Compression of Phase-Only Holograms with JPEG Standard and Deep Learning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
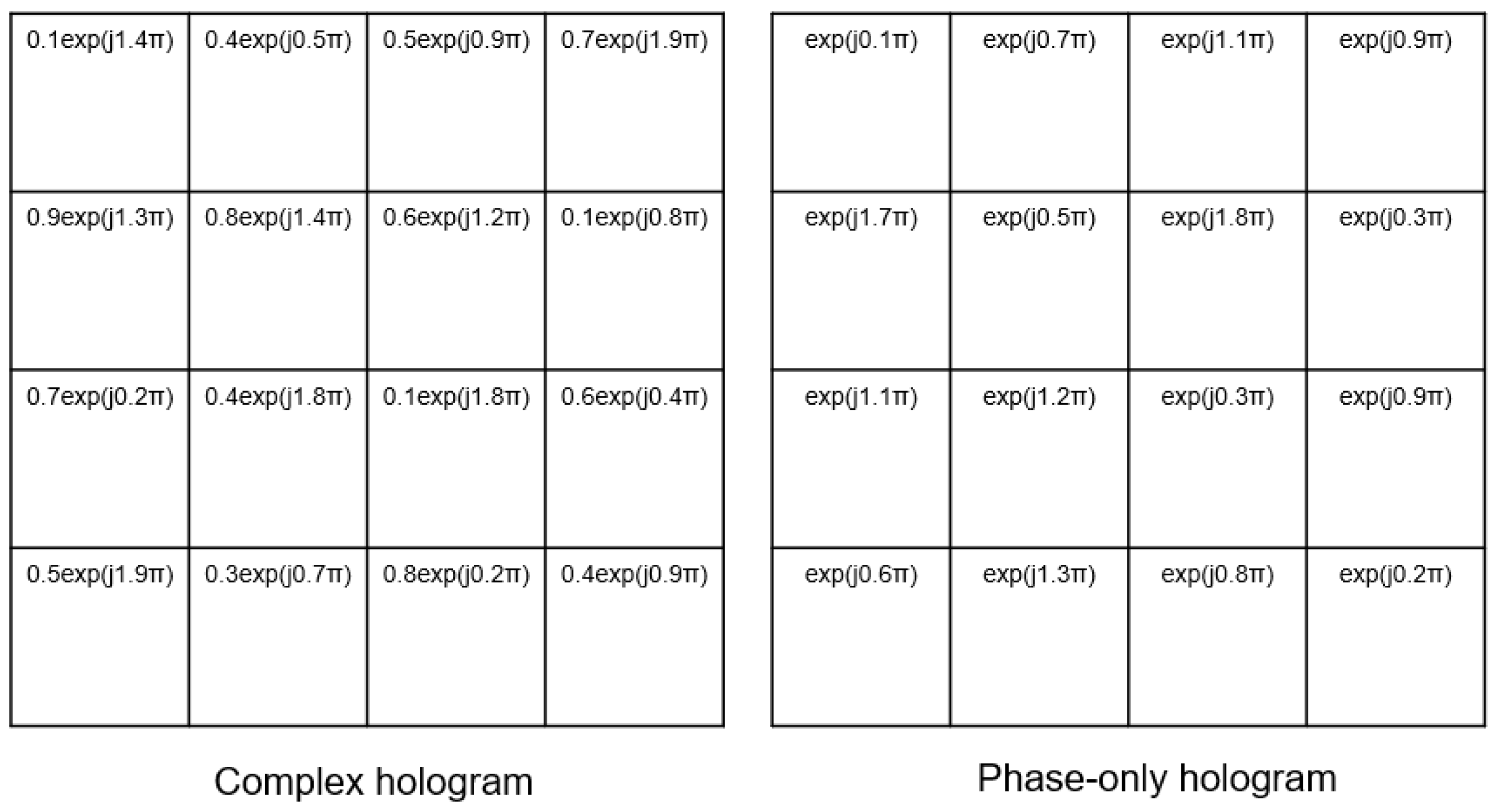
2. Computer Generated Phase-Only Hologram with Error Diffusion Method
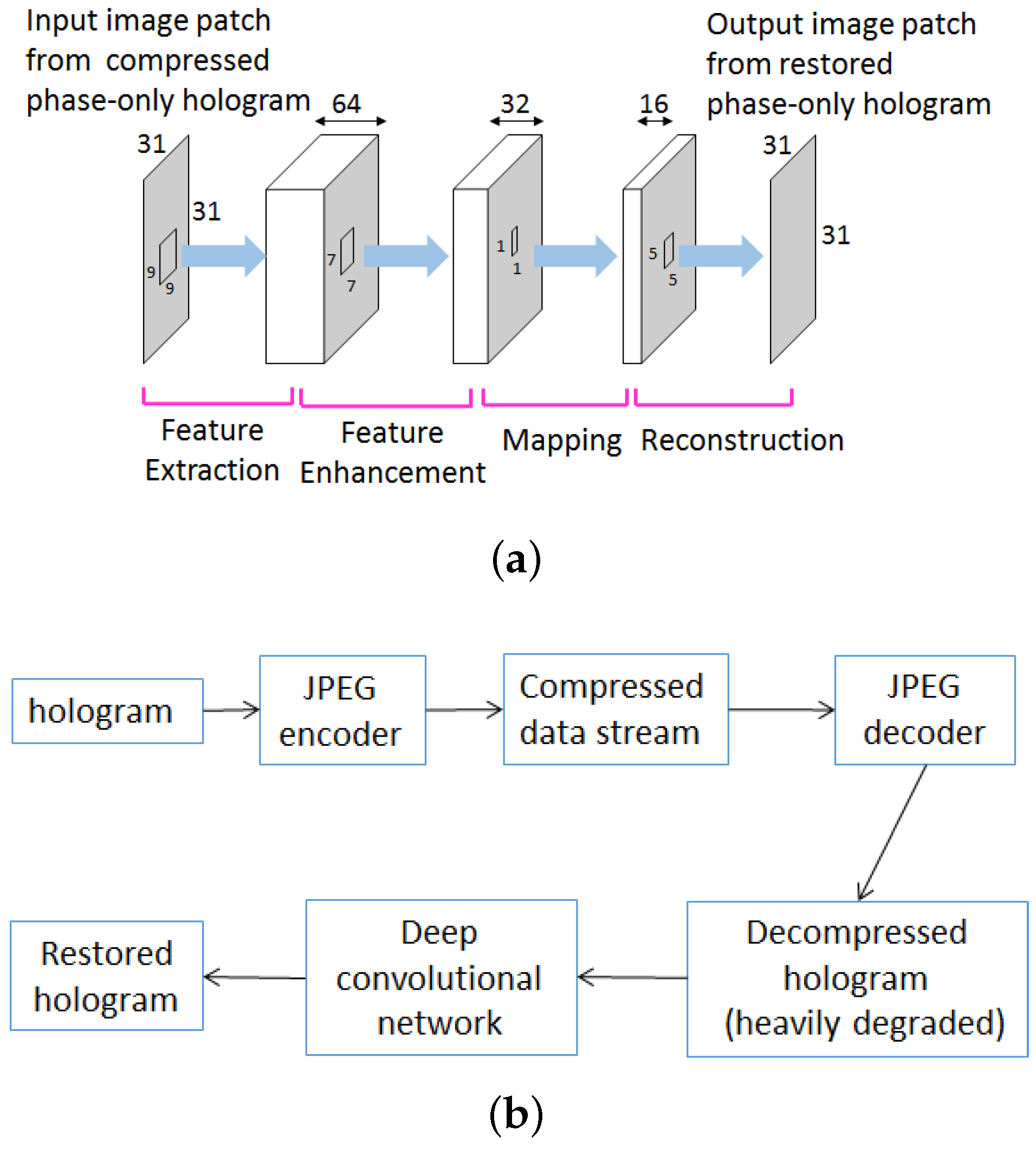
3. JPEG Image Compression and Proposed Artifact Reduction Scheme by Deep Convolutional Network
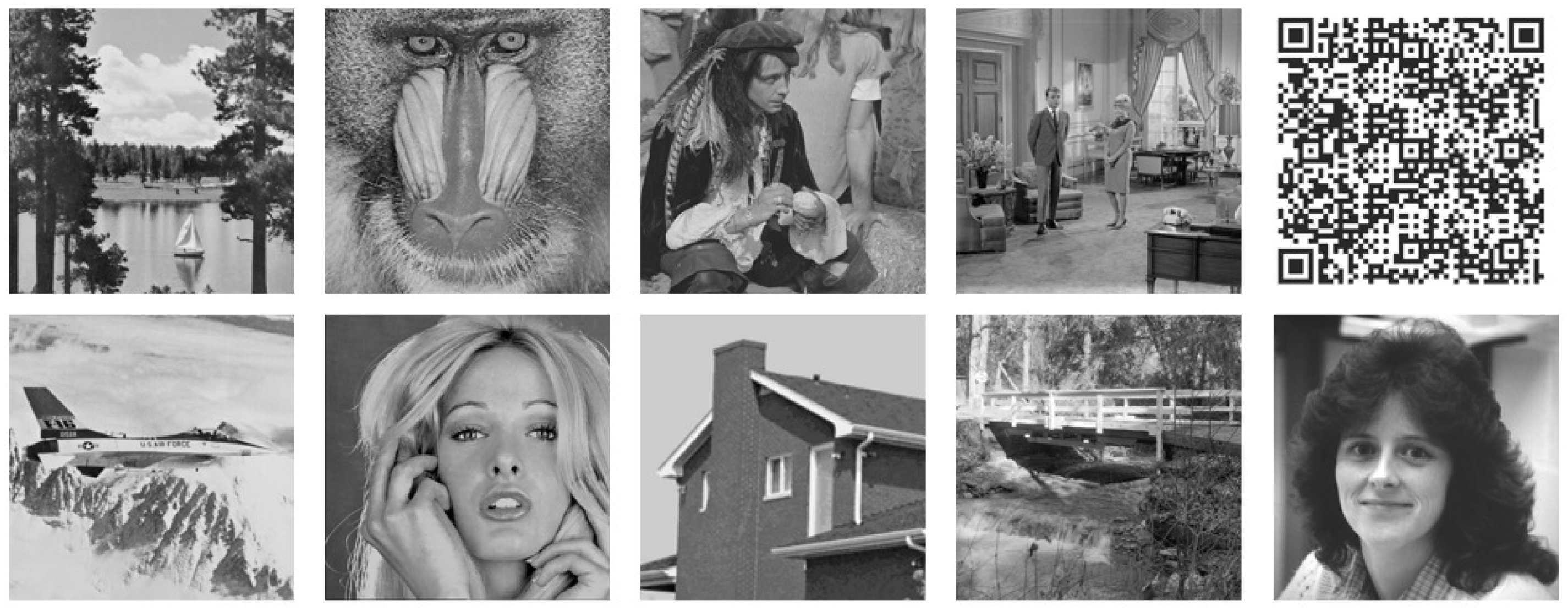
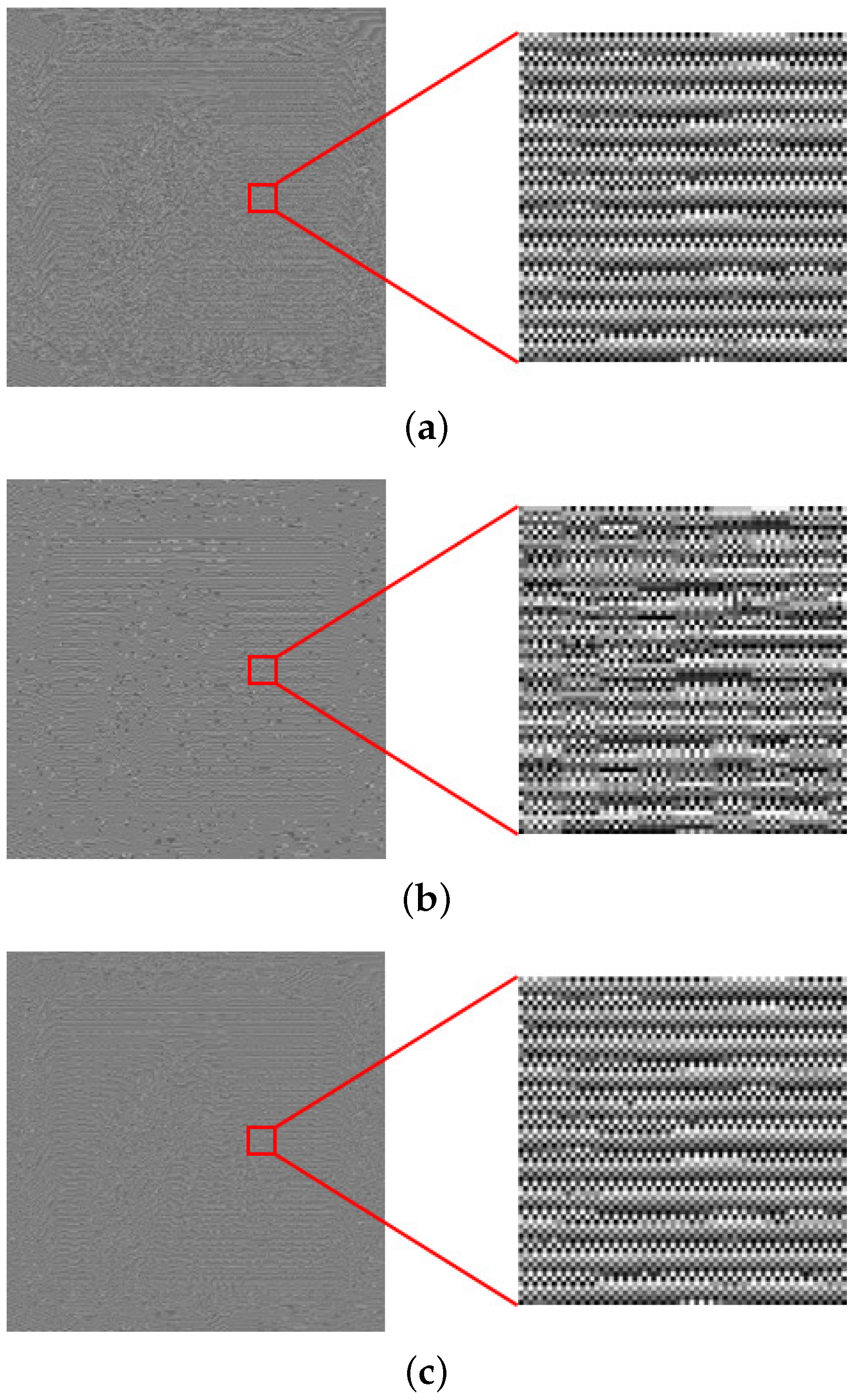
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yaraş, F.; Kang, H.; Onural, L. Real-time phase-only color holographic video display system using LED illumination. Appl. Opt. 2009, 48, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Li, X.; He, Z.; Su, Y.; Poon, T.C. Real-time dynamic holographic 3D display. Inf. Disp. 2012, 28, 17–20. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Jia, J.; Pan, Y.; Xie, J. Color holographic display using a phase-only spatial light modulator. In Digital Holography and Three-Dimensional Imaging; Optical Society of America: San Jose, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Buckley, E. Holographic laser projection. J. Disp. Technol. 2011, 7, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.; Gu, H.; Tan, Q. Holographic projection with higher image quality. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 19179–19184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Chang, C.; Xia, J. Speckleless holographic display by complex modulation based on double-phase method. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 30368–30378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimobaba, T.; Makowski, M.; Kakue, T.; Oikawa, M.; Okada, N.; Endo, Y.; Hirayama, R.; Ito, T. Lensless zoomable holographic projection using scaled Fresnel diffraction. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 25285–25290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maimone, A.; Georgiou, A.; Kollin, J.S. Holographic near-eye displays for virtual and augmented reality. ACM Trans. Graph. 2017, 36, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Liu, J.; Duan, X.; Zhao, T.; Li, X.; Liu, P. Compact see-through 3D head-mounted display based on wavefront modulation with holographic grating filter. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 8412–8424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liesener, J.; Reicherter, M.; Haist, T.; Tiziani, H.J. Multi-functional optical tweezers using computer-generated holograms. Opt. Commun. 2000, 185, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.R.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.J.; Sun, W.J. Optical image encryption based on binary Fourier transform computer-generated hologram and pixel scrambling technology. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2007, 45, 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Z.; Jiao, S.; Zou, W.; Li, X. Embedding intensity image into a binary hologram with strong noise resistant capability. Opt. Commun. 2017, 403, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishitsuji, T.; Shimobaba, T.; Kakue, T.; Ito, T. Review of Fast Calculation Techniques for Computer-generated Holograms with the Point Light Source-based Model. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 2017, 13, 2447–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimobaba, T.; Masuda, N.; Ito, T. Simple and fast calculation algorithm for computer-generated hologram with wavefront recording plane. Opt. Lett. 2009, 34, 3133–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimobaba, T.; Ito, T.; Masuda, N.; Ichihashi, Y.; Takada, N. Fast calculation of computer-generated-hologram on AMD HD5000 series GPU and OpenCL. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 9955–9960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Pan, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, Q.; Jiang, W. Reducing the memory usage for effectivecomputer-generated hologram calculation using compressed look-up table in full-color holographic display. Appl. Opt. 2013, 52, 1404–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, S.; Zhuang, Z.; Zou, W. Fast computer generated hologram calculation with a mini look-up table incorporated with radial symmetric interpolation. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerchberg, R.W.; Saxton, W.O. A practical algorithm for the determination of the phase from image and diffraction plane pictures. Optik 1972, 35, 237–246. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.; Xia, J.; Yang, L.; Lei, W.; Yang, Z.; Chen, J. Speckle-suppressed phase-only holographic three-dimensional display based on double-constraint Gerchberg—Saxton algorithm. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, 6994–7001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.Y.; Li, W.C.; Chang, H.T.; Chuang, C.H.; Chang, T.J. 3-D modified Gerchberg—Saxton algorithm developed for panoramic computer-generated phase-only holographic display. JOSA B 2017, 34, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, P.W.M.; Poon, T.C. Novel method for converting digital Fresnel hologram to phase-only hologram based on bidirectional error diffusion. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 23680–23686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsang, P.W.M.; Jiao, A.S.M.; Poon, T.C. Fast conversion of digital Fresnel hologram to phase-only hologram based on localized error diffusion and redistribution. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 5060–5066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.P.; Wang, S.Y.; Tsang, P.W.M.; Poon, T.C. Nonlinearity compensation and complex-to-phase conversion of complex incoherent digital holograms for optical reconstruction. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 14582–14588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Cao, A.; Shi, L.; Deng, Q. Non-iterative phase-only Fourier hologram generation with high image quality. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 14323–14333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naydenova, I. Advanced Holography: Metrology and Imaging; InTech: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Tsang, P.W.M.; Chow, Y.T.; Poon, T.C. Generation of edge-preserved noise-added phase-only hologram. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2016, 14, 100901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, P.W.M.; Chow, Y.T.; Poon, T.C. Generation of patterned-phase-only holograms (PPOHs). Opt. Express 2017, 25, 9088–9093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsang, P.W.M.; Chow, Y.T.; Poon, T.C. Generation of phase-only Fresnel hologram based on down-sampling. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 25208–25214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, W.K.; Tsang, P.W.M.; Poon, T.C.; Zhou, C. Enhanced method for the generation of binary Fresnel holograms based on grid-cross downsampling. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2011, 9, 120005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufaux, F.; Xing, Y.; Pesquet-Popescu, B.; Schelkens, P. Compression of digital holographic data: An overview. In Applications of Digital Image Processing; International Society for Optics and Photonics: San Diego, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Darakis, E.; Soraghan, J.J. Use of Fresnelets for phase-shifting digital hologram compression. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2006, 15, 3804–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, L.T.; Ali, Z.; Quang, P.D.; Park, J.H.; Kim, N. Compression of digital hologram for three-dimensional object using Wavelet-Bandelets transform. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 8019–8031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsang, P.; Cheung, K.W.; Poon, T.C. Low-bit-rate computer-generated color Fresnel holography with compression ratio of over 1600 times using vector quantization. Appl. Opt. 2011, 50, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheremkhin, P.A.; Kurbatova, E.A. Compression of digital holograms using 1-level wavelet transforms, thresholding and quantization of wavelet coefficients. In Digital Holography and Three-Dimensional Imaging; Optical Society of America: JeJu Island, Korea, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, G.K. The JPEG still picture compression standard. Commun. ACM 1992, 34, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringh, A.; Karlsson, J.; Lindquist, A. Multidimensional Rational Covariance Extension with Applications to Spectral Estimation and Image Compression. SIAM J. Control Opt. 2018, 54, 1950–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorzi, M. An interpretation of the dual problem of the THREE-like approaches. Automatica 2015, 62, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiao, S.; Zou, W. Processing of digital holograms: segmentation and inpainting. In Holography, Diffractive Optics, and Applications VII; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Beijing, China, 2016; Volume 10022, p. 1002206. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Zuo, W.; Chen, Y.; Meng, D.; Zhang, L. Beyond a gaussian denoiser: Residual learning of deep cnn for image denoising. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 3142–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Zuo, W.; Gu, S.; Zhang, L. Learning deep cnn denoiser prior for image restoration. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, J.-L.; Chen, B.-H.; Li, Y. Highly Accurate Image Reconstruction for Multimodal Noise Suppression Using Semisupervised Learning on Big Data. In IEEE Transactions on Multimedia; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, G.; Ghanem, B. L0TV: A new method for image restoration in the presence of impulse noise. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.; Bui, V.; Lam, V.; Raub, C.B.; Chang, L.C.; Nehmetallah, G. Automatic phase aberration compensation for digital holographic microscopy based on deep learning background detection. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 15043–15057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitkaaho, T.; Manninen, A.; Naughton, T.J. Performance of Autofocus Capability of Deep Convolutional Neural Networks in Digital Holographic Microscopy. In Digital Holography and Three-Dimensional Imaging; Optical Society of America: JeJu Island, Korea, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Shimobaba, T.; Kuwata, N.; Homma, M.; Takahashi, T.; Nagahama, Y.; Sano, M.; Hasegawa, S.; Hirayama, R.; Kakue, T.; Shiraki, A.; et al. Convolutional neural network-based data page classification for holographic memory. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, 7327–7330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, A.; Lee, J.; Li, S.; Barbastathis, G. Lensless computational imaging through deep learning. Optica 2017, 4, 1117–11253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivenson, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Günaydın, H.; Teng, D.; Ozcan, A. Phase recovery and holographic image reconstruction using deep learning in neural networks. Light Sci. Appl. 2018, 7, 17141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Xu, Z.; Lam, E.Y. Learning-based nonparametric autofocusing for digital holography. Optica 2018, 5, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horisaki, R.; Takagi, R.; Tanida, J. Deep-learning-generated holography. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, 3859–3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C.; Deng, Y.; Loy, C.C.; Tang, X. Compression artifacts reduction by a deep convolutional network. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV 2015), Santiago, Chile, 11–18 December 2015; pp. 576–584. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, K.; Dong, C.; Loy, C.C.; Tang, X. Deep convolution networks for compression artifacts reduction. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1608.02778. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, A.S.M.; Tsang, P.W.M.; Poon, T.C. Restoration of digital off-axis Fresnel hologram by exemplar and search based image inpainting with enhanced computing speed. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2015, 193, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Shelhamer, E.; Donahue, J.; Karayev, S.; Long, J.; Girshick, R.; Guadarrama, S.; Darrell, T. Caffe: Convolutional architecture for fast feature embedding. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM international conference on Multimedia, Orlando, FL, USA, 3–7 November 2014; pp. 675–678. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C. Mean squared error: Love it or leave it? A new look at signal fidelity measures. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2009, 26, 98–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, H.R.; Bovik, A.C. Image information and visual quality. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2006, 15, 430–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sheikh, H.R.; Bovik, A.C.; de Veciana, G. An information fidelity criterion for image quality assessment using natural scene statistics. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2005, 14, 2117–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
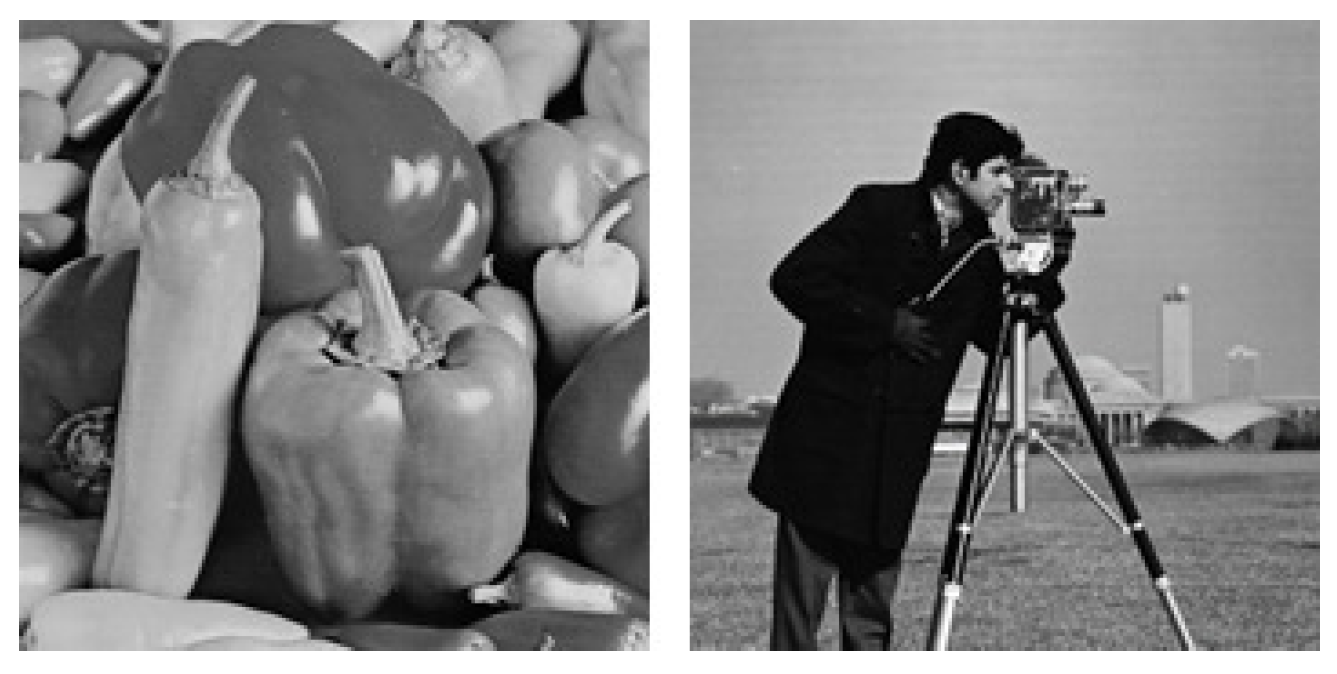







| Cameraman | Pepper | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 m | 0.3 m | 0.5 m | 0.3 m | ||
| Compression ratio | 7.2113 | 7.1111 | 7.2113 | 7.1608 | |
| Reconstructed image from compressed hologram | PSNR | 19.10 | 17.83 | 18.92 | 17.64 |
| SSIM | 0.1651 | 0.0967 | 0.2007 | 0.1036 | |
| MS-SSIM | 0.6091 | 0.4628 | 0.6907 | 0.5252 | |
| VIF | 0.3946 | 0.2183 | 0.6396 | 0.3438 | |
| IFC | 0.4522 | 0.2519 | 0.5543 | 0.2835 | |
| Reconstructed image from restored hologram | PSNR | 28.86 | 26.86 | 29.88 | 27.16 |
| SSIM | 0.6036 | 0.4465 | 0.6767 | 0.4852 | |
| MS-SSIM | 0.8798 | 0.8022 | 0.9138 | 0.8343 | |
| VIF | 0.5378 | 0.4316 | 0.6841 | 0.6306 | |
| IFC | 0.9027 | 0.5098 | 1.2064 | 0.6379 | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiao, S.; Jin, Z.; Chang, C.; Zhou, C.; Zou, W.; Li, X. Compression of Phase-Only Holograms with JPEG Standard and Deep Learning. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8081258
Jiao S, Jin Z, Chang C, Zhou C, Zou W, Li X. Compression of Phase-Only Holograms with JPEG Standard and Deep Learning. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(8):1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8081258
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiao, Shuming, Zhi Jin, Chenliang Chang, Changyuan Zhou, Wenbin Zou, and Xia Li. 2018. "Compression of Phase-Only Holograms with JPEG Standard and Deep Learning" Applied Sciences 8, no. 8: 1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8081258
APA StyleJiao, S., Jin, Z., Chang, C., Zhou, C., Zou, W., & Li, X. (2018). Compression of Phase-Only Holograms with JPEG Standard and Deep Learning. Applied Sciences, 8(8), 1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8081258





