Influence of Gemini Surfactants on Biochemical Profile and Ultrastructure of Aspergillus brasiliensis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microorganisms
2.2. Antimicrobial Agents
2.3. Enzymatic Profiles of Mycelia after Surfactant Treatments
2.4. Preparation of Extracellular Protein Extracts
2.5. SDS-PAGE Analysis of Extracellular Proteins
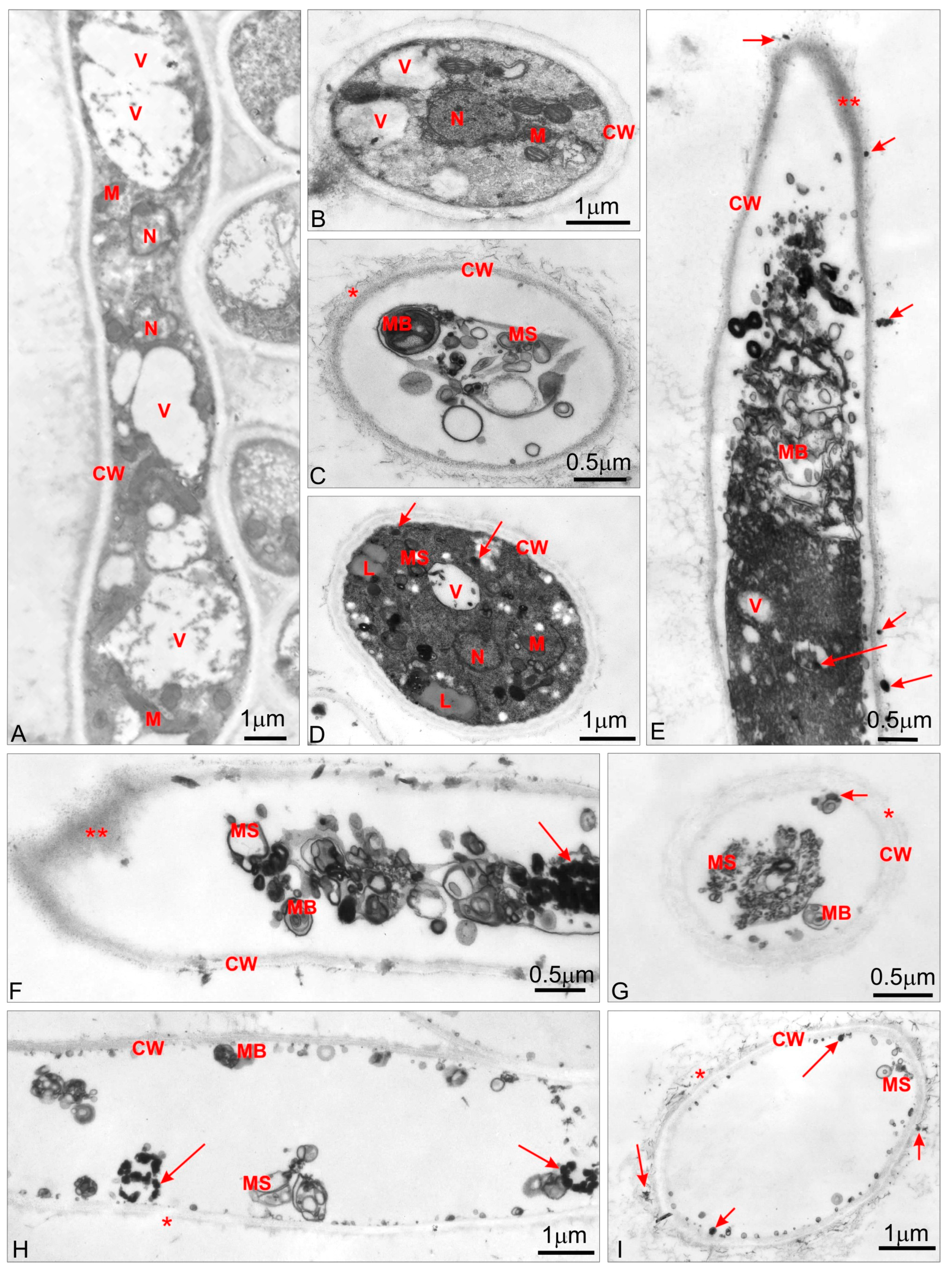
2.6. TEM Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Influence of Gemini Surfactants on Enzymatic Profile of Mycelia
3.2. Extracellular Protein Profiles after Treatment with Gemini Surfactants
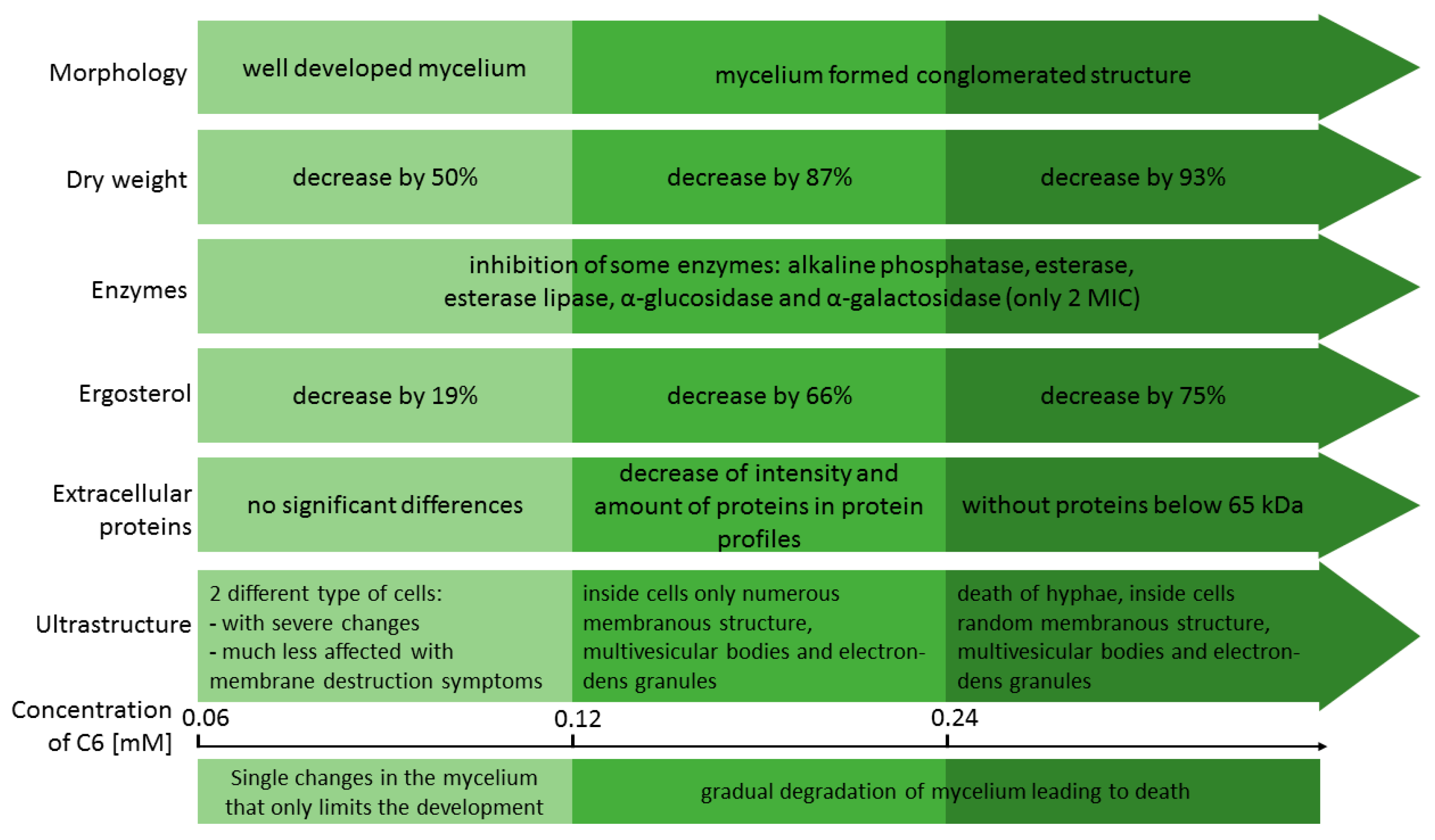
3.3. TEM Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Filtenborg, O.; Frisved, J.C.; Thrane, U. Moulds in food spoilage. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1996, 33, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutarowska, B. Moulds in biodeterioration of technical materials. Foilia Biologica et Oecologica 2014, 10, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlita, A. Microbial biodeterioration of leather and its control: A review. Int. Biodeter. Biodegr. 2004, 53, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.-R.; Shi, Q.-S.; Ouyang, Y.-S.; Chen, Y.-B.; Duan, S.-S. Antifungal effects of citronella oil against Aspergillus niger ATCC 16404. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 7483–7492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, C.; Chowdhary, A. Molecular bases of antifungal resistance in filamentous fungi. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2017, 50, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrashev, R.; Stoitsova, S.; Krumova, E.; Pashova, S.; Paunova-Krasteva, T.; Vassilev, S.; Dolashka-Angelova, P. Temperatire- stress tolerance of the fungal strain Aspergillus niger 26: Physiological and ultrastructural changes. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 30, 1661–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakai, S.; Arazoe, T.; Ogino, C.; Kondo, A. Future insights in fungal metabolic engineering. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 245, 1314–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, E.; Dunn-Coleman, N.; Frisvad, J.C.; van Dijick, P.W.M. On the safety of Aspergillus niger—A review. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2002, 59, 426–435. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, J.G.; Rowan, N.J.; MacGregor, S.J.; Fouracre, R.A.; Farish, O. Inactivation of food-borne enteropathogenic bacteria and spoilage fungi using pulsed-light. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2000, 28, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutarowska, B. Metabolic activity of moulds as a factor of building materials biodegradation. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2010, 59, 119–124. [Google Scholar]
- Nemeth-Konda, L.; Füleky, G.; Morovjana, G.; Csokana, P. Sorption behaviour of acetochlor, atrazine, carbendazim, diazinon, imidacloprid and isoproturon on Hungarian agricultural soil. Chemosphere 2002, 48, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollmann, U.E.; Vollertsen, J.; Carmeliet, J.; Bester, K. Dynamics of biocide emissions from buildings in a suburban stormwater catchment- concentrations, mass loads and emisiion processes. Water Res. 2014, 56, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazu, T.K.; Bricker, B.A.; Flores-Rozas, H.; Ablordeppey, S.Y. The mechanistic targets of antifungal agents: An overview. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 555–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obłąk, E.; Adamski, R.; Lachowicz, T.M. pH-dependent influence of a quaternary ammonium salt and an aminoester on the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae ultrastructure. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2003, 8, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shirai, A.; Sumitomo, T.; Kurimoto, M.; Maeda, H.; Kourai, H. The mode of the antifungal activity of gemini-pyridinium salt against yeast. Biocontrol Sci. 2009, 14, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koziróg, A.; Brycki, B.; Pielech-Przybylska, K. Impact of cationic and neutral gemini surfactants on conidia and hyphal forms of Aspergillus brasiliensis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papamanoli, E.; Tzanetakis, N.; Litopoulou-Tzanetaki, E.; Kotzekidou, P. Characterization of lactic acid bacteria isolated from a Greek, dry-fermented sausage inrespect of their technological and probiotic properties. Meat Sci. 2003, 65, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkowska, K.; Otlewska, A.; Kunicka-Styczyńska, A.; Krajewska, A. Candida albicans impairments induced by peppermint and clove oils at sub-inhibitory concentrations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during assembly of head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dice, L.R. Measures of the amount of ecologic association between species. Ecology 1945, 26, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, E.S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 1963, 17, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurung, N.; Ray, S.; Bose, S.; Rai, V. Abroader view: Microbial enzymes and their relevance in industries, medicine and beyond. BioMed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 329121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietrzak, K.; Twarużek, M.; Czyżowska, A.; Kosicki, R.; Gutarowska, B. Influence of silver nanoparticles on metabolism and toxicity of moulds. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2015, 62, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, V.C.; Thaker, V.S. Acid phosphatase and invertase activities of Aspergillus niger. Mycosciences 2009, 50, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurnatowski, P.; Wójcik, A.; Błaszkowska, J.; Góralska, K. The hydrolytic enzymes produced by fungi strains isolated from the sand and soil of recreation areas. Ann. Parasitol. 2016, 62, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancianti, F.; Rum, A.; Nardoni, S.; Corazza, M. Extracellular enzymatic activity of Malassezia spp. isolates. Mycopathologia 2000, 149, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabrdalik, M. Harmfulness of mould fungi occurring in the human environment. Prot. Corros. 2008, 1, 28–33. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Weenink, X. Protein Secretion in the Filamentous Fungus Aspergillus niger. Ph.D. Thesis, Universiteit Leiden, Leiden, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Carberry, S.; Neville, C.M.; Kavanagh, K.A.; Doyle, S. Analysis of major intracellular proteins of Aspergillus fumigatus by MALDI mass spectrometry: Identification and characterisation of an elongation factor 1B protein with glutathione transferase activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 341, 1096–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, K.; Kakizono, D.; Yamada, O.; Iefuji, H.; Akita, O.; Iwashita, K. Proteomic analysis of extracellular proteins from Aspergillus oryzae grown under submerged and solid-state culture conditions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 3448–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Sun, J.; Nimtz, M.; Wissing, J.; Zeng, A.-P.; Rinas, U. The intra- and extracellular proteome of Aspergillus niger growing on defined medium with xylose or maltose as carbon substrate. Microb. Cell Fact. 2010, 9, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, Y.; Shang, Y.; Peng, C.; Liu, H.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, J. Interactions between bovine serum albumin and gemini surfactant alkanediyl-α, ω-bis(dimethyldodecyl-ammonium bromide). Biopolymers 2006, 83, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Xu, G.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, H.; Mao, H.; Feng, Y. Interaction between proteins and cationic gemini surfactant. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 708–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obłąk, E.; Gamian, A. The biological activity of quaternary ammonium salts (QASs). Postepy Hig. Med. Dosw. 2010, 64, 201–211. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Razzaghi-Abyaneh, M.; Shams-Ghahfarokhi, M.; Kawachi, M.; Eslamifar, A.; Schmidt, O.J.; Schmidt, A.; Allameh, A.; Yoshinari, T. Ultrastructural evidences of growth inhibitory effects of a novel biocide, Akacid®plus, on an aflatoxigenic Aspergillus parasiticus. Toxicon 2006, 48, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolouee, M.; Alinezhad, S.; Saberi, R.; Eslamifar, A.; Zad, S.J.; Jaimand, K.; Taeb, J.; Razaee, M.-B.; Kawachi, M.; Shams-Ghahfarokhi, M.; et al. Effect of Matricaria chamomilla L. flower essential oil on the growth and ultrastructure of Aspergillus niger van Tieghem. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 139, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, A.D. Similarities and differences in the responses of microorganisms to biocides. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 52, 750–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tortorano, A.M.; Viviani, M.A.; Biraghi, E.; Rigoni, A.L.; Prigitano, A.; Grillot, R. In vitrotesting of fungicidal activity of biocides against Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Med. Microbiol. 2005, 54, 955–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Type of Sample | Biocide Concentration | Symbol of Enzyme in API-ZYM Test | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 16 | 18 | ||
| K | 0 | ||||||||
| C5 | ½ MIC | ||||||||
| MIC | |||||||||
| 2 MIC | |||||||||
| C6 | ½ MIC | ||||||||
| MIC | |||||||||
| 2 MIC | |||||||||
| A5 | ½ MIC | ||||||||
| MIC | |||||||||
| 2 MIC | |||||||||
| A6 | ½ MIC | ||||||||
| MIC | |||||||||
| 2 MIC | |||||||||
| Type of Sample | Biocide Concentration | Dice Index of Similarity (%) |
|---|---|---|
| C5 | ½ MIC | 92.3 |
| MIC | 62.5 | |
| 2 MIC | 54.5 | |
| C6 | ½ MIC | 92.3 |
| MIC | 66.7 | |
| 2 MIC | 54.5 | |
| A5 | MIC | 72.7 |
| A6 | MIC | 72.7 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koziróg, A.; Otlewska, A.; Gapińska, M.; Michlewska, S. Influence of Gemini Surfactants on Biochemical Profile and Ultrastructure of Aspergillus brasiliensis. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9020245
Koziróg A, Otlewska A, Gapińska M, Michlewska S. Influence of Gemini Surfactants on Biochemical Profile and Ultrastructure of Aspergillus brasiliensis. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(2):245. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9020245
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoziróg, Anna, Anna Otlewska, Magdalena Gapińska, and Sylwia Michlewska. 2019. "Influence of Gemini Surfactants on Biochemical Profile and Ultrastructure of Aspergillus brasiliensis" Applied Sciences 9, no. 2: 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9020245
APA StyleKoziróg, A., Otlewska, A., Gapińska, M., & Michlewska, S. (2019). Influence of Gemini Surfactants on Biochemical Profile and Ultrastructure of Aspergillus brasiliensis. Applied Sciences, 9(2), 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9020245







