GARLM: Greedy Autocorrelation Retrieval Levenberg–Marquardt Algorithm for Improving Sparse Phase Retrieval
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Problem Formulation
3. Greedy Autocorrelation Retrieval Levenberg–Marquardt Algorithm
3.1. The Improved Levenberg–Marquardt Method
| Algorithm 1. ILM Algorithm. |
| Input: Symmetric matrices , and measurement , the given indices set , the maximum number of iterations , and the stopping threshold . Output: The optimal estimate of sparse signal x of (5).
|
3.2. 2-Opt Method of the Support Information
| Algorithm 2. 2-Opt Algorithm. |
| Input: Symmetric matrices , the measurement , the stopping threshold , and the maximum number of index exchanging T. Output: The optimal estimate of sparse signal for Formulation (5).
|
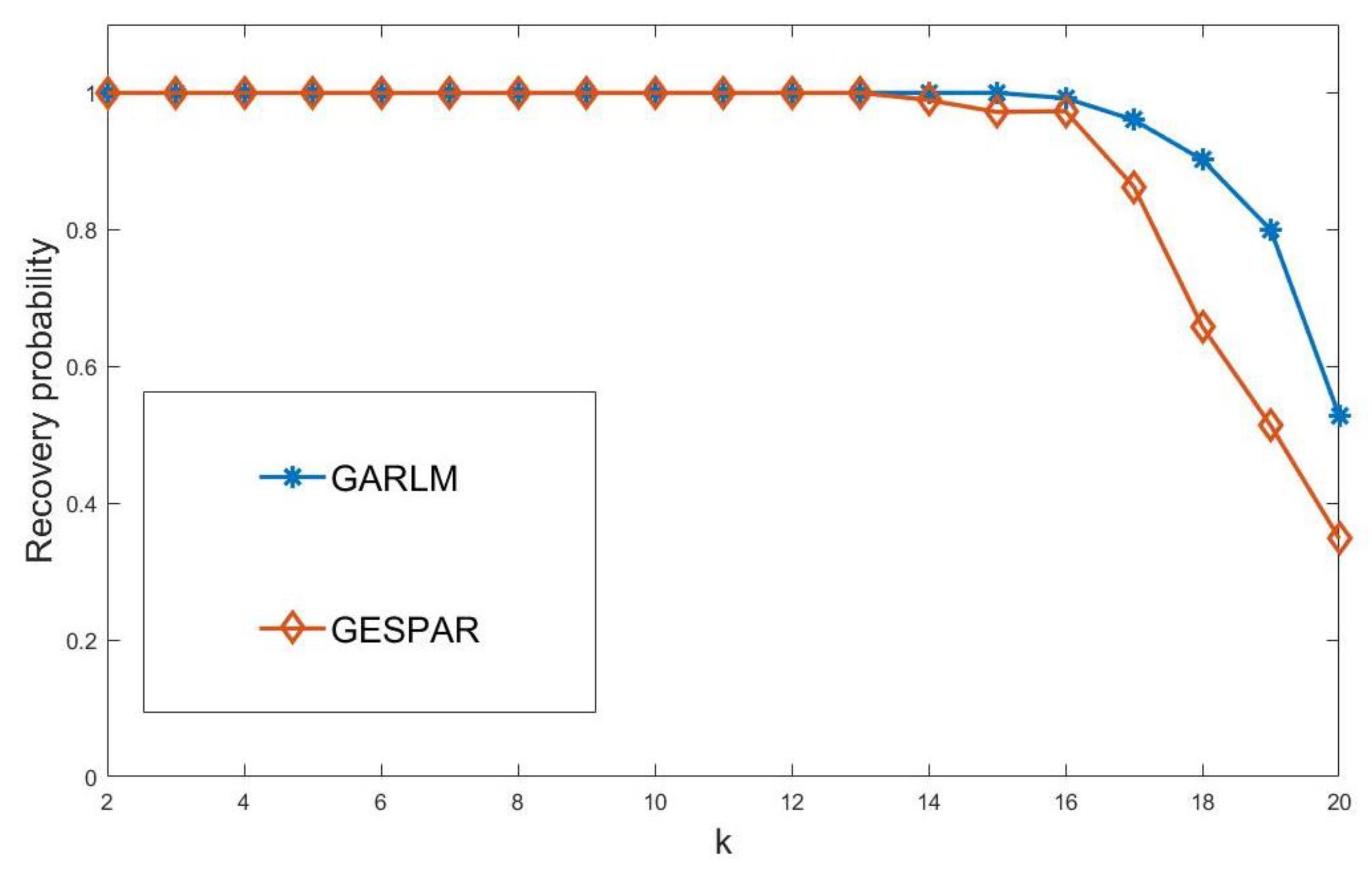
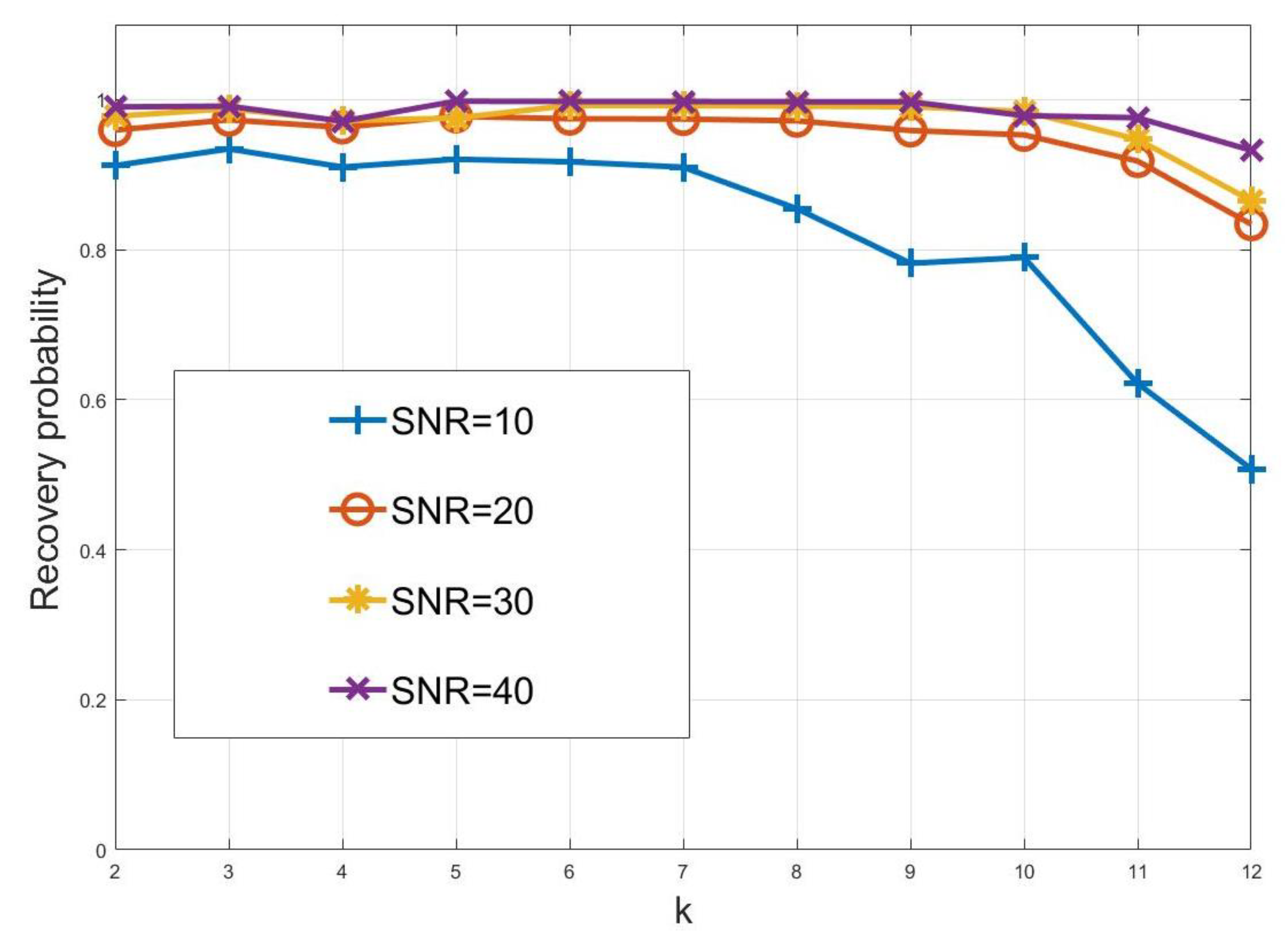
4. Simulation Results and Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Donnell, R. Sampling—50 Years After Shannon. Proc. IEEE 2000, 88, 567–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldar, Y.C.; Werther, T. General Framework for Consistent Sampling in Hilbert Spaces. Int. J. Wavel. Multiresolut. Inf. Process. 2005, 3, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldar, Y.C. Sampling and reconstruction in arbitrary spaces and oblique dual frame vectors. J. Fourier Anal. Appl. 2003, 1, 77–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorkind, T.G.; Eldar, Y.C.; Matusiak, E. Nonlinear and nonideal sampling: Theory and methods. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2008, 56, 5874–5890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldar, Y.C.; Unser, M. Nonideal sampling and interpolation from noisy observations in shift-invariant spaces. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2006, 54, 2636–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dardari, D.; Pasolini, G.; Zabini, F. An efficient method for physical fields mapping through crowdsensing. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 2018, 48, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reise, G.; Matz, G.; Gröchenig, K. Distributed field reconstruction in wireless sensor networks based on hybrid shift-invariant spaces. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2012, 60, 5426–5439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masry, E. Random sampling of deterministic signals: Statistical analysis of Fourier transform estimates. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2006, 54, 1750–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarczynski, A.; Allay, N. Spectral analysis of randomly sampled signals: Suppression of aliasing and sampler jitter. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2004, 52, 3324–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marvasti, F.A. Signal Recovery from Nonuniform Samples and Spectral Analysis on Random Nonuniform Samples. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Tokyo, Japan, 7–11 April 1986; Volume 11, pp. 1649–1652. [Google Scholar]
- Zabini, F.; Conti, A. Process estimation from randomly deployed wireless sensors with position uncertainty. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Global Telecommunications Conference (GLOBECOM), Kathmandu, Nepal, 5–9 December 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zabini, F.; Conti, A. Inhomogeneous Poisson Sampling of Finite-Energy Signals with Uncertainties in Rd. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2016, 64, 4679–4694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dardari, D.; Conti, A.; Buratti, C.; Verdone, R. Mathematical evaluation of environmental monitoring estimation error through energy-efficient wireless sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2007, 6, 790–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabini, F.; Conti, A. Ginibre sampling and signal reconstruction. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory (ISIT), Barcelona, Spain, 10–15 July 2016; pp. 865–869. [Google Scholar]
- Zabini, F.; Pasolini, G.; Conti, A. On random sampling with nodes attraction: The case of Gauss-Poisson process. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory (ISIT), Aachen, Germany, 25–30 June 2017; pp. 2278–2282. [Google Scholar]
- Särkkä, S.; Solin, A.; Hartikainen, J. Spatio-Temporal Learning via Infinite-Dimensional Bayesian Filtering and Smoothing. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2013, 30, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Choi, J. Spatial prediction with mobile sensor networks using Gaussian processes with built-in Gaussian Markov random fields. Automatica 2012, 48, 1735–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, A.; Singh, A.; Guestrin, C. Near-Optimal Sensor Placements in Gaussian Processes: Theory, Efficient Algorithms and Empirical Studies. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2008, 9, 235–284. [Google Scholar]
- Krause, A.; Guestrin, C. Nonmyopic active learning of Gaussian processes: An exploration-exploitation approach. In Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Corvalis, OR, USA, 20–24 June 2007; pp. 449–456. [Google Scholar]
- Hurt, N.E. Phase Retrieval and Zero Crossings: Mathematical Methods in Image Reconstruction; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2001; Volume 52. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, R.W. Phase problem in crystallography. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1993, 10, 1046–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, A. The Question of Phase Retrieval in Optics. Opt. Acta Int. J. Opt. 1963, 10, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, L.K.; Rigling, B.D. Phase retrieval for radar waveform optimization. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2012, 48, 3287–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Roux, J.; Vincent, E. Consistent Wiener Filtering for Audio Source Separation. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2013, 20, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.; Ishikawa, T.; Johnson, B.; Anderson, E.H.; Lai, B.; Hodgson, K.O. High resolution 3D X-ray diffraction microscopy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 89, 088303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturmel, N.; Daudet, L. Signal reconstruction from STFT magnitude: A state of the art. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Digital Audio Effects (DAFx’11), Paris, France, 19–23 September 2011; Volume 2012, pp. 375–386. [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson, H.; Eldar, Y.C. On conditions for uniqueness in sparse phase retrieval. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Florence, Italy, 4–9 May 2014; pp. 1841–1845. [Google Scholar]
- Jaganathan, K.; Oymak, S.; Hassibi, B. Recovery of sparse 1-D signals from the magnitudes of their Fourier transform. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory, Cambridge, MA, USA, 1–6 July 2012; pp. 1473–1477. [Google Scholar]
- Eldar, Y.C.; Mendelson, S. Phase retrieval: Stability and recovery guarantees. Appl. Comput. Harmon. Anal. 2014, 36, 473–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.M.; Vetterli, M. Sparse spectral factorization: Unicity and reconstruction algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Prague, Czech Republic, 22–27 May 2011; pp. 5976–5979. [Google Scholar]
- Fienup, J.R.R. Phase retrieval algorithms: A comparison. Appl. Opt. 1982, 21, 2758–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerchberg, R.W.; Saxton, W.O. A practical algorithm for the determination of phase from image and diffraction plane pictures. Optik 1972, 35, 237–246. [Google Scholar]
- Bauschke, H.H.; Combettes, P.L.; Luke, D.R. Phase retrieval, error reduction algorithm, and Fienup variants: A view from convex optimization. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A Opt. Image Sci. Vis. 2002, 19, 1334–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shechtman, Y.; Eldar, Y.C.; Szameit, A.; Segev, M. Sparsity based sub-wavelength imaging with partially incoherent light via quadratic compressed sensing. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 14807–14822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candes, E.J.; Eldar, Y.C.; Strohmer, T.; Voroninski, V. Phase retrieval via matrix completion. SIAM Rev. 2015, 57, 225–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candès, E.J.; Strohmer, T.; Voroninski, V. PhaseLift: Exact and stable signal recovery from magnitude measurements via convex programming. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 2013, 66, 1241–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, J.; Tang, X.; Mo, Q. A Sharp Condition for Exact Support Recovery with Orthogonal Matching Pursuit. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2017, 65, 1370–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Li, D.; Zhu, F. Stable recovery of sparse signals via lp-minimization. Appl. Comput. Harmon. Anal. 2015, 38, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Zhou, B.; Mow, W.H.; Chang, X. An Efficient Algorithm for Optimally Solving a Shortest Vector Problem in Compute-and-Forward Design. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2016, 15, 6541–6555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Chang, X. Success Probability of the Babai Estimators for Box-Constrained Integer Linear Models. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2017, 63, 631–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Fan, S.; Yang, J.; Xiong, J.; Cheng, X.; Sari, H.; Adachi, F.; Gui, G. Sparse adaptive iteratively-weighted thresholding algorithm (SAITA) for Lp-regularization using the multiple sub-dictionary representation. Sensors 2017, 17, 2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Lin, Y.; Cheng, X.; Xiao, Z.; Shu, F.; Gui, G. Nonconvex Penalized Regularization for Robust Sparse Recovery in the Presence of SαS Noise. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 25474–25485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fan, S.; Yang, J.; Xiong, J.; Cheng, X.; Gui, G.; Sari, H. MUSAI-L1/2: MUltiple Sub-Wavelet-Dictionaries-Based Adaptively-Weighted Iterative Half Thresholding Algorithm for Compressive Imaging. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 16795–16805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shechtman, Y.; Beck, A.; Eldar, Y.C. GESPAR: Efficient phase retrieval of sparse signals. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2014, 62, 928–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourakis, M.I.A. A Brief Description of the Levenberg-Marquardt Algorithm Implemened by levmar. Found. Res. Technol. 2005, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Steihaug, T. The Conjugate Gradient Method and Trust Regions in Large Scale Optimization. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 1983, 20, 626–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhao, D.; Gui, G. GARLM: Greedy Autocorrelation Retrieval Levenberg–Marquardt Algorithm for Improving Sparse Phase Retrieval. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1797. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8101797
Xiao Z, Zhang Y, Zhang K, Zhao D, Gui G. GARLM: Greedy Autocorrelation Retrieval Levenberg–Marquardt Algorithm for Improving Sparse Phase Retrieval. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(10):1797. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8101797
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Zhuolei, Yerong Zhang, Kaixuan Zhang, Dongxu Zhao, and Guan Gui. 2018. "GARLM: Greedy Autocorrelation Retrieval Levenberg–Marquardt Algorithm for Improving Sparse Phase Retrieval" Applied Sciences 8, no. 10: 1797. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8101797
APA StyleXiao, Z., Zhang, Y., Zhang, K., Zhao, D., & Gui, G. (2018). GARLM: Greedy Autocorrelation Retrieval Levenberg–Marquardt Algorithm for Improving Sparse Phase Retrieval. Applied Sciences, 8(10), 1797. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8101797





