A Game Player Expertise Level Classification System Using Electroencephalography (EEG)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- EEG-based data are recorded from multiple participants during the play of a mobile game to automatically classify the player as expert or novice on the basis of brain activity.
- Those significant brain areas are highlighted and selected as being affected during the game play after a careful statistical analysis.
- Thirteen morphological features are extracted in the time domain for classification purposes.
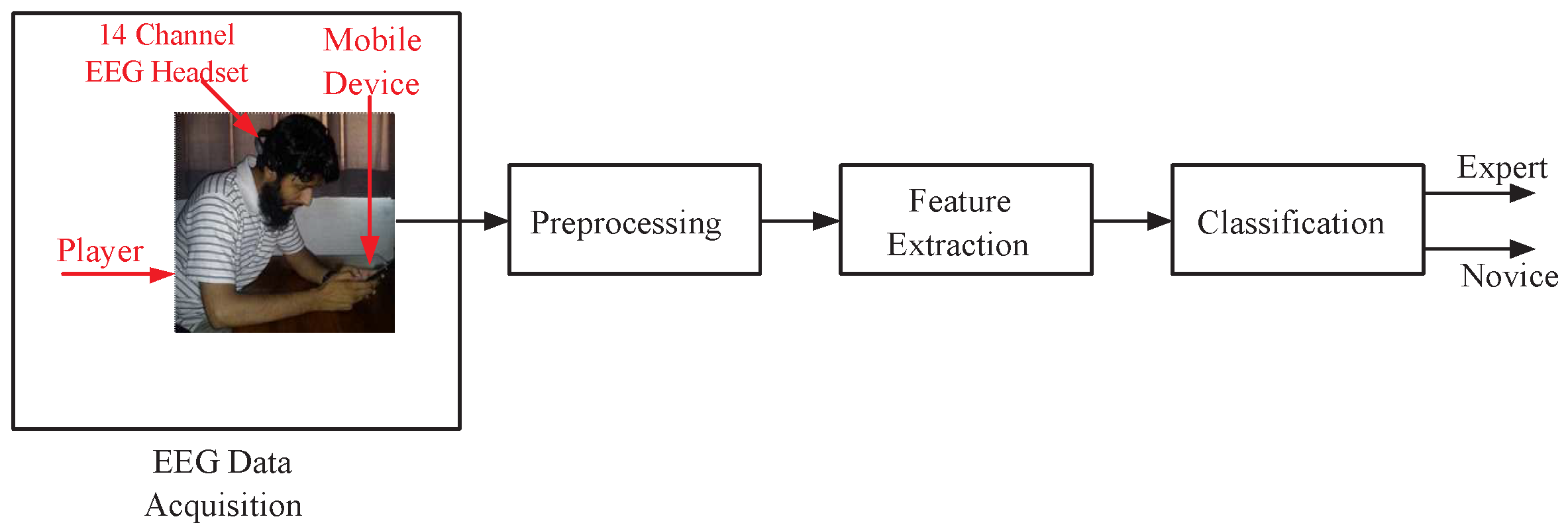
2. Proposed Methodology
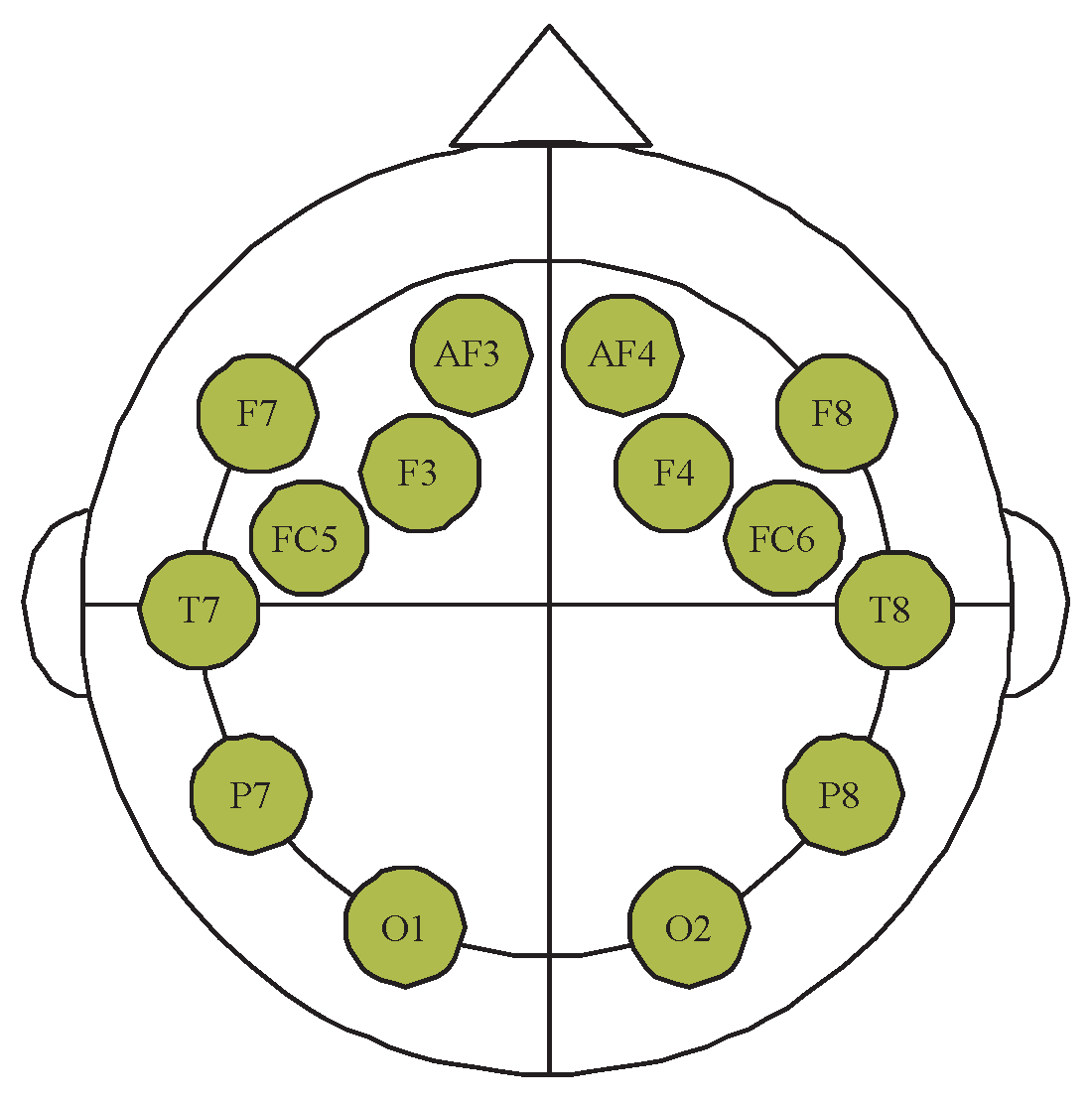
2.1. EEG Data Acquisition
2.1.1. Stimuli
2.1.2. Participants
2.1.3. Apparatus
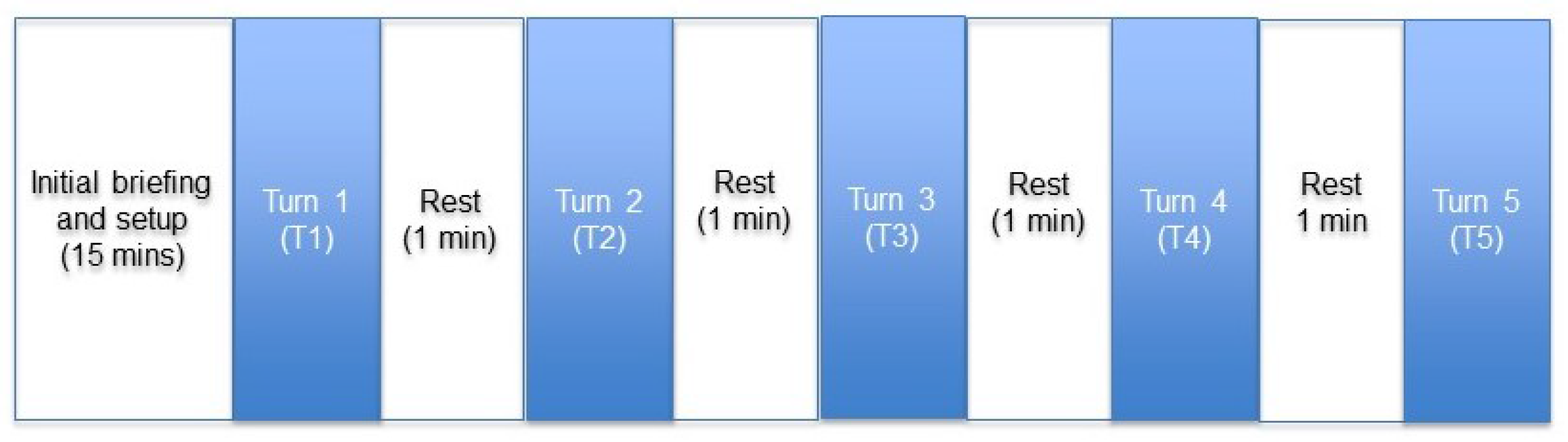
2.1.4. Procedure
2.2. Preprocessing
2.3. Feature Extraction
- Maximum value ():
- Maximum value time ():where is the signal maximum value.
- Minimum value ():
- Minimum value time ():where is the signal minimum value.
- Maximum absolute value ():
- Peak to peak signal value ():
- Latency to maximum value ratio ():
- Latency to minimum value ratio ():
- Peak to peak time window ():
- Sum of values (S):where the summation is performed over a period of time.
- Mean ():where N is the total number of samples.
- Signal power (P):where T is the time period.
- Signal energy (E):
2.4. Classification
2.4.1. Support Vector Machine
2.4.2. Naive Bayes Classifier
2.4.3. Multilayer Perceptron
3. Experimental Results
3.1. Configuration and Parameter Settings
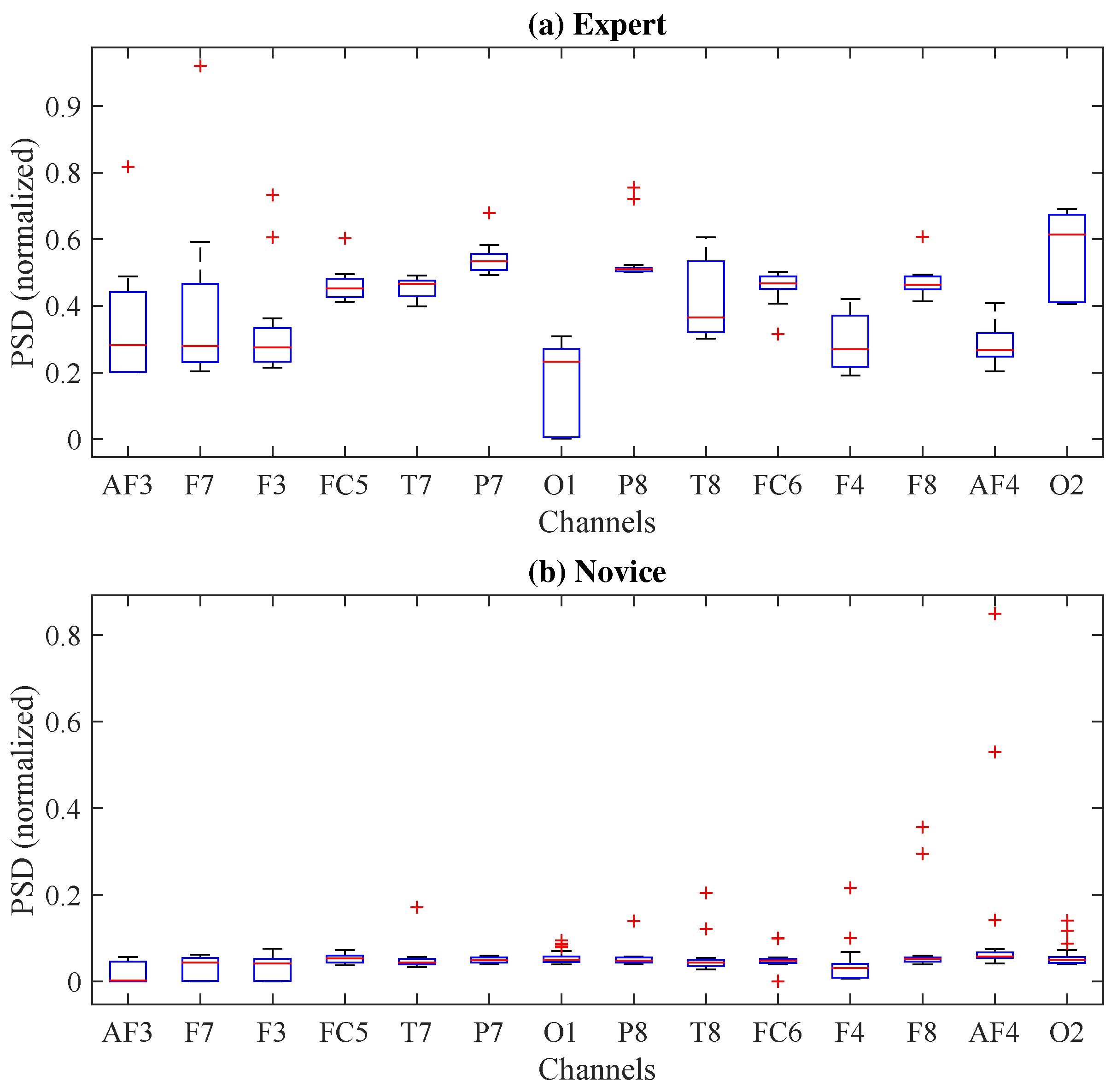
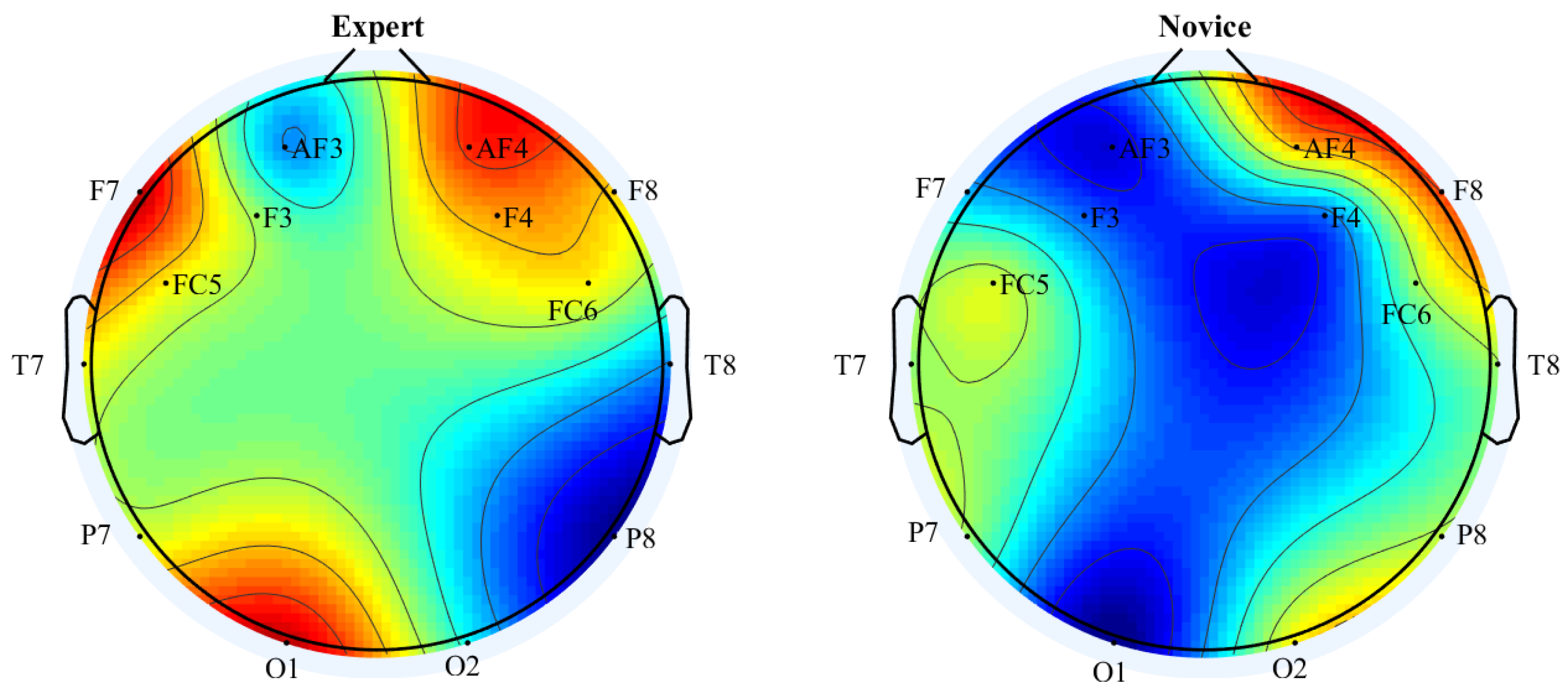
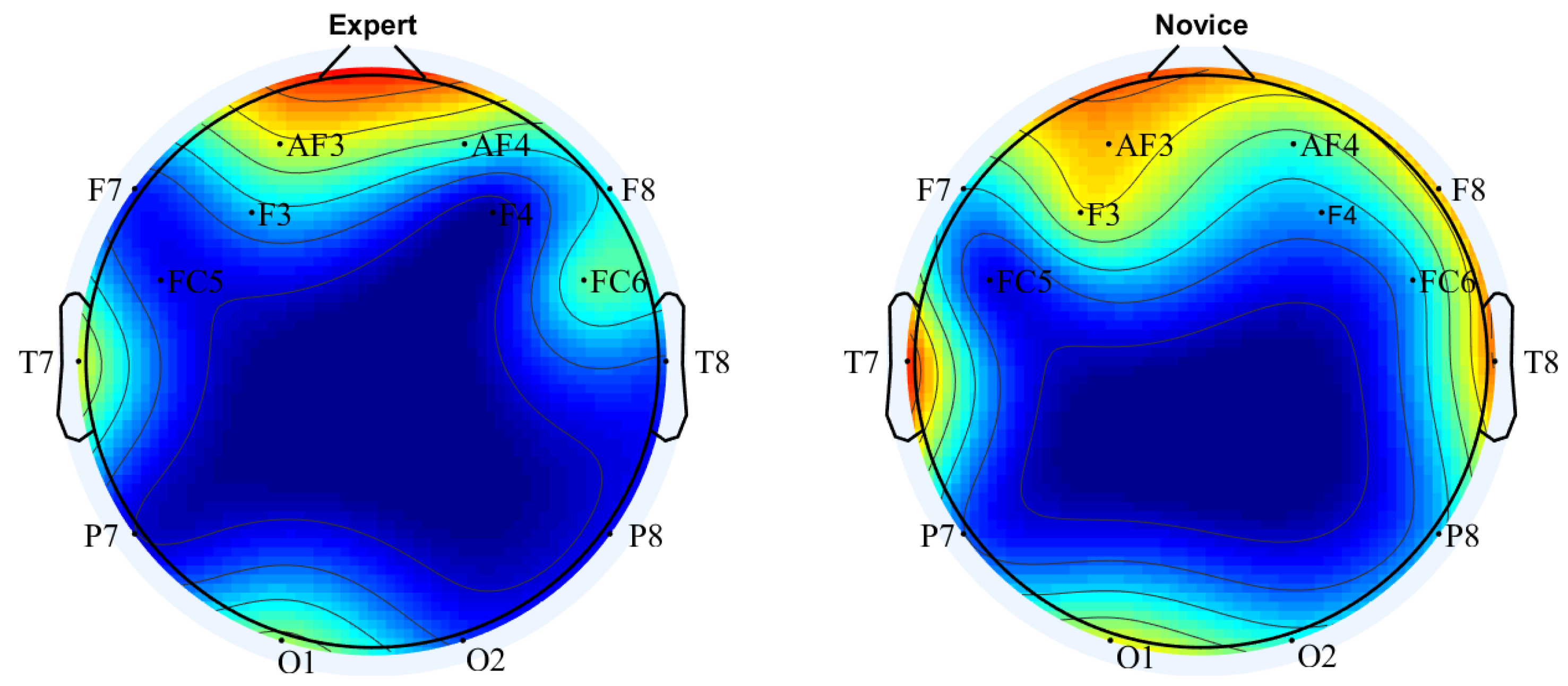
3.2. Channel Selection
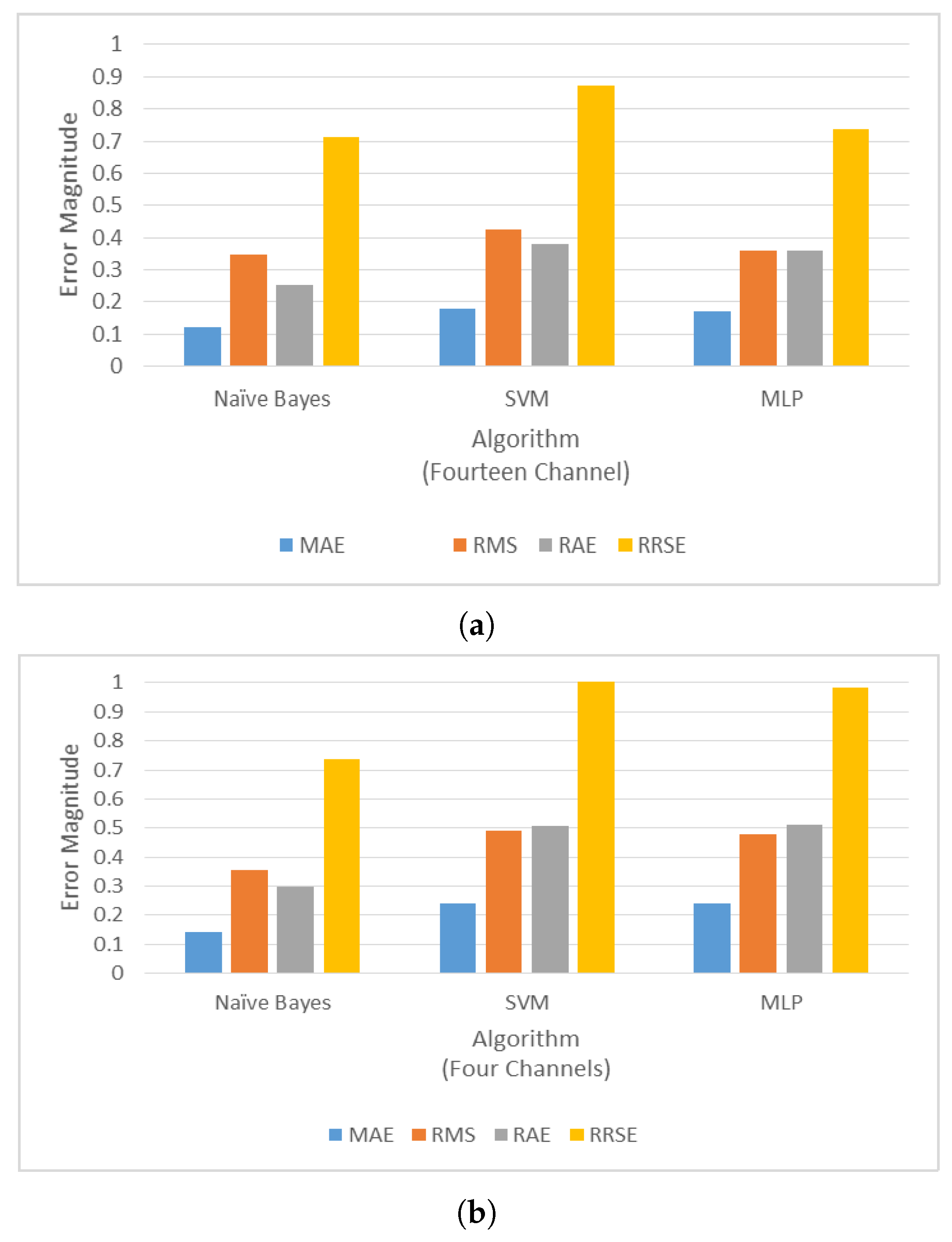
3.3. Performance Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Foehr, U.G.; Rideout, V.; Roberts, D.F. Generation M: Media in the Lives of 8–18 Year-Olds. 2005. Available online: https://kaiserfamilyfoundation.files.wordpress.com/2013/01/generation-m-media-in-the-lives-of-8-18-year-olds-report.pdf (accessed on 30 October 2017).
- Sourina, O.; Wortley, D.; Kim, S. Subconscious Learning via Games and Social Media; Springer: Singapore, Singapore, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cain, M.S.; Landau, A.N.; Shimamura, A.P. Action video game experience reduces the cost of switching tasks. Atten. Percept. Psychophys. 2012, 74, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irons, J.L.; Remington, R.W.; McLean, J.P. Not so fast: Rethinking the effects of action video games on attentional capacity. Aust. J. Psychol. 2011, 63, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhishek, A.M.; Suma, H. Stress analysis of a computer game player using electroencephalogram. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Circuits, Communication, Control and Computing (I4C), Bangalore, India, 21–22 November 2014; pp. 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.H.; Tzeng, Y.L.; Huang, Y.M. Understanding the relationship between physiological signals and digital game-based learning outcome. J. Comput. Educ. 2014, 1, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anguera, J.A.; Boccanfuso, J.; Rintoul, J.L.; Al-Hashimi, O.; Faraji, F.; Janowich, J.; Kong, E.; Larraburo, Y.; Rolle, C.; Johnston, E.; et al. Video game training enhances cognitive control in older adults. Nature 2013, 501, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hisham, S.; Rahman, A.W.A. Lesson Learnt from an EEG-Based Experiment with ADHD Children in Malaysia. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Universal Access in Human-Computer Interaction, Toronto, ON, Canada, 17–22 July 2016; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2016; pp. 73–81. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, K.P.; Vinod, A.; Guan, C. Enhancement of attention and cognitive skills using EEG based neurofeedback game. In Proceedings of the 2013 6th IEEE International IEEE/EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering (NER), San Diego, CA, USA, 6–8 November 2013; pp. 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Jiang, Q.; Tan, C.H.; Wei, K.K. Enhancing user-game engagement through software gaming elements. J. Manag. Inf. Syst. 2014, 30, 115–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijholt, A.; Bos, D.P.O.; Reuderink, B. Turning shortcomings into challenges: Brain–computer interfaces for games. Entertain. Comput. 2009, 1, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, S. U.S. Consumers Now Spend 5 Hours Per Day on Mobile Devices. 2017. Available online: https://techcrunch.com/2017/03/03/u-s-consumers-now-spend-5-hours-per-day-on-mobile-devices/ (accessed on 30 October 2017).
- Van de Laar, B.; Gürkök, H.; Bos, D.P.O.; Poel, M.; Nijholt, A. Experiencing BCI control in a popular computer game. IEEE Trans. Comput. Intell. AI Games 2013, 5, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, M.; Ravaja, N. Oscillatory brain responses evoked by video game events: The case of Super Monkey Ball 2. CyberPsychol. Behav. 2007, 10, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheikholeslami, C.; Yuan, H.; He, E.J.; Bai, X.; Yang, L.; He, B. A high resolution EEG study of dynamic brain activity during video game play. In Proceedings of the 29th IEEE EMBS 2007 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Lyon, France, 23–26 August 2007; pp. 2489–2491. [Google Scholar]
- Saeed, S.M.; Anwar, S.M.; Majid, M. Quantification of Human Stress using Commercially Available Single Channel EEG Headset. IEICE Trans. Inf. Syst. 2017, E100D. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nacke, L. Affective Ludology: Scientific Measurement of User Experience in Interactive Entertainment. Ph.D. Thesis, Blekinge Institute of Technology, Karlskrona, Sweden, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wolpaw, J.R.; Birbaumer, N.; Heetderks, W.J.; McFarland, D.J.; Peckham, P.H.; Schalk, G.; Donchin, E.; Quatrano, L.A.; Robinson, C.J.; Vaughan, T.M.; et al. Brain-computer interface technology: A review of the first international meeting. IEEE Trans. Rehabil. Eng. 2000, 8, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derbali, L.; Frasson, C. Prediction of players motivational states using electrophysiological measures during serious game play. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE 10th International Conference on Advanced Learning Technologies (ICALT), Sousse, Tunisia, 5–7 July 2010; pp. 498–502. [Google Scholar]
- Loh, C.S.; Sheng, Y.; Li, I.H. Predicting expert–novice performance as serious games analytics with objective-oriented and navigational action sequences. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2015, 49, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahan, T.; Parberry, I.; Parsons, T.D. Modality specific assessment of video game player’s experience using the Emotiv. Entertain. Comput. 2015, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, S.M.; Saeed, S.M.U.; Majid, M. Classification of Expert-Novice Level of Mobile Game Players Using Electroencephalography. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on IEEE Frontiers of Information Technology (FIT), Islamabad, Pakistan, 19–21 December 2016; pp. 315–318. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatti, A.M.; Majid, M.; Anwar, S.M.; Khan, B. Human emotion recognition and analysis in response to audio music using brain signals. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 65, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, S.M.; Majid, M.; Haq, M.E.; Khan, B. Mapping brain activity using wearable eeg sensors for mobile applications. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Multimedia and Human-Computer Interaction, Prague, Czech Republic, 14–15 August 2014; Volume 1415. [Google Scholar]
- Zarkowski, P.; Shin, C.; Dang, T.; Russo, J.; Avery, D. EEG and the variance of motor evoked potential amplitude. Clin. EEG Neurosci. 2006, 37, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, T.P.; Makeig, S.; Humphries, C.; Lee, T.W.; Mckeown, M.J.; Iragui, V.; Sejnowski, T.J. Removing electroencephalographic artefacts by blind source separation. Psychophysiology 2000, 37, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delorme, A.; Makeig, S. EEGLAB: an open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 2004, 134, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abootalebi, V.; Moradi, M.H.; Khalilzadeh, M.A. A new approach for EEG feature extraction in P300-based lie detection. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2009, 94, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashashati, A.; Fatourechi, M.; Ward, R.K.; Birch, G.E. A survey of signal processing algorithms in brain–computer interfaces based on electrical brain signals. J. Neural Eng. 2007, 4, R32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenoy, P.; Rao, R.P. Dynamic Bayesian Networks for Brain-Computer Interfaces. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Advances in neural information processing systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2005; pp. 1265–1272. [Google Scholar]
- Lotte, F.; Congedo, M.; Lécuyer, A.; Lamarche, F.; Arnaldi, B. A review of classification algorithms for EEG-based brain–computer interfaces. J. Neural Eng. 2007, 4, R1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del R Millan, J.; Mouriño, J.; Franzé, M.; Cincotti, F.; Varsta, M.; Heikkonen, J.; Babiloni, F. A local neural classifier for the recognition of EEG patterns associated to mental tasks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2002, 13, 678–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suykens, J.A.; Vandewalle, J. Least squares support vector machine classifiers. Neural Process. Lett. 1999, 9, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, R.; Faust, O.; Kannathal, N.; Chua, T.; Laxminarayan, S. Non-linear analysis of EEG signals at various sleep stages. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2005, 80, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thenmozhi, M. Forecasting stock index returns using neural networks. Delhi Bus. Rev. 2006, 7, 59–69. [Google Scholar]
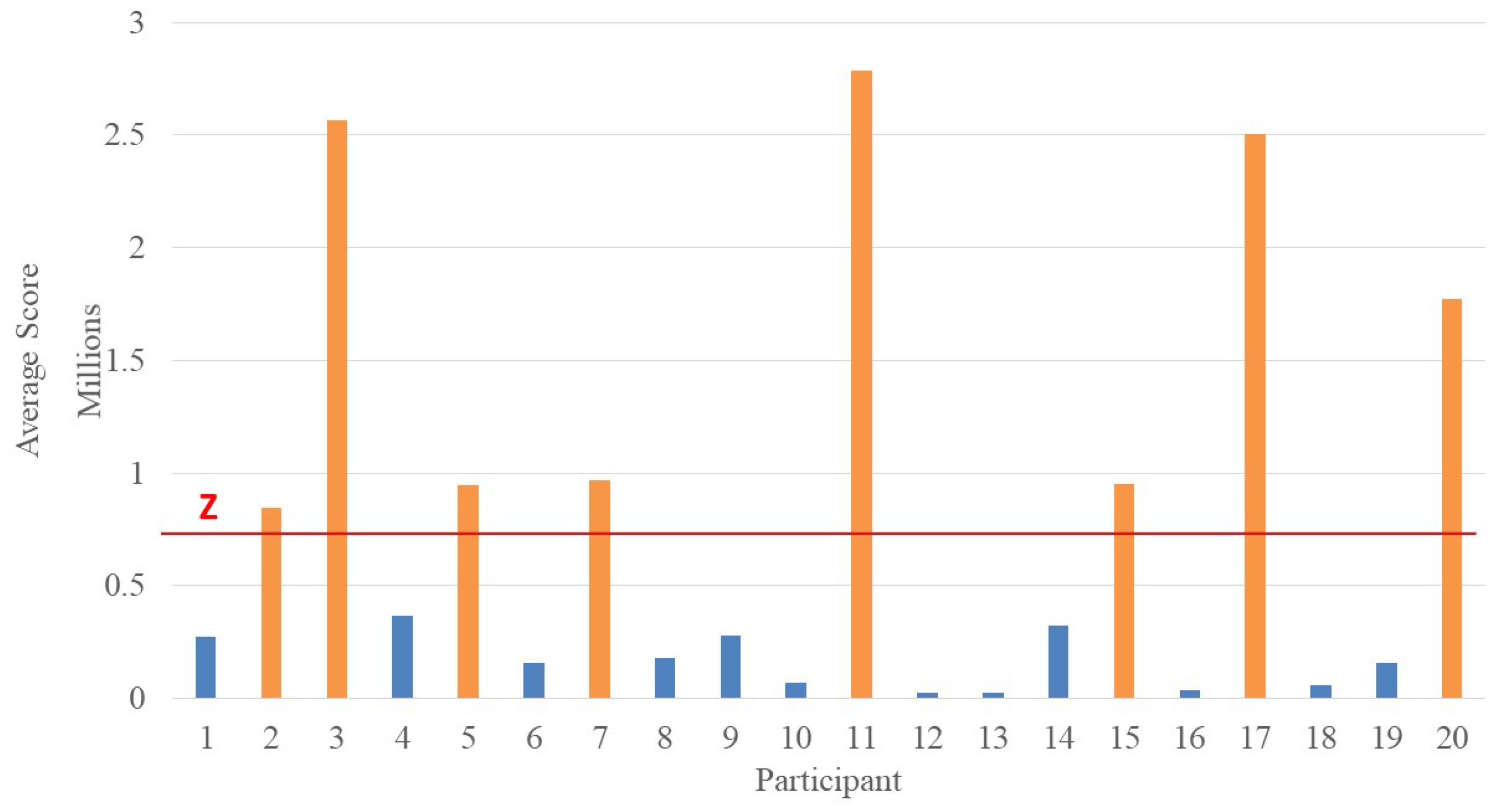
| Player | T1 | R1 | T2 | R2 | T3 | R3 | T4 | R4 | T5 | Total Time (Minutes) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.70 | 1 | 0.90 | 1 | 0.60 | 1 | 0.50 | 1 | 1.30 | 8 |
| 2 | 1.60 | 1 | 1.80 | 1 | 2.20 | 1 | 2.05 | 1 | 2.42 | 14.07 |
| 3 | 7.60 | 1 | 5.40 | 1 | 6.00 | 1 | 5.95 | 1 | 6.80 | 35.75 |
| 4 | 1.20 | 1 | 1.40 | 1 | 1.20 | 1 | 1.70 | 1 | 1.80 | 11.30 |
| 5 | 2.45 | 1 | 2.68 | 1 | 2.20 | 1 | 2.90 | 1 | 2.10 | 16.33 |
| 6 | 0.84 | 1 | 0.64 | 1 | 0.76 | 1 | 0.90 | 1 | 0.54 | 7.68 |
| 7 | 2.60 | 1 | 3.30 | 1 | 1.10 | 1 | 2.47 | 1 | 2.33 | 15.83 |
| 8 | 0.61 | 1 | 0.72 | 1 | 0.90 | 1 | 0.40 | 1 | 0.80 | 7.44 |
| 9 | 0.95 | 1 | 0.89 | 1 | 0.84 | 1 | 0.87 | 1 | 0.80 | 8.35 |
| 10 | 0.50 | 1 | 0.70 | 1 | 0.70 | 1 | 0.80 | 1 | 0.30 | 7.00 |
| 11 | 7.30 | 1 | 6.70 | 1 | 3.20 | 1 | 8.10 | 1 | 7.70 | 37.00 |
| 12 | 0.40 | 1 | 0.80 | 1 | 0.60 | 1 | 0.25 | 1 | 1.10 | 7.15 |
| 13 | 0.25 | 1 | 0.45 | 1 | 0.70 | 1 | 0.40 | 1 | 0.80 | 6.60 |
| 14 | 2.10 | 1 | 0.60 | 1 | 1.50 | 1 | 1.02 | 1 | 0.90 | 10.12 |
| 15 | 3.20 | 1 | 2.20 | 1 | 1.50 | 1 | 2.65 | 1 | 2.10 | 15.65 |
| 16 | 0.80 | 1 | 0.70 | 1 | 0.50 | 1 | 0.40 | 1 | 1.20 | 7.60 |
| 17 | 6.40 | 1 | 3.00 | 1 | 6.80 | 1 | 5.20 | 1 | 5.90 | 31.30 |
| 18 | 0.50 | 1 | 0.60 | 1 | 0.80 | 1 | 0.90 | 1 | 0.65 | 7.45 |
| 19 | 0.30 | 1 | 0.45 | 1 | 0.60 | 1 | 0.45 | 1 | 0.89 | 6.69 |
| 20 | 3.30 | 1 | 2.40 | 1 | 5.80 | 1 | 4.80 | 1 | 4.40 | 24.70 |
| Number of Channels | Classification Algorithm | Correctly Classified | Incorrectly Classified | Time Taken (s) | kappa Statistics | Precision | Recall | ROC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 channels | Naive Bayes | 84 | 16 | |||||
| SVM | 86 | 14 | ||||||
| MLP | 84 | 16 | ||||||
| 14- channels | Naive Bayes | 88 | 12 | |||||
| SVM | 82 | 18 | ||||||
| MLP | 82 | 18 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anwar, S.M.; Saeed, S.M.U.; Majid, M.; Usman, S.; Mehmood, C.A.; Liu, W. A Game Player Expertise Level Classification System Using Electroencephalography (EEG). Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8010018
Anwar SM, Saeed SMU, Majid M, Usman S, Mehmood CA, Liu W. A Game Player Expertise Level Classification System Using Electroencephalography (EEG). Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(1):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8010018
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnwar, Syed Muhammad, Sanay Muhammad Umar Saeed, Muhammad Majid, Saeeda Usman, Chaudhry Arshad Mehmood, and Wei Liu. 2018. "A Game Player Expertise Level Classification System Using Electroencephalography (EEG)" Applied Sciences 8, no. 1: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8010018
APA StyleAnwar, S. M., Saeed, S. M. U., Majid, M., Usman, S., Mehmood, C. A., & Liu, W. (2018). A Game Player Expertise Level Classification System Using Electroencephalography (EEG). Applied Sciences, 8(1), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8010018






