A Novel Remote Sensing Index for Extracting Impervious Surface Distribution from Landsat 8 OLI Imagery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Extraction of Impervious Surface Distribution
2.2.1. Proposed Method
2.2.2. Comparison of Methods
2.2.3. Method for Accuracy Assessment
3. Results
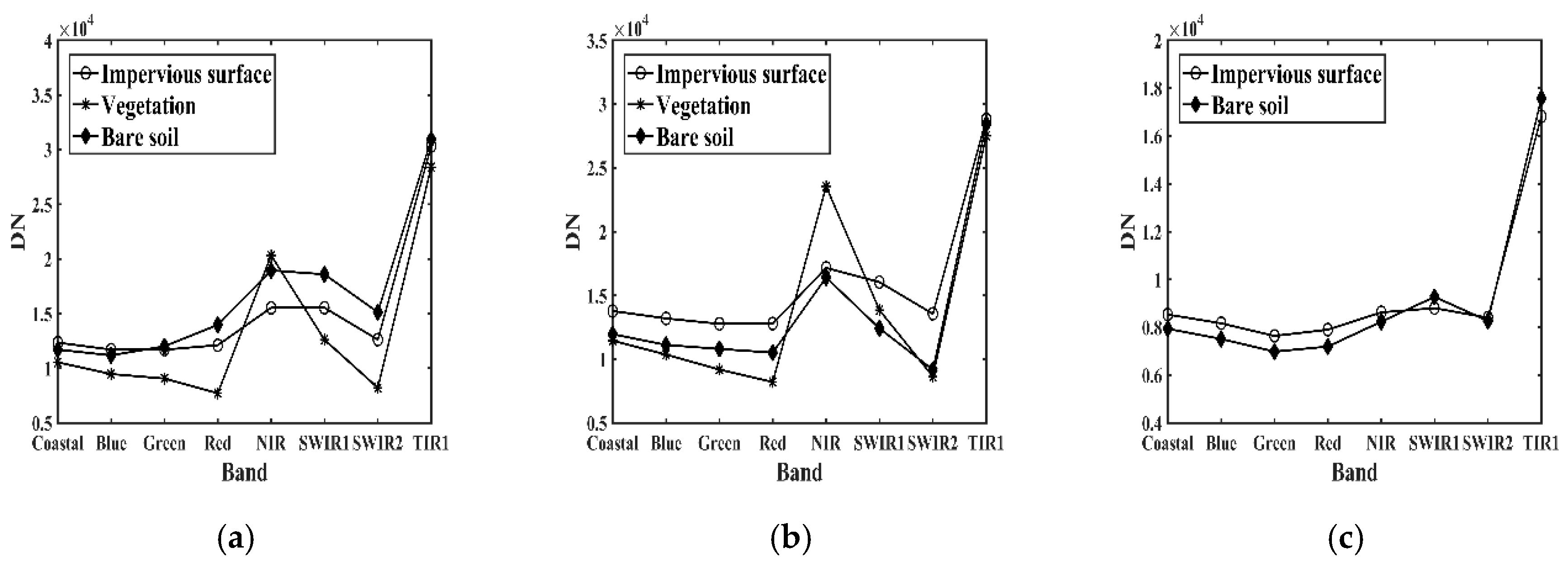
3.1. Spectral Features of Impervious Surfaces, Bare Soil, and Vegetation
3.2. Results of Extraction of Impervious Surface Distribution
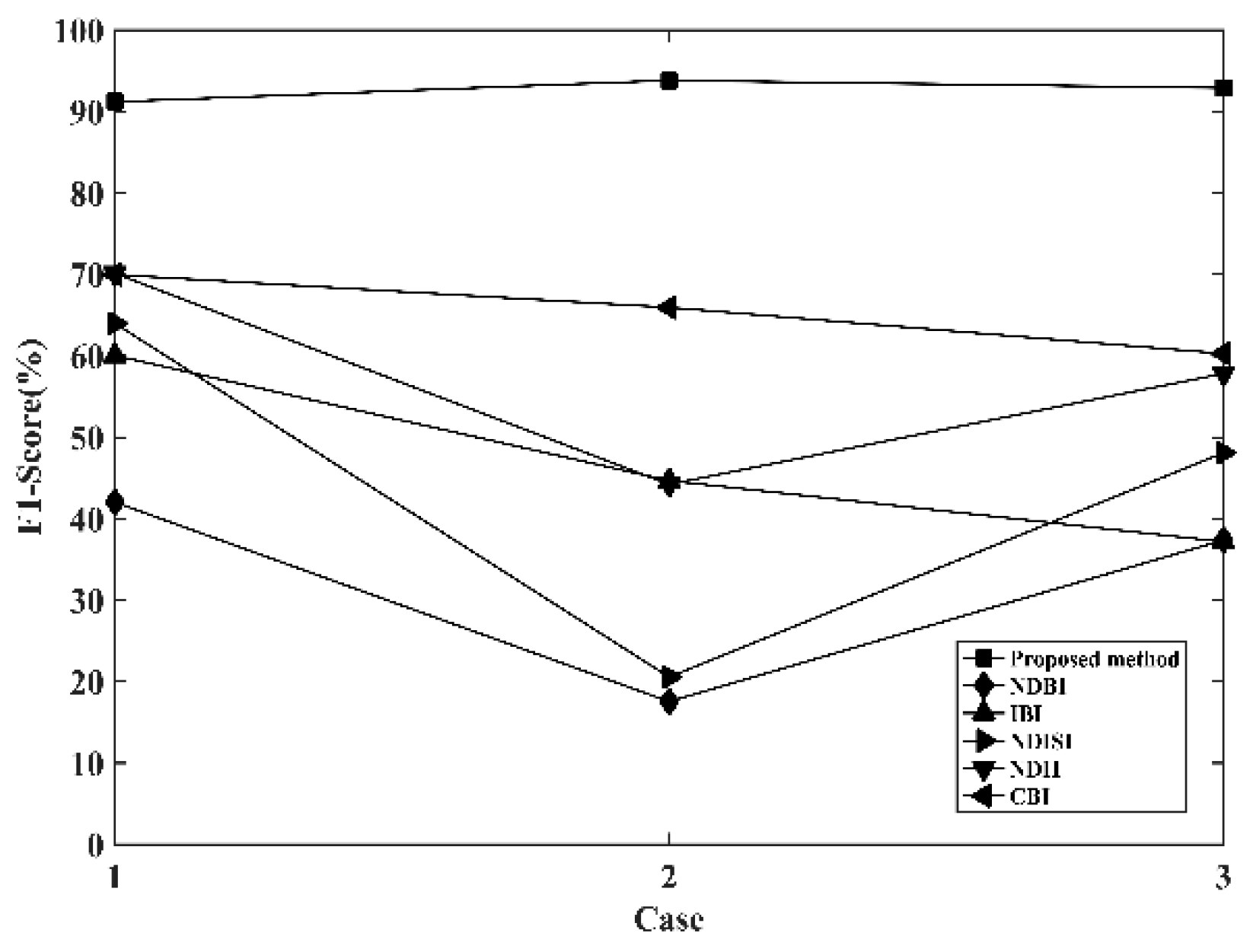
3.3. Accuracy
4. Discussion
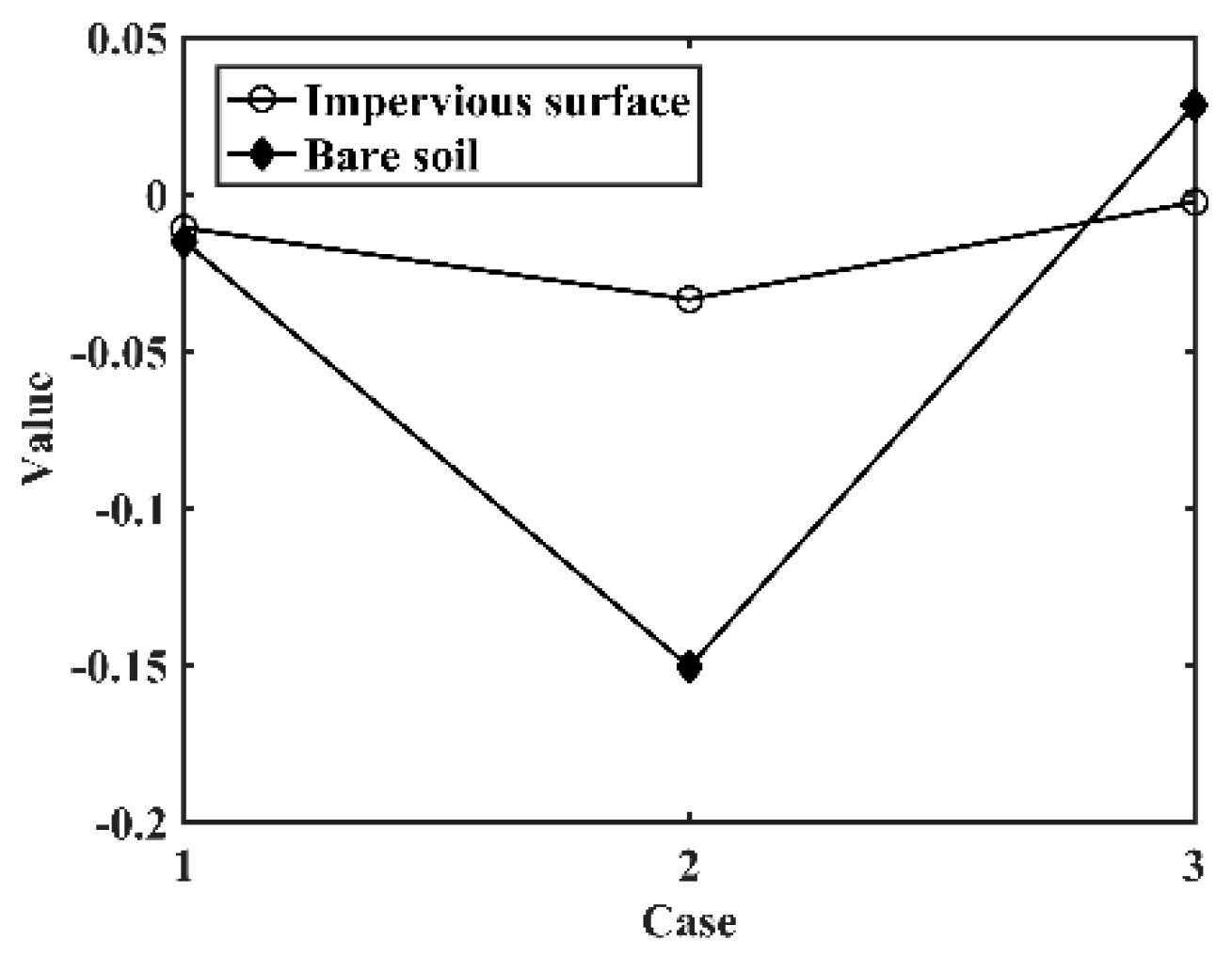
4.1. Ability of the Proposed Method to Distinguish Impervious Surfaces from Vegetation and Bare Soil
4.2. Extraction of Impervious Surface Distribution by Different Methods
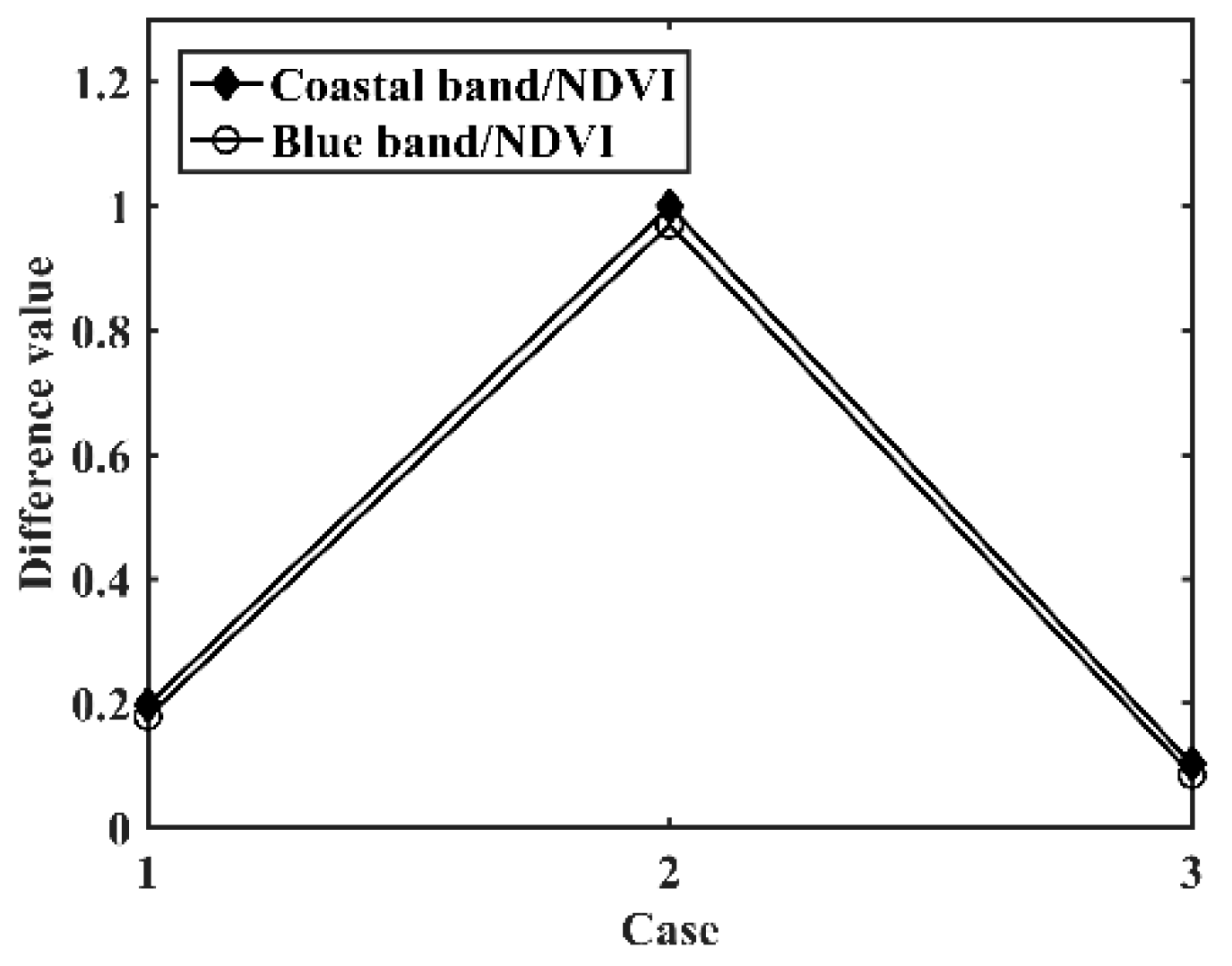
4.3. Atmospheric Effect of the Proposed Method
4.4. Alternatives to the Coastal Band
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weng, Q. Remote sensing of impervious surfaces in the urban areas: Requirements, methods, and trends. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mckinney, M.L. Urbanization, biodiversity, and conservation the impacts of urbanization on native species are poorly studied, but educating a highly urbanized human population about these impacts can greatly improve species conservation in all ecosystems. Bioscience 2002, 52, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, M.Z.; Ten Hoeve, J.E. Effects of urban surfaces and white roofs on global and regional climate. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 1028–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huszar, P.; Halenka, T.; Belda, M.; Zak, M.; Sindelarova, K.; Miksovsky, J. Regional climate model assessment of the urban land-surface forcing over central europe. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 18541–18589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, Y.; Li, P. Impervious surface extraction in urban areas from high spatial resolution imagery using linear spectral unmixing. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2015, 1, 61–71. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.; Liu, X. Support vector machine and object-oriented classification for urban impervious surface extraction from satellite imagery. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Agro-geoinformatics, Beijing, China, 11–14 August 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zha, Y.; Ni, S.X.; Yang, S. An effective approach to automatically extract urban land-use from tm lmagery. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 7, 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.Q. A new index for delineating built-up land features in satellite imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 4269–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Q. Analysis of impervious surface and its impact on urban heat environment using the normalized difference impervious surface index (ndisi). Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2010, 76, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Gang, C.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, J. Application of a normalized difference impervious index (ndii) to extract urban impervious surface features based on landsat tm images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 1055–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.Y.; Chen, X.L.; Jia, X.P.; Yao, Y.J.; Wang, Z.J. Combinational build-up index (cbi) for effective impervious surface mapping in urban areas. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 2081–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voorde, T.V.D.; Roeck, T.D.; Canters, F. A comparison of two spectral mixture modelling approaches for impervious surface mapping in urban areas. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 4785–4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xu, J. Impervious surface extraction with linear spectral mixture analysis integrating principal components analysis and normalized difference building index. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Earth Observation and Remote Sensing Applications, Guangzhou, China, 4–6 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, D.A.; Gardner, M.; Church, R.; Ustin, S.; Scheer, G.; Green, R.O. Mapping chaparral in the santa monica mountains using multiple endmember spectral mixture models. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 65, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.; Deng, Y. Enhancing endmember selection in multiple endmember spectral mixture analysis (mesma) for urban impervious surface area mapping using spectral angle and spectral distance parameters. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 33, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreiseitl, S.; Ohno-Machado, L. Logistic regression and artificial neural network classification models: A methodology review. J. Biomed. Inform. 2002, 35, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehrany, M.S.; Pradhan, B.; Jebuv, M.N. A comparative assessment between object and pixel-based classification approaches for land use/land cover mapping using spot 5 imagery. Geocarto Int. 2014, 29, 351–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.; Mukherjee, R. Extraction of impervious features from spectral indices using artificial neural network. Arab. J. Geosci. 2015, 8, 3729–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, C.; Valero, S.; Inglada, J.; Champion, N.; Dedieu, G. Assessing the robustness of random forests to map land cover with high resolution satellite image time series over large areas. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 187, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, S.S.; Tripathi, N.K. Built-up area extraction using landsat 8 oli imagery. Gisci. Remote Sens. 2014, 51, 445–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geospatial Data Cloud. Available online: http://www.gscloud.cn (accessed on 10 January 2019).
- Ridd, M.K. Exploring a v-i-s (vegetation-impervious surface-soil) model for urban ecosystem analysis through remote sensing: Comparative anatomy for cities. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1995, 16, 2165–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanapura, P.; Helder, D.L.; Burckhard, S.; Warmath, E.; O’Neill, M.; Galster, D. Mapping urban land cover using quickbird ndvi and gis spatial modeling for runoff coefficient determination. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2015, 73, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.C.; Jie, Y.W.; Zhang, L.L. An enhanced normalized difference impervious surface index. Sci. Surv. Mapp. 2018, 43, 83–87. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Li, X.T. Effects of New Characteristics of Landsat 8 Operational Land Imager (OLI) Data on Land-cover Remote Sensing Classification. J. Subtrop. Resour. Environ. 2015, 10, 79–86. [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsu, N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mapper, E. Er Mapper 6.0 User Guide; 922 oldal; Earth Resource Mapping Pty Ltd.: West Perth, Australia, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Rouse, J.W.J.; Haas, R.H.; Schell, J.A.; Deering, D.W. Monitoring vegetation systems in the great plains with erts. Nasa Spec. Publ. 1973, 351, 309–317. [Google Scholar]
- Huete, A.R. A soil-adjusted vegetation index (savi). Remote Sens. Environ. 1988, 25, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Q. Modification of normalised difference water index (ndwi) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcfeeters, S.K. The use of the normalized difference water index (ndwi) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.H. Machine Learning; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mohajerani, A.; Bakaric, J.; Jeffrey-Bailey, T.; Mohajerani, A.; Bakaric, J. The urban heat island effect, its causes, and mitigation, with reference to the thermal properties of asphalt concrete. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 197, 522–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Q.; Wang, M.Y. Remote sensing-based retrieval of ground impervious surfaces. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 20, 1270–1289. [Google Scholar]
- Jordan, C.F. Derivation of leaf-area index from quality of light on the forest floor. Ecology 1969, 50, 663–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, C.J. Red and photographic infrared linear combinations for monitoring vegetation. Remote Sens. Environ. 1979, 8, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.; Lan, X.J.; Wu, Z.G.; Chen, S.B. Monitoring analysis of heat island effects in Changshu city based on Landsat8. J. Jiangxi Univ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 37, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Li, Q.X.; Jiang, Z.H. Analysis of the Influence of Urban Heat Island Effect on Temperature Warming in Southeastern China. In Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Chinese Meteorological Society, Hangzhou, China, 13–16 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Song, C.; Woodcock, C.E.; Seto, K.C.; Lenney, M.P.; Macomber, S.A. Classification and change detection using landsat tm data: When and how to correct atmospheric effects. Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 75, 230–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
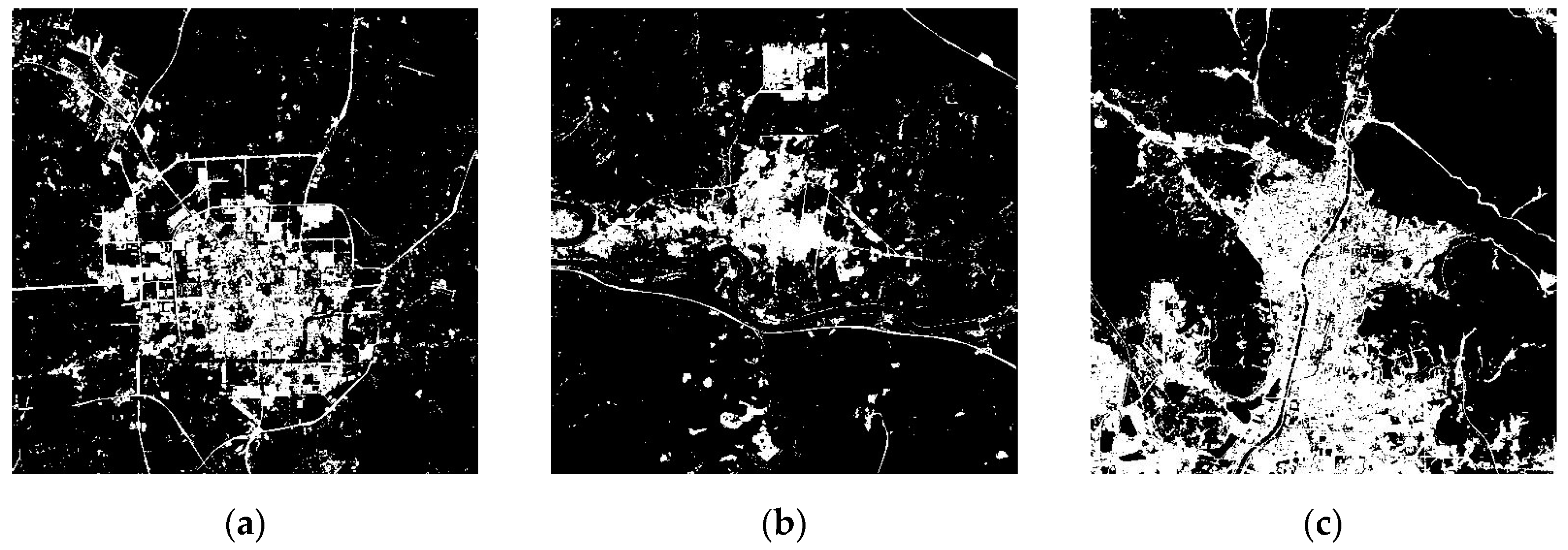
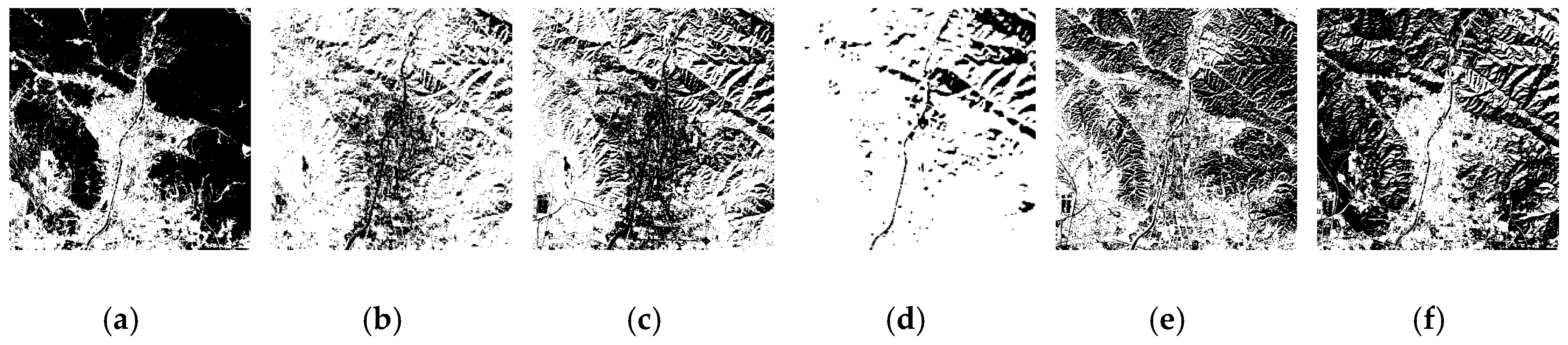
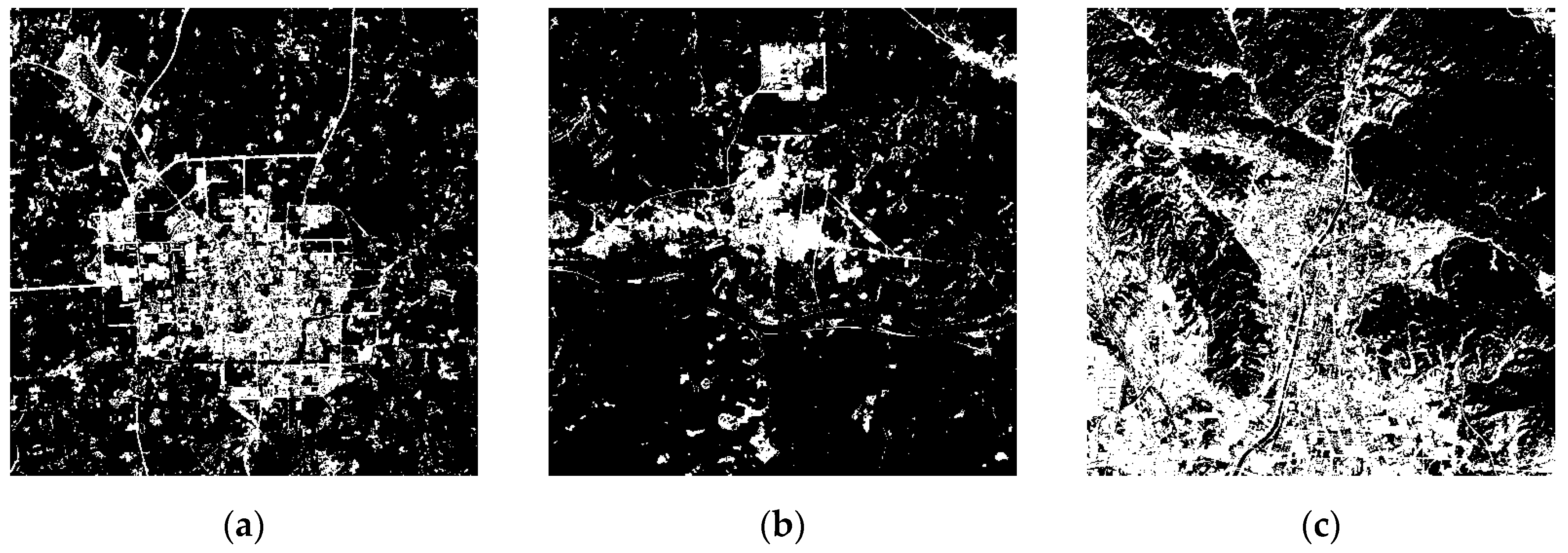
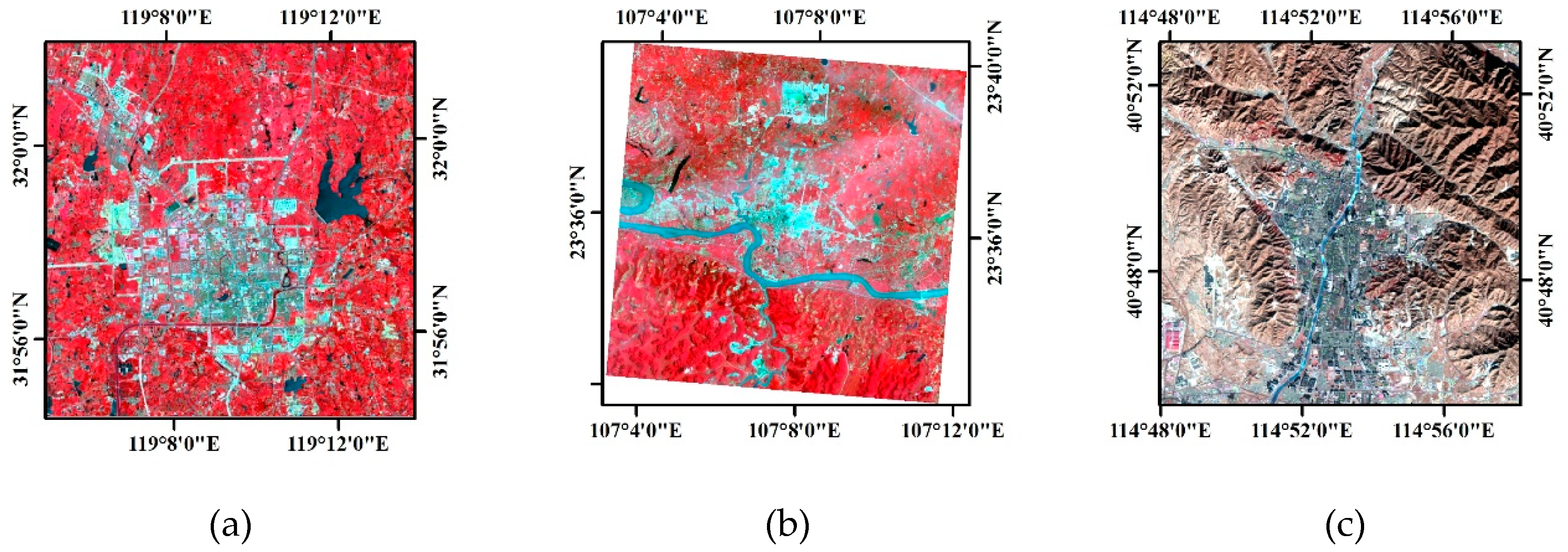







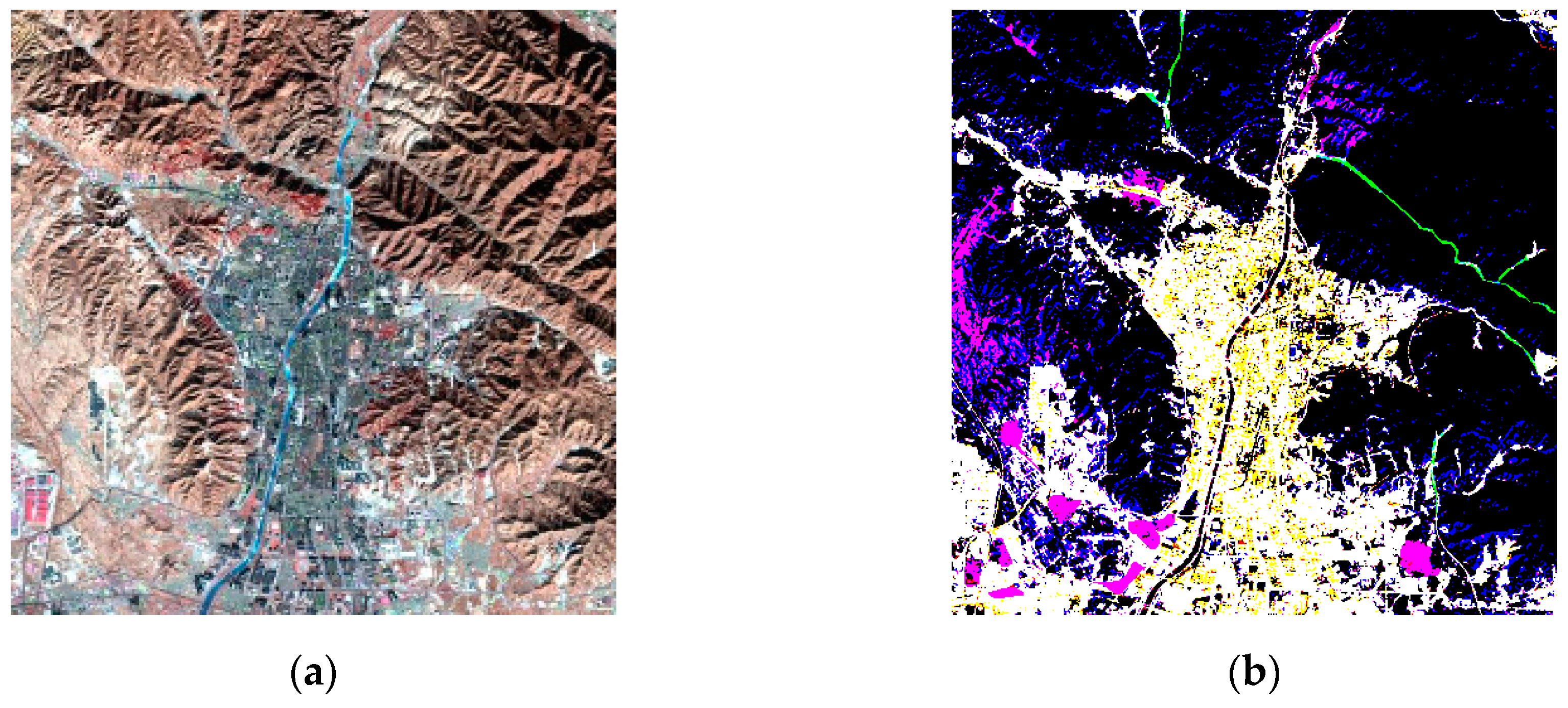
| Case | (5, 4, 3) False Colour Composite Images with a Linear Stretch of 2% | Images after Water Bodies were Masked by the WI | The Impervious Surface Distribution Extracted by the RISI |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  |  |  |
| 2 |  |  |  |
| 3 |  |  |  |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, H.; Wei, Y.; Dai, Q. A Novel Remote Sensing Index for Extracting Impervious Surface Distribution from Landsat 8 OLI Imagery. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2631. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9132631
Fang H, Wei Y, Dai Q. A Novel Remote Sensing Index for Extracting Impervious Surface Distribution from Landsat 8 OLI Imagery. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(13):2631. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9132631
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Hong, Yuchun Wei, and Qiuping Dai. 2019. "A Novel Remote Sensing Index for Extracting Impervious Surface Distribution from Landsat 8 OLI Imagery" Applied Sciences 9, no. 13: 2631. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9132631
APA StyleFang, H., Wei, Y., & Dai, Q. (2019). A Novel Remote Sensing Index for Extracting Impervious Surface Distribution from Landsat 8 OLI Imagery. Applied Sciences, 9(13), 2631. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9132631




