Featured Application
Energy harvesting is the principal application for Volume Holographic Optical Elements, thus promoting cheap solar concentrators applied for piped sunlight indoor illumination. Moreover, a further interesting potential application is in the aerospace sector where low weight holographic concentrators could be useful for recovering electricity in long missions or in space bases.
Abstract
Generally, to reduce the area of a photovoltaic cell, which is typically very expensive, solar concentrators based on a set of mirrors or mechanical structures are used. However, such solar concentrators have some drawbacks, as they need a tracking system to track the sun’s position and also they suffer for the overheat due to the concentration of both light and heat on the solar cell. The fundamental advantages of volume holographic optical elements are very appealing for lightweight and cheap solar concentrators applications and can become a valuable asset that can be integrated into solar panels. In this paper, a review of volume holographic-based solar concentrators recorded on different holographic materials is presented. The physical principles and main advantages and disadvantages, such as their cool light concentration, selective wavelength concentrations and the possibility to implement passive solar tracking, are discussed. Different configurations and strategies are illustrated and the state-of-the-art is presented including commercially available systems.
1. Introduction
Solar energy conversion processes provide clean, sustainable and renewable energy, thus there is a growing interest in research and development in the study of conversion systems and their cost effectiveness. An improvement in this sense needs simultaneous consideration of three issues: initial cost, durability-reliability and performance [1]. Considering the current technology, photovoltaic (PV) cells with triple-junction InGaAs are the most efficient (37%); nevertheless, their high cost makes them unattractive, even if their use for domestic applications, as well as in the aerospace industry, is desirable. This problem can be solved by using optical concentrators that allow focussing the sun’s rays onto the active solar cell area, thus letting to reduce a significant amount of the expensive PV material [2]. Consequently, in the last 15 years, solar concentration technologies were explored to direct all the available light towards small solar cells.
Currently, there are two principal types of concentrators involved in conversion technology: conventional solar concentrators (e.g., lenses or mirrors) and holographic solar concentrators. Holographic optical elements (HOEs) could in part overcome the limitations of the conventional solar concentrator, such as complex designs, thermal management due to the excessively heated of the solar cell when illuminated with concentrated solar radiation and active solar tracking. Additionally, holography is much more versatile and cheaper with respect to other concentrating optical systems.
In particular, volume holographic optical elements (V-HOEs) have been proposed for use as solar concentrators [3,4] thanks to the following features: (i) potential to achieve nearly 100% efficiency for certain wavelengths and directions; (ii) very rapid and low-cost effective manufacturing and easy customizability of the recorded devices; (iii) narrowness and lightness; (iv) potential to fabricate elements with multiple optical responses (multiplexing); and (v) potential to be very inexpensive in mass production. V-HOEs applications range from spectral splitting applications to increase the conversion efficiency of PV cells [3,5,6] to simultaneous concentration and spectral splitting applications [7].
Despite all these advantages offered by V-HOEs, currently only a few holographic concentrators, patented by Prism Solar Technologies [8], are on market. They work by total internal reflection by means of multiplexed gratings [9], have low cost (around 1 $/W) and are easy to be integrated into buildings [10]. Nevertheless, Prism Solar Modules are still under test and maybe this is the main reason for which this technology is not yet so diffused.
However, with the aim of obtaining high performance of V-HOEs as solar concentrators, it is necessary to keep in mind that volume holograms have high efficiency only when the incident rays vary in a given portion of the plane (angular selectivity) and their efficiency depends on the wavelength: it is high for a bandwidth centred on a wavelength determined by both the refractive index modulation obtained in the recording material and the angle of incidence (chromatic selectivity) [4]. Thus, V-HOEs should be designed to have a high efficiency for the spectrum of the sunlight inside the PV conversion range (for multijunction PV cells, 350 ÷ 1750 nm [11]).
It is worth noting that, due to the chromatic selectivity, the V-HOE diffraction efficiency depends on the wavelength [10]. Exploiting this feature, the heating of the cell, due to the solar spectrum region associated with wavelengths above 1200 nm, can be managed. Thus, one of the main problems of conventional solar concentrators can be overcome allowing a higher conversion efficiency and so lower cost/watt [12,13].
V-HOEs can be used as solar concentrators in both earth and space (satellites) applications. Regarding the first application, several studies are reported in the literature, whereas for aerospace applications only a few works are available [4,14,15,16], maybe due to the hostile space environment that has to be taken into account.
To obtain an efficient V-HOE as solar concentrator, the main requirements are: (i) the recording material, (ii) the concentration ratio, (iii) the angular selectivity, (iv) the possibility to implement the passive solar tracking, (v) the efficiency of single and multiplexed elements and (vi) the possibility to split the solar spectrum. The resulting system performance depends on each of these points. However, in our knowledge, the aforementioned focusing points required to achieve an efficient V-HOE as solar concentrator are never considered all together. Thus, we think that future researches should be focused on all of these features.
The purpose of the present manuscript is to give an overview of different solar concentrator based on volume holographic devices. Thus, after a brief introduction to the theory behind it and the recording materials commonly used, we analyse the configuration and the performance of several significant results reported in the literature.
2. Theoretical Background
Kogelnik’s theory [17] is widely accepted for modelling the performance of volume holograms. This theory shows that high diffraction efficiency can be related to some physical characteristics, such as thickness, spatial frequency and refractive index modulation. According to Kogelnik’s theory, the diffraction efficiency (η) can be theoretically evaluated as: [18]
where the parameters ξ and υ are defined as:
In Equations (2) and (3) d is the holographic film thickness, Δn is the refractive index modulation; λ is the wavelength of the reconstructing beam; θBragg is Bragg diffraction angle; Δθ is the deviation from the Bragg angle and is the grating vector, normal to the fringes with a magnitude , with Λ grating period:
here λ is the recording wavelength and Ɵ is the angle between the incident and diffracted angles inside the medium.
When the Bragg condition is satisfied, that is, Δθ = 0, the volume holographic grating (VHG) diffraction efficiency η can be theoretically evaluated as [17,19]:
Depending on the applications, the holographic optical element and in particular for solar applications the holographic lens, requires particular values of angular and/or wavelength selectivity. Due to the chromatic selectivity, hologram diffraction efficiency depends on wavelength; while regarding the angular selectivity, the hologram diffraction efficiency decreases very quickly when the direction of the incident radiation does not fulfil the Bragg condition in the recording plane [10]. It is important to point out that the main difference between conventional optics and holographic optics is that to determine diffracted ray direction, Snell’s law is replaced by the grating equation [20].
As expected, the angle at which the diffraction intensity reaches its maximum is strictly related to the incident wavelength [21]. In particular, the angle increases as the wavelength increases. This behaviour is due to Bragg phase-matching condition for VHG, which (considering a non-slanted transmission grating, i.e., gratings with a grating period vector forming an angle of 90° with the perpendicular to the plane of incidence) is defined as:
where are the magnitude of the incident and diffracted wave vectors inside the medium and angles θi, θd are the incident and diffracted angles inside the medium. is the grating vector defined above.
Generally, two regimes in which phase gratings operate are defined: the Raman-Nath regime, in which several diffracted waves are produced and the Bragg regime, where basically only one diffracted wave is formed and this occurs only for near Bragg incidence. It has been usual to refer to gratings that work in the Raman-Nath or the Bragg regimes as thin and thick gratings, respectively. A confirmation that the recorded hologram is a volume and not a surface hologram can be obtained by evaluating a parameter called Q factor. Indeed, the criterion for whether a hologram is thick or thin is given by the Q factor as:
where λ is the recording wavelength, d is the photosensitive layer thickness, n is the refraction index of the material and Λ is the fringe spacing. A holographic grating is considered to be thin (surface hologram) when Q ≤ 1, thick (volume hologram) when Q ≥ 10 [22].
Over the Q parameter, there is another parameter ρ defined as:
where Λ and Δn are defined before, λ0 is the vacuum wavelength of the light, n0 is the mean refractive index. This parameter can be used to predict whether a grating is in the Raman-Nath regime or in the Bragg regime: if ρ is nearly zero, the diffraction effect will be prominent, otherwise it can be neglected in the case where ρ very large [23].
3. V-HOE Recording Process
The simplest V-HOE is a VHG which acts as a non-focusing element; therefore, it basically redirects the light [21]. Usually, a hologram can be recorded by interference between two beams, namely reference and object beam, respectively. When the two interfering beams are two collimated light beams, a VHG can be recorded. A scheme of the experimental setup typically used to record VHGs is shown in Figure 1a; the angle α between two incident beams is related to the final grating period of the recorded VHG. The interference fringe pattern leads to a photoinduced modulation of the refractive index in a photosensitive thick film.
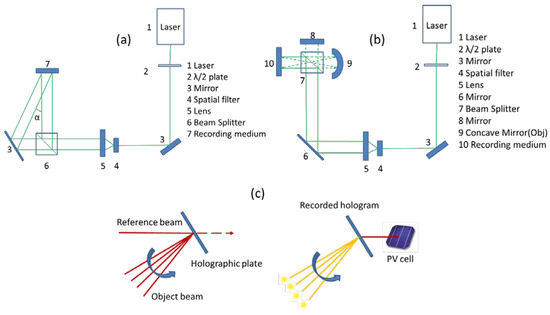
Figure 1.
(a) Set-up for volume holographic grating recording; (b) Set-up for volume phase holographic lenses recording; (c) Schematic representation of the recording of multiplexed holographic lenses: the reference beam is fixed while the object beam incident angle is changed during the process. The multiplexed holographic lenses recorded behaves like a passive solar tracker: the light coming from the sun in different positions, that is, at different times of the day, is always focused on the same point, where a photovoltaic cell is positioned.
When in the object beam path a focusing optics is placed during the recording process, the interference between a reference (collimated) beam and an object (converging) beam is induced. Thus, an interferometric pattern that replaces the response of the focusing optical systems used as object is generated, obtaining a V-HOE that acts as a focusing element. This V-HOE shows the same effect as spherical or cylindrical lenses [4,24]. A typical recording setup is reported in Figure 1b.
Conventional concentration modules need the aid of complex mechanical systems (active solar tracking) to improve their efficiency. These aiding systems increase the complexity of the PV cell power system design, the panel volume and development costs. The possibility to reduce or even eliminate, the moving system using multiplexed holographic lenses as passive solar trackers, makes the system more competitive in the perspective of new generation solar panel development. As a result, there are fewer problems related both to the wear of moving parts and possible vibrations due to movements [16]. Multiplexed V-HOEs can be achieved by changing the angle between the two incident wavefronts during the writing process, as schematically shown in Figure 1c. In this way, a V-HOE that addresses the solar radiation incident with different angles, on a single photovoltaic cell, can be realized.
4. Holographic Materials for Solar Concentrators
The holographic recording medium should be able to resolve fully all the fringes resulting from interference between the two incident beams. These fringe spacing can range from tens of micrometres to less than one micrometre, corresponding to spatial frequencies in the range of a few hundred to several thousand cycles/mm. If the performance of the recording medium for these spatial frequencies is low, the diffraction efficiency of the hologram will be poor.
Currently, to record a V-HOE several photosensitive materials can be used, among them substrates based on silver halide emulsions, dichromatic gelatines and photopolymers are the most widely used.
4.1. Silver Halide Emulsions
Silver halide emulsion is one of the oldest recording materials for holography. It is a fine suspension of microscopic grains of silver halide (usually silver bromide, grain size in the range of tens of nanometres) in a colloid sol, usually consisting of gelatin. Typically, a layer of emulsion with a thickness in the range of 5 to 15 µm, is coated onto glass or film substrate. The recorded image is then developed by chemical post-processing, allowing multiple holograms recording. Additionally, emulsions show high sensitivity (10−5 to 10−3 mJ/cm2) and good resolution (greater than 6000 lines/mm).
Silver halide emulsions were recently used to obtain a panchromatic holographic material for the fabrication of wavelength multiplexed holographic solar concentrators [25].
4.2. Dichromatic Gelatines
Dichromatic gelatine (DCG) is composed of ammonium or potassium dichromate, gelatin and water and needs chemical post-processing. Ammonium dichromate becomes progressively harder on exposure to light, inducing high refractive index modulation, thus allowing high diffraction efficiency, high resolution, low noise and high optical quality [26,27,28]. The drawback of DCG is its low exposure sensitivity and limited spectral response.
Even if DCG can be considered an ideal recording material for volume phase holograms, it is very sensitive to environmental changes, therefore it requires a cover plate to ensure environmental stability thus weighting the structure [29]. This reason makes it virtually less eligible for solar concentration applications.
4.3. Photopolymers
Photopolymers are the most studied holographic materials since the 1970s; they are based on polymerization and cross-linking reactions induced by absorption of light and they offer several advantages respect to silver halide and DCG. Indeed, photopolymerizable materials show high diffraction efficiencies, allow real-time monitoring of the recording process, do not require development processes but only a bleaching process, can be produced from raw materials at low cost and give the possibility to modulate the properties through chemical synthesis [4]. Additional, photopolymers can be mass produced allowing to reducing production costs [30,31].
Typically, a photopolymer is made from a photoinitiator system, one or more polyfunctional monomers or oligomers and a polymeric binder. When it is exposed to light, the polymerization occurs in the areas of constructive interference (high-light intensity areas) leading to increased consumption of the monomers, while the polymerization is limited or absent in the areas of destructive interference (low-light intensity areas). The difference of monomer consumption rate leads to a concentration gradient that drives monomer diffusion from dark to illuminated areas [32,33,34]. Thus, the polymer concentration distribution will take over the sinusoidal pattern of the light intensity, resulting in a permanent modulation of the refractive index, that is, a volume-phase hologram.
Some examples of the most commonly used photopolymers as recording material for holography are: (i) a photopolymer developed within Bayer MaterialScience based upon an orthogonal two chemistry formulation; it is capable of achieving transmission above 90% in the film samples [35]; (ii) photopolymer materials developed by DuPont for recording volume phase holograms, in particular new materials with panchromatic sensitivity, designed for multicolour holographic recording have been developed [36]; (iii) acrylamide-based photopolymers have also been extensively used for fabrication of HOEs in solar energy applications [37].
Regarding the resistance of these materials for holographic concentrators in environmental conditions, there are durability tests on some of the most widely used photopolymers in conventional Fresnel-type solar concentrators, such as acrylic polymers [38].
The fabrication of lenses for concentrators and protective layers for photovoltaic cells is often made by using polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) [39] since it allows a good resistance to UV radiation and high transmittance (>92%). The UV sensitivity can be further reduced by introducing protective layers or by adding radical scavengers or antioxidants to the formulation of the material. Also polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) shows very high stability against UV radiation and making it suitable for use in the space environment [40]. Additional, PDMS features greater optical transmittance compared to PMMA.
Considering all the advantages offered by photopolymeric materials, to obtain solar compliant holographic materials that should be less sensitive to thermal and photochemical degradation phenomena, the study of new photopolymers based on inorganics or hybrid organic/inorganic components instead of organic material is still in progress. Some examples in this sense are photopolymers containing nanoparticles of inorganic species such as SiO2, ZrO2 and TiO2 [41], that show a lower shrinkage due to the polymerization and a higher refractive index modulation [42,43] and photopolymer containing zeolite nanocrystals as inorganic dopant, that allows to improve compatibility between inorganic particles and polymer and reduce the optical losses due to scattering [44]. Finally, the sol-gel chemistry versatility allows obtaining a high level of interpenetration between the organic and inorganic networks, as reported in Refs. [4,45,46,47]. Photopolymer with a very low outgassing level and a high resistance to strong thermal excursions, that can be useful for some applications, was obtained by sol-gel techniques [4].
5. V-HOE Based Solar Concentrators
5.1. Solar Concentrator and Spectral Splitting
Since the pioneering work published by Ludman in 1982 [48], V-HOEs have been proposed as solar concentrators; additionally, by using DCG as a recording material, they have been employed to obtain a spatial separation of the solar spectrum allowing the use of solar cell materials with optimized band gaps achieving high PV efficiency [3,49]. Moreover, an optimized holographic concentrating and spectral splitting systems can reduce the cooling requirements of the photovoltaic cells and, considering V-HOE design versatility, PV cells can be placed on a side of the hologram, thus avoiding shadow effects and simplifies cooling, as can be seen in Figure 2 [5,50]. In this case, the hologram not only concentrates the solar radiation but also split and directs the red and near-infrared spectrum on one PV cell and the green and blue spectrum on another one, while the far-infrared wavelengths of the solar spectrum are diffracted away from the cells, reducing the main cause of overheating.
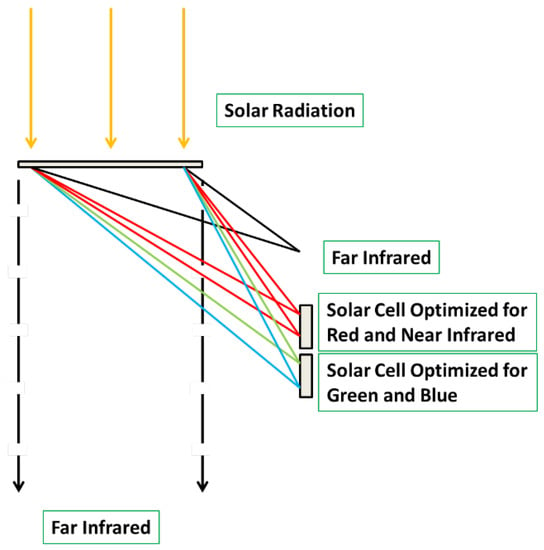
Figure 2.
Holographic solar concentrator with spectral splitting systems [5,50].
The authors also demonstrated that this holographic system concentrates higher power than a Fresnel-based solar concentrator and shows a larger relative efficiency; additionally, large heat sinks are not required leading to a decrease of both the bulk and the cost.
With the aim of providing a holographic solar concentrator that reduces solar cell exposure to harmful radiations, Okorogu et al. [51] patented a structure composed of hybrid transmission and reflection VHOEs that spectrally and spatially separate the incident solar spectrum into component wavelength bands. Using internal reflection, the separated solar radiation is propagated through a waveguide far away from the incident direction. At the end of the waveguide, band selection reflecting HOEs inject the solar radiation into PV cells of appropriate band gap energies.
5.2. Multiplexed Hologram
To improve the angular selectivity, multiplexed solutions have been considered. Bainier et al. [7] reported a detailed study on superimposed transmission holograms recorded on the same holographic medium based on DCG. In particular, the authors compared a system consisting of a single holographic element as a concentrator with the maximum of reconstruction wavelength (620 nm) centred in the middle of the range of the PV cell (i.e., 500–800 nm) and a system composed of two holographic recordings with the two maximum reconstruction wavelengths (514.5 and 620 nm) designed both to overlap the operating spectrum of the PV cell (GaAs with an efficiency of 23%) and to avoid the coupling effect. Both the reflecting and transmitting version for the double hologram system were characterized, with one of the two holograms superimposed on the same holographic medium in the transmission configuration. Theoretical and experimental evaluation of the energy efficiency of the holographic systems were carried out. Values of 6 and 5% for the single holographic elements and of 11 and 9% for the double holographic element were obtained, respectively.
A newsworthy structure with a double superimposed slanted reflecting hologram tilted of 30° and recorded on DCG by using 488 and 632 nm laser sources, was proposed in 2010 [52]. This geometry gives rise to a total internal reflection at the surfaces of the holographic medium. The PV cells were placed at the edges of the holographic plate where the collected light emerges. A sketch of the experimental set-up used for the doubly slanted layer structures is reported in Figure 3a, while the diffraction pattern of normally incident white light for the doubly slanted hologram is showed in Figure 3b,c.
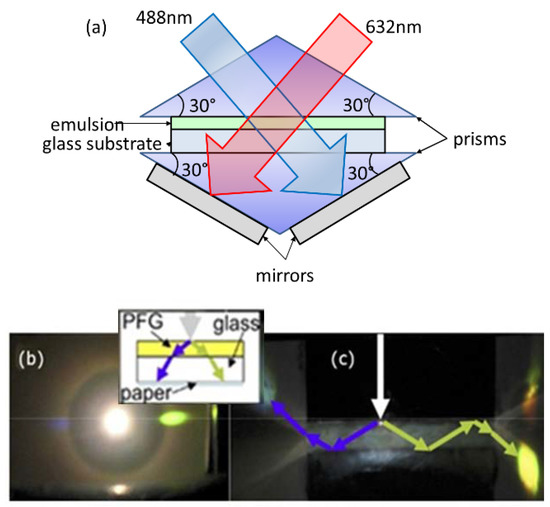
Figure 3.
(a) A schematic representation of the experimental set-up used in Reference [52] for the doubly slanted layer structure. Red and blue arrows are the incident laser sources emitting at 632 nm and 488 nm, respectively, used to record the double superimposed slanted reflecting hologram. Diffraction patterns evaluated taken from behind (b) and above (c). Here, the arrow represents the incident light.
Lee’s group [53] realized an angular multiplexed HOE recorded on a photopolymer. They optimized a suitable recording method for an angular multiplexed HOE solar concentrator and find that by using the iterative recording method, the low efficiency of multiplexed holograms due to overexposure is compensated. Moreover, the authors evaluated the performance of the HOE as a solar concentrator by introducing a new efficiency calculation method, named concentrated diffraction efficiency (CDE), that is considered as the percentage ratio between the effective concentration rate (ECR) of the HOE and the ECR of the convex lens used in the recording process. The fabricated HOE that uses the modified iterative recording method shows CDEs of 26.73%, 35.31% and 22.78% from incidence angles −10°, 0° and +10°, respectively. These values are considerably higher than those obtained considering multiplexed holograms recorded with equal exposure time without considering the saturation time.
Naydenova et al. recorded a focusing HOE as well as multiplexed gratings on an acrylamide-based photopolymer. High diffraction efficiency HOE consisting of a single spherical lens using thin layers and lower spatial frequency was recorded and a larger acceptance angle was obtained respect to the optical component. Regarding the multiplexed geometry, the authors calibrated the intensity of the beam and then the exposure energy to obtain high efficiency. A diffraction efficiency of three multiplexed gratings at 51.9 ± 3.5% was demonstrated [54].
5.3. Holographic Solar Deflector
In 2010, Castro et al. [9] designed and characterized a holographic grating, recorded on dichromatic emulsion, able to deflect the direct sunlight on a PV cell with the higher energy efficiency possible. A detailed study of the effects of incident spectra that vary hourly, daily and seasonally was performed, and, in order to maximize the energy collection efficiency per year, the authors proposed the structure illustrated in Figure 4a. The designed cell is composed by two cascaded holographic grating on each side of the PV cell (holograms A and B), that are conjugated (i.e., A and A’ or B and B’) to provide peak energy collection at different seasons.
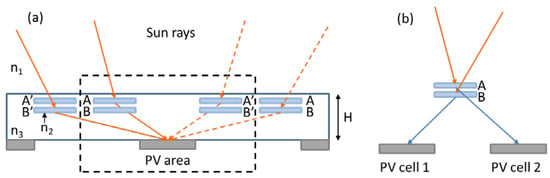
Figure 4.
(a) Holographic solar concentrator structure realized by Castro et al. [9]. In the dashed box the unit cell is highlighted. (b) Holographic design to reduce the optical crosstalk.
The optical crosstalk of the V-HOEs was reduced by designing the two cascaded holograms to diffract light in opposite directions with the incident angles in different quadrants of the Bragg circle (Figure 4b). To guarantee that maximum of the diffracted rays of the sunlight within the solar responsivity spectrum of PV cell can reach the surface of the cell independently of the incident angle, the geometrical parameters of the system (i.e., the hologram width and the distance hologram-PV cell) have been optimized, too. Results reported an average daily energy increase of 147% due to the concentrator and approximately 50% of the total energy that reaches the hologram areas can be collected by PV cells without the need of tracking.
An interesting application of V-HOE-based solar concentrator for solar control of domestic conservatories and sunrooms was published in 2005 [55]. In particular, selective use of HOE with given working angles is predicted to maintain the daytime temperatures to an acceptable level when only 62% of glazed the area is used with HOE. Additionally, thanks to the angular selectivity of the V-HOEs, during the winter months theoretically none of the incident beam radiation is attenuated allowing to obtain a comfortable temperature.
5.4. Cylindrical Holographic Lenses
Cylindrical holographic lenses, that allow obtaining a compact and wide-angle structure, were also considered as a solar concentrator. With the aim to take into account a specific set of designed parameter, such as bandwidth, angular selectivity, PV cell size, optical polarization and so on, a proper simulation tool has been developed [10,13]. The possibility to realize a high-efficient system that only requires one-axis tracking was demonstrated.
An interesting application of cylindrical holographic lenses is reported in Figure 5a where the conceptual recording set-up is illustrated [56]. Here, the reference and object beams are an edge-lit and a cylindrical converging beam, respectively, allowing to simultaneously record a combination of a lens and a mirror. An array of V-HOEs is then recorded simply by shifting the medium and by repeating the recording process; this method allows having a large angular acceptance. In fact, the diffracted wave of the incident sunlight coming from different incident angles is guided to the edge of the recording medium where a PV cell is positioned (Figure 5b). When a 2 mm thick holographic recording material (phenanthrenequinone doped PMMA photopolymer) was used to record the proposed architecture, the collection angle from increases 0.01° to 6°.
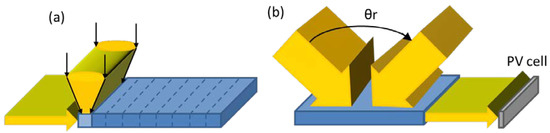
Figure 5.
(a) Recording set-up and (b) configuration of volume holographic concentrator [56].
Recently, Marin-Saez et al. [57] theoretically and experimentally explored a novel approach to overcoming the problem related to the V-HOEs chromatic selectivity by using HOEs operating in the transition regime, which led to a lower chromatic selectivity while maintaining rather high efficiencies. In particular, they developed a model that takes into account the recording material’s response to evaluate the index modulation reached for different spatial frequency and exposure dosage. Three cylindrical holographic lenses with different spatial frequency ranges were recorded in Bayfol HX photopolymer to experimentally validate the method. Promising results were obtained when a system composed of two cylindrical holographic lenses with lower spatial frequencies and a mono-c Si PV cell is implemented (see Figure 6). Indeed, a total current intensity of 3.72 times respect that would be reached without the concentrator was achieved.
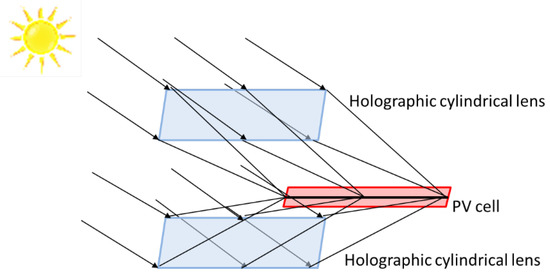
Figure 6.
Schematic of the system considered: each cylindrical holographic lens redirects sun rays towards a PV cell [48].
5.5. Commercial and Space Holographic Concentrators
Regarding commercial systems that make use of holographic concentrators, the best performing solutions are offered by Prismsolar, which propose patented enhanced glass-on-glass holographic modules composed of highly efficient bifacial N-type silicon cells with holographic technology. A single module is made alternating strips of bifacial solar cells with parallel strips of holographic film. It allows to collect not only the light that hits the solar cells directly, as normally occurs but also the light that hits the holographic film, which diffracts the light and a portion of this light is guided to the cell through total internal reflection, thus increasing the total harvested sunlight [8,58].
Finally, as a possible future application, taking into account their thin, lightweight and flexible, holographic elements can be studied, designed and fabricated for space solar concentrators. In fact, the solar power conversion is the primary power source for most of the satellite and loss of power, even for a short time, can lead to catastrophic consequences [50]. Thus, an enhancement of the collected light is desirable. Of course, in the space the holographic materials must be able to withstand much more drastic conditions respect to earth applications, due to strong thermal excursions, high vacuum and the presence of high-energy gamma, electronic and protonic radiation originating from the solar wind [4,46,47].
6. Conclusions and Perspectives
The growing demand for new devices able both to improve the harvested sunlight by a PV cell and to reduce the amount of expensive PV material is the main motivation of this work.
In this field, the goal is to find and develop solar concentrators that can overcome the limit presented by conventional solar concentrators, such as active solar tracking, overheating induced on the PV cell, cost and size. With this aim, V-HOEs seem to be the best candidate, satisfying, at the same time, various technological and economic requirements. In fact, V-HOEs can be recorded very easily and allow superimposed structures permitting passive solar tracking. Moreover, a key factor for an efficient V-HOE is the recording material; currently, the most used are silver halides, dichromate gelatins and photopolymers. However, the development of new holographic recording materials is an on ongoing research field; for solar applications this study must be guided by a clear understanding of the behaviour of these new materials in given environmental conditions, that are different for earth and space applications.
In this review, the state of the art of V-HOE based solar concentrators is reported. A number of investigations regarding V-HOE recorded on different material and with different geometry have been described and discussed. However, there is a crucial point that we want to highlight: despite the literature, only a few commercial solutions are available for earth applications, while, to date no hologram solar concentrator has been used for space applications.
Considering the increasing need to obtain clean, renewable and sustainable energy for the welfare of the whole planet and the stringent requirements to reduce area, weight and footprint occupied by photovoltaic cells for space missions, V-HOEs with their low cost for mass production, planar configuration, high efficiency with self-tracking and easy installation, can play a significant role in solar energy conversion applications. Thus, we strongly encourage new research in this field.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.A.F., V.S. and G.C.; writing—original draft preparation, M.A.F., V.S. and G.C.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Call, P.J. Overview of solar energy conversion technologies: Quantum processes and thermal processes. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1982, 53, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, V.J. Power and propulsion at NASA Glenn Research Center: Historic perspective of major accomplishments. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2013, 26, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloss, W.H.; Griesinger, M.; Reinhardt, E.R. Dispersive concentrating systems based on transmission phase holograms for solar applications. Appl. Opt. 1982, 21, 3739–3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, M.A.; Bianco, G.; Borbone, F.; Centore, R.; Striano, V.; Coppola, G. Volume holographic optical elements as solar concentrators. In Holographic Materials and Optical Systems; Naydenova, I., Ed.; InTechOpen: London, UK, 2017; pp. 27–50. ISBN 978-953-51-3038-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludman, J.; Riccobono, J.; Reinhand, N.; Semenova, I.; Martin, J.; Tai, W.; Li, X.L. Holographic solar concentrator for terrestrial photovoltaics. In Proceedings of the 1994 IEEE First World Conference on Photovoltaic Energy Conversion, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 5–9 December 1994; IEEE: Waikoloa, HI, USA, 1994; pp. 1212–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imenes, A.G.; Mills, D.R. Spectral beam splitting technology for increased conversion efficiency in solar concentrating systems: A review. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2004, 84, 19–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bainier, C.; Hernandez, C.; Courjon, D. Solar concentrating systems using holographic lenses. Sol. Wind Technol. 1988, 5, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prismsolar. Prism Solar Technologies. Available online: http://www.prismsolar.com (accessed on 1 December 2018).
- Castro, J.M.; Zhang, D.; Myer, B.; Kostuk, R.K. Energy collection efficiency of holographic planar solar concentrators. Appl. Opt. 2010, 49, 858–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemisana, D.; Collados, M.V.; Quintanilla, M.; Atencia, J. Holographic lenses for building integrated concentrating photovoltaics. Appl. Energy 2013, 110, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimroth, F.; Karam, N.H.; Ermer, J.H.; Haddad, M.; Colter, P.; Isshiki, T.; Yoon, H.; Cotal, H.L.; Joslin, D.E.; Krut, D.D.; et al. Next generation GaInP/GaInAs/Ge multi-junction space solar cells. In Proceedings of the 17th European Photovoltaic Solar Energy Conference, Munich, Germany, 22–26 October 2001; ETA: Florence, Italy; WIP: Munich, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Riccobono, J.R.; Ludman, J.E. Solar holography. In Holography for the New Millennium; Ludman, J., Caulfield, H.J., Riccobono, J., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 157–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios, P.B.; Álvarez-Álvarez, S.; Marín-Sáez, J.; Collados, M.V.; Chemisana, D.; Atencia, J. Broadband behavior of transmission volume holographic optical elements for solar concentration. Opt. Express 2015, 23, A671–A681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renk, K.; Jacques, Y.; Felts, C.; Chovit, A. Holographic Solar Energy Concentrators for Solar Thermal Rocket Engines; No. NTS-6006; NTS Engineering: Long Beach, CA, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Loicq, J.; Venancio, L.M.; Stockman, Y.; Georges, M.P. Performances of volume phase holographic grating for space applications: Study of the radiation effect. Appl. Opt. 2013, 52, 8338–8346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, G.; Ferrara, M.A.; Borbone, F.; Roviello, A.; Pagliarulo, V.; Grilli, S.; Ferraro, P.; Striano, V.; Coppola, G. Multiplexed holographic lenses: Realization and optical characterization. In Proceedings of the 17th Italian Conference on Photonics Technologies, Fotonica AEIT 2015, Turin, Italy, 6–8 May 2015; IET: Stevenage, UK, 2015; Volume 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogelnik, H. Coupled-wave theory of thick hologram gratings. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1969, 48, 2909–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.; Akbari, H.; Keshri, S.; Bade, D.; Naydenova, I.; Murphy, K.; Toal, V. Holographically Recorded Low Spatial Frequency Volume Bragg Gratings and Holographic Optical Elements. In Holographic Materials and Optical Systems; Naydenova, I., Ed.; InTechOpen: London, UK, 2017; Chapter 4; pp. 73–98. ISBN 978-953-51-3038-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, J.W. Introduction to Fourier Optics, 2nd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1996; ISBN 978-0974707723. [Google Scholar]
- Close, D.H. Holographic Optical Elements. Opt. Eng. 1975, 14, 408–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barden, S.C.; Arns, J.A.; Colburn, W.S. Volume-phase holographic gratings and their potential for astronomical applications. Proc. SPIE 1998, 3355, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kress, B.C.; Meyureis, P. Applied Digital Optics: From Micro-Optics to Nanophotonics; John Wiley & Sons: Chippenham, UK, 2009; 638p, ISBN 978-0-470-02263-4. [Google Scholar]
- Moharam, M.G.; Young, L. Criterion for Bragg and Raman-Nath diffraction regimes. Appl. Opt. 1978, 17, 1757–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leutz, R.; Suzuki, A. Solar concentration in space. In Nonimaging Fresnel Lenses: Design and Performance of Solar Concentrators; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; pp. 246–256. ISBN 978-3-540-45290-4. [Google Scholar]
- Vadivelan, V. Recording of holographic solar concentrator in ultra-fine grain visible wavelength sensitive silver halide emulsion. Am. J. Electron. Commun. 2015, 2, 15–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hull, J.; Lauer, J.; Broadbent, D. Holographic solar concentrators. Energy 1987, 12, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, J.A.; Boj, P.G.; Crespo, J.; Pardo, M.; Satorre, M.A. Line-focusing holographic mirrors for solar ultraviolet energy concentration. Appl. Opt. 1997, 36, 3689–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, R.; Khan, A.; Chakraborty, N.R.; Yadav, H.L. Use of holographic lenses recorded in dichromated gelatin film for PV concentrator applications to minimize solar tracking. In Energy Problems and Environmental Engineering; Perlovsky, L., Dionysiou, D.D., Zadeh, L.A., Kostic, M.M., Gonzalez-Concepcion, C., Jaberg, H., Sopian, K., Eds.; WSEAS Press: Athens, Greece, 2009; pp. 49–52. ISBN 978-960-474-093-2. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, B.J. Dichromated Gelatin Holograms and Their Applications. Opt. Eng. 1980, 19, 195642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruder, F.K.; Fäcke, T.; Grote, F.; Hagen, R.; Hönel, D.; Koch, E.; Rewitz, C.; Walze, G.; Wewer, B. Mass Production of Volume Holographic Optical Elements (vHOEs) Using Bayfol® HX Photopolymer Film in a Roll-to-Roll Copy Process. In Practical Holography XXXI: Materials and Applications, Proceedings of the SPIE, San Francisco, CA, USA, 6 April 2017; SPIE: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; Volume 10127, pp. 101270A-1–101270A-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vather, D.; Naydenova, I.; Cody, D.; Zawadzka, M.; Martin, S.; Mihaylova, E.; Curran, S.; Duffy, P.; Portillo, J.; Connell, D.; et al. Serialized holography for brand protection and authentication. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, E131–E137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Mouroulis, P. Diffusion model of hologram formation in dry photopolymer materials. J. Mod. Opt. 1994, 41, 1929–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackey, D.; O’Reilly, P.; Naydenova, I. Theoretical modelling of the effect of polymer chain immobilization rates on holographic recording in photopolymers. JOSA A 2016, 33, 920–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleeson, M.R.; Sheridan, J.T.; Bruder, F.K.; Rölle, T.; Berneth, H.; Weiser, M.S.; Fäcke, T. Comparison of a new self developing photopolymer with AA/PVA based photopolymer utilizing the NPDD model. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 26325–26342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurbergs, D.; Bruder, F.K.; Deuber, F.; Fäcke, T.; Hagen, R.; Hönel, D.; Rölle, T.; Weiser, M.S.; Volkov, A. New recording materials for the holographic industry. Proc. SPIE 2001, 7233, 72330K-1–72330K-10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, S.H. DuPont multicolor holographic recording films. Proc. SPIE 1997, 3011, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, H.; Naydenova, I.; Martin, S. Using Acrylamide Based Photopolymers for Fabrication of Holographic Optical Elements in Solar Energy Applications. Appl. Opt. 2014, 53, 1343–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, D.C.; Kurtz, S.R. Durability of Fresnel lenses: A review specific to the concentrating photovoltaic application. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2011, 95, 2037–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schissel, P.; Jorgensen, G.; Kennedy, C.; Goggin, R. Silvered-PMMA reflectors. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 1994, 33, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dever, J.A.; Banks, B.A.; Yan, L. Effects of vacuum ultraviolet radiation on DC93-500 silicone. J. Spacecr. Rocket. 2006, 43, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaia, R.A.; Dennis, C.L.; Natarajan, L.V.; Tondiglia, V.P.; Tomlin, D.W.; Bunning, T.J. Onestep, micrometer-scale organization of nano- and mesoparticles using holographic photopolymerization: A generic technique. Adv. Mater. 2001, 13, 1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Jun-He, H.; Ruo-Ping, L.; Long-Ge, W.; Ming-Ju, H. Resisting shrinkage properties of volume holograms recorded in TiO2 nanoparticle-dispersed acrylamide-based photopolymer. Chin. Phys. B 2013, 22, 124207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, N.; Tomita, Y.; Ohmori, K.; Hidaka, M.; Chikama, K. Highly transparent ZrO2 nanoparticle-dispersed acrylate photopolymers for volume holographic recording. Opt. Express 2006, 14, 12712–12719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moothanchery, M.; Naydenova, I.; Mintova, S.; Toal, V. Nanozeolites doped photopolymer layers with reduced shrinkage. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 25786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheben, P.; del Monte, F.; Levy, D.; Belenguer, T.; Nuñez, A. Holographic diffraction gratings recording in organically modified silica gels. Opt. Lett. 1996, 21, 1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianco, G.; Ferrara, M.A.; Borbone, F.; Roviello, A.; Pagliarulo, V.; Grilli, S.; Ferraro, P.; Striano, V.; Coppola, G. Volume Holographic Gratings: Fabrication and Characterization. Proc. SPIE 2015, 9508, 950807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, G.; Ferrara, M.A.; Borbone, F.; Roviello, A.; Striano, V.; Coppola, G. Photopolymer-based volume holographic optical elements: Design and possible applications. J. Eur. Opt. Soc. 2015, 10, 15057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludman, J. Holographic solar concentrator. Appl. Opt. 1982, 21, 3057–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frohlich, K.; Wagemann, U.; Schulat, J.; Schutte, H.; Stojanoff, C.G. Fabrication and test of a holographic concentrator for two color PV-operation. Proc. SPIE 1994, 2255, 812–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludman, J.E.; Riccobono, J.; Semenova, I.V.; Reinhand, N.O.; Tai, W.; Li, X.; Syphers, G.; Rallis, E.; Sliker, G.; Martín, J. The optimization of a holographic system for solar power generation. Sol. Energy 1997, 60, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okorogu, A.O.; Marvin, D.C.; Liu, S.H.; Prater, A. Holographic Solar Concentrator. U.S. Patent 2010/0186818A1, 29 July 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, J.; Chan, P.S.; Sun, C.; Ho, C.W.; Tam, W.Y. Doubly slanted layer structures in holographic gelatin emulsions: Solar concentrators. J. Opt. 2010, 12, 045104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Wu, H.-Y.; Piao, M.-L.; Kim, N. Holographic Solar Energy Concentrator Using Angular Multiplexed and Iterative Recording Method. IEEE Photonics J. 2016, 8, 8400511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naydenova, I.; Akbari, H.; Dalton, C.; Yahya, M.; Pang Tee Wei, C.; Toal, V.; Martin, S. Photopolymer Holographic Optical Elements for Application in Solar Energy Concentrators. In Holography—Basic Principles and Contemporary Applications; Mihaylova, E., Ed.; InTechOpen: London, UK, 2013; pp. 129–145. ISBN 978-953-51-1117-7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, P.A.B.; Bahaj, A.S. Holographic optical elements: Various principles for solar control of conservatories and sunrooms. Sol. Energy 2005, 78, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, M.; Lin, S.; Hsu, K.Y.; Burr, J.; Lin, S. An efficient solar concentrator using volume hologram. In CLEO:2011–Laser Applications to Photonic Applications, OSA Technical Digest; Optical Society of America: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2011; p. PDPB8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin-Saez, J.; Atencia, J.; Chemisana, D.; Collados, M.V. Full modeling and experimental validation of cylindrical holographic lenses recorded in Bayfol HX photopolymer and partly operating in the transition regime for solar concentration. Opt. Express 2018, 26, A398–A412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- aSolarus. Bifacial Solar PV. Available online: http://www.asolarus.com/product-distribution/bifacial-solar-pv/#prettyPhoto (accessed on 1 December 2018).
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).