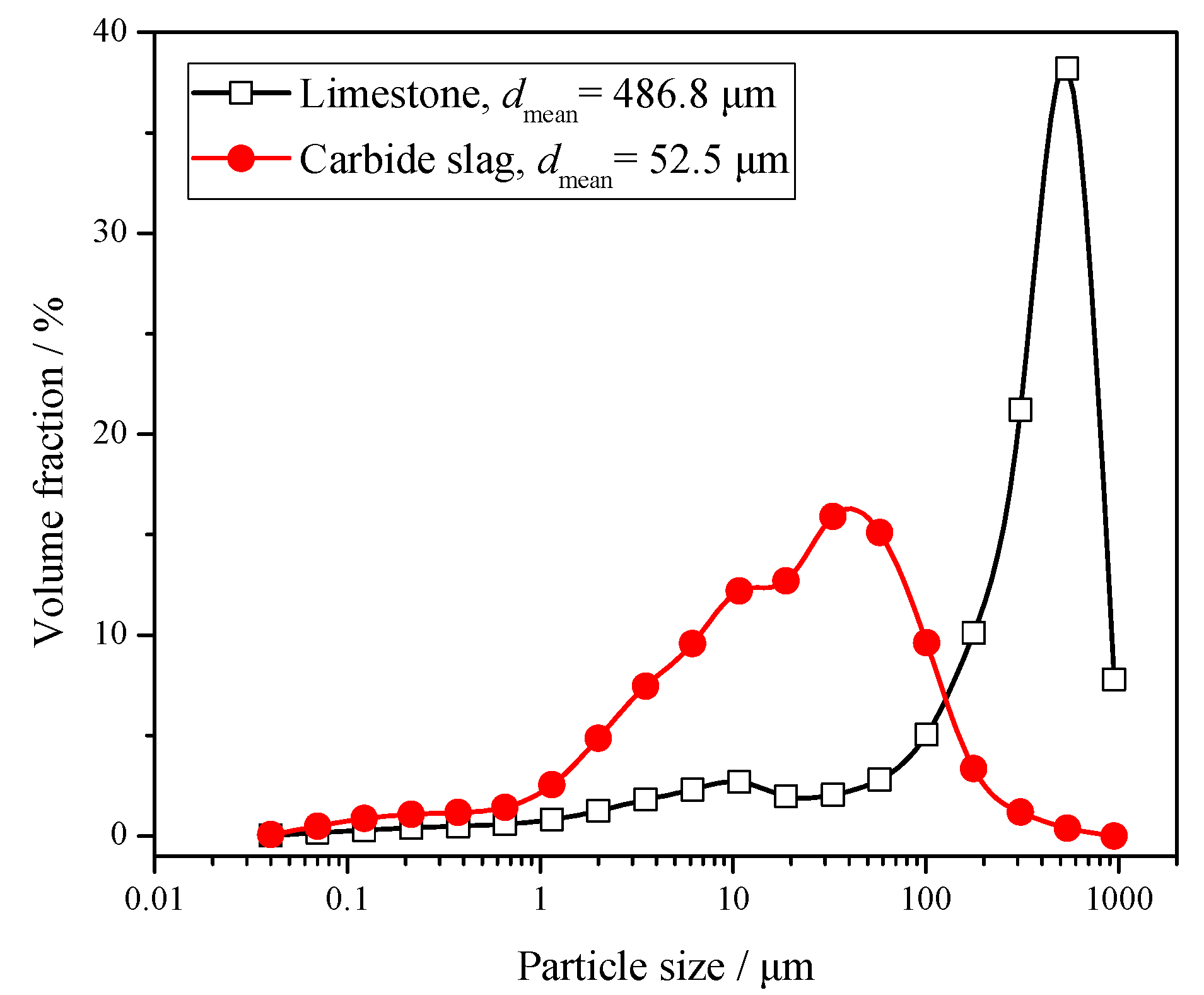
2.1. Limestone, Carbide Slag and Coal
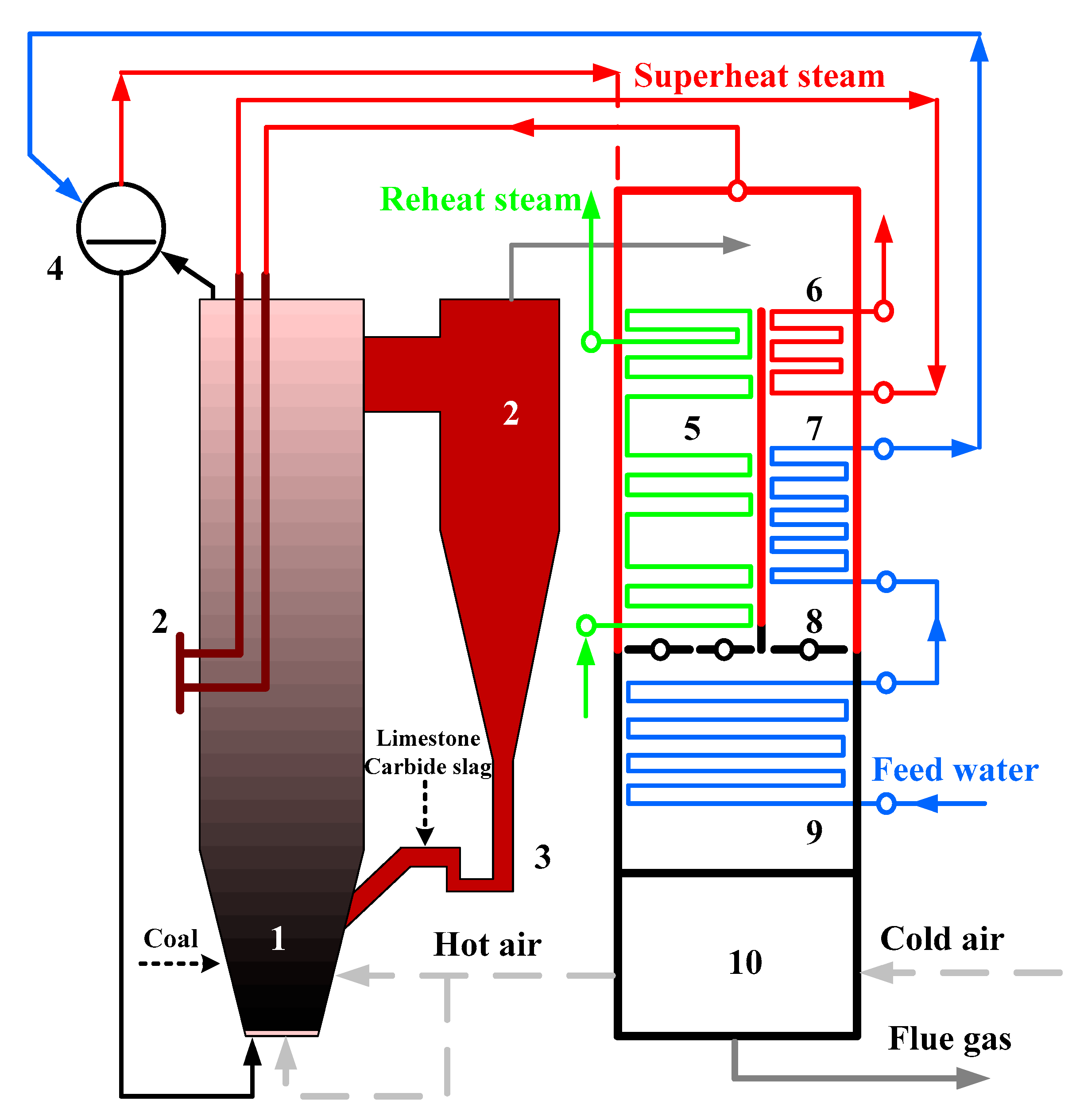
2.2. Brief Introduction of 1 MWth Pilot Boiler and 690 t·h−1 CFB Boiler
3. Results and Discussion
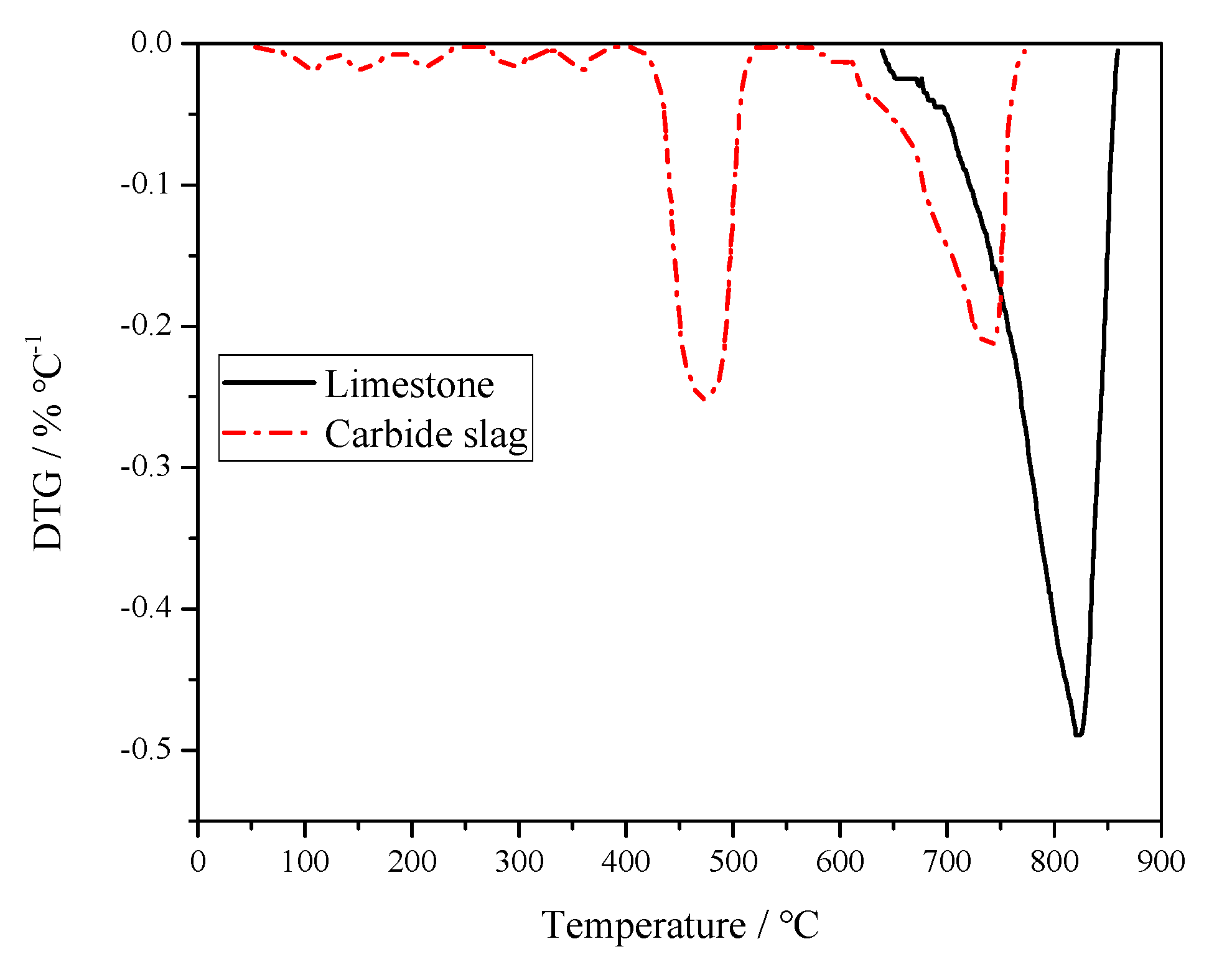
3.1. Comparison of Reactivity between Limestone and Carbide Slag
3.2. The 1MWth Pilot CFB boiler Tests
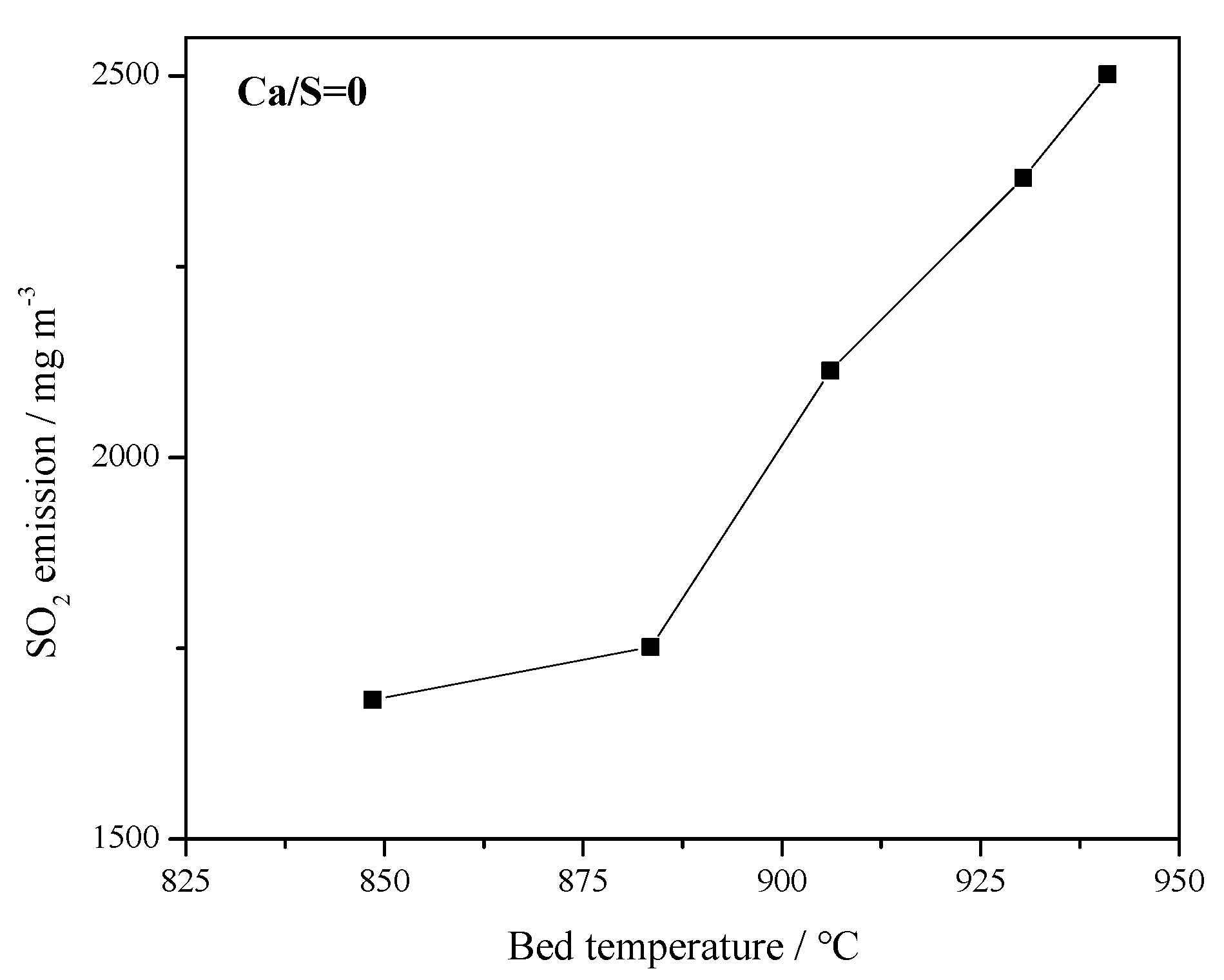
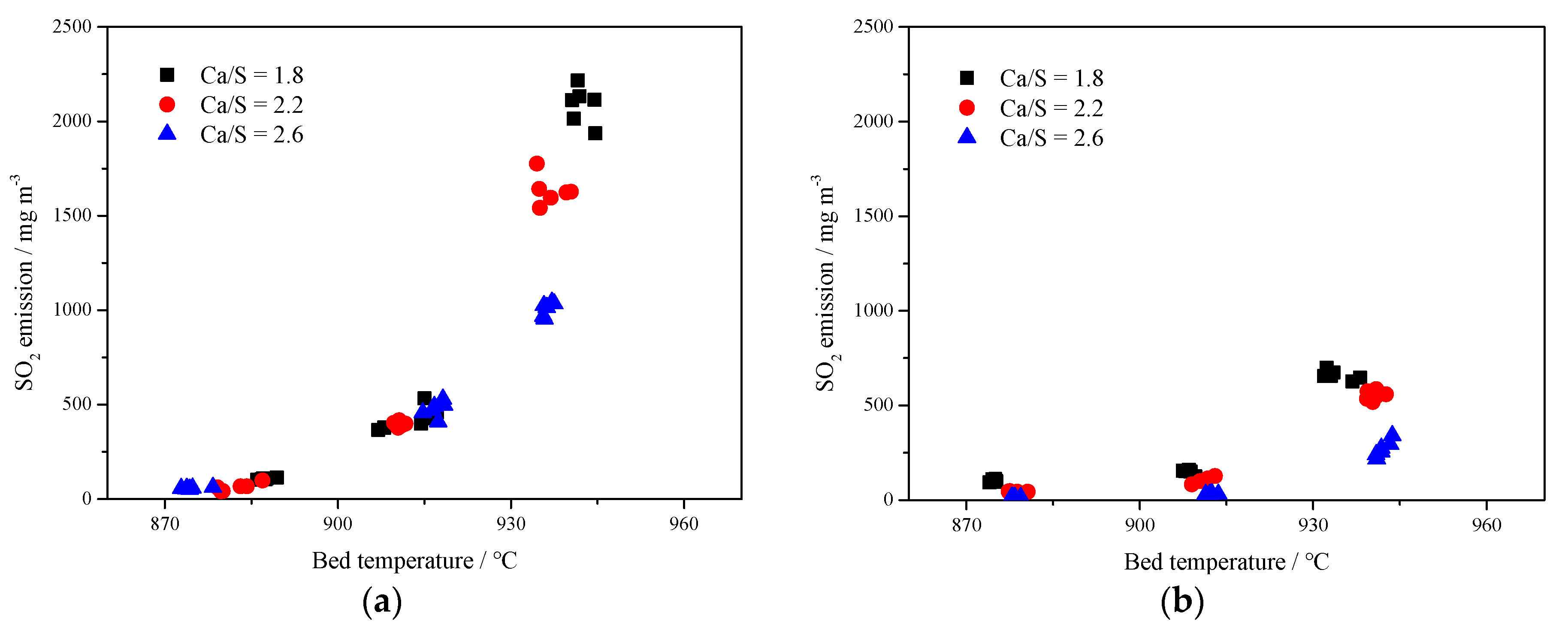
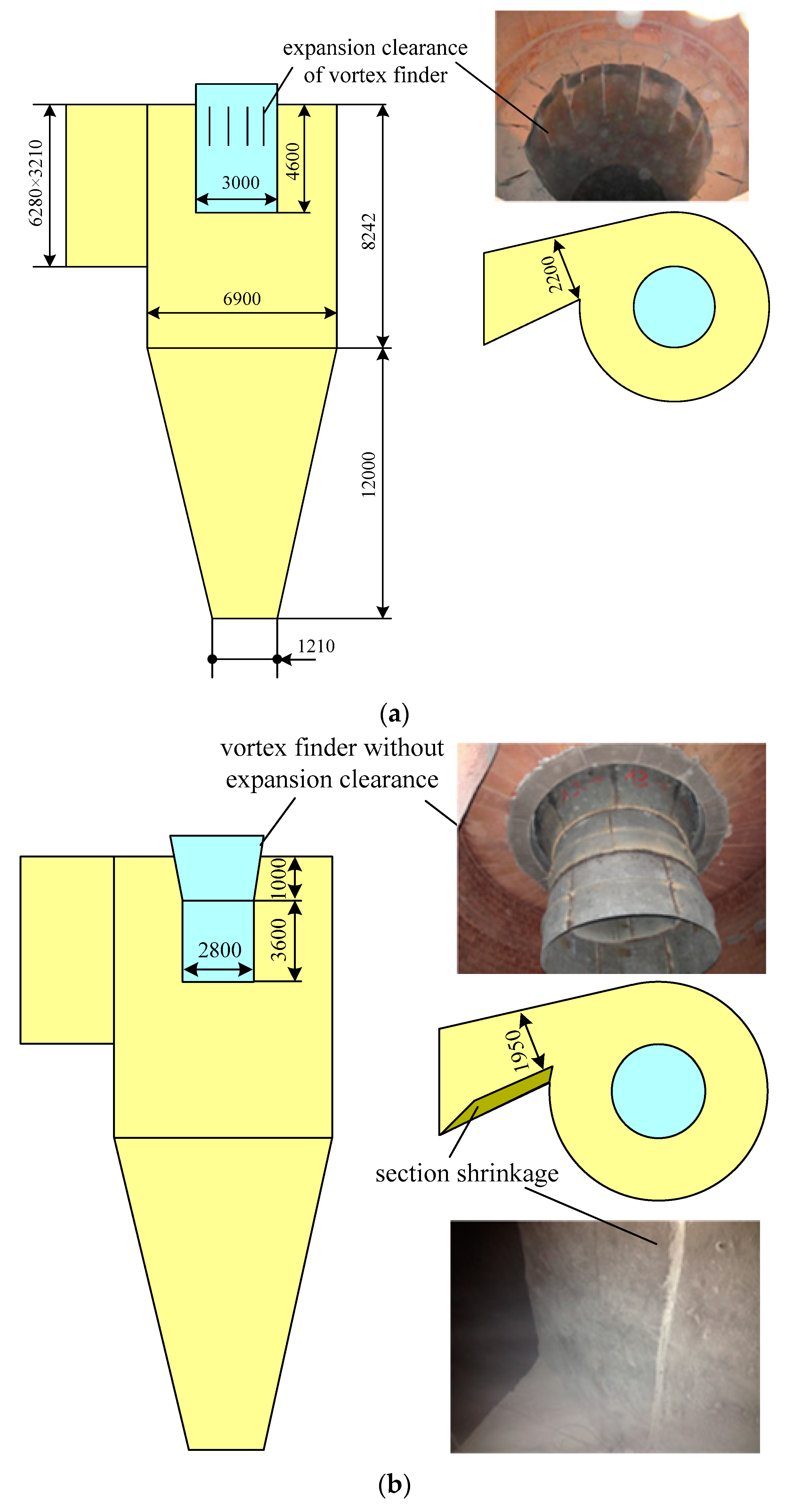
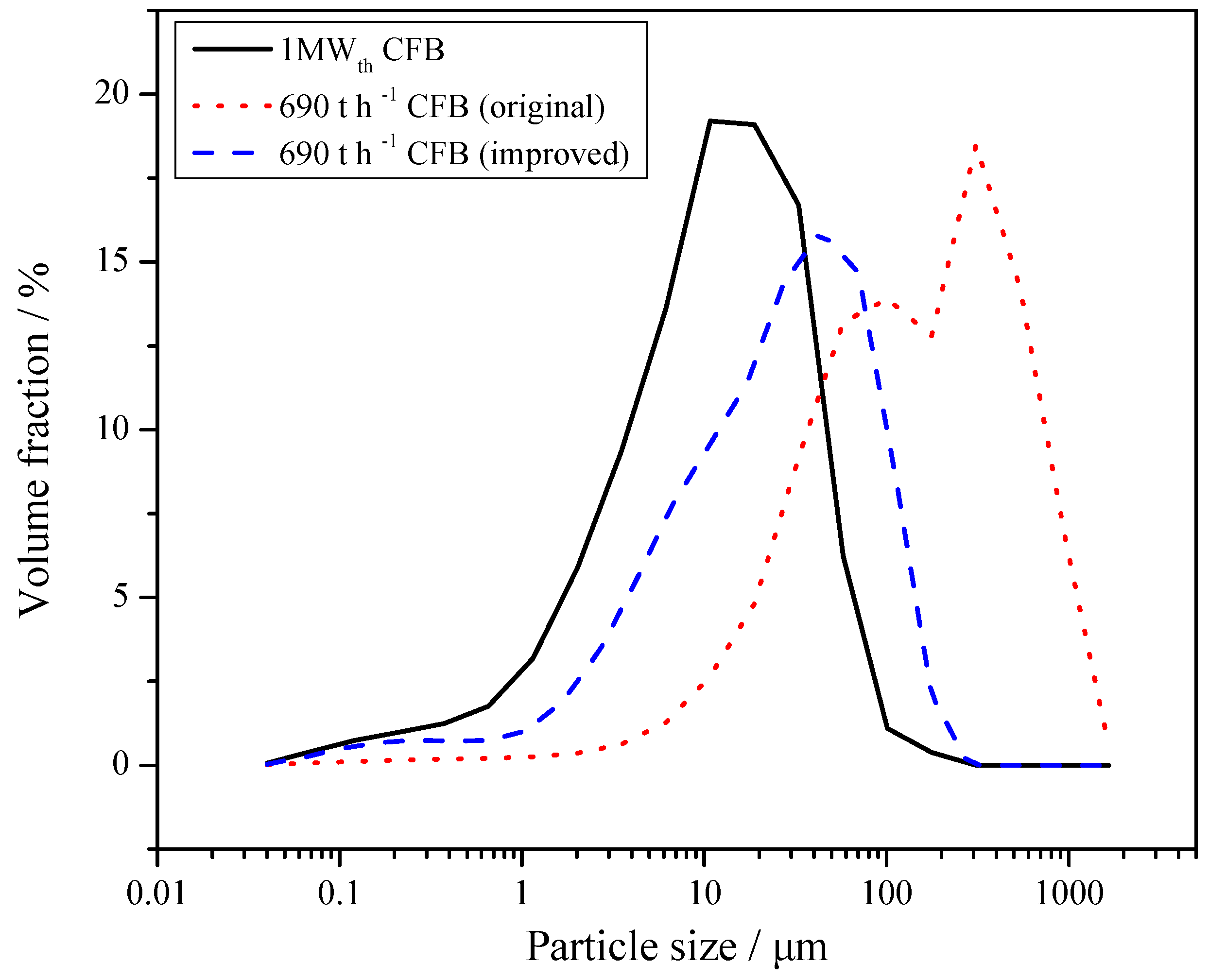
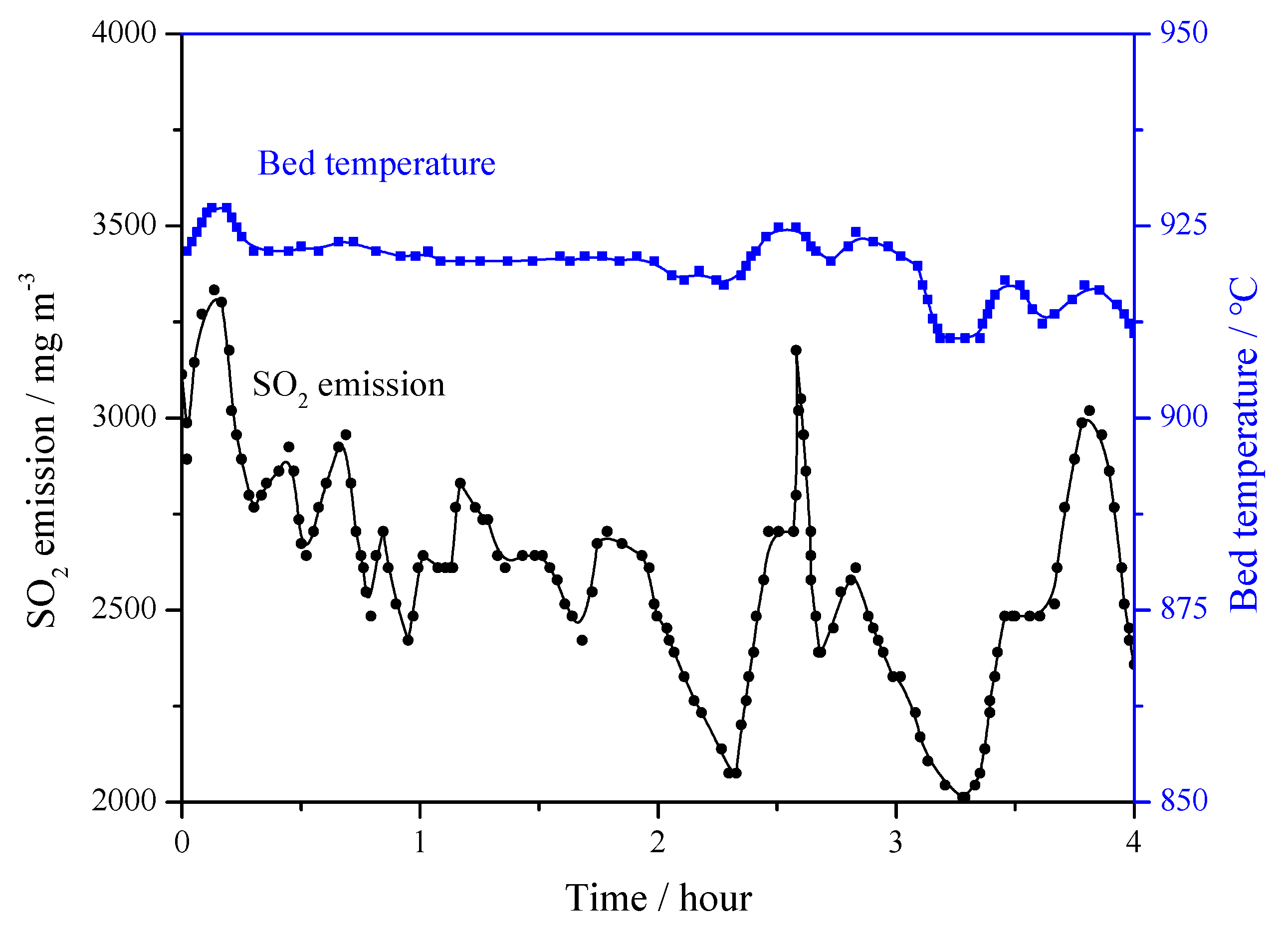
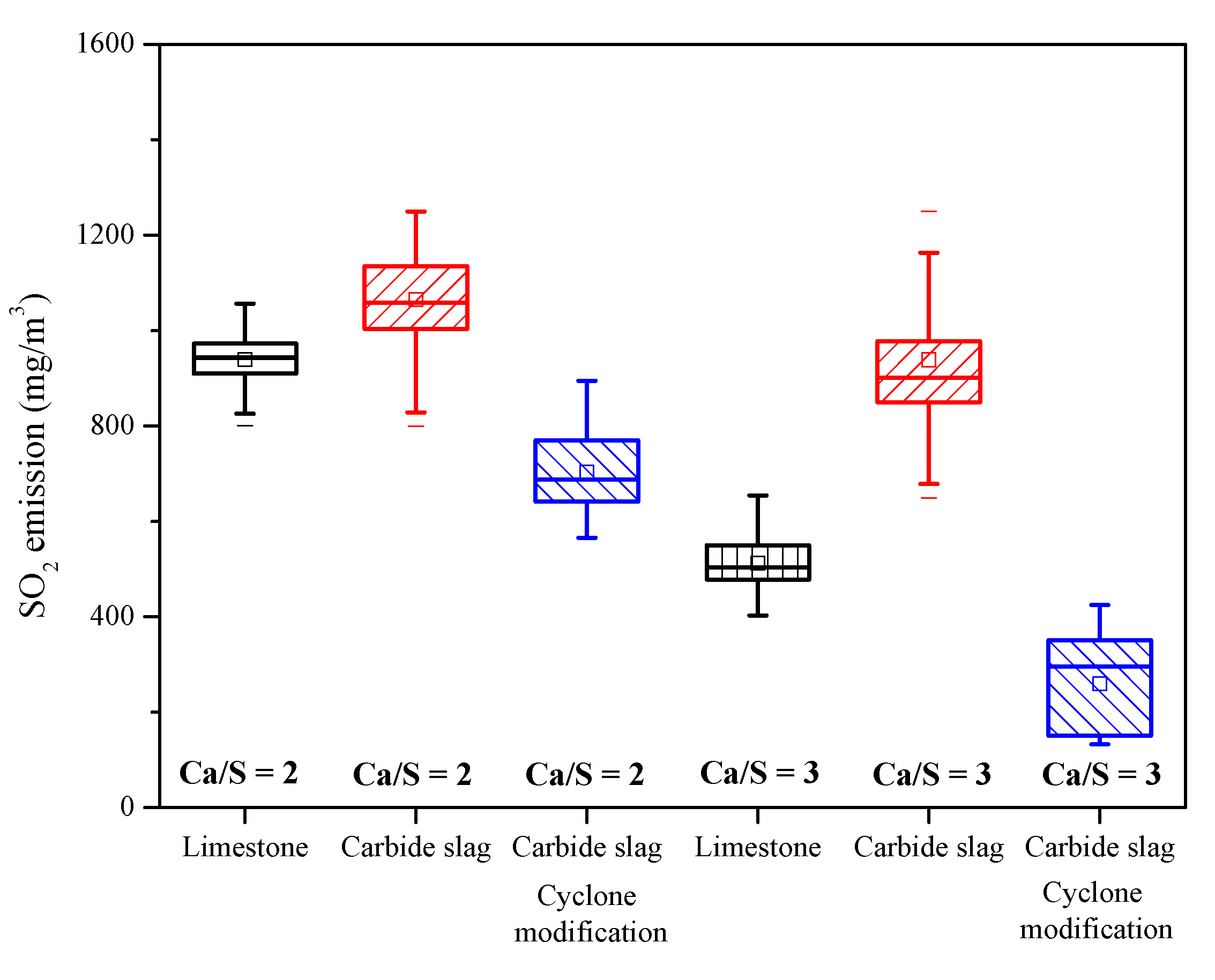
3.3. The 690 t·h−1 CFB Boiler Field Tests
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Aar | ash content in coal as received basis (%) |
| Bcoal | coal consumption (t·h−1) |
| Bcs | carbide slag consumption (t·h−1) |
| Blim | limestone consumption (t·h−1) |
| Car | carbon content in coal as received basis (%) |
| FCar | fixed carbon content in coal as received basis (%) |
| Har | hydrogen content in coal as received basis (%) |
| Mar | moisture content in coal as received basis (%) |
| mcs | Ca/S mole ratio of carbide slag (−) |
| mlim | Ca/S mole ratio of limestone (−) |
| Nar | nitrogen content in coal as received basis (%) |
| Oar | oxygen content in coal as received basis (%) |
| Sar | sulfur content in coal as received basis (%) |
| Var | volatile content in coal as received basis (%) |
| ηCaCO3 | CaCO3 content in limestone (%) |
| ηCa(OH)2 | Ca(OH)2 content in carbide slag (%) |
References
- Yue, G.; Cai, R.; Lu, J.; Zhang, H. From a CFB reactor to a CFB boiler—The review of R & D progress of CFB coal combustion technology in China. Powder Technol. 2017, 316, 18–28. [Google Scholar]
- Rydén, M.; Hanning, M.; Corcoran, A.; Lind, F. Oxygen Carrier Aided Combustion (OCAC) of Wood Chips in a Semi–Commercial Circulating Fluidized Bed Boiler Using Manganese Ore as Bed Material. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, W.; Mirek, P. Circulating fluidized bed combustion. In Fluidized Bed Technologies for Near-Zero Emission Combustion and Gasification; Scala, F., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Energy: Cambridge, UK, 2013; pp. 701–764. [Google Scholar]
- Basu, P. Combustion and Gasification in Fluidized Beds; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ahlstrom Pyropower. Activation/Reuse of Fluidized Bed Waste: Phase I—Literature Review; Report to the Canadian Electrical Association; Centre for Energy Advancement through Technological Innovation (CEATI) Project 9131 G 891; CEATI: Montreal, QC, Canada, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich, S. A coal-fired fluidized bed boiler. In Proceedings of the Institute of Fuel Symposium, 1975; pp. C4-1, C4-10. [Google Scholar]
- Fields, R.B.; Burdett, N.A.; Davidson, J.F. Reaction of sulfur dioxide with limestone particles: The influence of sulfur-trioxide. Trans. Inst. Chem. Eng. 1979, 57, 276–280. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Duan, Y.; Yao, T.; Liu, M.; Lu, J.; Tan, H.; Wang, X.; Wu, L. Study on the mercury emission and transformation in an ultra—Low emission coal—Fired power plant. Fuel 2017, 199, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.; Ning, C.; Fu, X. Development of sulfur fixation and ombustion-supporting agent for llose coal using red mud and black liquor of papermaking. Environ. Eng. 2004, 22, 57–59. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Sun, R.; Zhao, J.; Han, K.; Lu, C. Sulfation behavior of white mud from paper manufacture as SO2 sorbent at fluidized bed combustion temperatures. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2012, 107, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wu, X.; Cheng, J.; Zhou, J.; CaO, X.; Cen, K. The desulfurization characteristics of industrial wastes during coal combustion. ACTA Sci. Circumstantiae 2000, 20, 790–793. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.; Wu, Z. Comparative study on desulfurization performance of several alkaline waste slags. Environ. Eng. 2002, 20, 42–44. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.; Zhou, J.; Liu, J.; Cao, X.; Cen, K. Physicochemical Characterizations and Desulfurization Properties in Coal Combustion of Three Calcium and Sodium Industrial Wastes. Energy Fuels 2009, 23, 2506–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Li, Y.J.; Liu, C.T.; Wang, W.J. HCl absorption by CaO/Ca3Al2O6 sorbent from CO2 capture cycles using calcium looping. Fuel Process Technol. 2015, 138, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, P.; Wang, S.; Nabi, M.; Wang, H. Thermo—Carbide slag pretreatment of energy plants for enhancing enzymatic hydrolysis. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 120, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Lu, C.; Wang, Z. Simultaneous CO2/SO2 adsorption performance of carbide slag in adsorption/desorption cycles. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 94, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyngfelt, A.; Leckner, B. Sulphur capture in circulating fluidized—Bed boilers: Can the efficiency be predicted. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1999, 54, 5573–5584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, Q.; Cao, L.; Geng, J. Pore, mechanics and acoustic emission characteristics of limestone under the influence of temperature. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 123, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Anthony, E.C. The kinetics and pore structure of sorbents during the simultaneous calcination/sulfation of limestone in CFB. Fuel 2017, 208, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, G.H.; Chen, S.L.; Kramlich, J.C. Role of porosity loss in limiting SO2 capture by calcium based sorbents. AIChE J. 1989, 35, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgwardt, R.H.; Bruce, K.R.; Blake, J. An investigation of product—Layer diffusivity for calcium oxide sulfation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1987, 26, 1993–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunauer, S.; Emmett, P.; Teller, E. Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1938, 60, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masthan, S.; Rao, K.; Prasad, P.; Rao, P. Derivation of the expanded form of the BJH equation and its application to the pore structure analysis of mesoporous adsorbents. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 1992, 9, 212–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, P. Circulating Fluidized Bed Boilers—Design, Operation and Maintenance; Springer International Publishing: Basel, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Las, O.M.; Diego, L.F.; GARCÍA-LABIANO, F.; Rufas, A.; Abad, A.; Gayán, P.; Gayán, J. Modeling of limestone sulfation for typical oxy—Fuel fluidized bed combustion conditions. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 2266–2274. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, T.; Lee, Y.Y. Improving Limestone Utilization Circulation Fluidized Bed Combustors through the Reactivation and Recycle of Partially Utilized Limestone in the Ash; ASME: New York, NY, USA, 1995; pp. 831–840. [Google Scholar]
- Borgwardt, R.H. Calcination kinetics and surface area of dispersed limestone particles. AIChE J. 1985, 31, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silcox, G.D.; Kramlich, J.C.; Pershing, D.W. A mathematical model for the flash calcination of dispersed calcium carbonate and calcium hydroxide particles. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1989, 28, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laursen, K.; Grace, J.; Lim, C. Enhancement of the Sulfur Capture Capacity of Limestones by the Addition of Na2CO3 and NaCl. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 4384–4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laursen, K.; Ker, A.; Grace, J.; Lim, C.J. Characterization of the enhancement effect of Na2CO3 on the sulfur capture capacity of limestones. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 3709–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Martínez, J.; Bueno-López, A.; García-García, A.; Linares-Solano, A. SO2 retention at low temperatures by Ca(OH)2—Derived CaO: A model for CaO regeneration. Fuel 2003, 81, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, E.J.; Granatstein, D.L. Sulfation phenomena in fluidized bed combustion systems. Progress Energy Combust. Sci. 2001, 27, 215–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasek, J.; Kazalski, K. Sulfur Self—Retention during Cocombustion of Fossil Fuels with Biomass. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 2780–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siagi, Z.; Mbarawa, M.; Mohamed, A.; Lee, K.T.; Dahlan, I. The effects of limestone type on the sulphur capture of slaked lime. Fuel 2007, 86, 2660–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saastamoinen, J.J. Particle—Size optimization for SO2 capture by limestone in a circulating fluidized bed. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 7308–7316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scala, F.; Salatino, P. Limestone fragmentation and attrition during fluidized bed oxyfiring. Fuel 2010, 89, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scala, F.; Salatino, P. Attrition of limestones by impact loading in fluidized beds: The influence of reaction conditions. Fuel Process. Technol. 2010, 91, 1022–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Ultimate Analysis | Proximate Analysis | Lower Heating Value (kJ kg−1) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Car | Har | Oar | Nar | Sar | Aar | Var | FCar | Mar | |
| 49.05 | 3.02 | 9.35 | 0.44 | 1.19 | 21.35 | 25.90 | 37.15 | 15.60 | 18170 |
| Item | Unit | Limestone | Carbide Slag |
|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | wt, % | 3.72 | 8.77 |
| Al2O3 | wt, % | 0.61 | 3.08 |
| Fe2O3 | wt, % | 0.31 | 1.20 |
| CaO | wt, % | 49.92 | 57.28 |
| MgO | wt, % | 2.75 | 0.65 |
| Na2O | wt, % | 0.08 | 0.07 |
| K2O | wt, % | 0.11 | 0.52 |
| TiO2 | wt, % | <0.01 | 0.16 |
| SO3 | wt, % | <0.01 | 0.49 |
| MnO2 | wt, % | <0.001 | / |
| P2O5 | wt, % | / | 0.10 |
| True density | kg m−3 | 2860 | 2720 |
| Bulk density | kg m−3 | 1380 | 550 |
| No. | Bed Temperature/°C | Desulfurizer | Ca/S | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test 1-1 | 915 ± 10 | / | / | without desulfurizer |
| Test 2-1 | Limestone | 2 | cyclone original design | |
| Test 2-2 | 3 | cyclone original design | ||
| Test 3-1 | Carbide slag | 2 | cyclone original design | |
| Test 3-2 | 3 | cyclone original design | ||
| Test 3-3 | 2 | cyclone modification | ||
| Test 3-4 | 3 | cyclone modification |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Z.; Long, J.; Deng, L.; Che, D. Feasibility Study of Using Carbide Slag as In-Bed Desulfurizer in Circulating Fluidized Bed Boiler. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4517. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9214517
Huang Z, Long J, Deng L, Che D. Feasibility Study of Using Carbide Slag as In-Bed Desulfurizer in Circulating Fluidized Bed Boiler. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(21):4517. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9214517
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Zhong, Jimiao Long, Lei Deng, and Defu Che. 2019. "Feasibility Study of Using Carbide Slag as In-Bed Desulfurizer in Circulating Fluidized Bed Boiler" Applied Sciences 9, no. 21: 4517. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9214517
APA StyleHuang, Z., Long, J., Deng, L., & Che, D. (2019). Feasibility Study of Using Carbide Slag as In-Bed Desulfurizer in Circulating Fluidized Bed Boiler. Applied Sciences, 9(21), 4517. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9214517






