Information-Bottleneck Decoding of High-Rate Irregular LDPC Codes for Optical Communication Using Message Alignment
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Instead of executing the conventional arithmetic exactly or approximated in the nodes with discrete values, the node operations are replaced by relevant-information-maximizing look-up tables which map discrete input messages onto discrete output messages. The required message mappings are designed using a relevant-information-preserving clustering technique, such as the information bottleneck method as shown in [10,11] or using similar algorithms [12,14].
- The relevant-information-maximizing look-up tables let messages that are log-likelihood ratios (LLRs) become obsolete. Instead, integer-valued pointers to look-up table entries, sometimes called cluster indices, are exchanged, which do not represent LLRs.
- We introduce a novel tree-like look-up pattern. With this strategy, the relation between the number of look-ups required per iteration and node degree changes from linear to logarithmic.
- We derive the underlying information-theoretic problem formulation and explain how the intermediate optimization technique called message alignment can be incorporated.
- We construct a 4-bit information bottleneck decoder for irregular LDPC codes with a code rate , where all conventional arithmetic in the nodes is replaced by simple look-up tables and only 4-bit integer-valued messages are passed.
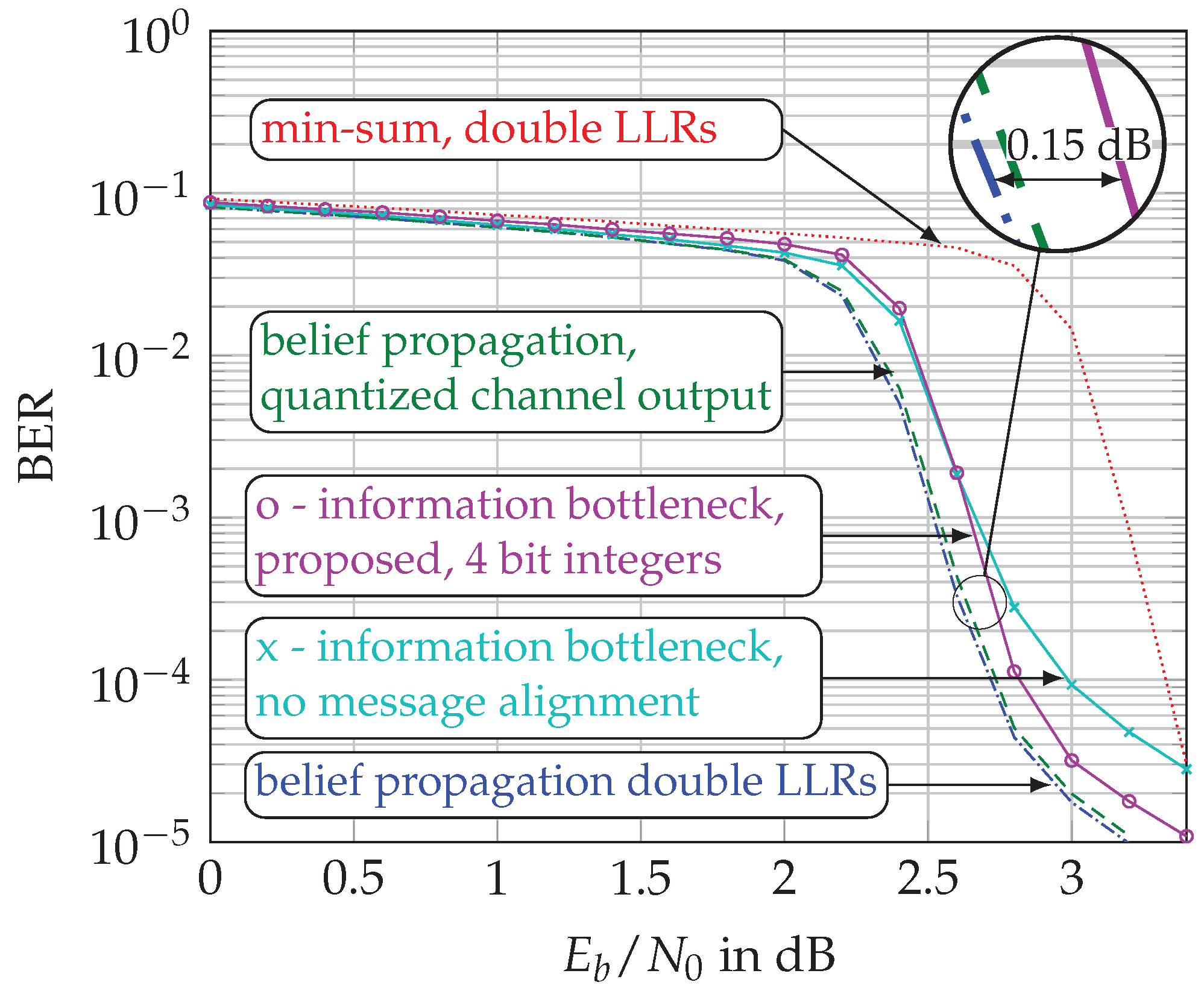
- Our proposed decoder achieves error-rates superior to min-sum decoding and only dB away from double-precision belief propagation decoding.
2. Prerequisites
2.1. Low-Density Parity-Check (LDPC) Codes
2.2. The Information Bottleneck Method
2.3. Information-Bottleneck Signal Processing and Information Bottleneck Graphs
3. Information Bottleneck Decoders for Irregular LDPC Codes Using Message Alignment
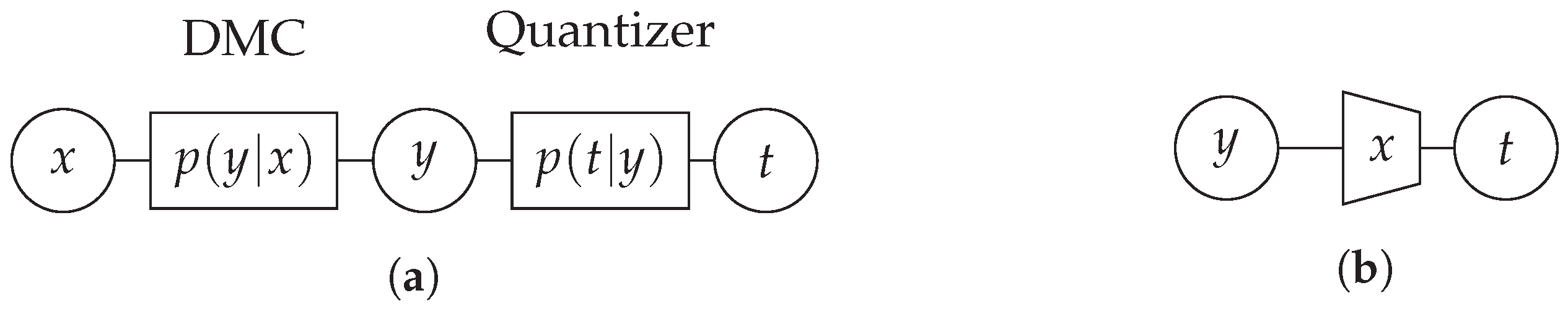
3.1. Information-Bottleneck Channel Quantizer for Arbitrary Discrete Memoryless Channels
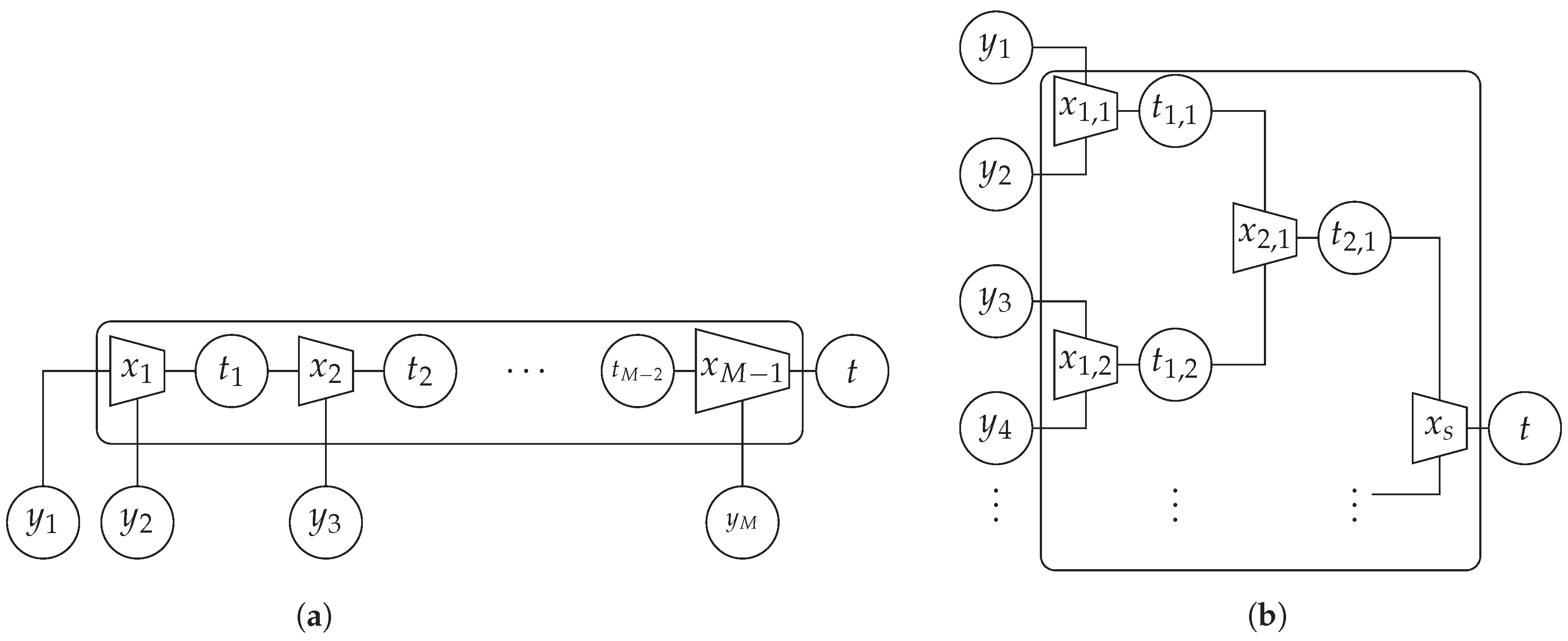
3.2. Information Bottleneck Decoders for Regular LDPC Codes
3.3. Relevant-Information-Preserving Clusterings for Arbitrary Irregular LDPC Codes
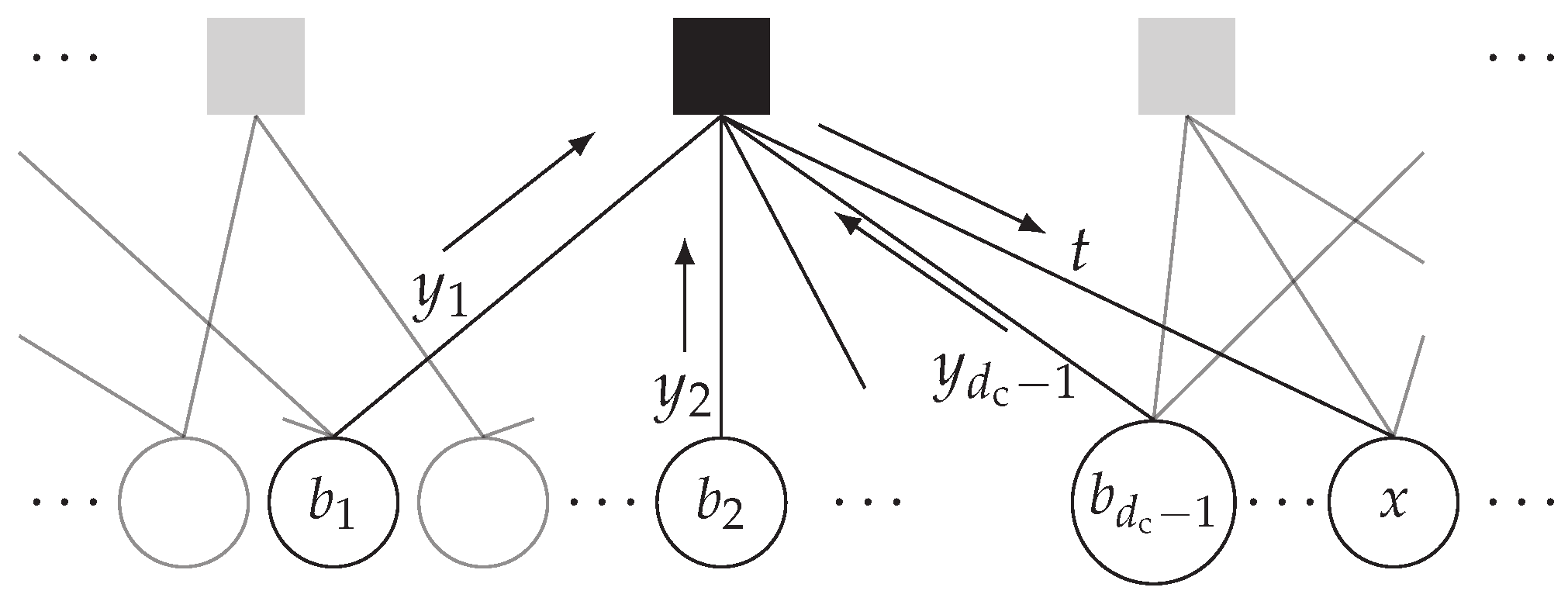
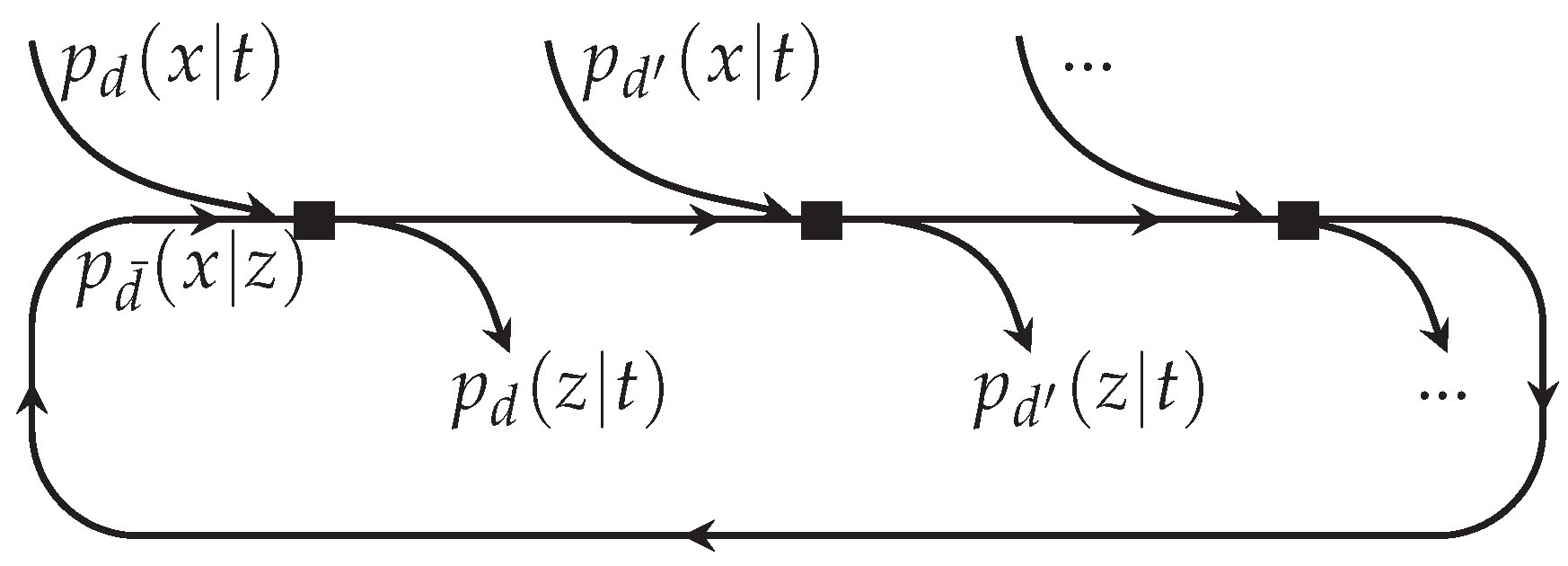
3.4. Message Alignment—A Graphical Perspective
3.5. Message Alignment—An Information-Theoretic Perspective
3.6. Message Alignment Algorithm
4. Optimizing the Node Structure
Reusing Intermediate Results
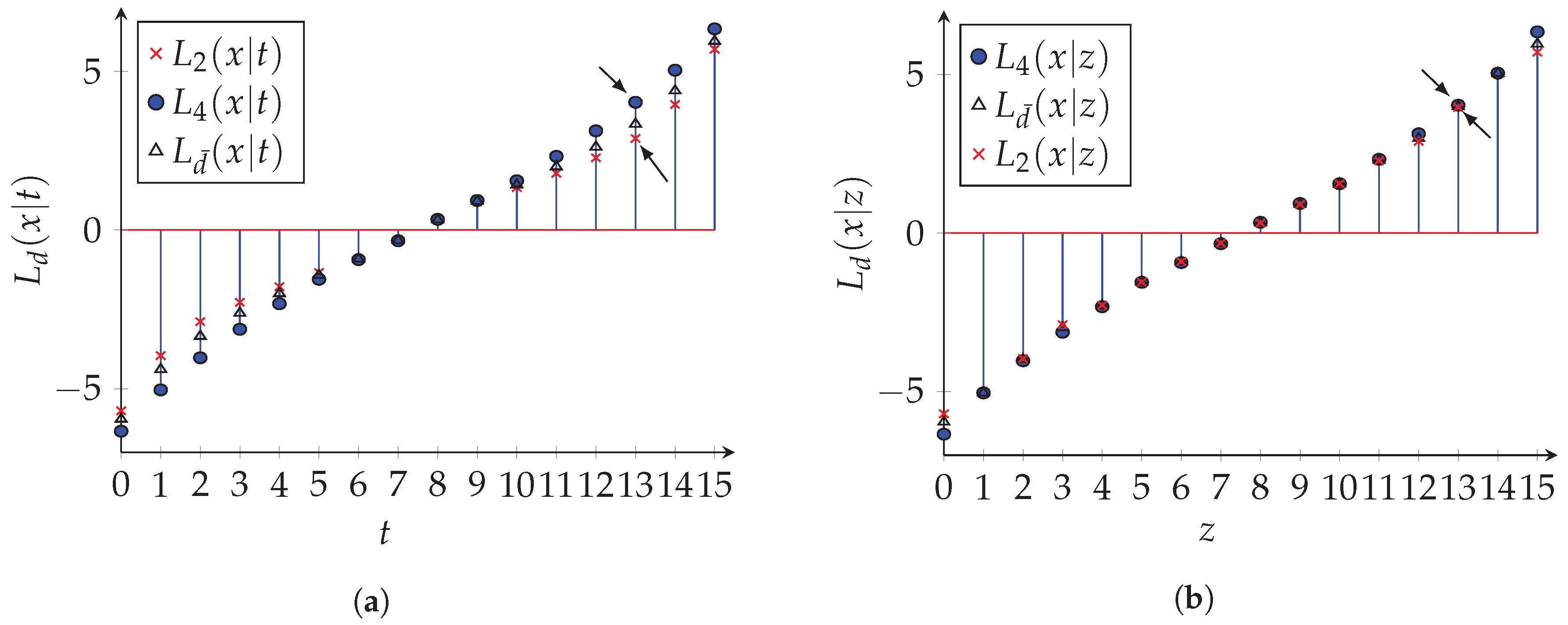
5. Investigation and Results
5.1. Code Properties
5.2. Memory Demand
5.3. Bit Error Rate (BER) Performance
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Derivation of the Depth of the Tree-Like Information Bottleneck Graph
Appendix A.1. Number of Look-Up Stages

References
- Chung, S.Y.; Forney, G.D.; Richardson, T.J.; Urbanke, R. On the design of low-density parity-check codes within 0.0045 dB of the Shannon limit. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2001, 5, 58–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.; Yu, F.; Xiao, Z.; Li, Y.; Stojanovic, N.; Xie, C.; Shi, X.; Xu, X.; Xiong, Q. FPGA Verification of a Single QC-LDPC Code for 100 Gb/s Optical Systems without Error Floor down to BER of 10−15. In Proceedings of the 2011 Optical Fiber Communication Conference/National Fiber Optic Engineers Conference, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 6–10 March 2011; OSA: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; p. OTuN2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koike-Akino, T.; Millar, D.S.; Kojima, K.; Parsons, K.; Miyata, Y.; Sugihara, K.; Matsumoto, W. Iteration-Aware LDPC Code Design for Low-Power Optical Communications. J. Lightw. Technol. 2016, 34, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmalen, L.; Suikat, D.; Rosener, D.; Aref, V.; Leven, A.; ten Brink, S. Spatially coupled codes and optical fiber communications: An ideal match? In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 16th International Workshop on Signal Processing Advances in Wireless Communications (SPAWC), Stockholm, Sweden, 28 June–1 July 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugihara, K.; Miyata, Y.; Sugihara, T.; Kubo, K.; Yoshida, H.; Matsumoto, W.; Mizuochi, T. A Spatially-coupled Type LDPC Code with an NCG of 12 dB for Optical Transmission beyond 100 Gb/s. In Proceedings of the 2013 Optical Fiber Communication Conference/National Fiber Optic Engineers Conference, Anaheim, CA, USA, 17–21 March 2013; OSA: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; p. OM2B.4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Ryan, W.E.; Li, Y. Design of Efficiently Encodable Moderate-Length High-Rate Irregular LDPC Codes. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2004, 52, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Xie, C. Enabling Technologies for High Spectral-Efficiency Coherent Optical Communication Networks; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Leven, A.; Schmalen, L. Status and Recent Advances on Forward Error Correction Technologies for Lightwave Systems. J. Lightw. Technol. 2014, 32, 2735–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meidlinger, M.; Matz, G. On irregular LDPC codes with quantized message passing decoding. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 18th International Workshop on Signal Processing Advances in Wireless Communications (SPAWC’17), Sapporo, Japan, 3–6 July 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Lewandowsky, J.; Bauch, G. Information-Optimum LDPC Decoders Based on the Information Bottleneck Method. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 4054–4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowsky, J.; Stark, M.; Bauch, G. Optimum message mapping LDPC decoders derived from the sum-product algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC’16), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 22–27 May 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Romero, F.J.C.; Kurkoski, B.M. LDPC decoding mappings that maximize mutual information. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2016, 34, 2391–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurkoski, B.M.; Yamaguchi, K.; Kobayashi, K. Noise thresholds for discrete LDPC decoding mappings. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Global Communications Conference, New Orleans, LO, USA, 30 November–4 December 2008; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Meidlinger, M.; Balatsoukas-Stimming, A.; Burg, A.; Matz, G. Quantized message passing for LDPC codes. In Proceedings of the 2015 49th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 8–11 November 2015; pp. 1606–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauch, G.; Lewandowsky, J.; Stark, M.; Oppermann, P. Information-Optimum Discrete Signal Processing for Detection and Decoding. In Proceedings of the IEEE 87th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC-Spring’18), Porto, Portugal, 3–6 June 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ghanaatian, R.; Balatsoukas-Stimming, A.; Muller, T.C.; Meidlinger, M.; Matz, G.; Teman, A.; Burg, A. A 588-Gb/s LDPC Decoder Based on Finite-Alphabet Message Passing. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2018, 26, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, M.; Lewandowsky, J.; Bauch, G. Information-Optimum LDPC Decoders with Message Alignment for Irregular Codes. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Global Communications Conference: Signal Processing for Communications (Globecom2018 SPC), Abu Dhabi, UAE, 9–13 December 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lewandowsky, J.; Stark, M.; Bauch, G. Message Alignment for Discrete LDPC Decoders with Quadrature Amplitude Modulation. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory, Aachen, Germany, 25–30 June 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 2925–2929. [Google Scholar]
- Stark, M.; Lewandowsky, J.; Bauch, G. Iterative Message Alignment for Quantized Message Passing between Distributed Sensor Nodes. In Proceedings of the IEEE 87th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC-Spring’18), Porto, Portugal, 3–6 June 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, W.; Lin, S. Channel Codes: Classical and Modern; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Tishby, N.; Pereira, F.C.; Bialek, W. The information bottleneck method. In Proceedings of the 37th Allerton Conference on Communication and Computation, Monticello, IL, USA, 22–24 September 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Slonim, N. The Information Bottleneck: Theory and Applications. Ph.D. Thesis, Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Jerusalem, Israel, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hassanpour, S.; Wuebben, D.; Dekorsy, A. Overview and Investigation of Algorithms for the Information Bottleneck Method. In Proceedings of the 11th International ITG Conference on Systems, Communications and Coding, Hamburg, Germany, 6–9 February 2017; VDE: Frankfurt am Main, Germany, 2017; Volume 268. [Google Scholar]
- Stark, M.; Shah, S.A.A.; Bauch, G. Polar Code Construction using the Information Bottleneck Method. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference Workshops (WCNCW): Polar Coding for Future Networks: Theory and Practice (IEEE WCNCW PCFN 2018), Barcelona, Spain, 15–18 April 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kern, D.; Kuehn, V. On Compress and Forward with Multiple Carriers in the 3-Node Relay Channel Exploiting Information Bottleneck Graphs. In Proceedings of the 11th International ITG Conference on Systems, Communications and Coding, Hamburg, Germany, 6–9 February 2017; VDE: Frankfurt am Main, Germany, 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Kuehn, V. Alternating information bottleneck optimization for the compression in the uplink of C-RAN. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 23–27 May 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowsky, J.; Stark, M.; Bauch, G. Information Bottleneck Graphs for receiver design. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory, Barcelona, Spain, 10–15 July 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 2888–2892. [Google Scholar]
- Kschischang, F.R.; Frey, B.J.; Loeliger, H.A. Factor graphs and the sum-product algorithm. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2001, 47, 498–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minka, T. Divergence Measures and Message Passing; Technical Report; Microsoft Research: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]

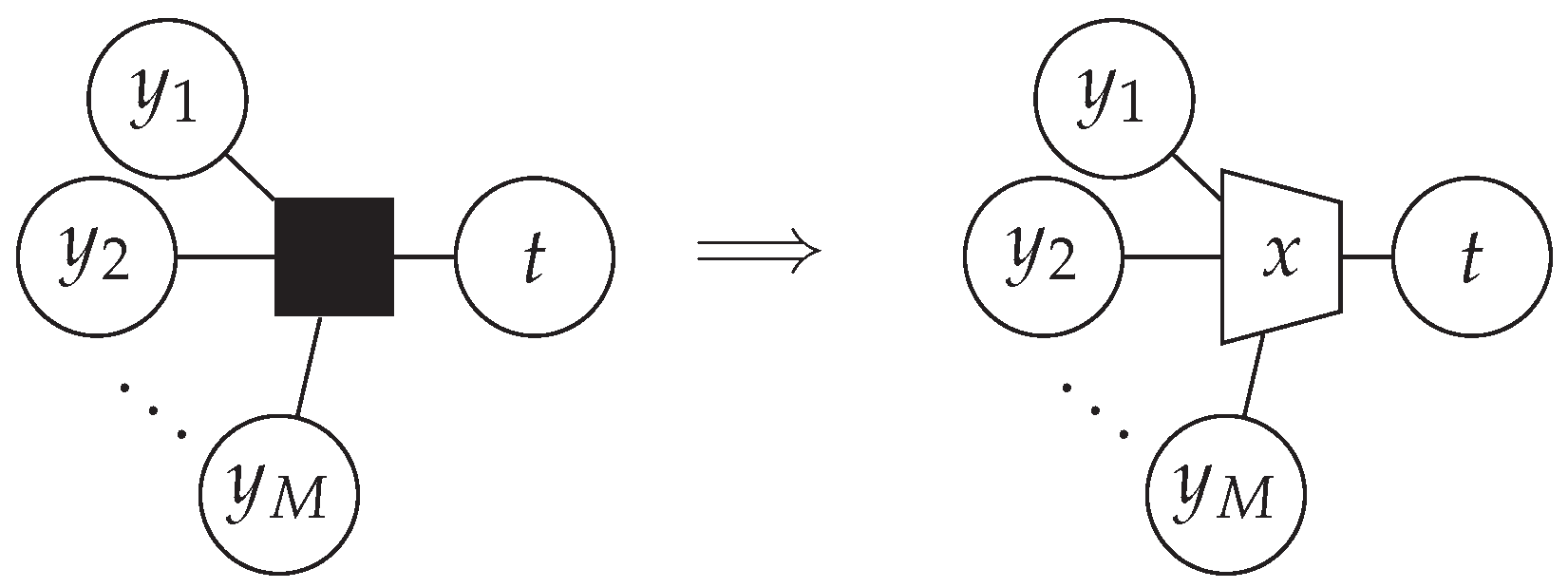
| Node Structure | Entries per Table | Look-Up Tables | Total Memory Demand |
|---|---|---|---|
| direct | 1 | ||
| sequential propagation | |||
| proposed (tree-like) |
| Node Degree | Direct | Sequential | Proposed (Tree-Like) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entries | Look-Ups | Entries | Look-Ups | Entries | Look-Ups | |
| 4096 | 2 | 512 | 3 | 512 | 3 | |
| 3 | 768 | 7 | 512 | 6 | ||
| 12 | 3072 | 88 | 1280 | 33 | ||
| 22 | 5376 | 250 | 1536 | 70 | ||
| 23 | 5632 | 273 | 1536 | 92 | ||
| Total per Iteration | 62 | 621 | 5376 | 204 | ||
| Total for | 3100 | 31,050 | 10,200 | |||
| Memory for in kByte | - | 384 | - | - | ||
| Decoder | Node | Messages | Messages | Message |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Operations | (Internal) | (Channel) | Alignment | |
| belief propagation | arithmetic | 64 bit | 64 bit | - |
| belief propagation, quantized channel output | arithmetic | 64 bit | 4 bit | - |
| min-sum | approx. arithmetic | 64 bit | 64 bit | - |
| information-bottleneck decoder [10] | look-up Table | 4 bit | 4 bit | no |
| proposed | look-up table | 4 bit | 4 bit | yes |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stark, M.; Lewandowsky, J.; Bauch, G. Information-Bottleneck Decoding of High-Rate Irregular LDPC Codes for Optical Communication Using Message Alignment. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1884. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8101884
Stark M, Lewandowsky J, Bauch G. Information-Bottleneck Decoding of High-Rate Irregular LDPC Codes for Optical Communication Using Message Alignment. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(10):1884. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8101884
Chicago/Turabian StyleStark, Maximilian, Jan Lewandowsky, and Gerhard Bauch. 2018. "Information-Bottleneck Decoding of High-Rate Irregular LDPC Codes for Optical Communication Using Message Alignment" Applied Sciences 8, no. 10: 1884. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8101884
APA StyleStark, M., Lewandowsky, J., & Bauch, G. (2018). Information-Bottleneck Decoding of High-Rate Irregular LDPC Codes for Optical Communication Using Message Alignment. Applied Sciences, 8(10), 1884. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8101884






