A Blind Nonlinearity Compensator Using DBSCAN Clustering for Coherent Optical Transmission Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
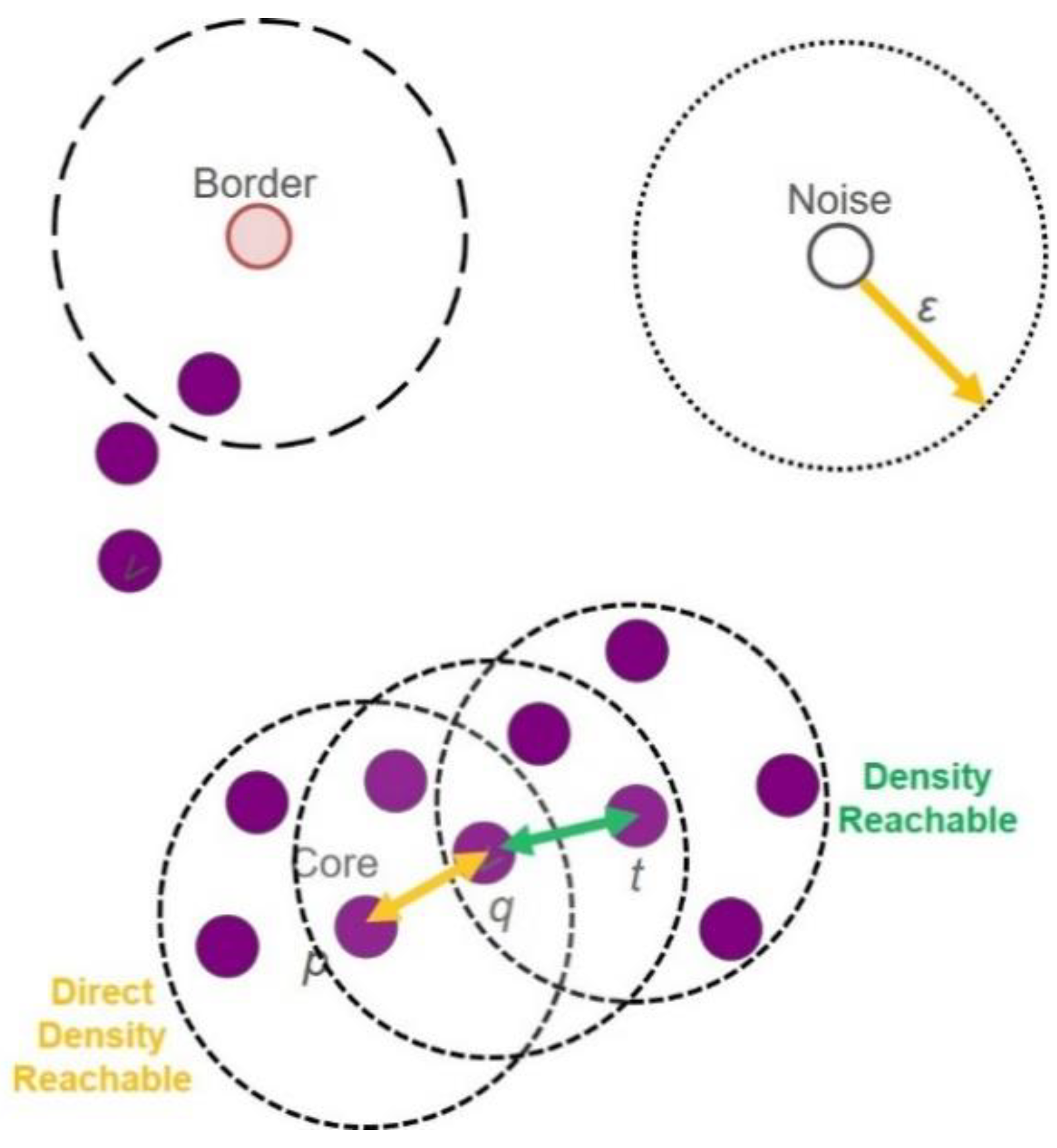
2. Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise (DBSCAN) Description
- Epsilon neighbourhood (Nε): A set of all constellation points within a distance ε.
- Core point: A constellation point whose Nε contains at least a “minimum point” (including itself).
- Direct Density Reachable: A point q is directly density reachable from a point p, if p is a core point and q ∈ Nε.
- Density Reachable: Two constellation points (p, t) are density reachable if there is a chain of “direct density reachable” points that link these two points (p, q, t).
- Border Point: A constellation point that is “direct density reachable” but not a core point.
- Noise: Constellation points not belonging to any point’s Nε.
- Randomly select a point p (referred in Figure 1) in the constellation map.
- Retrieve all constellation points directly density reachable from p that satisfy the condition of the radius ε limits.
- If the constellation point p is a core point, a cluster is formed. Search recursively and find all of its density-connected points and assign them to the same cluster as p.
- If p is not a core point, the DBSCAN algorithm “scans” for the rest of the unvisited constellation points.
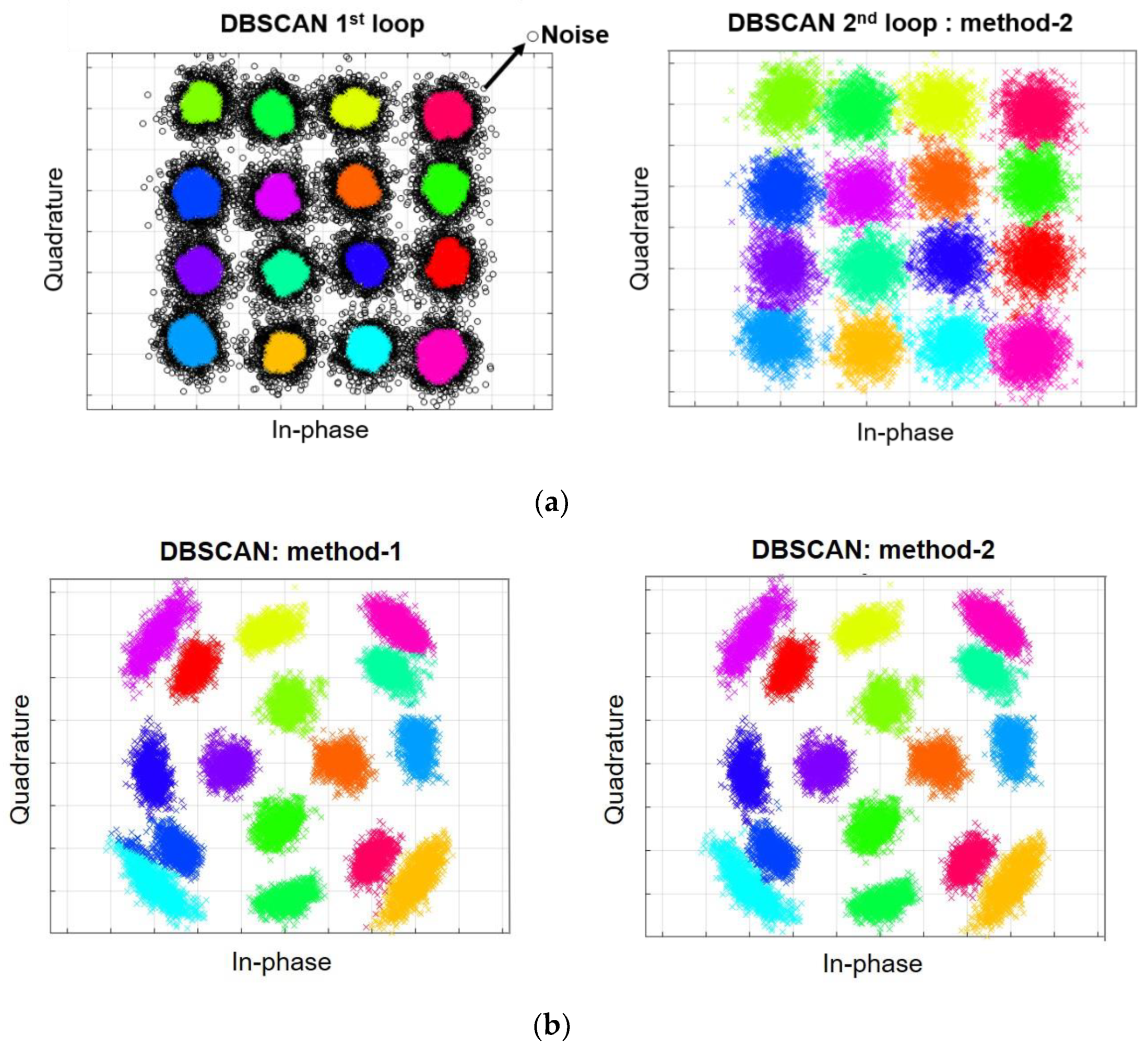
- DBSCAN 1st loop: Points that are un-clustered are labelled as zero points (“noisy points”) where linear equalisation is performed only on these points, and then the conventional DBSCAN algorithm stops.
- DBSCAN 2nd loop (extra novel step):
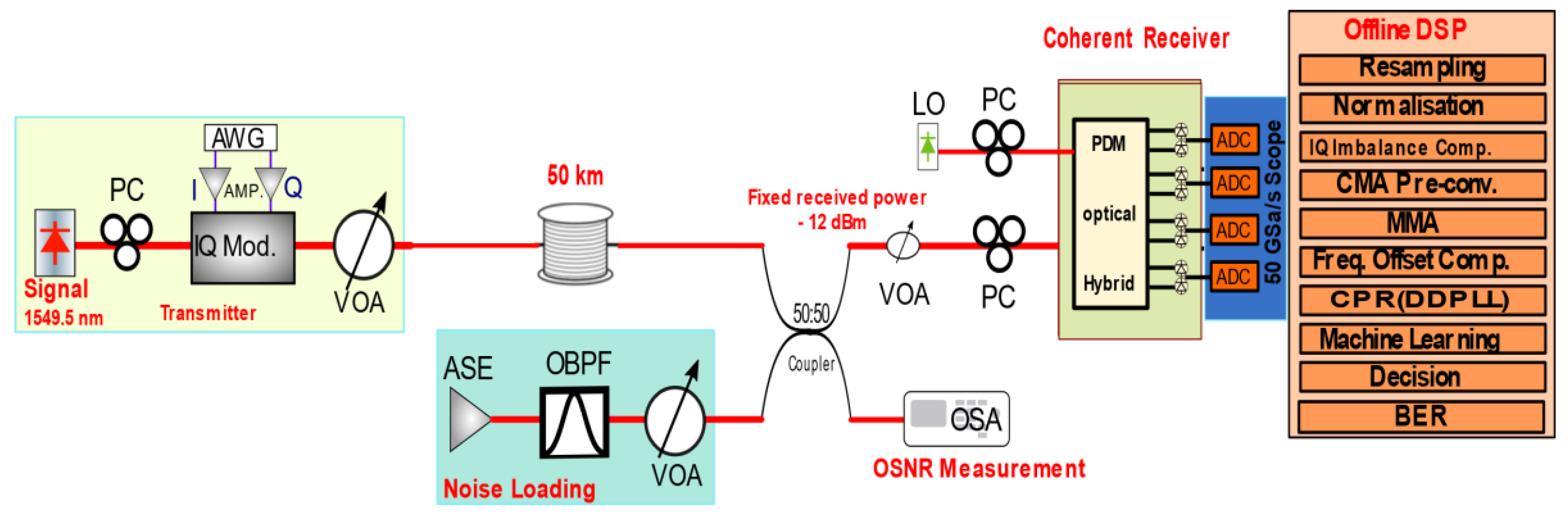
3. Experimental Setup
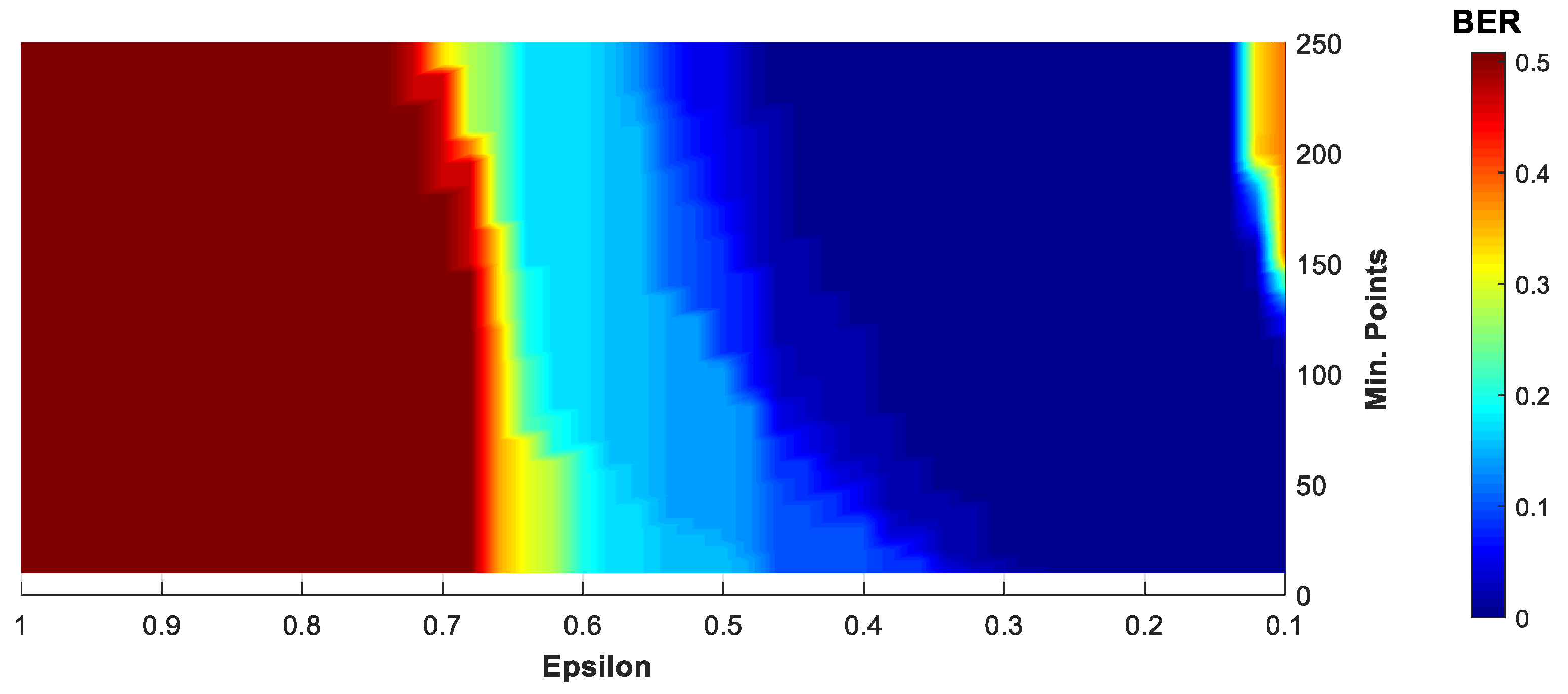
4. Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chagnon, M. Optical Communications for Short Reach. J. Lightwave Technol. 2019, 37, 1779–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.; Yamamoto, S.; Taga, H.; Edagawa, N.; Yoshida, Y.; Wakabayashi, H. Long-haul coherent optical fiber communication systems using optical amplifiers. J. Lightwave Technol. 1991, 9, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, A.D.; Zhao, J.; Cotter, D. Approaching the nonlinear Shannon-limit. J. Lightwave Technol. 2010, 28, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khateeb, M.A.Z.; McCarthy, M.E.; Sánchez, C.; Ellis, A.D. Nonlinearity compensation using optical phase conjugation deployed in discretely amplified transmission systems. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 23945–23959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temprana, E.; Myslivets, E.; Kuo, B.P.; Liu, L.; Ataie, V.; Alic, N.; Radic, S. Overcoming Kerr-induced capacity limit in optical fiber transmission. Science 2015, 348, 1445–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, R.; Galdino, L.; Sato, M.; Xu, T.; Shi, K.; Kilmurray, S.; Savory, S.J.; Thomsen, B.C.; Killey, R.I.; Bayvel, P. Linear and nonlinear impairment mitigation in a Nyquist spaced DP-16QAM WDM transmission system with full-field DBP. In Proceedings of the ECOC, Cannes, France, 21–25 September 2014; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014; p. 5.10. [Google Scholar]
- Lowery, A.J. Fiber nonlinearity pre-and post-compensation for long-haul optical links using OFDM. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 12965–12970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacoumidis, E.; Aldaya, I.; Jarajreh, M.A.; Tsokanos, A.; Le, S.T.; Farjady, F.; Jaouën, Y.; Ellis, A.D.; Doran, N.J. Volterra-based reconfigurable nonlinear equalizer for dual-polarization multiband coherent OFDM. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2014, 26, 1383–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X. Phase-conjugated twin waves for communication beyond the Kerr nonlinearity limit. Nat. Photonics 2013, 7, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, S.T.; Aref, V.; Buelow, H. Nonlinear signal multiplexing for communication beyond the Kerr nonlinearity limit. Nat. Photonics 2017, 11, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacoumidis, E. Blind Nonlinearity Equalization by Machine Learning based Clustering for Single-and Multi-Channel Coherent Optical OFDM. IEEE J. Lightwave Technol. 2018, 36, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, W.; Gao, M.; Shen, G. K-means-clustering-based fiber nonlinearity equalization techniques for 64-QAM coherent optical communication system. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 27570–27580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacoumidis, E. Affinity propagation clustering for blind nonlinearity compensation in coherent optical OFDM. In Proceedings of the CLEO, San Jose, CA, USA, 13–18 May 2018; OSA: Rochester, NY, USA, 2018; p. STh1C.5. [Google Scholar]
- Zibar, D.; Piels, M.; Jones, R.; Schäeffer, C.G. Machine Learning Techniques in Optical Communication. IEEE J. Lightwave Technol. 2016, 34, 1442–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ester, M.; Kriegel, H.P.; Sander, J.; Xu, X. A Density-Based Algorithm for Discovering Clusters in Large Spatial Databases with Noise. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Portland, OR, USA, 2–4 August 1996; pp. 226–231. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J. Real-Time Superpixel Segmentation by DBSCAN Clustering Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 25, 5933–5942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boada, R.; Borkowski, R.; Monroy, I.T. Clustering algorithms for Stokes space modulation format recognition. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 15521–15531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X. An I-Q-Time 3-dimensional post-equalization algorithm based on DBSCAN of machine learning in CAP VLC system. Opt. Commun. 2019, 430, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yu, J.; Chien, H.C. Advanced linear and nonlinear compensations for 16QAM SC-400G unrepeatered transmission system. Opt. Commun. 2018, 409, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Mhatli, S.; Giacoumidis, E.; Van Compernolle, L.; Wuilpart, M.; Mégret, P. Fiber nonlinearity equalizer based on support vector classification for coherent optical OFDM. Photonics J. 2016, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacoumidis, E.; Mhatli, S.; Nguyen, T.; Le, S.T.; Aldaya, I.; McCarthy, M.E.; Ellis, A.D.; Eggleton, B.J. Comparison of DSP-based nonlinear equalizers for intra-channel nonlinearity compensation in coherent optical OFDM. Opt. Lett. 2016, 41, 2509–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacoumidis, E.; Mhatli, S.; Stephens, M.F.; Tsokanos, A.; Wei, J.; McCarthy, M.E.; Doran, N.J.; Ellis, A.D. Reduction of Nonlinear Inter-Subcarrier Intermixing in Coherent Optical OFDM by a Fast Newton-based Support Vector Machine Nonlinear Equalizer. J. Lightwave Technol. 2017, 35, 2391–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacoumidis, E.; Mhatli, S.; Le, S.T.; Aldaya, I.; McCarthy, M.E.; Ellis, A.D.; Eggleton, B.J. Nonlinear Blind Equalization for 16-QAM Coherent Optical OFDM using Support Vector Machines. In Proceedings of the ECOC, Düsseldorf, Germany, 18–22 September 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; p. Th.2.P2. [Google Scholar]
- Mhatli, S.; Mhatli, S.; Mrabet, H.; Dayoub, I.; Giacoumidis, E. A novel SVM robust model Based Electrical Equalizer for CO-OFDM Systems. IET Commun. 2017, 11, 1091–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacoumidis, E.; Tsokanos, A.; Ghanbarisabagh, M.; Mhatli, S.; Barry, L.P. Unsupervised Support Vector Machines for Nonlinear Blind Equalization in CO-OFDM. Photonics Technol. Lett. 2018, 30, 1091–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giacoumidis, E.; Lin, Y.; Jarajreh, M.; O’Duill, S.; McGuinness, K.; Whelan, P.F.; Barry, L.P. A Blind Nonlinearity Compensator Using DBSCAN Clustering for Coherent Optical Transmission Systems. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4398. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9204398
Giacoumidis E, Lin Y, Jarajreh M, O’Duill S, McGuinness K, Whelan PF, Barry LP. A Blind Nonlinearity Compensator Using DBSCAN Clustering for Coherent Optical Transmission Systems. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(20):4398. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9204398
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiacoumidis, Elias, Yi Lin, Mutsam Jarajreh, Sean O’Duill, Kevin McGuinness, Paul F. Whelan, and Liam P. Barry. 2019. "A Blind Nonlinearity Compensator Using DBSCAN Clustering for Coherent Optical Transmission Systems" Applied Sciences 9, no. 20: 4398. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9204398
APA StyleGiacoumidis, E., Lin, Y., Jarajreh, M., O’Duill, S., McGuinness, K., Whelan, P. F., & Barry, L. P. (2019). A Blind Nonlinearity Compensator Using DBSCAN Clustering for Coherent Optical Transmission Systems. Applied Sciences, 9(20), 4398. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9204398





