Abstract
In this study, the interface structures, atom-resolved magnetism, density of states, and spin polarization of 10 possible atomic terminations in the Ti2CoAl/MgO(100) heterojunction were comprehensively investigated using first-principle calculations. In the equilibrium interface structures, the length of the alloy–Mg bond was found to be much longer than that of the alloy–O bond because of the forceful repulsion interactions between the Heusler interface atoms and Mg atoms. The competition among d-electronic hybridization, d-electronic localization, and the moving effect of the interface metal atoms played an important role in the interface atomic magnetic moment. Unexpected interface states appeared in the half-metallic gap for all terminations. The “ideal” half-metallicity observed in the bulk had been destroyed. In TiAl–Mg and AlAl–O terminations, the maximal spin polarization of about 65% could be reserved. The tunnel magnetoresistance (TMR) value was deduced to be lower than 150% in the Ti2CoAl/MgO(100) heterojunction at low temperature.
1. Introduction
The magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) usually has a large tunnel magnetoresistance (TMR) value and has become a key component of many advanced magnetic devices, such as the read heads in hard-disk drives [1,2,3,4], magnetoresistive random access memories [5], and the next generation of high-density, nonvolatile memories and logic devices [6,7,8,9,10] The core component of MTJ is a “sandwich” stack usually consisting of two ferromagnetic layers and a seeding layer. The direction of the two magnetizations of the ferromagnetic layers can be switched individually by an external magnetic field. If the magnetizations are in a parallel orientation, the electrons tend to tunnel through the seeding layer more than if they are in the antiparallel orientation. Consequently, such a MTJ can be switched between two states of electrical resistance—one with low and one with very high resistance. In MTJ, the TMR value is the most important parameter, which can be defined by the Julliere formula with the spin polarizations of the ferromagnetic electrodes as follows [11]:
where P1 and P2 denote the spin-polarized values of two ferromagnetic layers. The P value can be defined as follows:
where N↑ and N↓ are the spin-up and spin-down state densities at the Fermi level, respectively. Obviously, the key technologies for MTJ applications aim to increase the spin polarization of ferromagnetic films in MTJ devices. However, achieving such aim is a very complicated task. Atomic disordering [12,13], surface states [14], interface states [15], and thermal effects [16,17,18] are the fatal reasons for depolarizing ferromagnetic films.
TMR = 2P1P2/(1 − P1P2),
P = (N↑ − N↓)/(N↑ + N↓),
As a major breakthrough in this field, the fabrication of epitaxial Heusler MTJ can exploit coherent electronic tunneling to produce a large TMR, even at room temperature. In 2004, Parkin and co-workers obtained TMR values of up to 220% at room temperature and 300% at low temperatures for CoFeB/MgO/CoFeB MTJ-oriented (100) MgO tunnel barriers and CoFe electrodes [19]. In 2011, a TMR value of about 600% was reported for Co2MnAlSi/MgO/CoFe MTJ [20]. The current record for the highest Heusler TMR observed experimentally is held by Co2MnSi/MgO/Co2MnSi, which produced a TMR ratio of 1995% at 4 K [21]. From the ab initio calculation, a theoretical TMR value of about 106 was detected in Co2CrSi/Cu2CrAl/Co2CrSi [22]. Recently, an extremely high TMR value exceeding 25,000% was detected in a binary all-Heusler stack Fe3Al/BiF3/Fe3Al at low bias [23]. Therefore, the MgO-based Heusler MTJ holds great potential for TMR device applications.
Heusler alloys are a large family of binary (X3Z), ternary (X2YZ), and quaternary (X1X2YZ) compounds with more than 1500 known members and an impressive range of properties [24]. In these compounds, X and Y generally denote a transition metal, while Z denotes an sp-element or a main group element. In general, ternary Heusler alloys have two high-ordered structures, namely, the classic Cu2MnAl-type structure and the newly discovered Hg2CuTi-type structure. The conventional Cu2MnAl-type Heusler alloy X2YZ with FM-3M space group consists of four fcc sublattices. In Wyckoff coordinates, X is located at (0, 0, 0) and (0.5, 0.5, 0.5), Y is located at (0.25, 0.25, 0.25), and Z is located at (0.75, 0.75, 0.75). Each X atom has four Y and Z atoms as nearest neighbors, thereby presenting the same X atomic surrounding. Unlike the Cu2MnAl-type structure, the Hg2CuTi-type Heusler alloy, also known as the inverse Heusler alloy, has composition X2YZ bear F-43M space group. The neighbor X atoms occupy the locations at (0, 0, 0) and (0.25, 0.25, 0.25), the residual Y enters (0.5, 0.5, 0.5), and Z is located at (0.75, 0.75, 0.75). Given the different surroundings of neighboring X atoms, the d-states hybridization must be remodulated according to magnetic atomic electronegativity. Such remodulation results in novel magnetism and electronic properties and surface or interface behaviors.
Given that high Curie temperature and magnetism follow the Slater–Pauling rule, the Cu2MnAl-type Heusler alloys have received attention in earlier studies. Many Cu2MnAl-type Heusler alloys, such as Co2MnX (X = Si, Ge, Sn) [25], Mn2CoZ (Z = Al, Ga, In, Si, Ge, Sn, Sb), [26] and Cr2MnZ (Z = P, As, Sb, and Bi) [27], have been predicted with half-metallicity from theoretical ab initio calculations and experimental investigations. TMR experiments of the classic Heusler compound MTJs highlighted significant magnetoresistive effects of these junctions and their potential applications [21,22,28]. However, inverse Ti-based Heusler alloys, such as Ti2VAl [29], Ti2FeIn [30], and Ti2MnGa [31], have been previously predicted with “ideal” half-metallicity in the bulk phase from first-principle calculations. The relatively high experimental TMR values of approximately 262% at a low temperature and 159% at room temperature have been reported for the Fe-based inverse Heusler Fe2CoSi/MgO/Co3Fe [32]. However, research on the MTJs of inverse Heusler alloys is still in its infancy. Moreover, to the best of our knowledge, the theoretical or experimental evidence supporting high spin polarization in MTJs for inverse Heusler alloy systems remains scarce.
In our previous work, the inverse Heusler alloy Ti2CoAl was intensively studied owing to its theoretical 100% spin polarization in the bulk phase from first-principle calculations. The doping effects of d-electrons on the electronic structure and magnetism of the inverse Heusler alloy Ti2CoAl were also investigated by substituting Nb and V atoms with Ti(A) and Ti(B) atoms. The doped compounds Ti1.25V0.75CoAl and Ti1.5Nb0.5CoAl effectively inhibited the spin-flip excitation and were shown to be promising candidates for spintronic applications [33]. We also investigated the effect of swap, antisite, and vacancy defects on the inverse Heusler alloy Ti2CoAl. A Ti vacancy and a high spin polarization of around 95% were observed in the Co–Al swap [12]. For Heusler MTJ applications, evidence of high spin polarization on the surface are crucial because the potential surface states appearing in the minority spin gap can easily destruct the “ideal” spin polarization in the bulk phase, as has been reported many times in Cu2MnAl-type Heusler alloys. Moreover, (100) surfaces have been comprehensively detected for the Ti2CoAl system by researchers. Given the surface states, the calculated surfaces failed to preserve the half-metallicity observed in the bulk, and high surface spin polarizations were predicted in only the CoCo and AlAl terminations [34].
To obtain direct evidence of inverse Heusler MTJs, we extended our research to Ti2CoAl heterojunctions. Given its popular use as a binary semiconductor and its well-matching structure with that of Heusler alloys, MgO was selected as the seeding layer in Ti2CoAl MTJ. Therefore, the Ti2CoAl(100)/MgO interfaces were further examined in this work. Given the fact that interface atomic disorder can significantly change the spin polarization of Heusler MTJs [14], apart from the standard epitaxial Heusler terminated surfaces cleaved along the Miller indices (100) crystal direction (i.e., TiCo and TiAl terminations), the modified artificial terminations that cape the pure atoms (i.e., TiTi, CoCo, and AlAl terminations) were also examined to extensively search for possible films with a high spin polarization. In this work, inverse Heusler surfaces were epitaxially grown on an MgO(100) substrate to create possible Ti2CoAl(100)/MgO heterojunctions. To understand the physical and chemical properties of the inverse alloy Ti2CoAl/MgO interface, the structures, magnetism, and electronic properties of Ti2CoAl(100)/MgO heterojunctions with varying atomic interfaces were comprehensively investigated.
2. Structures and Calculation Methods
In the calculations, the Ti2CoAl bulks with an Hg2CuTi structure were geometrically optimized to find the minimal energy structures. Afterward, the optimized bulk structure was cleaved along the Miller indices (100) crystal direction to create all cases of “ideal” epitaxial terminated surfaces, namely, TiCo and TiAl terminations. The modified TiTi, CoCo, and AlAl terminations were created by the surface atoms that act as substitutes for the Ti, Co, and Al atoms in the “ideal” terminations. In the interface calculations, nine and seven atomic layers were taken for Heusler alloys and MgO, respectively, and they were connected with each other to form a supercell. When all possible atomic interfaces came in contact with one another, 10 potential Ti2CoAl/MgO(100) junctions were created, as shown in Figure 1. The thicknesses of these junctions were large enough for the central regions. The tested calculations revealed that the atomic moments in the middle layer were extremely close to the bulk values. In the interface calculations, we only focused on the region of three interface layers in the heterojunction given that they produced the greatest influence on the electronic and magnetic properties of Ti2CoAl/MgO(100) junctions.
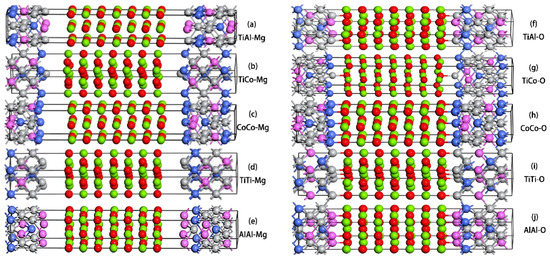
Figure 1.
10 lowest energy terminations in the Ti2CoAl/MgO(100) heterojunction after geometry optimization. (a) TiAl–Mg termination; (b) TiCo–Mg termination; (c) CoCo–Mg termination; (d) TiTi–Mg termination; (e) AlAl–Mg termination; (f) TiAl–O termination; (g) TiCo–O termination; (h) CoCo–O termination; (i) TiTi–O termination; and (j) AlAl–O termination. Color code: O (red), Mg (green), Ti (gray), Co (blue) and Al (pink).
All calculations were performed using the CASTEP Package and by adopting the density functional theory (DFT). The exchange–correlation interaction was described by performing Perdew–Burke–Ernzerhof (PBE) generalized gradient approximation (GGA) [35]. To deal with the electron–ion interaction, we adopted Vanderbilt-type ultrasoft pseudopotentials [36] and the valence electron configurations of Ti (3d24s2), Co (3d7s2), Al (3s23p1), Mg (3s2), and O (2s22p4). For the optimizations of the bulks, we initially assumed that all alloys were ferromagnetic and then applied spin polarization and the 7 × 7 × 7 mesh of special k-points in the Brillouin zone. In the self-consistent calculation, we selected the refined 1 × 10−6 eV/atom and 360 eV as the self-consistent field (SCF) convergence criterion and energy cutoff, respectively. When the positions of atoms were relaxed, we set a convergence criterion of 0.02 eV/Å. To investigate the electronic density of states, we inserted a refined 0.3 Å grid space between k-points in the Brillouin zone. For the interface calculations, we geometrically optimized all supercells using the same parameters employed in the bulk calculation. All technical parameters were tested carefully to ensure the accuracy of the results.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Interface Structures
The structures in Figure 1 represent the lowest-energy configurations after the geometry optimization. The interface atomic layers were planar before the optimization, and the optimized atomic layers were uneven due to the different atomic interactions. As can be seen in Figure 1a–e, in the alloy–Mg terminations, all interface atoms, especially the Co atoms, demonstrated an inward movement, which was similar to their surface behaviors in Heusler alloys [14,34]. In the Heusler terminations where the interface atoms came in contact with the top Mg atoms, the Heusler and MgO atomic layers were repelled very far. For the alloy–O terminations, the distance between the Heusler and MgO layers was reduced due to the atomic bonding interaction at the interface layers (see Figure 1f–j). The shrinking phenomenon of interface atoms could still be observed.
Table 1 lists the bond types and lengths at different interfaces. The Co–Mg bond in the CoCo–Mg termination had the longest length, while the Al–O bond in the AlAl–O termination had the shortest length. The bond lengths in the alloy–Mg terminations were obviously longer than those in the alloy–O terminations because of the forceful repulsion interactions between the Heusler interface atoms and the Mg atoms, especially those between the metal and Mg atoms. Moreover, the interface repulsion interactions of metal–Mg or metal–O were more vigorous than those of Al–Mg or Al–O. In the TiCo–Mg and TiCo–O terminations, the bond lengths of Co–Mg and Co–O were longer than those of Ti–Mg and Ti–O, thereby creating an uneven interface atomic layer that led to further spin electronic scattering from the mechanical mismatch interface layers to weaken the spin polarization [37].

Table 1.
Bond lengths at the interfaces.
3.2. Interface Magnetic Behaviors
Table 2 summarizes the atom-resolved magnetic moments (AMMs) at the interface and subinterface layers in Ti2CoAl and at the interface layer in MgO for various terminations of the Ti2CoAl/MgO(100) interface. To facilitate comparisons with the bulk and surface values, the calculated atom-resolved magnetic moments per cell in Ti2CoAl bulk and (100) surfaces (TiAl termination and TiCo termination) are also listed in this table. The AMMs from the middle layers were close to the corresponding bulk values, thereby indicating that the implemented GGA + PBE scheme could reliably deal with the Heusler hertrojunction system. The middle layer is also called the bulk-like layer. Following the reduction of atomic coordination numbers at the surfaces, the crystal field was weakened, and the localization of d-electron atoms were enhanced, thereby resulting in the rehybridization of Ti and Co atoms. As a result, the surface Ti AMM was obviously enhanced when compared with the bulk value. For the surface and subsurface Co atoms, the AMM slightly decreased owing to the enhanced d-electronic hybridization caused by the surface Co atomic shrink. This same result had also been obtained in our previous work [34]. Similar surface behaviors were also observed in Ti2FeGe(001) [38] and Co2MnGe(111) [39].

Table 2.
Atom-resolved magnetic moments at interface and subinterface layers in Ti2CoAl and the interface layer in MgO. The number following “*” denotes the atoms at the subinterface, while the number enclosed in brackets denotes the magnetism coming from different atomic sites.
Interface AMMs are various and complex. The Ti may be located at the (0, 0, 0) or (0.25, 0.25, 0.25) sites and presents different AMMs in the bulk [29]. Table 2 shows that in the alloy–Mg terminations, the interface and subinterface Ti AMMs were slightly larger than those at the middle layers, thereby suggesting that the d-electron localization originating from relatively large metal–Mg bond lengths was enhanced. However, for the interface Co atom, the fierce inward shrink promoted the d-electron hybridization to resist d-electronic localization. Therefore, the interface Co AMMs, except for the CoCo–Mg termination, slightly decreased. In the alloy–O terminations, the relatively short metal–O bond lengths reduced the part of d-electron localization, thereby leading to a remarkable direct magnetic exchange. Therefore, the interface or subinterface Ti and Co AMMs in the alloy–O terminations, except for the CoCo–O termination, had low values. The modified CoCo–O or CoCo–Mg terminations were created by the surface atoms substituted for the Ti atoms in the “ideal” TiCo–Mg or TiCo–O terminations. Therefore, the two interface Co atoms had different magnetic properties. In the CoCo–Mg and CoCo–O terminations, given that the periodic structure of the Heusler crystal field was cut off and considering the competition between the localization and hybridization of d-electrons, the interface Co AMM was a large value, especially in the CoCo–Mg termination. Meanwhile, for the interface Al atom, the absolute value of AMMs decreased as a result of the reduced magnetic atoms. In MgO films, the interface or subinterface Co and Mg atoms suffered from an extremely small spin polarization and had zero spin magnetism in most cases.
3.3. Interface Electronic Properties
In order to analyze the electronic properties of interface layer atoms, the densities of state (DOS) of the two outermost layer atoms in Heusler alloy Ti2CoAl and the first interface layer atom in MgO for 10 potential terminations were analyzed in the Ti2CoAl/MgO surpercell. Figure 2 shows that the atom-resolved DOS at the middle layer was extremely close to the feature of the bulk. In all 10 terminations, we could find that the spin-down gap in the bulk had been destroyed. In TiAl–Mg and AlAl–O termination, the spin-down gap narrowed down compared with the middle layers. In the rest of the eight terminations, some peaks from interface/subinterface Co or Ti atoms appeared in the spin-down gap and crossed the Fermi level. For the interface/subinterface Al atom, a slight spin polarization was observed at the Fermi level. In all 10 terminations, all interface Mg and O atoms suffered an extremely small spin polarization at the Fermi level, thereby indicating that the interface alloy–Mg and alloy–O bonding was not strong enough to contribute to the electronic properties at the Fermi level. Unfortunately, unexpected interface states appeared at the Fermi level and destroyed the “ideal” half-metallicity observed in the bulk. Meanwhile, the interface states in the AlAl–Mg, TiTi–Mg, TiCo–Mg and TiTi–O terminations had entirely filled the spin-metallic gaps in the spin-down channel at the Fermi level. By contrast, in the CoCo–Mg and CoCo–O terminations, the electronic structure was very similar to the behavior of the middle layer atoms. Evidence of high spin polarization has been previously reported in the CoCo termination of the Ti2CoAl(100) surface system [34]. In the TiAl–Mg and AlAl–O terminations, the half-metallic gap suffered minimal destruction, and the DOSs were in accordance with that of the middle layer atoms. We deduced that a high spin polarization might be reserved in these terminations.
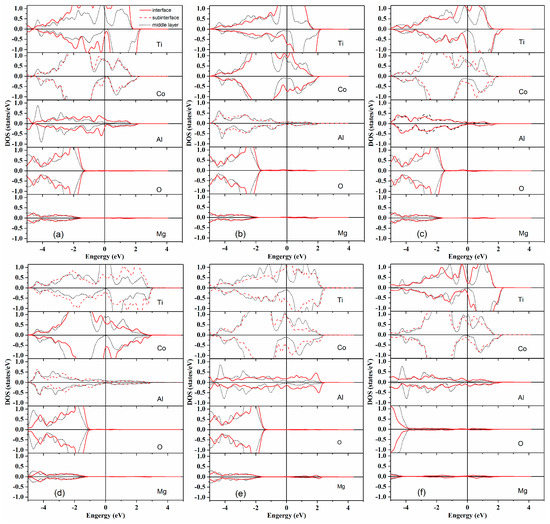
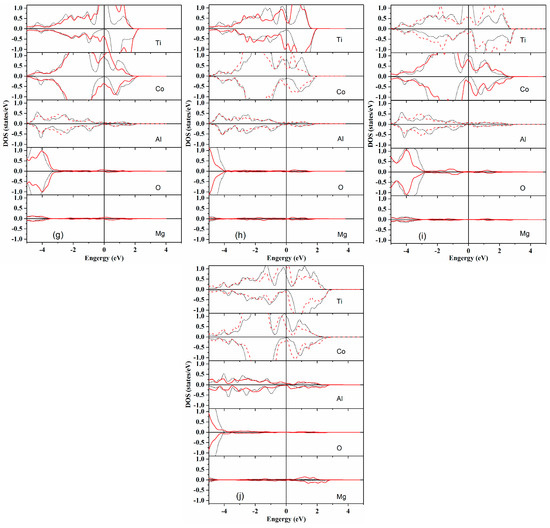
Figure 2.
The densities of state (DOS) of the two outermost layer atoms in Heusler alloy Ti2CoAl and the first interface layer atom in MgO for 10 potential terminations in Ti2CoAl/MgO junctions. (a) TiAl–Mg termination; (b) TiCo–Mg termination; (c) TiTi–Mg termination; (d) CoCo–Mg termination; (e) AlAl–Mg termination; (f) TiAl–O termination; (g) TiCo–O termination; (h) TiTi–O termination; (i) CoCo–O termination; and (j) AlAl–O termination.
Given the significance of interface polarization in MTJs, we examined the interface spin polarizations in various terminations, especially for the several interface layers in contact with the MgO slab. Table 3 summarizes the spin polarization P, spin-up state density N↑, and spin-down state density N↓ at the Fermi level. The contributions from the interface and subinterface layers in Ti2CoAl (labeled I-type) and from the three interface layers with the addition of the first interface layer in MgO (labeled II-type) were also analyzed. Surprisingly, the lowest value was less than 1% in three interface layers for the TiTi–Mg terminations for the TiCo–Mg, TiAl–Mg, and AlAl–Mg terminations. However, for the first two interface layers in the Ti2CoAl slab, the P value was the largest. According to the Julliere formula, we could deduce that the TMR value was not larger than 150% in the Ti2CoAl/MgO(100) heterojunction at low temperature.

Table 3.
Spin polarization P, spin-up state density N↑ at the Fermi level, and spin-down state density N↓ at the Fermi level. I-type includes the interface and subinterface layers in Ti2CoAl, while the II-type comprises I-type layers and the interface layer in MgO.
4. Conclusions
Using the first-principle calculations within DFT, the interface structures, atom-resolved magnetism, atom-resolved DOS, and spin polarization of 10 atomic terminations in the Ti2CoAl/MgO(100) heterojunction were systematically examined. The results revealed that in equilibrium interface structures, the length of the alloy–Mg bond was much longer than that of the alloy–O bond because of the forceful repulsion interactions between the Heusler interface atoms and Mg atoms, especially those between metal atoms and Mg atoms. Owing to the competition among d-electron hybridization, d-electron localization originating from interface atomic bonding, and the moving effect of interface metal atoms, the interface atomic magnetic moments were complex and varied. In general, the interface atomic magnetism was slightly larger than the corresponding bulk-like layer atoms in alloy–Mg terminations. However, the opposite magnetic behavior was observed in alloy–O terminations. Analyzing the electronic properties near the Fermi level, we found that unexpected interface states appeared at the Fermi level for all terminations and destroyed the “ideal” half-metallicity observed in the bulk. A minimal destruction in the half-metallic gap and a maximal spin polarization of approximately 65% could only be observed in TiAl–Mg and AlAl–O terminations. From the Julliere formula, we could deduce that the TMR value was not larger than 150% in the Ti2CoAl/MgO(100) heterojunction at low temperature.
Author Contributions
Methodology, B.W.; software, G.Z. and X.W.; data curation, Y.F. and Y.C.; writing—original draft preparation, H.H.; writing—review and editing, B.W.
Funding
This work was partly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (11304410), Key Laboratory and Scientific Research Foundation of Zunyi City (SSKH [2015] 55), Natural Science Foundation of Technology Department (QKHJZ-LKZS [2014] 10, QJHJZ-LKZS [2012]03, and KHJZ[2014]2170), Youth Science Foundation of Education Ministry (QJHKZ [2012] 084, QJHKY[2018]310), and the Key Support Discipline ([2011]275) of Guizhou Province of China.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Segu, D.Z.; Khan, P.V.; Hwang, P. Experimental and direct numerical analysis of hard-disk drive. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2018, 32, 3507–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, T.; Ina, Y.; Wen, Z.; Takanashi, K. Interface Tailoring Effect for Heusler Based CPP-GMR with an L12-Type Ag3Mg Spacer. Materials 2018, 11, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satoshi, S.; Susumu, H.; Masayuki, T.; Yuzo, K.; Hitoshi, I. All-metallic nonlocal spin valves using polycrystalline Co2(FeMn)Si Heusler alloy with large output. Appl. Phys. Express 2015, 8, 023103. [Google Scholar]
- Koki, M.; Shinya, K.; Yukiko, K.T.; Kouta, K.; Yoshichika, O.; Seiji, M.; Kazuhiro, H. High output voltage of magnetic tunnel junctions with a Cu(In0.8Ga0.2)Se2 semiconducting barrier with a low resistance–area product. Appl. Phys. Express 2017, 10, 013008. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Takahashi, Y.K.; Sakuraba, Y.; Chen, J.; Furubayashi, T.; Mryasov, O.; Faleev, S.; Hono, K. Current-perpendicular-to-plane giant magnetoresistive properties in Co2Mn(Ge0.75Ga0.25)/Cu2TiAl/Co2Mn(Ge0.75Ga0.25) all-Heusler alloy pseudo spin valve. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 119, 093911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakır, A.; Acet, M. Non-volatile high-temperature shell-magnetic pinning of Ni-Mn-Sn Heusler precipitates obtained by decomposition under magnetic field. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 448, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, A.K.; Kumar, V.; Ma, T.; Werner, P.; Pippel, E.; Sahoo, R.; Damay, F.; Rößler, U.K.; Felser, C.; Parkin, S.S.P. Magnetic antiskyrmions above room temperature in tetragonal Heusler materials. Nature 2017, 548, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; D’souza, S.W.; Nayak, J.; Suard, E.; Chapon, L.; Senyshyn, A.; Petricek, V.; Skourski, Y.; Nicklas, M.; Felser, C.; et al. Room-temperature tetragonal non-collinear Heusler antiferromagnet Pt2MnGa. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.; Fenglong, W.; Gesang, D.; Jinli, Y.; Changjun, J. Piezostrain tuning non-volatile 90° magnetic easy axis rotation in Co2FeAl Heusler alloy film grown on Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-PbTiO3 heterostructures. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2016, 49, 455001. [Google Scholar]
- Dutta, S.; Nikonov, D.E.; Manipatruni, S.; Young, I.A.; Naeemi, A. Overcoming thermal noise in non-volatile spin wave logic. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julliere, M. Tunneling between ferromagnetic films. Phys. Lett. A 1975, 54, 225–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, B.; Yuan, H.; Feng, Y.; Chen, H. The defect-induced changes of the electronic and magnetic properties in the inverse Heusler alloy Ti2CoAl. J. Solid State Chem. 2015, 221, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasileiadis, T.; Waldecker, L.; Foster, D.; Da Silva, A.; Zahn, D.; Bertoni, R.; Palmer, R.E.; Ernstorfer, R. Ultrafast heat flow in heterostructures of Au nanoclusters on thin-films: Atomic-disorder induced by hot electrons. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1803.00074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bo, W.; Hongkuan, Y.; Anlong, K.; Yu, F.; Hong, C. Tunable magnetism and half-metallicity in bulk and (100) surface of quaternary Co2MnGe1−xGax Heusler alloy. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2011, 44, 405301. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, X.; Yu, G.; Zhang, C.; Wang, T.; Huang, X.; Chen, W. A theoretical study on the structures and electronic and magnetic properties of new boron nitride composite nanosystems by depositing superhalogen Al13 on the surface of nanosheets/nanoribbons. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 15424–15433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Li, D.; Wang, S.; Ma, Q.; Liang, S.; Wei, H.; Han, X.; Hesjedal, T.; Ward, R.; Kohn, A. Effect of interfacial structures on spin dependent tunneling in epitaxial L10-FePt/MgO/FePt perpendicular magnetic tunnel junctions. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 117, 083904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, A.; Shi, L.; Zhao, T. Thermal effects on the sedimentation behavior of elliptical particles. Int. J. Heat Mass Tran. 2018, 126, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, R.; Marchi, S. Direct thermal effects of the Hadean bombardment did not limit early subsurface habitability. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2018, 485, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkin, S.S.; Kaiser, C.; Panchula, A.; Rice, P.M.; Hughes, B.; Samant, M.; Yang, S.-H. Giant tunnelling magnetoresistance at room temperature with MgO (100) tunnel barriers. Nat. Mater. 2004, 3, 862–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozawa, E.; Tsunegi, S.; Oogane, M.; Naganuma, H.; Ando, Y. The effect of inserting thin Co2MnAl layer into the Co2MnSi/MgO interface on tunnel magnetoresistance effect. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2011, 266, 012104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.-X.; Honda, Y.; Taira, T.; Matsuda, K.-I.; Arita, M.; Uemura, T.; Yamamoto, M. Giant tunneling magnetoresistance in epitaxial Co2MnSi/MgO/Co2MnSi magnetic tunnel junctions by half-metallicity of Co2MnSi and coherent tunneling. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 132418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Lu, Y.; Shen, L.; Ko, V.; Han, G.; Feng, Y. Transport properties of high-performance all-Heusler Co2CrSi/Cu2CrAl/Co2CrSi giant magnetoresistance device. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 093911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotjanapittayakul, W.; Prasongkit, J.; Rungger, I.; Sanvito, S.; Pijitrojana, W.; Archer, T. Search for alternative magnetic tunnel junctions based on all-Heusler stacks. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1805.08603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, T.; Felser, C.; Parkin, S.S. Simple rules for the understanding of Heusler compounds. Prog. Solid State Chem. 2011, 39, 1–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taira, T.; Ishikawa, T.; Itabashi, N.; Matsuda, K.-I.; Uemura, T.; Yamamoto, M. Spin-dependent tunnelling characteristics of fully epitaxial magnetic tunnel junctions with a Heusler alloy Co2MnGe thin film and a MgO barrier. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2009, 42, 084015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furubayashi, T.; Kodama, K.; Sukegawa, H.; Takahashi, Y.; Inomata, K.; Hono, K. Current-perpendicular-to-plane giant magnetoresistance in spin-valve structures using epitaxial Co2FeAl0.5Si0.5/Ag/Co2FeAl0.5Si0.5 trilayers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 122507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsnelson, M.; Irkhin, V.Y.; Chioncel, L.; Lichtenstein, A.; De Groot, R.A. Half-metallic ferromagnets: From band structure to many-body effects. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2008, 80, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Guo, Q.; Li, Y.D.; Wen, L. Total ionizing dose and synergistic effects of magnetoresistive random-access memory. Nucl. Sci. Tech. 2018, 29, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayar, E.; Kervan, N.; Kervan, S. Half-metallic ferrimagnetism in the Ti2CoAl Heusler compound. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2011, 323, 2945–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drief, M.; Guermit, Y.; Benkhettou, N.; Rached, D.; Rached, H.; Lantri, T. First-Principle Study of Half-Metallic Ferrimagnet Behavior in Titanium-Based Heusler Alloys Ti2FeZ (Z = Al, Ga, and In). J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2018, 31, 1059–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahmane, F.; Benalia, S.; Djoudi, L.; Tadjer, A.; Khenata, R.; Doumi, B.; Aourag, H. First-principles study of structural, electronic, magnetic and half-metallic properties of the Heusler alloys Ti2ZAl (Z = Co, Fe, Mn). J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2015, 28, 3099–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterwerf, C.; Meinert, M.; Schmalhorst, J.-M.; Reiss, G. High TMR ratio in Co2FeSi and Fe2CoSi based magnetic tunnel junctions. arXiv, 2013; arXiv:1308.2072. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, B.; Feng, Y.; Yuan, H.-K.; Chen, H. Half-metallicity and magnetism of the quaternary inverse full-Heusler alloy Ti2−xMxCoAl (M = Nb, V) from the first-principles calculations. Eur. Phys. J. B 2014, 87, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Wu, B.; Yuan, H.; Kuang, A.; Chen, H. Magnetism and half-metallicity in bulk and (100) surface of Heusler alloy Ti2CoAl with Hg2CuTi-type structure. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 557, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanderbilt, D. Soft self-consistent pseudopotentials in a generalized eigenvalue formalism. Phys. Rev. B 1990, 41, 7892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippov, S.; Magadov, K.Y. Spin polarization-scaling quantum maps and channels. Lobachevskii J. Math. 2018, 39, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, J.-M. First-principles study on the thermodynamic stability, magnetism, and half-metallicity of full-Heusler alloy Ti2FeGe (001) surface. Phys. Lett. A 2017, 381, 1592–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.X.; Xia, T.S. Spin Injection into Graphene from Heusler Alloy Co2MnGe (111) Surface: A First Principles Study. Mater. Sci. Forum 2018, 914, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).