Multiple Signal Classification-Based Impact Localization in Composite Structures Using Optimized Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Optimized EEMD Based 2D-MUSIC Method
2.1. 2D-MUSIC Algorithm for Impact Localization
2.2. Fast EEMD for Impact Signal Extraction
- Throughout the whole length of a single IMF, the number of extrema (maxima and minima) and the number of zero-crossings must either be equal or differ at most by one, i.e.,
- At any time point , the mean value of the envelope and respectively defined by the local maxima and the local minima are zero, i.e.,where is the time interval.
- Identify all the local maxima and minima and connect all of them using a cubic spline as the upper and lower envelope and , respectively. Then, calculate the mean value of and as
- Obtain the first component by taking the difference between the data and the local mean as
- Treat as the data and repeat steps 1 and 2 as many times as is required until the two properties of IMF as shown in Equations (4) and (5) are satisfied. Then, the final is designated as an IMF .
- Treat , () as the data and repeat steps 1–3. Finally, we obtain additional IMFs and the final residual , which are represented by Equation (3).
- Add a white noise series (noise level is Nl) to the targeted data and decompose the data with added white noise into IMFs aswhere and q is the average time (ensemble number).
- Repeat step1 q times with different white noise series .
- Obtain the (ensemble) means of corresponding IMFs of the decompositions as the final result, that iswhere is the jth IMFs of EEMD decomposition asand is the final residual of EEMD decomposition as
2.3. Impact Localiaztion Process
3. Experimental Investigations
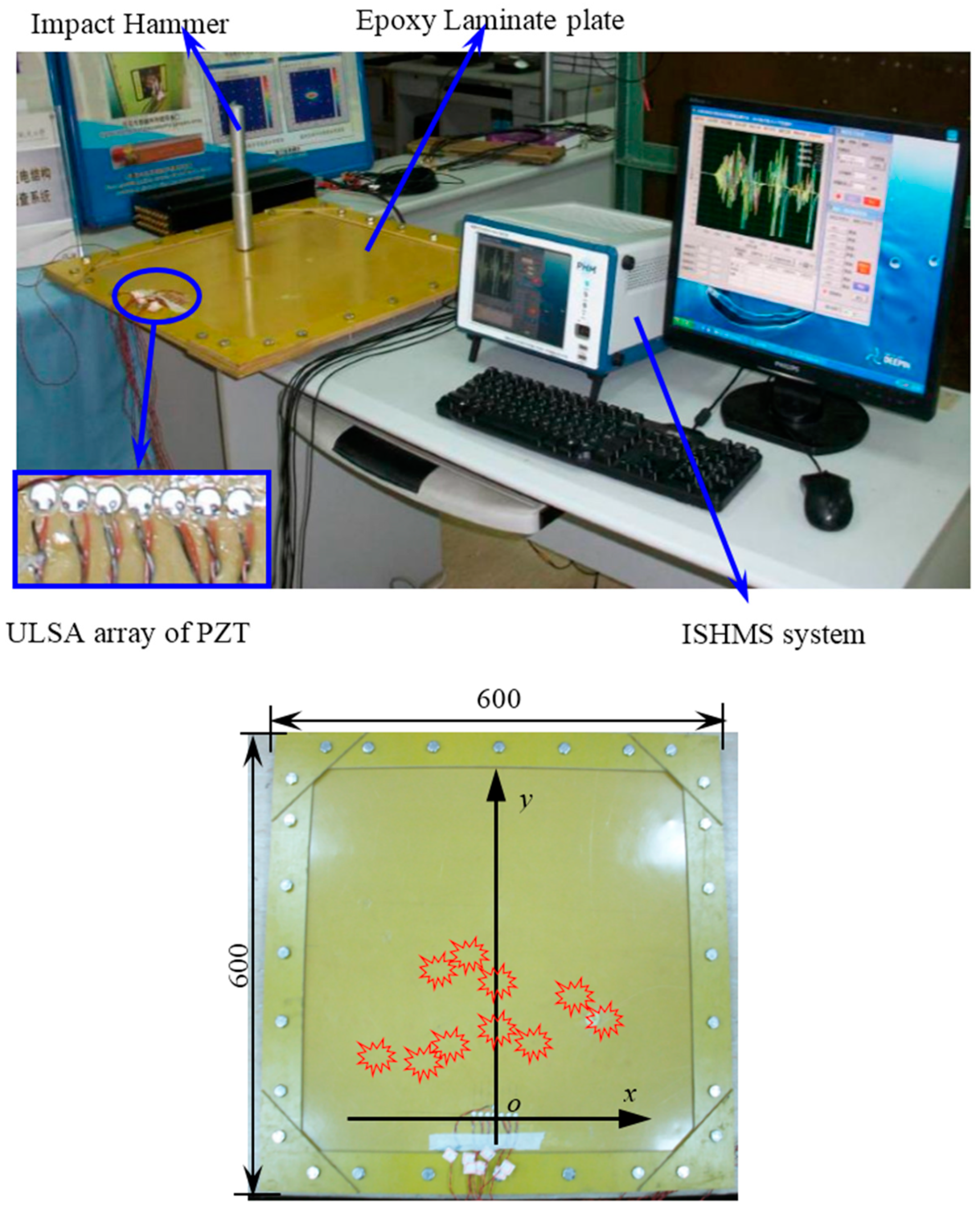
3.1. Experiment Setup
3.2. Impact Localization Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kersemans, M.; Martens, A.; Degrieck, J.; Abeele, K.V.D.; Delrue, S.; Pyl, L.; Zastavnik, F.; Sol, H.; Paepegem, W.V. The ultrasonic polar scan for composite characterization and damage assessment: Past, present and future. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Cui, Z.; Kundu, T. Acoustic source localization in anisotropic plates with “z” shaped sensor clusters. Ultrasonics 2018, 84, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, D.C.; He, T.; Pan, Q.; Liu, X.D.; Wang, J.; Shan, Y.C. A novel acoustic emission beamforming method with two uniform linear arrays on plate-like structures. Ultrasonics 2014, 54, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, K.; Macháň, R. Multiple signal classification algorithm for super-resolution fluorescence microscopy. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, R.O. Multiple emitter location and signal parameter estimation. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1986, 34, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.B.; Gu, F.S.; Ball, A. Acoustic emission monitoring of mechanical seals using MUSIC algorithm based on higher order statistics. Key Eng. Mater. 2009, 413, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engholm, M.; Stepinski, T. Direction of arrival estimation of Lamb waves using circular arrays. Struct. Health Monit. 2011, 10, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, S.K. Impact source localization in plate utilizing multiple signal classification. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2013, 227, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.F.; Bao, Q.; Qiu, L.; Zhong, Y.T. A single frequency component-based re-estimated music algorithm for impact localization on complex composite structures. Smart Mater. Struct. 2015, 24, 105021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.T.; Yuan, S.F.; Qiu, L. Multiple damage detection on aircraft composite structures using near-field MUSIC algorithm. Sens. Actuators A 2014, 214, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.F.; Zhong, Y.T.; Qiu, L.; Wang, Z.L. Two-dimensional near-field multiple signal classification algorithm–based impact localization. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2015, 26, 400–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.R.; Wu, M.C.; Shih, H.H.; Zheng, Q.; Yen, N.C.; Tung, C.C.; Liu, H.H. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.X.; He, Z.J.; Zi, Y.Y. A comparative study on the local mean decomposition and empirical mode decomposition and their applications to rotating machinery health diagnosis. J. Vib. Acoust. Trans. 2010, 132, 021010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, N.E. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A noise assisted data analysis method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 2009, 1, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Looney, D.; Hemakom, A.; Mandic, D.P. Intrinsic multi-scale analysis: A multi-variate empirical mode decomposition framework. Proc. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2015, 471, 20140709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, N.U.; Park, C.; Huang, N.E.; Mandic, D.P. EMD via MEMD: Multivariate noise-aided computation of standard EMD. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 2013, 5, 1350007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandic, D.P.; Rehman, N.U.; Wu, Z.; Mandic, D.P. Empirical Mode Decomposition-Based Time-Frequency Analysis of Multivariate Signals: The Power of Adaptive Data Analysis. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2013, 30, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leo, M.; Looney, D.; D’Orazio, T.; Mandic, D.P. Identification of Defective Areas in Composite Materials by Bivariate EMD Analysis of Ultrasound. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2011, 61, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Yeh, C.H.; Young, H.W.V.; Hu, K.; Lo, M.T. On the computational complexity of the empirical mode decomposition algorithm. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2014, 400, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



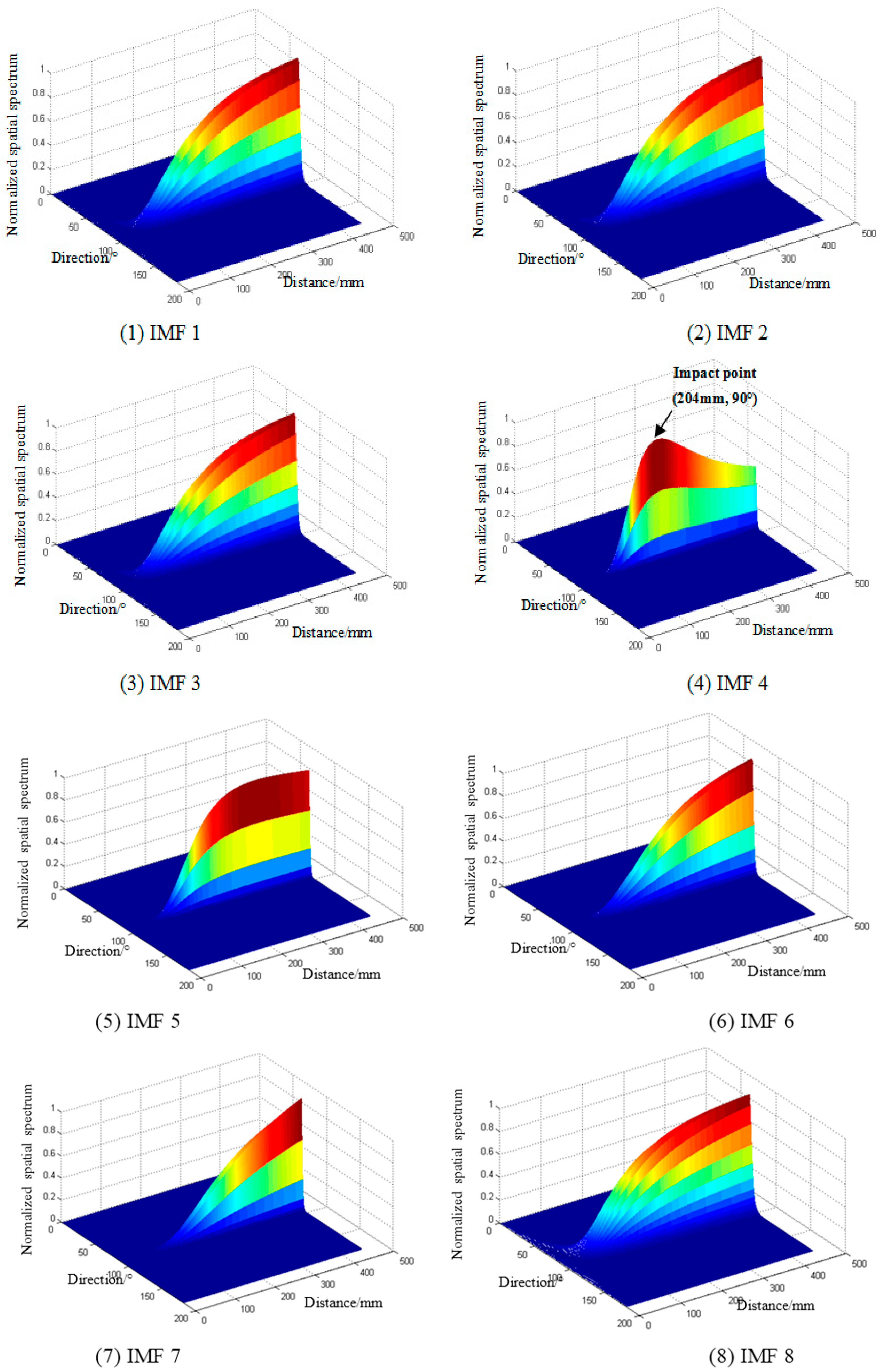
| Parameter | Actual Positions | Estimated Positions | Errors | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Impacts | r/mm | θ/° | IMF4 | IMF5 | r/mm | θ/° | |
| 1 | 150 | 45 | (135,43) | - | 15 | 2 | |
| 2 | 200 | 56 | (208,54) | - | 8 | 2 | |
| 3 | 124 | 75 | (109,76) | - | 15 | 1 | |
| 4 | 150 | 90 | (155,90) | - | 5 | 0 | |
| 5 | 200 | 90 | (194,90) | - | 6 | 0 | |
| 6 | 255 | 100 | - | (242,100) | 13 | 0 | |
| 7 | 255 | 110 | - | (245,112) | 10 | 2 | |
| 8 | 150 | 124 | (140,123) | - | 10 | 1 | |
| 9 | 150 | 135 | (146,133) | - | 4 | 2 | |
| 10 | 255 | 150 | - | (235,147) | 20 | 3 | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, Y.; Xiang, J.; Chen, X.; Jiang, Y.; Pang, J. Multiple Signal Classification-Based Impact Localization in Composite Structures Using Optimized Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1447. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8091447
Zhong Y, Xiang J, Chen X, Jiang Y, Pang J. Multiple Signal Classification-Based Impact Localization in Composite Structures Using Optimized Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(9):1447. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8091447
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Yongteng, Jiawei Xiang, Xiaoyu Chen, Yongying Jiang, and Jihong Pang. 2018. "Multiple Signal Classification-Based Impact Localization in Composite Structures Using Optimized Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition" Applied Sciences 8, no. 9: 1447. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8091447
APA StyleZhong, Y., Xiang, J., Chen, X., Jiang, Y., & Pang, J. (2018). Multiple Signal Classification-Based Impact Localization in Composite Structures Using Optimized Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition. Applied Sciences, 8(9), 1447. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8091447






