The Performance and Fouling Control of Submerged Hollow Fiber (HF) Systems: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Submerged Membrane-Filtration Applications and Benefits
2.1. Surface-Water Treatment
2.2. Pretreatment for RO Desalination and Reclamation
2.3. Membrane Bioreactors (MBRs)
3. Fouling and Concentration Polarization in Submerged HF Systems
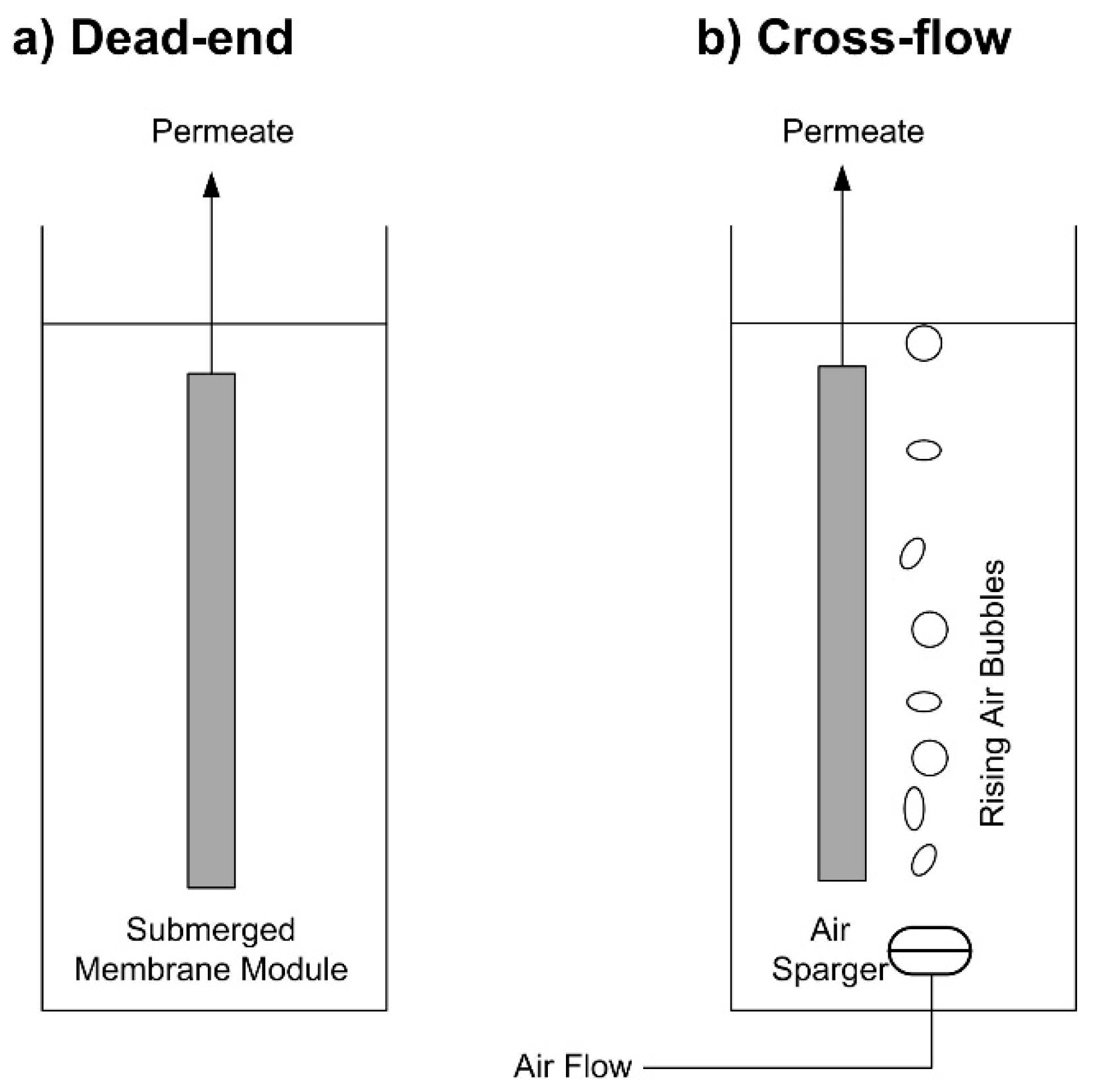
3.1. Fouling in Submerged Dead-End Filtration
3.2. Fouling in Submerged Cross-Flow Filtration
4. Blocking and Blocking Mitigation in Submerged HF Modules
5. Parameters Affecting the Performance of a Submerged Hollow Fiber System
5.1. Membrane Properties and Module Configurations
5.1.1. Membrane Materials and Surface Morphology
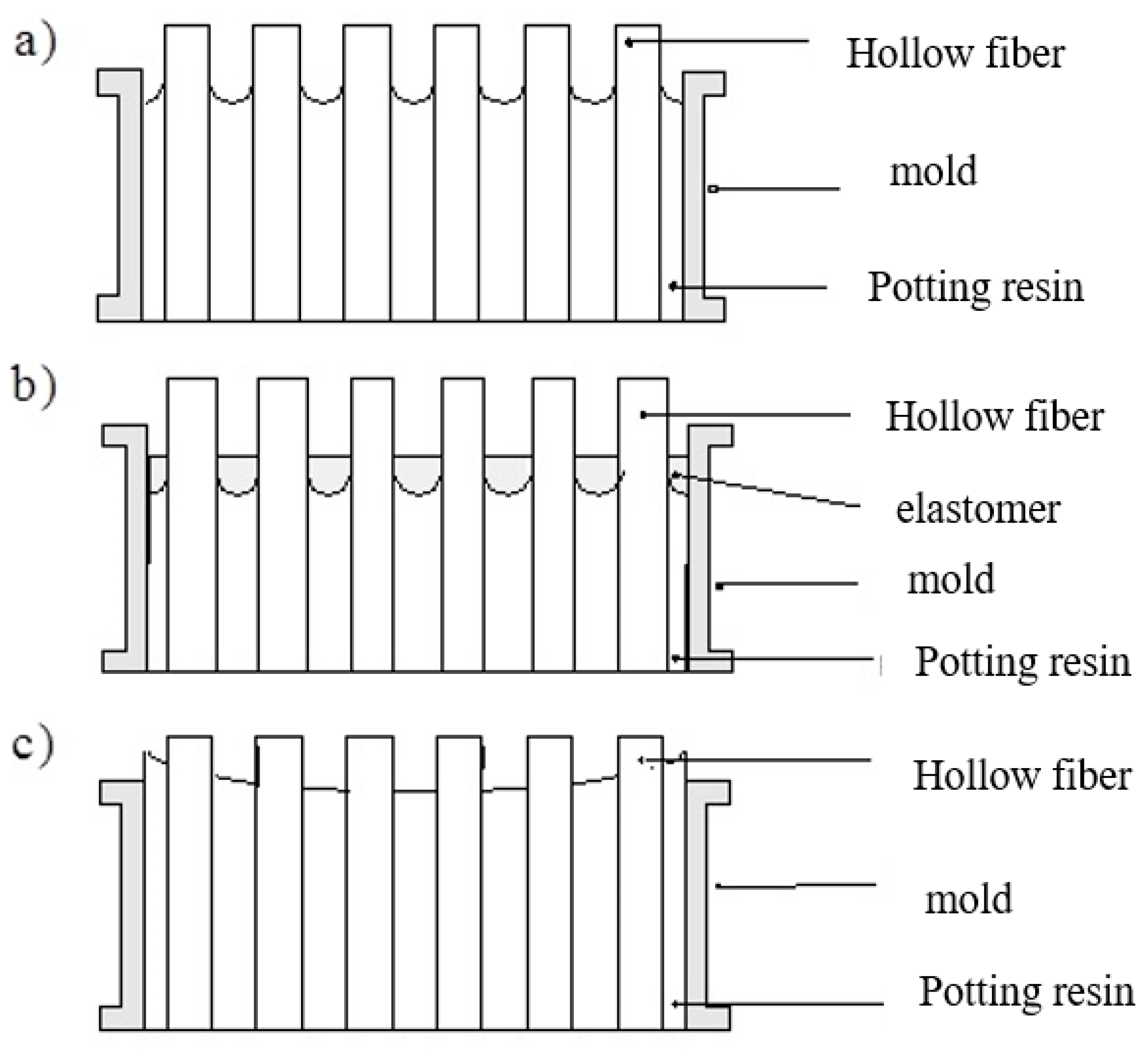
5.1.2. Fiber/Module Arrangement
5.1.3. Fiber Looseness
5.1.4. Fiber Diameter
5.1.5. Fiber Length
5.2. Hydrodynamics in Submerged HF Membranes
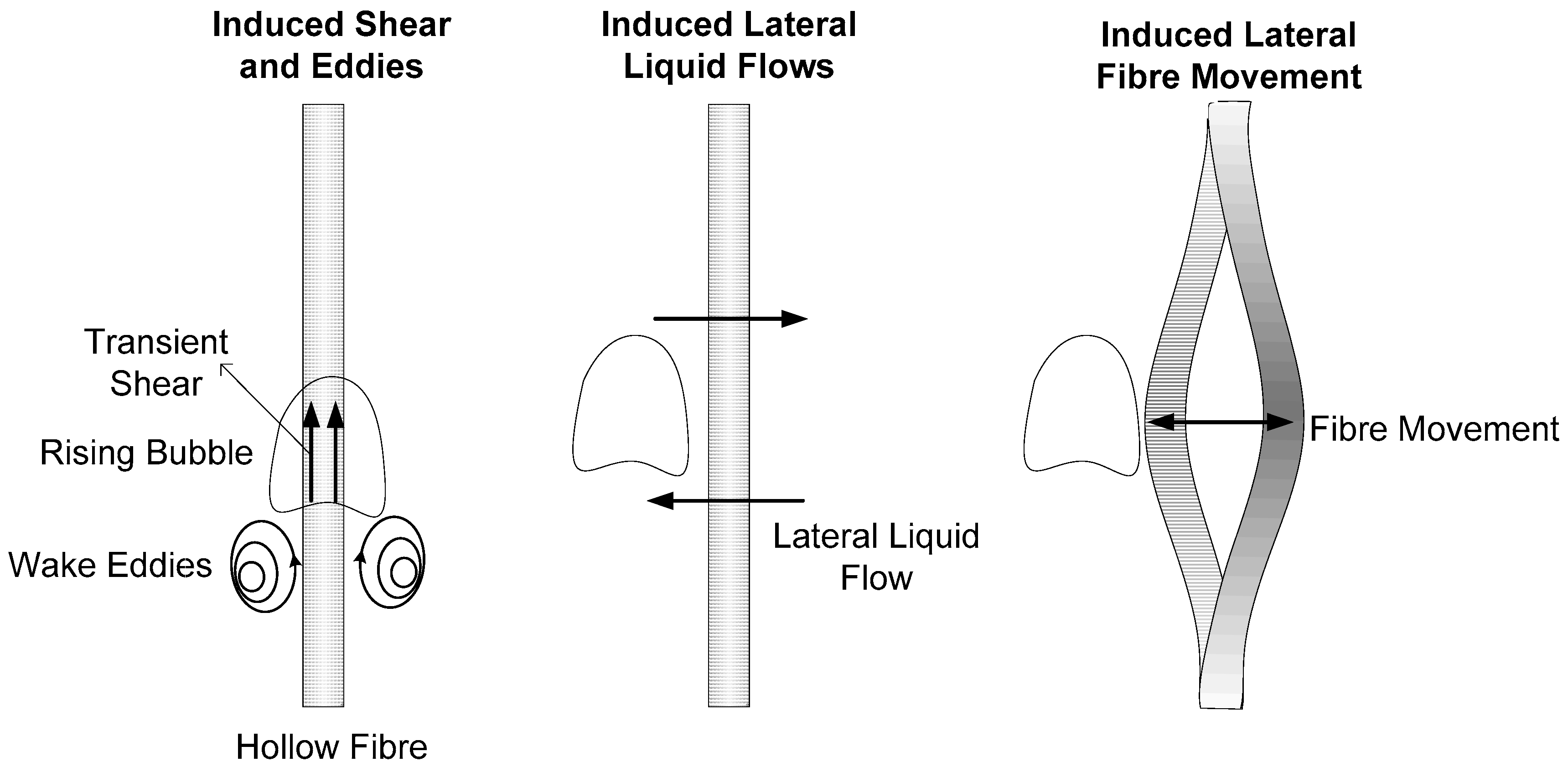
5.2.1. Role of Air Bubbles
5.2.2. Bubble Characteristics
5.2.3. Effect of Gas Flowrate
5.2.4. Aeration Modes
5.3. Shear Stress on Membrane Surface by Non-Bubbling Techniques
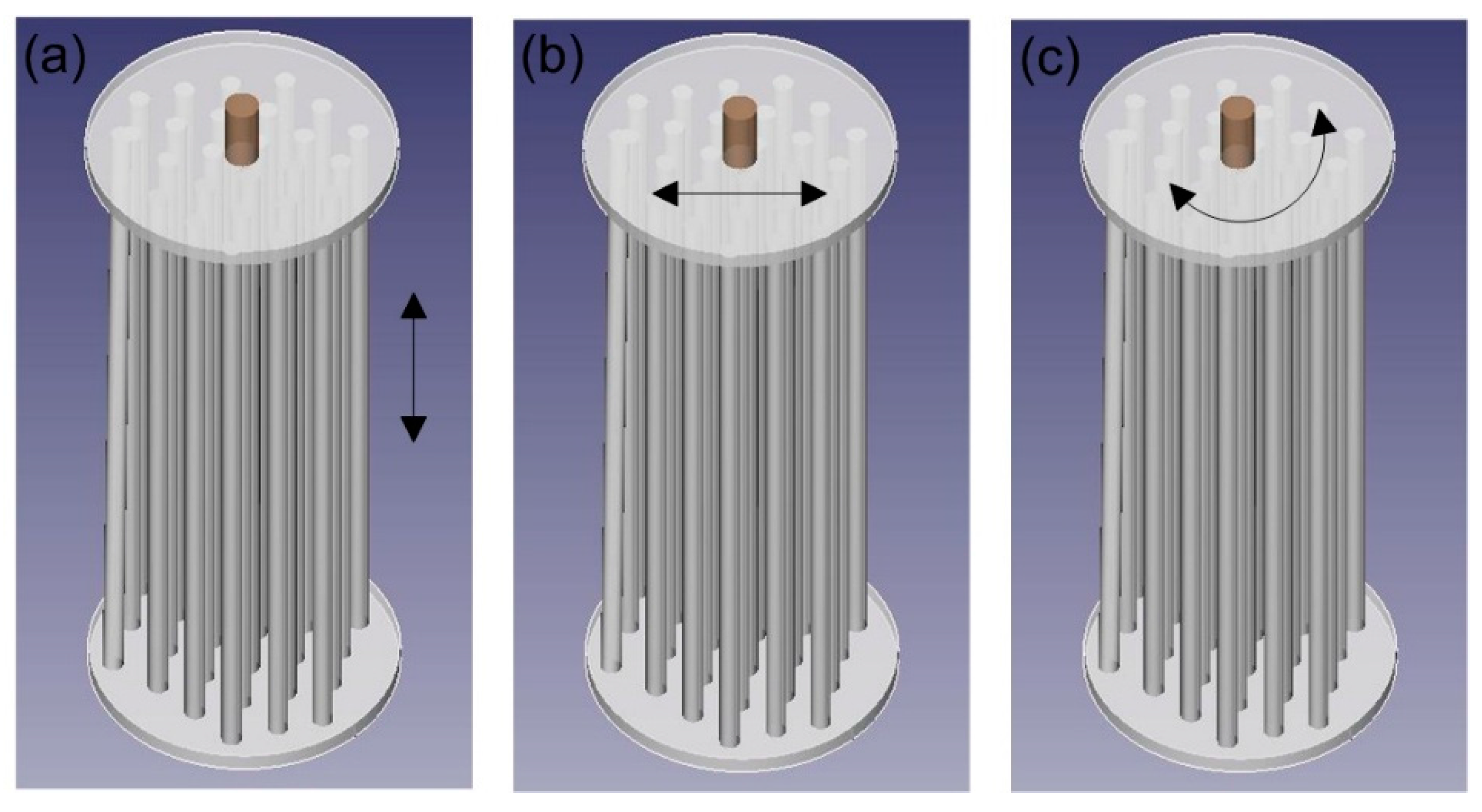
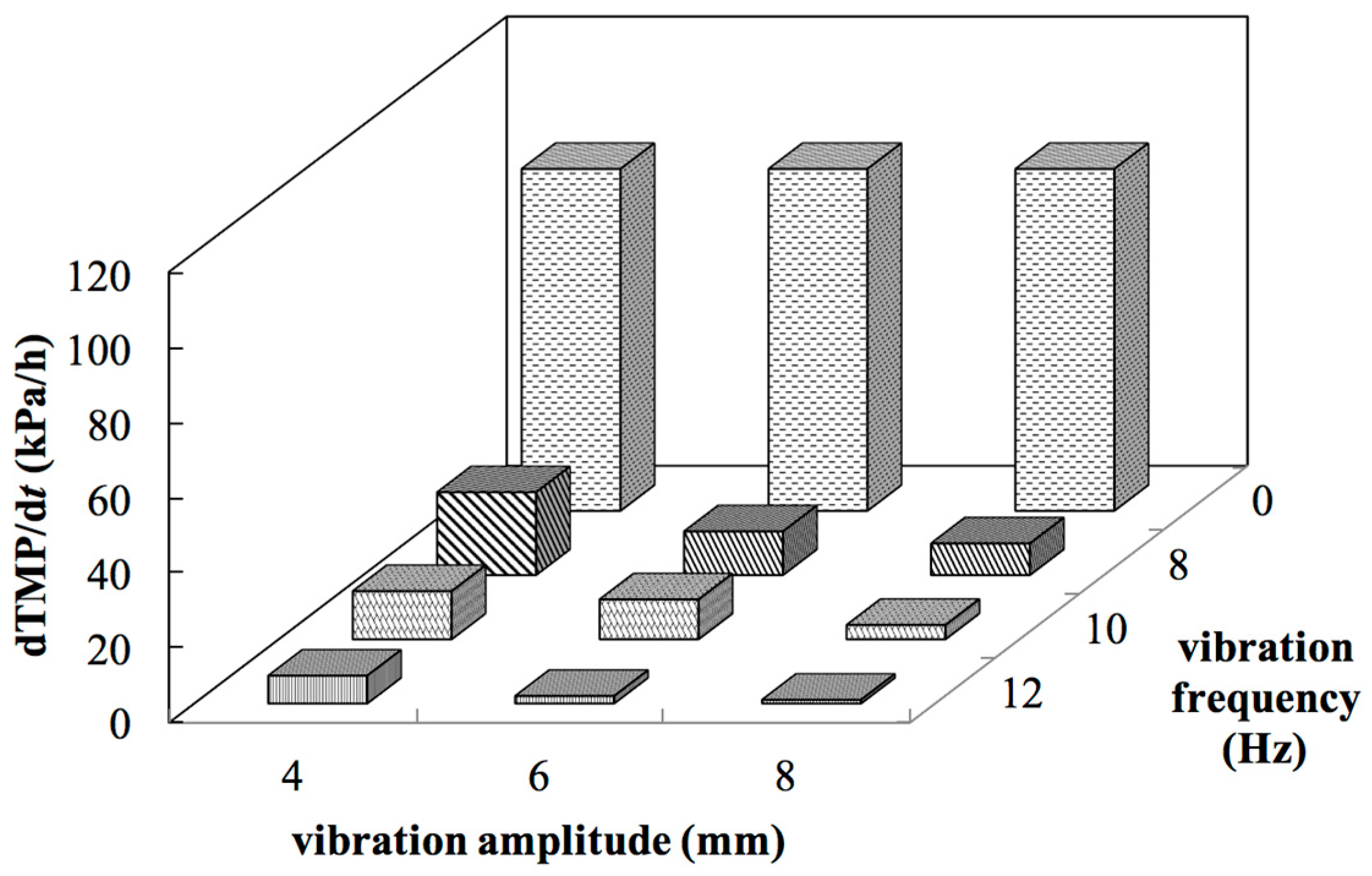
5.3.1. Vibrations
5.3.2. Particle Scouring
6. Techniques for Fouling Control in Dead-End Submerged Membrane Systems
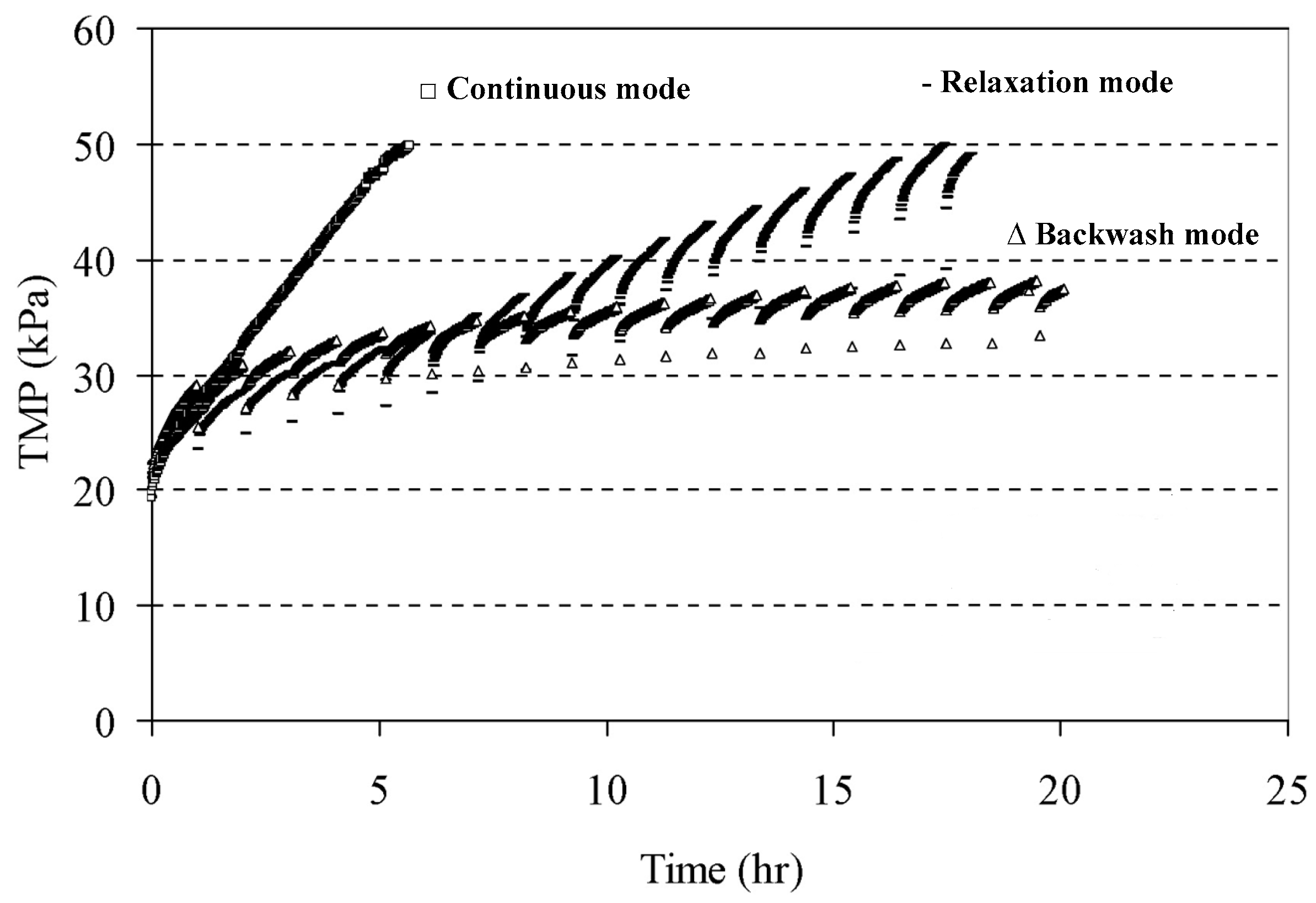
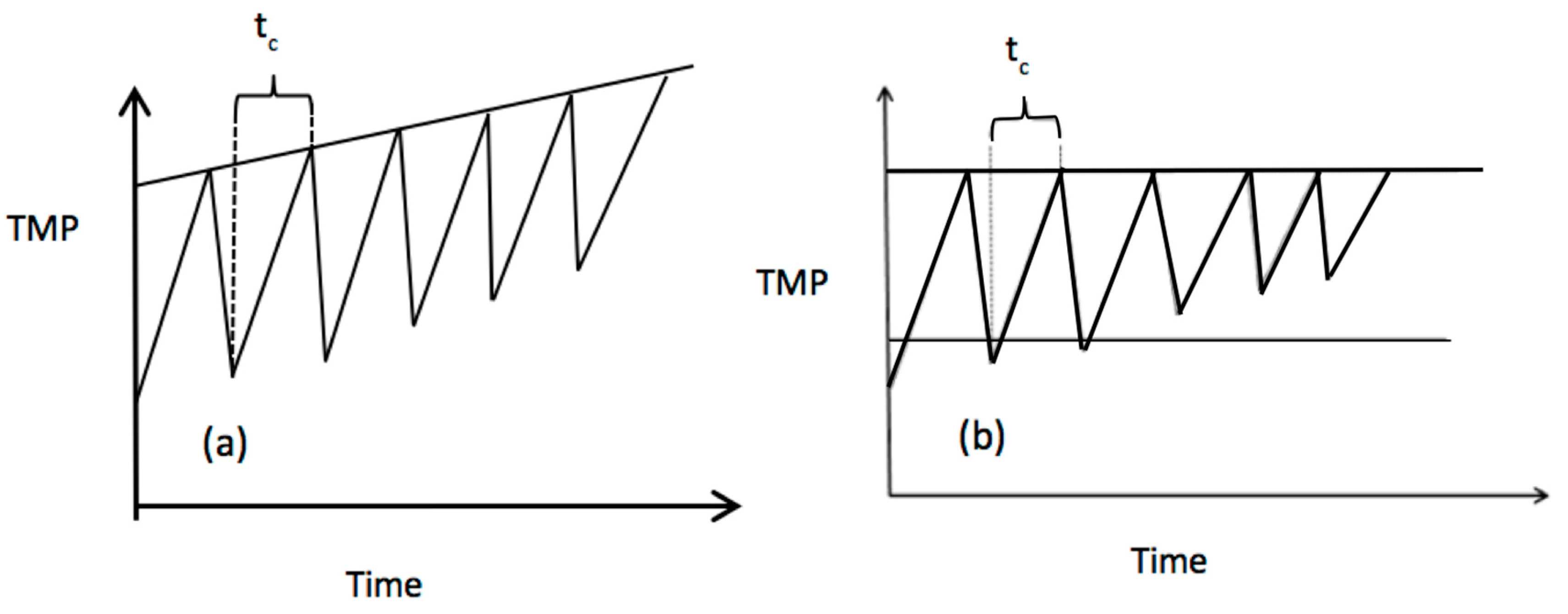
6.1. Backwashing
6.2. Relaxation
7. Chemical Cleaning in Submerged HF Membranes—Procedure, Effect on Membrane Performance
8. Submerged HF Membrane Integrity and Failure
8.1. Ageing
8.2. Failure
8.3. Chemical Oxidation
8.4. Module Design
8.5. Excessive Fiber Movement
8.6. Foreign Bodies
8.7. Future Trends for Integrity Assessment
9. Conclusions and Research Opportunities
9.1. Hydrodynamics and Bubbling
9.2. Non-Bubbled Hydrodynamics
9.3. Backwashing and Relaxation
9.4. Identifying Sustainable Flux
9.5. Potential Non-Filtration Applications
9.6. Membrane Integrity
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Laîné, J.M.; Vial, D.; Moulart, P. Status after 10 years of operation—Overview of uf technology today. Desalination 2000, 131, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.-J.; Oh, H.; Lee, S.; Nam, S.-H.; Hwang, T.-M. Investigation of the filtration characteristics of pilot-scale hollow fiber submerged mf system using cake formation model and artificial neural networks model. Desalination 2012, 297, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fane, A.G. Submerged membranes. In Advanced Membrane Technology and Applications; Li, N.N., Fane, A.G., Ho, W.S.W., Matsuura, T., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; Chapter 10. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Y.; Le Clech, P.; Chen, V.; Fane, A.G.; Jefferson, B. Fouling mechanisms of alginate solutions as model extracellular polymeric substances. Desalination 2005, 175, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatsuka, S.; Nakate, I.; Miyano, T. Drinking water treatment by using ultrafiltration hollow fiber membranes. Desalination 1996, 106, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günther, J.; Schmitz, P.; Albasi, C.; Lafforgue, C. A numerical approach to study the impact of packing density on fluid flow distribution in hollow fiber module. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 348, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Profio, G.; Ji, X.; Curcio, E.; Drioli, E. Submerged hollow fiber ultrafiltration as seawater pretreatment in the logic of integrated membrane desalination systems. Desalination 2011, 269, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chellam, S.; Jacangelo, J.G.; Bonacquisti, T.P. Modeling and experimental verification of pilot-scale hollow fiber, direct flow microfiltration with periodic backwashing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffin, M.; Germain, E.; Judd, S.J. Influence of backwashing, flux and temperature on microfiltration for wastewater reuse. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 96, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aimar, P. Slow colloidal aggregation and membrane fouling. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 360, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.Y.; Chong, T.H.; Fane, A.G. Colloidal interactions and fouling of nf and ro membranes: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 164, 126–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fane, A.G.; Chong, T.H.; Le-Clech, P. Fouling in membrane processes. In Membrane Operations, Innovative Separations and Transformations; Drioli, E., Giorno, L., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2009; Chapter 6. [Google Scholar]
- Vigneswaran, S.; Kwon, D.Y.; Ngo, H.H.; Hu, J.Y. Improvement of microfiltration performance in water treatment: Is critical flux a viable solution? Water Sci. Technol. 2000, 41, 309–315. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Z.F.; Chang, S.; Fane, A.G. The use of gas bubbling to enhance membrane processes. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 221, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicaksana, F.; Fane, A.G.; Chen, V. Fibre movement induced by bubbling using submerged hollow fibre membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 271, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Fane, A.G. Filtration of biomass with laboratory-scale submerged hollow fibre modules—Effect of operating conditions and module configuration. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2002, 77, 1030–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomaa, H.G.; Rao, S. Analysis of flux enhancement at oscillating flat surface membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 374, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le-Clech, P.; Chen, V.; Fane, T.A.G. Fouling in membrane bioreactors used in wastewater treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 284, 17–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radjenović, J.; Matošić, M.; Mijatović, I.; Petrović, M.; Barceló, D. Membrane bioreactor (MBR) as an advanced wastewater treatment technology. In Emerging Contaminants from Industrial and Municipal Waste; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 37–101. [Google Scholar]
- Le-Clech, P. Membrane bioreactors and their uses in wastewater treatments. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 88, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Ding, Z.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Ma, R. The influence of bubble characteristics on the performance of submerged hollow fiber membrane module used in microfiltration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 61, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.-Y.; Xu, Y.-P.; Chen, Z.-L.; Nan, J.; Li, G.-B. Air bubbling for alleviating membrane fouling of immersed hollow-fiber membrane for ultrafiltration of river water. Desalination 2010, 260, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Law, A.W.-K.; Cetin, M.; Fane, A.G. Fouling control of submerged hollow fibre membranes by vibrations. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 427, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, K.; Ye, H.; Lee, E.; Shin, C.; McCarty, P.L.; Bae, J. Anaerobic fluidized bed membrane bioreactor for wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 576–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilal, N.; Ogunbiyi, O.O.; Miles, N.J.; Nigmatullin, R. Methods employed for control of fouling in mf and uf membranes: A comprehensive review. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2005, 40, 1957–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Sim, L.N.; Herulah, B.; Chen, V.; Fane, A.G. Effects of operating conditions on submerged hollow fibre membrane systems used as pre-treatment for seawater reverse osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 365, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, M.; Charfi, A.; Lesage, G.; Heran, M.; Kim, J. Membrane bioreactors for wastewater treatment: A review of mechanical cleaning by scouring agents to control membrane fouling. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 307, 897–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzeminski, P.; Leverette, L.; Malamis, S.; Katsou, E. Membrane bioreactors—A review on recent developments in energy reduction, fouling control, novel configurations, lca and market prospects. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 527, 207–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnal, J.M.; Garcia-Fayos, B.; Verdu, G.; Lora, J. Ultrafiltration as an alternative membrane technology to obtain safe drinking water from surface water: 10 years of experience on the scope of the aquapot project. Desalination 2009, 248, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madaeni, S.S. The application of membrane technology for water disinfection. Water Res. 1999, 33, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, C.; Jain, R. Low Cost Emergency Water Purification Technologies: Integrated Water Security Series; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 1–205. [Google Scholar]
- Loo, S.L.; Fane, A.G.; Krantz, W.B.; Lim, T.T. Emergency water supply: A review of potential technologies and selection criteria. Water Res. 2012, 46, 3125–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iannelli, R.; Ripari, S.; Casini, B.; Buzzigoli, A.; Privitera, G.; Verani, M.; Carducci, A. Feasibility assessment of surface water disinfection by ultrafiltration. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2014, 14, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal, G.; Branch, A.; Sisson, S.A.; Roser, D.J.; van den Akker, B.; Monis, P.; Reeve, P.; Keegan, A.; Regel, R.; Khan, S.J. Virus removal by ultrafiltration: Understanding long-term performance change by application of bayesian analysis. Water Res. 2017, 122, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zularisam, A.W.; Ismail, A.F.; Sakinah, M. Application and challenges of membrane in surface water treatment. J. Appl. Sci. 2010, 10, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zularisam, A.W.; Ismail, A.F.; Salim, R. Behaviours of natural organic matter in membrane filtration for surface water treatment—A review. Desalination 2006, 194, 211–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Shen, B.; Chen, W.; Zhang, X. Interaction mechanisms associated with organic colloid fouling of ultrafiltration membrane in a drinking water treatment system. Desalination 2014, 332, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guastalli, A.R.; Simon, F.X.; Penru, Y.; de Kerchove, A.; Llorens, J.; Baig, S. Comparison of dmf and uf pre-treatments for particulate material and dissolved organic matter removal in swro desalination. Desalination 2013, 322, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamaly, S.; Darwish, N.N.; Ahmed, I.; Hasan, S.W. A short review on reverse osmosis pretreatment technologies. Desalination 2014, 354, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.; Park, Y.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.; Lee, K.; Lee, J.; Chon, H.T. Pre-treatment of swro pilot plant for desalination using submerged mf membrane process: Trouble shooting and optimization. Desalination 2011, 279, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, K.T.; Hawlader, M.N.A.; Malek, A. Pretreatment of seawater: Results of pilot trials in singapore. Desalination 2003, 159, 225–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Fane, A.G. Microbial relevant fouling in membrane bioreactors: Influencing factors, characterization, and fouling control. Membranes 2012, 2, 565–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, L.; Huanga, X. Fouling characteristics and cleaning strategies in a coagulation-microfiltration combination process for water purification. Desalination 2003, 159, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Schwab, K.; Jacangelo, J.G. Pretreatment for low pressure membranes in water treatment: A review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 3011–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; O’Melia, C.R. Direct-flow microfiltration of aquasols: II. On the role of colloidal natural organic matter. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 325, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, C.; Benjamin, M.M.; Chang, Y. Fouling and natural organic matter removal in adsorbent/membrane systems for drinking water treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 1663–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, K.L.; O’Melia, C.R. Protein and humic acid adsorption onto hydrophilic membrane surfaces: Effects of ph and ionic strength. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 165, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorain, O.; Hersant, B.; Persin, F.; Grasmick, A.; Brunard, N.; Espenan, J.M. Ultrafiltration membrane pre-treatment benefits for reverse osmosis process in seawater desalting. Quantification in terms of capital investment cost and operating cost reduction. Desalination 2007, 203, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, G.; Talo, S.; Chida, K.; Basha, A.; Gulamhusein, A. Pretreatment options for large scale swro plants: Case studies of of trials at kindasa, saudi arabia, and conventional pretreatment in spain. Desalination 2004, 167, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, G.K. The case for UF/MF pretreatment to RO in seawater applications. Desalination 2007, 203, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, G.K. UF/MF pre-treatment to RO in seawater and wastewater reuse applications: A comparison of energy costs. Desalination 2008, 222, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brehant, A.; Bonnelye, V.; Perez, M. Comparison of MF/UF pretreatment with conventional filtration prior to RO membranes for surface seawater desalination. Desalination 2002, 144, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnélye, V.; Guey, L.; Del Castillo, J. UF/MF as RO pre-treatment: The real benefit. Desalination 2008, 222, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, C.K.; Hawlader, M.N.A.; Malek, A. An experiment with different pretreatment methods. Desalination 2003, 156, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, J.; Valavala, R.; Han, J.; Her, N.; Yoon, Y. Pretreatment in reverse osmosis seawater desalination: A short review. Environ. Eng. Res. 2011, 16, 205–212. [Google Scholar]
- Akhondi, E.; Wu, B.; Sun, S.; Marxer, B.; Lim, W.; Gu, J.; Liu, L.; Burkhardt, M.; McDougald, D.; Pronk, W.; et al. Gravity-driven membrane filtration as pretreatment for seawater reverse osmosis: Linking biofouling layer morphology with flux stabilization. Water Res. 2015, 70, 158–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Hochstrasser, F.; Akhondi, E.; Ambauen, N.; Tschirren, L.; Burkhardt, M.; Fane, A.G.; Pronk, W. Optimization of gravity-driven membrane (GDM) filtration process for seawater pretreatment. Water Res. 2016, 93, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Judd, S.; Judd, C. The MBR Book: Principles and Applications of Membrane Bioreactors for Water and Wastewater Treatment, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Boston, MA, USA; London, UK, 2006; pp. 207–272. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, A.; Ma, W.; Judd, S.J. Membrane bioreactors: Two decades of research and implementation. Desalination 2011, 273, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Singh, S.; Stuckey, D.C. Fouling reduction using adsorbents/flocculants in a submerged anaerobic membrane bioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 239, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svojitka, J.; Dvořák, L.; Studer, M.; Straub, J.O.; Frömelt, H.; Wintgens, T. Performance of an anaerobic membrane bioreactor for pharmaceutical wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 229, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Guo, W.; Ngo, H.H.; Chang, S.W.; Duc Nguyen, D.; Dan Nguyen, P.; Bui, X.T.; Wu, Y. Impact of reactor configurations on the performance of a granular anaerobic membrane bioreactor for municipal wastewater treatment. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 121, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozgun, H.; Dereli, R.K.; Ersahin, M.E.; Kinaci, C.; Spanjers, H.; van Lier, J.B. A review of anaerobic membrane bioreactors for municipal wastewater treatment: Integration options, limitations and expectations. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 118, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johir, M.A.H.; George, J.; Vigneswaran, S.; Kandasamy, J.; Sathasivan, A.; Grasmick, A. Effect of imposed flux on fouling behavior in high rate membrane bioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 122, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monsalvo, V.M.; McDonald, J.A.; Khan, S.J.; Le-Clech, P. Removal of trace organics by anaerobic membrane bioreactors. Water Res. 2014, 49, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, B.-Q.; Kraemer, J.T.; Bagley, D.M. Anaerobic membrane bioreactors: Applications and research directions. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 36, 489–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, H.Y.; Hermanowicz, S.W. Membrane bioreactor operation at short solids retention times: Performance and biomass characteristics. Water Res. 2005, 39, 981–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, I.S.; Kim, S.N. Wastewater treatment using membrane filtration—Effect of biosolids concentration on cake resistance. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 1307–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sablani, S.; Goosen, M.; Al-Belushi, R.; Wilf, M. Concentration polarization in ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis: A critical review. Desalination 2001, 141, 269–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, A.I.; Fane, A.G.; Waite, T.D. Fouling effects on rejection in the membrane filtration of natural waters. Desalination 2000, 131, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zydney, A.L.; Colton, C.K. A concentration polarization model for the filtrate flow in cross-flow microfiltration of particulate suspensions. Chem. Eng. Commun. 1986, 47, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goosen, M.F.A.; Sablani, S.S.; Al-Hinai, H.; Al-Obeidani, S.; Al-Belushi, R.; Jackson, D. Fouling of reverse osmosis and ultrafiltration membranes: A critical review. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2004, 39, 2261–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoustin, E.; Schäfer, A.I.; Fane, A.G.; Waite, T.D. Ultrafiltration of natural organic matter. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2001, 22, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peinemann, K.V.; Pereira, N.S. Membrane Technology: Volume 4: Membranes for Water Treatmen; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Young, T.A.; Jacangelo, J.G. Unified membrane fouling index for low pressure membrane filtration of natural waters: Principles and methodology. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cogan, N.G.; Chellam, S. Incorporating pore blocking, cake filtration, and eps production in a model for constant pressure bacterial fouling during dead-end microfiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 345, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.-C.; Zydney, A.L. A combined pore blockage and cake filtration model for protein fouling during microfiltration. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 232, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iritani, E.; Katagiri, N.; Takenaka, T.; Yamashita, Y. Membrane pore blocking during cake formation in constant pressure and constant flux dead-end microfiltration of very dilute colloids. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 122, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrasoul, A.; Doan, H.; Lohi, A.; Cheng, C.H. Modeling of fouling and foulant attachments on heterogeneous membranes in ultrafiltration of latex solution. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 135, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Elimelech, M. Chemical and physical aspects of natural organic matter (NOM) fouling of nanofiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1997, 132, 159–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.K.; Chen, V.; Fane, A.G. Natural organic matter (NOM) fouling in low pressure membrane filtration —Effect of membranes and operation modes. Desalination 2008, 218, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibisono, Y.; Cornelissen, E.R.; Kemperman, A.J.B.; Van Der Meer, W.G.J.; Nijmeijer, K. Two-phase flow in membrane processes: A technology with a future. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 453, 566–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fane, A.G.; Fell, C.J.D. A review of fouling and fouling control in ultrafiltration. Desalination 1987, 62, 117–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, G.A.; Dalmau, M.; Vargas, A.; Comas, J.; Rodriguez-Roda, I.; Rapaport, A.; Vande Wouwer, A. Validation of a simple fouling model for a submerged membrane bioreactor. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2015, 48, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.Y.; Fu, Q.S.; Criddle, C.S.; Leckie, J.O. Effect of flux (transmembrane pressure) and membrane properties on fouling and rejection of reverse osmosis and nanofiltration membranes treating perfluorooctane sulfonate containing wastewater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 2008–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrijenhoek, E.M.; Hong, S.; Elimelech, M. Influence of membrane surface properties on initial rate of colloidal fouling of reverse osmosis and nanofiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 188, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iritani, E. A review on modeling of pore-blocking behaviors of membranes during pressurized membrane filtration. Dry. Technol. 2013, 31, 146–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, L.; González, E.; Díaz, O.; Delgado, S. Application of a backwashing strategy based on transmembrane pressure set-point in a tertiary submerged membrane bioreactor. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 470, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, N.P.; Basu, O.D. Relaxation: A beneficial operational step for the reduction of fouling in hollow fiber membranes for drinking water treatment. In Proceedings of the Water Quality Technology Conference and Exposition 2012, Toronto, ON, Canada, 4–8 Novemmmber 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Akhondi, E.; Wicaksana, F.; Fane, A.G. Evaluation of fouling deposition, fouling reversibility and energy consumption of submerged hollow fiber membrane systems with periodic backwash. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 452, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhondi, E.; Wicaksana, F.; Krantz, W.B.; Fane, A.G. Influence of dissolved air on the effectiveness of cyclic backwashing in submerged membrane systems. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 456, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khirani, S.; Smith, P.J.; Manéro, M.H.; Aim, R.B.; Vigneswaran, S. Effect of periodic backwash in the submerged membrane adsorption hybrid system (SMAHS) for wastewater treatment. Desalination 2006, 191, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zsirai, T.; Buzatu, P.; Aerts, P.; Judd, S. Efficacy of relaxation, backflushing, chemical cleaning and clogging removal for an immersed hollow fibre membrane bioreactor. Water Res. 2012, 46, 4499–4507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.P.; Bae, T.H.; Tak, T.M.; Hong, S.; Randall, A. Fouling control in activated sludge submerged hollow fiber membrane bioreactors. Desalination 2002, 143, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.H. Modeling of fouling of cross-flow microfiltration membranes. Sep. Purif. Methods 1992, 21, 75–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, E.; Alliet, M.; Schetrite, S.; Albasi, C. Aeration and hydrodynamics in submerged membrane bioreactors. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 379, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, S.Z.; Wray, H.E.; Bérubé, P.R.; Andrews, R.C. Distribution of surface shear stress for a densely packed submerged hollow fiber membrane system. Desalination 2015, 357, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicaksana, F.; Fane, A.G.; Chen, V. The relationship between critical flux and fibre movement induced by bubbling in a submerged hollow fibre system. Water Sci. Technol. 2005, 51, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.; Fane, A.G.; Vigneswaran, S. Modeling and optimizing submerged hollow fiber membrane modules. AIChE J. 2002, 48, 2203–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; DiGiano, F.A. Defining critical flux in submerged membranes: Influence of length-distributed flux. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 280, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fane, A.G.; Chang, S.; Chardon, E. Submerged hollow fibre membrane module—Design options and operational considerations. Desalination 2002, 146, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madec, A.; Buisson, H.; Ben Aim, R. Aeration to enhance membrane critical flux. In Proceedings of the World Filtration Congress, Brighton, UK, 3–7 April 2000; pp. 199–202. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Huang, S.; Mai, S.; Yang, C.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Z. Effects of various factors on critical flux in submerged membrane bioreactors for municipal wastewater treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 62, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, S.; Judd, C. Design. In The MBR Book: Principles and Applications of Membrane Bioreactors for Water and Wastewater Treatment, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Boston, MA, USA; London, UK, 2006; Chapter 3; pp. 123–162. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, B.D.; Fane, A.G. Fouling transients in nominally sub-critical flux operation of a membrane bioreactor. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 209, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chua, H.C.; Zhou, J.; Fane, A.G. Factors affecting the membrane performance in submerged membrane bioreactors. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 284, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, S. The status of membrane bioreactor technology. Trends Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, A.; Fane, A.G. Performance of individual fibers in a submerged hollow fiber bundle. Water Sci. Technol. 2005, 51, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Judd, S.; Judd, C. Fundamentals. In The Mbr Book: Principles and Applications of Membrane Bioreactors for Water and Wastewater Treatment, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Boston, MA, USA; London, UK, 2006; Chapter 2; pp. 22–121. [Google Scholar]
- Yeo, A.P.S.; Law, A.W.K.; Fane, A.G. Factors affecting the performance of a submerged hollow fiber bundle. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 280, 969–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, M.J.; Fane, A.G.; Hogan, P.A.; Schofield, R.W. The effect of shell side hydrodynamics on the performance of axial-flow hollow-fiber modules. J. Membr. Sci. 1993, 80, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.M.; Xu, Y.Y.; Xu, Z.K. Flow distribution in a randomly packed hollow fiber membrane module. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 211, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chen, V. Shell-side mass transfer performance of randomly packed hollow fiber modules. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 172, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramasinghe, S.R.; Semmens, M.J.; Cussler, E.L. Mass-transfer in various hollow fiber geometries. J. Membr. Sci. 1992, 69, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipnizki, F.; Field, R.W. Mass transfer performance for hollow fibre modules with shell-side axial feed flow: Using an engineering approach to develop a framework. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 193, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, J.; Cruse, A.; Marquardt, W. Modeling submerged hollow-fiber membrane filtration for wastewater treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 288, 94–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.W.; Liu, L.Y.; Ma, R.Y. Study on the effect of flow maldistribution on the performance of the hollow fiber modules used in membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 215, 11–23. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.X.; Zhang, L.Z. Flow maldistribution and performance deteriorations in a counter flow hollow fiber membrane module for air humidification/dehumidification. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2014, 74, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, R.; Fane, A.G. Novel designs for improving the performance of hollow fiber membrane distillation modules. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 384, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Fane, A.G.; Waite, T.D.; Yeo, A. Unstable filtration behavior with submerged hollow fiber membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 308, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Cao, C.; Xu, L.L.; Xiao, T.H.; Jiang, G.L. Experimental velocity measurements and effect of flow maldistribution on predicted permeator performances. J. Membr. Sci. 1998, 139, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicaksana, F.; Fane, A.G.; Law, A.W.K. The use of constant temperature anemometry for permeate flow distribution measurement in a submerged hollow fibre system. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 339, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, F.; Chew, J.W.; Akhondi, E.; Krantz, W.B.; Fane, A.G. Unsteady-state shear strategies to enhance mass-transfer for the implementation of ultrapermeable membranes in reverse osmosis: A review. Desalination 2015, 356, 328–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabarron, S.; Gomez, M.; Dvorak, L.; Ruzickova, I.; Rodriguez-Roda, I.; Comas, J. Ragging in mbr: Effects of operational conditions, chemical cleaning, and pre-treatment improvements. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2014, 49, 2115–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, A.; Buntner, D.; Garrido, J.M. Impact of methanogenic pre-treatment on the performance of an aerobic mbr system. Water Res. 2013, 47, 1229–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.Z.; Xu, L.; Graham, N.; Qu, J.H. Pre-treatment for ultrafiltration: Effect of pre-chlorination on membrane fouling. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.S. Pilot scale study on a new membrane bioreactor hybrid system in municipal wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 141, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, K.; Lee, M.Y.; Lai, W.W.P.; Lee, C.H.; Lin, A.Y.C.; Lin, C.F.; Lin, J.G. Removal of pharmaceuticals and organic matter from municipal wastewater using two-stage anaerobic fluidized membrane bioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 165, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldon, M.S.; Zeelie, P.J.; Edwards, W. Treatment of paper mill effluent using an anaerobic/aerobic hybrid side-stream membrane bioreactor. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 65, 1265–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, J.; Shin, C.; Lee, E.; Kim, J.; Mccarty, P.L. Anaerobic treatment of low-strength wastewater: A comparison between single and staged anaerobic fluidized bed membrane bioreactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 165, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Ma, J.; Tang, C.Y.; Kimura, K.; Wang, Q.; Han, X. Membrane cleaning in membrane bioreactors: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 468, 276–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.B.; Cicek, N.; Ilg, J. State-of-the-art of membrane bioreactors: Worldwide research and commercial applications in north america. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 270, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, K.H.; Kang, I.J.; Yoon, S.H.; Park, H.; Kim, J.H.; Adiya, S.; Lee, C.H. Approaches to membrane fouling control in anaerobic membrane bioreactors. Water Sci. Technol. 2000, 41, 363–371. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, I.J.; Yoon, S.H.; Lee, C.H. Comparison of the filtration characteristics of organic and inorganic membranes in a membrane-coupled anaerobic bioreactor. Water Res. 2002, 36, 1803–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.M.; Jung, J.Y.; Chung, Y.C. Novel method for enhancing permeate flux of submerged membrane system in two-phase anaerobic reactor. Water Res. 2001, 35, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brepols, C.; Drensla, K.; Janot, A.; Trimborn, M.; Engelhardt, N. Strategies for chemical cleaning in large scale membrane bioreactors. Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 57, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brannock, M.W.D.; De Wever, H.; Wang, Y.; Leslie, G. Computational fluid dynamics simulations of mbrs: Inside submerged versus outside submerged membranes. Desalination 2009, 236, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Huang, X.; Wang, C.; Chen, L.; Qian, Y. Study on hydraulic characteristics in a submerged membrane bioreactor process. Process Biochem. 2000, 36, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brannock, M.; Wang, Y.; Leslie, G. Mixing characterisation of full-scale membrane bioreactors: CFD modelling with experimental validation. Water Res. 2010, 44, 3181–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, J.; Li, J.F.; Qiu, J.P.; Li, X.D. Polyacrylamide-starch composite flocculant as a membrane fouling reducer: Key factors of fouling reduction. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 131, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, N.; Mehrnia, M.R.; Sarrafzadeh, M.H.; Nabizadeh, R. Performance of membrane bioreactor in presence of flocculants. Desalination Water Treat. 2014, 52, 2933–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.F.; Gao, Z.Y.; Zhang, L.H.; Song, L.F. Performance enhancement and fouling mitigation by organic flocculant addition in membrane bioreactor at high salt shock. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 164, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo-Guimaraes, A.; Torner-Morales, F.J.; Duran-Alvarez, J.C.; Jimenez-Cisneros, B.E. Removal and fate of emerging contaminants combining biological, flocculation and membrane treatments. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 67, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Guo, W.S.; Ngo, H.H.; Vigneswaran, S. A new combined inorganic-organic flocculant (CIOF) as a performance enhancer for aerated submerged membrane bioreactor. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 75, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johir, M.A.; Shanmuganathan, S.; Vigneswaran, S.; Kandasamy, J. Performance of submerged membrane bioreactor (SMBR) with and without the addition of the different particle sizes of gac as suspended medium. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 141, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.N.; Hai, F.I.; Kang, J.G.; Price, W.E.; Nghiem, L.D. Removal of trace organic contaminants by a membrane bioreactor-granular activated carbon (MBR-GAC) system. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 113, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gur-Reznik, S.; Katz, I.; Dosoretz, C.G. Removal of dissolved organic matter by granular-activated carbon adsorption as a pretreatment to reverse osmosis of membrane bioreactor effluents. Water Res. 2008, 42, 1595–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abegglen, C.; Joss, A.; Boehler, M.; Buetzer, S.; Siegrist, H. Reducing the natural color of membrane bioreactor permeate with activated carbon or ozone. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 60, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.F.; Xia, S.Q.; Lu, Y.J. Characteristics of combined submerged membrane bioreactor with granular activated carbon (GAC) in treating lineal alkylbenzene sulphonates (LAS) wastewater. AIP Conf. Proc. 2010, 1251, 65–68. [Google Scholar]
- Hai, F.I.; Yamamoto, K.; Nakajima, F.; Fukushi, K. Bioaugmented membrane bioreactor (MBR) with a gac-packed zone for high rate textile wastewater treatment. Water Res. 2011, 45, 2199–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, T.T.; Nguyen, V.A.; Van der Bruggen, B. Pilot-scale evaluation of gac adsorption using low-cost, high-performance materials for removal of pesticides and organic matter in drinking water production. J. Environ. Eng. 2013, 139, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Yi, S.; Fane, A.G. Microbial behaviors involved in cake fouling in membrane bioreactors under different solids retention times. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 2511–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Judd, S.; Judd, C. Commercial technologies. In The Mbr Book: Principles and Applications of Membrane Bioreactors for Water and Wastewater Treatment, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Boston, MA, USA; London, UK, 2006; Chapter 4; pp. 163–205. [Google Scholar]
- Zamani, F.; Ullah, A.; Akhondi, E.; Tanudjaja, H.J.; Cornelissen, E.R.; Honciuc, A.; Fane, A.G.; Chew, J.W. Impact of the surface energy of particulate foulants on membrane fouling. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 510, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botton, S.; Verliefde, A.R.D.; Quach, N.T.; Cornelissen, E.R. Influence of biofouling on pharmaceuticals rejection in nf membrane filtration. Water Res. 2012, 46, 5848–5860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornelissen, E.R.; van den Boomgaard, T.; Strathmann, H. Physicochemical aspects of polymer selection for ultrafiltration and microfiltration membranes. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1998, 138, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Oss, C.J. Introduction. In Interfacial Forces in Aqueous Media, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; Chapter 1. [Google Scholar]
- Field, R.W.; Pearce, G.K. Critical, sustainable and threshold fluxes for membrane filtration with water industry applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 164, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bildyukevich, A.V.; Plisko, T.V.; Liubimova, A.S.; Volkov, V.V.; Usosky, V.V. Hydrophilization of polysulfone hollow fiber membranes via addition of polyvinylpyrrolidone to the bore fluid. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 524, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhondi, E.; Zamani, F.; Law, A.W.K.; Krantz, W.B.; Fane, A.G.; Chew, J.W. Influence of backwashing on the pore size of hollow fiber ultrafiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 521, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, D.; Matsuura, T. Surface modifications for antifouling membranes. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 2448–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, A.D.; Munro, P.A.; Trägårdh, G. The effect of protein fouling in microfiltration and ultrafiltration on permeate flux, protein retention and selectivity: A literature review. Desalination 1993, 91, 65–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasmore, M.; Todd, P.; Smith, S.; Baker, D.; Silverstein, J.; Coons, D.; Bowman, C.N. Effects of ultrafiltration membrane surface properties on pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm initiation for the purpose of reducing biofouling. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 194, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brant, J.A.; Childress, A.E. Colloidal adhesion to hydrophilic membrane surfaces. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 241, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochkodan, V.; Hilal, N. A comprehensive review on surface modified polymer membranes for biofouling mitigation. Desalination 2015, 356, 187–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, A.V.R.; Mohan, D.J.; Bhattacharya, A.; Shah, V.J.; Ghosh, P.K. Surface modification of ultrafiltration membranes by preadsorption of a negatively charged polymer: I. Permeation of water soluble polymers and inorganic salt solutions and fouling resistance properties. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 214, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Li, K.; Teo, W.K. Preparation and characterization of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) hollow fiber membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 163, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochkodan, V.; Johnson, D.J.; Hilal, N. Polymeric membranes: Surface modification for minimizing (bio) colloidal fouling. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 206, 116–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardes, P.C.; De Andrade, N.J.; Da Silva, L.H.M.; De Carvalho, A.F.; Fernandes, P.E.; Araújo, E.A.; Lelis, C.A.; Mol, P.C.G.; De Sá, J.P.N. Modification of polysulfone membrane used in the water filtration process to reduce biofouling. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 6355–6367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Loo, H.-E.; Bai, R. A novel membrane showing both hydrophilic and oleophobic surface properties and its non-fouling performances for potential water treatment applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 436, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Ahn, C.H.; Hong, S.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.; Baek, Y.; Yoon, J. Evaluation of surface properties of reverse osmosis membranes on the initial biofouling stages under no filtration condition. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 351, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulbricht, M.; Richau, K.; Kamusewitz, H. Chemically and morphologically defined ultrafiltration membrane surfaces prepared by heterogeneous photo-initiated graft polymerization. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1998, 138, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susanto, H.; Ulbricht, M. Photografted thin polymer hydrogel layers on pes ultrafiltration membranes: Characterization, stability, and influence on separation performance. Langmuir 2007, 23, 7818–7830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.-Y.; Xu, Z.-L.; Shen, H.-M.; Yang, H. Preparation and characterization of PVDF–SiO2 composite hollow fiber uf membrane by sol–gel method. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 337, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, A.; Liu, Z.; Xiao, C.; Zhang, Y. Effect of micro-sized SiO2-particle on the performance of PVDF blend membranes via tips. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 360, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Li, Y.S.; Xiang, C.B. Preparation of poly (vinylidene fluoride)(PVDF) ultrafiltration membrane modified by nano-sized alumina (Al2O3) and its antifouling research. Polymer 2005, 46, 7701–7706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Li, Y.S.; Xiang, C.B.; Xianda, S. Effect of nano-sized al2o3-particle addition on PVDF ultrafiltration membrane performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 276, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, M.J.; Hwang, H.Y.; Kim, D.J.; Kim, H.J.; Hong, Y.T.; Nam, S.Y. Preparation and characterization of porous PVDF-hfp/clay nanocomposite membranes. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2010, 26, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, H.; Ghaemi, N.; Madaeni, S.S.; Daraei, P.; Khadivi, M.A.; Falsafi, M. Nanoclay embedded mixed matrix PVDF nanocomposite membrane: Preparation, characterization and biofouling resistance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 313, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Xie, T.; Wang, J.; Liu, P.; Wang, F. An anti-fouling poly (vinylidene fluoride) hybrid membrane blended with functionalized ZrO2 nanoparticles for efficient oil/water separation. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 5262–5271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; He, Y.; Zeng, G.; Zhan, Y.; Pan, Y.; Shi, H.; Chen, Q. Novel hydrophilic PVDF ultrafiltration membranes based on a ZrO2. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 8965–8976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.C.; Hou, J.; Chen, V.; Xu, Z.K. Surface and interface engineering for organic-inorganic composite membranes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 9716–9729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.J.; Kim, N.; Lee, Y.T. Preparation and characterization of PVDF/TiO2 organic–inorganic composite membranes for fouling resistance improvement. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 345, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Liu, Y.; Mao, L.; Jiang, C.; Ang, J.; Lu, X. Doping polysulfone ultrafiltration membrane with TiO2-PDA nanohybrid for simultaneous self-cleaning and self-protection. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 532, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; He, Y. Effects of nano sized zinc oxide on the performance of PVDF microfiltration membranes. Desalination 2012, 302, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Xiao, K.; Mo, Y.; Huang, X. A novel zno nanoparticle blended polyvinylidene fluoride membrane for anti-irreversible fouling. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 394, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Fane, A.G. The effect of fibre diameter on filtration and flux distribution—Relevance to submerged hollow fibre modules. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 184, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulton, B.G.; Bérubé, P.R. Optimizing the sparging condition and membrane module spacing for a ZW500 submerged hollow fiber membrane system. Desalination Water Treat. 2012, 42, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, Y.; Okuno, Y.-I.; Uryu, K.; Ohtsubo, S.; Watanabe, A. Filtration characteristics of hollow fiber microfiltration membranes used in membrane bioreactor for domestic wastewater treatment. Water Res. 1996, 30, 2385–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Fridjonsson, E.O.; Johns, M.L.; Wang, R.; Fane, A.G. A non-invasive study of flow dynamics in membrane distillation hollow fiber modules using low-field nuclear magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 451, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bérubé, P.R.; Lei, E. The effect of hydrodynamic conditions and system configurations on the permeate flux in a submerged hollow fiber membrane system. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 271, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Waite, T.D.; Leslie, G. Numerical simulations of impact of membrane module design variables on aeration patterns in membrane bioreactors. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 520, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Waite, T.D.; Leslie, G. Fluid structure interaction analysis of lateral fibre movement in submerged membrane reactors. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 504, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, A.P.S.; Law, A.W.K.; Fane, A.G. The relationship between performance of submerged hollow fibers and bubble-induced phenomena examined by particle image velocimetry. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 304, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; DiGiano, F.A. Particle fouling in submerged microfiltration membranes: Effects of hollow-fiber length and aeration rate. J. Water Supply Res. Technol.-Aqua 2006, 55, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Kim, J. Analysis of local fouling in a pilot-scale submerged hollow-fiber membrane system for drinking water treatment by membrane autopsy. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 95, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
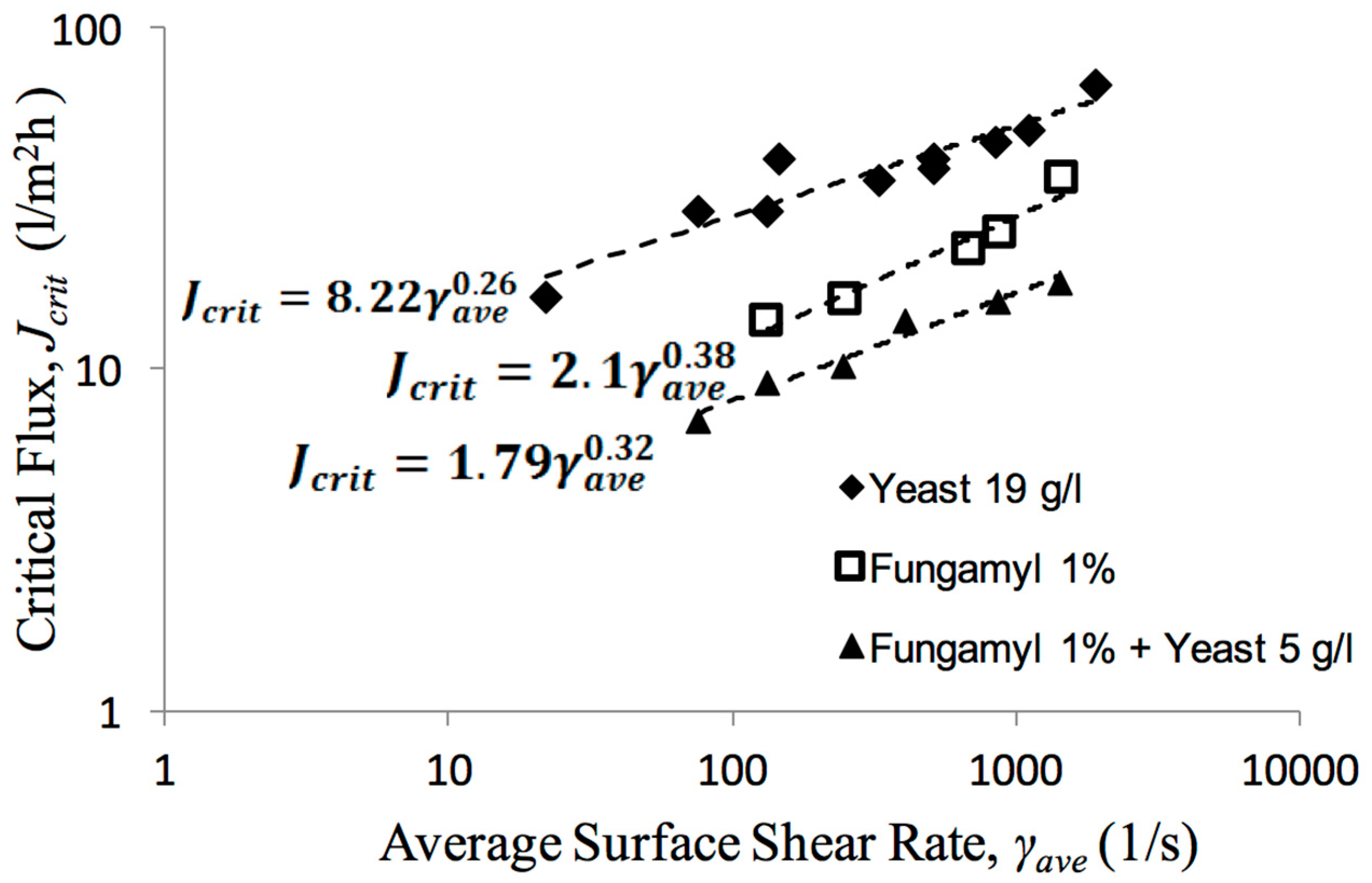
- Li, X.; Li, J.; Cui, Z.; Yao, Y. Modeling of filtration characteristics during submerged hollow fiber membrane microfiltration of yeast suspension under aeration condition. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 510, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-J.; Rao, P.; Shirazi, S. Effect of operating parameters on permeate flux decline caused by cake formation—A model study. Desalination 2005, 171, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, M.; Aryal, R.; Vigneswaran, S.; Kandasamy, J. Application of air flow for mitigation of particle deposition in submerged membrane microfiltration. Desalination Water Treat. 2011, 32, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visvanathan, C.; Ben Aim, R.; Parameshwaran, K. Membrane separation bioreactors for wastewater treatment. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 30, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Qu, F.-S.; Liang, H.; Li, K.; Bai, L.-M.; Li, G.-B. Control of submerged hollow fiber membrane fouling caused by fine particles in photocatalytic membrane reactors using bubbly flow: Shear stress and particle forces analysis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 172, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, B.J.L.; Goh, S.; Livingston, A.G.; Fane, A.G. Controlling biofilm development in the extractive membrane bioreactor. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabassud, C.; Laborie, S.; Durand-Bourlier, L.; Lainé, J.M. Air sparging in ultrafiltration hollow fibers: Relationship between flux enhancement, cake characteristics and hydrodynamic parameters. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 181, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fane, A.G.; Chew, J.W. Effect of bubble characteristics on critical flux in the microfiltration of particulate foulants. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 535, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Zhang, Q.; Chin, G.-L.; Ong, E.-H.; Lou, J.; Kang, C.-W.; Liu, W.; Jordan, E. Experimental investigation of hydrodynamic behavior in a real membrane bio-reactor unit. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 353, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen Cong Duc, E.; Fournier, L.; Levecq, C.; Lesjean, B.; Grelier, P.; Tazi-Pain, A. Local hydrodynamic investigation of the aeration in a submerged hollow fibre membranes cassette. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 321, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulton, B.G.; Redwood, J.; Tourais, M.; Bérubé, P.R. Distribution of surface shear forces and bubble characteristics in full-scale gas sparged submerged hollow fiber membrane modules. Desalination 2011, 281, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buetehorn, S.; Volmering, D.; Vossenkaul, K.; Wintgens, T.; Wessling, M.; Melin, T. CFD simulation of single- and multi-phase flows through submerged membrane units with irregular fiber arrangement. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 384, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhabila, E.H.; Ben Aïm, R.; Buisson, H. Microfiltration of activated sludge using submerged membrane with air bubbling (application to wastewater treatment). Desalination 1998, 118, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, T.; Hata, K.; Kikuoka, Y.; Seino, O. Effects of aeration on suction pressure in a submerged membrane bioreactor. Water Res. 1997, 31, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Fane, A.G. Filtration of biomass with axial inter-fibre upward slug flow: Performance and mechanisms. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 180, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaisrani, T.M.; Samhaber, W.M. Impact of gas bubbling and backflushing on fouling control and membrane cleaning. Desalination 2011, 266, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.C.V.; Bérubé, P.R.; Hall, E.R. Relationship between types of surface shear stress profiles and membrane fouling. Water Res. 2011, 45, 6403–6416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, L.; Law, A.W.-K.; Fane, A.G. Hydrodynamic effects of air sparging on hollow fiber membranes in a bubble column reactor. Water Res. 2013, 47, 3762–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeom, I.-T.; Nah, Y.-M.; Ahn, K.-H. Treatment of household wastewater using an intermittently aerated membrane bioreactor. Desalination 1999, 124, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guibert, D.; Aim, R.B.; Rabie, H.; Côté, P. Aeration performance of immersed hollow-fiber membranes in a bentonite suspension. Desalination 2002, 148, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, K.-L.; Damodar, H.-R.; Damodar, R.-A.; Tsai, J.-H.; Chen, C.-H.; You, S.-J.; Huang, M.-S. Imaging the effect of aeration on particle fouling mitigation in a submerged membrane filtration using a photointerrupt sensor array. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffrin, M.Y. Dynamic shear-enhanced membrane filtration: A review of rotating disks, rotating membranes and vibrating systems. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 324, 7–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourbozorg, M.; Li, T.; Law, A.W.K. Effect of turbulence on fouling control of submerged hollow fibre membrane filtration. Water Res. 2016, 99, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kola, A.; Ye, Y.; Ho, A.; Le-Clech, P.; Chen, V. Application of low frequency transverse vibration on fouling limitation in submerged hollow fibre membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 409–410, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kola, A.; Ye, Y.; Le-Clech, P.; Chen, V. Transverse vibration as novel membrane fouling mitigation strategy in anaerobic membrane bioreactor applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 455, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, S.C.; Juan, H.H.; Siong, L.K. A combined VSEP and membrane bioreactor system. Desalination 2005, 183, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Law, A.W.-K.; Fane, A.G. Submerged hollow fibre membrane filtration with transverse and longitudinal vibrations. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 455, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genkin, G.; Waite, T.D.; Fane, A.G.; Chang, S. The effect of vibration and coagulant addition on the filtration performance of submerged hollow fibre membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 281, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prip Beier, S.; Jonsson, G. A vibrating membrane bioreactor (VMBR): Macromolecular transmission—Influence of extracellular polymeric substances. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2009, 64, 1436–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourbozorg, M.; Li, T.; Law, A.W.K. Fouling of submerged hollow fiber membrane filtration in turbulence: Statistical dependence and cost-benefit analysis. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 521, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruigomez, I.; Gonzalez, E.; Guerra, S.; Rodriguez-Gomez, L.E.; Vera, L. Evaluation of a novel physical cleaning strategy based on hf membrane rotation during the backwashing/relaxation phases for anaerobic submerged mbr. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 526, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzikonstantinou, K.; Tzamtzis, N.; Aretakis, N.; Pappa, A. The effect of various high-frequency powerful vibration (HFPV) types on fouling control of hollow fiber membrane elements in a small pilot-scale smbr system. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 27905–27913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beier, S.P.; Guerra, M.; Garde, A.; Jonsson, G. Dynamic microfiltration with a vibrating hollow fiber membrane module: Filtration of yeast suspensions. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 281, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beier, S.P.; Jonsson, G. Dynamic microfiltration with a vibrating hollow fiber membrane module. Desalination 2006, 199, 499–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beier, S.P.; Jonsson, G. Separation of enzymes and yeast cells with a vibrating hollow fiber membrane module. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 53, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, F.; Law, A.W.K.; Fane, A.G. Hydrodynamic analysis of vibrating hollow fibre membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 429, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krantz, W.B.; Bilodeau, R.R.; Voorhees, M.E.; Elgas, R.J. Use of axial membrane vibrations to enhance mass transfer in a hollow tube oxygenator. J. Membr. Sci. 1997, 124, 283–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, N. Liquid–solids fluidization. In Handbook of Fluidization and Fluid-Particle Systems; Yang, W.-C., Ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kunii, D.; Levenspiel, O. Fluidization Engineering; Butterworth-Heinemann: Newton, MA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Bixler, H.J.; Rappe, G.C. Ultrafiltration Process. U.S. Patent 3,541,006, 17 November 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, E.; Durkee, E.L. Dynamic turbulence promotion in reverse osmosis processing of liquid foods. J. Food Sci. 1971, 36, 31–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Waal, M.J.; van der Velden, P.M.; Koning, J.; Smolders, C.A.; Vanswaay, W.P.M. Use of fluidized-beds as turbulence promotors in tubular membrane systems. Desalination 1977, 22, 465–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamer, E.A.G. Semipermeable Membrane Cleaning Means. U.S. Patent 3,425,562, 4 February 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, C.H.; Huang, X.; Wang, C.W.; Wen, X.H. Effect of a suspended carrier on membrane fouling in a submerged membrane bioreactor. Water Sci. Technol. 2006, 53, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.Y.; Chen, J.H.; Zhang, F. Membrane fouling control in a submerged membrane bioreactor with porous, flexible suspended carriers. Desalination 2006, 189, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boer, R.; Zomerman, J.J.; Hiddink, J.; Aufderheyde, J.; Vanswaay, W.P.M.; Smolders, C.A. Fluidized-beds as turbulence promoters in the concentration of food liquids by reverse-osmosis. J. Food Sci. 1980, 45, 1522–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.X.; Liu, X.; Chen, R.Z.; Xing, W.H.; Xu, N.P. Adding microsized silica particles to the catalysis/ultrafiltration system: Catalyst dissolution inhibition and flux enhancement. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 4933–4938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, M.; McCarty, P.L.; Bae, J.; Kim, J. The effect of fluidized media characteristics on membrane fouling and energy consumption in anaerobic fluidized membrane bioreactors. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 132, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbain, V.; Benoit, R.; Manem, J. Membrane bioreactor: A new treatment tool. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 1996, 88, 75–86. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, M.D.; Pirbazari, M. Membrane bioreactor process for removing biodegradable organic matter from water. Water Res. 2007, 41, 3880–3893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.Z.; He, Y.L.; Liu, Y.H.; Yang, S.C.; Zhang, G.J. Comparison of the filtration characteristics between biological powdered activated carbon sludge and activated sludge in submerged membrane bioreactors. Desalination 2005, 174, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, A.; Stuckey, D.C. Flux and performance improvement in a submerged anaerobic membrane bioreactor (SAMBR) using powdered activated carbon (PAC). Process Biochem. 2008, 43, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyawali, Y.; Balakrishnan, M. Effect of pac addition on sludge properties in an mbr treating high strength wastewater. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1577–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, C.A.; Sun, D.; Fane, A.G. Operation of membrane bioreactor with powdered activated carbon addition. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2006, 41, 1447–1466. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.S.; Lee, C.H. Effect of powdered activated carbon on the performance of an aerobic membrane bioreactor: Comparison between cross-flow and submerged membrane systems. Water Environ. Res. 2003, 75, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munz, G.; Gori, R.; Mori, G.; Lubello, C. Powdered activated carbon and membrane bioreactors (MBRPAC) for tannery wastewater treatment: Long term effect on biological and filtration process performances. Desalination 2007, 207, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.Y.; Liang, H.; Yang, Y.L.; Tian, S.; Li, G.B. Membrane adsorption bioreactor (MABR) for treating slightly polluted surface water supplies: As compared to membrane bioreactor (MBR). J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 325, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Choo, K.H.; Lee, C.H. Flux enhancement with powdered activated carbon addition in the membrane anaerobic bioreactor. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1999, 34, 2781–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remy, M.; Potier, V.; Temmink, H.; Rulkens, W. Why low powdered activated carbon addition reduces membrane fouling in mbrs. Water Res. 2010, 44, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, C.A.; Sun, D.; Zhang, J.S.; Wu, B.; Fane, A.G. Mechanisms of fouling control in membrane bioreactors by the addition of powdered activated carbon. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 873–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, A.Y.; Stuckey, D.C. Activated carbon addition to a submerged anaerobic membrane bioreactor: Effect on performance, transmembrane pressure, and flux. J. Environ. Eng. 2007, 133, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, R.; Kim, J.; McCarty, P.L.; Bae, J. Anaerobic treatment of municipal wastewater with a staged anaerobic fluidized membrane bioreactor (SAF-MBR) system. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 120, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, J.; Yoo, R.; Lee, E.; McCarty, P.L. Two-stage anaerobic fluidized-bed membrane bioreactor treatment of settled domestic wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 68, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, R.H.; Kim, J.H.; McCarty, P.L.; Bae, J.H. Effect of temperature on the treatment of domestic wastewater with a staged anaerobic fluidized membrane bioreactor. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 69, 1145–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, C.; McCarty, P.L.; Kim, J.; Bae, J. Pilot-scale temperate-climate treatment of domestic wastewater with a staged anaerobic fluidized membrane bioreactor (SAF-MBR). Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 159, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, D.W.; Hu, Q.; Yao, C.; Ren, N.Q.; Wu, W.M. Integrated anaerobic fluidized-bed membrane bioreactor for domestic wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 240, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ge, Z.; He, Z. A fluidized bed membrane bioelectrochemical reactor for energy-efficient wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 167, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, L.J.; Ahn, Y.; Logan, B.E. A two-stage microbial fuel cell and anaerobic fluidized bed membrane bioreactor (MFC-AFMBR) system for effective domestic wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 4199–4206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Luo, S.; He, Z. Cathodic fluidized granular activated carbon assisted-membrane bioelectrochemical reactor for wastewater treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 169, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahyadi, A.; Yang, S.; Chew, J.W. CFD study on the hydrodynamics of fluidized granular activated carbon in anfmbr applications. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 178, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, B.; Yang, S.; Liu, Y.; Fane, A.G.; Chew, J.W. Characterizing the scouring efficiency of granular activated carbon (GAC) particles in membrane fouling mitigation via wavelet decomposition of accelerometer signals. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 498, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zamani, F.; Cahyadi, A.; Toh, J.Y.; Yang, S.; Wu, B.; Liu, Y.; Fane, A.G.; Chew, J.W. Correlating the hydrodynamics of fluidized granular activated carbon (GAC) with membrane-fouling mitigation. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 510, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, B.; Liu, Y.; Fane, A.G.; Chew, J.W. Effect of fluidized granular activated carbon (GAC) on critical flux in the microfiltration of particulate foulants. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 523, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Zamani, F.; Lim, W.; Liao, D.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chew, J.W.; Fane, A.G. Effect of mechanical scouring by granular activated carbon (GAC) on membrane fouling mitigation. Desalination 2017, 403, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Wang, Y.; Lim, W.; Chew, J.W.; Fane, A.G.; Liu, Y. Enhanced performance of submerged hollow fibre microfiltration by fluidized granular activated carbon. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 499, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, C.; Kim, K.; McCarty, P.L.; Kim, J.; Bae, J. Integrity of hollow-fiber membranes in a pilot-scale anaerobic fluidized membrane bioreactor (AFMBR) after two-years of operation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 162, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, M.; McCarty, P.L.; Shin, C.; Bae, J.; Kim, J. Low energy single-staged anaerobic fluidized bed ceramic membrane bioreactor (AFCMBR) for wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 240, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charfi, A.; Aslam, M.; Lesage, G.; Heran, M.; Kim, J. Macroscopic approach to develop fouling model under gac fluidization in anaerobic fluidized bed membrane bioreactor. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 49, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Wong, P.C.Y.; Fane, A.G. The potential roles of granular activated carbon in anaerobic fluidized membrane bioreactors: Effect on membrane fouling and membrane integrity. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 53, 1450–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Li, Y.; Lim, W.; Lee, S.L.; Guo, Q.; Fane, A.G.; Liu, Y. Single-stage versus two-stage anaerobic fluidized bed bioreactors in treating municipal wastewater: Performance, foulant characteristics, and microbial community. Chemosphere 2017, 171, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, D.W.; Hu, Q.; Yao, C.; Ren, N.Q. Treatment of domestic wastewater by an integrated anaerobic fluidized-bed membrane bioreactor under moderate to low temperature conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 159, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCurry, D.L.; Bear, S.E.; Bae, J.; Sedlak, D.L.; McCarty, P.L.; Mitch, W.A. Superior removal of disinfection byproduct precursors and pharmaceuticals from wastewater in a staged anaerobic fluidized membrane bioreactor compared to activated sludge. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2014, 1, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Düppenbecker, B.; Engelhart, M.; Cornel, P. Fouling mitigation in anaerobic membrane bioreactor using fluidized glass beads: Evaluation fitness for purpose of ceramic membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 537, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, M.; Charfi, A.; Kim, J. Membrane scouring to control fouling under fluidization of non-adsorbing media for wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarty, P.L.; Bae, J.; Kim, J. Domestic wastewater treatment as a net energy producer—Can this be achieved? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 7100–7106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohn, T.; Jami, M.S.; Iritani, E.; Mukai, Y.; Katagiri, N. Filtration behaviors in constant rate microfiltration with cyclic backwashing of coagulated sewage secondary effluent. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2003, 38, 951–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.C.T.; Lee, D.J.; Huang, C. Membrane fouling mitigation: Membrane cleaning. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 858–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Bowman, C.N.; Davis, R.H. Membrane fouling reduction by backpulsing and surface modification. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 173, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Hakim, L.F.; Bowman, C.N.; Davis, R.H. Factors affecting membrane fouling reduction by surface modification and backpulsing. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 189, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, N.P.; Basu, O.D. Comparative analysis of physical cleaning operations for fouling control of hollow fiber membranes in drinking water treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 436, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, O.; Lefèvre, B.; Prats, G.; Bernat, X.; Gibert, O.; Paraira, M. Reversibility of fouling on ultrafiltration membrane by backwashing and chemical cleaning: Differences in organic fractions behaviour. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 8593–8607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Le-Clech, P.; Stuetz, R.M.; Fane, A.G.; Chen, V. Effects of relaxation and backwashing conditions on fouling in membrane bioreactor. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 324, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessiere, Y.; Guigui, C.; Remize, P.J.; Cabassud, C. Coupling air-assisted backwash and rinsing steps: A new way to improve ultrafiltration process operation for inside-out hollow fibre modules. Desalination 2009, 240, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Le-Clech, P.; Stuetz, R.M.; Fane, A.G.; Chen, V. Novel filtration mode for fouling limitation in membrane bioreactors. Water Res. 2008, 42, 3677–3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.; Chen, V.; Le-Clech, P. Evolution of fouling deposition and removal on hollow fibre membrane during filtration with periodical backwash. Desalination 2011, 283, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, K.J.; Marwah, A.; Chiu, K.-P.; Adham, S.S. Effect of membrane configuration on bench-scale mf and uf fouling experiments. Water Res. 2007, 41, 3842–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhondi, E.; Zamani, F.; Chew, J.W.; Krantz, W.B.; Fane, A.G. Improved design and protocol for evapoporometry determination of the pore-size distribution. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 496, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krantz, W.B.; Greenberg, A.R.; Kujundzic, E.; Yeo, A.; Hosseini, S.S. Evapoporometry: A novel technique for determining the pore-size distribution of membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 438, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, C.; Durand-Bourlier, L.; Clifton, M.J.; Moulin, P.; Rouch, J.-C.; Aptel, P. Use of air sparging to improve backwash efficiency in hollow-fiber modules. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 161, 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, M.L.; Bugge, T.V.; Hede, B.H.; Nierychlo, M.; Larsen, P.; Jørgensen, M.K. Effects of relaxation time on fouling propensity in membrane bioreactors. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 504, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, I.S.; Le Clech, P.; Jefferson, B.; Judd, S. Membrane fouling in membrane bioreactors for wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Eng. 2002, 128, 1018–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drews, A. Membrane fouling in membrane bioreactors-characterisation, contradictions, cause and cures. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 363, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.G.; Chae, S.R.; Drews, A.; Kraume, M.; Shin, H.S.; Yang, F.L. Recent advances in membrane bioreactors (MBRs): Membrane fouling and membrane material. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1489–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.P.; Kim, S.L.; Ting, Y.P. Optimization of membrane physical and chemical cleaning by a statistically designed approach. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 219, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcelli, N.; Judd, S. Effect of cleaning protocol on membrane permeability recovery: A sensitivity analysis. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 2010, 102, 78–86. [Google Scholar]
- Trägårdh, G. Membrane cleaning. Desalination 1989, 71, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Bligh, M.W.; Wang, Y.; Leslie, G.L.; Bustamante, H.; Waite, T.D. Cleaning strategies for iron-fouled membranes from submerged membrane bioreactor treatment of wastewaters. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 475, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kweon, J.H.; Jung, J.H.; Lee, S.R.; Hur, H.W.; Shin, Y.; Choi, Y.H. Effects of consecutive chemical cleaning on membrane performance and surface properties of microfiltration. Desalination 2012, 286, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cote, P.; Alam, Z.; Penny, J. Hollow fiber membrane life in membrane bioreactors (MBR). Desalination 2012, 288, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, I.H.; Williams, K. Autopsy and failure analysis of ultrafiltration membranes from a waste-water treatment system. Desalination 2004, 165, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wilde, W.; Thoeye, C.; De Gueldre, G. Membrane life expectancy assessment after 3 years of MBR operation at WWTP schilde. In Proceedings of the 4th International Water Association Conference on Membranes for Water and Wastewater Treatment, Harrogate, UK, 15–17 May 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Benavente, J.; Vázquez, M. Effect of age and chemical treatments on characteristic parameters for active and porous sublayers of polymeric composite membranes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 273, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thominette, F.; Farnault, O.; Gaudichet-Maurin, E.; Machinal, C.; Schrotter, J.-C. Ageing of polyethersulfone ultrafiltration membranes in hypochlorite treatment. Desalination 2006, 200, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton, E.; Alvarez, J.R.; Palacio, L.; Pradanos, P.; Hernandez, A.; Pihlajamaki, A.; Luque, S. Ageing of polyethersulfone ultrafiltration membranes under long-term exposures to alkaline and acidic cleaning solutions. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 134, 178–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhondi, E. Submerged Hollow Fibre Membrane Fouling: Characterization and Control. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mallevialle, J.; Odendaal, P.E.; Foundation, A.R.; Wiesner, M.R.; eaux-Dumez, L.D.; Commission, S.A.W.R. Water Treatment Membrane Processes; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Childress, A.; Le-Clech, P.; Daugherty, J.; Chen, C.; Leslie, G. Mechanical analysis of hollow fiber membrane integrity in water reuse applications. Desalination 2005, 180, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gijsbertsen-Abrahamse, A.J.; Cornelissen, E.R.; Hofman, J.A.M.H. Fiber failure frequency and causes of hollow fiber integrity loss. Desalination 2006, 194, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, W.; MacCormick, T. Issues of operational integrity in membrane drinking water plants. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2003, 3, 73–80. [Google Scholar]
- Arkhangelsky, E.; Kuzmenko, D.; Gitis, N.; Vinogradov, M.; Kuiry, S.; Gitis, V. Hypochlorite cleaning causes degradation of polymer membranes. Tribol. Lett. 2007, 28, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antony, A.; Leslie, G. Degradation of polymeric membranes in water and wastewater treatment. In Advanced Membrane Science and Technology for Sustainable Energy and Environmental Applications; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2011; pp. 718–745. [Google Scholar]
- Gaudichet-Maurin, E.; Thominette, F. Ageing of polysulfone ultrafiltration membranes in contact with bleach solutions. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 282, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, D. Effect of hypochlorite cleaning on the physiochemical characteristics of polyvinylidene fluoride membranes. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 162, 1050–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regula, C.; Carretier, E.; Wyart, Y.; Gésan-Guiziou, G.; Vincent, A.; Boudot, D.; Moulin, P. Chemical cleaning/disinfection and ageing of organic uf membranes: A review. Water Res. 2014, 56, 325–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zappia, L.R.; Hayes, D.; Nolan, P. Source water characterisation and implications for ultrafiltration in the east kimberly, western australia. In Proceedings of the AWA Membranes and Desalination Conference, Brisbane, Australia, 1 July 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chew, J.W.; Hays, R.; Findlay, J.G.; Knowlton, T.M.; Karri, S.B.R.; Cocco, R.A.; Hrenya, C.M. Reverse core-annular flow of geldart group b particles in risers. Powder Technol. 2012, 221, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, D.H.; Smith, J.W. Wall mass transfer in liquid-fluidized beds. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 1967, 45, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Grace, J.R.; Lim, C.J. Tube wear in gas-fluidized beds. 1. Experimental findings. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1990, 45, 1003–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Lim, C.J.; Grace, J.R.; Lund, J.A. Tube wear in gas-fluidized beds. 2. Low velocity impact erosion and semiempirical model for bubbling and slugging fluidized-beds. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1991, 46, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethune, B. Surface cracking of glassy polymers under a sliding spherical indenter. J. Mater. Sci. 1976, 11, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicek, N.; Dionysiou, D.; Suidan, M.T.; Ginestet, P.; Audic, J.M. Performance deterioration and structural changes of a ceramic membrane bioreactor due to inorganic abrasion. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 163, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, T.E.; Frimmel, F.H. Cross-flow microfiltration with periodical back-washing for photocatalytic degradation of pharmaceutical and diagnostic residues-evaluation of the long-term stability of the photocatalytic activity of TiO2. Water Res. 2005, 39, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawn, B.; Wilshaw, R. Indentation fracture—Principles and applications. J. Membr. Sci. 1975, 10, 1049–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, D.W. Finite Element Analysis: Thermomechanics of Solids; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Z.; Swain, M.V.; Hoffman, M.J. Structural integrity of enamel: Experimental and modeling. J. Dent. Res. 2009, 88, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacchin, P.; Aimar, P.; Field, R.W. Critical and sustainable fluxes: Theory, experiments and applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 281, 42–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phattaranawik, J.; Fane, A.G.; Pasquier, A.C.S.; Bing, W. A novel membrane bioreactor based on membrane distillation. Desalination 2008, 223, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, W.J.; Zhang, J.S.; Lay, W.C.L.; Cao, B.; Fane, A.G.; Liu, Y. State of the art of osmotic membrane bioreactors for water reclamation. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 122, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achilli, A.; Cath, T.Y.; Childress, A.E. Power generation with pressure retarded osmosis: An experimental and theoretical investigation. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 343, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cath, T.Y.; Childress, A.E.; Elimelech, M. Forward osmosis: Principles, applications, and recent developments. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 281, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krantz, W.B.; Lin, C.S.; Sin, P.C.Y.; Yeo, A.; Fane, A.G. An integrity sensor for assessing the performance of low pressure membrane modules in the water industry. Desalination 2011, 283, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Application | Operation Mode | Intermittent Fouling Control | Is Bubbling Implemented? | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface-water treatment | Dead-end with intermittent foulant removal | Backwashing, relaxation, chemical cleaning | With or without bubbling during foulant removal | Less chemical requirements; consistent quality of the filtrate [35,36,37] |
| Pretreatment of RO (reverse osmosis) | Dead-end with intermittent foulant removal | Backwashing, relaxation, chemical cleaning | With or without bubbling during foulant removal | Improved water quality; smaller footprint; less chemical requirements; consistent quality of the filtrate; lowered energy cost for RO plants [38,39,40,41] |
| Membrane bioreactors (MBRs) | Cross-flow with tangential shear | Continuous bubbling, sometimes backwash and relaxation | Continuous bubbling | Small footprint; complete solid-liquid separation; high volumetric organic removal rate; higher effluent quality [19,20,42] |
| Operation Mode | Fouling Control Technique | Important Parameters | Applications | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cross-flow | Bubbling | Bubble characteristics, gas flowrate, bubbling modes (intermittent or continuous) | MBR, AnMBR | Unsteady or transient shear stress; changes biomass properties |
| Vibration | Vibration amplitude and frequency | AnMBR, MF, UF, MD, FO | Low energy cost; surface shear; effective cake removal; facilitates separation of macromolecules | |
| Particle Scouring | Size, fluidization rate | AFBR-AFMBR, IAFMBR | Reduced fouling; low energy cost; amenability for scale-up (disadvantages: membrane damage, blockage) | |
| Dead-end | Backwashing | Backwash flux, backwash duration, backwash frequency | All HF systems | Internal fouling control; can be applied with air scouring |
| Relaxation | Relaxation duration, relaxation frequency | All HF systems, especially MBR | - |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akhondi, E.; Zamani, F.; Tng, K.H.; Leslie, G.; Krantz, W.B.; Fane, A.G.; Chew, J.W. The Performance and Fouling Control of Submerged Hollow Fiber (HF) Systems: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7080765
Akhondi E, Zamani F, Tng KH, Leslie G, Krantz WB, Fane AG, Chew JW. The Performance and Fouling Control of Submerged Hollow Fiber (HF) Systems: A Review. Applied Sciences. 2017; 7(8):765. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7080765
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkhondi, Ebrahim, Farhad Zamani, Keng Han Tng, Gregory Leslie, William B. Krantz, Anthony G. Fane, and Jia Wei Chew. 2017. "The Performance and Fouling Control of Submerged Hollow Fiber (HF) Systems: A Review" Applied Sciences 7, no. 8: 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7080765
APA StyleAkhondi, E., Zamani, F., Tng, K. H., Leslie, G., Krantz, W. B., Fane, A. G., & Chew, J. W. (2017). The Performance and Fouling Control of Submerged Hollow Fiber (HF) Systems: A Review. Applied Sciences, 7(8), 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7080765






