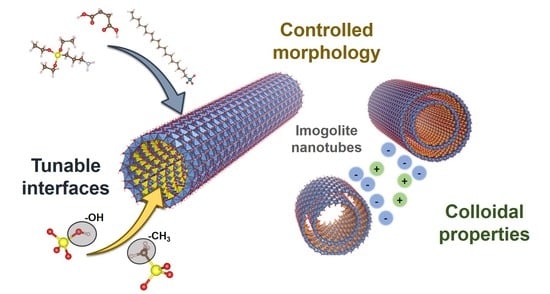
Imogolite Nanotubes: A Flexible Nanoplatform with Multipurpose Applications
Abstract
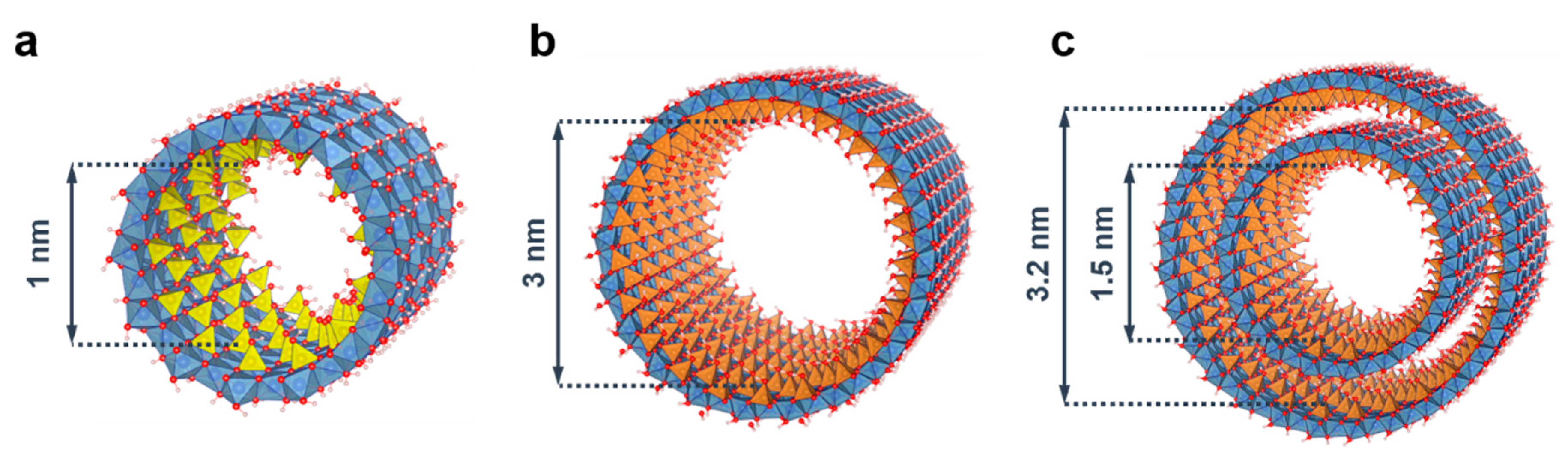
1. Introduction
2. Imogolite Synthesis
2.1. Synthesis Routes for Aluminosilicate INTs
2.2. The Selection of Precursors
2.3. Effects of Ge Substitution
3. Surface Properties and Modifications
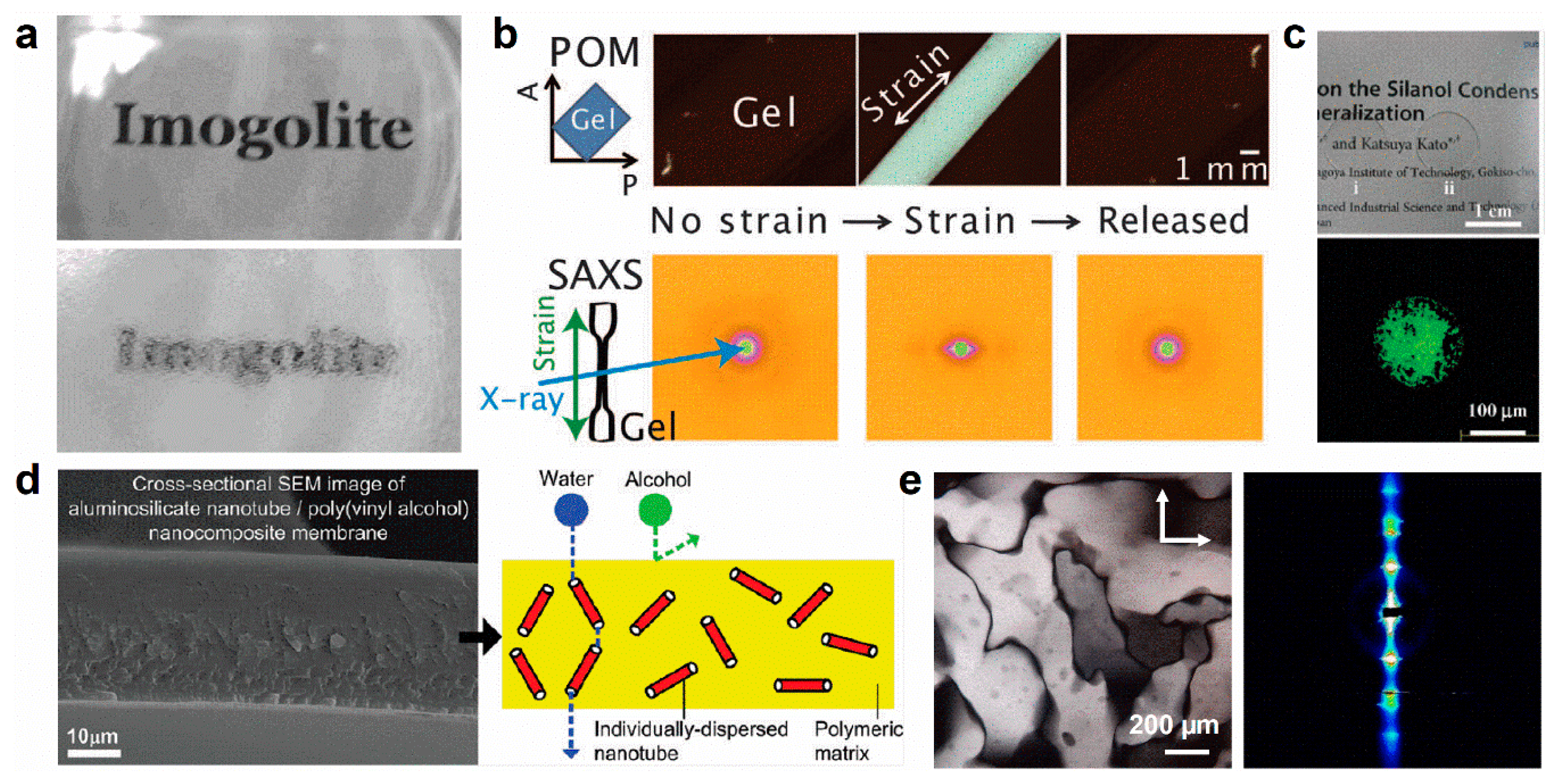
3.1. Colloidal Behavior
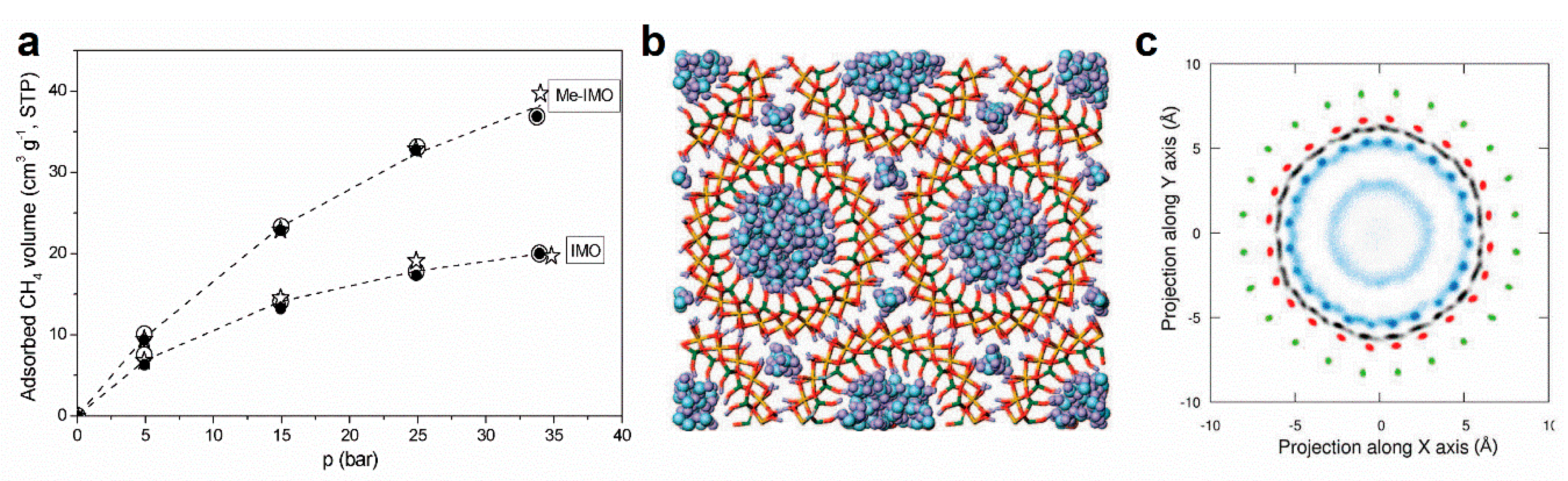
3.2. Modification of the Inner Cavity
3.3. Modification of the Outer Surface of Imogolite
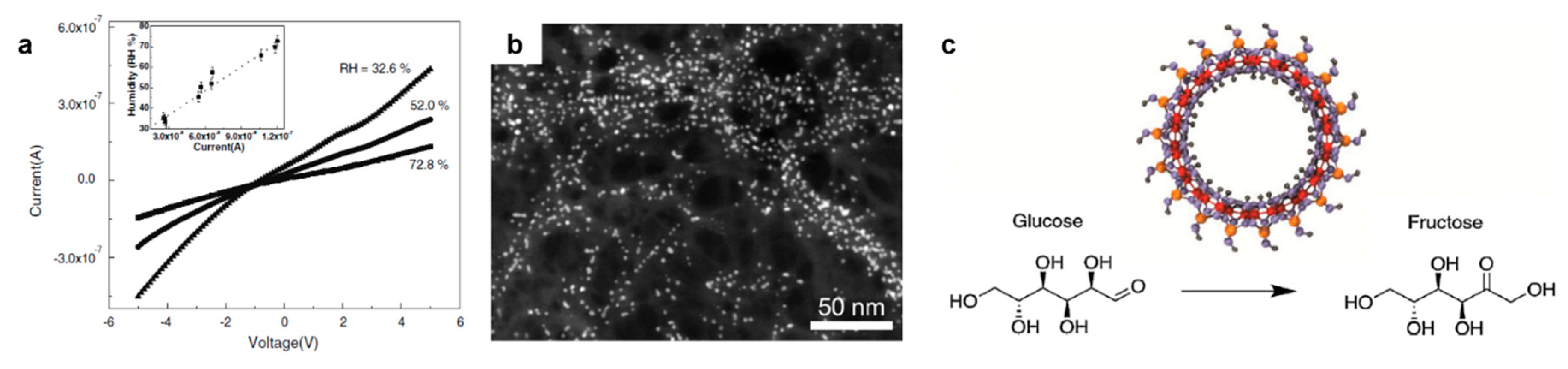
4. Applications
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iijima, S. Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature 1991, 354, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, S.; Ichihashi, T. Single-shell carbon nanotubes of 1-nm diameter. Nature 1993, 363, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethune, D.S.; Kiang, C.H.; De Vries, M.S.; Gorman, G.; Savoy, R.; Vazquez, J.; Beyers, R. Cobalt-catalysed growth of carbon nanotubes with single-atomic-layer walls. Nature 1993, 363, 605–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, N.G.; Luyken, R.J.; Cherrey, K.; Crespi, V.H.; Cohen, M.L.; Louie, S.G.; Zettl, A. Boron nitride nanotubes. Science 1995, 269, 966–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenne, R.; Margulis, L.; Genut, M.; Hodes, G. Polyhedral and cylindrical structures of tungsten disulphide. Nature 1992, 360, 444–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remškar, M. Inorganic nanotubes. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 1497–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joussein, E.; Petit, S.; Churchman, J.; Theng, B.; Righi, D.; Delvaux, B. Halloysite clay minerals—A review. Clay Miner. 2005, 40, 383–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Wang, X. Single-walled MoO3 nanotubes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 8126–8127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, B.; Liu, H.; Wang, P.; He, J.; Wang, X. General synthesis of inorganic single-walled nanotubes. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, K.; Gabriel, J.-C.P.; Grüner, G. Flexible nanotube electronics. Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 1353–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Meshot, E.R.; Kuykendall, T.; Cabrini, S.; Fornasiero, F. Nanofluidic transport through isolated carbon nanotube channels: Advances, controversies, and challenges. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 5726–5737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, J.; Kim, K.; Zhang, J.; Escalada, A.; Tunuguntla, R.; Comolli, L.R.; Allen, F.I.; Shnyrova, A.V.; Cho, K.R.; Munoz, D. Stochastic transport through carbon nanotubes in lipid bilayers and live cell membranes. Nature 2014, 514, 612–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siria, A.; Poncharal, P.; Biance, A.-L.; Fulcrand, R.; Blase, X.; Purcell, S.T.; Bocquet, L. Giant osmotic energy conversion measured in a single transmembrane boron nitride nanotube. Nature 2013, 494, 455–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.G.; Jung, Y. Carbon nanofluidics of rapid water transport for energy applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serp, P.; Castillejos, E. Catalysis in carbon nanotubes. ChemCatChem 2010, 2, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Ballester, N.M.; Ramesh, G.V.; Tanabe, T.; Koudelkova, E.; Liu, J.; Shrestha, L.K.; Lvov, Y.; Hill, J.P.; Ariga, K.; Abe, H. Activated interiors of clay nanotubes for agglomeration-tolerant automotive exhaust remediation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 6614–6619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lvov, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, L.; Fakhrullin, R. Halloysite clay nanotubes for loading and sustained release of functional compounds. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 1227–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzara, G.; Cavallaro, G.; Panchal, A.; Fakhrullin, R.; Stavitskaya, A.; Vinokurov, V.; Lvov, Y. An assembly of organic-inorganic composites using halloysite clay nanotubes. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 35, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cradwick, P.D.G.; Wada, K.; Russell, J.; Yoshinaga, N.; Masson, C.; Farmer, V. Imogolite, a Hydrated Aluminum Silicate of Tubular Structure. Nat. Phys. Sci. 1972, 240, 187–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parfitt, R.L. Allophane and imogolite: Role in soil biogeochemical processes. Clay Miner. 2009, 44, 135–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, J.L.; Fairén, A.G.; Michalski, J.R.; Gago-Duport, L.; Baker, L.L.; Velbel, M.A.; Gross, C.; Rampe, E.B. Surface clay formation during short-term warmer and wetter conditions on a largely cold ancient Mars. Nat. Astron. 2018, 2, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, V.; Fraser, A.; Tait, J. Synthesis of Imogolite—Tubular Aluminum Silicate Polymer. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1977, 462–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konduri, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Nair, S. Strain energy minimum and vibrational properties of single-walled aluminosilicate nanotubes. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 74, 033401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimaraes, L.; Enyashin, A.N.; Frenzel, J.; Heine, T.; Duarte, H.A.; Seifert, G. Imogolite nanotubes: Stability, electronic, and mechanical properties. ACS Nano 2007, 1, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teobaldi, G.; Beglitis, N.S.; Fisher, A.J.; Zerbetto, F.; Hofer, A.A. Hydroxyl vacancies in single-walled aluminosilicate and aluminogermanate nanotubes. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2009, 21, 195301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lourenco, M.P.; Guimaraes, L.; da Silva, M.C.; de Oliveira, C.; Heine, T.; Duarte, H.A. Nanotubes With Well-Defined Structure: Single- and Double-Walled Imogolites. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 5945–5953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, E.; Elliott, J.D.; Hine, N.D.M.; Mostofi, A.A.; Teobaldi, G. Large-scale density functional theory simulation of inorganic nanotubes: A case study on Imogolite nanotubes. Mater. Res. Innov. 2015, 19, S272–S282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillet, P.; Levard, C.; Spalla, O.; Masion, A.; Rose, J.; Thill, A. Growth kinetic of single and double-walled aluminogermanate imogolite-like nanotubes: An experimental and modeling approach. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 2682–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yucelen, G.I.; Kang, D.-Y.; Schmidt-Krey, I.; Beckham, H.W.; Nair, S. A generalized kinetic model for the formation and growth of single-walled metal oxide nanotubes. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2013, 90, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monet, G.; Amara, M.S.; Rouzière, S.; Paineau, E.; Chai, Z.; Elliott, J.D.; Poli, E.; Liu, L.-M.; Teobaldi, G.; Launois, P. Structural resolution of inorganic nanotubes with complex stoichiometry. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, E.; Goze, C.; Bernier, P.; Rubio, A. Elastic properties of C and BxCyNz composite nanotubes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 80, 4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, G.; Terrones, H.; Terrones, M.; Jungnickel, G.; Frauenheim, T. Structure and electronic properties of MoS2 nanotubes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasbakhsh, P.; Churchman, G.J. Natural Mineral Nanotubes: Properties and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; ISBN 1-4822-6225-8. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, P.; Thill, A.; Bergaya, F. Nanosized tubular Clay Minerals: Halloysite and Imogolite; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 7, ISBN 0-08-100292-0. [Google Scholar]
- Farmer, V.; Adams, M.; Fraser, A.; Palmieri, F. Synthetic Imogolite—Properties, Synthesis, and Possible Applications. Clay Miner. 1983, 18, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, S.; Budd, P.; Price, C. The Synthesis and Characterization of Imogolite. Eur. Polym. J. 1991, 27, 609–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzan, L.L.; Philipse, A.P. Synthesis of platinum nanoparticles in aqueous host dispersions of inorganic (imogolite) rods. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1994, 90, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denaix, L.; Lamy, I.; Bottero, J.Y. Structure and affinity towards Cd2+, Cu2+, Pb2+ of synthetic colloidal amorphous aluminosilicates and their precursors. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1999, 158, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levard, C.; Masion, A.; Rose, J.; Doelsch, E.; Borschneck, D.; Dominici, C.; Ziarelli, F.; Bottero, J.-Y. Synthesis of Imogolite Fibers from Decimolar Concentration at Low Temperature and Ambient Pressure: A Promising Route for Inexpensive Nanotubes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 17080–17081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chemmi, A.; Brendle, J.; Marichal, C.; Lebeau, B. Key Steps Influencing the Formation of Aluminosilicate Nanotubes by the Fluoride Route. Clays Clay Miner. 2015, 63, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, C.H.; Yang, A.-C.; Chi, H.-Y.; Chan, K.-Y.; Hsieh, C.-C.; Kang, D.-Y. Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Highly Monodispersed Single-Walled Alunminosilicate Nanotubes. ChemistrySelect 2016, 1, 6212–6216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huling, J.C.; Bailey, J.K.; Smith, D.M.; Brinker, C.J. Imogolite as a material for fabrication of inorganic membranes. MRS Online Proc. Libr. Arch. 1992, 271, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, W.; Smith, D.; Huling, J.; Kim, Y.; Bailey, J.; Brinker, C. Gas Vapor Adsorption in Imogolite—A Microporous Tubular Aluminosilicate. Langmuir 1993, 9, 1051–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yucelen, G.I.; Kang, D.-Y.; Guerrero-Ferreira, R.C.; Wright, E.R.; Beckham, H.W.; Nair, S. Shaping Single-Walled Metal Oxide Nanotubes from Precursors of Controlled Curvature. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arancibia-Miranda, N.; Escudey, M.; Ramirez, R.; Gonzalez, R.I.; van Duin, A.C.T.; Kiwi, M. Advancements in the Synthesis of Building Block Materials: Experimental Evidence and Modeled Interpretations of the Effect of Na and K on Imogolite Synthesis. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 12658–12668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, K.; Huang, P. Influence of Citric-Acid on the Natural Formation of Imogolite. Nature 1984, 308, 58–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidin, Z.; Matsue, N.; Henmi, T. Differential formation of allophane and imogolite: Experimental and molecular orbital study. J. Comput. Aided Mater. Des. 2007, 14, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, S.; Wada, K. Effects of substitution of germanium for silicon in imogolite. Clays Clay Miner. 1982, 30, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Bartlow, V.A.; Nair, S. Phenomenology of the growth of single-walled aluminosilicate and aluminogermanate nanotubes of precise dimensions. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 4900–4909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levard, C.; Rose, J.; Masion, A.; Doelsch, E.; Borschneck, D.; Olivi, L.; Dominici, C.; Grauby, O.; Woicik, J.C.; Bottero, J.-Y. Synthesis of large quantities of single-walled aluminogermanate nanotube. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 5862–5863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maillet, P.; Levard, C.; Larquet, E.; Mariet, C.; Spalla, O.; Menguy, N.; Masion, A.; Doelsch, E.; Rose, J.; Thill, A. Evidence of Double-Walled Al-Ge Imogolite-Like Nanotubes. A Cryo-TEM and SAXS Investigation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 1208–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thill, A.; Maillet, P.; Guiose, B.; Spalla, O.; Belloni, L.; Chaurand, P.; Auffan, M.; Olivi, L.; Rose, J. Physico-chemical Control over the Single- or Double-Wall Structure of Aluminogermanate Imogolite-like Nanotubes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 3780–3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konduri, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Nair, S. Controlling nanotube dimensions: Correlation between composition, diameter, and internal energy of single-walled mixed oxide nanotubes. ACS Nano 2007, 1, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thill, A.; Guiose, B.; Bacia-Verloop, M.; Geertsen, V.; Belloni, L. How the Diameter and Structure of (OH)(3)Al2O3SixGe1-xOH Imogolite Nanotubes Are Controlled by an Adhesion versus Curvature Cornpetition. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 26841–26849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amara, M.-S.; Paineau, E.; Bacia-Verloop, M.; Krapf, M.-E.M.; Davidson, P.; Belloni, L.; Levard, C.; Rose, J.; Launois, P.; Thill, A. Single-step formation of micron long (OH)3Al2O3Ge(OH) imogolite-like nanotubes. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 11284–11286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafsson, J.P. Modelling competitive anion adsorption on oxide minerals and an allophane-containing soil. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2001, 52, 639–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donkai, N.; Inagaki, H.; Kajiwara, K.; Urakawa, H.; Schmidt, M. Dilute-solution properties of imogolite. Makromol. Chem. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 1985, 186, 2623–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karube, J. Hysteresis of the colloidal stability of imogolite. Clays Clay Miner. 1998, 46, 583–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philipse, A.P.; Wierenga, A.M. On the density and structure formation in gels and clusters of colloidal rods and fibers. Langmuir 1998, 14, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paineau, E.; Krapf, M.-E.M.; Amara, M.-S.; Matskova, N.V.; Dozov, I.; Rouziere, S.; Thill, A.; Launois, P.; Davidson, P. A liquid-crystalline hexagonal columnar phase in highly-dilute suspensions of imogolite nanotubes. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paineau, E.; Amara, M.S.; Monet, G.; Peyre, V.; Rouzière, S.; Launois, P. Effect of Ionic Strength on the Bundling of Metal Oxide Imogolite Nanotubes. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 21740–21749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amara, M.S.; Rouziere, S.; Paineau, E.; Bacia-Verloop, M.; Thill, A.; Launois, P. Hexagonalization of Aluminogermanate Imogolite Nanotubes Organized into Closed-Packed Bundles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 9299–9306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karube, J.; Abe, Y. Water retention by colloidal allophane and imogolite with different charges. Clays Clay Miner. 1998, 46, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, F.; Tomura, S.; Akaku, K.; Hayashi, S.; Wada, S.I. Characterization of synthetic imogolite nanotubes as gas storage. J. Mater. Sci. 2004, 39, 1799–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creton, B.; Bougeard, D.; Smirnov, K.S.; Guilment, J.; Poncelet, O. Molecular dynamics study of hydrated imogolite—2. Structure and dynamics of confined water. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2008, 10, 4879–4888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, C.; McBride, M. Cation and anion retention by natural and synthetic allophane and imogolite. Clays Clay Miner. 1984, 32, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, C.; McBride, M. Chemisorption of Cu(II) and Co(II) on allophane and imogolite. Clays Clay Miner. 1984, 32, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harsh, J.; Traina, S.; Boyle, J.; Yang, Y. Adsorption of cations on imogolite and their effect on surface-charge characteristics. Clays Clay Miner. 1992, 40, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, Y.; McBeath, M.; Bargar, J.R.; Joye, J.; Davis, J.A. Uranyl adsorption and surface speciation at the imogolite-water interface: Self-consistent spectroscopic and surface complexation models. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2006, 70, 2492–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levard, C.; Doelsch, E.; Rose, J.; Masion, A.; Basile-Doelsch, I.; Proux, O.; Hazemann, J.-L.; Borschneck, D.; Bottero, J.-Y. Role of natural nanoparticles on the speciation of Ni in andosols of la Reunion. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 4750–4760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.; Pinnavaia, T. Hydrolysis of (gamma-aminopropyl)triethoxysilane-silylated imogolite and formation of a silylated tubular silicate-layered nanocomposite. Langmuir 1991, 7, 2636–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.-Y.; Brunelli, N.A.; Yucelen, G.I.; Venkatasubramanian, A.; Zang, J.; Leisen, J.; Hesketh, P.J.; Jones, C.W.; Nair, S. Direct synthesis of single-walled aminoaluminosilicate nanotubes with enhanced molecular adsorption selectivity. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, D.-Y.; Zang, J.; Jones, C.W.; Nair, S. Single-Walled Aluminosilicate Nanotubes with Organic-Modified Interiors. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 7676–7685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, M.; Paineau, E.; Bacia-Verloop, M.; Thill, A. Aqueous dispersion state of amphiphilic hybrid aluminosilicate nanotubes. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 96, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottero, I.; Bonelli, B.; Ashbrook, S.E.; Wright, P.A.; Zhou, W.; Tagliabue, M.; Armandi, M.; Garrone, E. Synthesis and characterization of hybrid organic/inorganic nanotubes of the imogolite type and their behaviour towards methane adsorption. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 744–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanzottera, C.; Vicente, A.; Celasco, E.; Fernandez, C.; Garrone, E.; Bonelli, B. Physico-Chemical Properties of Imogolite Nanotubes Functionalized on Both External and Internal Surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 7499–7506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amara, M.S.; Paineau, E.; Rouziere, S.; Guiose, B.; Krapf, M.-E.M.; Tache, O.; Launois, P.; Thill, A. Hybrid, Tunable-Diameter, Metal Oxide Nanotubes for Trapping of Organic Molecules. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 1488–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, N.; Deshpande, N.; Gunduz, S.; Ozkan, U.S.; Brunelli, N.A. Utilizing imogolite nanotubes as a tunable catalytic material for the selective isomerization of glucose to fructose. Catal. Today 2018, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.; Pinnavaia, T. Silylation of a tubular aluminosilicate polymer (imogolite) by reaction with hydrolyzed (gamma-aminopropyl)triethoxysilane. Langmuir 1990, 6, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Yoon, H.; Lee, S.-H.; Yoon, J.; Kim, S.-J. Surface-modified imogolite by 3-APS-OsO4 complex: Synthesis, characterization and its application in the dihydroxylation of olefins. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2008, 14, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, D.L.; Batista, A.C.; Viana, R.R.; Airoldi, C. Adsorption of rubidium on raw and MTZ- and MBI-imogolite hybrid surfaces: An evidence of the chelate effect. Desalination 2011, 275, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilment, J.; Martin, D.; Poncelet, O. Hybrid organic-inorganic materials designed to clean wash water in photographic processing: Genesis of a sot-gel industrial product the Kodak Water Saving Treatment System. In Organic/Inorganic Hybrid Materials-2002; Sanchez, C., Laine, R.M., Yang, S., Brinker, C.J., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002; Volume 726, pp. 217–222. ISBN 1-55899-662-1. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, K.; Otsuka, H.; Wada, S.; Takahara, A. Surface modification of aluminosilicate nanofiber “imogolite”. Chem. Lett. 2001, 1162–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Otsuka, H.; Takahara, A.; Wada, S.I. Preparation of a novel (polymer/inorganic nanofiber) composite through surface modification of natural aluminosilicate nanofiber. J. Adhes. 2002, 78, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Lee, Y.; Kim, B.; Lee, J.; Jeong, Y.; Noh, J.; Takahara, A.; Sohn, D. Two-dimensional alignment of imogolite on a solid surface. Chem. Commun. 2007, 28, 2917–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Brant, J.A. Dispersing surface-modified imogolite nanotubes in polar and non-polar solvents. J. Nanopart. Res. 2018, 20, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picot, P.; Tache, O.; Malloggi, F.; Coradin, T.; Thill, A. Behaviour of hybrid inside/out Janus nanotubes at an oil/water interface. A route to self-assembled nanofluidics? Faraday Discuss. 2016, 191, 391–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bac, B.H.; Song, Y.; Kim, M.H.; Lee, Y.-B.; Kang, I.M. Surface-modified aluminogermanate nanotube by OPA: Synthesis and characterization. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2009, 12, 1045–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Kim, J.; Otsuka, H.; Takahara, A. Surface Modification of Individual Imogolite Nanotubes with Alkyl Phosphate from an Aqueous Solution. Chem. Lett. 2011, 40, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Otsuka, H.; Wada, S.I.; Sohn, D.; Takahara, A. Preparation and properties of [poly(methyl methacrylate)/imogolite] hybrid via surface modification using phosphoric acid ester. Polymer 2005, 46, 12386–12392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yah, W.O.; Irie, A.; Jiravanichanun, N.; Otsuka, H.; Takahara, A. Molecular Aggregation State and Electrical Properties of Terthiophenes/Imogolite Nanohybrids. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2011, 84, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Otsuka, H.; Takahara, A. Poly(methyl methacrylate) grafted imogolite nanotubes prepared through surface-initiated ARGET ATRP. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 5813–5815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shikinaka, K.; Kaneda, K.; Mori, S.; Maki, T.; Masunaga, H.; Osada, Y.; Shigehara, K. Direct Evidence for Structural Transition Promoting Shear Thinning in Cylindrical Colloid Assemblies. Small 2014, 10, 1813–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shikinaka, K.; Kikuchi, H.; Maki, T.; Shigehara, K.; Masunaga, H.; Sato, H. Chiral-Linkage-Induced Hierarchical Ordering of Colloidal Achiral Nanotubes in their Thixotropic Gel. Langmuir 2016, 32, 3665–3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiravanichanun, N.; Yamamoto, K.; Irie, A.; Otsuka, H.; Takahara, A. Preparation of hybrid films of aluminosilicate nanofiber and conjugated polymer. Synth. Met. 2009, 159, 885–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, S.; Teramoto, N.; Shibata, M. Nanocomposites composed of poly(epsilon-caprolactone) and oligocaprolactone-modified imogolite utilizing biomimetic chelating method. J. Polym. Res. 2016, 23, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikinaka, K.; Abe, A.; Shigehara, K. Nanohybrid film consisted of hydrophobized imogolite and various aliphatic polyesters. Polymer 2015, 68, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Kim, B.; Yi, W.; Takahara, A.; Sohn, D. Conducting properties of polypyrrole coated imogolite. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2006, 27, 1815–1818. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, S.; Park, J.; Jang, J.; Lee, J.; Lee, J.; Yi, W. Effect of UV irradiation during synthesis of polypyrrole by a one-step deposition/polymerization process. J. Vacuum Sci. Technol. B 2007, 25, 670–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Ryu, J.; Kim, D.; Joo, Y.; Lee, S.U.; Sohn, D. Preparation of an imogolite/poly(acrylic acid) hybrid gel. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 406, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, J.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.; Ko, J.; Sohn, D. Dynamic behavior of hybrid poly (acrylic acid) gel prepared by γ-ray irradiated imogolite. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 535, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ookawa, M.; Inoue, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Suzuki, M.; Yamaguchi, T. Synthesis and characterization of Fe containing imogolite. Clay Sci. 2006, 12, 280–284. [Google Scholar]
- Ookawa, M. Synthesis and Characterization of Fe-Imogolite as an Oxidation Catalyst. Clay Miner. Nat. Their Charact. Modif. Appl. 2013, 239–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafia, E.; Esposito, S.; Manzoli, M.; Chiesa, M.; Tiberto, P.; Barrera, G.; Menard, G.; Allia, P.; Freyria, F.S.; Garrone, E.; et al. Al/Fe isomorphic substitution versus Fe2O3 clusters formation in Fe-doped aluminosilicate nanotubes (imogolite). J. Nanopart. Res. 2015, 17, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafia, E.; Esposito, S.; Armandi, M.; Manzoli, M.; Garrone, E.; Bonelli, B. Isomorphic substitution of aluminium by iron into single-walled alumino-silicate nanotubes: A physico-chemical insight into the structural and adsorption properties of Fe-doped imogolite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 224, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadori, E.; Vaiano, V.; Esposito, S.; Armandi, M.; Sannino, D.; Bonelli, B. Photo-activated degradation of tartrazine by H2O2 as catalyzed by both bare and Fe-doped methyl-imogolite nanotubes. Catal. Today 2018, 304, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avellan, A.; Levard, C.; Kumar, N.; Rose, J.; Olivi, L.; Thill, A.; Chaurand, P.; Borschneck, D.; Masion, A. Structural incorporation of iron into Ge-imogolite nanotubes: A promising step for innovative nanomaterials. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 49827–49830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neouze, M.-A.; Schubert, U. Surface modification and functionalization of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles by organic ligands. Monatshefte Chem. Chem. Mon. 2008, 139, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Ramirez, F. First Principles Studies of Fe-Containing Aluminosilicate and Aluminogermanate Nanotubes. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2009, 5, 3224–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Ramirez, F. Theoretical Study of (OH)(3)N2O3MOH, M = C, Si, Ge, Sn and N = Al, Ga, In, with Imogolite-Like Structure. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 2009, 6, 1120–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimaraes, L.; Pinto, Y.N.; Lourenco, M.P.; Duarte, H.A. Imogolite-like nanotubes: Structure, stability, electronic and mechanical properties of the phosphorous and arsenic derivatives. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 4303–4309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonelli, B.; Bottero, I.; Ballarini, N.; Passeri, S.; Cavani, F.; Garrone, E. IR spectroscopic and catalytic characterization of the acidity of imogolite-based systems. J. Catal. 2009, 264, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanzottera, C.; Armandi, M.; Esposito, S.; Garrone, E.; Bonelli, B. CO2 Adsorption on Aluminosilicate Single-Walled Nanotubes of Imogolite Type. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 20417–20425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.A.; Lee, G.S.H.; Taylor, R.C. Benzene displacement on imogolite. Clays Clay Miner. 2002, 50, 348–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonelli, B.; Zanzottera, C.; Armandi, M.; Esposito, S.; Garrone, E. IR spectroscopic study of the acidic properties of alumino-silicate single-walled nanotubes of the imogolite type. Catal. Today 2013, 218, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonelli, B.; Armandi, M.; Garrone, E. Surface properties of alumino-silicate single-walled nanotubes of the imogolite type. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 13381–13390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konduri, S.; Tong, H.M.; Chempath, S.; Nair, S. Water in single-walled aluminosilicate nanotubes: Diffusion and adsorption properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 15367–15374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalfi, L.; Fraux, G.; Boutin, A.; Coudert, F.-X. Structure and Dynamics of Water Confined in Imogolite Nanotubes. Langmuir 2018, 34, 6748–6756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, J.K.; Park, H.G.; Wang, Y.; Stadermann, M.; Artyukhin, A.B.; Grigoropoulos, C.P.; Noy, A.; Bakajin, O. Fast mass transport through sub-2-nanometer carbon nanotubes. Science 2006, 312, 1034–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falk, K.; Sedlmeier, F.; Joly, L.; Netz, R.R.; Bocquet, L. Molecular origin of fast water transport in carbon nanotube membranes: Superlubricity versus curvature dependent friction. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 4067–4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paineau, E.; Albouy, P.-A.; Rouziere, S.; Orecchini, A.; Rols, S.; Launois, P. X-ray Scattering Determination of the Structure of Water during Carbon Nanotube Filling. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 1751–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardina, S.D.; Paineau, E.; Brubach, J.-B.; Judeinstein, P.; Rouziere, S.; Launois, P.; Roy, P. Water in Carbon Nanotubes: The Peculiar Hydrogen Bond Network Revealed by Infrared Spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 10437–10443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Picot, P.; Lainé, M.; Brubach, J.-B.; Roy, P.; Thill, A.; Le Caër, S. Tuning the properties of confined water in standard andhybrid nanotubes: An infrared spectroscopic study. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 4759–4773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, J.; Chempath, S.; Konduri, S.; Nair, S.; Sholl, D.S. Flexibility of Ordered Surface Hydroxyls Influences the Adsorption of Molecules in Single-Walled Aluminosilicate Nanotubes. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 1235–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, Y.; Usuki, A.; Kawasumi, M.; Okada, A.; Fukushima, Y.; Kurauchi, T.; Kamigaito, O. Mechanical properties of nylon 6-clay hybrid. J. Mater. Res. 1993, 8, 1185–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.S.; Okamoto, M. Polymer/layered silicate nanocomposites: A review from preparation to processing. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2003, 28, 1539–1641. [Google Scholar]
- Bitinis, N.; Hernández, M.; Verdejo, R.; Kenny, J.M.; Lopez-Manchado, M.A. Recent advances in clay/polymer nanocomposites. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 5229–5236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, K.; Otsuka, H.; Wada, S.I.; Sohn, D.; Takahara, A. Transparent polymer nanohybrid prepared by in situ synthesis of aluminosilicate nanofibers in poly(vinyl alcohol) solution. Soft Matter 2005, 1, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, H.; Ito, T.; Donkai, N.; Urakawa, H.; Kajiwara, K. Lyotropic mesophase formation in PVA/imogolite mixture. Polym. Bull. 1992, 29, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.H.; Cho, Y.W.; Ha, W.S.; Lyoo, W.S.; Lee, C.J.; Ji, B.C.; Han, S.S.; Yoon, W.S. Preparation and characterization of syndiotacticity-rich ultra-high molecular weight poly(vinyl alcohol) imogolite blend film. Polym. Int. 1998, 47, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.-C.; Li, Y.-S.; Lam, C.H.; Chi, H.-Y.; Cheng, I.-C.; Kang, D.-Y. Solution-processed ultra-low-k thin films comprising single-walled aluminosilicate nanotubes. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 17427–17432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.-Y.; Yang, A.-C.; Jiang, J.-S.; Yang, Z.-H.; Huang, Y.-S.; Kang, D.-Y.; Hua, C.-C. Properties of Single-Walled Aluminosilicate Nanotube/Poly (vinyl alcohol) Aqueous Dispersions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 122, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, D.-Y.; Tong, H.M.; Zang, J.; Choudhury, R.P.; Sholl, D.S.; Beckham, H.W.; Jones, C.W.; Nair, S. Single-Walled Aluminosilicate Nanotube/Poly(vinyl alcohol) Nanocomposite Membranes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 965–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barona, G.N.B.; Choi, M.; Jung, B. High permeate flux of PVA/PSf thin film composite nanofiltration membrane with aluminosilicate single-walled nanotubes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 386, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, D.-Y.; Lydon, M.E.; Yucelen, G.I.; Jones, C.W.; Nair, S. Solution-Processed Ultrathin Aluminosilicate Nanotube-Poly(vinyl alcohol) Composite Membranes with Partial Alignment of Nanotubes. ChemNanoMat 2015, 1, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.; Ko, J.; Lee, H.; Shin, T.-G.; Sohn, D. Structural Response of Imogolite-Poly(acrylic acid) Hydrogel under Deformation. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 1873–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikinaka, K.; Yokoi, T.; Koizumi-Fujii, Y.; Shimotsuya, M.; Shigehara, K. Robust imogolite hydrogels with tunable physical properties. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 46493–46500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Otsuka, H.; Takahara, A. Preparation and properties of PVC/PMMA-g-imogolite nanohybrid via surface-initiated radical polymerization. Polymer 2011, 52, 5543–5550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, Y.; Tamakoshi, M.; Murakami, J.; Kuroda, K. Fabrication of hierarchically ordered porous films composed of imogolite via colloidal templating. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2007, 115, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, Y.; Kuroda, K. Layer-by-layer assembly of imogolite nanotubes and polyelectrolytes into core-shell particles and their conversion to hierarchically porous spheres. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2008, 9, 025018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroda, Y.; Kuroda, K. Formation of Hierarchically Porous Hollow Spheres Composed of Dehydroxylated Imogolite and Carbonaceous Materials. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2011, 84, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, Y.; Kuroda, K. Expansion of Intertubular Mesopores of Imogolite Nanotubes by Thermal Decomposition of an Imogolite-Poly(sodium 4-styrenesulfonate) Composite. Chem. Lett. 2011, 40, 46–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikinaka, K.; Koizumi, Y.; Osada, Y.; Shigehara, K. Reinforcement of hydrogel by addition of fiber-like nanofiller. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2011, 22, 1212–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikinaka, K.; Koizumi, Y.; Kaneda, K.; Osada, Y.; Masunaga, H.; Shigehara, K. Strain-induced reversible isotropic-anisotropic structural transition of imogolite hydrogels. Polymer 2013, 54, 2489–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barona, G.N.B.; Lim, J.; Choi, M.; Jung, B. Interfacial polymerization of polyamide-aluminosilicate SWNT nanocomposite membranes for reverse osmosis. Desalination 2013, 325, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.-H.; Zhao, Q.-Y.; Gu, L.; Wu, Q.-Y. Thin film nanocomposite membranes based on imologite nanotubes blended substrates for forward osmosis desalination. Desalination 2017, 421, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Brant, J.A. Synthesis of Polyamide Thin-Film Nanocomposite Membranes Using Surface Modified Imogolite Nanotubes. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 563, 664–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikinaka, K. Design of stimuli-responsive materials consisting of the rigid cylindrical inorganic polymer “imogolite”. Polym. J. 2016, 48, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikinaka, K.; Taki, N.; Kaneda, K.; Tominaga, Y. Quasi-solid electrolyte: A thixotropic gel of imogolite and an ionic liquid. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 613–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshino, H.; Yamana, M.; Donkai, N.; Sinigersky, V.; Kajiwara, K.; Miyamoto, T.; Inagaki, H. Lyotropic mesophase formations of HPC/imogolite mixture. Polym. Bull. 1992, 28, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yah, W.O.; Irie, A.; Otsuka, H.; Sasaki, S.; Yagi, N.; Sato, M.; Koganezawa, T.; Takahara, A. Molecular Aggregation States of Imogolite/P3HT Nanofiber Hybrid. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2011, 272, 012021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levard, C.; Thill, A.; Avellan, A.; Mauroy, C.; Vidal, V.; Campos, A.P.C.; Masion, A.; Rose, J. Alignment of Ge-imogolite nanotubes in isomalt with tunable inter-tube distances. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 21323–21327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, K.; Inukai, K.; Fujikura, K.; Kasuga, T. Effective encapsulation of laccase in an aluminium silicate nanotube hydrogel. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 3591–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, N.; Otsuka, H.; Wada, S.I.; Takahara, A. (Inorganic nanofiber/enzyme) hybrid hydrogel: Preparation, characterization, and enzymatic activity of imogolite/pepsin conjugate. Chem. Lett. 2006, 35, 194–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teramoto, N.; Hayashi, A.; Yamanaka, K.; Sakiyama, A.; Nakano, A.; Shibata, M. Preparation and Mechanical Properties of Photo-Crosslinked Fish Gelatin/Imogolite Nanofiber Composite Hydrogel. Materials 2012, 5, 2573–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiravanichanun, N.; Yamamoto, K.; Kato, K.; Kim, J.; Horiuchi, S.; Yah, W.-O.; Otsuka, H.; Takahara, A. Preparation and Characterization of Imogolite/DNA Hybrid Hydrogels. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.-L.; Ma, W.; Higaki, Y.; Takahara, A. Design and characterization of hybrid hydrogels composed of imogolite fibrous nanotubular clay and hyaluronic acid. Polymer 2016, 100, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonini, M.; Gabbani, A.; Del Buffa, S.; Ridi, F.; Baglioni, P.; Bordes, R.; Holmberg, K. Adsorption of Amino Acids and Glutamic Acid-Based Surfactants on Imogolite Clays. Langmuir 2017, 33, 2411–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelli, R.; Del Buffa, S.; Tempesti, P.; Bonini, M.; Ridi, F.; Baglioni, P. Enhanced formation of hydroxyapatites in gelatin/imogolite macroporous hydrogels. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 511, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauroy, C.; Levard, C.; Moreau, C.; Vidal, V.; Rose, J.; Cathala, B. Elaboration of Cellulose Nanocrystal/Ge-Imogolite Nanotube Multilayered Thin Films. Langmuir 2018, 34, 3386–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liou, K.-H.; Kang, D.-Y.; Lin, L.-C. Investigating the Potential of Single-Walled Aluminosilicate Nanotubes in Water Desalination. ChemPhysChem 2017, 18, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fornasiero, F.; Park, H.G.; Holt, J.K.; Stadermann, M.; Grigoropoulos, C.P.; Noy, A.; Bakajin, O. Ion exclusion by sub-2-nm carbon nanotube pores. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 17250–17255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kajiwara, K.; Donkai, N.; Hiragi, Y.; Inagaki, H. Lyotropic mesophase of imogolite, 1. Effect of polydispersity on phase-diagram. Makromol. Chem. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 1986, 187, 2883–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onsager, L. The effects of shape on the interaction of colloidal particles. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1949, 51, 627–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Chang, S.; Jang, J.; Roh, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.; Sohn, D.; Yi, W.; Jung, Y.; Kim, S.-J. Imogolite as an electron emitter and a water sensor. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2007, 18, 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, C.; Arancibia-Miranda, N.; Acuna-Rougier, C.; Escudey, M.; Tasca, F. Spectroscopic and Electrochemical Studies of Imogolite and Fe-Modified Imogolite Nanotubes. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroda, Y.; Fukumoto, K.; Kuroda, K. Uniform and high dispersion of gold nanoparticles on imogolite nanotubes and assembly into morphologically controlled materials. Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 55, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liz-Marzán, L.; Philipse, A. Stable hydrosols of metallic and bimetallic nanoparticles immobilized on imogolite fibers. J. Phys. Chem. 1995, 99, 15120–15128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, H.; Michalik, J.; Sadlo, J.; Perlinska, J.; Takenouchi, S.; Shimomura, S.; Uchida, Y. Electron spin resonance studies on silver atoms in imogolite fibers. Appl. Clay Sci. 2001, 19, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arancibia-Miranda, N.; Escudey, M.; Pizarro, C.; Denardin, J.C.; Teresa Garcia-Gonzalez, M.; Fabris, J.D.; Charlet, L. Preparation and characterization of a single-walled aluminosilicate nanotube-iron oxide composite: Its applications to removal of aqueous arsenate. Mater. Res. Bull. 2014, 51, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerat, Y.J.; Poncelet, O.J. Dressing and Antiseptic Agent Containing Silver. Patent US7323614B2, 19 January 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Geraldo, D.A.; Arancibia-Miranda, N.; Villagra, N.A.; Mora, G.C.; Arratia-Perez, R. Synthesis of CdTe QDs/single-walled aluminosilicate nanotubes hybrid compound and their antimicrobial activity on bacteria. J. Nanopart. Res. 2012, 14, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yucelen, G.I.; Connell, R.E.; Terbush, J.R.; Westenberg, D.J.; Dogan, F. Synthesis and immobilization of silver nanoparticles on aluminosilicate nanotubes and their antibacterial properties. Appl. Nanosci. 2016, 6, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, S.; Kokubu, T.; Yamashita, T.; Okamoto, Y.; Kajiwara, K.; Kanai, H. Shape-selective copper-loaded Imogolite catalyst. J. Catal. 1996, 160, 137–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsumata, K.; Hou, X.; Sakai, M.; Nakajima, A.; Fujishima, A.; Matsushita, N.; MacKenzie, K.J.D.; Okada, K. Visible-light-driven photodegradation of acetaldehyde gas catalyzed by aluminosilicate nanotubes and Cu(II)-grafted TiO2 composites. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 138, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ookawa, M.; Takata, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Inukai, K.; Maekawa, T.; Yamaguchi, T. Oxidation of aromatic hydrocarbons with H(2)O(2) catalyzed by a nano-scale tubular aluminosilicate, Fe-containing imogolite. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2008, 34, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafia, E.; Esposito, S.; Armandi, M.; Bahadori, E.; Garrone, E.; Bonelli, B. Reactivity of bare and Fe-doped alumino-silicate nanotubes (imogolite) with H2O2 and the azo-dye Acid Orange 7. Catal. Today 2016, 277, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, H.; Han, B.-G.; Lee, J.K.; Walian, P.; Jap, B.K. Structural basis of water-specific transport through the AQP1 water channel. Nature 2001, 414, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen-Tanugi, D.; Grossman, J.C. Water desalination across nanoporous graphene. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 3602–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Yoreo, J.J.; Gilbert, P.U.; Sommerdijk, N.A.; Penn, R.L.; Whitelam, S.; Joester, D.; Zhang, H.; Rimer, J.D.; Navrotsky, A.; Banfield, J.F. Crystallization by particle attachment in synthetic, biogenic, and geologic environments. Science 2015, 349, aaa6760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tunuguntla, R.H.; Henley, R.Y.; Yao, Y.-C.; Pham, T.A.; Wanunu, M.; Noy, A. Enhanced water permeability and tunable ion selectivity in subnanometer carbon nanotube porins. Science 2017, 357, 792–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’brien, F.J. Biomaterials & scaffolds for tissue engineering. Mater. Today 2011, 14, 88–95. [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa, K.; Abe, S.; Yawaka, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Watari, F. Osteoblastic cellular responses to aluminosilicate nanotubes, imogolite using Saos-2 and MC3T3-E1 cells. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2010, 118, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, K.; Akasaka, T.; Abe, S.; Yawaka, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Watari, F. Application of imogolite, almino-silicate nanotube, as scaffold for the mineralization of osteoblasts. Bioceram. Dev. Appl. 2011, 1, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, E.; Elliott, J.D.; Ratcliff, L.E.; Andrinopoulos, L.; Dziedzic, J.; Hine, N.D.M.; Mostofi, A.A.; Skylaris, C.-K.; Haynes, P.D.; Teobaldi, G. The potential of imogolite nanotubes as (co-)photocatalysts: A linear-scaling density functional theory study. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2016, 28, 074003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, J.D.; Poli, E.; Scivetti, I.; Ratcliff, L.E.; Andrinopoulos, L.; Dziedzic, J.; Hine, N.D.M.; Mostofi, A.A.; Skylaris, C.-K.; Haynes, P.D.; et al. Chemically Selective Alternatives to Photoferroelectrics for Polarization-Enhanced Photocatalysis: The Untapped Potential of Hybrid Inorganic Nanotubes. Adv. Sci. 2017, 4, 1600153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhavanasi, V.; Kusuma, D.Y.; Lee, P.S. Polarization Orientation, Piezoelectricity, and Energy Harvesting Performance of Ferroelectric PVDF-TrFE Nanotubes Synthesized by Nanoconfinement. Adv. Energy Mater. 2014, 4, 1400723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Shen, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, D.; Yang, G.; Gao, C.; Yang, Y. Silver-Modified Nanosized Ferroelectrics as a Novel Photocatalyst. Small 2015, 11, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Compound | Acronym | Strategy a | INT | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (3-aminopropyl)triethoxysilane | APTES | post. | Si | [71] |
| (aminomethyl)triethoxysilane | AMTES | direct | Si | [72] |
| Methyltrimethoxysilane | MTMS | post. | Si | [73] |
| direct | Si | [74] | ||
| Methyltriethoxysilane | MTES | direct | Si | [30,74,75,76,77,78] |
| Trichlorosilane | TCIS | post. | Si | [73] |
| Acethyl chloride | AcCl | post. | Si | [73] |
| Methyltriethoxygermane | MTEG | direct | Ge | [30,77] |
| Functional Group | Compound | Acronym | INT | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silane | (3-aminopropyl)triethoxysilane | APTES | Si | [71,76,79,80] |
| (3-chloropropyl)triethoxysilane | CTES | Si | [81] | |
| (3-mercaptopropyl)trimethoxysilane | MPTMS | Si | [82] | |
| Phosphonate | Octadecylphosphonic acid | ODPA | Si Ge | [83,84,85,86,87] [88] |
| Tetradecylphosphonic acid | TDPA | Si | [85] | |
| Vinylphosphonic acid | VPA | Si | [86] | |
| Dodecylphosphate | DDPO4 | Si | [89] | |
| 2-Acidphosphoxyethyl methacrylate | P-HEMA | Si | [90] | |
| Terthiophenes derivatives | HT3P HT3OP | Si | [91] | |
| 8-(2-bromo-2-methylpropanoyloxy)octylphosphate | BMPOPO4 | Si | [92] | |
| Carboxylate | Stearic acid | SA | Si | [84] |
| Dicarboxylic acid | DA | Si | [93,94] | |
| Sulfonate | Poly[disodium 2,5-bis(3-sulfonatopropoxy)-1,4-phenylene-alt-1,4-phenylene) | WS-PPP | Si | [95] |
| Others | 4-(hydroxyethylthioacetyl)catechol | HETAC | Si | [96] |
| Benzaldehyde | BA | Si | [97] | |
| Polypyrrole a | ppy | Si | [98,99] | |
| γ-ray irradiation (peroxides) | - | Si | [100,101] | |
| Isomorphic substitution (Al → Fe) | Fe-INT | Si Ge | [102,103,104,105,106] [107] |
| Type of Polymer | Acronym | Form | INT | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poly(vinyl alcohol) | PVA | Film | Si | [84,128,129,130,131] |
| Fiber | Si | [132] | ||
| Membrane | Si | [133,134,135] | ||
| Poly(methyl methacrylate) | PMMA | Film | Si | [90] |
| Poly(ε-caprolactone) | PCL | Film | Si | [96] |
| Hydrogel | Si | [97] | ||
| Poly(lactic acid) | PLA | Hydrogel | Si | [97] |
| Poly(butylene succinate) | PBS | Hydrogel | Si | [97] |
| Poly(acrylic acid) | PAA | Hydrogel a | Si | [100,101,136] |
| Hydrogel | Si | [137] | ||
| Poly(hydroxyethyl acrylate) | PHEA | Hydrogel | Si | [137] |
| Poly(vinyl chloride) | PVC | Film | Si | [138] |
| Polystyrene | PS | Film | Si | [139,140,141,142] |
| Polyamide | PA | Hydrogel | Si | [137,143,144] |
| Membrane | Si | [145,146,147] | ||
| Dicarboxilic acid | DA | Hydrogel | Si | [93,94,148,149] |
| Hydroxypropyl cellulose | HPC | Film | Si | [150] |
| Poly(hexylthiophene) | P3HT | Fiber | Si | [151] |
| Sugar alcohol | Isomalt | Fiber | Ge | [152] |
| Biopolymers | Hydrogel | Si | [153,154,155,156,157,158,159] | |
| Film | Ge | [160] |
© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paineau, E. Imogolite Nanotubes: A Flexible Nanoplatform with Multipurpose Applications. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1921. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8101921
Paineau E. Imogolite Nanotubes: A Flexible Nanoplatform with Multipurpose Applications. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(10):1921. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8101921
Chicago/Turabian StylePaineau, Erwan. 2018. "Imogolite Nanotubes: A Flexible Nanoplatform with Multipurpose Applications" Applied Sciences 8, no. 10: 1921. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8101921
APA StylePaineau, E. (2018). Imogolite Nanotubes: A Flexible Nanoplatform with Multipurpose Applications. Applied Sciences, 8(10), 1921. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8101921