Abstract
Kaolinite-based wastes are researched as an alternative means of extracting metakaolinite, a pozzolanic product for the manufacture of eco-efficient cements. However, both crystallinity and the content of this crystalline phase play important roles during their thermal activation and, therefore, in their subsequent behavior in the matrix with cementitious properties. In this study, the initial compositions of two thermally activated products (paper sludge and coal waste) are studied for both the mineralogy and the mechanical properties of binary cements. The elemental composition of the materials was analyzed with X-ray Fluorescence (XRF). The mineralogy of the crystalline materials was determined by X-ray Diffraction (XRD). The sample morphology was determined with scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The pozzolanic activity is measured by accelerated methods and the preparation of the specimens of blended cement is prepared following the procedure described by Kock-Steinegger. The results showed that the pozzolanic activity of the waste (in terms of fixed lime) was similar at 90 days but that its reaction rate was different. The pozzolanic reaction of both wastes produced stratlingite and C-S-H gels, with the presence of C4AH13. The C-S-H gel generated with coal waste had very short chains, was poorer in Ca and was rich in Al. The addition of both wastes to the cement modified its mineralogical composition in comparison with a conventional cement, favoring the formation of C4AH13 over the formation of ettringite.
1. Introduction
The cement industry is well known as being a driver of social and economic development in society, but at the same time it is associated with significant negative effects because of the release of greenhouse gases, principally CO2 (800–850 kg/ton) [1] and due to high energetic production costs. One of the strategies to circumvent these negative effects covers the incorporation of active additions of a different nature [2,3,4,5,6], including different types of pozzolans, a great variety of which (slags, fly-ash, silica fume, etc.) are quite widely used.
Additionally, clayey minerals are found among the pozzolans specified in the standards that are in force [7]. However, their use in the manufacture of commercial cements is very rare or non-existent, due principally to the environmental problems caused during their extraction and transport, and the need to protect natural areas. The scientific community is currently investigating clayey minerals, principally in relation to kaolinite (K), which needs a process of thermal activation for its complete transformation into metakaolinite (MK) [8,9,10,11,12,13,14]. Clay is in a very reactive state with regards to the thermal activation of the material because it produces the destruction of the structures beginning with the elimination of the hydroxyl groups on the laminar edges [15,16]. The thermal transformations of kaolinite have been the subject of numerous investigations, showing that the parameters of thermal treatment such as temperature, heating rate, and time, as well as the cooling parameters at the end of the production cycle, significantly influence the dehydroxylation process [17,18,19].
Over recent years, investigations have looked at obtaining recycled MK from kaolinite-based industrial waste [20], with the subsequent benefits that such a process entails (environmental and social). This line of investigation is within the European strategy on the Circular Economy, which prioritizes the recycling of industrial wastes as secondary raw materials for the manufacture of commercial cements that are both innovative and eco-efficient. Along these lines, this research is focused on two principal kaolinite-based wastes: (a) paper-making sludge from the paper industry that uses recycled paper as a raw material to obtain cellulose [21,22,23]; and (b) coal waste from coal mining [13]. In all cases, the pozzolanic behavior of this recycled MK is suitable. It is comparable with natural MK and silica fume (SF), and also shows excellent performance in both cement mixtures [24,25,26,27], and blended cement matrices.
However, little is known about the effects of these properties on the microstructures of the final C-S-H gels that are produced. Likewise, the question of whether the composition and morphology of C-S-H gels depends only on the initial composition of the sample is still a topic for further discussion.
An in-depth study is presented in this paper on the effect that the initial composition of the activated products have on the mineralogy and the mechanical properties of binary cements. Accordingly, binary cements with substitutions of 10 and 20% of MK-based waste, thermically activated with different ratios of CaO/SiO2 and SiO2/Al2O3, were prepared, and their influence was studied on the hydrated phases and the mechanical properties at 28 days of hydration.
2. Materials and Methods
Two metakaolin-based wastes were used: (a) coal waste (CW) from the open-cast coal mines was supplied by the Sociedad Anónima Hullera Vasco-Leonesa, located in Santa Lucía, Leon, Spain; and (b) paper sludge (PS) was supplied by the firm Holmen Paper Madrid, which uses 100% recycled paper as a raw material for recycling the cellulose. The organic material contained in the sludge was at almost 32.35%.
Both wastes, once characterized, were subjected to a process of thermal activation at 600 °C over 2 h in an oven, which are the optimal conditions from the energetic and environmental points of view. Under these conditions, the organic material is eliminated, the total transformation of K into MK takes place, and the decarbonation of the carbonates takes place, avoiding the formation of free lime (CaO), a compound known for its expansive properties during the hydration phase of the cement. Subsequently, the products were ground and sieved through a 63-micron mesh.
An extra pure calcium hydroxide (PhEur, USP, BP chemical reagent) was used in the pozzolan/lime system, with a minimum content of 99% CaO.
The cement employed in this study is a Portland cement classified as CEM I 52.5R, supplied by Financiera y Minera (Italcementi Group, Bergamo, Italy).
The elemental composition of the materials was analyzed via X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) equipment using an energy dispersive Philips Pw-1404 spectrometer, anode Sc/Mo, under working conditions of 80 kV and 35 mA. The mineralogy of the crystalline materials was determined by X-ray Diffraction (XRD), using a SIEMENS D-5000 (Madrid, Spain) X-ray powder diffractometer with an automatic divergence slit, and graphite Cu Kα radiation with a graphite monochromator. The XRD data were collected at an angular interval of 3° ≤ 2θ ≤ 65° with steps of 0.03° and with 3 s count times. The current intensity and voltage of the X-ray generator tube was 30 mA and 40 kW, and the divergence and reception slits were set at 1° and 0.18°, respectively. The characterization of the bulk samples was performed via the Rietveld method [28,29]. Rutile was used as an internal reference patron at a concentration of around 5% in all cases.
The sample morphology was determined with scanning electron microscopy (SEM) with a PHILIPS XL-30 ((Hillsboro, OR, USA) equipped with a Wolfram cathode. The powder samples were fixed on the metallic runner by means of a graphite plate, on the BIO-RED SC-502 (General Electric, New York, NY, USA) equipment. The energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) test was done by chemical analysis with a silicon/lithium X-ray detector and a DX41 analyzer.
The combined CaO (mmol/L) was obtained as the difference between the concentration in the lime-saturated control solution (17.68 mmol/L) and the CaO content in the solution in contact with the sample. At the end of the reaction time, the hydrated solid sample was filtered, washed with ethanol and heated at 60 °C for 24 h, to stop the hydration reaction. The calculations are based on the European standard of the pozzolanicity test for pozzolanic cements [30].
The 1 × 1 × 16 cm specimens of cement paste were prepared following the procedure described by Kock-Steinegger [31], with partial substitutions of 10 and 20% of each of the activated paper sludge (APS) and the activated coal waste (ACW) pozzolans, with a water/cement ratio of 0.5 and a curing time of 28 days. The same pozzolan and water/cement ratios were used in the case of the cement mortars, as described in the current norms [30], but in this case, the dimensions of the prismatic specimens were 4 × 4 × 16 cm. The specimens were cured under water for 28 days.
3. Results and Discussion
The thermal activation of many clayey materials within the range of 600 °C to 900 °C causes the total or partial decomposition of the crystalline network, due to dehydroxylation, passing through a transition state or phase with high reactivity. The clay is found in its most reactive state when calcination leads to a loss of hydroxyls and results in a collapsed and disordered clayey structure. The calcination temperature for K that produces the active state of MK is found within the 600 °C/800 °C interval [21,32], where the quantity and the type of the amorphous phase might have influenced the pozzolan activity. In both cases, wastes were thermally activated at 600 °C in an oven for over 2 h.
The silica-aluminous nature of the chemical composition of the CW should be highlighted, in which the sum of both oxides was over 70% of the total (Table 1). The presence of trace elements was also detected, such as Cr (180 ppm), V (141 ppm), Ni (53 ppm), Mo (21 ppm), Pb (4 ppm), Zn (25 ppm) As (2 ppm), and Co (22 ppm), in addition to chlorides (82 ppm). The crystalline mineralogical composition of CW was principally composed of quartz (37%), phyllosilicates (micas 25%, illite 52% and kaolinite 14%), calcite (17%), dolomite (5%) and potassium feldspar (2%) (Figure 1).

Table 1.
The chemical composition of the studied materials via X-ray Fluorescence (XRF).
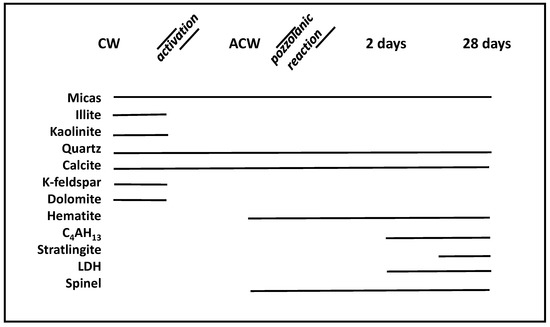
Figure 1.
Presence/absence of crystalline materials in the coal mining residues before CW/after ACW thermal activation and after the pozzolanic reaction at 2 and 28 days. CW: coal waste; ACW: activated coal waste; LDH: Layered Double Hydroxides.
The thermically ACW [32] maintained their silica-aluminous nature, the sum of their principal oxides SiO2, Al2O3 and Fe2O3 amounting to 80.19%, which is a higher value than the 70% that is specified for the standardized pozzolans of the same nature (fly ash and calcined natural pozzolan) in the American standard (ASTM 618-12) (Table 1). The presence of Cr (228 ppm), Ni (43 ppm), Pb (5 ppm) and Zn (46 ppm) was also detected as trace elements.
The main phases identified by XRD were quartz (54%), hematite (3%), phyllosilicates (20%), calcite (22%) and reflections at 2.43 Å (36.98° 2θ) and 2.85 Å (31.38° 2θ) due to the spinel phase (1%), the formation of which is related to the warming of clayey minerals containing a high quantity of aluminum [33] (Figure 1).
The results of the chemical composition (Table 1) of PS show that these wastes presented a silicate-aluminum-calcite nature, in which the three oxides amounted to 42%. The loss on calcination at 950 °C during 1 h in an electric furnace (loss on ignition (LOI) = 55.71%) was very high due to the presence of calcite and organic material. The main crystalline mineralogical compounds of the PS sample were calcite (35%), dolomite (1%), kaolinite (21%), as well as other minerals such as phyllosilicates (2%), mica (7%) and quartz (6%), while the rest was formed of organic matter (Figure 2).
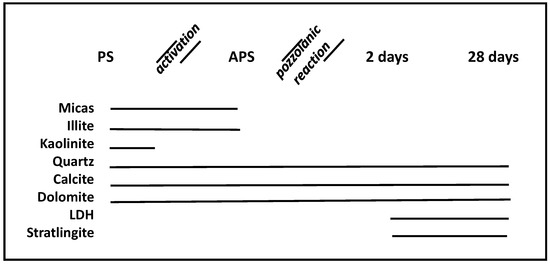
Figure 2.
Presence/absence of crystalline materials in paper sludge residues before PS/after APS thermal activation and after the pozzolanic reaction at 2 and 28 days.
The chemical composition of this APS presents silica, aluminum and lime as its principal oxides, a composition that is maintained with regard to its original material, PS, the sum of its three oxides (CaO + SiO2 + Al2O3) amounting to 69.3%, while the sum of SiO2 + Al2O3 + Fe2O3 is only 61.5% (Table 1).
The main crystalline compounds of APS are mica (2%), quartz (1%), illite (1%), dolomite (1%) and calcite (95%) (Figure 2). The absence of the characteristic peaks of K is notable in the two thermally activated wastes, which demonstrates their total transformation in the MK amorphous phase.
The elemental analysis of Ordinary Portland cement (OPC) by means of XRF determines the concentration of the principal elements in the cement (Ca, Si, Fe, Al), which in accordance with the Bogue formula [34] can be used to determine its mineralogical composition: C3S (41.7%), C2S (28.0%), Al2O3 (8.33%) and C4AF (8.89%).
The pozzolanic properties of the samples were determined by the quantity of lime that they fixed between 1 and 90 days. In Figure 3, the results of the lime that is fixed in the samples over various reaction times are shown. Through these chemical values, the presence or absence of pozzolanic activity may be valued, an essential condition for material to be used as an active addition to cement. In general, both wastes presented a high pozzolanic activity, as between 70–80% of the lime was available 6 days into the reaction of the fixed lime, progressively increasing up to 80–90% at 90 days. These values are comparable to those obtained for a 100% natural MK.
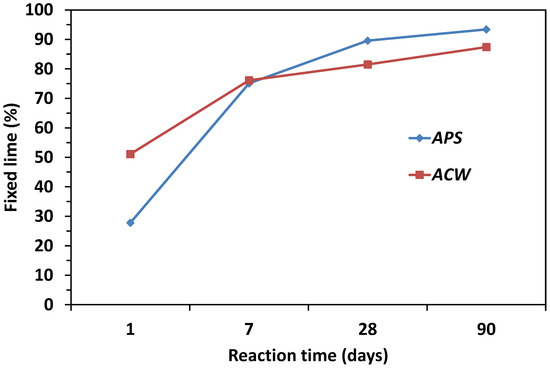
Figure 3.
Evolution of the pozzolanic activity for activated products.
Different pozzolanic behaviors were observed between the clayey wastes under analysis. The most important differences were those observed during the first 24 h of the reaction, where factors such as fineness, reactive silica content and morphology of the MK particles play a principal role in the short-term rate of reaction. Thus the ACW consumed half (50%) of the available lime; while the APS only reacted with a quarter (25%) of the lime, despite the latter waste presenting a higher quantity of kaolinite (21%) in its initial chemical composition. This fact could be related to the loss of specific surface of the MK with the increase of the calcination temperature [35]. Consequently, although both wastes were activated under the same conditions (600 °C and 2 h), the presence of organic matter (cellulose) in the APS changed those conditions.
The analysis of ACW in how it reacts with calcium hydroxide at 2 and at 28 days into the pozzolanic reaction (ACW/Ca(OH)2 system) presents the following crystalline phases:
Tetracalcium aluminate hydrate was observed in trace concentrations by XRD two days into the reaction, while after 28 days it increased by 5% (Figure 1). Stratlingite, inexistent at 2 days, quickly formed until it had a concentration of 20% after 28 days. In turn, monosulfoaluminate hydrate reached 5% after two days of reaction time, and was almost imperceptible after 28 days. Layered Double Hydroxides (LDH) compounds (phyllosilicate/carbonate), which at an early age had a concentration of 1%, reached 13% after 28 days. Both the micas (2%) (Figure 4F) and the spinel (1%) as well as the calcite (30%) remained constant at both ages, while the quartz evolved from 61% at two days to 29% at 28 days of reaction time.
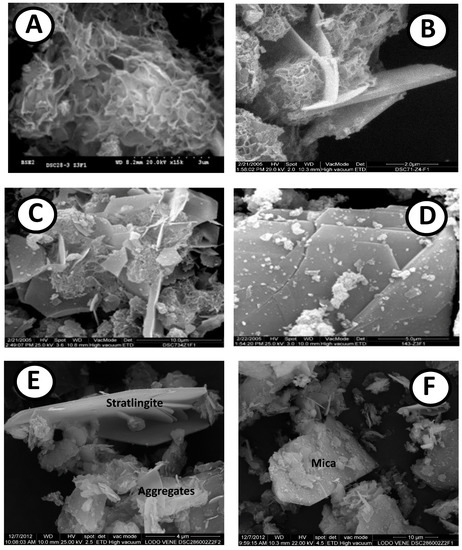
Figure 4.
(A) Gels of a spongy nature in ACW; (B) Monosulfoaluminate crystals with C-S-H gels in ACW; (C) LDH and C-S-H gels in APS; (D) Type II gels in APS; (E) Stratlingite in APS waste with aggregates (F) Mica in ACW waste.
SEM/EDX as an amorphous majority phase (Figure 4A) identified C-S-H gels, rich in calcium and presenting a spongy appearance. The nanostructure of the C-S-H gels consisted of interlaminar Ca with chains of silica tetrahedra linked on the sides with some aluminum substituting the silica in the tetrahedra. The CaO/SiO2 ratio was 1.26 (Table 1), which, according to the Taylor classification [36], corresponds to gel type I. In addition, laminar forms of LDH were recognizable: stratlingite, monosulfoaluminate (Figure 4B) and tetracalcium in various sizes and intergrown with the gels, forming aggregates, indicating successive phases of growth (Figure 4E).
For the APS/Ca(OH)2 system, in the APS sample, crystalline compounds of calcite were identified by XRD as a stable mineral for both reaction times, at a quantity of 66%. The new compounds such as LDH (Figure 4C) had already appeared at two days of reaction time, at an amount of 2%, and were conserved after 28 days (Figure 2). Stratlingite, non-existent at an early age, appeared at 28 days with a concentration of 1%, and the majority components at both 2 and 28 days were the C-S-H gels (Figure 4C, whose value, 30%, was practically constant for both control points.
The SEM technique permits the identification of amorphous phases such as C-S-H gels. An EDX analysis permits the calculation of the CaO/SiO2 ratio in the compounds that varied between 1.60 and 1.63 [36] (Table 2). This interval corresponds to gel type II (Figure 4D), according to the Taylor classification, which is the principal compound of hydration. The structural order increases when the aforementioned relation grows, linked to the reaction time. Thus, in the short term (2 days) the C-S-H gels have a rounded appearance, while in the longer-term (28 days) they appear interspersed between the LDH structures and the stratlingite (Figure 4E), both similar to each other and with a hexagonal laminar appearance, and only identified by their chemical composition through EDX.

Table 2.
Chemical analysis by energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) of C-S-H gels in the APS and ACW at 2 days and 28 days.
Table 3 shows the Si/Al, Ca/Si, and Ca/Al ratios, obtained by SEM/EDX of each one of the C-S-H gels at 2 and at 28 days of hydration. The Ca/Si ratio of the gel that formed is higher in the APS (with less Si and more Ca than ACW) than in the ACW, for both study ages. Initially, the ACW fixed more lime than the APS (Figure 3); however, calcium was not incorporated in the gel and it reacted to form calcite, as identified by XRD. The C-S-H gels formed via the APS in no way modified the Ca/Si ratio over the hydration time, while the gel formed with the ACW increased that ratio; and given that it increased the quantity of fixed lime to a lesser extent, we can assume that it produced changes in the structure of the C-S-H gels that were formed (Figure 5).

Table 3.
Si/Al, Ca/Si and Ca/Al ratios from the thermically activated wastes.
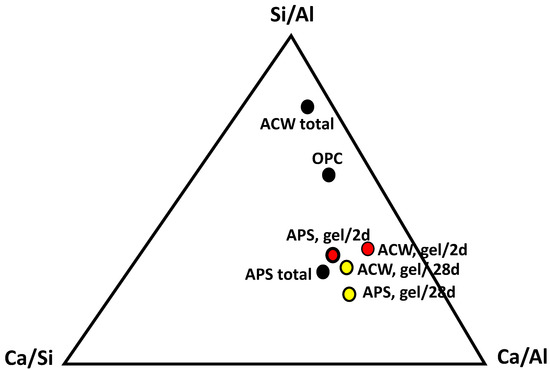
Figure 5.
Si/Al, Ca/Si and Ca/Al ratios in the studied residues, standard cement and C-S-H gels at 2 (red) and 28 (yellow) days of reaction.
Thus, recent studies [37,38] have indicated that the Ca/Si ratio of the C-S-H gels can provide information on their structure; with low Ca/Si ratios below 1.0, the gels present structures with a high percentage of Q2 units, while the upper Ca/Si ratios increase the number of Q1 units, therefore producing shorter chains. Therefore, they change from foil-like structures to fibrillary structures. Consequently, the gel obtained in the ACW sample may be considered to have shorter gel chains than the one obtained in the pozzolanic reaction of the APS.
The Si/Al ratio was, nevertheless, modified in an opposing way in both gels, increasing over time in the APS samples and decreasing in the ACW samples. It may be observed from Table 2 that the quantity of Al decreases in the APS sample, while the concentrations of calcium and silicate increase. The C-S-H gel that was formed therefore initially incorporated the entire Al, and with the hydration it modified the structure by breaking up the chains and decreasing the Ca/Si ratio. In the case of the gels generated in the ACW sample, the behavior was different. The gels increased the content of Al, increasing the polymerization of the chain, confirming the results obtained from the analysis of the Ca/Si ratios. It is interesting to note that the ACW sample initially contained a higher content of Al; however, the incorporation of Al in the gel was not initially present, which explains the decrease in the Si/Al ratio from 2 to 28 days.
Having characterized the gels obtained in the lime/waste system, cement pastes were mixed with two proportions of waste (10 and 20%), to determine the influence of the waste on their physical and mineralogical characterizations.
In the 10% ACW/cement system, the following hydrated crystalline phases were identified: portlandite (64%), ettringite (18%), and C4AH13 (18%). At substitutions of 20%, the same mineralogical phases were identified, but at different concentrations, some increasing and others decreasing; thus, the concentrations of portlandite and ettringite decreased to 41% and to 13% respectively, while the concentration of C4AH13 increased to 36%. This fact means that an increase in the substitution of cement for this thermally activated industrial waste favours the formation of aluminates and calcium carboaluminates to the detriment of portlandite and ettringite.
With respect to the APS, the crystalline phases were modified with respect to the earlier pozzolan, due to their different calcium nature. Thus, portlandite (45%) appeared at a substitution of 10%, calcite appeared from the original material (36%), as did C4AH13 (19%). An increase from 10% to 20% APS when substituting with pozzolan caused the portlandite to decrease to 37%, the calcite to slightly increase to a concentration 40%, and the C4AH13 to remain practically constant (18%); and for the first time an LDH neo-formation phase was identified (5%).
Table 4 shows the analyses of the C-S-H gels and the Ca/Si, Si/Al and Al/Ca gels determined by SEM/EDX in the different cement paste matrices with substitutions of 0, 10 and 20%.

Table 4.
Analysis by EDX from the C-S-H gels.
The incorporation of the waste in the pastes decreased the Ca/Si ratio of the gel, initially caused by increased amounts of silica present in the waste. In the case of the samples that incorporated APS and as seen in the activated sludge by itself (Table 3), the reaction time hardly modified the Ca/Si ratio. Likewise, the presence of ACW generated an increase in that signal, because the higher content of Al produced more polymerized gels (Figure 6).
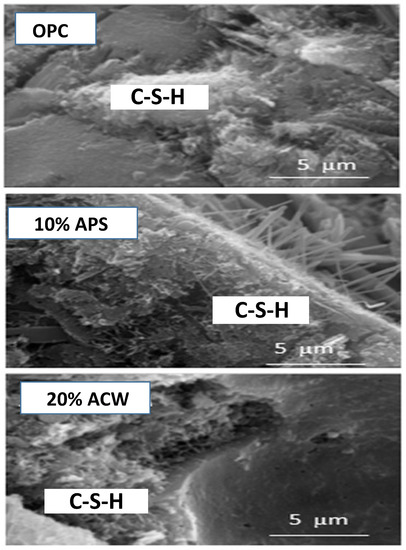

Figure 6.
Morphologies of the C-S-H gels at 28 days of cure time.
Furthermore, the lower concentration of Al in the APS produced C-S-H gels with higher Si/Al ratios [39]. Richardson [40] suggested that C-A-S-H gels incorporate more aluminum as the Ca/Si ratio decreases, as is confirmed in the samples with APS. However, the presence of cement in the case of the ACW samples inhibited the incorporation of aluminum in the gel and favoured the formation of aluminate phases, as observed through XRD. Finally, the higher levels of Al in the C-S-H gels formed in the cement/APS mixtures meant a lower Ca/Si ratio [41].
The influence of the percentage substitution on the relative compressive strengths(blended mortar/OPC mortar) of the standardized mortars at 2 and 28 days of hydration is represented in Figure 7. The progressive increase in strength may be clearly seen in the first 48 h of the reaction, increasingly so when the percentage substitution was higher for the case of the APS pozzolan, although with substitutions of 10% the compressive strength was slightly lower than the reference mortar [42]. However, the activated carbon waste showed a significant gain in compressive strength with substitutions of 10%, falling behind the reference mortar with incorporations of 20%. With a longer hydration time of 28 days, the APS pozzolan increased in strength in both proportions with respect to the OPC mortar; however, the ACW pozzolan never reached the reference values, decreasing with the increase in the percentage substitution. This development of compressive strengths would be directly related with the evolution of the fixed lime, as commented earlier (Figure 3).
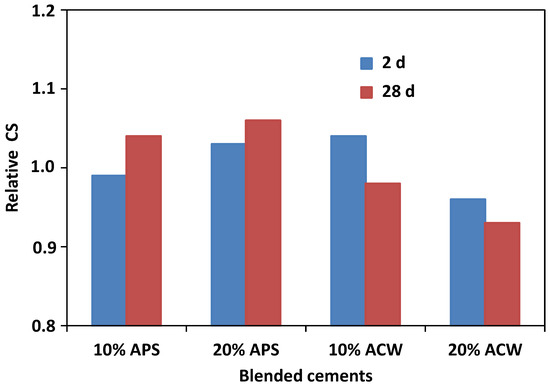
Figure 7.
Evolution of the resistances relative to compression (CS) with the hydration time.
4. Conclusions
The kaolinite-based industrial wastes selected in the present study were of different natures and presented different kaolinite contents. The CW was of a silico-aluminous nature with 14% kaolinite; while the PS was of a silico-aluminum-calcite nature with 21% kaolinite.
Thermal activation at 600 °C and over 2 h in an oven were sufficient for a total transformation of the K into MK, a highly reactive pozzolan. The rest of the minerals present in the wastes remained unaltered under these activation conditions.
The MK-based activated products, ACW and APS, presented a high pozzolanic activity, taking into account the high values of fixed lime after 28 days of reaction time. However, a turning point was observed on day 7 of the reaction. Clearly, it may be seen that the reaction rate of the APS pozzolan in the short term was 50% lower than the one presented by the ACW pozzolan, but after day 28 its pozzolanic activity slightly improved with regard to the CW.
The results showed that the pozzolanic activity of the waste (in terms of fixed lime) was similar up to 90 days but that its reaction rate was different.
Due to these pozzolanic differences between the studied wastes, both the formation and the evolution of the mineralogical crystalline phases formed during the pozzolanic reaction, in APS, were stratlingite and LDH, while in the ACW, C4AH13 appeared in addition to the latter two (stratlingite and LDH compounds).
The C-S-H gel is the principal non-crystalline mineralogical phase from hydration in the two types of wastes. In the ACW waste, type I gels were identified, while type II gels were identified in the APS. Type II gels present different Ca/Si ratios, due to the APS waste that generates gels that are rich in calcium and poor in Al, unlike those obtained with the ACW waste. Likewise, the chains of the gel obtained with the ACW are shorter than those obtained with APS waste. From the point of view of the Ca/Si ratio of the final product, the initial concentration of the sample (Al, Si, etc.) is not as important as the mineralogical phases present and their reactivity.
The C-S-H gel generated with coal waste had very short chains, was poorer in Ca and rich in Al. The addition of both wastes to cement modified its mineralogical composition in comparison with a conventional cement, favoring the formation of C4AH13 over the formation of ettringite.
With both additions to the cement, the formation of C4AH13 was favoured, but with some differences. In the case of the APS pozzolan no ettringite was formed and LDH appeared at 28 days, while ettringite was initially formed with ACW, although it decreased at 28 days to the detriment of the formation of C4AH13. This reaction produced gels with a low incorporation of Al even at 28 days in the ACW samples, but with high Ca/Si ratios. Besides, the gels obtained from the cement plus APS mixture incorporated more Al in its structure and therefore had lower Ca/Si ratios.
The evolution of the compressive strengths in both pozzolans was different: APS showed better mechanical behavior than ACW and even exceeded the mechanical performance of the reference mortar in relation to both percentages of substitution and also in relation to the same curing times. However, ACW, at any age, shows a worse mechanical strength than OPC used as the reference.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competiveness (MINECO/FEDER) by the financial support (BIA2015-65558-C3-1/2/3-R) y a la Sociedad Anónima Hullera Vasco-Leonesa (León, Spain) and the Spanish Cement Institute (IECA, Madrid, Spain) for their support in this research.
Author Contributions
Rosario García-Giménez has designed the paper and performed the XRD analysis. Moisés Frias has carried out the mechanical and pozzolanic tests. Raquel Vigil de la Villa has performed and interpreted the SEM/EDX analysis and Sagrario Martínez-Ramírez, the XFR and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sabir, B.B.; Wild, S.; Bai, J. Metakaolin and calcined clays as pozzolans for concrete: A review. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2001, 441, 423–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samet, B.; Mnif, T.; Chaabouni, M. Use of a kaolinitic clay as a pozzolanic material for cements: Formulation of blended cement. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2007, 741, 729–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, N.H.; Granados, R.J.; Blanco-Varela, M.T.; Cortina, J.L.; Martínez-Ramírez, S.; Marsal, M.; Guillem, M.; Puig, J.; Fos, C.; Larrotcha, E.; et al. Evaluation of a lime-mediated sewage sludge stabilisation process. Product characterization and technological validation for its use in the cement industry. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juenger, M.C.G.; Siddique, R. Recent advances in understanding the role of supplementary cementitious materials in concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 78, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas, M.A.; Monzo, J.; Payá, J.; Reig, L.; Borrachero, M.V. Ceramic tiles waste as replacement material in Portland cement. Adv. Cem. Res. 2016, 28, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, E.V.; Villar-Cociña, E.; Frías, M. Effects of calcining conditions on the microstructure of sugar cane waste ashes: Influence in the pozzolanic activation. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2009, 31, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Composition, Specification and Conformity Criteria for Common Cements; European Standard EN 197-1; European Standard: Madrid, Spain, 2011.
- Rios, C.A.; Williams, C.D.; Fullen, M.A. Hydrogarnet and Tobermorite at 175 °C from Kaolinite and Metakaolinite in the CaO-Al2O3-SiO2-H2O System: A Comparative Study. Appl. Clay Sci. 2009, 43, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vejmelkova, E.; Pavlikova, M.; Kepprt, M.; Kersner, Z.; Rovnanikova, P.; Ondracek, M.; Sedlmayer, M.; Cerny, R. High Performance Concrete with Czech Metakaolin: Experimental Analysis of Strength, Toughness and Durability Characteristics. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 1404–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janotka, I.; Puertas, F.; Palacios, M.; Kuliffayova, M.; Varga, C. Metakaolin sand Blended Cement Pastes: Rheology, Hydration Process and Mechanical Properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 791–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ptacek, P.; Frajkorova, F.; Soukal, F.; Opravil, T. Kinetics and mechanism of three stages of thermal transformation of kaolinite to metakaolinite. Powder Technol. 2014, 264, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesce, G.L.; Bowen, C.R.; Rocha, J.; Sardo, M.; Allen, G.C.; Walker, P.J.; Denuault, G.; Serrapede, M.; Ball, R.J. Monitoring hydration in lime-MK composites using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Clay Minecraft 2014, 4, 341–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frías, M.; de la Villa, R.V.; de Soto, I.; Garcia, R.; Baloa, T.A. Influence of activated drinking-water treatment waste on binary cement-based composite behavior: Characterization and properties. Compos. Part B 2014, 60, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tironi, A.; Castellano, C.C.; Bonavetti, V.L.; Trezza, M.A.; Scian, A.N.; Irassar, E.F. Kaolinitic calcined clays—Portland cement system: Hydration and properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 64, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habert, G.; Choupay, N.; Montel, J.M.; Guillaume, D.; Escadeillas, G. Effects of the secondary minerals of the natural pozzolans on their pozzolanic activity. Cem. Concr. Res. 2008, 38, 963–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habert, G.; Choupay, N.; Escadeillas, G.; Guillaume, D.; Montel, J.M. Clay content of argillites: Influence on cement based mortars. Appl. Clay Sci. 2009, 322, 330–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Villa, R.V.; Fernández, R.; Rodríguez, O.; García, R.; Villar-Cociña, E.; Frías, M. Evolution of the pozzolanic activity of a thermally treated zeolite. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 3213–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frías, M.; de la Villa, R.V.; García, R.; de Soto, I.; Medina, C.; de Rojas, M.S. Scientific and technical aspects of blended cement matrices containing activated slate waste. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2014, 348, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, R.; de la Villa, R.V.; Frías, M.; Rodríguez, O.; Martínez-Ramírez, S.; Fernández-Carrasco, L.; de Soto, I.S.; Villar-Cociña, E. Mineralogical study of calcined coal waste in a pozzolan/Ca(OH)2 system. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 108, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotopoulou, C.H.; Kontori, E.; Perraki, T.H.; Kakali, G. Dissolution of aluminosilicate minerals and by-products in alkaline media. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 2967–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigil, R.; Frías, M.; de Rojas, M.S.; Vegas, I.; García, R. Mineralogical and Morphological Changes of Calcined Paper Sludge at Different Temperatures and Retention in Furnace. Appl. Clay Sci. 2007, 36, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frías, M.; Rodríguez, O.; García, R.; Vegas, I. Influence of Activation Temperature on Reaction Kinetics in Recycled Clay Waste—Calcium Hydroxide Systems. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2008, 91, 4044–4051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakchouk, A.; Trifi, L.; Samet, B.; Bouaziz, S. Formulation of blended cement: Effect of process variables on clay pozzolanic activity. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 1365–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Chaipanich, A.; Kinuthia, J.M.; O’Farrell, M.; Sabir, B.B.; Wild, S.; Lewis, M.H. Compressive Strength and Hydration of Waste Paper Sludge Ash Ground Granulated Blast furnace Slag Blended Pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2003, 33, 1189–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vegas, I.; Frias, M.; Urreta, J.; San Jose, T. Obtaining a Pozzolanic Addition from the Controlled Calcinations of Paper Mill Sludge. Performance in Cement Matrices. Mater. Constr. 2006, 56, 49–60. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez, O.; de Rojas, M.S.; García, R.; Vigil, R. Effect of thermally activated paper sludge on the mechanical properties and porosity of cement pastes. Mater. Constr. 2009, 59, 17–28. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez, O.; de la Villa, R.V.; de Rojas, M.S.; Frías, M. Novel use of kaolin wastes in blended cements. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2009, 92, 2443–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietveld, H.M. A profile refinement method for nuclear and magnetic structures. J. Appl. Cryst. 1969, 2, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, C.D.; Ward, C.R. Quantitative X-ray powder diffraction analysis of clay minerals in Australian coals using Rietveld methods. Appl. Clay Sci. 2002, 21, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Methods of Testing Cement—Part 5: Pozzolanicity Test for Pozzolanic Cement; UNE-EN 196-5; European Standard: Madrid, Spain, 2011.
- Koch, A.; Steinegger, H. A Rapid Method for Testing the Resistance of Cements to Sulphate Attack. Zem. Kalk Gips 1960, 13, 317–324. [Google Scholar]
- García, R.; Vigil, R.; Rodríguez, O.; Frías, M. Study of hydrated phases present in calcined paper sludge (metakaolinite)/saturated CaO dissolution system cured at 40 °C and 28 days of reaction. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 3936–3941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frías, M.; Vigil, R.; García, R.; Rodríguez, O.; Goñi, S.; Vegas, I. Evolution of mineralogical phases produced during the pozzolanic reaction of different metakaolinite by-products: Influence of the activation process. Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 56, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cementos: Cálculo de la Composición Potencial del Clinker Portland; Norma española UNE 80304:2006; European Standard: Madrid, Spain, 2006.
- Frías, M.; de Rojas, M.S.; Rodriguez, O.; García, R.; Vigil, R. Characterization of calcined paper sludge as an environmentally friendly source of MK for manufacture of cementitious materials. Adv. Cem. Res. 2008, 20, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, H.F.W. Cement Chemistry, 2nd ed.; Thomas Telford Ltd.: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Tajuelo-Rodriguez, E.; Richardson, I.G.; Black, L.; Boehm-Courjault, P.; Nonat, A.; Skibsted, J. Composition, silicate anion structure and morphology of calcium silicate hydrates (C-S-H) synthesised by silica-lime reaction and by controlled hydration of tricalcium silicate (C3S). Adv. Appl. Certif. 2015, 114, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grangeon, S.; Fernandez-Martinez, A.; Baronnet, A.; Marty, N.; Poulain, A.; Elkäm, E.; Roosz, C.; Gaboreau, S.; Henocq, P.; Claret, F. Quantitative X-ray pair distribution function analysis of nanocrystalline calcium silicate hydrates: A contribution to the understanding of cement chemistry. J. Appl. Cryst. 2017, 50, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lizcano, M.; Kim, H.S.; Basu, S.; Radovic, M. Mechanical properties of sodium and potassium activated metakaolin-based geopolymers. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 2607–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, I.G. Model structures for C-(A)-S-H (I). Acta Cryst. B 2014, 70, 903–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- L’Hôpital, E.; Lothenbach, B.; Kulik, D.A.; Scrivener, K. Influence of calcium to silica ratio on aluminium uptake in calcium silicate hydrate. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 85, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kani, E.N.; Allahverdi, A. Effects of curing time and temperature on strength development of inorganic polymeric binder based on natural pozzolan. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 3088–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).