Demonstration of Subretinal Injection Using Common-Path Swept Source OCT Guided Microinjector
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
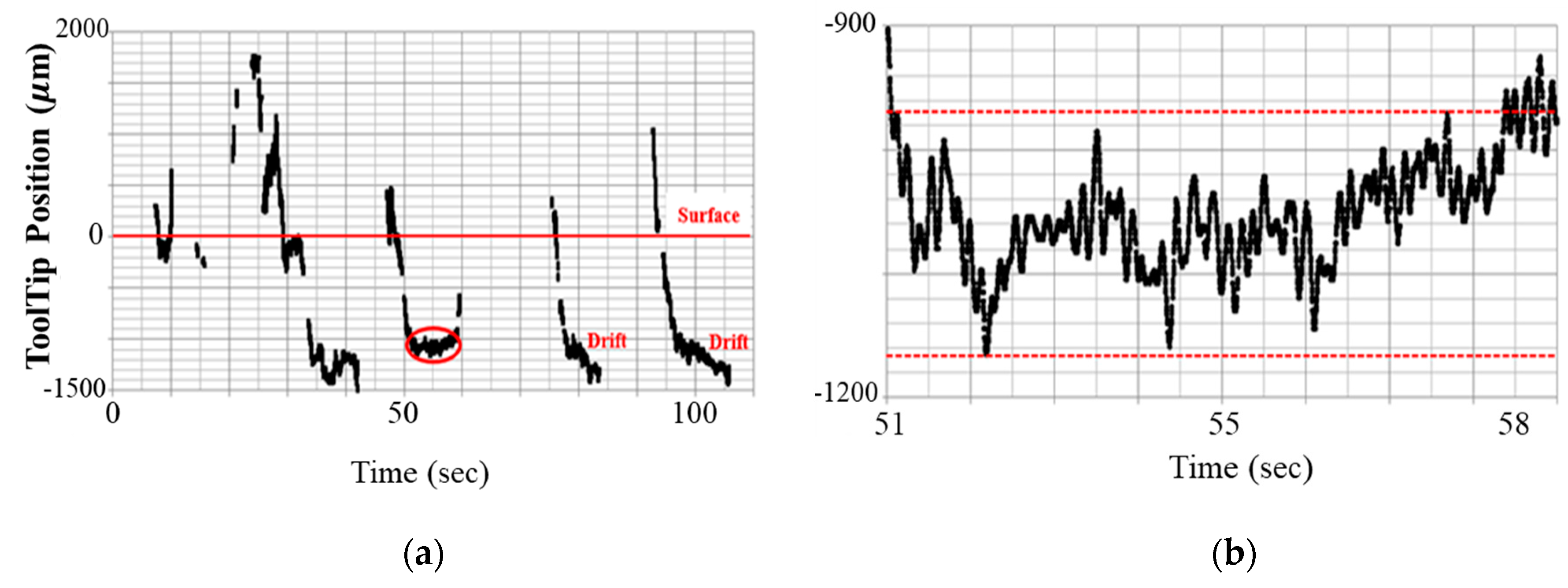
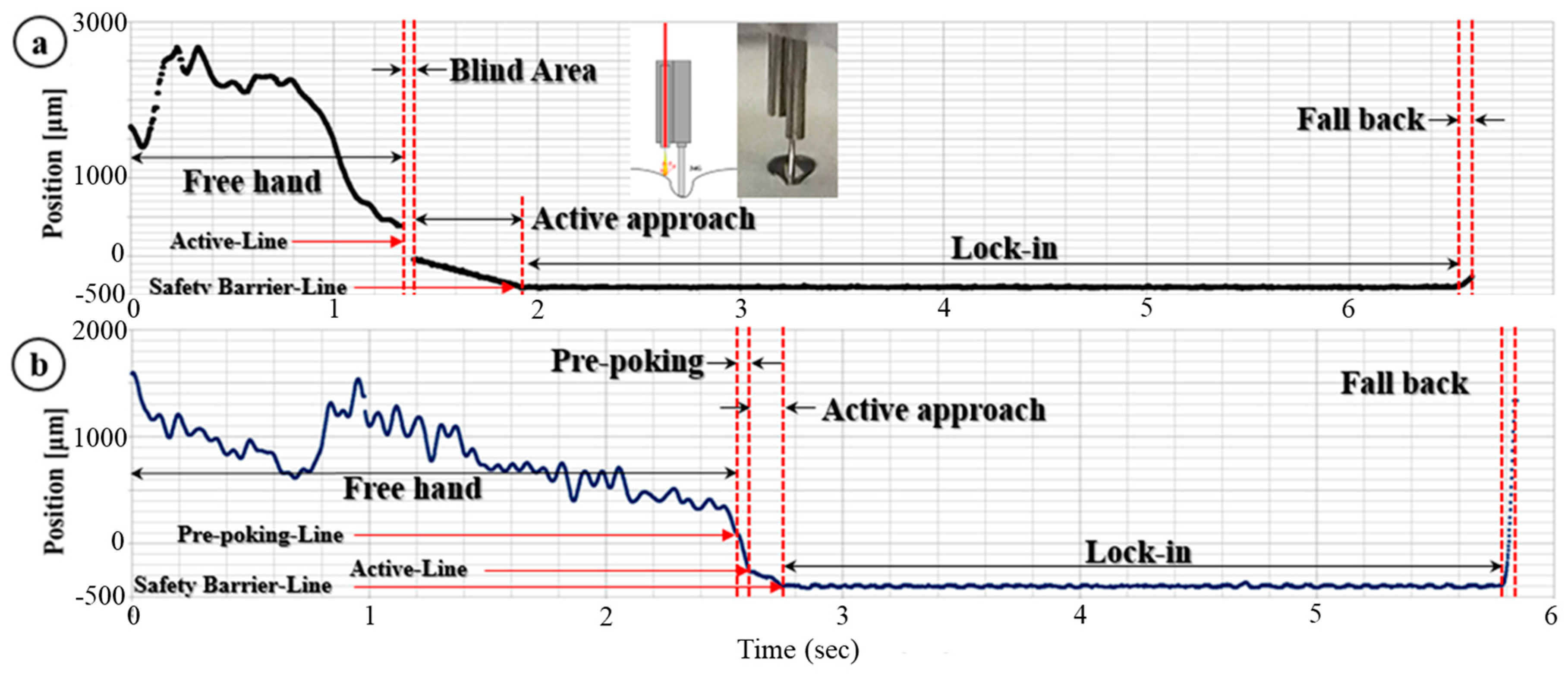
2.1. Limitation of Freehand Manipulation
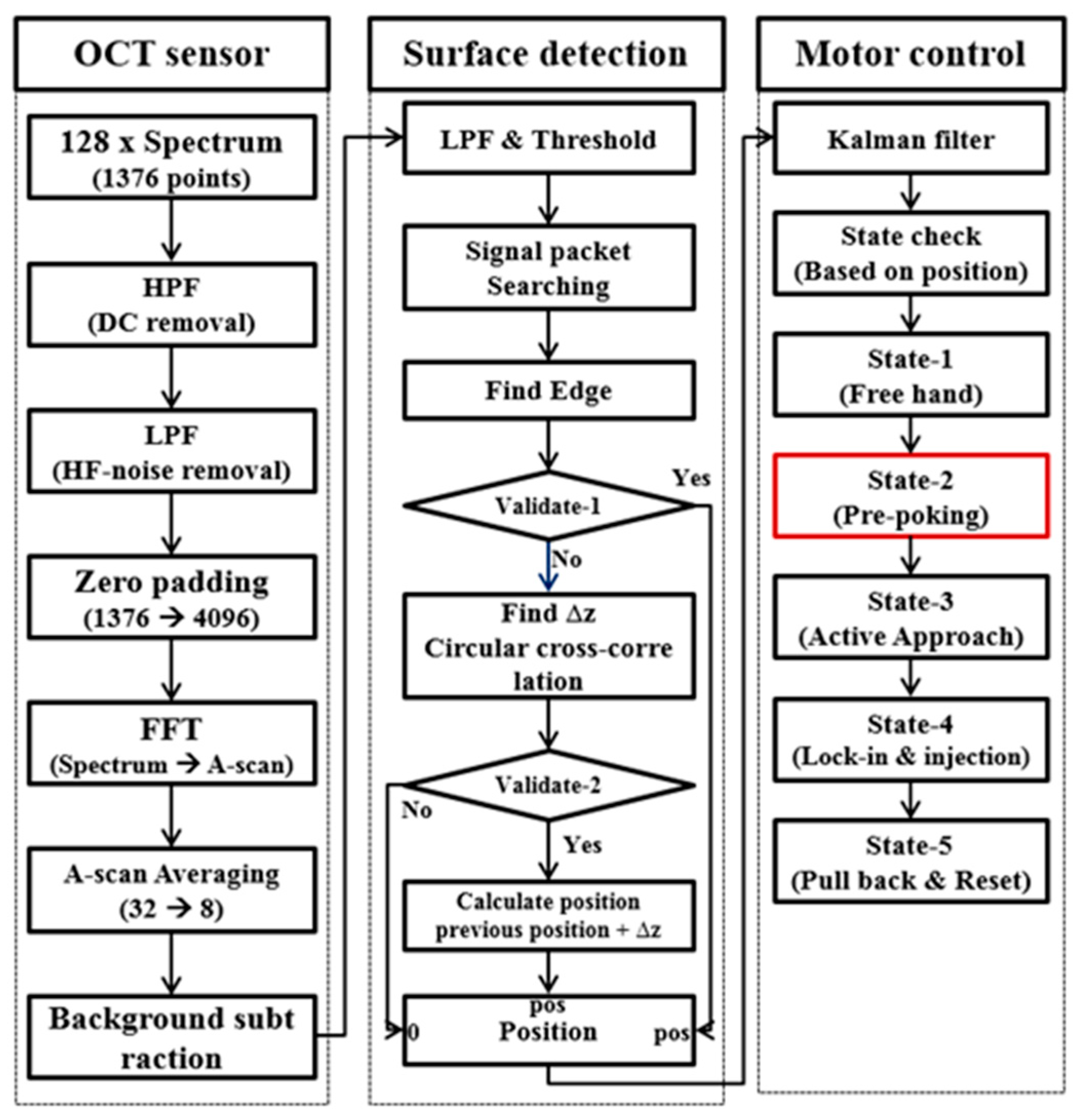
2.2. Microinjector System Configuration
2.3. Gelatin Phantom Injection Test
2.4. Modified Needle Guidance Method
3. Results
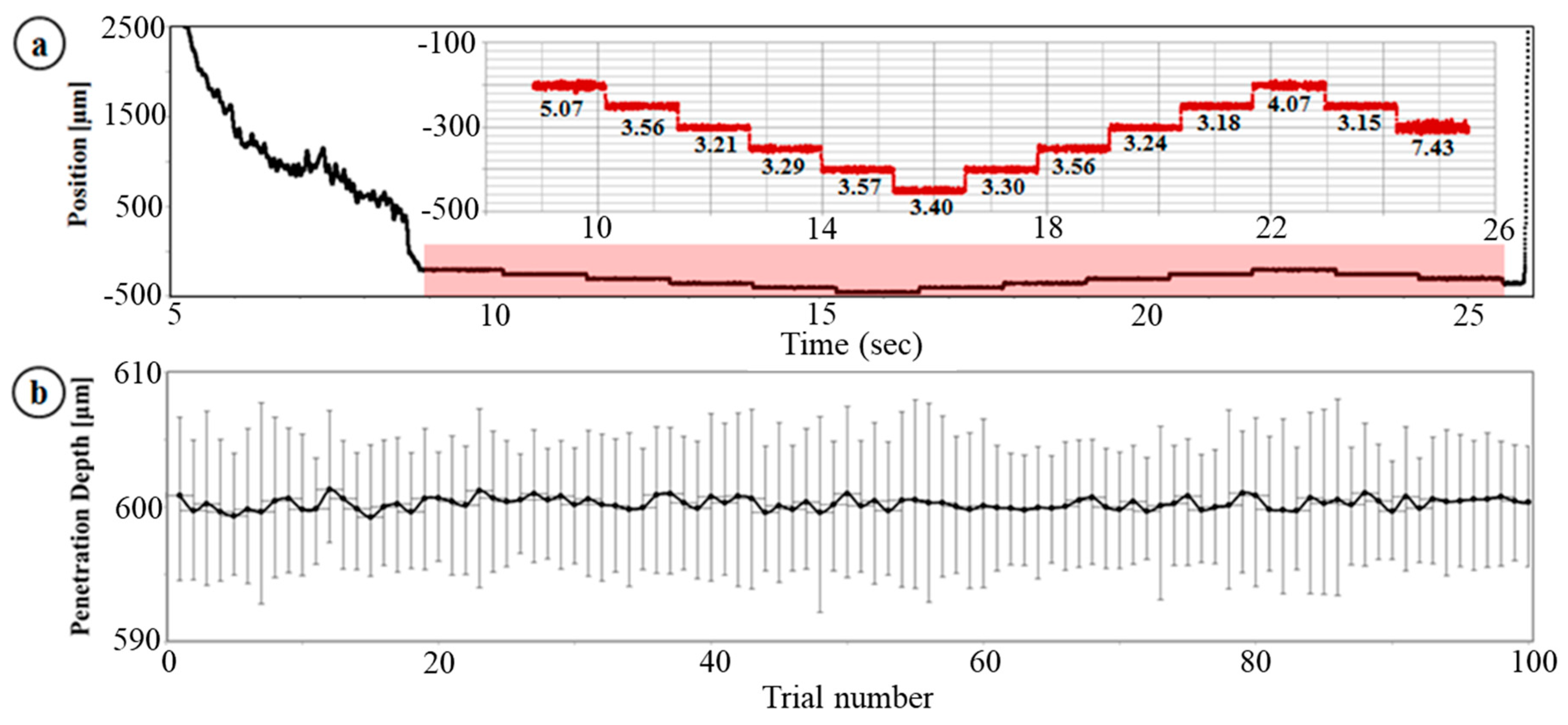
3.1. Dynamic Insertion Test
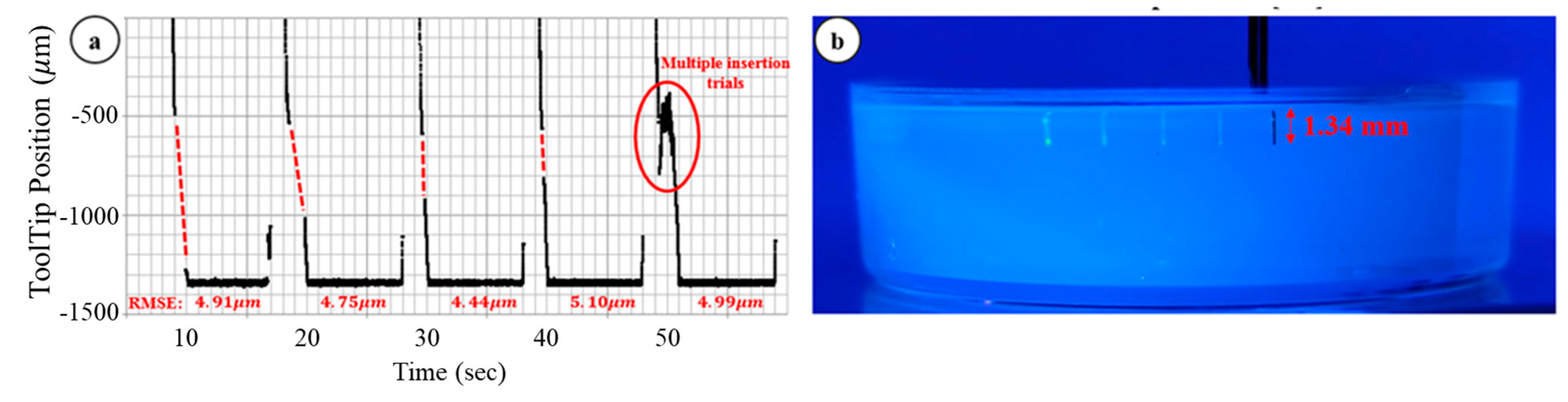
3.2. Multiple Injection, Gelatin Test
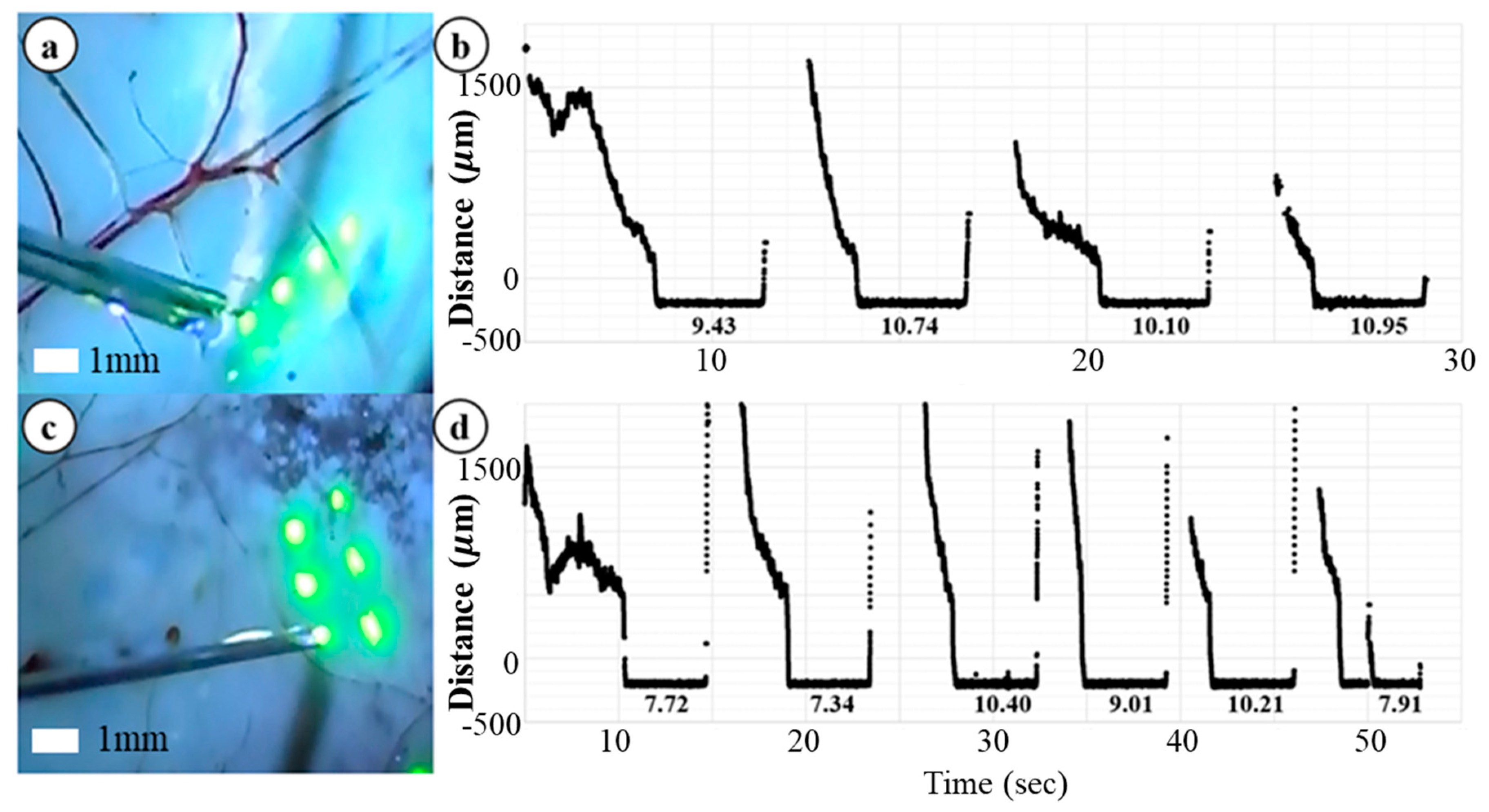
3.3. Ex-Vivo Bovine Eye Injection Test
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boye, S.E.; Boye, S.L.; Lewin, A.S.; Hauswirth, W.W. A comprehensive review of retinal gene therapy. Mol. Ther. 2013, 21, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cideciyan, A.V.; Jacobson, S.G.; Beltran, W.A.; Sumaroka, A.; Swider, M.; Iwabe, S.; Roman, A.J.; Olivares, M.B.; Schwartz, S.B.; Komaromy, A.M.; et al. Human retinal gene therapy for Leber congenital amaurosis shows advancing retinal degeneration despite enduring visual improvement. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 110, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seow, Y.; Wood, M.J. Biological gene delivery vehicles: Beyond viral vectors. Mol. Ther. 2009, 17, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.P.N.; Riviere, C.N. Physiological tremor amplitude during retinal microsurgery. In Proceedings of the IEEE 28th Annual Northeast Bioengineering Conference, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 21 April 2002; pp. 171–172. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Liu, X.; Gelinas, D.; Ciruna, B.; Sun, Y. A fully automated robotic system for microinjection of zebrafish embryos. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleming, I.; Balicki, M.; Koo, J.; Iordachita, I.; Mitchell, B.; Handa, J.; Hager, G.; Taylor, R. Cooperative robot assistance for retinal microsurgery. Proc. Med. Image Comput. Comput. Assist. Interv. 2008, 11, 543–550. [Google Scholar]
- Ota, T.; Patronick, N.A.; Schwartzman, D.; Riviere, C.N.; Zenati, M.A. Minimally invasive epicardial injections using a novel semiautonomous robotic device. Circulartion 2008, 118, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, B.C.; Yang, S.; MacLachlan, R.A.; Riviere, C.N. Towards vision-based control of a handheld micromanipulator for retinal cannulation in an eyeball phantom. In Proceedings of the 4th IEEE RAS and EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (BioRob), Rome, Italy, 24–27 June 2012; pp. 44–49. [Google Scholar]
- Gonenc, B.; Gehlbach, P.L.; Handa, J.; Taylor, R.H.; Iordachita, I. Force-sensing microneedle for assisted retinal vein cannulation. Proc. IEEE Sens. 2014, 698–701, 698–701. [Google Scholar]
- Ehlers, J.P.; Tao, Y.K.; Farsiu, S.; Maldonado, R.; Izatt, J.A.; Toth, C.A. Integration of a spectral domain optical coherence tomography system into a surgical microscope for intraoperative imaging. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 3153–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, P.; Migacz, J.; O’Connell, R.; Izatt, J.A.; Toth, C.A. Unprocessed real-time imaging of vitreoretinal surgical maneuvers using a microscope-integrated spectral-domain optical coherence tomography system. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2013, 251, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, P.; Migacz, J.; O’Donnell, R.; Day, S.; Lee, A.; Lin, P.; Vann, R.; Kuo, A.; Fekrat, S.; Mruthyunjaya, P.; et al. Preclinical evaluation and intraoperative human retinal imaging with a highresolution microscope-integrated spectral domain optical coherence tomography device. Retina 2013, 33, 1328–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joos, K.M.; Shen, J.H. Miniature real-time intraoperative forward-imaging optical coherence tomography probe. Biomed. Opt. Express 2013, 4, 1342–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Shen, J.; Shah, R.J.; Simaan, N.; Joos, K.M. Evaluation of microsurgical tasks with OCT-guided and/or robot-assisted ophthalmic forceps. Biomed. Opt. Express 2015, 6, 457–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vakhtin, A.B.; Kane, D.J.; Wood, W.R.; Peterson, K.A. Common-path interferometer for frequency-domain optical coherence tomography. Appl. Opt. 2003, 42, 6953–6958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, U.; Fried, N.M.; Kang, J.U. All-Fiber Common-Path Optical Coherence Tomography: Sensitivity Optimization and System Analysis. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2005, 11, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Kang, J.U. Graphics processing unit accelerated non-uniform fast Fourier transform for ultrahigh-speed, real-time Fourier-domain OCT. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 23472–23487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, W.; Han, J.; Kang, J.U. A surface topology and motion compensation system for microsurgery guidance and intervention based on common-path optical coherence tomography. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2009, 56, 2318–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Kang, J.U. Common-path low-coherence interferometry fiber-optic sensor guided microincision. J. Biomed. Opt. 2011, 16, 095003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Lin, C.; Kang, J.U. Motion compensated fiber-optic confocal microscope based on a common-path optical coherence tomography distance sensor. Opt. Eng. 2011, 50, 083201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, X.; Song, C.; Kang, J.U. Motion-compensated hand-held common-path Fourier-domain optical coherence tomography probe for image-guided intervention. Biomed. Opt. Express 2012, 3, 3105–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Gehlbach, P.L.; Kang, J.U. Active tremor cancellation by a “smart” handheld vitreoretinal microsurgical tool using swept source optical coherence tomography. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 23414–23421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Park, D.Y.; Gehlbach, P.L.; Park, S.J.; Kang, J.U. Fiber-optic OCT sensor guided “SMART” micro-forceps for microsurgery. Biomed. Opt. Express 2013, 4, 1045–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheon, G.W.; Huang, Y.; Cha, J.; Gehlbach, P.L.; Kang, J.U. Accurate real-time depth control for CP-SSOCT distal sensor based handheld microsurgery tools. Biomed. Opt. 2015, 6, 1942–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahvash, M.; Dupont, P.E. Fast needle insertion to minimize tissue deformation and damage. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Kobe, Japan, 12–17 May 2009; pp. 3097–3102. [Google Scholar]
- Mahvash, M.; Dupont, P.E. Mecahnics of dynamic needle insertion into a biological material. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 57, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, D.S.; Marshall, J. The interpretation of optical coherence tomography images of the retina. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1999, 40, 2332–2342. [Google Scholar]
- Bagci, A.M.; Shahidi, M.; Ansari, R.; Blair, M.; Zelkha, R. Thickness profiles of reintal layers by optical coherence tomography image segmentation. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2008, 146, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, D.C.; Salinas, H.M.; Puliafito, C.A. Automated detection of retinal layer structures on optical coherence tomography images. Opt. Express 2005, 13, 10200–10216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, J.U.; Cheon, G.W. Demonstration of Subretinal Injection Using Common-Path Swept Source OCT Guided Microinjector. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1287. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8081287
Kang JU, Cheon GW. Demonstration of Subretinal Injection Using Common-Path Swept Source OCT Guided Microinjector. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(8):1287. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8081287
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Jin U., and Gyeong Woo Cheon. 2018. "Demonstration of Subretinal Injection Using Common-Path Swept Source OCT Guided Microinjector" Applied Sciences 8, no. 8: 1287. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8081287
APA StyleKang, J. U., & Cheon, G. W. (2018). Demonstration of Subretinal Injection Using Common-Path Swept Source OCT Guided Microinjector. Applied Sciences, 8(8), 1287. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8081287



