Deep Activation Pooling for Blind Image Quality Assessment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
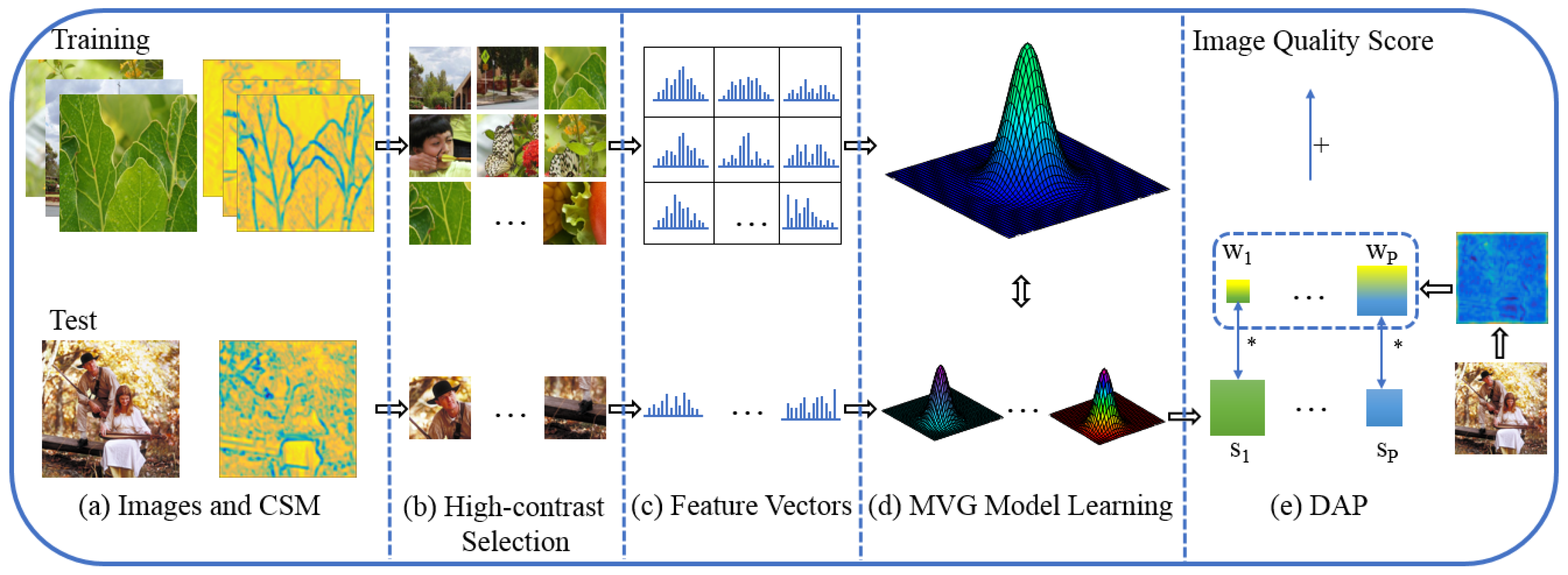
2. Approach
2.1. Convolutional Summing Map
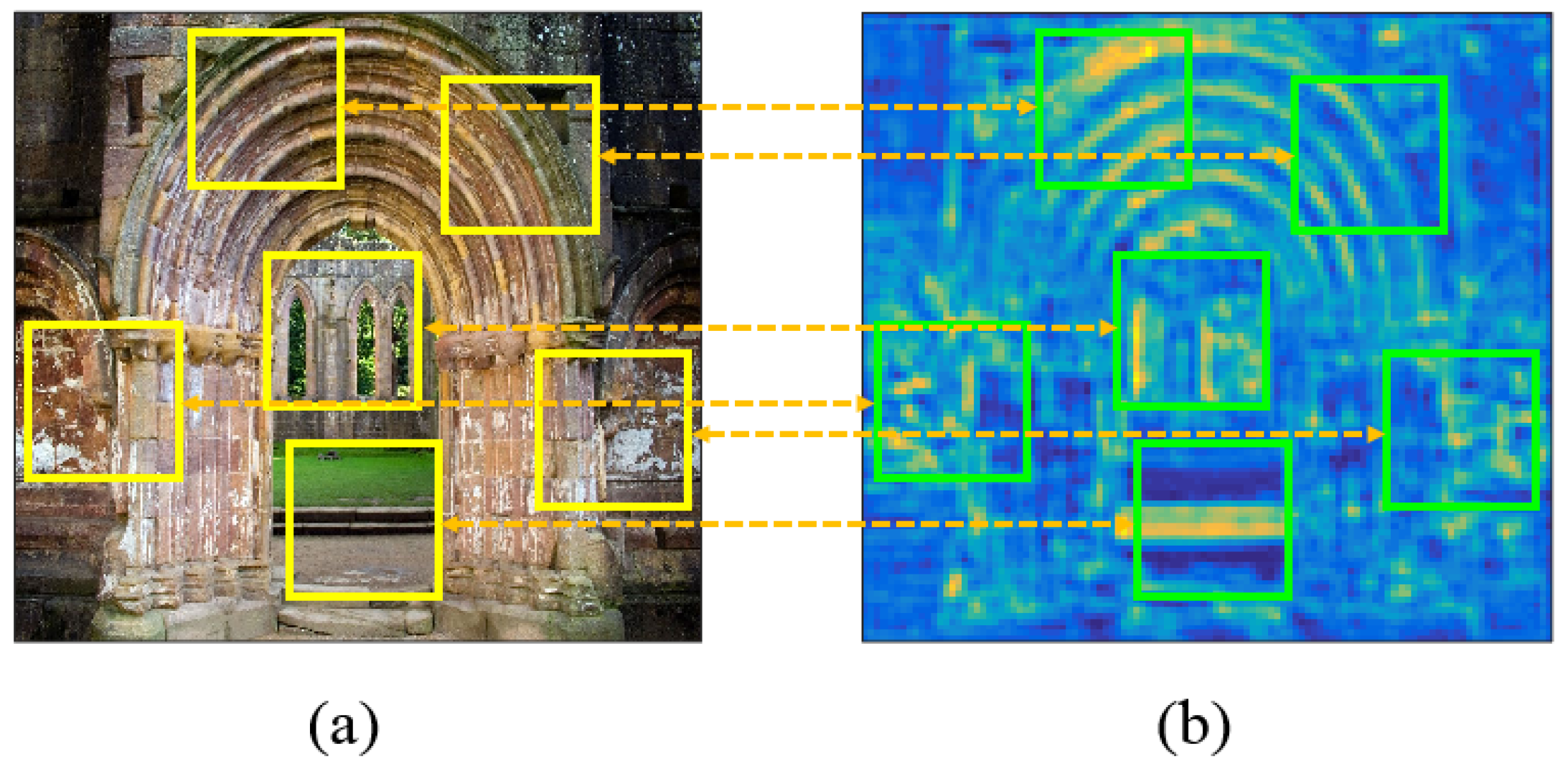
2.2. High-Contrast Patch Selection
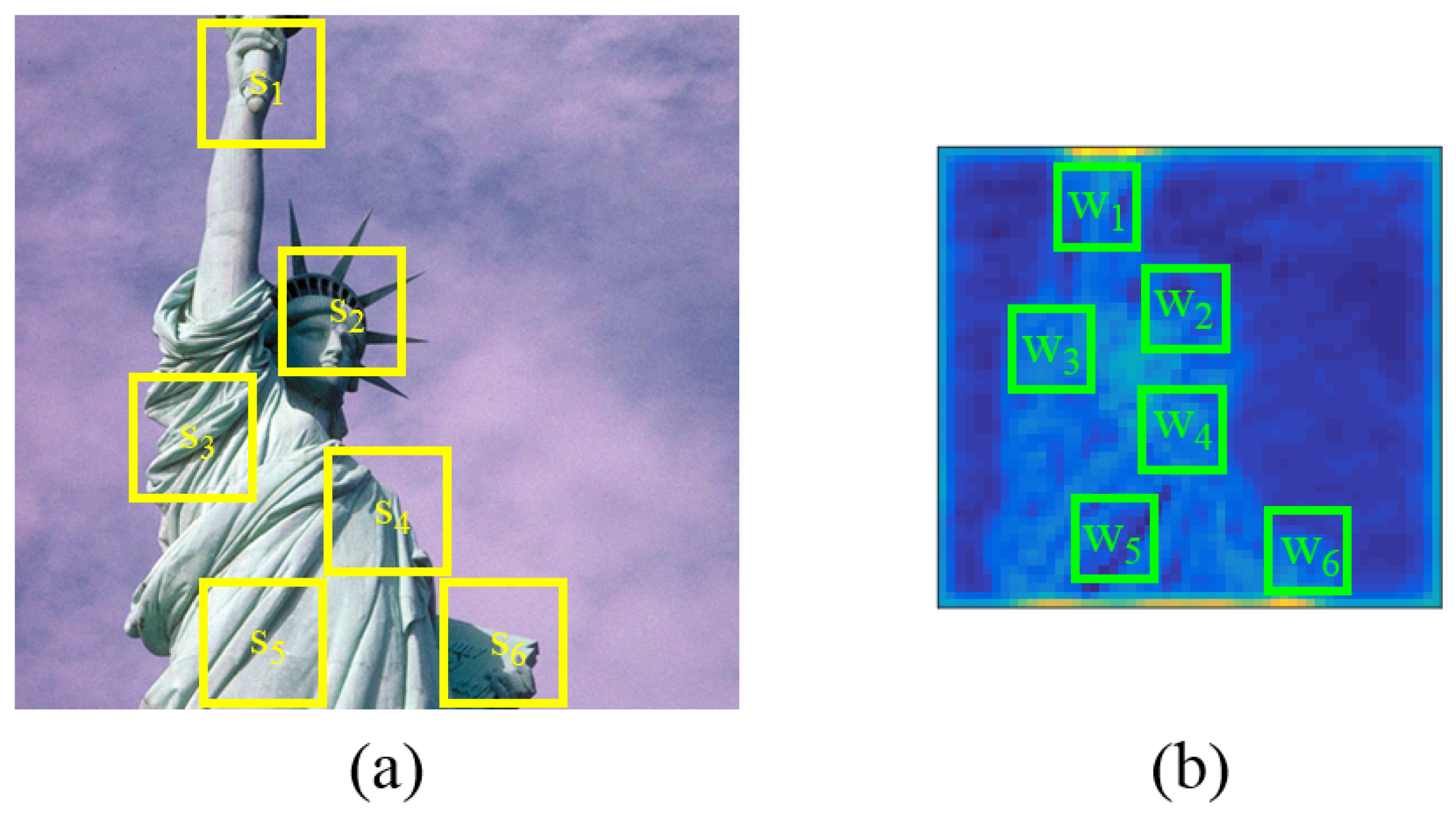
2.3. Deep Activation Pooling
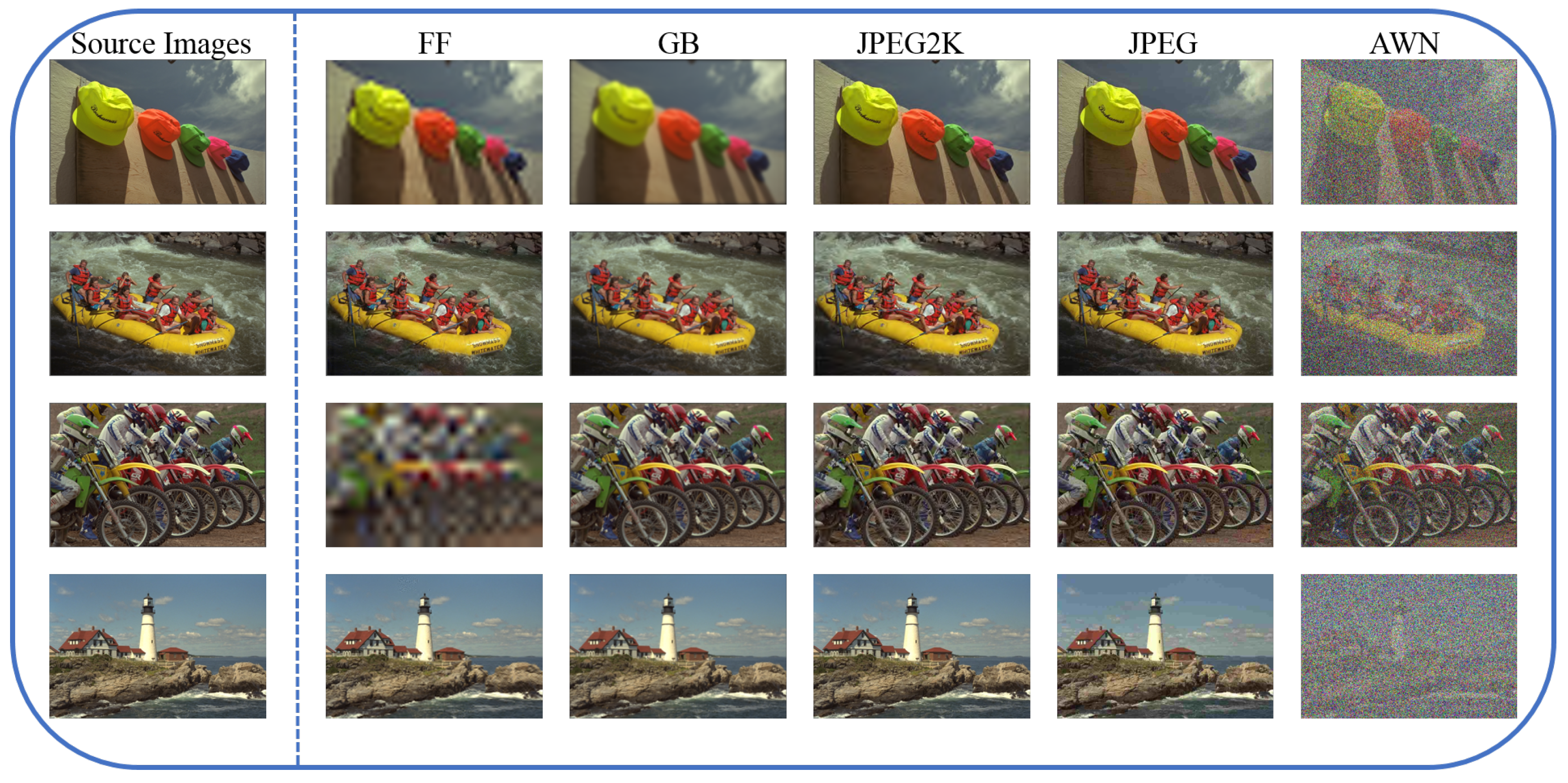
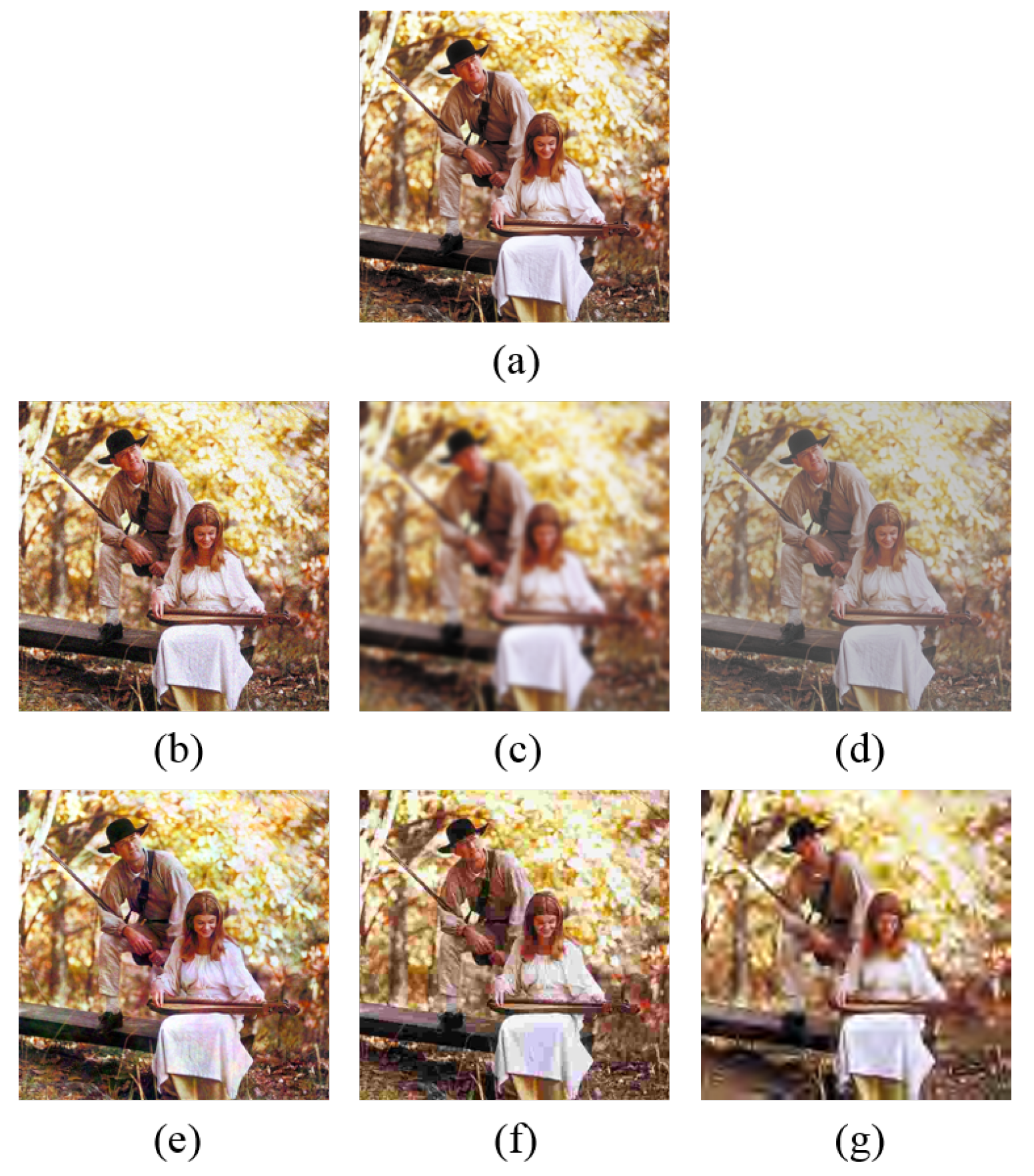
3. Experiments
3.1. Evaluation Protocols and Databases
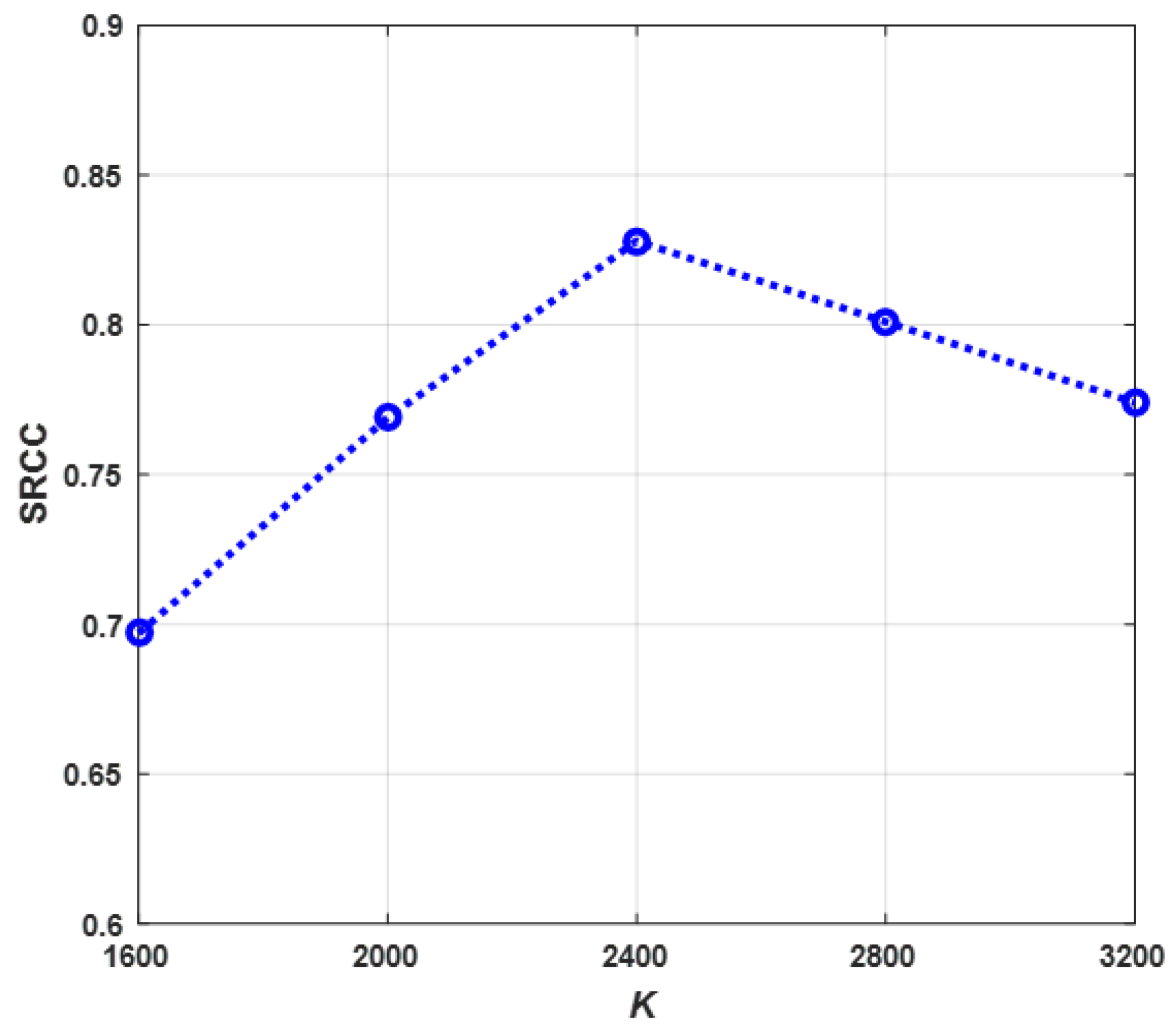
3.2. Implementation Details
3.3. Performance Comparison with Other Methods
3.4. Performance on Generalization Ability
3.5. Performance on Individual Distortion Types
3.6. Influence of Each Kind of Features
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Chen, L.; Zhu, Y.; An, F.; Wang, H.; Feng, S. A Hardware-efficient vector quantizer based on self-organizing map for high-speed image compression. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gau, Y.T.A.; Le, H.N.; Bergles, D.E.; Kang, J.U. Image analysis of dynamic brain activity based on gray distance compensation. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.O.; Han, H.S.; Park, R.H. Gradient information-based image quality metric. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2010, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Mou, X.; Zhang, D. FSIM: A feature similarity index for image quality assessment. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2011, 20, 2378–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, W.; Zhang, L.; Mou, X.; Bovik, A.C. Gradient magnitude similarity deviation: A highly efficient perceptual image quality index. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2014, 23, 684–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, F.; Lin, X.; Rahardja, S.; Lin, W.; Ong, E.; Yao, S.; Yang, X. A locally adaptive algorithm for measuring blocking artifacts in images and videos. Signal Process Image 2004, 19, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Klomp, N.; Heynderickx, I. A no-reference metric for perceived ringing artifacts in images. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2010, 20, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Wang, S.; Chen, J.; Ma, S.; Zhao, D.; Gao, W. No-reference perceptual image quality metric using gradient profiles for JPEG2000. Signal Process Image 2010, 25, 502–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosse, S.; Maniry, D.; Müller, K.R.; Wiegand, T.; Samek, W. Deep neural networks for no-reference and full-reference image quality assessment. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 206–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moorthy, A.K.; Bovik, A.C. Blind image quality assessment: from natural scene statistics to perceptual quality. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2011, 20, 3350–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Joshi, N.; Kapoor, A. Learning a blind measure of perceptual image quality. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 20–25 June 2011; pp. 305–312. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Bovik, A.C.; Wu, X. Blind image quality assessment using a general regression neural network. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2011, 22, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ma, K.; Liu, W.; Zhang, K.; Duanmu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zuo, W. End-to-end blind image quality assessment using deep neural networks. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 1202–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, A.; Moorthy, A.K.; Bovik, A.C. No-reference image quality assessment in the spatial domain. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2012, 21, 4695–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chandler, D.M. No-reference image quality assessment based on log-derivative statistics of natural scenes. J. Electron. Imaging 2013, 22, 043025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Mou, X.; Zhang, L.; Bovik, A.C.; Feng, X. Blind image quality assessment using joint statistics of gradient magnitude and laplacian features. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2014, 23, 4850–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, A.; Soundararajan, R.; Bovik, A.C. Making a “completely blind” image quality analyzer. IEEE Signal Proc. Lett. 2013, 20, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Zhang, L.; Mou, X. Learning without human scores for blind image quality assessment. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 995–1002. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Bovik, A.C. A feature-enriched completely blind image quality evaluator. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2015, 24, 2579–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Shi, C.; Wang, C.; Xiao, B.; Qi, C. Multi-order co-occurrence activations encoded with Fisher Vector for scene character recognition. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2017, 97, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimpoi, M.; Maji, S.; Vedaldi, A. Deep filter banks for texture recognition and segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 8–10 June 2015; pp. 3828–3836. [Google Scholar]
- Sheikh, H.R.; Sabir, M.F.; Bovik, A.C. A statistical evaluation of recent full reference image quality assessment algorithms. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2006, 15, 3440–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, E.C.; Chandler, D.M. Most apparent distortion: full-reference image quality assessment and the role of strategy. J. Electron. Imaging 2010, 19, 011006. [Google Scholar]
- Sheikh, H.R.; Wang, Z.; Cormack, L.; Bovik, A.C. Live Image Quality Assessment Database Release 2. Available online: http://live.ece.utexas.edu./research/quality (accessed on 17 July 2007).
- Saad, M.A.; Bovik, A.C.; Charrier, C. Model-based blind image quality assessment using natural dct statistics. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2011, 21, 3339–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, P.; Kumar, J.; Kang, L.; Doermann, D. Unsupervised feature learning framework for no-reference image quality assessment. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 20–25 June 2011. [Google Scholar]



| Block Number | Convolution Stride | Spatial Padding | Building Blocks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Block1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Block2 | 1 | 1 | |
| Block3 | 1 | 1 | |
| Block4 | 1 | 1 | |
| Block5 | 1 | 1 | |
| FC-4096 | |||
| FC-4096 | |||
| FC-1000 | |||
| 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | |
| 3 | 0.742 | 0.765 | 0.752 | 0.742 | 0.738 | 0.720 |
| 4 | 0.769 | 0.787 | 0.784 | 0.771 | 0.767 | 0.753 |
| 5 | 0.793 | 0.807 | 0.803 | 0.795 | 0.781 | 0.750 |
| 6 | 0.804 | 0.815 | 0.811 | 0.802 | 0.794 | 0.780 |
| 7 | 0.812 | 0.828 | 0.820 | 0.813 | 0.801 | 0.797 |
| 8 | 0.802 | 0.814 | 0.808 | 0.794 | 0.783 | 0.769 |
| BIQA Models | CSIQ | LIVE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SRCC | PRCC | SRCC | PRCC | |
| CORNIA [27] | 0.714 | 0.781 | 0.940 | 0.944 |
| BRISQUE [14] | 0.775 | 0.817 | 0.933 | 0.931 |
| BLIINDS2 [26] | 0.780 | 0.832 | 0.924 | 0.927 |
| NIQE [17] | 0.627 | 0.725 | 0.908 | 0.908 |
| IL-NIQE [19] | 0.822 | 0.865 | 0.902 | 0.906 |
| HPSP+DAP | 0.824 | 0.867 | 0.908 | 0.907 |
| Proposed HPSC+DAP | 0.829 | 0.871 | 0.919 | 0.921 |
| IQA Models | CSIQ | |
|---|---|---|
| SRCC | PRCC | |
| CORNIA [27] | 0.663 | 0.764 |
| BRISQUE [14] | 0.557 | 0.742 |
| BLIINDS2 [26] | 0.577 | 0.724 |
| NIQE [17] | 0.627 | 0.716 |
| IL-NIQE [19] | 0.815 | 0.854 |
| Proposed HPSC+DAP | 0.828 | 0.867 |
| Databases | Distortion Types | BRISQUE [14] | BLIINDS2 [26] | CORNIA [27] | NIQE [17] | IL-NIQE [19] | Proposed HPSC+DAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSIQ | AWN | 0.925 | 0.801 | 0.746 | 0.810 | 0.850 | 0.863 |
| GB | 0.903 | 0.892 | 0.917 | 0.895 | 0.858 | 0.869 | |
| CTD | 0.024 | 0.012 | 0.302 | 0.227 | 0.501 | 0.523 | |
| PGN | 0.253 | 0.379 | 0.420 | 0.299 | 0.874 | 0.891 | |
| JPEG | 0.909 | 0.900 | 0.908 | 0.882 | 0.899 | 0.916 | |
| JPEG2K | 0.867 | 0.895 | 0.914 | 0.907 | 0.906 | 0.921 | |
| LIVE | FF | - | - | - | 0.864 | 0.833 | 0.841 |
| GB | - | - | - | 0.933 | 0.915 | 0.929 | |
| JPEG2K | - | - | - | 0.919 | 0.894 | 0.920 | |
| JPEG | - | - | - | 0.941 | 0.942 | 0.947 | |
| AWN | - | - | - | 0.972 | 0.981 | 0.980 |
| Database | - MSCN | - MSCN Products | - Gradients | - Log-Gabor | - Color |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSIQ | 0.7713 | 0.7893 | 0.7462 | 0.7324 | 0.8048 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, S.; Durrani, T.S. Deep Activation Pooling for Blind Image Quality Assessment. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8040478
Zhang Z, Wang H, Liu S, Durrani TS. Deep Activation Pooling for Blind Image Quality Assessment. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(4):478. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8040478
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhong, Hong Wang, Shuang Liu, and Tariq S. Durrani. 2018. "Deep Activation Pooling for Blind Image Quality Assessment" Applied Sciences 8, no. 4: 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8040478
APA StyleZhang, Z., Wang, H., Liu, S., & Durrani, T. S. (2018). Deep Activation Pooling for Blind Image Quality Assessment. Applied Sciences, 8(4), 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8040478





