A Multitask-Based Neural Machine Translation Model with Part-of-Speech Tags Integration for Arabic Dialects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Neural Machine Translation
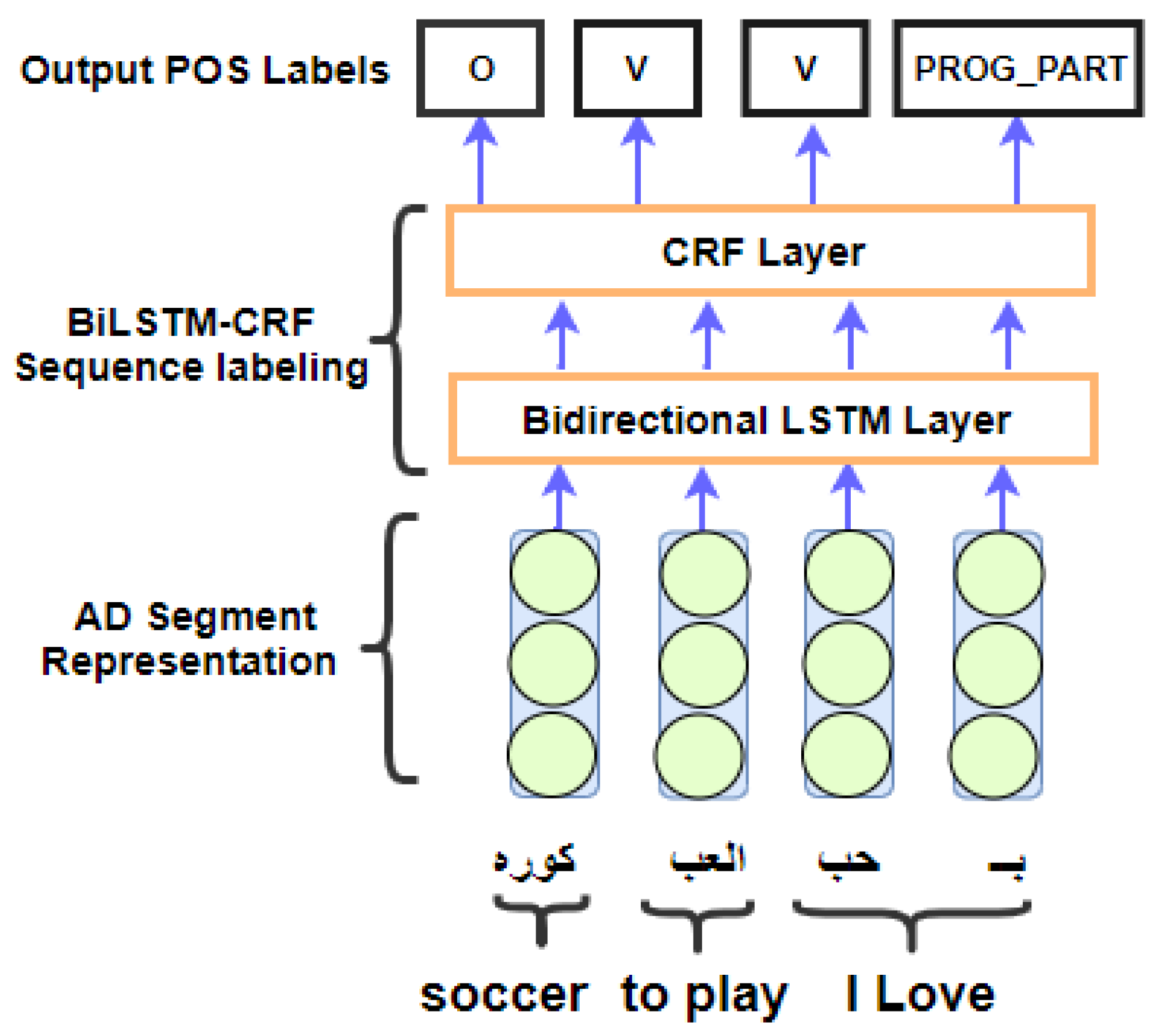
4. Segment Level Bi-LSTM—CRF Model for Arabic Dialect POS Tagging
5. Methodology
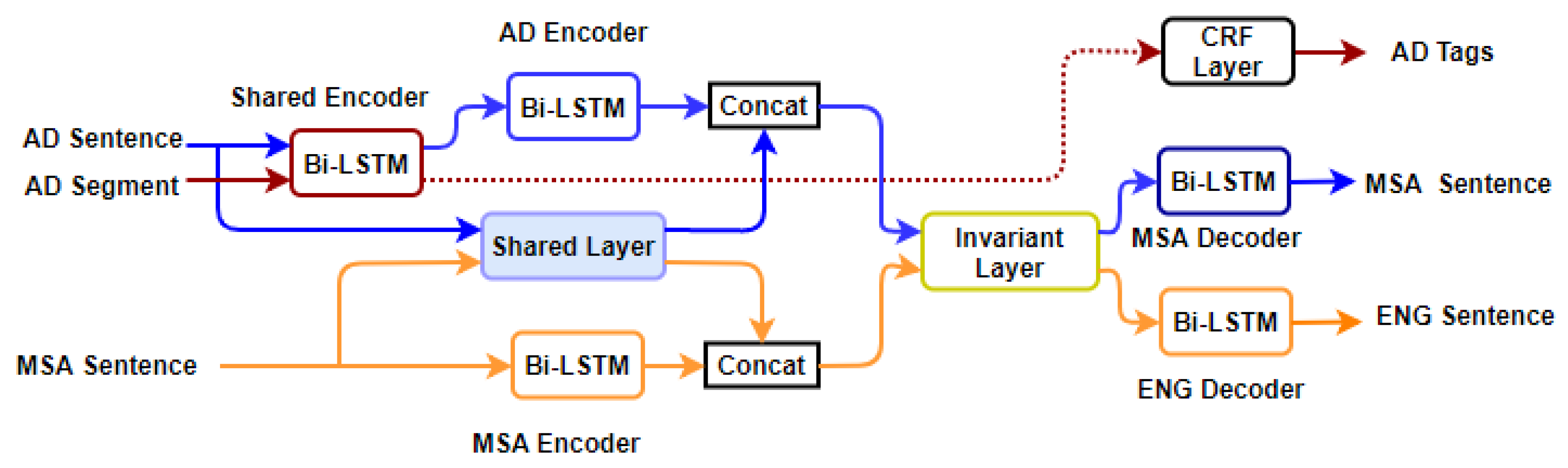
6. Proposed Model
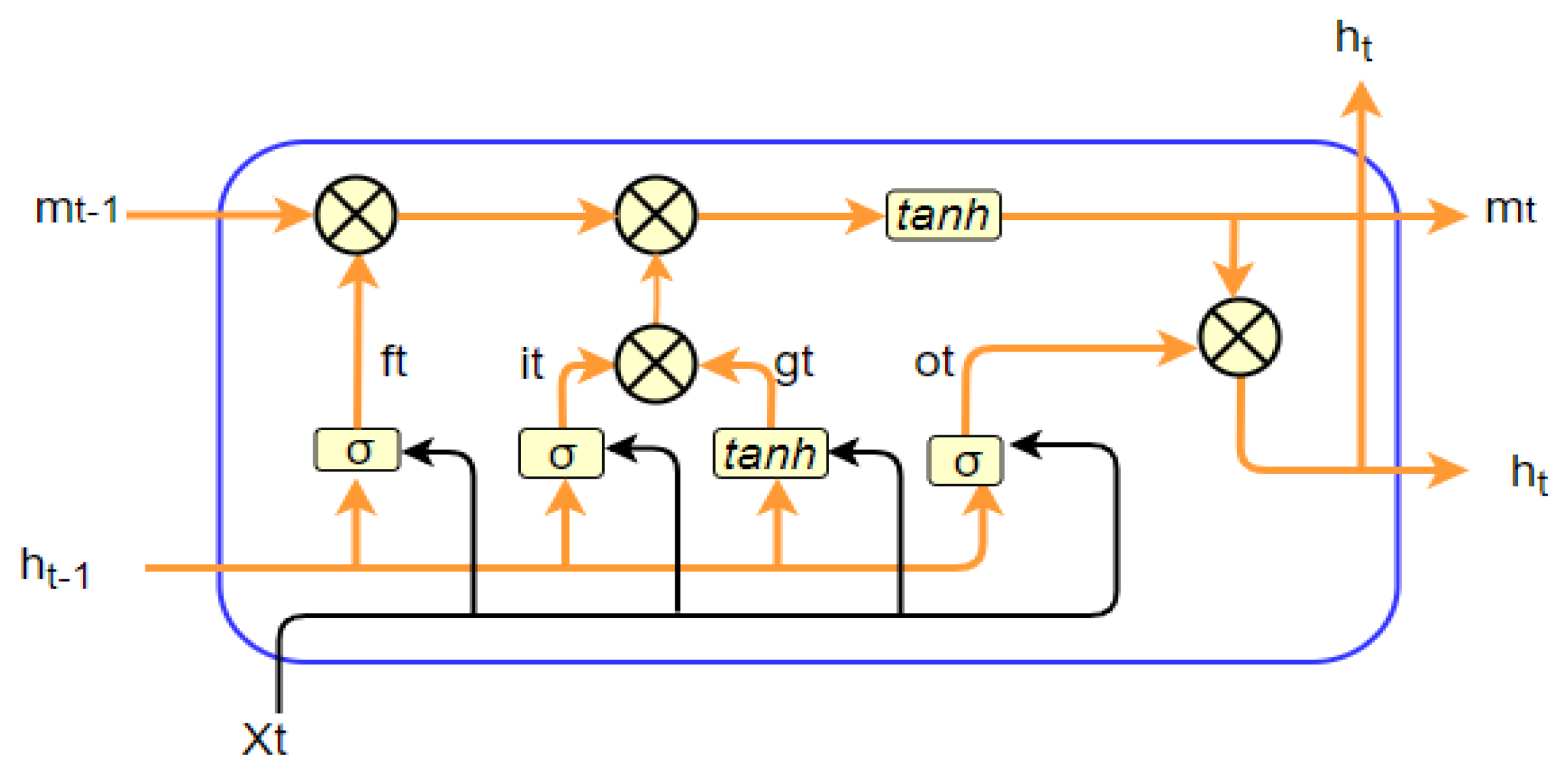
6.1. Arabic Dialect Encoding with Bi-LSTM
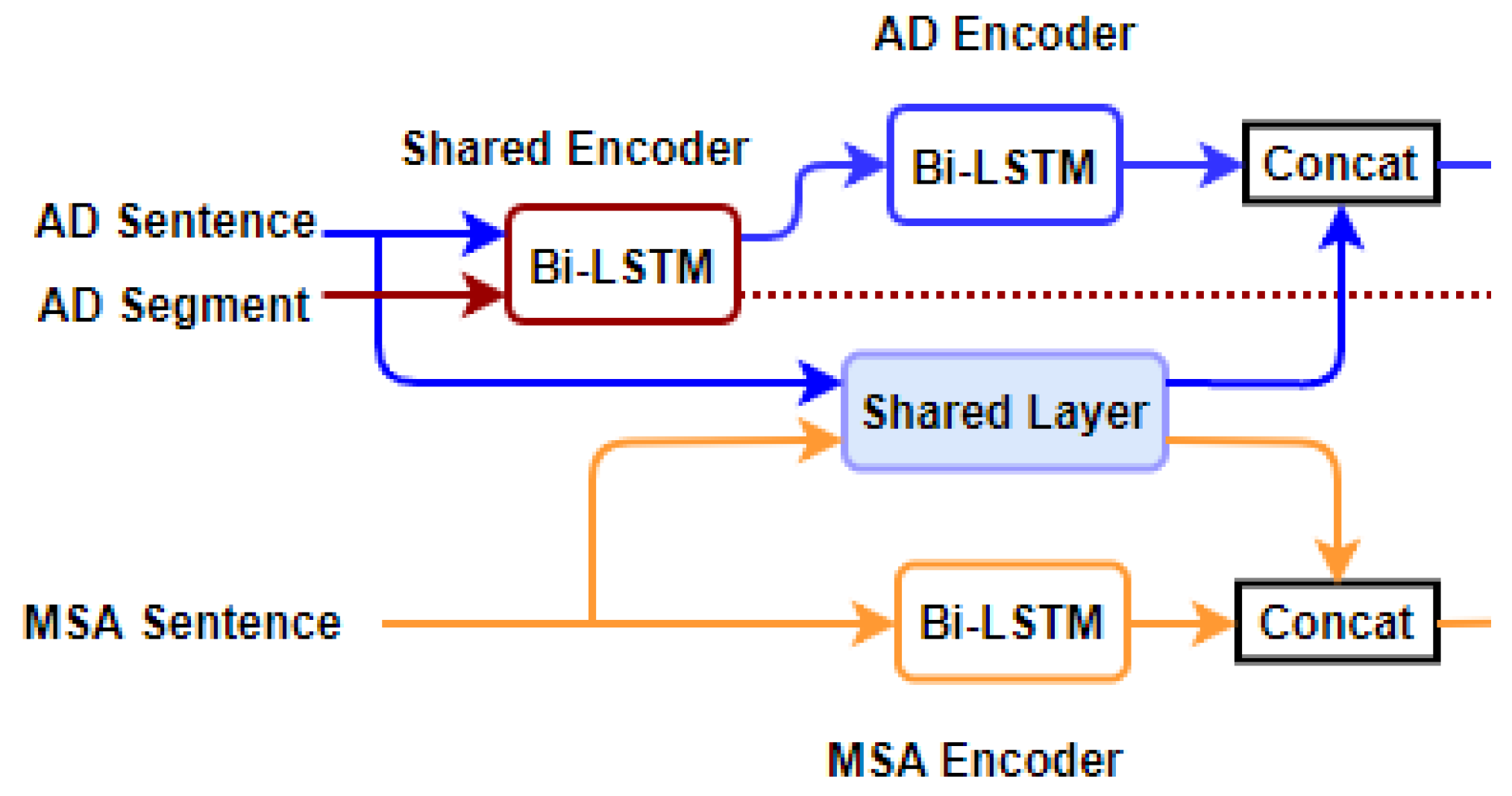
6.2. Shared-Private Scheme
6.3. NMT Decoding for Arabic Dialects Sentence
6.4. Optimization
7. Experiments and Results
7.1. Data
7.2. Training
7.3. Results
7.3.1. Automatic Metric
7.3.2. Human Evaluation
8. Model Analysis and Discussion
9. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hung, J.-W.; Lin, J.-S.; Wu, P.-J. Employing Robust Principal Component Analysis for Noise-Robust Speech Feature Extraction in Automatic Speech Recognition with the Structure of a Deep Neural Network. Appl. Syst. Innov. 2018, 1, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal Chowdhury, A.; Kulkarni, P.; Nazm Bojnordi, M. MB-CNN: Memristive Binary Convolutional Neural Networks for Embedded Mobile Devices. J. Low Power Electron. Appl. 2018, 8, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salerno, V.; Rabbeni, G. An extreme learning machine approach to effective energy disaggregation. Electronics 2018, 7, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo Bakr, H.; Shaalan, K.; Ziedan, I. A hybrid approach for converting written Egyptian colloquial dialect into diacritized Arabic. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Informatics and Systems, Cairo, Egypt, 27–29 March 2008; Cairo University: Cairo, Egypt, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Meftouh, K.; Harrat, S.; Jamoussi, S.; Abbas, M.; Smaili, K. Machine translation experiments on padic: A parallel Arabic dialect corpus. In Proceedings of the 29th Pacific Asia Conference on Language, Information and Computation, Shanghai, China, 30 October–1 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Gaphari, G.H.; Al-Yadoumi, M. A method to convert Sana’ani accent to Modern Standard Arabic. Int. J. Inf. Sci. Manag. 2012, 8, 39–49. [Google Scholar]
- Ridouane, T.; Bouzoubaa, K. A hybrid approach to translate Moroccan Arabic dialect. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Intelligent Systems: Theories and Applications, Rabat, Morocco, 7–8 May 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Salloum, W.; Habash, N. Elissa: A dialectal to standard Arabic machine translation system. In Proceedings of the COLING 2012 24th International Conference on Computational Linguistics, Mumbai, India, 8–15 December 2012; pp. 385–392. [Google Scholar]
- Sadat, F.; Mallek, F.; Boudabous, M.; Sellami, R.; Farzindar, A. Collaboratively Constructed Linguistic Resources for Language Variants and their Exploitation in NLP Application—The case of Tunisian Arabic and the Social Media. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Lexical and Grammatical Resources for Language Processing, Dublin, Ireland, 24 August 2014; pp. 102–110. [Google Scholar]
- Papineni, K.; Roukos, S.; Ward, T.; Zhu, W.J. BLEU: A method for automatic evaluation of machine translation. In Proceedings of the 40th Annual Meeting on Association for Computational Linguistics, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 7–12 July 2002; pp. 311–318. [Google Scholar]
- Baniata, L.H.; Park, S.Y.; Park, S.B. A Neural Machine Translation Model for Arabic Dialects That Utilises Multi-Task Learning (MTL). Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2018, (in press). [Google Scholar]
- Collobert, R.; Weston, J.; Bottou, L.; Karlen, M.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Kuksa, P. Natural language processing (almost) from scratch. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2493–2537. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Qiu, X.; Huang, X. Adversarial multi-task learning for text classification. arXiv, 2017; arXiv:1704.05742. [Google Scholar]
- Costa-Jussà, M.R. Why Catalan-Spanish neural machine translation? analysis, comparison and combination with standard rule and phrase-based technologies. In Proceedings of the Fourth Workshop on NLP for Similar Languages, Varieties and Dialects (VarDial), Valencia, Spain, 3 April 2017; pp. 55–62. [Google Scholar]
- Hassani, H. Kurdish interdialect machine translation. In Proceedings of the Fourth Workshop on NLP for Similar Languages, Varieties and Dialects (VarDial), Valencia, Spain, 3 April 2017; pp. 63–72. [Google Scholar]
- Costa-jussà, M.R.; Zampieri, M.; Pal, S. A Neural Approach to Language Variety Translation. In Proceedings of the Fifth Workshop on NLP for Similar Languages, Varieties and Dialects (VarDial), Santa Fe, NM, USA, 20–21 August 2018; pp. 275–282. [Google Scholar]
- Sennrich, R.; Haddow, B. Linguistic input features improve neural machine translation. arXiv, 2016; arXiv:1606.02892. [Google Scholar]
- Niehues, J.; Cho, E. Exploiting linguistic resources for neural machine translation using multi-task learning. arXiv, 2017; arXiv:1708.00993. [Google Scholar]
- Neco, R.P.; Forcada, M.L. Asynchronous translations with recurrent neural nets. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Networks, Houston, TX, USA, 9–12 June 1997; pp. 2535–2540. [Google Scholar]
- Schwenk, H.; Dchelotte, D.; Gauvain, J.L. Continuous space language models for statistical machine translation. In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Computational Linguistics and 44th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (COLING/ACL), Sydney, Australia, 17–18 July 2006; pp. 723–730. [Google Scholar]
- Kalchbrenner, N.; Blunsom, P. Recurrent continuous translation models. In Proceedings of the 2013 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Seattle, WA, USA, 18–21 October 2013; pp. 1700–1709. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, K.; Van Merriënboer, B.; Gulcehre, C.; Bahdanau, D.; Bougares, F.; Schwenk, H.; Bengio, Y. Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation. arXiv, 2014; arXiv:1406.1078. [Google Scholar]
- Sutskever, I.; Vinyals, O.; Le, Q.V. Sequence to sequence learning with neural networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–13 December 2014; pp. 3104–3112. [Google Scholar]
- Passban, P.; Liu, Q.; Way, A. Translating low-resource languages by vocabulary adaptation from close counterparts. ACM Trans. Asian Low-Resour. Lang. Inf. Process. 2017, 16, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, D.; Wu, H.; He, W.; Yu, D.; Wang, H. Multi-task learning for multiple language translation. In Proceedings of the 53rd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 7th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing, Beijing, China, 26–31 July 2015; pp. 1723–1732. [Google Scholar]
- Firat, O.; Cho, K.; Bengio, Y. Multi-way, multilingual neural machine translation with a shared attention mechanism. arXiv, 2016; arXiv:1601.01073. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, T.L.; Niehues, J.; Waibel, A. Toward multilingual neural machine translation with universal encoder and decoder. arXiv, 2016; arXiv:1611.04798. [Google Scholar]
- Duh, K.; Kirchhoff, K. POS tagging of dialectal Arabic: A minimally supervised approach. In Proceedings of the ACL Workshop on Computational Approaches to Semitic Languages, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 29 June 2005; pp. 55–62. [Google Scholar]
- Habash, N.; Roth, R.; Rambow, O.; Eskander, R.; Tomeh, N. Morphological analysis and disambiguation for dialectal Arabic. In Proceedings of the 2013 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Atlanta, GA, USA, 9–14 June 2013; pp. 426–432. [Google Scholar]
- Darwish, K.; Mubarak, H.; Abdelali, A.; Eldesouki, M.; Samih, Y.; Alharbi, R.; Attia, M.; Magdy, W.; Kallmeyer, L. Multi-Dialect Arabic POS Tagging: A CRF Approach. In Proceedings of the Language Resources and Evaluation Conference (LREC), Miyazaki, Japan, 7–12 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Eldesouki, M.; Samih, Y.; Abdelali, A.; Attia, M.; Mubarak, H.; Darwish, K.; Laura, K. Arabic Multi-Dialect Segmentation: Bi-LSTM-CRF vs. SVM. arXiv, 2017; arXiv:1708.05891. [Google Scholar]
- Bouamor, H.; Habash, N.; Oflazer, K. A Multidialectal Parallel Corpus of Arabic. In Proceedings of the Language Resources and Evaluation Conference (LREC), Reykjavik, Iceland, 26–31 May 2014; pp. 1240–1245. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, K.C. Some remarks on protein attribute prediction and pseudo amino acid composition. J. Theor. Biol. 2011, 273, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manavalan, B.; Shin, T.H.; Lee, G. PVP-SVM: Sequence-based prediction of phage virion proteins using a support vector machine. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Zhou, C.; Chen, H.; Song, J.; Su, R. ACPred-FL: A sequence-based predictor based on effective feature representation to improve the prediction of anti-cancer peptides. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 4007–4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basith, S.; Manavalan, B.; Shin, T.H.; Lee, G. iGHBP: Computational identification of growth hormone binding proteins from sequences using extremely randomised tree. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, X.; Zhou, C.; Ye, X.; Du, P.F.; Su, R.; Wei, L. CPPred-FL: A sequence-based predictor for large-scale identification of cell-penetrating peptides by feature representation learning. Brief. Bioinform. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manavalan, B.; Govindaraj, R.G.; Shin, T.H.; Kim, M.O.; Lee, G. iBCE-EL: A new ensemble learning framework for improved linear B-cell epitope prediction. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Rfou, R.; Perozzi, B.; Skiena, S. Polyglot: Distributed word representations for multilingual NLP. arXiv, 2013; arXiv:1307.1662. [Google Scholar]
- Bojanowski, P.; Grave, E.; Joulin, A.; Mikolov, T. Enriching word vectors with subword information. arXiv, 2016; arXiv:1607.04606. [Google Scholar]


| Pairs | Embedding Type | Embedding Size | Hidden Size | Epochs | BLEU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LA-MSA | Random | 150 | 150 | 102 | 0.36 |
| MA-MSA | Random | 150 | 150 | 102 | 0.26 |
| MSA-ENG | Random | 150 | 150 | 49 | 0.29 |
| ENG-GER | Random | 150 | 150 | 45 | 0.34 |
| LA-MSA | FastText | 300 | 150 | 52 | 0.33 |
| MA-MSA | FastText | 300 | 150 | 52 | 0.32 |
| LA-MSA | Polyglot | 64 | 150 | 64 | 0.26 |
| MA-MSA | Polyglot | 64 | 150 | 64 | 0.25 |
| Model | Pairs | Embedding Type | Epochs | BLEU | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NMT + POS_LEV | LA-MSA | FastText | 90 | 0.43 | |
| NMT + POS_LEV | MSA-ENG | FastText | 50 | 0.30 | |
| NMT + POS_LEV | POS_LEV | Random | 40 | 98% | |
| NMT + POS_MA | MA-MSA | FastText | 50 | 0.34 | |
| NMT + POS_MA | MSA-ENG | FastText | 30 | 0.29 | |
| NMT + POS_MA | POS_MA | Random | 20 | 99% |
| Model | Pairs | Embedding Type | Embedding Size | Epochs | BLEU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single NMT | LA-MSA | Random | 150 | 120 | 0.17 |
| Multitask | LA-MSA | Random | 150 | 170 | 0.41 |
| Single NMT | MA-MSA | Random | 180 | 120 | 0.16 |
| Multitask | MA-MSA | Random | 180 | 230 | 0.30 |
| Single NMT | MSA-ENG | Random | 160 | 120 | 0.10 |
| Multitask | MSA-ENG | Random | 150 | 170 | 0.27 |
| Outcome | Average Score |
|---|---|
| Multitask NMT | 1.4 |
| Multitask NMT + POS | 5.9 |
| Outcome | Average Score |
|---|---|
| Multitask NMT | 1.3 |
| Multitask NMT + POS | 4.4 |
| Levantine Arabic | حتى نقدر نحكي |
|---|---|
| Reference—MSA | حتى نتمكن من الكلام |
| Multi-Task without POS | حتى نتمكن اجل |
| Multi-Task + POS | حتى نتمكن في الكلام |
| English Translation | So we can speak |
| Maghrebi Arabic | مشيت على ود التحاليل |
|---|---|
| Reference—MSA | ذهبت من اجل التحاليل |
| Multi-Task without POS | ذهبت عند ذهبت |
| Multi-Task + POS | ذهبت على شديد التحاليل |
| English Translation | I went for analysis |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baniata, L.H.; Park, S.; Park, S.-B. A Multitask-Based Neural Machine Translation Model with Part-of-Speech Tags Integration for Arabic Dialects. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2502. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8122502
Baniata LH, Park S, Park S-B. A Multitask-Based Neural Machine Translation Model with Part-of-Speech Tags Integration for Arabic Dialects. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(12):2502. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8122502
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaniata, Laith H., Seyoung Park, and Seong-Bae Park. 2018. "A Multitask-Based Neural Machine Translation Model with Part-of-Speech Tags Integration for Arabic Dialects" Applied Sciences 8, no. 12: 2502. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8122502
APA StyleBaniata, L. H., Park, S., & Park, S.-B. (2018). A Multitask-Based Neural Machine Translation Model with Part-of-Speech Tags Integration for Arabic Dialects. Applied Sciences, 8(12), 2502. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8122502





