Three-Dimensional Identification for Unbalanced Mass of Rotor Systems in Operation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
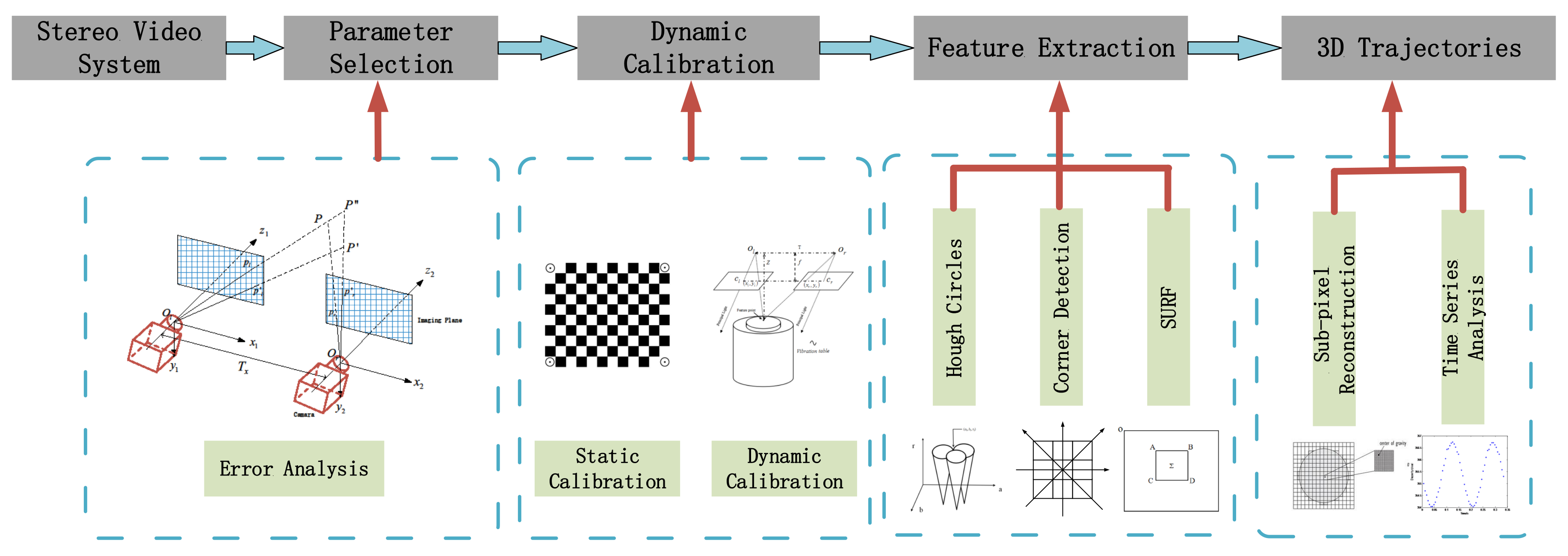
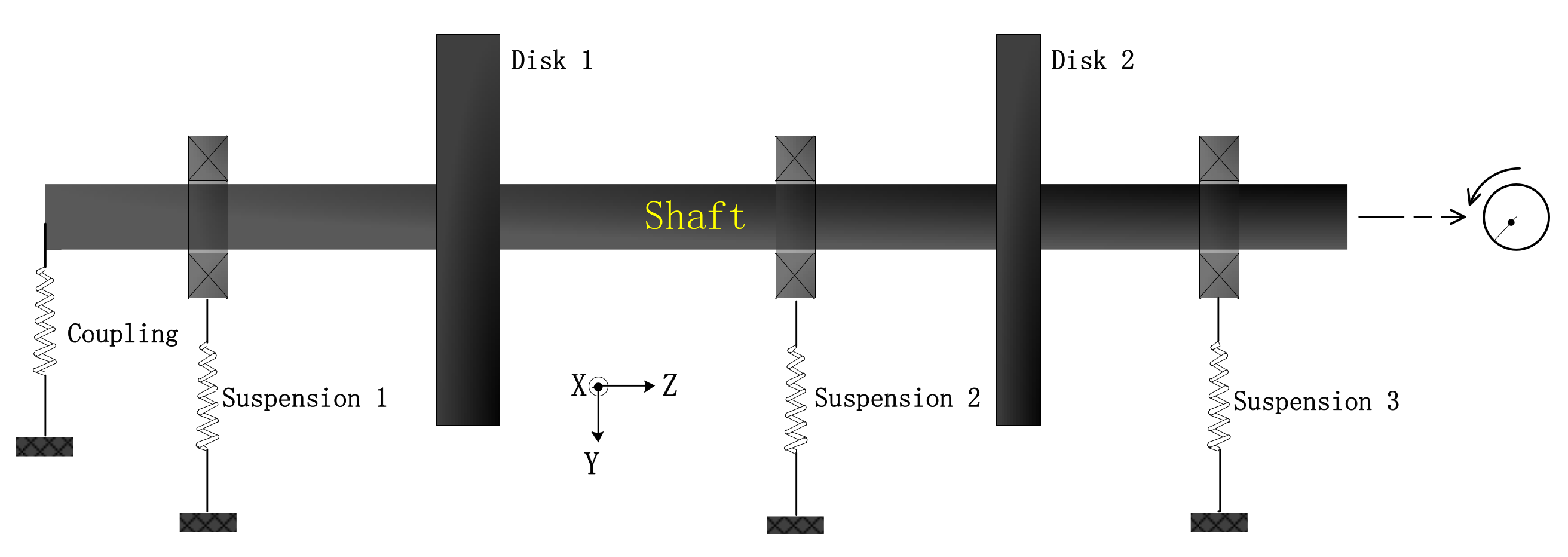
2. Model and Measurement Procedure
2.1. Model Error Analysis
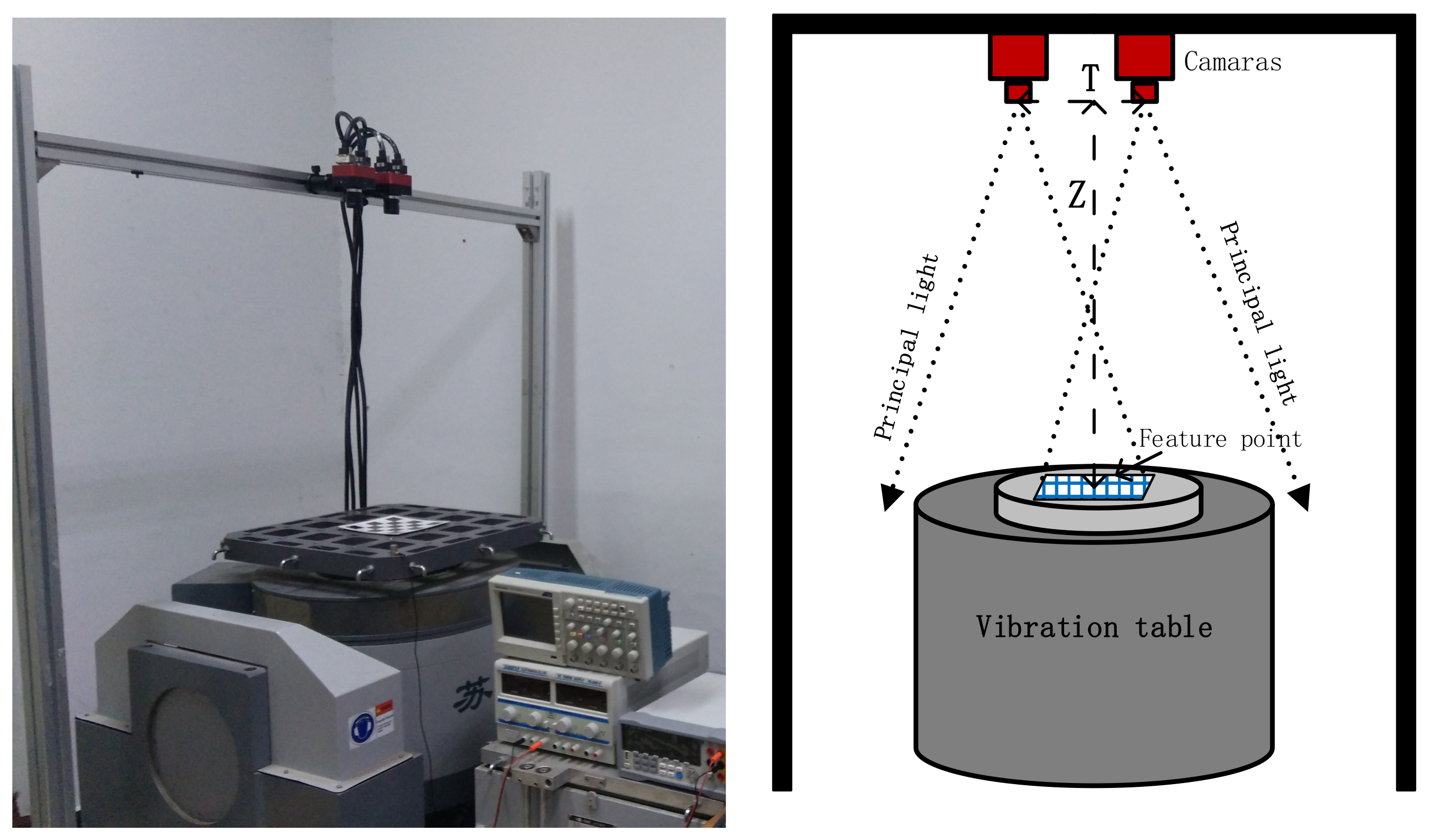
2.2. Dynamic Calibration
- Calibrate cameras for intrinsic and extrinsic parameters.
- Operate the vibration table at the standard frequency and amplitude.
- Compensate dynamic errors.
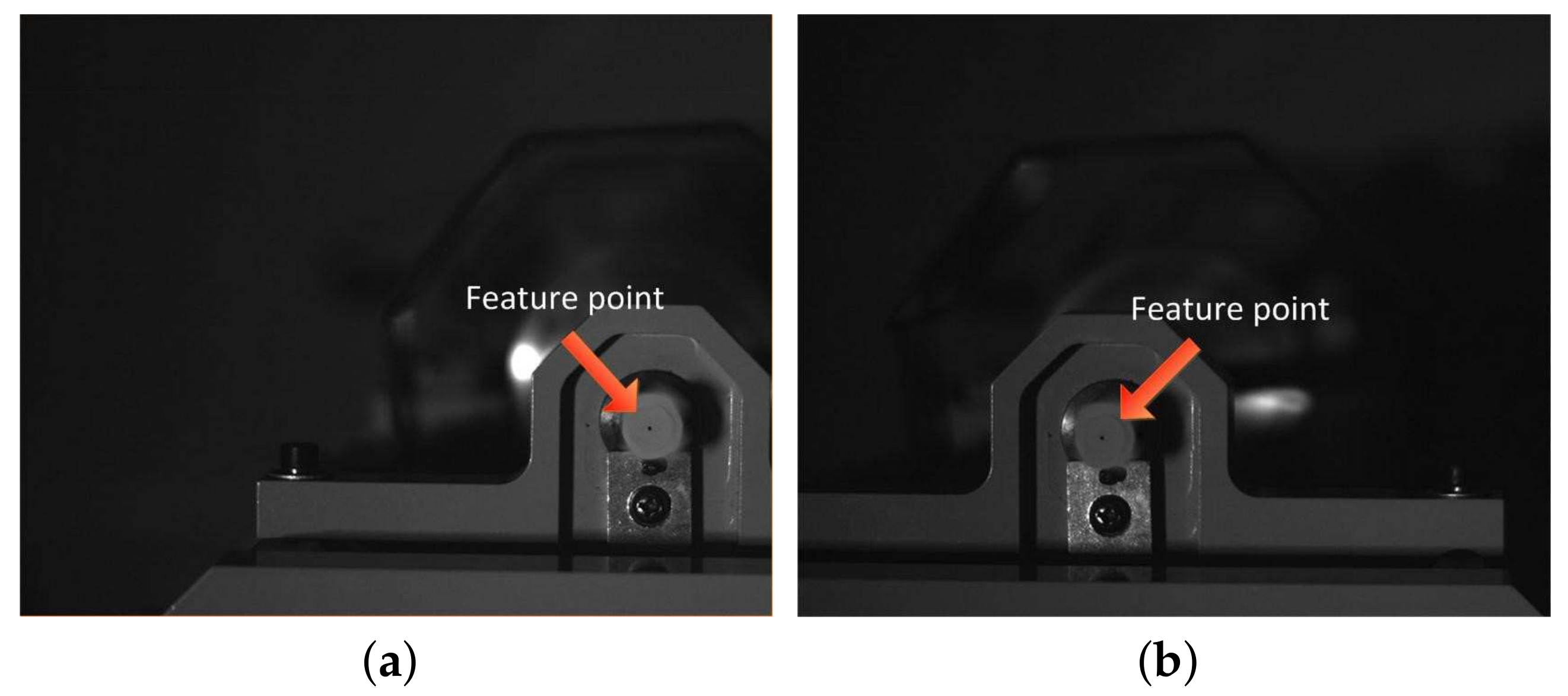
2.3. Feature Extraction
2.4. 3D Reconstruction
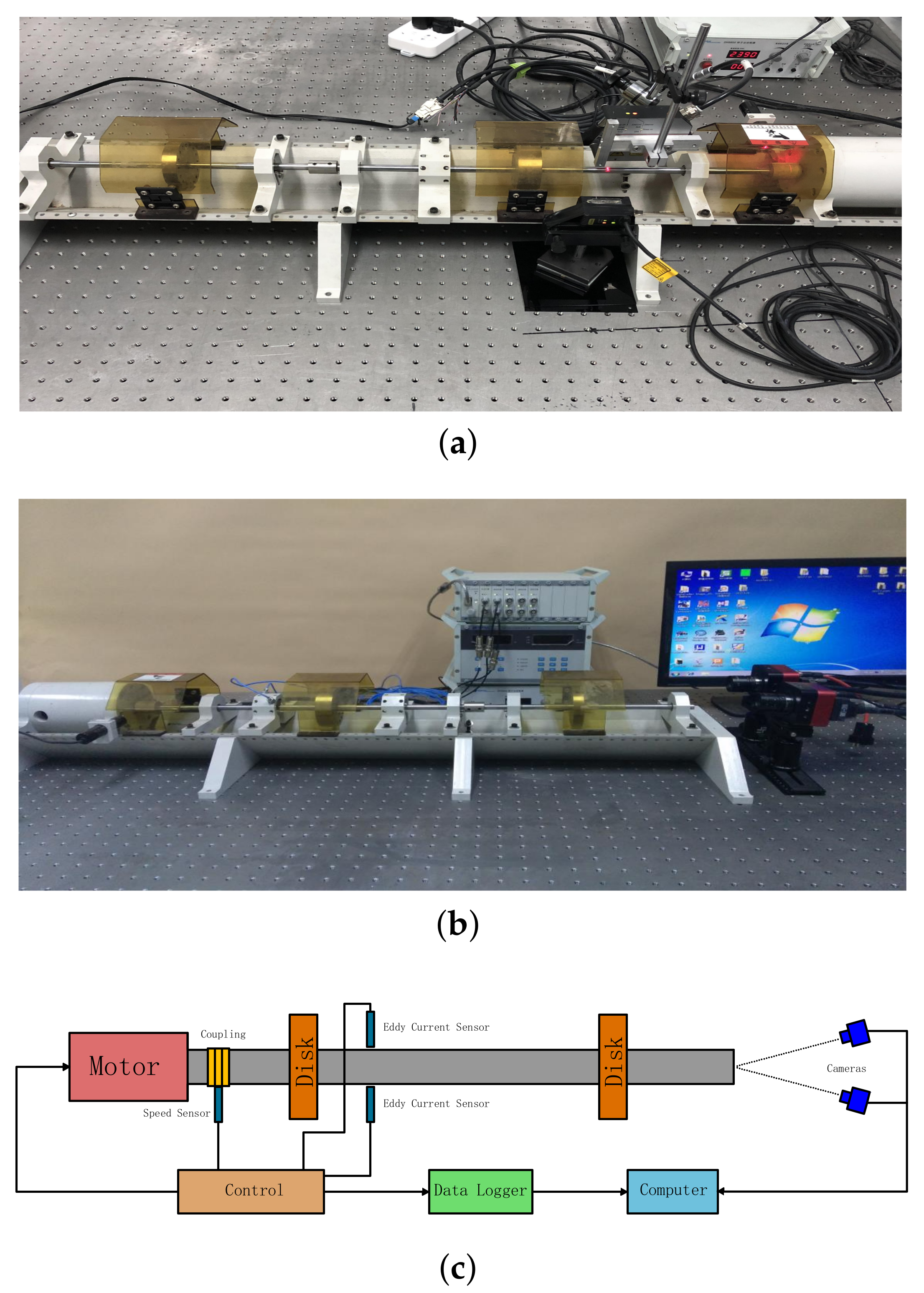
3. Experiment
4. Results and Discussion
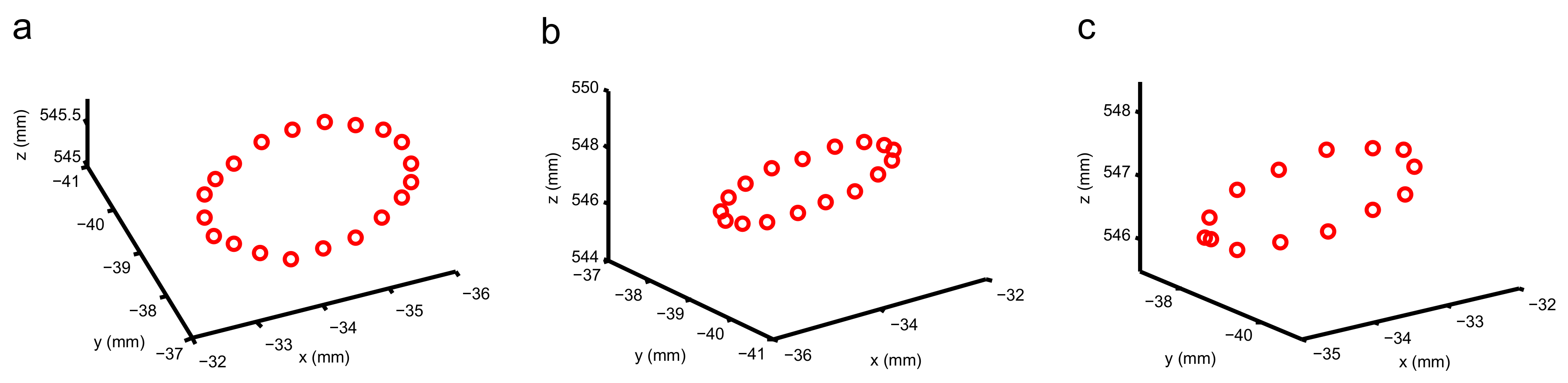
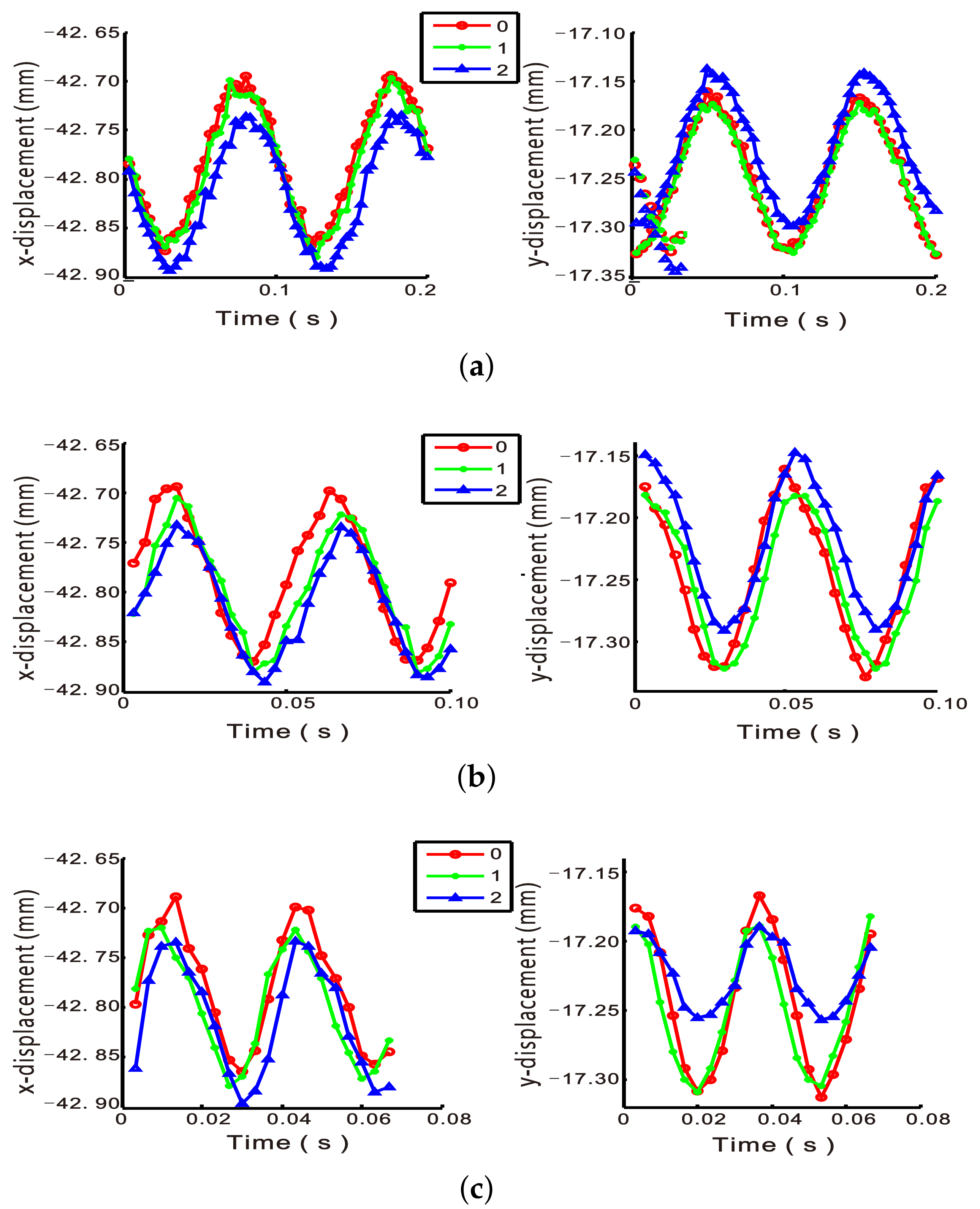
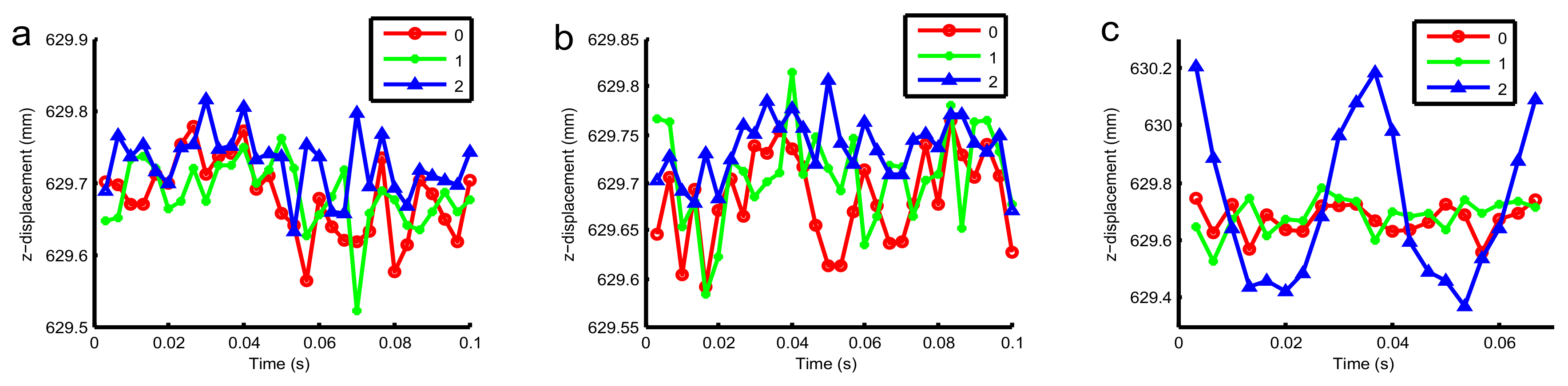
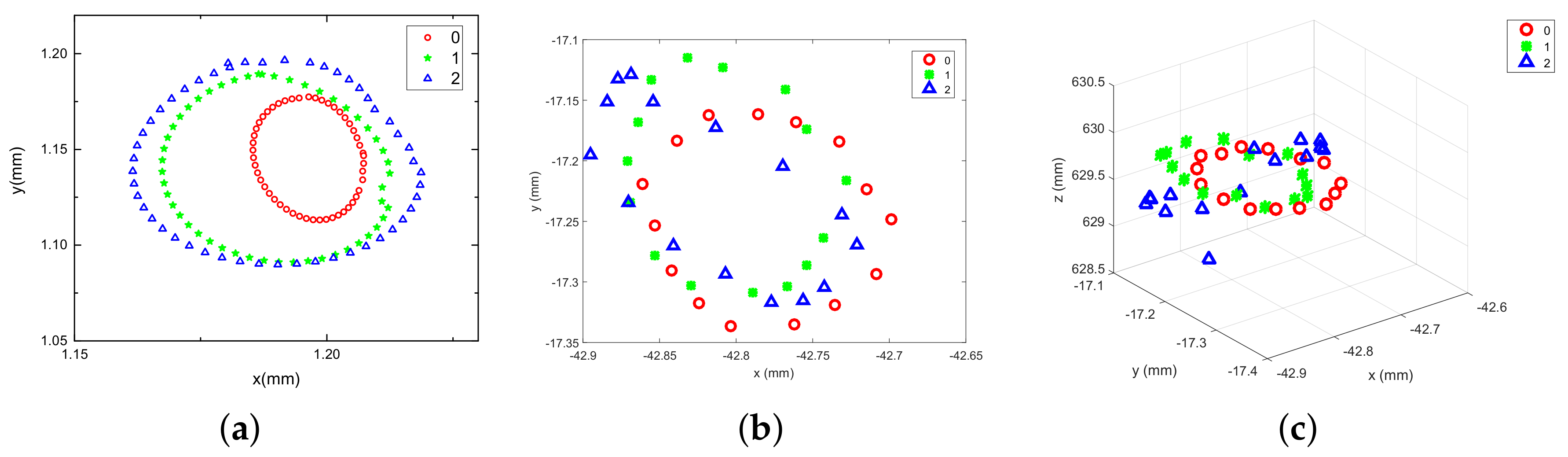
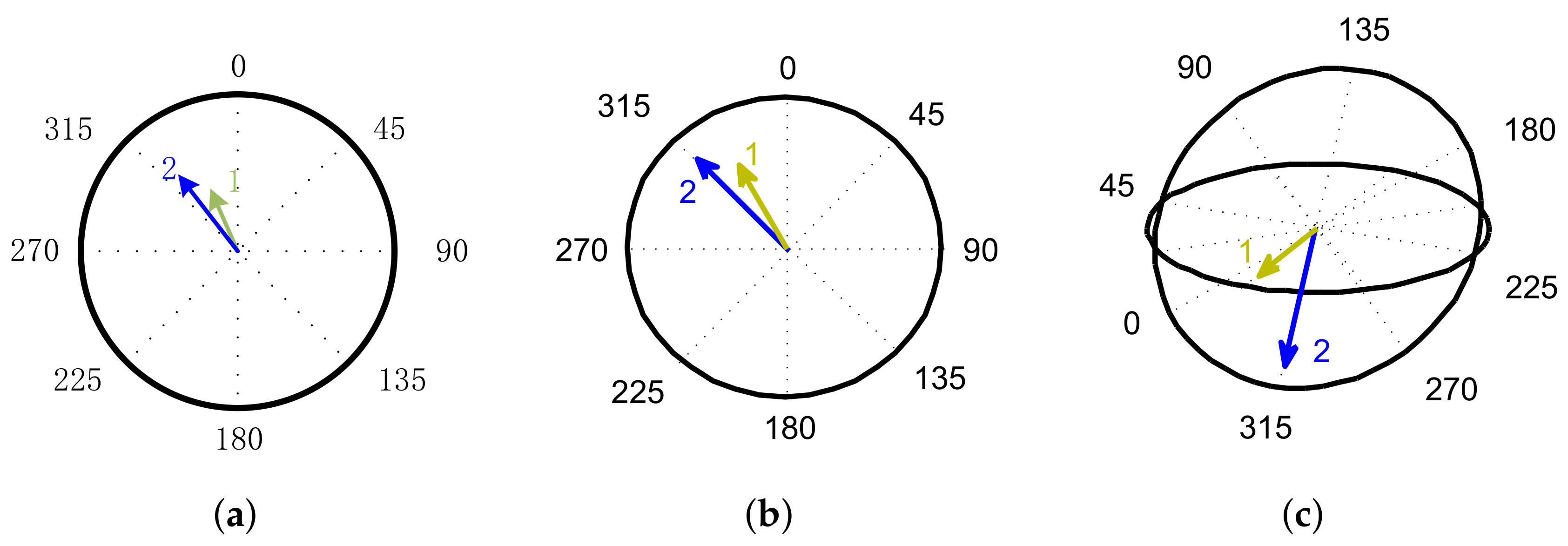
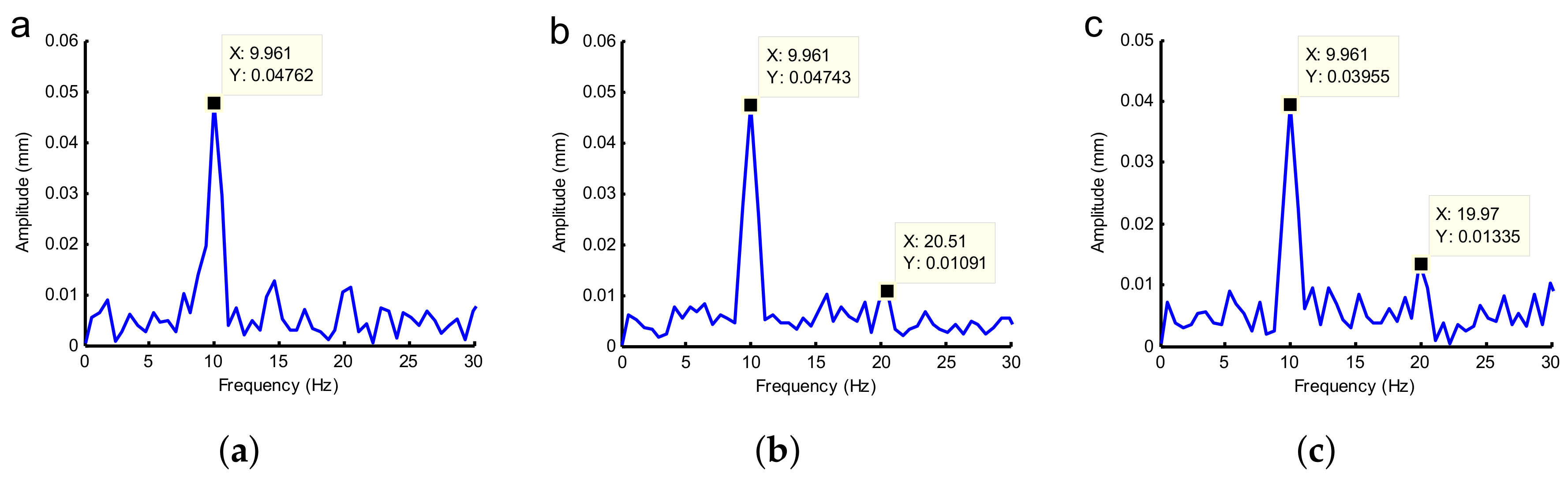
4.1. Non-Imbalance Experiment
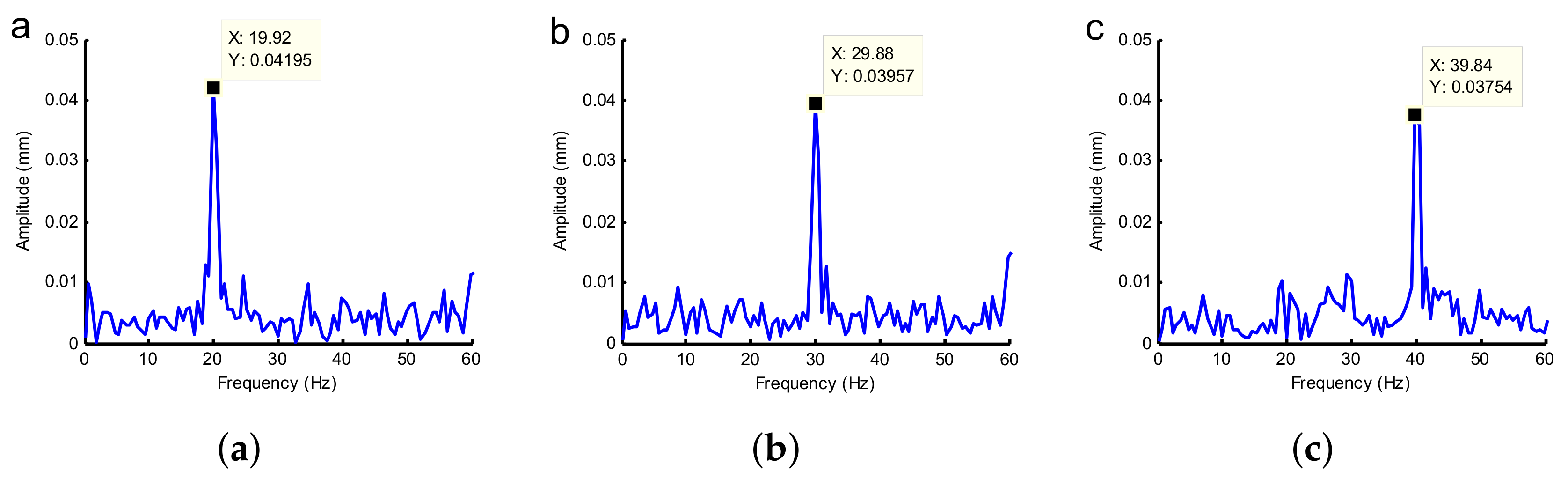
4.2. Different Unbalanced Mass Experiments
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wenhu, H.; Xinhua, W.; Yinghou, J. Review of Nonlinear Rotor Dynamics. J. Vib. Eng. 2000, 13, 5–17. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.; Lee, J.M.; Hwang, Y. Determination of engineering strain distribution in a rotor blade with fibre Bragg grating array and a rotary optic coupler. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2008, 46, 758–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharafi, M.M.; Nikravesh, M.Y.; Safarpour, P. Analytical approach to calculate bending, longitudinal and torsional local stiffness of an asymmetric circumferential crack with contact condition. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 94, 448–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Cecati, C.; Ding, S.X. A Survey of Fault Diagnosis and Fault-Tolerant Techniques-Part I: Fault Diagnosis With Model-Based and Signal-Based Approaches. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 3757–3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darlow, M.S. Balancing of high-speed machinery: Theory, methods and experimental results. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 1987, 1, 105–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.; Kim, B.; Lee, S. Development of the active balancing device for high-speed spindle system using influence coefficients. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2006, 46, 978–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smail, M.; Thomas, M.; Lakis, A. ARMA models for modal analysis: effect of model orders and sampling frequency. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 1999, 13, 925–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, R.G.; Guo, Z. Expert System Source Identification of Excessive Vibration. Int. J. Rotating Mach. 2003, 9, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widodo, A.; Yang, B.S. Support vector machine in machine condition monitoring and fault diagnosis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2007, 21, 2560–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lees, A.; Sinha, J.; Friswell, M. Model-based identification of rotating machines. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2009, 23, 1884–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Zi, Y.; He, Z. A 3D finite element-based model order reduction method for parametric resonance and whirling analysis of anisotropic rotor-bearing systems. J. Sound Vib. 2015, 359, 116–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammer, D.C. Sensor set expansion for modal vibration testing. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2005, 19, 700–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothberg, S.; Bell, J. On the application of laser vibrometry to translational and rotational vibration measurements on rotating shafts. Measurement 2004, 35, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borza, D.N. High-resolution time-average electronic holography for vibration measurement. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2004, 41, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Yang, S.; Gan, C. Torsional vibration measurements on rotating shaft system using laser doppler vibrometer. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2012, 50, 1596–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlowska-Kowalska, T.; Dybkowski, M. Stator-Current-Based MRAS Estimator for a Wide Range Speed-Sensorless Induction-Motor Drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 1296–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trebuňa, F.; Hagara, M. Experimental modal analysis performed by high-speed digital image correlation system. Measurement 2014, 50, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Kang, Y. Digital image correlation technique. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2015, 65, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orteu, J.J. 3-D computer vision in experimental mechanics. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2009, 47, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felipe-Sesé, L.; Siegmann, P.; Díaz, F.A.; Patterson, E.A. Simultaneous in-and-out-of-plane displacement measurements using fringe projection and digital image correlation. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2014, 52, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Ji, H.; Yang, G.; He, X. Shape and deformation measurement system by combining fringe projection and digital image correlation. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2013, 51, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Kieu, H.; Nguyen, H.; Le, M. Digital image correlation in experimental mechanics and image registration in computer vision: Similarities, differences and complements. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2015, 65, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Xie, H.; Pan, B. Speeding up digital image correlation computation using the integral image technique. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2015, 65, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieu, H.; Pan, T.; Wang, Z.; Le, M.; Nguyen, H.; Vo, M. Accurate 3D shape measurement of multiple separate objects with stereo vision. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2014, 25, 035401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Chen, J.Y.; Hu, X.; Wang, X. A Study of 3d Coordinate Measuring Based on Binocular Stereo Vision. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2015, 740, 531–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Deng, H.; Fan, R. Three-dimensional Reconstruction Coordinate Error Induced by Asynchronous Cameras for Moving Objects. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Symposium on Precision Mechanical Measurements, Guiyang, China, 10 October 2013; Ye, S., Fei, Y., Eds.; Volume 8916, pp. 89160J–89160J-9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, P.; Deng, H.; Wang, J. High-accuracy three-dimensional reconstruction of vibration based on stereo vision. Opt. Eng. 2016, 55, 091410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baqersad, J.; Niezrecki, C.; Avitabile, P. Full-field dynamic strain prediction on a wind turbine using displacements of optical targets measured by stereophotogrammetry. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2015, 62–63, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Peng, C.; Xiao, J.; Zeng, J.; Yuan, Y. Application of videometric technique to deformation measurement for large-scale composite wind turbine blade. Appl. Energy 2012, 98, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. A flexible new technique for camera calibration. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2000, 22, 1330–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bay, H.; Ess, A.; Tuytelaars, T.; Gool, L.V. Speed up robust features (SURF). Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2008, 110, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikolajczyk, K.; Schmid, C. A performance evaluation of local descriptor. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2005, 27, 1615–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.R.; Kim, H.C. Feasibility of in situ blade deflection monitoring of a wind turbine using a laser displacement sensor within the tower. Smart Mater. Struct. 2012, 22, 027002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciang, C.C.; Lee, J.R.; Bang, H.J. Structural health monitoring for a wind turbine system: a review of damage detection methods. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2008, 19, 122001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colin Ocampo, J.; Wing, E.S.G.; Ramirez Moroyoqui, F.J.; Abundez Pliego, A.; Blanco Ortega, A.; Mayen, J. A novel methodology for the angular position identification of the unbalance force on asymmetric rotors by response polar plot analysis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 95, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
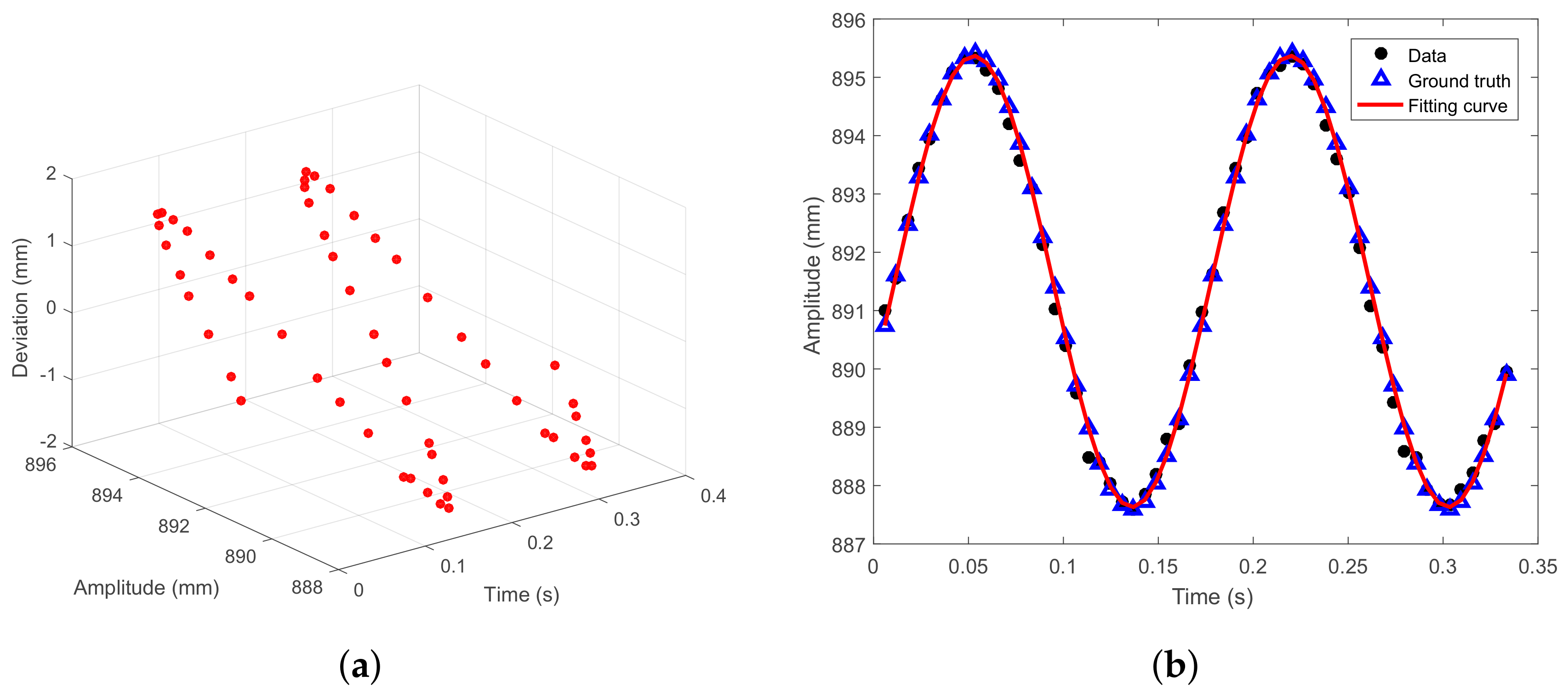

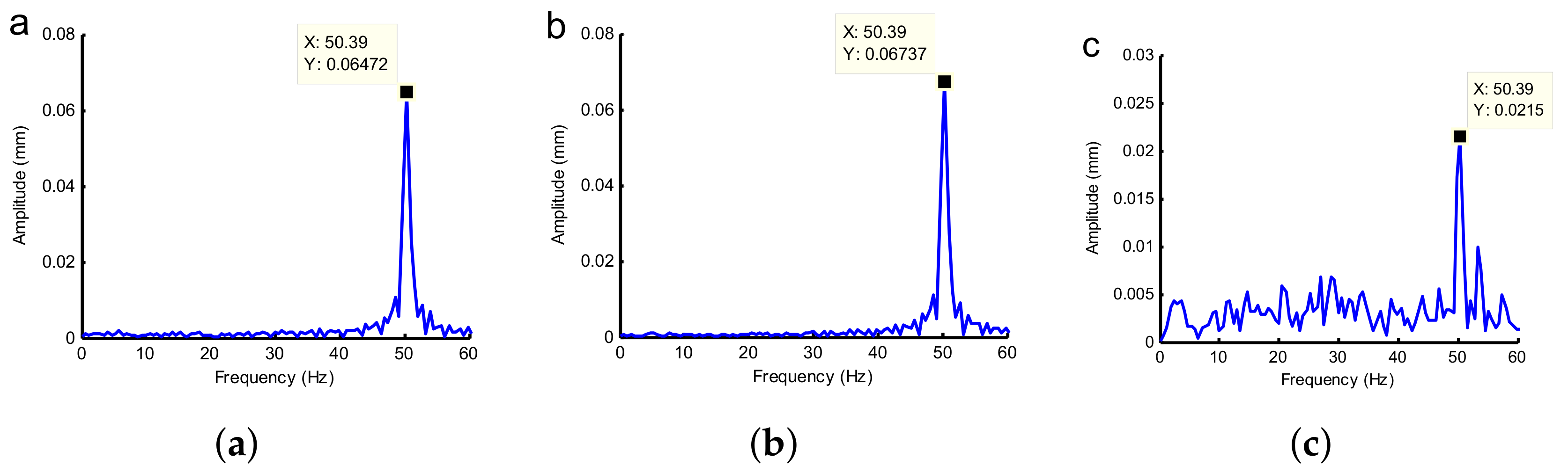
| Amplitude (mm) | Frequency (Hz) | SSE | R-Square | RMSE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ground truth | 3.87 | 6 | - | - | - |
| Detection value | 3.91 | 6 | 0.5510 | 0.9981 | 0.1029 |
| Methods | Eccentricity (mm) | Balance Accuracy (mm·s) | Relative Error | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 g | 1 g | 2 g | 0 g | 1 g | 2 g | ||
| Ground truth | 0 | 0.049 | 0.098 | - | 1.950 | 3.900 | - |
| Current eddy | 0.039 | 0.042 | 0.052 | 1.557 | 1.674 | 2.065 | 30.6% |
| Laser | 0.011 | 0.034 | 0.047 | 0.439 | 1.367 | 1.866 | 41.3% |
| Videometric | 0.033 | 0.051 | 0.097 | 1.327 | 2.024 | 3.872 | 2.2% |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, H.; Diao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, P.; Ma, M.; Zhong, X.; Yu, L. Three-Dimensional Identification for Unbalanced Mass of Rotor Systems in Operation. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8020173
Deng H, Diao Y, Zhang J, Zhang P, Ma M, Zhong X, Yu L. Three-Dimensional Identification for Unbalanced Mass of Rotor Systems in Operation. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(2):173. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8020173
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Huaxia, Yifan Diao, Jin Zhang, Peng Zhang, Mengchao Ma, Xiang Zhong, and Liandong Yu. 2018. "Three-Dimensional Identification for Unbalanced Mass of Rotor Systems in Operation" Applied Sciences 8, no. 2: 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8020173
APA StyleDeng, H., Diao, Y., Zhang, J., Zhang, P., Ma, M., Zhong, X., & Yu, L. (2018). Three-Dimensional Identification for Unbalanced Mass of Rotor Systems in Operation. Applied Sciences, 8(2), 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8020173






