Wireless Power Transfer System Based on Strapping Resonators
Abstract
:1. Introduction
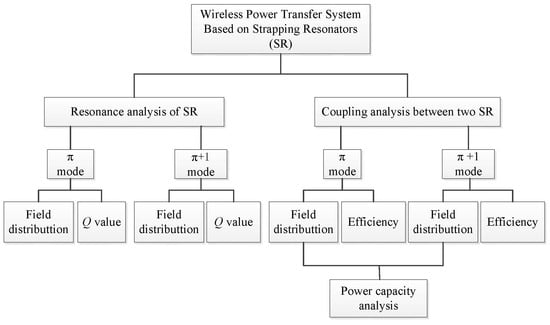
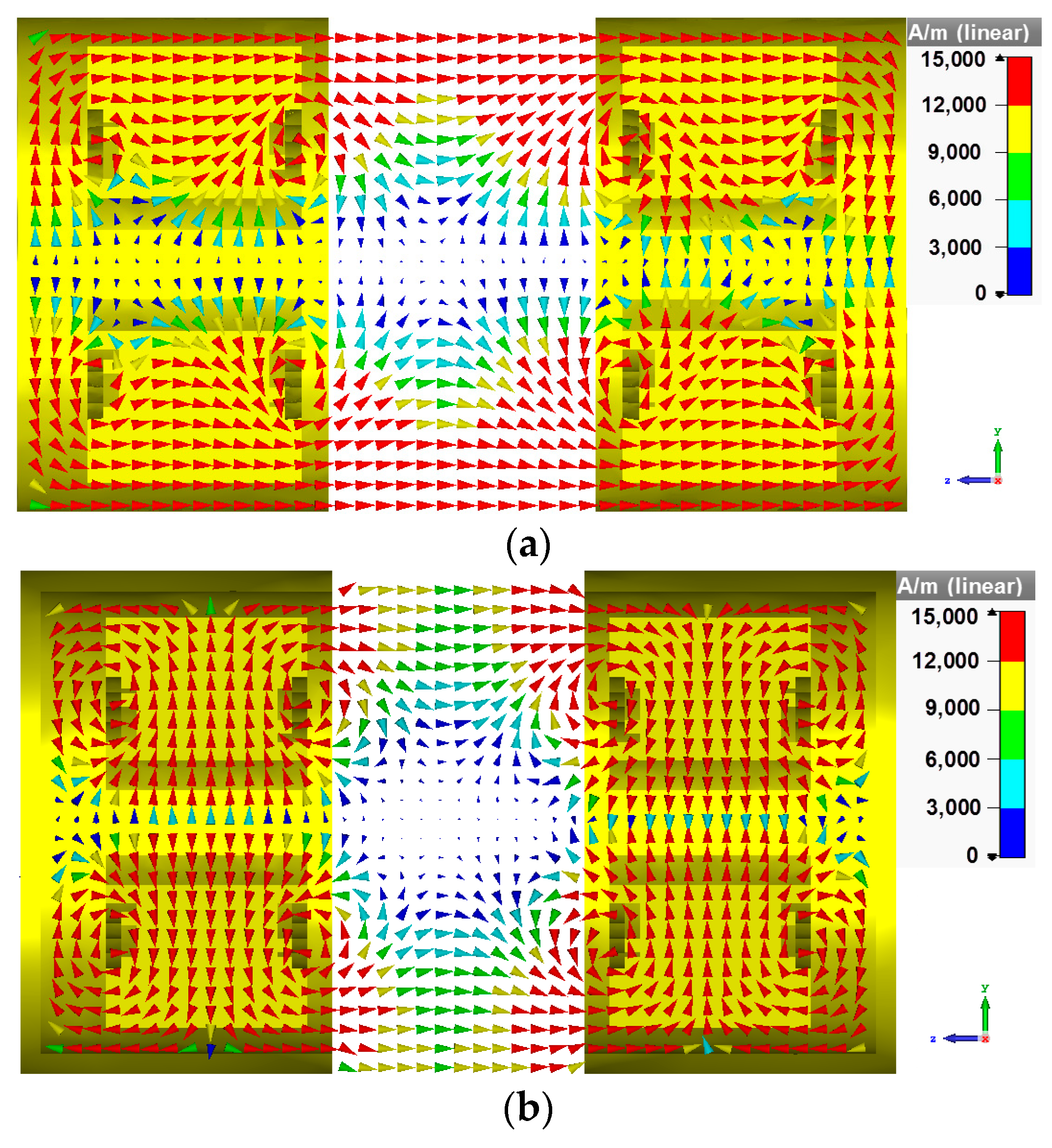
2. Analysis of the Strapped Resonator
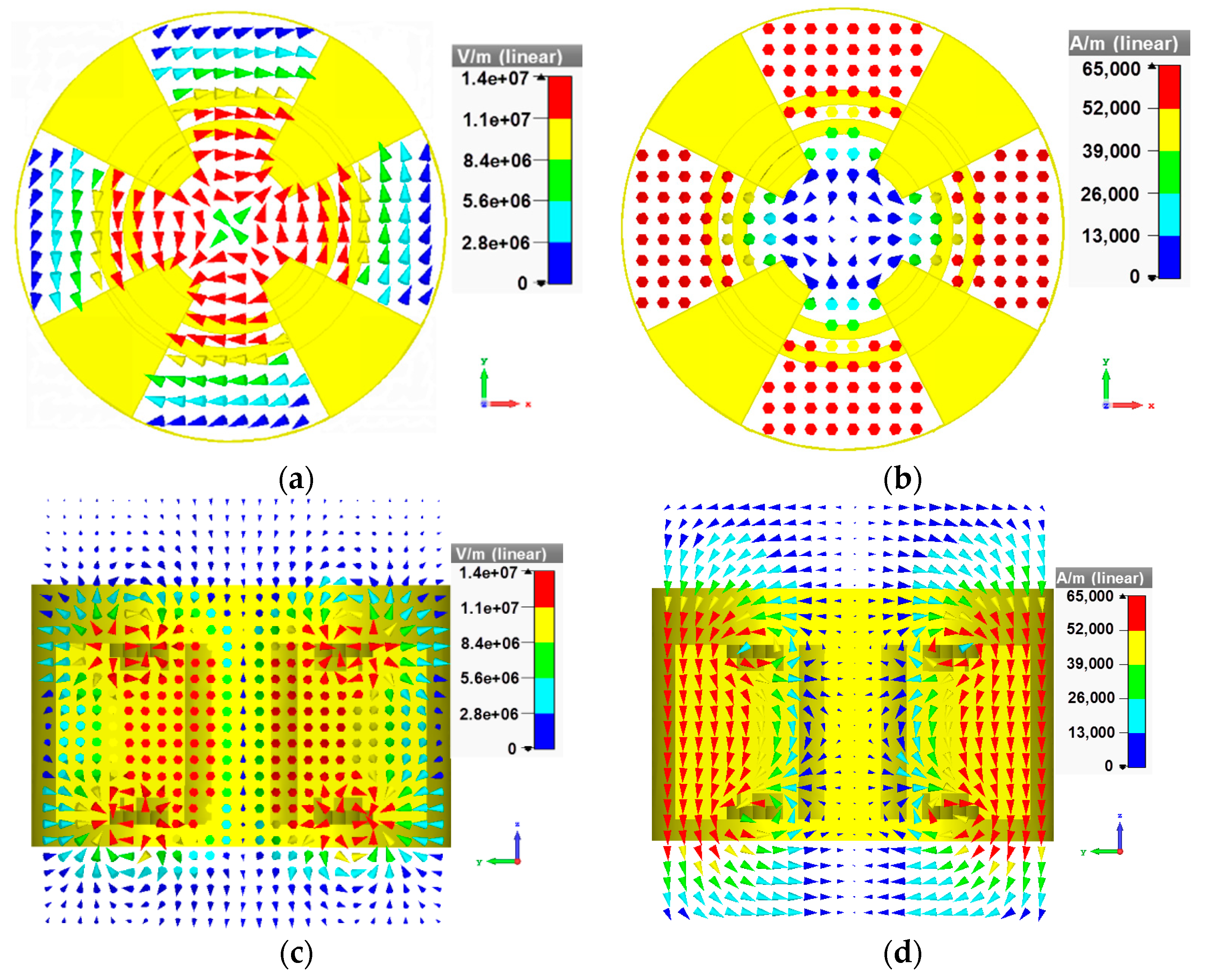
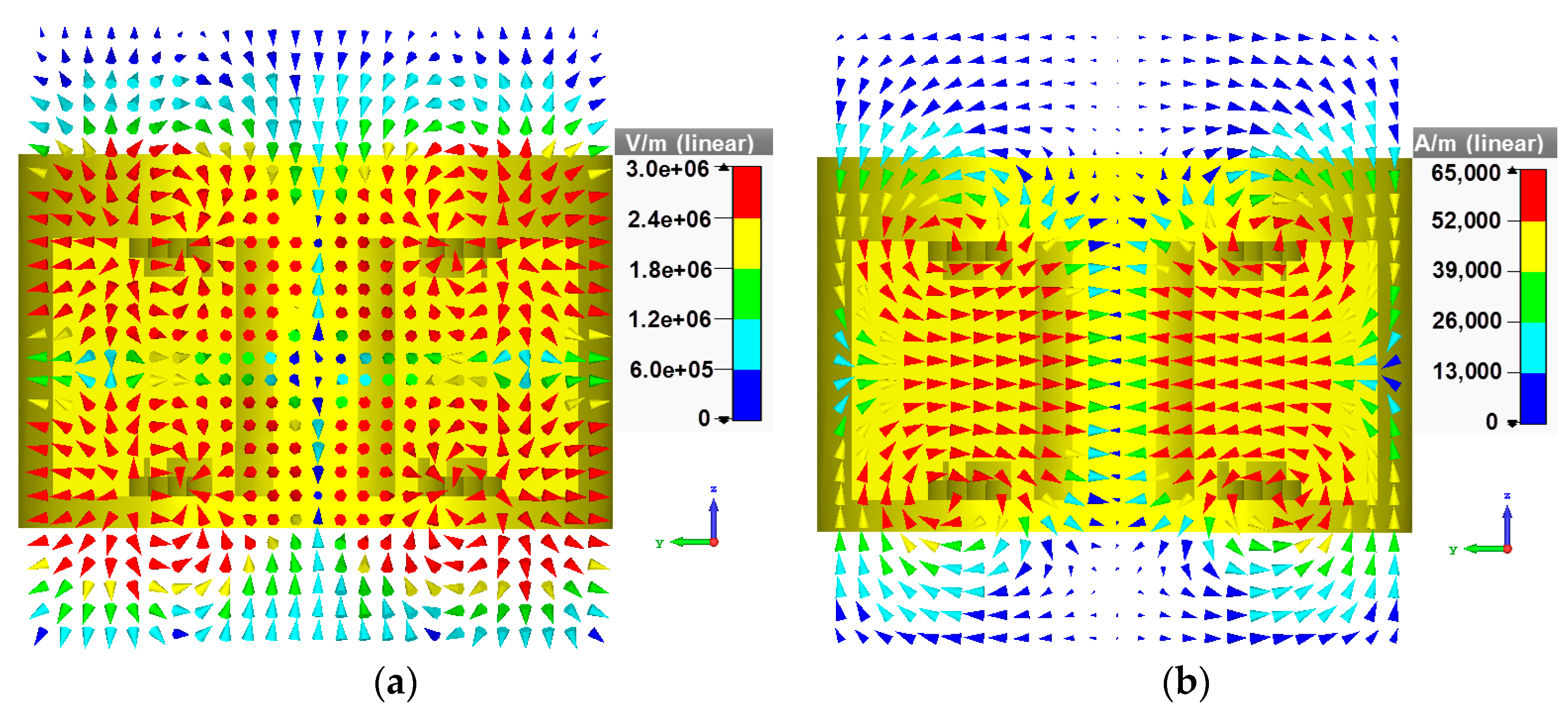
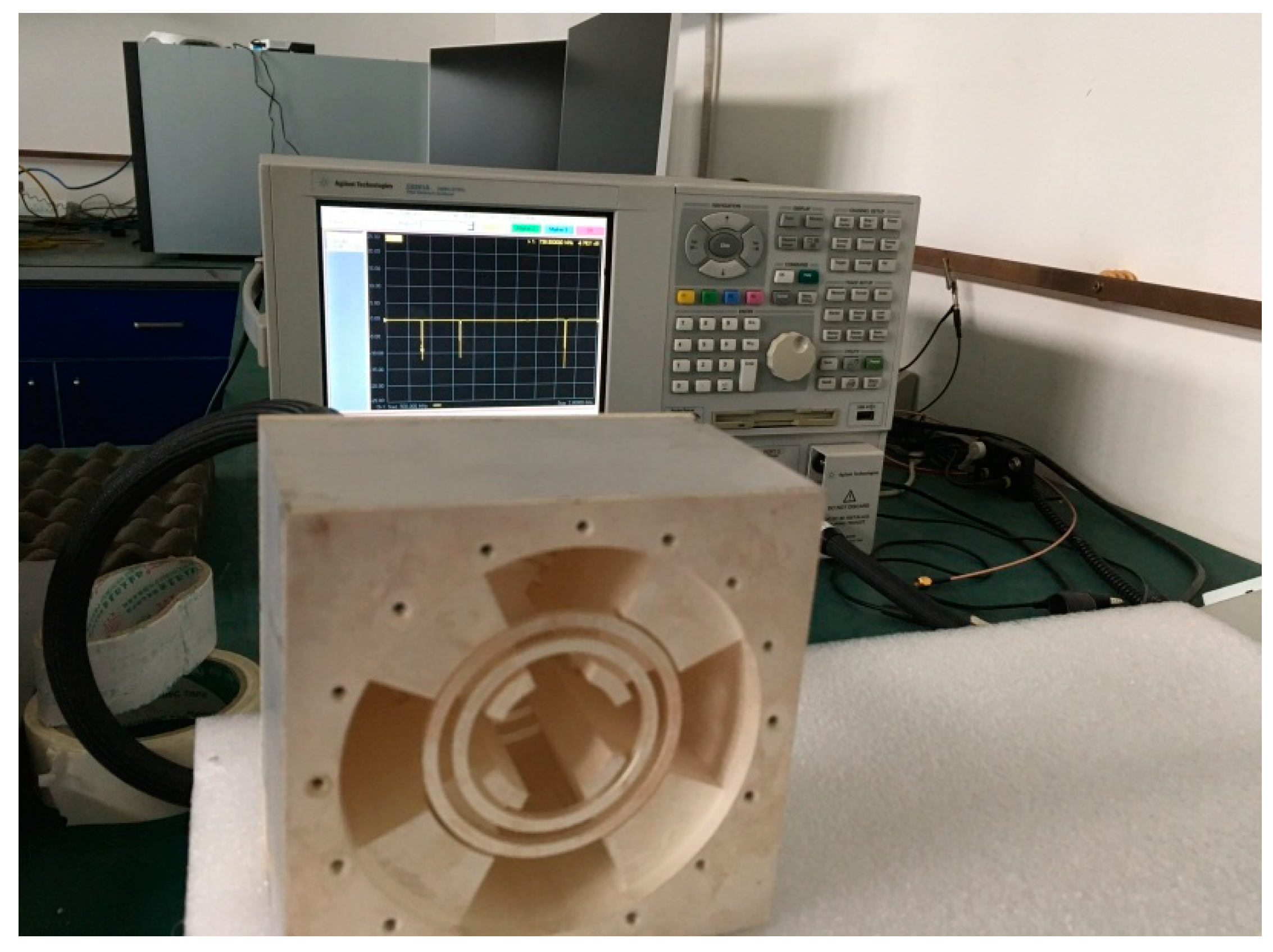
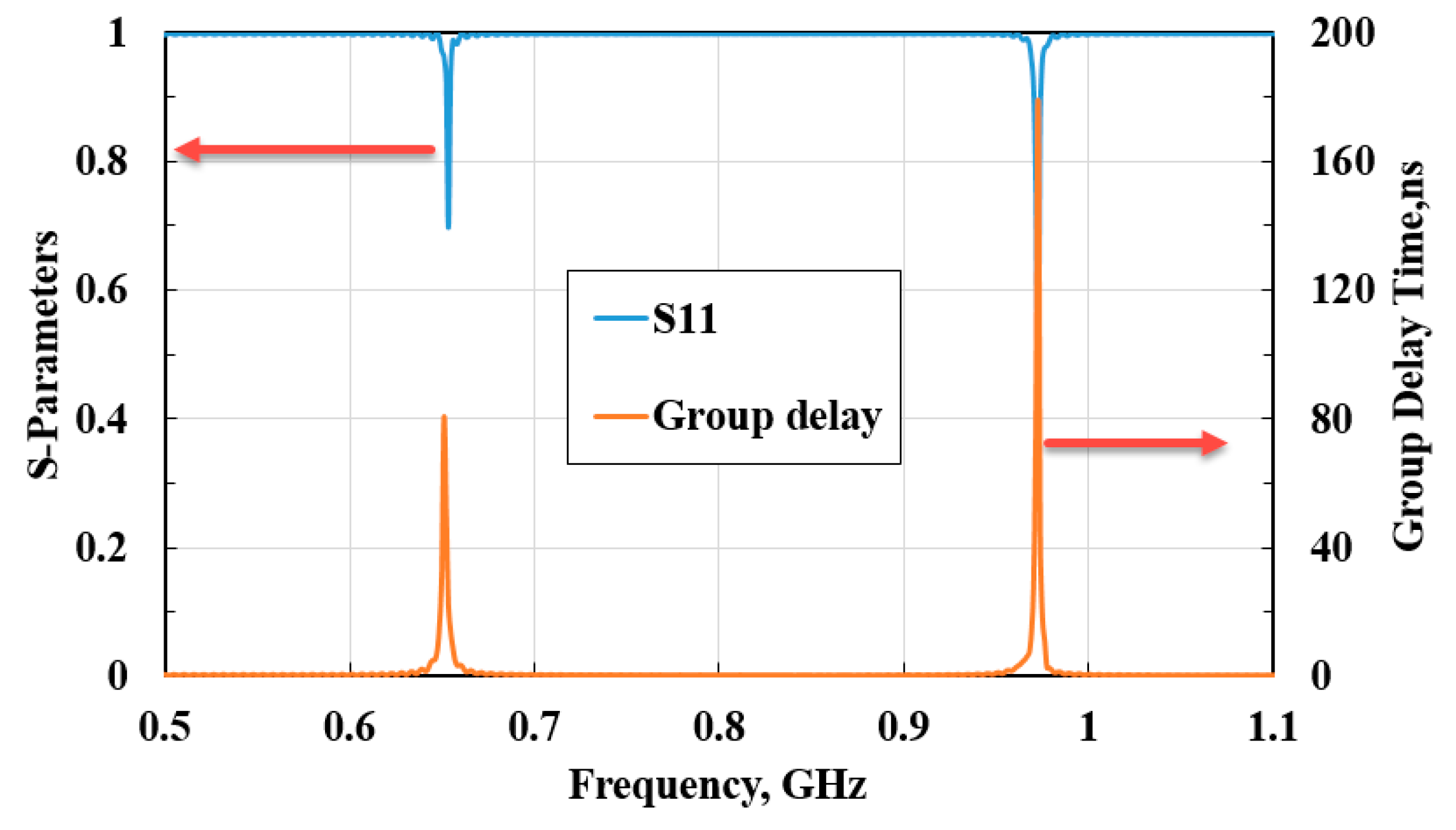
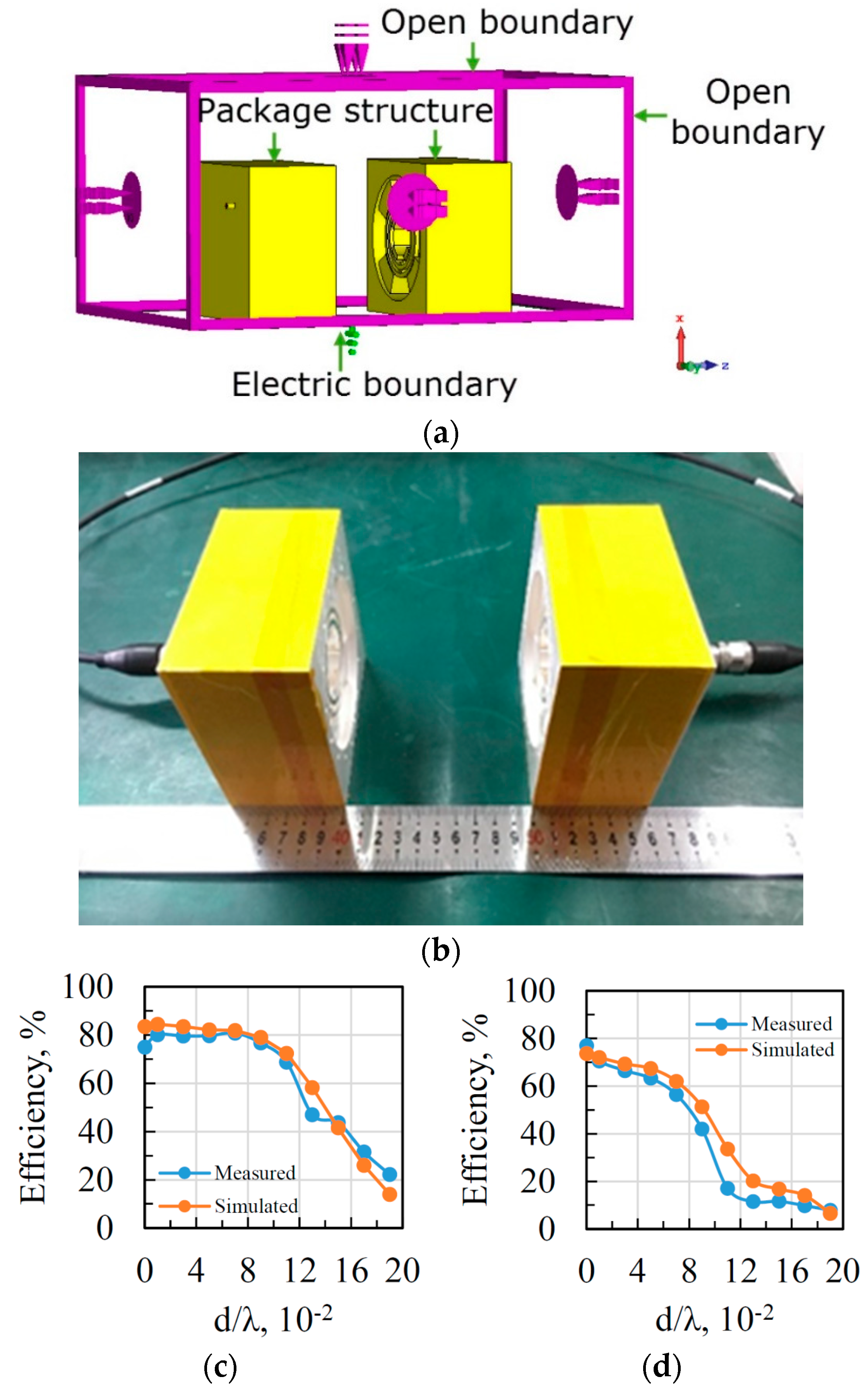
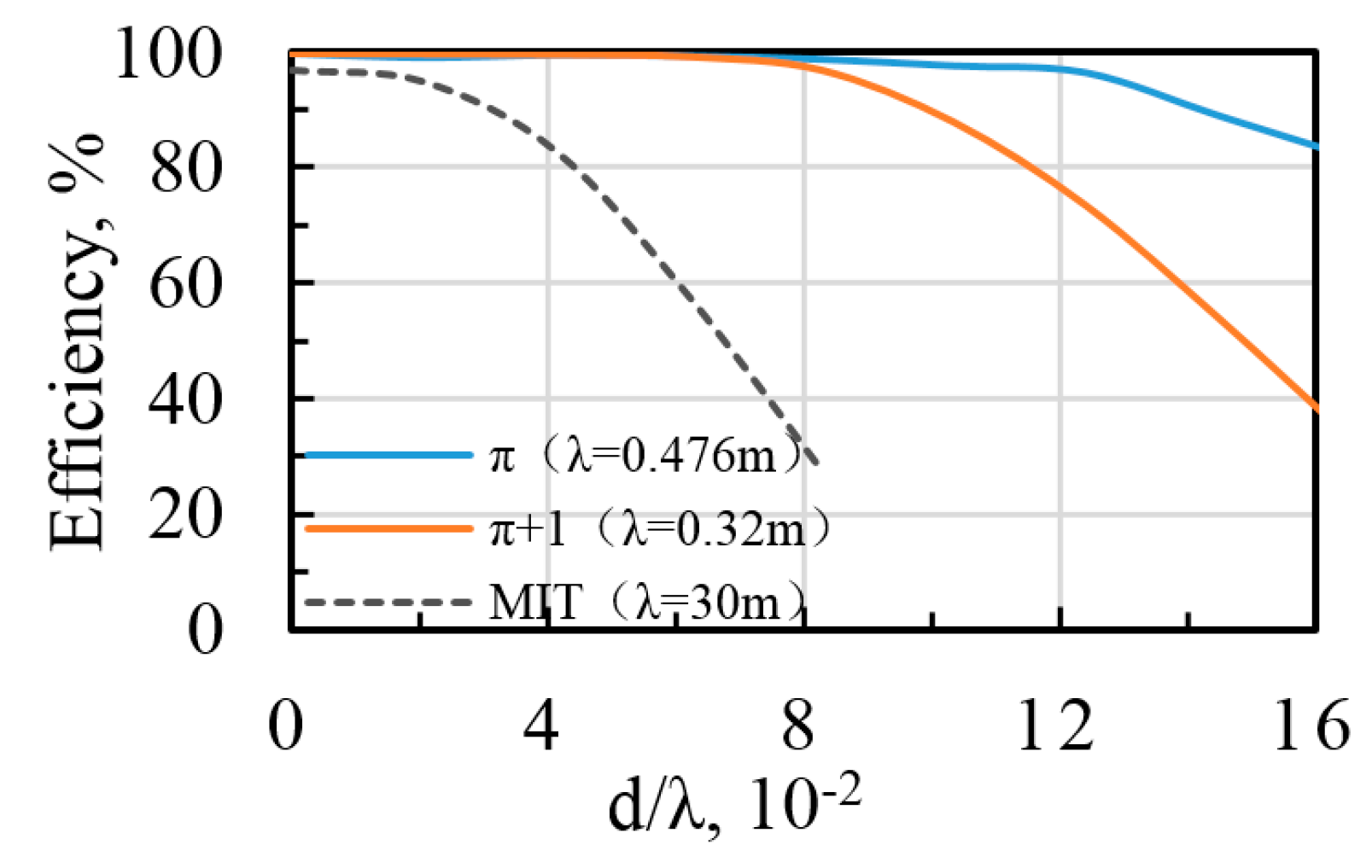
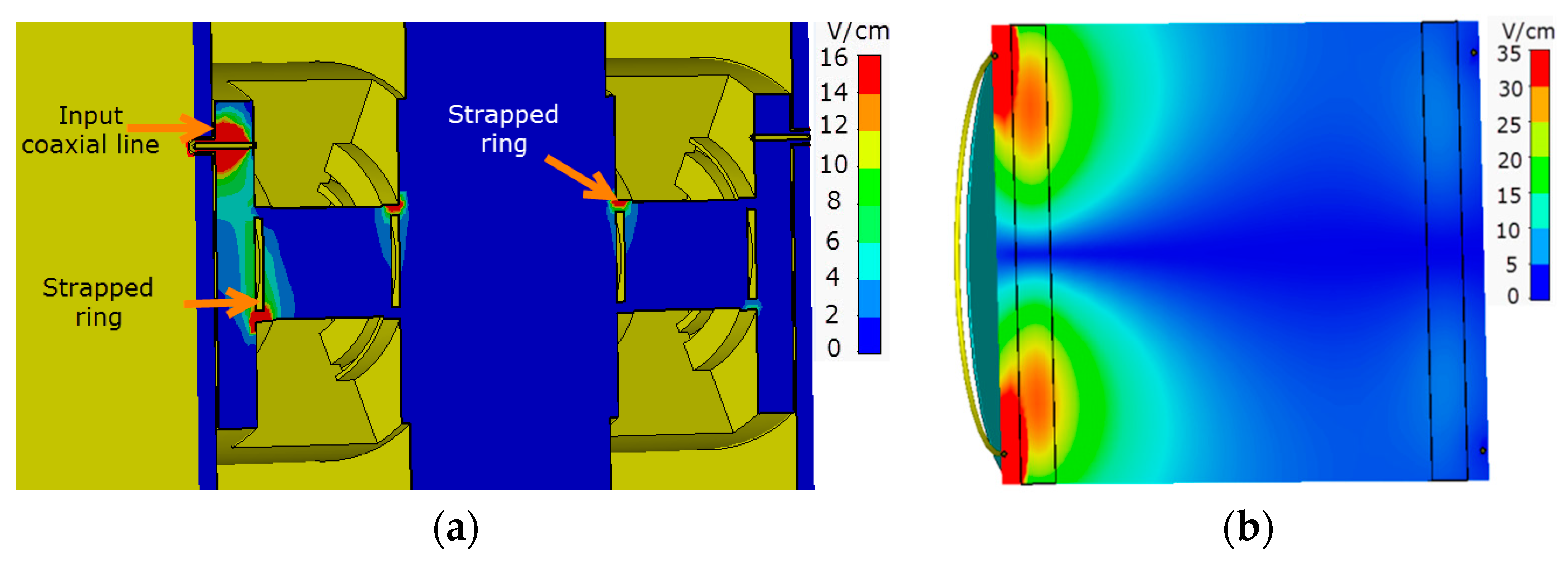
3. Simulation and Experiment Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, W. The history of power transmission by radio waves. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 1984, 32, 1230–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Chau, K.T.; Liu, C.; Lee, C.H.T. An Overview of Resonant Circuits for Wireless Power Transfer. Energies 2017, 10, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurs, A.; Karalis, R.; Moffatt, R.; Joannopoulos, J.; Fisher, P.; Soljacic, M. Wireless power transfer via strongly coupled magnetic resonances. Science 2007, 317, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Jandhyala, V. Design of retrodirective antenna array for short-range wireless power transmission. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2012, 60, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, D.; Hong, S. A study on magnetic field repeater in wireless power transfer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, G. A Novel Wireless Power Transfer System with Double Intermediate Resonant Coils. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 2174–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.Z.; Lorsh, L.; Kapitanova, P.; Nenasheva, E.; Belov, P. Wireless power transfer based on magnetic quadrupole coupling in dielectric resonators. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 108, 023902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, B.L.; Hoburg, J.F.; Stancil, D.D.; Goldstein, S.C. Magnetic resonant coupling as a potential means for wireless power transfer to multiple small receivers. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2009, 24, 1819–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Ma, D.B. Wireless Power Transfer System Architectures for Portable or Implantable Applications. Energies 2016, 9, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabalko, M.J.; Sample, A.P. Three-Dimensional Charging via Multimode Resonant Cavity Enabled Wireless Power Transfer. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 6163–6173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, D.W.; Lee, J.H. Frequency Tuning Method Using the Reflection Coefficient in a Wireless Power Transfer System. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2017, 27, 959–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Hemour, S.; Wu, K. Coupled Resonance Energy Transfer Over Gigahertz Frequency Range Using Ceramic Filled Cavity for Medical Implanted Sensors. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2014, 62, 956–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.H.; Vu, V.B.; Choi, W. Design of a High-Efficiency Wireless Power Transfer System with Intermediate Coils for the On-Board Chargers of Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nenasheva, E.A.; Kartenko, N.F.; Gaidamaka, I.M.; Trubitsyna, O.N.; Redozubov, S.S.; Dedyk, A.I.; Kanareykin, A.D. Low loss microwave ferroelectric ceramics for high power tunable devices. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 30, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, G.B. Microwave Magnetrons; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1948; Section 3; pp. 84–88. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, S.; Jia, B.F.; Li, F.; Zhu, J.J. 3-D simulation of 5.8 GHz magnetron. J. Electromagn. Waves Appl. 2008, 22, 1925–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozar, D.M. Microwave Engineering, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Section 3; pp. 84–88. ISBN 978-0-470-63155-3. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, S.; Jia, B.F.; Li, F.X.; Han, S.H. Power capacity research in cavity bandpass filters. J. Electromagn. Waves Appl. 2008, 22, 905–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.R.; Ryoo, H.J.; Ahn, S.H. Development and optimization of high-voltage power supply system for industrial magnetron. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 1453–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
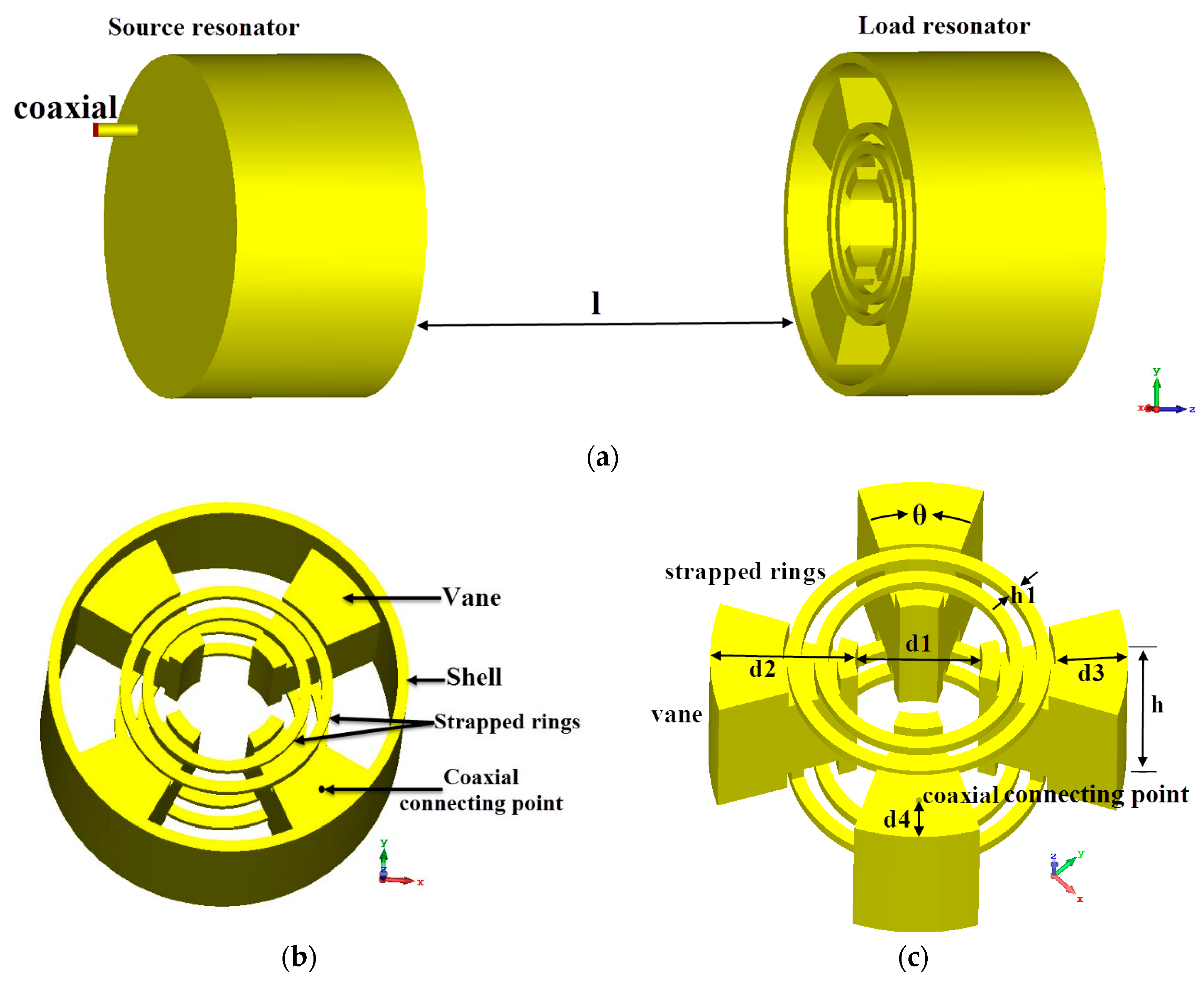
| Parameter | Unit | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| θ | degree | 35 | aperture angel of the vane |
| h | mm | 40 | height of the vane |
| h1 | mm | 3 | width of the strapped ring |
| d1 | mm | 28 | inner diameter of the SR |
| d2 | mm | 32 | length of the vane |
| d3 | mm | 16 | position of the strapped ring connecting point |
| d4 | mm | 8.5 | position of the coaxial connecting point |
| l | mm | 35 | distance between source resonator and load resonator |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, F.-F.; Ding, S.; Wang, B.-Z. Wireless Power Transfer System Based on Strapping Resonators. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2341. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8122341
Guo F-F, Ding S, Wang B-Z. Wireless Power Transfer System Based on Strapping Resonators. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(12):2341. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8122341
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Fei-Fei, Shuai Ding, and Bing-Zhong Wang. 2018. "Wireless Power Transfer System Based on Strapping Resonators" Applied Sciences 8, no. 12: 2341. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8122341
APA StyleGuo, F.-F., Ding, S., & Wang, B.-Z. (2018). Wireless Power Transfer System Based on Strapping Resonators. Applied Sciences, 8(12), 2341. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8122341