NIRS-EMG for Clinical Applications: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Electromyography
2.1. Detection of the Activation Timing (On/OFF)
2.2. Force/EMG Signal Relationship
2.3. EMG for Measuring Fatigue
2.4. EMG in Motor Control
3. Near Infrared Spectroscopy
3.1. Different NIRS Techniques
3.2. NIRS Parameters
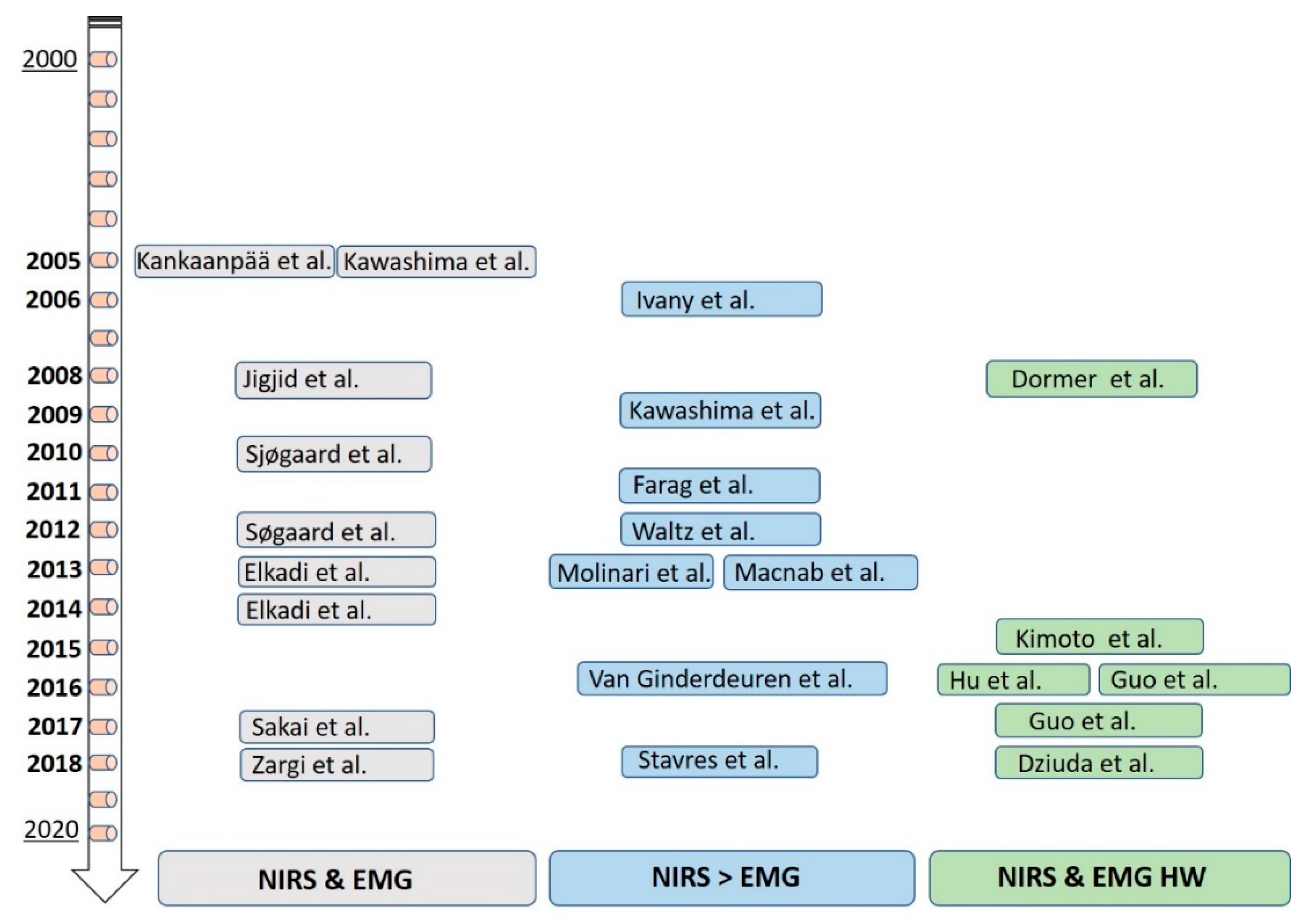
4. NIRS-EMG: Review of Studies in Clinical Practice
4.1. NIRS and EMG
4.2. NIRS > EMG
4.3. NIRS and EMG HW
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Teasell, R.W.; Foley, N.C.; Bhogal, S.K.; Speechley, M.R. An evidence-based review of stroke rehabilitation. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2003, 10, 29–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zech, A.; Hübscher, M.; Vogt, L.; Banzer, W.; Hänsel, F.; Pfeifer, K. Neuromuscular training for rehabilitation of sports injuries: A systematic review. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 1831–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, L.; Oldridge, N.; Thompson, D.R.; Zwisler, A.-D.; Rees, K.; Martin, N.; Taylor, R.S. Exercise-Based Cardiac Rehabilitation for Coronary Heart Disease: Cochrane Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 67, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobo-Prat, J.; Kooren, P.N.; Stienen, A.H.; Herder, J.L.; Koopman, B.F.J.M.; Veltink, P.H. Non-invasive control interfaces for intention detection in active movement-assistive devices. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2014, 11, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassi, B.; Quaresima, V. Near-infrared spectroscopy and skeletal muscle oxidative function in vivo in health and disease: A review from an exercise physiology perspective. J. Biomed. Opt. 2016, 21, 091313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peake, J.M.; Kerr, G.; Sullivan, J.P. A Critical Review of Consumer Wearables, Mobile Applications, and Equipment for Providing Biofeedback, Monitoring Stress, and Sleep in Physically Active Populations A Review of Health and Sports Performance Technologies. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sheng, Y.; Liu, H. Corticomuscular Coherence and Its Applications: A Review. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrey, S. Non-invasive NIR spectroscopy of human brain function during exercise. Methods 2008, 45, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarelli, A.M.; Zappasodi, F.; Di Pompeo, F.; Merla, A. Simultaneous functional near-infrared spectroscopy and electroencephalography for monitoring of human brain activity and oxygenation: A review. Neurophotonics 2017, 4, 041411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, D.; Merletti, R.; Enoka, R.M. The extraction of neural strategies from the surface EMG: An update. J. Appl. Physiol. 2014, 117, 1215–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazmi, N.; Rahman, M.A.A.; Yamamoto, S.I.; Ahmad, S.A.; Zamzuri, H.; Mazlan, S.A. A review of classification techniques of EMG signals during isotonic and isometric contractions. Sensors (Switzerland) 2016, 16, 1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, R.H.; Reaz, M.B.I.; Bin Mohd Ali, M.A.; Bakar, A.A.A.; Chellappan, K.; Chang, T.G. Surface electromyography signal processing and classification techniques. Sensors (Switzerland) 2013, 13, 12431–12466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golabchi, F.N.; Sapienza, S.; Severini, G.; Reaston, P.; Tomecek, F.; Demarchi, D.; Reaston, M.; Bonato, P. Assessing aberrant muscle activity patterns via the analysis of surface EMG data collected during a functional evaluation. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2019, 20, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Holobar, A.; Gazzoni, M.; Merletti, R.; Rymer, W.Z.; Zhou, P. Examination of Post-stroke Alteration in Motor Unit Firing Behavior Using High Density Surface EMG Decomposition. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 62, 1242–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, L.H.; Hirata, R.P.; Graven-Nielsen, T. Reorganized Trunk Muscle Activity During Multidirectional Floor Perturbations After Experimental Low Back Pain: A Comparison of Bilateral Versus Unilateral Pain. J. Pain 2016, 17, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, E.; Chipchase, L.S.; Schabrun, S.M. Temporal and spatial characteristics of post-silent period electromyographic bursting in low back muscles: Comparison between persons with and without low back pain. Int. J. Neurosci. 2017, 127, 1074–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakeling, J.M. Patterns of motor recruitment can be determined using surface EMG. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2009, 19, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, C.A.; Corona, F.; Murgia, M.; Pili, R.; Pau, M.; Côté, J.N. Electromyographical Gait Characteristics in Parkinson’s Disease: Effects of Combined Physical Therapy and Rhythmic Auditory Stimulation. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, M.G.; Piperno, R.; Simoncini, L.; Bonato, P.; Tonini, A.; Giannini, S. Gait abnormalities in minimally impaired multiple sclerosis patients. Mult. Scler. J. 1999, 5, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauraugh, J.; Light, K.; Kim, S.; Thigpen, M.; Behrman, A. Chronic Motor Dysfunction After Stroke. Stroke 2000, 31, 1360–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, M.; Mottola, L.; Quaresima, V. Principles, Techniques, and Limitations of Near Infrared Spectroscopy. Can. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004, 29, 463–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, D.M.; Bolinger, L.; Li, H.; Kendrick, K.; Chance, B.; Wilson, J.R. Validation of near-infrared spectroscopy in humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 1994, 77, 2740–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barstow, T.J. CORP: Understanding near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) and its application to skeletal muscle research. J. Appl. Physiol. 2019, 126, 1360–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poole, D.C.; Hirai, D.M.; Copp, S.W.; Musch, T.I. Muscle oxygen transport and utilization in heart failure: Implications for exercise (in)tolerance. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2012, 302, H1050–H1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirai, D.M.; Musch, T.I.; Poole, D.C. Exercise training in chronic heart failure: Improving skeletal muscle O 2 transport and utilization. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2015, 309, H1419–H1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boezeman, R.P.E.; Moll, F.L.; Ünlü, Ç.; de Vries, J.-P.P.M. Systematic review of clinical applications of monitoring muscle tissue oxygenation with near-infrared spectroscopy in vascular disease. Microvasc. Res. 2016, 104, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, B.L.; Bækgaard, N.; Quistorff, B. Muscle Mitochondrial Function in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Peripheral Arterial Disease: Implications in Vascular Surgery. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2009, 38, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassi, B.; Marzorati, M.; Lanfranconi, F.; Ferri, A.; Longaretti, M.; Stucchi, A.; Vago, P.; Marconi, C.; Morandi, L. Impaired oxygen extraction in metabolic myopathies: Detection and quantification by near-infrared spectroscopy. Muscle Nerve 2007, 35, 510–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, T.E.; Erickson, M.L.; Young, H.-J.; McCully, K.K. Case report: Endurance electrical stimulation training improves skeletal muscle oxidative capacity in chronic spinal cord injury. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2013, 94, 2559–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demoulin, C.; Crielaard, J.-M.; Vanderthommen, M. Spinal muscle evaluation in healthy individuals and low-back-pain patients: A literature review. Jt. Bone Spine 2007, 74, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Yang, Z.; Yuan, T.; Feng, W.; Wang, P. A Systemic Review of Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy for Stroke: Current Application and Future Directions. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrey, S.; Ferrari, M. Muscle Oximetry in Sports Science: A Systematic Review. Sports Med. 2018, 48, 597–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Mulla, M.R.; Sepulveda, F.; Colley, M. A review of non-invasive techniques to detect and predict localised muscle fatigue. Sensors 2011, 11, 3545–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes, J.J.A.; Vieira, M.E.M.; Pires, M.B.; Stevan, S.L. Sensor fusion and smart sensor in sports and biomedical applications. Sensors (Switzerland) 2016, 16, 1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, C.J. The Use of Surface Electromyography in Biomechanics. J. Appl. Biomech. 1997, 13, 135–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reaz, M.B.I.; Hussain, M.S.; Mohd-Yasin, F. Techniques of EMG signal analysis: Detection, processing, classification and applications. Biol. Proced. Online 2006, 8, 11–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merlo, A.; Farina, D.; Merletti, R. A fast and reliable technique for muscle activity detection from surface EMG signals. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2003, 50, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, P.; Aruin, A.S. Teager-kaiser energy operation of surface EMG improves muscle activity onset detection. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 35, 1532–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonato, P.; D’Alessio, T.; Knaflitz, M. A statistical method for the measurement of muscle activation intervals from surface myoelectric signal during gait. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1998, 45, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milner-Brown, H.S.; Stein, R.B. The relation between the surface electromyogram and muscular force. J. Physiol. 1975, 246, 549–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Ma, A.; Ma, G.; Ye, Y.; Li, R.; Lu, T. A Comparative Study of EMG Indices in Muscle Fatigue Evaluation Based on Grey Relational Analysis during All-Out Cycling Exercise. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizzi, E.; Cheung, V.C.K.; d’Avella, A.; Saltiel, P.; Tresch, M. Combining modules for movement. Brain Res. Rev. 2008, 57, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tresch, M.C.; Cheung, V.C.K.; d’Avella, A. Matrix Factorization Algorithms for the Identification of Muscle Synergies: Evaluation on Simulated and Experimental Data Sets. J. Neurophysiol. 2006, 95, 2199–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Avella, A.; Portone, A.; Fernandez, L.; Lacquaniti, F. Control of Fast-Reaching Movements by Muscle Synergy Combinations. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 7791–7810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Avella, A.; Fernandez, L.; Portone, A.; Lacquaniti, F. Modulation of Phasic and Tonic Muscle Synergies With Reaching Direction and Speed. J. Neurophysiol. 2008, 100, 1433–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, V.C.K.; Piron, L.; Agostini, M.; Silvoni, S.; Turolla, A.; Bizzi, E. Stability of muscle synergies for voluntary actions after cortical stroke in humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 19563–19568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, V.C.K.; Turolla, A.; Agostini, M.; Silvoni, S.; Bennis, C.; Kasi, P.; Paganoni, S.; Bonato, P.; Bizzi, E. Muscle synergy patterns as physiological markers of motor cortical damage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 14652–14656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scano, A.; Chiavenna, A.; Malosio, M.; Molinari Tosatti, L.; Molteni, F. Robotic Assistance for Upper Limbs May Induce Slight Changes in Motor Modules Compared With Free Movements in Stroke Survivors: A Cluster-Based Muscle Synergy Analysis. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scano, A.; Chiavenna, A.; Malosio, M.; Molinari Tosatti, L.; Molteni, F. Muscle Synergies-Based Characterization and Clustering of Poststroke Patients in Reaching Movements. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2017, 5, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.J.; Ting, L.H.; Zajac, F.E.; Neptune, R.R.; Kautz, S.A. Merging of healthy motor modules predicts reduced locomotor performance and muscle coordination complexity post-stroke. J. Neurophysiol. 2010, 103, 844–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safavynia, S.A.; Ting, L.H. Task-level feedback can explain temporal recruitment of spatially fixed muscle synergies throughout postural perturbations. J. Neurophysiol. 2012, 107, 159–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jöbsis, F.F. Noninvasive, infrared monitoring of cerebral and myocardial oxygen sufficiency and circulatory parameters. Science 1977, 198, 1264–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delpy, D.T.; Cope, M. Quantification in tissue near-infrared spectroscopy. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 1997, 352, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollonini, L.; Re, R.; Simpson, R.J.; Dacso, C.C. Integrated device for the measurement of systemic and local oxygen transport during physical exercise. In Proceedings of the 2012 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, San Diego, CA, USA, 28 August–1 September 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 3760–3763. [Google Scholar]
- Scholkmann, F.; Kleiser, S.; Metz, A.J.; Zimmermann, R.; Mata Pavia, J.; Wolf, U.; Wolf, M. A review on continuous wave functional near-infrared spectroscopy and imaging instrumentation and methodology. Neuroimage 2014, 85 Pt 1, 6–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.; Takasaki, S.; Ozaki, T.; Kobayashi, Y. A Tissue Oxygenation Monitor Using NIR Spatially Resolved Spectroscopy. In Proceedings of the BiOS ’99 International Biomedical Optics Symposium, San Jose, CA, USA, 15 July 1999; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Grieger, S.; Geraskin, D.; Steimers, A.; Kohl-bareis, M. Oxygen Transport to Tissue XXVIII. In Oxygen Transport to Tissue XXVIII; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2013; pp. 131–136. ISBN 9781461474111. [Google Scholar]
- Chance, B.; Cope, M.; Gratton, E.; Ramanujam, N.; Tromberg, B. Phase measurement of light absorption and scatter in human tissue. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1998, 69, 3457–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welcome to ISS. Available online: http://www.iss.com/index.html (accessed on 3 June 2019).
- Pifferi, A.; Contini, D.; Mora, A.D.; Farina, A.; Spinelli, L.; Torricelli, A. New frontiers in time-domain diffuse optics, a review. J. Biomed. Opt. 2016, 21, 091310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contini, D.; Spinelli, L.; Torricelli, A.; Pifferi, A.; Cubeddu, R. Novel method for depth-resolved brain functional imaging by time-domain NIRS. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Biomedical Optics, Munich, Germany, 17–21 June 2007; OSA: Washington, DC, USA, 2007; p. 6629_7. [Google Scholar]
- Re, R.; Contini, D.; Zucchelli, L.; Torricelli, A.; Spinelli, L. Effect of a thin superficial layer on the estimate of hemodynamic changes in a two-layer medium by time domain NIRS. Biomed. Opt. Express 2016, 7, 264–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Yamashita, Y. Time-Domain Near-Infrared Spectroscopy and Imaging: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, S.; Barstow, T.J.; Okushima, D.; Rossiter, H.B.; Kondo, N.; Ohmae, E.; Poole, D.C. Validation of a high-power, time-resolved, near-infrared spectroscopy system for measurement of superficial and deep muscle deoxygenation during exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 2015, 118, 1435–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Pirovano, I.; Contini, D.; Spinelli, L.; Torricelli, A. Time Domain Near Infrared Spectroscopy Device for Monitoring Muscle Oxidative Metabolism: Custom Probe and In Vivo Applications. Sensors 2018, 18, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porcelli, S.; Marzorati, M.; Lanfranconi, F.; Vago, P.; Pišot, R.; Grassi, B. Role of skeletal muscles impairment and brain oxygenation in limiting oxidative metabolism during exercise after bed rest. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 109, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kankaanpää, M.; Colier, W.N.; Taimela, S.; Anders, C.; Airaksinen, O.; Kokko-Aro, S.M.; Hänninen, O. Back extensor muscle oxygenation and fatigability in healthy subjects and low back pain patients during dynamic back extension exertion. Pathophysiology 2005, 12, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, Y.; Ito, S.; Hida, T.; Ito, K.; Koshimizu, H.; Harada, A. Low Back Pain in Patients with Lumbar Spinal Stenosis-Hemodynamic and electrophysiological study of the lumbar multifidus muscles. Spine Surg. Relat. Res. 2017, 1, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Elcadi, G.H.; Forsman, M.; Aasa, U.; Fahlstrom, M.; Crenshaw, A.G. Shoulder and forearm oxygenation and myoelectric activity in patients with work-related muscle pain and healthy subjects. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2013, 113, 1103–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elcadi, G.H.; Forsman, M.; Hallman, D.M.; Aasa, U.; Fahlstrom, M.; Crenshaw, A.G. Oxygenation and hemodynamics do not underlie early muscle fatigue for patients with work-related muscle pain. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjøgaard, G.; Rosendal, L.; Kristiansen, J.; Blangsted, A.K.; Skotte, J.; Larsson, B.; Gerdle, B.; Saltin, B.; Søgaard, K. Muscle oxygenation and glycolysis in females with trapezius myalgia during stress and repetitive work using microdialysis and NIRS. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 108, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Søgaard, K.; Blangsted, A.K.; Nielsen, P.K.; Hansen, L.; Andersen, L.L.; Vedsted, P.; Sjøgaard, G. Changed activation, oxygenation, and pain response of chronically painful muscles to repetitive work after training interventions: A randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2012, 112, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, N.; Nakazawa, K.; Akai, M. Muscle oxygenation of the paralyzed lower limb in spinal cord-injured persons. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2005, 37, 915–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jigjid, E.; Kawashima, N.; Ogata, H.; Nakazawa, K.; Akai, M.; Eto, F.; Haga, N. Effects of passive leg movement on the oxygenation level of lower limb muscle in chronic stroke patients. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2008, 22, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žargi, T.; Drobnič, M.; Stražar, K.; Kacin, A. Short-term preconditioning with blood flow restricted exercise preserves quadriceps muscle endurance in patients after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wȩgrzynowska-Teodorczyk, K.; Siennicka, A.; Josiak, K.; Zymliński, R.; Kasztura, M.; Banasiak, W.; Ponikowski, P.; Woźniewski, M. Evaluation of Skeletal Muscle Function and Effects of Early Rehabilitation during Acute Heart Failure: Rationale and Study Design. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 6982897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivany, L.; Hickey, A.; Prime, C.; Bunin, J.; Reading, S.; Albert, W.J. The Effect of Therapeutic Massage on Muscle Parameters in Fibromyalgia Patients a Pilot Study; University of New Brunswick: Fredericton, NB, Canada, 2006; p. 6. [Google Scholar]
- Van Ginderdeuren, E.; Caicedo, A.; Taelmans, J.; Goemans, N.; Van Den Hauwe, M.; Naulaers, G.; Van Huffel, S.; Buyse, G. Differences in contraction-induced hemodynamics and surface emg in duchenne muscular dystrophy. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 876, 71–77. [Google Scholar]
- Stavres, J.; Singer, T.J.; Brochetti, A.; Kilbane, M.J.; Brose, S.W.; McDaniel, J. The Feasibility of Blood Flow Restriction Exercise in Patients With Incomplete Spinal Cord Injury. PM R 2018, 10, 1368–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinari, F.; Acharya, U.R.; Martis, R.J.; De Luca, R.; Petraroli, G.; Liboni, W. Entropy analysis of muscular near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) signals during exercise programme of type 2 diabetic patients: Quantitative assessment of muscle metabolic pattern. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2013, 112, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawashima, N.; Suzuki, R.; Nakazawa, K.; Ohta, Y. Novel home-based rehabilitation device to prevent secondary diseases for patients with spinal cord injury. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics ICORR 2009, Kyoto, Japan, 23–26 June 2009; pp. 349–353. [Google Scholar]
- Farag, F.F.; Martens, F.M.; D’Hauwers, K.W.; Feitz, W.F.; Heesakkers, J.P. Near-infrared spectroscopy: A novel, noninvasive, diagnostic method for detrusor overactivity in patients with overactive bladder symptoms—A preliminary and experimental study. Eur. Urol. 2011, 59, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macnab, A.J.; Shadgan, B.; Stothers, L.; Afshar, K. Ambulant monitoring of bladder oxygenation and hemodynamics using wireless near-infrared spectroscopy. J. Can. Urol. Assoc. 2013, 7, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Waltz, X.; Pichon, A.; Lemonne, N.; Mougenel, D.; Lalanne-Mistrih, M.L.; Lamarre, Y.; Tarer, V.; Tressières, B.; Etienne-Julan, M.; Hardy-Dessources, M.D.; et al. Normal Muscle Oxygen Consumption and Fatigability in Sickle Cell Patients Despite Reduced Microvascular Oxygenation and Hemorheological Abnormalities. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merletti, R.; Botter, A.; Troiano, A.; Merlo, E.; Minetto, M.A. Technology and instrumentation for detection and conditioning of the surface electromyographic signal: State of the art. Clin. Biomech. 2009, 24, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dormer, C.; Ward, T.; Mcloone, S.; Maynooth, N.U.I. Towards enhanced biofeedback mechanisms for upper limb rehabilitation in stroke. In Proceedings of the 6th European Symposium on Biomedical Engineering, Crete, Greece, 19–21 June 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann, S.; Buchenrieder, K. Fusion of Myoelectric and Near-Infrared Signals for Prostheses Control. In Proceedings of the I-CREATe 2010: International Convention on Rehabilitation Engineering & Assistive Technology, Shanghai, China, 21–24 July 2010; Singapore Therapeutic, Assistive & Rehabilitative Technologies (START) Centre: Kaki Bukit TechPark II, Singapore, 2010. ISBN 9789810861995. [Google Scholar]
- Kimoto, A.; Yamada, Y. A new layered sensor for simultaneous measurement of EMG, MMG and oxygen consumption at the same position. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2015, 53, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Zhang, Q.; Ivkovic, V.; Strangman, G.E. Ambulatory diffuse optical tomography and multimodality physiological monitoring system for muscle and exercise applications. J. Biomed. Opt. 2016, 21, 091314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Sheng, X.; Liu, H.; Zhu, X. Development of a Multi-Channel Compact-Size Wireless Hybrid sEMG/NIRS Sensor System for Prosthetic Manipulation. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Sheng, X.; Liu, H.; Zhu, X. Toward an Enhanced Human-Machine Interface for Upper-Limb Prosthesis Control with Combined EMG and NIRS Signals. IEEE Trans. Hum.-Mach. Syst. 2017, 47, 564–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziuda, Ł.; Krej, M.; Śmietanowski, M.; Sobotnicki, A.; Sobiech, M.; Kwaśny, P.; Brzozowska, A.; Baran, P.; Kowalczuk, K.; Skibniewski, F.W. Development and evaluation of a novel system for inducing orthostatic challenge by tilt tests and lower body negative pressure. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, S.; Attenberger, A.; Buchenrieder, K. Prostheses Control with Combined Near-Infrared and Myoelectric Signals; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 601–608. [Google Scholar]
| Reference | Subjects | Aim | Target Muscle | Protocol | NIRS-EMG Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kankaanpää 2005 [67] | 17 patients with chronic low back pain, 12 control. | [CLINICAL RESEARCH] To assess if chronic low back pain patients have impaired paraspinal muscle O2 turnover and endurance capacity | L4, L5 level paraspinal muscle. | 90 s dynamic back endurance test (fatigue). | NIRS: O2Hb EMG: MPF, amplitude |
| Sakai 2017 [68] | 234 lower back pain patients. | [CLINICAL RESEARCH] To identify the features of motion-induced and walking-induced low back pain in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis. | Left and right posterior aspect of the lumbar multifidus muscle. | The lumbar spine was extended gradually 30° backward and forward for 15 s each. | NIRS: O2Hb EMG: RMS, MPF |
| Elcadi 2013 [69] | 18 patients with neck-shoulder-arm pain, 17 controls. | [RESEARCH] To test hypotheses of (a) reduced oxygen usage, oxygen recovery, blood flow, and oxygen consumption; (b) increased muscle activity for patients diagnosed with work-related muscle pain. | Extensor carpi radialis and trapezius descendes. | 20 s isometric contractions at 10%, 30%, 50% and 70% MVC. | NIRS: tHb, SO2%. From occlusion: also HHb slope EMG: RSM, MPF |
| Elcadi 2014 [70] | 18 patients with work related muscle pain, 17 control. | [RESEARCH] To test if oxygenation and hemodynamics are associated with early fatigue in muscles of patients suffering from work-related muscle pain. | Extensor carpi radialis and trapezius. | A low-level contraction of 15% maximal voluntary contraction sustained for 12–13 min. | NIRS: HHb, O2Hb, tHb EMG: RMS, MPF |
| Sjøgaard 2010 [71] | 43 females with trapezius myalgia, 19 controls. | [DIAGNOSTIC] To study females for differences between those with trapezius myalgia and without. | Descending part of trapezius muscle. | 40-min repetitive, low-force exercise: PEG task + 10 min Stroop test. | NIRS: O2Hb, HHb, tHb EMG: RMS, MPF |
| Søgaard 2012 [72] | 39 females with trapezius myalgia. | [DIAGNOSTIC] To assess changes in myalgic trapezius activation, muscle oxygenation, and pain intensity during repetitive and stressful work tasks in response to 10 weeks of training. | Descending part of trapezius muscle. | 40-min repetitive, low-force exercise: PEG task + 10 min Stroop test. | NIRS: O2Hb, HHb, tHb EMG: RMS, MPF |
| Kawashima 2005 [73] and Jigjid 2008 [74] | 15 chronic stroke patients. | [REHABILITATION] To evaluate the effects of passive leg movements in the lower limbs in chronic stroke patients. | Medial side of gastrocnemius muscle. EMG also on the soleus. | 10 min passive leg movement on a gait apparatus. | NIRS: O2Hb, HHb, tHB EMG: Mean Amplitude, RMS |
| Žargi 2018 [75] | 20 patients scheduled for an arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) reconstruction. | [TREATMENT ASSESSMENT] To test if short-term pre-conditioning with low-load blood flow restricted exercise can attenuate quadriceps femoris muscle endurance deterioration in the post-operative period. | Vastus medialis and lateralis muscle. | Sustained isometric contraction at 30% of maximal voluntary isometric contraction (MVIC) performed to volitional failure. | NIRS: Blood Flow EMG: RMS, Median Frequency |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scano, A.; Zanoletti, M.; Pirovano, I.; Spinelli, L.; Contini, D.; Torricelli, A.; Re, R. NIRS-EMG for Clinical Applications: A Systematic Review. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2952. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9152952
Scano A, Zanoletti M, Pirovano I, Spinelli L, Contini D, Torricelli A, Re R. NIRS-EMG for Clinical Applications: A Systematic Review. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(15):2952. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9152952
Chicago/Turabian StyleScano, Alessandro, Marta Zanoletti, Ileana Pirovano, Lorenzo Spinelli, Davide Contini, Alessandro Torricelli, and Rebecca Re. 2019. "NIRS-EMG for Clinical Applications: A Systematic Review" Applied Sciences 9, no. 15: 2952. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9152952
APA StyleScano, A., Zanoletti, M., Pirovano, I., Spinelli, L., Contini, D., Torricelli, A., & Re, R. (2019). NIRS-EMG for Clinical Applications: A Systematic Review. Applied Sciences, 9(15), 2952. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9152952









