Green Synthesis of a Cu/SiO2 Catalyst for Efficient H2-SCR of NO
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Characterization Techniques
2.3. Synthesis of Copper–Silica Catalysts
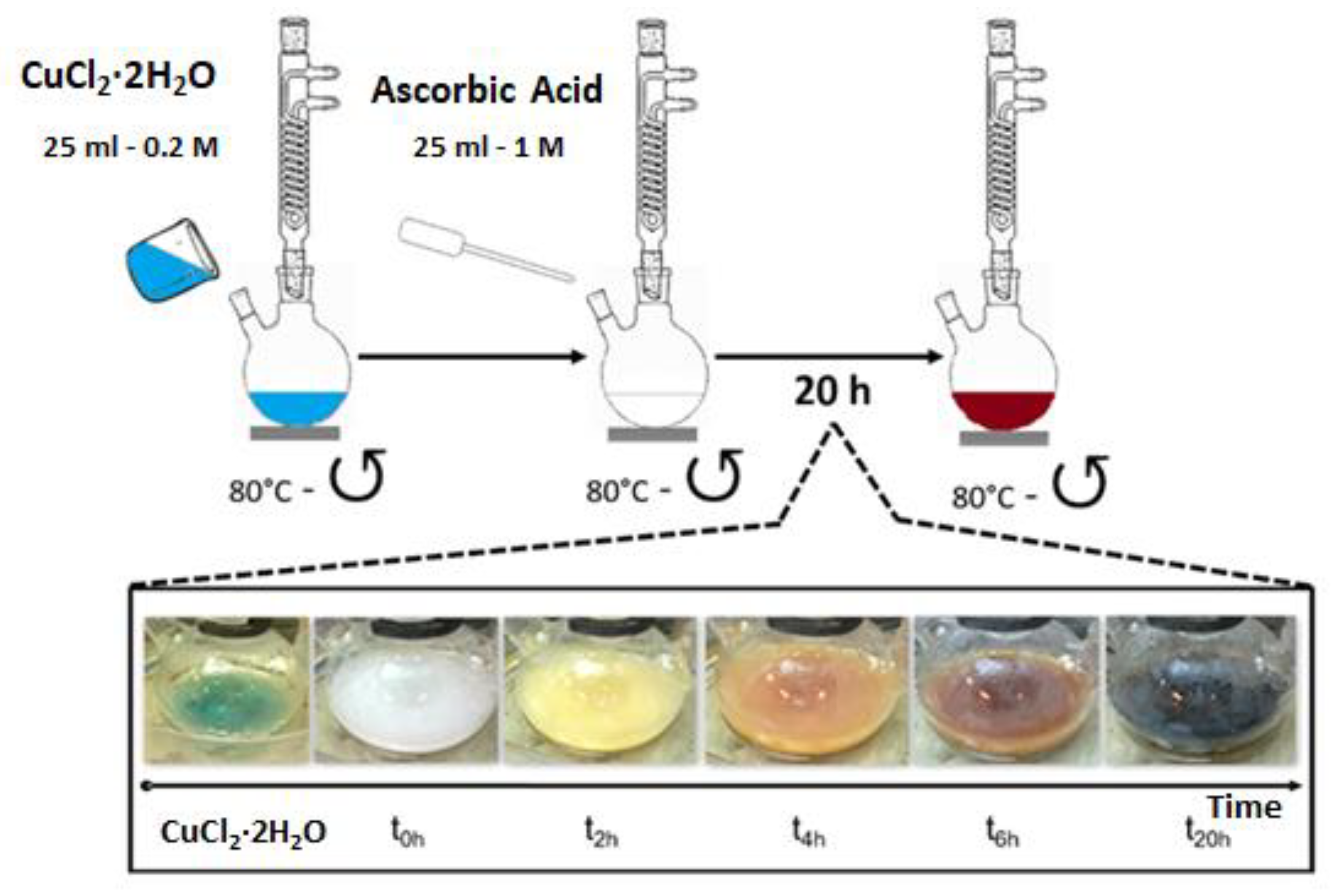
2.3.1. Synthesis of Copper Nanoparticles (CuNPs)
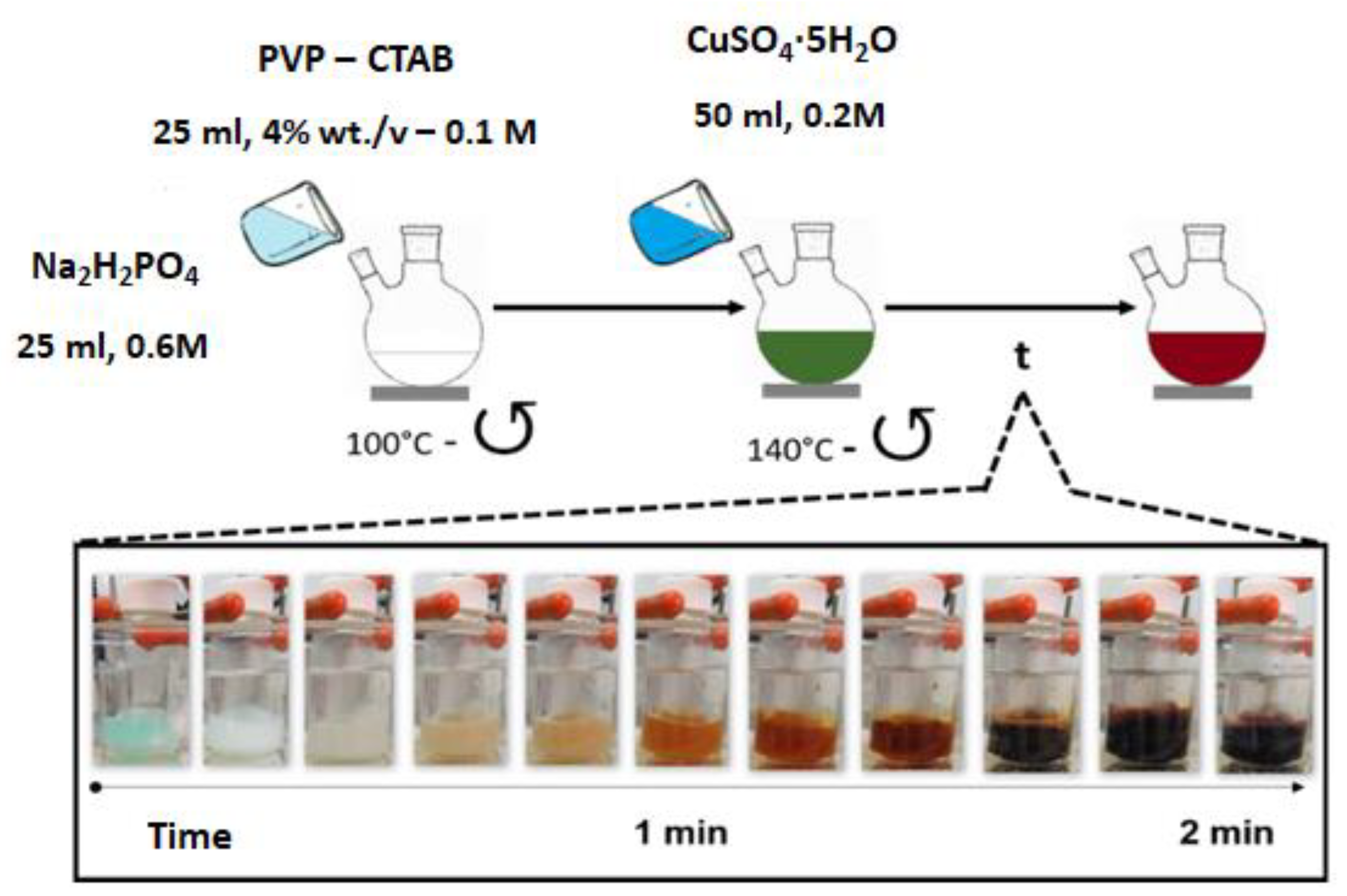
2.3.2. Preparation of the Cu–SiO2 Catalysts
2.4. Catalytic Reduction of NO with H2
3. Results and Discussion
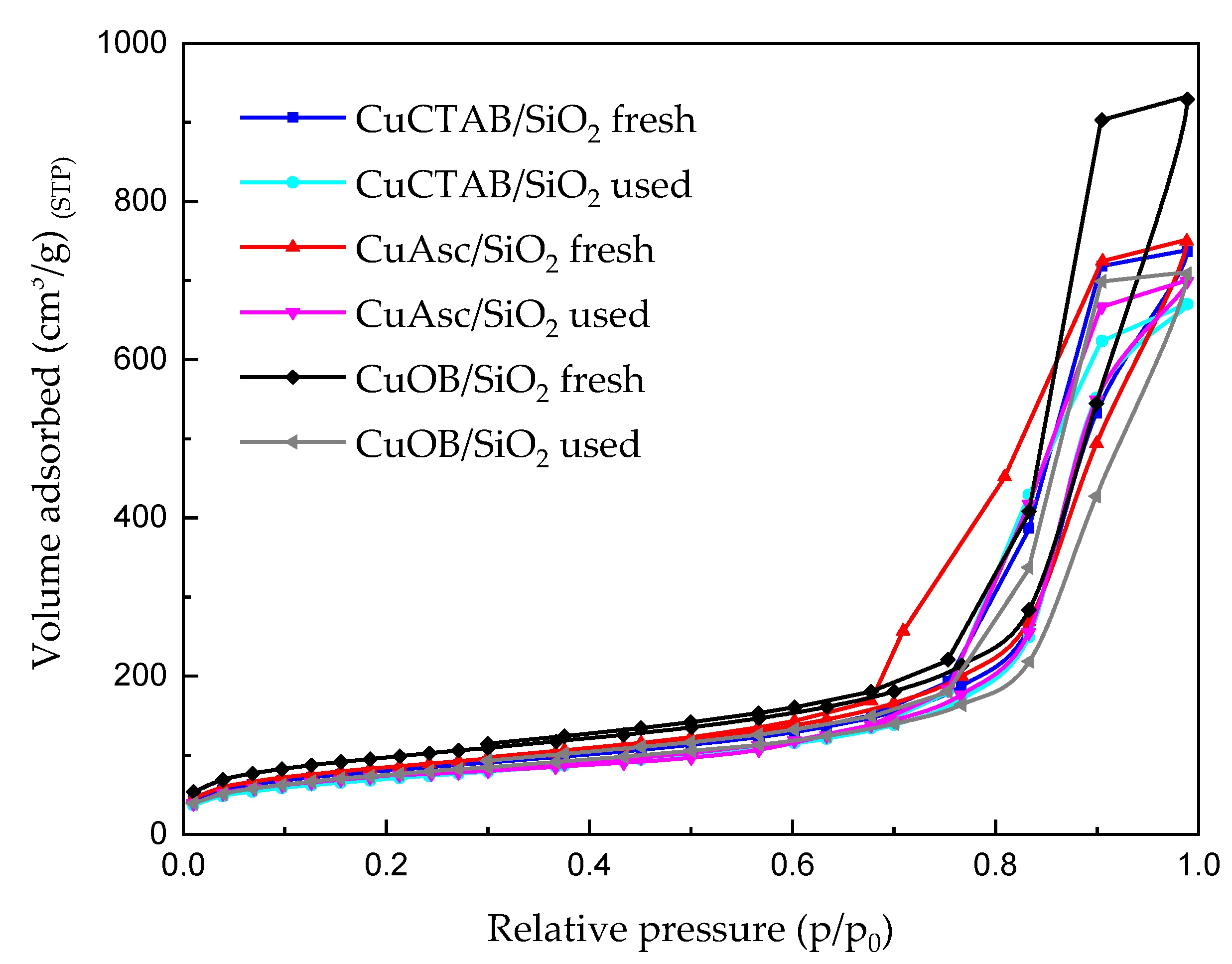
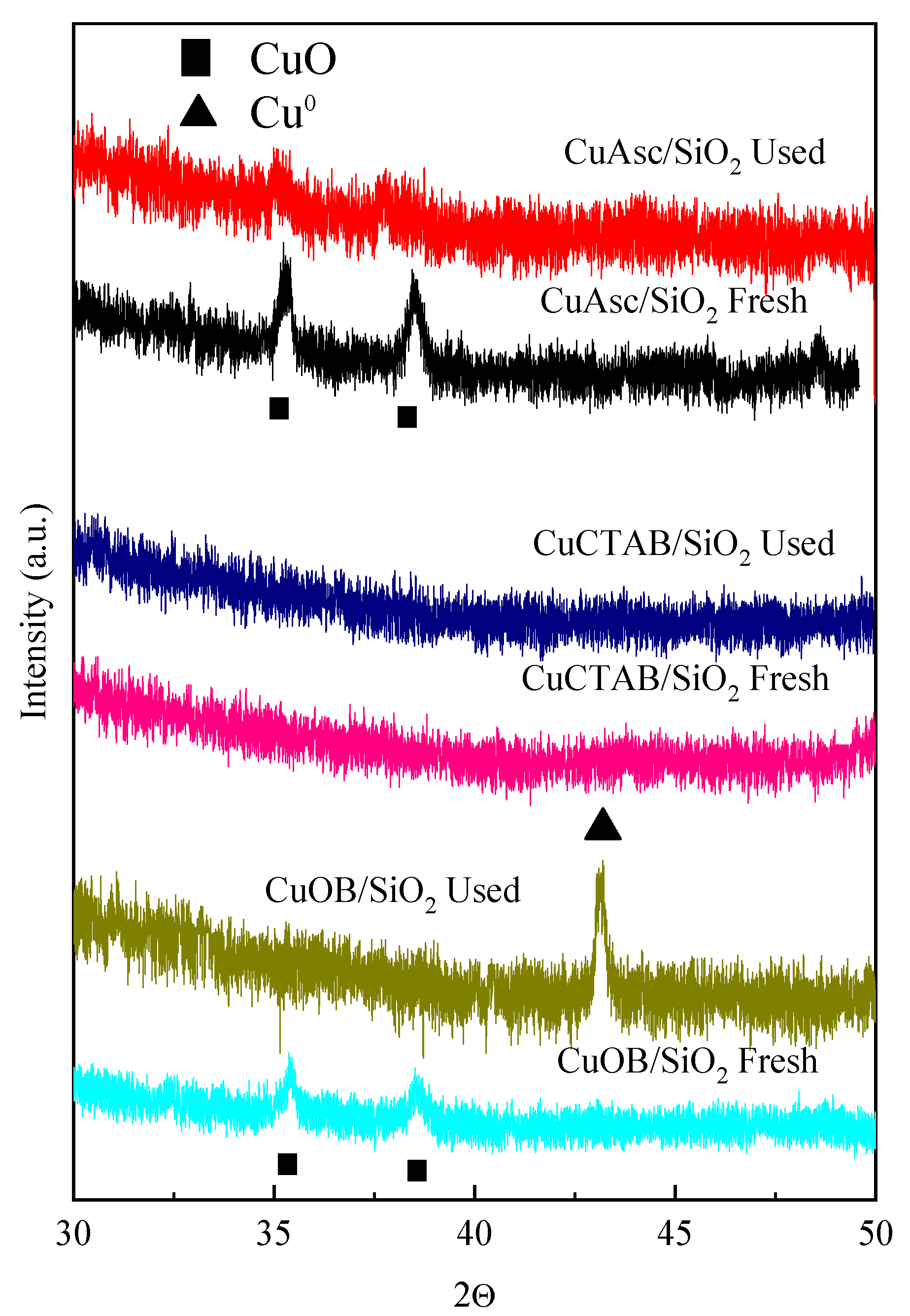
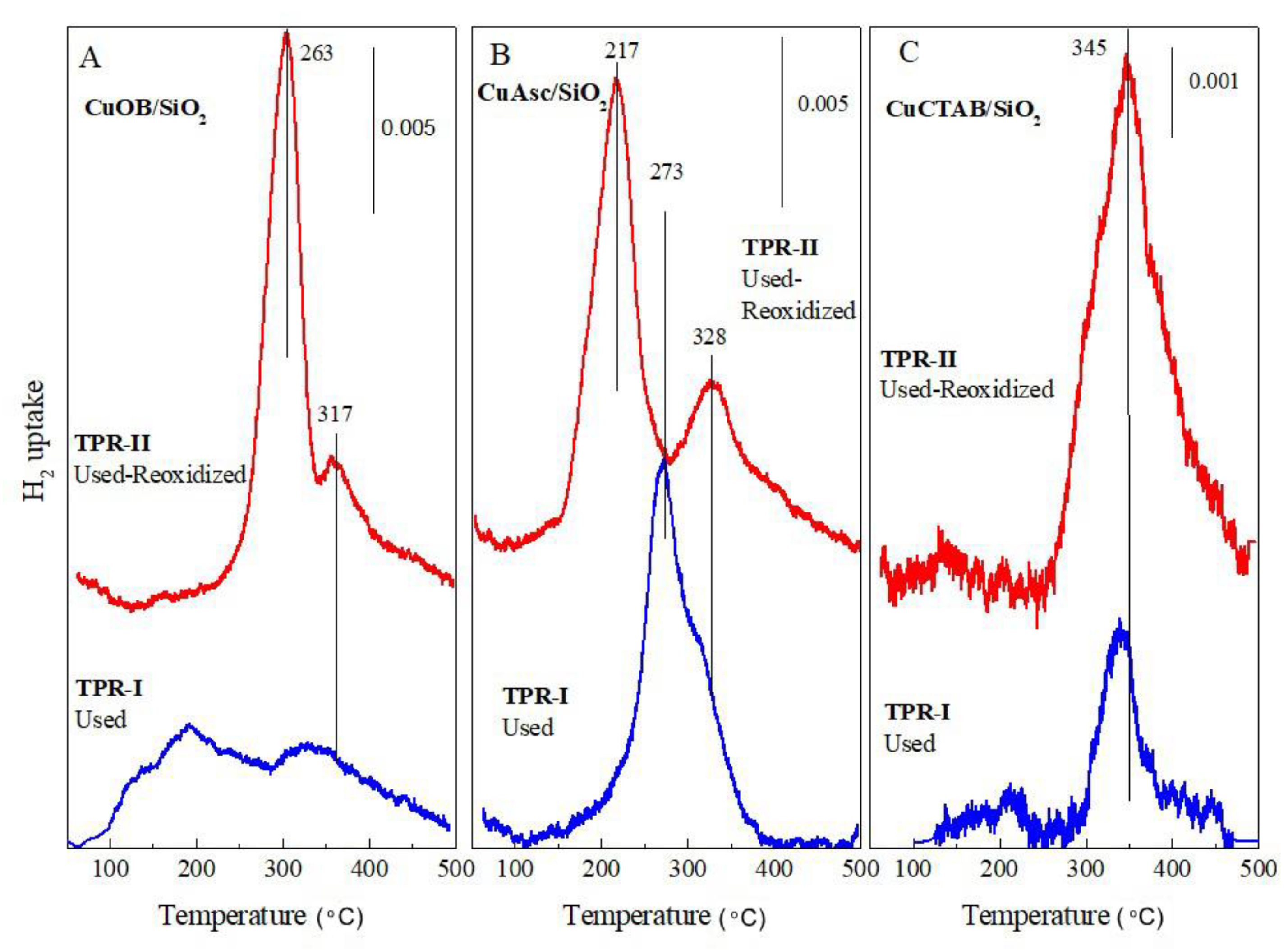
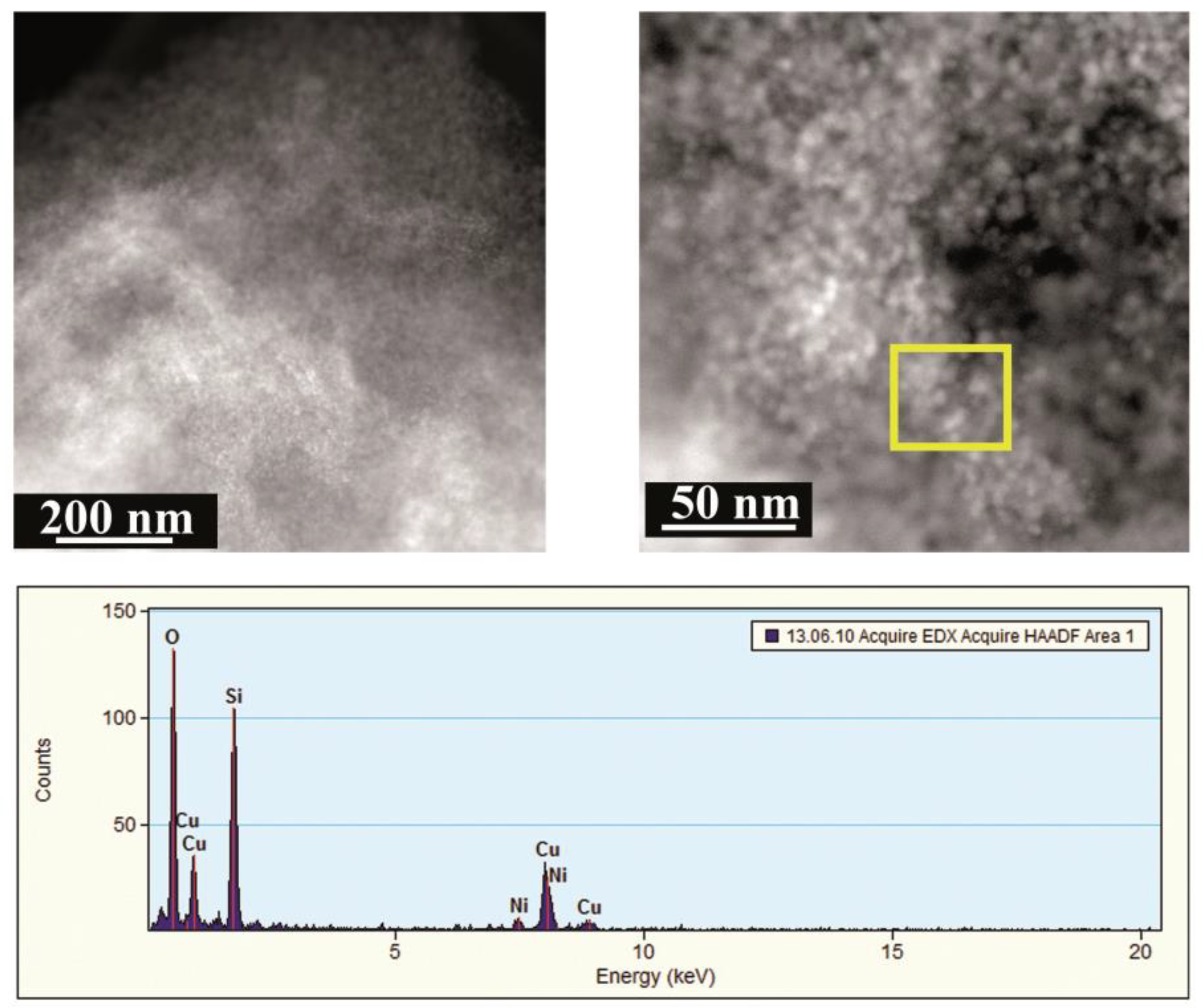
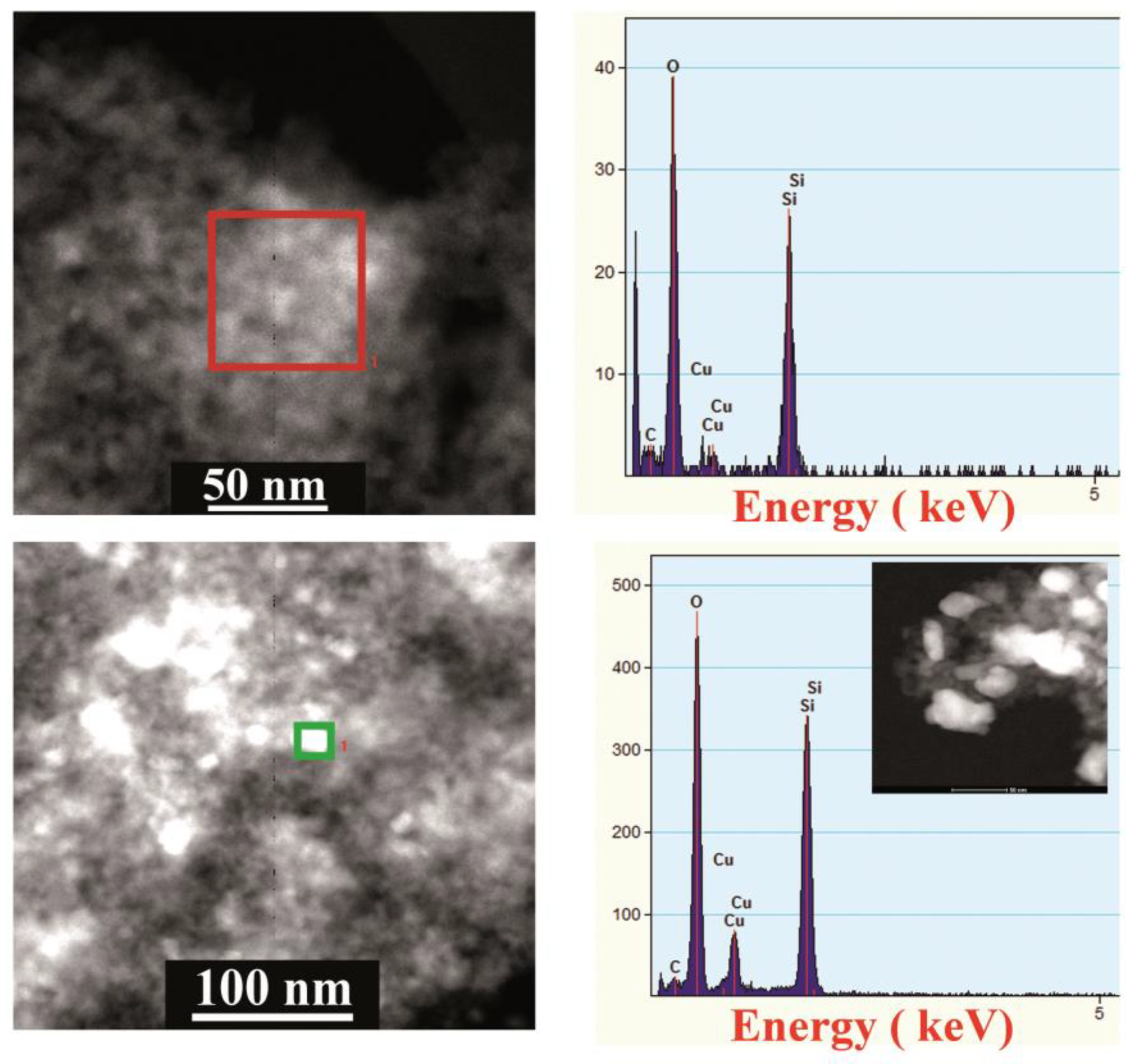
3.1. Characterization of the Cu/SiO2 Catalysts
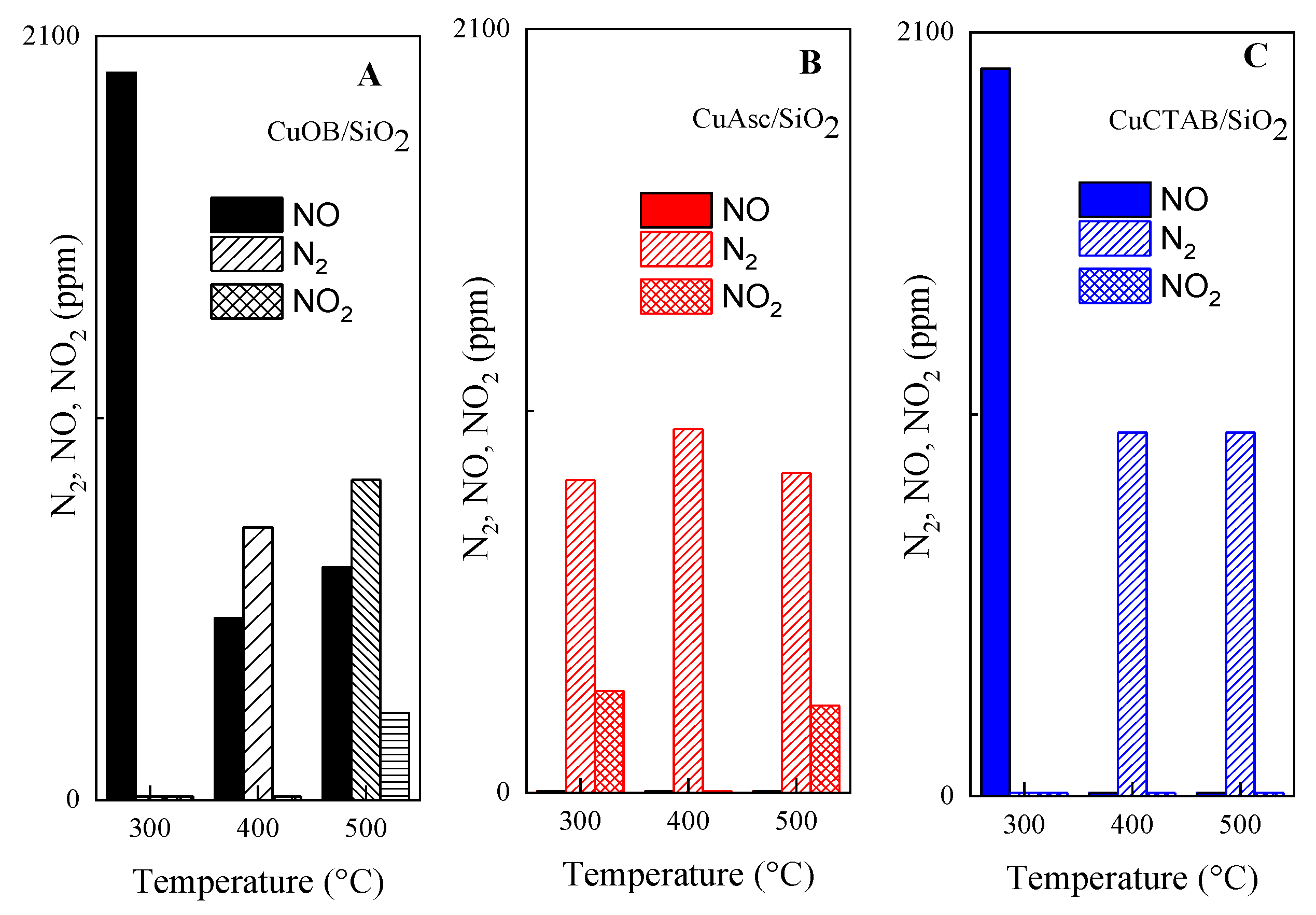
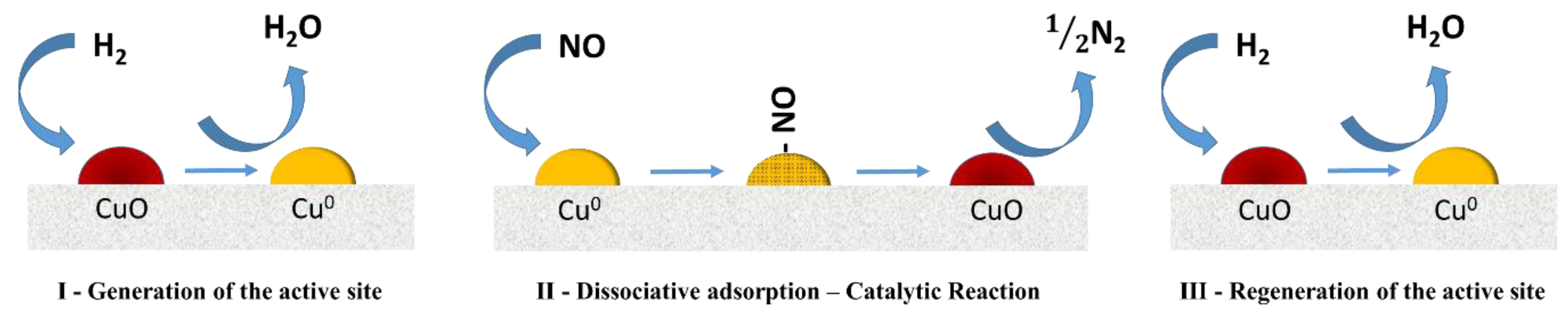
3.2. Catalytic Evaluation in the NO Reduction with Hydrogen
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brookshear, D.W.; Pihl, J.A.; Toops, T.J.; West, B.; Prikhodko, V. The selective catalytic reduction of NOx over Ag/Al2O3 with isobutanol as the reductant. Catal. Today 2016, 267, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Bai, S.; Crocker, M. Al2O3-based passive NOx adsorbers for low temperature applications. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 170–171, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.K.; Wachs, I.E. A Perspective on the Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) of NO with NH3 by Supported V2O5-WO3/TiO2 Catalysts. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 6537–6551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandenberger, S.; Kröcher, O.; Tissler, A.; Althoff, R. The state of the art in selective catalytic reduction of NOx by ammonia using metal-exchanged zeolite catalysts. J. Catal. Rev. 2008, 50, 492–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Li, C.; Lu, P.; Qu, L.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, M.; Fang, Y. A review on selective catalytic reduction of NOx by supported catalysts at 100–300°C—Catalysts, mechanism, kinetics. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resitoglu, I.A.; Keskin, A. Hydrogen applications in selective catalytic reduction of NOx emissions from diesel engines. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 23389–23394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Yu, Q. The effect of H2O on the H2-SCR of NOxover Pt/HZSM-5. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2015, 400, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, D.; Singh, P.; Prasad, R. MnCo2O4 spinel catalysts synthesized by nanocasting method followed by different calcination routes for low-temperature reduction of NOx using various reductants. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 5346–5357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.N.; Savva, P.G.; Fierro, J.L.G.; Efstathiou, A.M. Industrial H2-SCR of NO on a novel Pt/MgO-CeO2 catalyst. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2007, 75, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burch, R.; Coleman, M.D. An investigation of the NO/H2/O2 reaction on noble-metal catalysts at low temperatures under lean-burn conditions. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 1999, 23, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, M.; Bai, H. Selective catalytic reduction of NO using acetone solvent vapors as the reducing agent over Cu2+ and/or Al3+ions substituted MCM-41 catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 144, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, G.; Guan, N.; Li, L. NO selective reduction by hydrogen over bimetallic Pd-Ir/TiO2 catalyst. Catal. Commun. 2012, 24, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-jrai, A.; Tsolakis, A.; Megaritis, A. The influence of H2 and CO on diesel engine combustion characteristics, exhaust gas emissions, and after treatment selective catalytic NOx reduction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2007, 32, 3565–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hueso, J.L.; Cotrino, J.; Caballero, A.; Espinós, J.P.; González-Elipe, A.R. Plasma catalysis with perovskite-type catalysts for the removal of NO and CH4 from combustion exhausts. J. Catal. 2007, 247, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, A.; Morales, J.J.; Cordon, A.M.; Holgado, J.P.; Espinos, J.P.; Gonzalez-Elipe, A.R. An in situ XAS study of Cu/ZrO2 catalysts under de-NOx reaction conditions. J. Catal. 2005, 235, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caravaggio, G.; Nossova, L.; Burich, R. Influence of Supports on Pd Catalysts for the Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with H2 and CO. Emiss. Control Sci. Technol. 2016, 2, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schott, F.J.P.; Balle, P.; Adler, J.; Kureti, S. Reduction of NOx by H2 on Pt/WO3/ZrO2 catalysts in oxygen-rich exhaust. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2009, 87, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yin, C.; Yang, R.T. Selective catalytic reduction of nitric oxide with hydrogen on supported Pd: Enhancement by hydrogen spillover. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2016, 514, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breen, J.P.; Burch, R.; Hill, C.J. NOx storage during H2 assisted selective catalytic reduction of NOx reaction over a Ag/Al2O3 catalyst. Catal. Today 2009, 145, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huai, L.Y.; Wang, H.; He, C.Z.; Wen, H.; Yi, W.C.; Liu, J.Y. Effect of Subsurface Oxygen on Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO by H2 on Pt(100): A First-Principles Study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 24819–24826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Woo, S.I. Recent advances in the selective catalytic reduction of NOx by hydrogen in the presence of oxygen. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 8799–8814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereda-Ayo, B.; De La Torre, U.; Illán-Gómez, M.J.; Bueno-López, A.; González-Velasco, J.R. Role of the different copper species on the activity of Cu/zeolite catalysts for SCR of NOx with NH. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 147, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burch, R.; Scire, S. An investigation of the mechanism of the selective catalytic reduction of NO on various metal/ZSM-5 catalysts : Reactions of H2/NO mixtures. Catal. Lett. 1994, 27, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, J.A.; Contescu, C.; Contescu, A. Methods for Preparation of Catalytic Materials. Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 477–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinna, F. Supported metal catalysts preparation. Catal. Today 1998, 41, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, N.K.; Zyryanov, G.V.; Majee, A.; Charushin, V.N.; Chupakhin, O.N.; Santra, S. Copper nanoparticles as inexpensive and efficient catalyst: A valuable contribution in organic synthesis. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2017, 353, 1–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuyan, D.; Saikia, M.; Saikia, L. ZnO nanoparticles embedded in SBA-15 as an efficient heterogeneous catalyst for the synthesis of dihydropyrimidinones via Biginelli condensation reaction. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 256, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seth, J.; Nepak, D.; Chaudhari, V.R.; Prasad, B.L.V. Preparation of MgO supported platinum nanoparticle catalyst using toluene dispersed platinum sol. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 418, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, R.; Li, S.; Sun, X.; Ren, Q.; Chen, L.; Fu, M.; Wu, J.; Ye, D. Size effect of Pt nanoparticles on the catalytic oxidation of toluene over Pt/CeO2 catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 220, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaccheria, F.; Scotti, N.; Marelli, M.; Psaro, R.; Ravasio, N. Unravelling the properties of supported copper oxide: Can the particle size induce acidic behaviour? Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel-Sancho, N.; Martinez, G.; Sebastian, V.; Malumbres, A.; Florea, I.; Arenal, R.; Ortega-Liebana, M.C.; Hueso, J.L.; Santamaria, J. Pumping Metallic Nanoparticles with Spatial Precision within Magnetic Mesoporous Platforms: 3D Characterization and Catalytic Application. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 41529–41536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usón, L.; Colmenares, M.G.; Hueso, J.L.; Sebastián, V.; Balas, F.; Arruebo, M.; Santamaría, J. VOCs abatement using thick eggshell Pt/SBA-15 pellets with hierarchical porosity. Catal. Today 2014, 227, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, A.D.; Geetha, K. Synthesis of copper precursor, copper and its oxide nanoparticles by green chemical reduction method and its antimicrobial activity. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 3, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Karthikeyan, S.; Kumar, S.; Durndell, L.J.; Isaacs, M.A.; Parlett, C.M.A.; Coulson, B.; Douthwaite, R.E.; Jiang, Z.; Wilson, K.; Lee, A.F. Size-Dependent Visible Light Photocatalytic Performance of Cu2O Nanocubes. ChemCatChem 2018, 10, 3554–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Wang, Y.; Xue, Q.; Wu, X. Synthesis of highly stable dispersions of nanosized copper particles using l-ascorbic acid. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 900–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.F.; Yang, Z.G.; Wang, W.J. A simple way of preparing high-concentration and high-purity nano copper colloid for conductive ink in inkjet printing technology. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2010, 360, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoncheva, T.; Issa, G.; Blasco, T.; Dimitrov, M.; Popova, M.; Hernández, S.; Kovacheva, D.; Atanasova, G.; Nieto, J.M.L. Catalytic VOCs elimination over copper and cerium oxide modified mesoporous SBA-15 silica. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2013, 453, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Robles, F.; Garcia-Rodriguez, F.J.; Jimenez-Sandoval, S.; Gonzalez-Hernandez, J. Raman study of copper and iron oxide particles embedded in an SiO2 matrix. J. Raman Spectrosc. 1999, 30, 1099–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, T.Y.; Moghaddas, J. Cogeled copperesilica aerogel as a catalyst in hydrogen production from methanol steam reforming. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 1472–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balamurugan, B.; Mehta, B.R.; Avasthi, D.K.; Singh, F.; Arora, A.K.; Rajalakshmi, M.; Raghavan, G.; Tyagi, A.K.; Shivaprasad, S.M. Modifying the nanocrystalline characteristics—Structure, size, and surface states of copper oxide thin films by high-energy heavy-ion irradiation. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 92, 3304–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, B.; Rogach, A.L. Synthesis, optical properties and applications of light-emitting copper nanoclusters. Nanoscale Horizons 2017, 2, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Cui, F.; Kang, H.; Chen, J. Highly dispersed silica-supported copper nanoparticles prepared by precipitation—Gel method: A simple but efficient and stable catalyst for glycerol hydrogenolysis. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 5090–5099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.F.; Guo, P.J.; Qiao, M.H.; Yan, S.R.; Li, H.X.; Shen, W.; Xu, H.L.; Fan, K.N. Cu/SiO2 catalysts prepared by the ammonia-evaporation method: Texture, structure, and catalytic performance in hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate to ethylene glycol. J. Catal. 2008, 257, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchi, A.J.; Fierro, J.L.G.; Santamaría, J.; Monzón, A. Dehydrogenation of isopropylic alcohol on a Cu/SiO2catalyst: A study of the activity evolution and reactivation of the catalyst. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 1996, 142, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirichenko, O.; Kapustin, G.; Nissenbaum, V.; Strelkova, A.; Shuvalova, E.; Shesterkina, A.; Kustov, L. Thermal decomposition and reducibility of silica-supported precursors of Cu, Fe and Cu–Fe nanoparticles. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2018, 134, 233–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, A.; Tsoncheva, T.; Marelli, M.; Mihaylov, M.; Dimitrov, M.; Dal Santo, V.; Hadjiivanov, K. Size controlled copper nanoparticles hosted in mesoporous silica matrix: Preparation and characterization. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 126, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerreiro, E.D.; Gorriz, O.F.; Rivarola, J.B.; Arrúa, L.A. Characterization of Cu/SiO2 catalysts prepared by ion exchange for methanol dehydrogenation. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 1997, 165, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentry, S.J.; Walsh, P.T. Influence of silica and alumina supports on the temperature-programmed reduction of copper(II) oxide. Faraday Trans. 1982, 13, 1515–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Yu, J.; Wu, T.; Wang, G. Surface structure and catalytic behavior of silica-supported copper catalysts prepared by impregnation and sol-gel methods. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2003, 239, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.H.; Wang, A.Q.; Zheng, M.Y.; Wang, X.D.; Zhang, T. Factors influencing the catalytic activity of SBA-15-supported copper nanoparticles in CO oxidation. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2006, 297, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Grift, C.J.G.; Mulder, A.; Geus, J.W. Characterization of silica-supported copper catalysts by means of temperature-programmed reduction. Appl. Catal. 1990, 60, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spassova, I.; Stoeva, N.; Nickolov, R.; Atanasova, G.; Khristova, M. Impact of carbon on the surface and activity of silica-carbon supported copper catalysts for reduction of nitrogen oxides. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 369, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Yoshida, H.; Patlolla, A.; Takeda, S.; Frenkel, A.I.; Tao, F. Reduction of Nitric Oxide with Hydrogen on Catalysts of Singly Dispersed Bimetallic Sites Pt 1 Co m and Pd 1 Co n. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 840–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, A.; Haruta, M. Nitric Oxide Reduction with Hydrogen, Carbon Monoxide, and Hydrocarbons over Gold Catalysts. Gold Bull. 2011, 32, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelef, M.; Gandhi, H.S. Ammonia Formation in Catalytic Reduction of Nitric Oxide by Molecular Hydrogen. II. Noble Metal Catalysts. Ind. Eng. Chem. Prod. Res. Dev. 1972, 11, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, A.; Nakao, T.; Azuma, M.; Kobayashi, T. Two conversion maxima at 373 and 573 K in the reduction of nitrogen monoxide with hydrogen over Pd/TiO2 catalyst. Catal. Today 1998, 45, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Suárez, F.E.; Bueno-López, A.; Illán-Gómez, M.J. Cu/Al2O3 catalysts for soot oxidation: Copper loading effect. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2008, 84, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.A.; Kim, J.Y.; Hanson, J.C.; Pérez, M.; Frenkel, A.I. Reduction of CuO in H2: In situ time-resolved XRD studies. Catal. Lett. 2003, 85, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Rodriguez, A.; Hanson, J.C.; Frenkel, A.I.; Lee, P.L. Reduction of CuO and Cu2O with H2: H Embedding and kinetic effects in the formation of suboxides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 10684–10692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| CuNPs | Size (nm) 1 | Catalyst | Cu Loading (%) 2 Fresh Catalyst | Cu Loading (%) 2 Used Catalyst |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CuO | - | CuOB/SiO2 | 0.7 ± 0.1 | 0.7 ± 0.1 |
| CuAsc | 3.3 ± 0.9 | CuAsc/SiO2 | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 0.9 ± 0.1 |
| CuCTAB | 2.4 ± 0.7 | CuCTAB/SiO2 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 0.5 ± 0.1 |
| Specific Surface Area (m2.g−1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CuOB/SiO2 | CuAsc/SiO2 | CuCTAB/SiO2 | |||
| Fresh a | Used b | Fresh a | Used b | Fresh a | Used b |
| 280.4 | 230.4 | 265.5 | 233.5 | 275.3 | 239.2 |
| (↓18) c | (↓12) c | (↓15) c | |||
| Catalyst | H2/Cu: Total Molar H2 Consumption / Cu Molar Content | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fresh TPR-I | Fresh Re-Oxidized TPR-II | Used TPR-I | Used Re-Oxidized TPR-II | |
| CuOB/SiO2 | 1 | - | 0.06 | 1 |
| CuAsc/SiO2 | 1 | - | 0.65 | 1 |
| CuCTAB/SiO2 | 0.51 | 0.76 | 0.22 | 0.31 |
| Catalyst | Total NO Conversion CNO (%) 2 | NO to N2 Selectivity SN2 (%) 3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 300 °C | 400 °C | 500 °C | 300 °C | 400 °C | 500 °C | |
| CuOB/SiO2 | 0 | 75 ± 1 | 68 ± 1 | 0 | 75 ± 1 | 88 ± 1 |
| CuAsc/SiO2 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 85 ± 1 | 100 | 88 ± 1 |
| CuCTAB/SiO2 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 100 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gioria, E.; Marchesini, F.A.; Soldati, A.; Giorello, A.; Hueso, J.L.; Gutierrez, L. Green Synthesis of a Cu/SiO2 Catalyst for Efficient H2-SCR of NO. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4075. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9194075
Gioria E, Marchesini FA, Soldati A, Giorello A, Hueso JL, Gutierrez L. Green Synthesis of a Cu/SiO2 Catalyst for Efficient H2-SCR of NO. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(19):4075. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9194075
Chicago/Turabian StyleGioria, Esteban, F. Albana Marchesini, Analía Soldati, Antonella Giorello, Jose L. Hueso, and Laura Gutierrez. 2019. "Green Synthesis of a Cu/SiO2 Catalyst for Efficient H2-SCR of NO" Applied Sciences 9, no. 19: 4075. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9194075
APA StyleGioria, E., Marchesini, F. A., Soldati, A., Giorello, A., Hueso, J. L., & Gutierrez, L. (2019). Green Synthesis of a Cu/SiO2 Catalyst for Efficient H2-SCR of NO. Applied Sciences, 9(19), 4075. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9194075






