Computer Color Matching and Levelness of PEG-Based Reverse Micellar Decamethyl cyclopentasiloxane (D5) Solvent-Assisted Reactive Dyeing on Cotton Fiber
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Cotton Dyeing in Water
2.2.1. Preparation of Calibration Curves
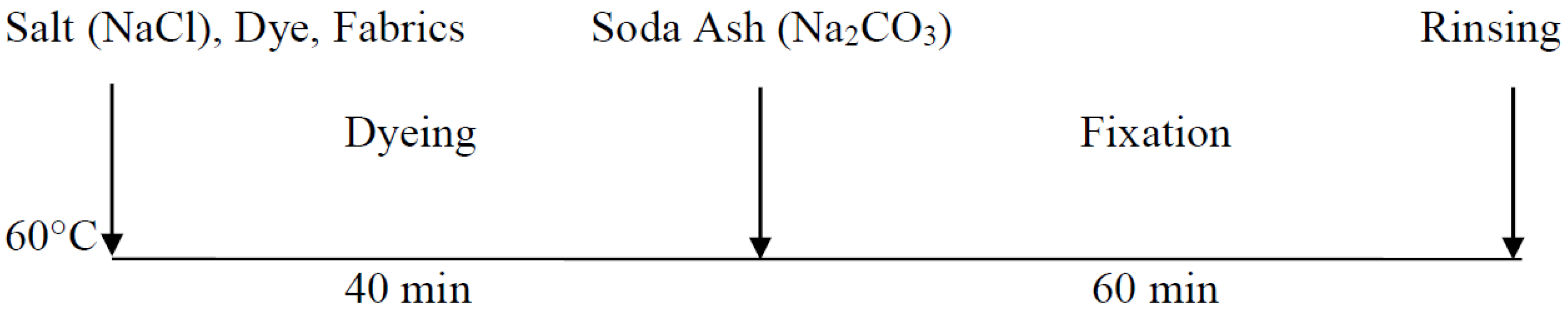
2.2.2. Conventional Dyeing Process
2.3. Cotton Dyeing in the Solvent Reverse Micellar System
2.3.1. Preparation of PEG-Based Reverse Micelle Dye Liquors
2.3.2. Preparation of Calibration Curves
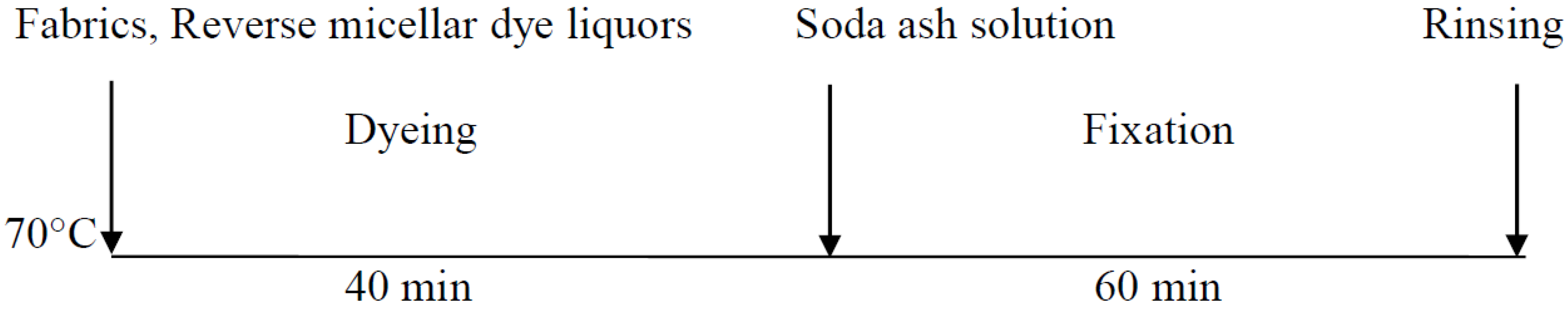
2.3.3. Reverse Micellar Dyeing Process
2.3.4. Simulated Dyeing with Known Concentration of Dye
2.3.5. Establishment of Calibration Curves
2.3.6. Prediction of the Dye Recipe with Different Color Difference Equations
2.3.7. Levelness Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
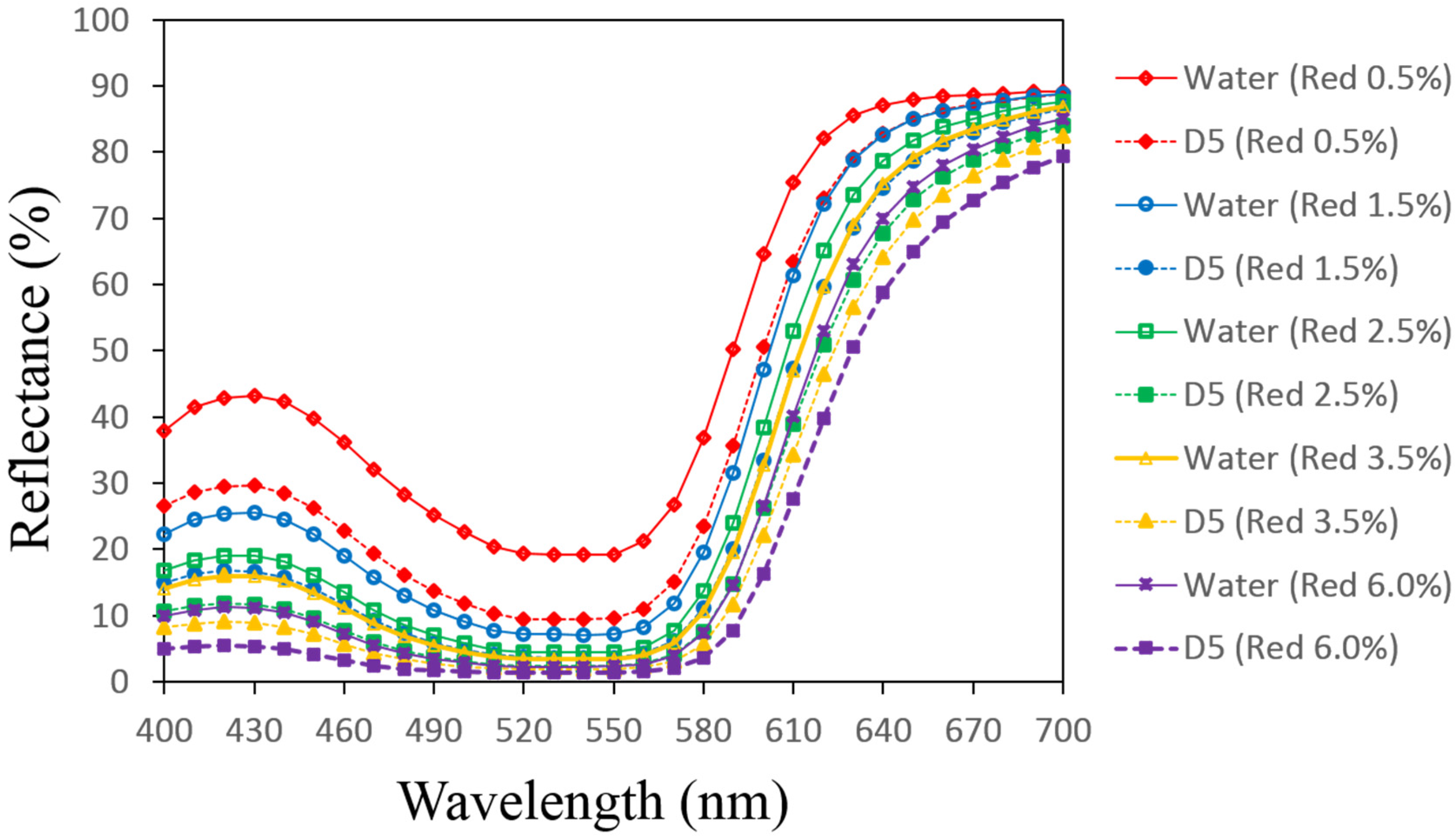
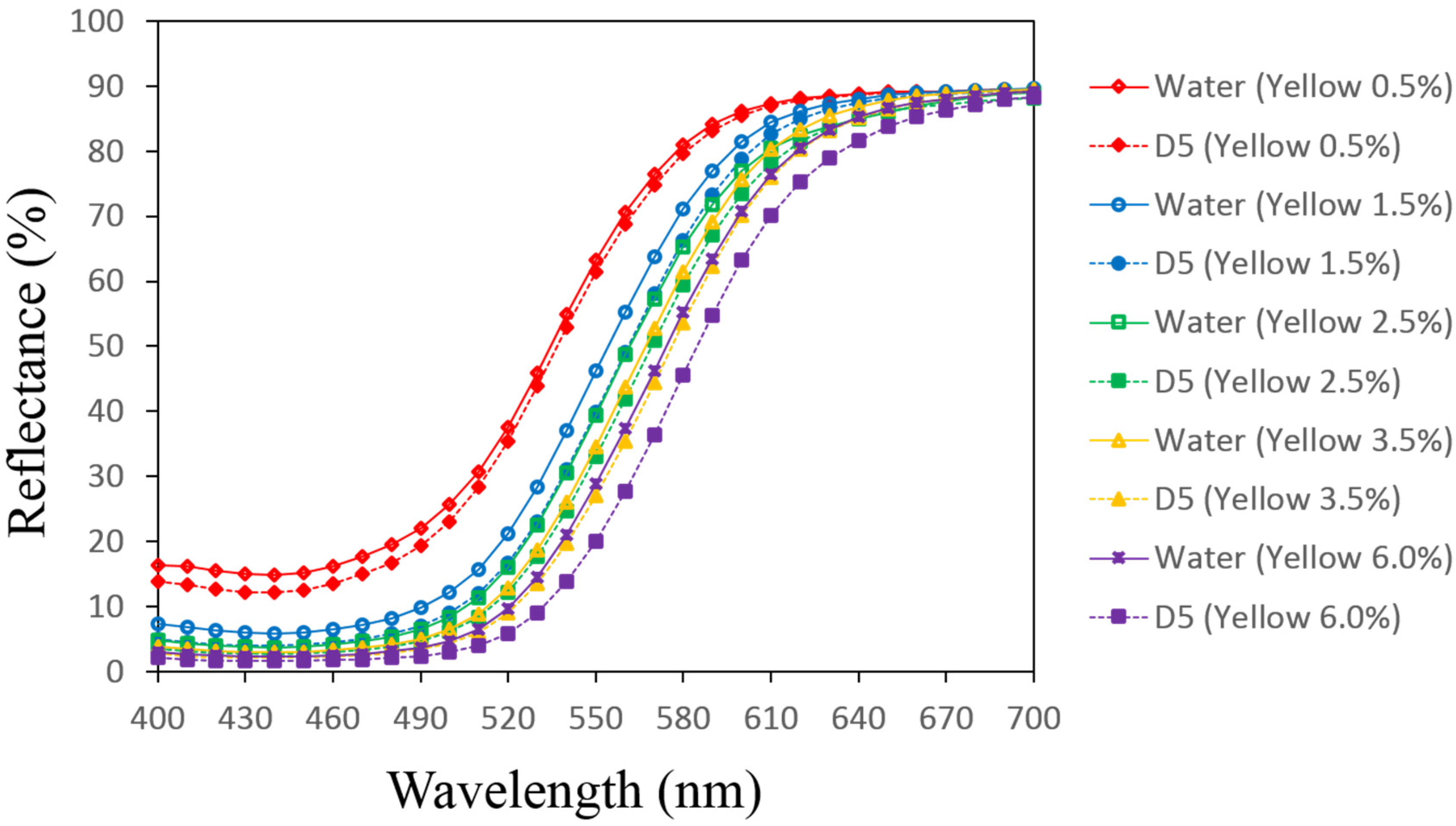
3.1. Reflectance Values of the Dyed Samples
3.2. Linearity of the Calibration Curves
3.3. Computer Color Matching
3.4. Relative Unlevelness Indices
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, C.; Zhu, H. Decoloration of three azo dyes in water by photocatalysis of Fe (III)-oxalate complexes/H2O2 in the presence of inorganic salts. Dyes Pigment. 2007, 73, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickman, W.S. Environmental aspects of textile processing. J. Soc. Dyers Colour. 1993, 109, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, W.S. Textile Coloration and Finishing; Carolina Academic Press: Durham, NC, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Srikulkit, K.; Santifuengkul, P. Salt-free dyeing of cotton cellulose with a model cationic reactive dye. Color. Technol. 2000, 116, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisuntornsug, C.; Yanumet, N.; O'Rear, E.A. Surface modification to improve dyeing of cotton fabric with a cationic dye. Color. Technol. 2002, 118, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, Y.; Lin, H.; Lu, Y. Synthesis of an amino-terminated hyperbranched polymer and its application in reactive dyeing on cotton as a salt-free dyeing auxiliary. Color. Technol. 2007, 123, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechtold, T.; Mussak, R.; Mahmud-Ali, A.; Ganglberger, E.; Geissler, S. Extraction of natural dyes for textile dyeing from coloured plant wastes released from the food and beverage industry. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2006, 86, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vankar, P.S.; Shanker, R.; Mahanta, D.; Tiwari, S. Ecofriendly sonicator dyeing of cotton with Rubia cordifolia Linn. using biomordant. Dyes Pigment. 2008, 76, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, M.; Nazarpoor, K.; Karimi, L. Eco-friendly dyeing of wool using natural dye from weld as co-partner with synthetic dye. J. Clean. Prod. 2011, 19, 1045–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Liu, L.; Liu, R.; Chen, J. Textile wastewater reuse as an alternative water source for dyeing and finishing processes: A case study. Desalination 2010, 258, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, J.; Sawada, K.; Takagi, T.; Kim, G.; Park, C.; Ueda, M. Effects of pressure and temperature on dyeing acrylic fibres with basic dyes in supercritical carbon dioxide. Color. Technol. 2005, 121, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, A.; Chen, B.; Dai, J.; Zhang, K. Using supercritical carbon dioxide as solvent to replace water in polyethylene terephthalate (PET) fabric dyeing procedures. J. Clean. Prod. 2010, 18, 1009–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Elmaaty, T.; Abd El-Aziz, E.; Ma, J.; El-Taweel, F.; Okubayashi, S. Eco-friendly disperse dyeing and functional finishing of nylon 6 using supercritical carbon dioxide. Fibers 2015, 3, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, K.; Ueda, M. Dyeing of protein fiber in a reverse micellar system. Dyes Pigment. 2003, 58, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lee, C.H.; Tang, Y.L.; Kan, C.W. Dyeing cotton in alkane solvent using polyethylene glycol-based reverse micelle as reactive dye carrier. Cellulose 2016, 23, 965–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luisi, P.L. Enzymes hosted in reverse micelles in hydrocarbon solution. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1985, 24, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Ma, J.; Cheng, H.; Zhao, Z. Investigation on the conductivity and microstructure of AOT/non-ionic surfactants/water/n-heptane mixed reverse micelles. Coll. Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp 1998, 135, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.; Dong, Y.; Li, B.; Ding, Z.; Huang, X.; Xue, L. Adsorption and fixation behaviour of CI reactive red 195 on cotton woven fabric in a nonionic surfactant Triton X-100 reverse micelle. Color. Technol. 2012, 128, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.; Deng, Y.; Sun, S. Adsorption and dyeing characteristics of reactive dyes onto cotton fiber in nonionic triton X-100 reverse micelles. Fiber Polym. 2014, 15, 2131–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.; Tong, X.; Sun, S.; Dai, F. Dyeing properties of CI reactive violet 2 on cotton fabric in non-ionic TX-100/Span40 mixed reverse micelles. Fiber Polym. 2015, 16, 1663–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, C.W.; Lo, C.K.; Man, W. Environmentally friendly aspects in coloration. Color. Technol. 2016, 132, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Li, H. Research on application for color matching in textile dyeing based on numerical analysis. In Proceedings of the Computer Science and Software Engineering International Conference, Wuhan, China, 12 December 2008; pp. 357–360. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, F.; Wang, K.; Chen, G. Study on the application of computer color-measuring and matching technology in fur dyeing. China Leather 2004, 15, 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Yang, L. Application of color matching system in dyeing of cotton. Progress Text. Sci. Technol. 2007, 2, 26–29. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, C.; Jia, S.; Li, Z. Application of computer color matching system to nylon fabric dyeing. J. Shaanxi Univ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 4, 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, C.; Yu, C.; Zhang, X. Application of computer color matching system in leather dyeing. Leather Sci. Eng. 2003, 13, 26–29. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, A.R. The CIE 1976 color-difference formulae. Color. Res. Appl. 1977, 2, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.R. Colour quality evaluation. In Total Colour Management in Textiles; Xin, J.H., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; pp. 57–75. [Google Scholar]
- Kuehni, R.G. Industrial color difference: Progress and problems. Color. Res. Appl. 1990, 15, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingamells, W. Colour for Textiles. Soc. Dyers Colour. 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, S.F.; Essa, D.; Osman, E. Statistical method for determining the levelness parameters of different coloured polymeric fabrics. Int. J. Chem. 2011, 3, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.G. Study on the color levelness of silk fabric dyed with vegetable dyes. Sustain. Chem. Process. 2015, 3, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, S. Instrumental measurement of the levelness of textile coloration. Text. Chem. Color. 1993, 25, 75–78. [Google Scholar]
- Chong, C.; Li, S.; Yeung, K. An objective method for the assessment of levelness of dyed materials. J. Soc. Dyers Colour. 1992, 108, 528–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Liu, J.; Li, S.; Lu, F.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y. Study on the preparation of D5 reverse micelle systems and their water solubilization performance. Appl. Chem. Ind. 2009, 10, 1417–1420. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, C.; Wang, J.; Shao, J.; Pu, D.; Chen, J.; Liu, J. A non-aqueous dyeing process of reactive dye on cotton. J. Text. Inst. 2015, 106, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Liu, J.; Li, Y. The impact of D5-washing on the fabric performance. J. Zhejiang Sci-Tech Univ. 2007, 24, 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.Q.; Miao, H.L.; Li, S.Z. Non-Aqueous Dyeing of Reactive Dyes in D5; Trans Tech Publications: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; pp. 138–144. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, H.; Fu, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J. Reactive dyeing of cotton in dye/decamethyl cyclopentasiloxane suspension system. J. Text. Res. 2013, 34, 64–69. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, H.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Fu, C.; Zhang, Y. Study on hydrolysis kinetics of reactive dyes in dye/D5 suspending system. J. Text. Res. 2013, 34, 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, J.H. Controlling colourant formulation. In Total Colour Management in Textiles; Woodhead Publishing: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; pp. 136–159. [Google Scholar]
- Israeli, O. A Shapley-based decomposition of the R-square of a linear regression. J. Econ. Inequal. 2007, 5, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

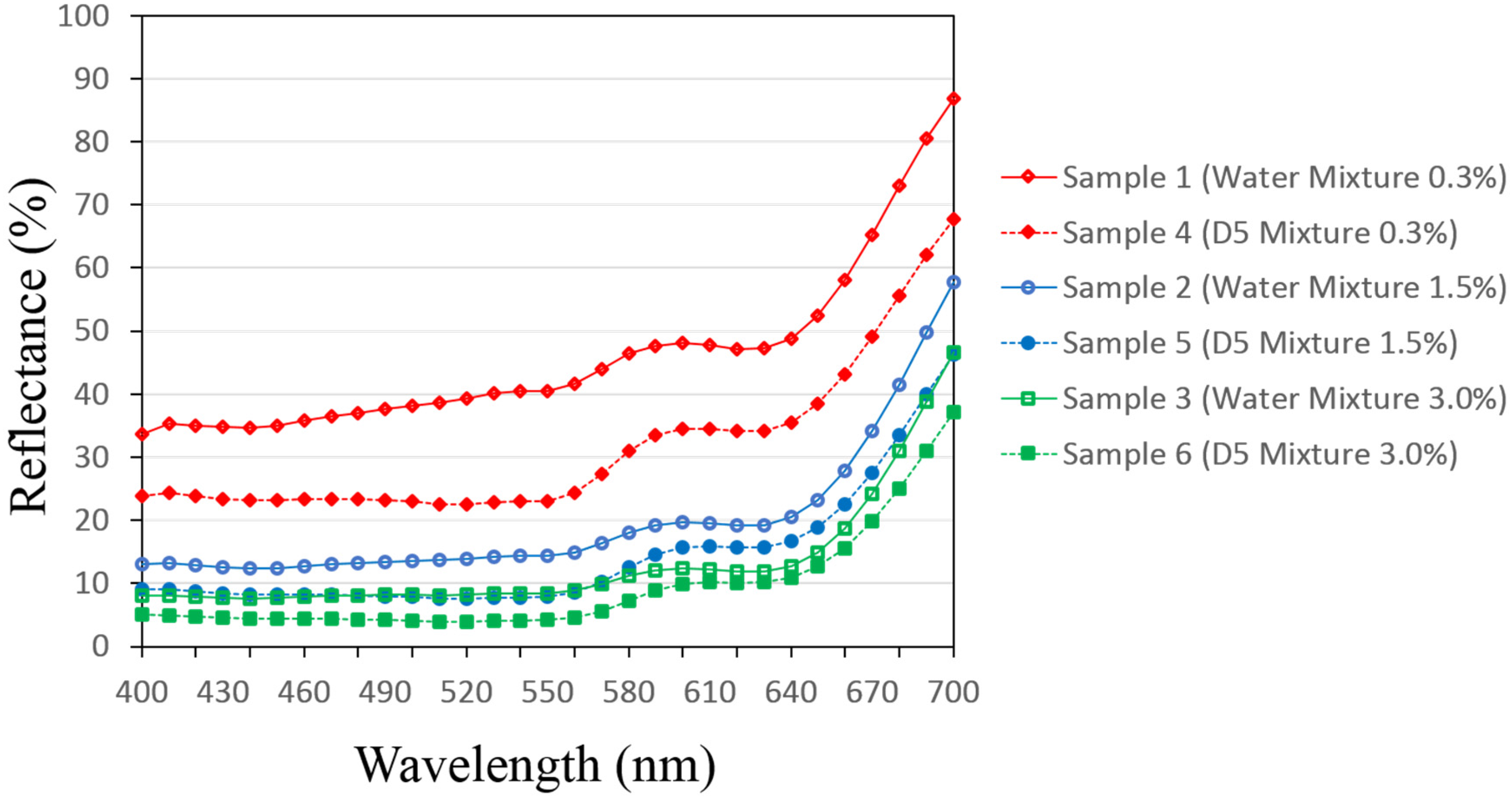
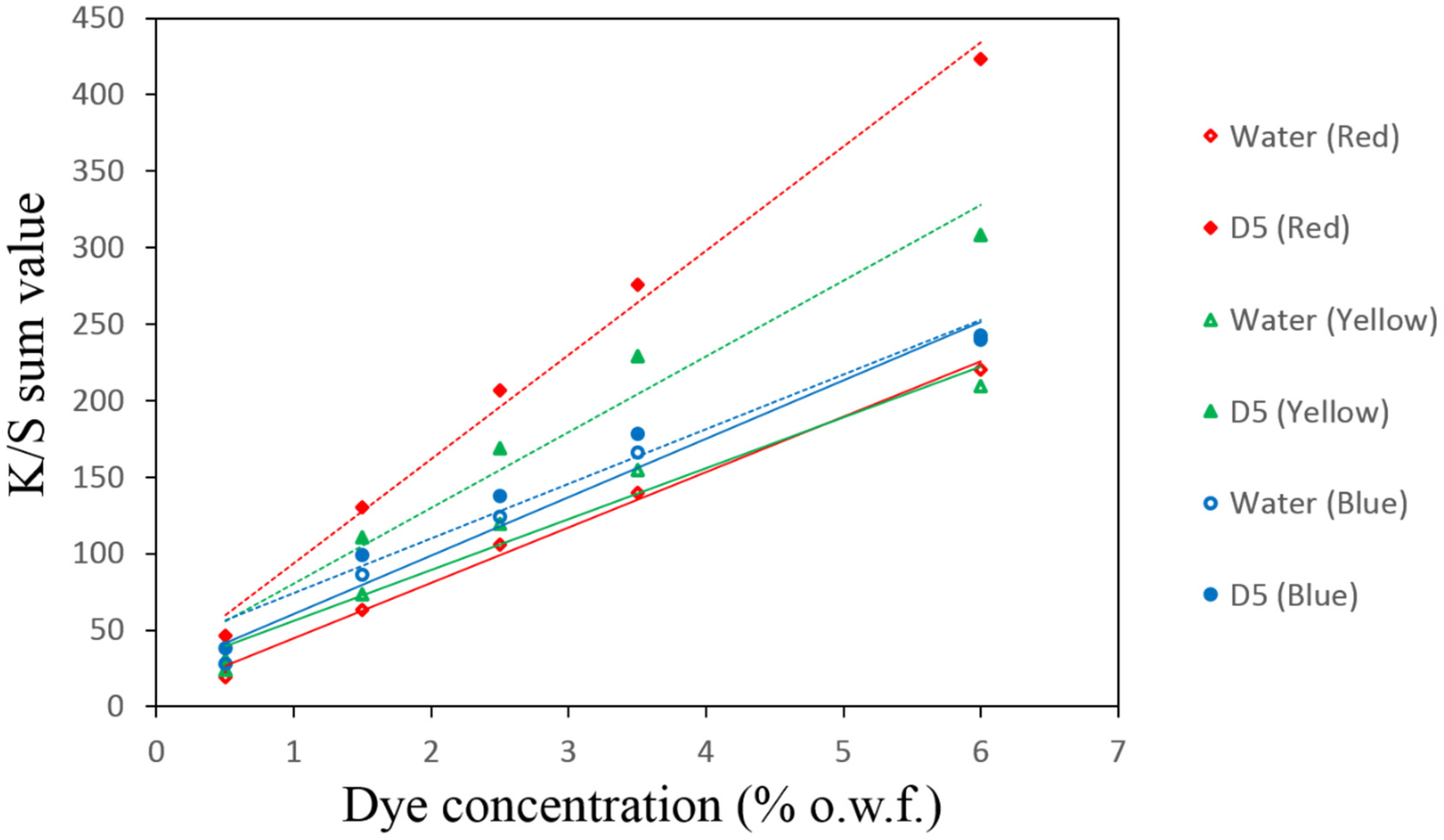
| Dye Conc. on Fabric (% owf) | Auxiliaries | |
|---|---|---|
| NaCl (g/L) | Na2CO3 (g/L) | |
| 0.5 | 20 | 5 |
| 1.5 | 42.5 | 5 |
| 2.5 | 55 | 5 |
| 3.5 | 65 | 5 |
| 6.0 | 80 | 5 |
| Dye Concentration (% owf) | Color Fixation Agent to Cotton Weight Ratio (g/g) |
|---|---|
| 0.5 | 0.060 |
| 1.5 | 0.080 |
| 2.5 | 0.085 |
| 3.5 | 0.090 |
| 6.0 | 0.115 |
| Dyeing Method | Sample | Red (%) | Yellow (%) | Blue (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional dyeing | Sample 1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Sample 2 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | |
| Sample 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Reverse micellar dyeing | Sample 4 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Sample 5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | |
| Sample 6 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| RUI | Visual Appearance of Levelness |
|---|---|
| <0.2 | Excellent levelness (unlevelness not detectable) |
| 0.2–0.49 | Good levelness (noticeable unlevelness under close examination) |
| 0.5–1.0 | Poor levelness (apparent unlevelness) |
| >1.0 | Bad levelness (conspicuous unlevelness) |
| Dyeing Method | R2 Value |
|---|---|
| Water (Red) | 0.9937 |
| Water (Yellow) | 0.9605 |
| Water (Blue) | 0.9829 |
| Heptane (Red) | 0.9933 |
| Heptane (Yellow) | 0.9596 |
| Heptane (Blue) | 0.9630 |
| Formulae | Color | Conventional Water-Based Dyeing | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 (0.3%) | Sample 2 (1.5%) | Sample 3 (3%) | ||
| Theoretical | Yellow | 0.10 | 0.50 | 1.00 |
| Blue | 0.10 | 0.50 | 1.00 | |
| Red | 0.10 | 0.50 | 1.00 | |
| CIEL*a*b* | Yellow | 0.12 | 0.62 | 1.10 |
| Blue | 0.08 | 0.50 | 0.96 | |
| Red | 0.07 | 0.44 | 0.86 | |
| CIEL*u*v* | Yellow | 0.12 | 0.62 | 1.10 |
| Blue | 0.08 | 0.50 | 0.96 | |
| Red | 0.07 | 0.44 | 0.86 | |
| ANLAB | Yellow | 0.12 | 0.62 | 1.10 |
| Blue | 0.08 | 0.50 | 0.96 | |
| Red | 0.07 | 0.44 | 0.86 | |
| Hunter lab | Yellow | 0.12 | 0.62 | 1.10 |
| Blue | 0.08 | 0.50 | 0.96 | |
| Red | 0.07 | 0.44 | 0.86 | |
| FMC2 | Yellow | 0.12 | 0.62 | 0.93 |
| Blue | 0.08 | 0.50 | 0.82 | |
| Red | 0.07 | 0.44 | 0.83 | |
| JPC79 | Yellow | 0.12 | 0.53 | 1.10 |
| Blue | 0.08 | 0.45 | 0.96 | |
| Red | 0.07 | 0.45 | 0.86 | |
| CMC 1.0 | Yellow | 0.12 | 0.62 | 1.10 |
| Blue | 0.08 | 0.50 | 0.96 | |
| Red | 0.07 | 0.44 | 0.86 | |
| BFD 1.0 | Yellow | 0.12 | 0.62 | 1.10 |
| Blue | 0.08 | 0.50 | 0.96 | |
| Red | 0.07 | 0.44 | 0.86 | |
| CIE94 1.0 | Yellow | 0.12 | 0.62 | 1.10 |
| Blue | 0.08 | 0.50 | 0.96 | |
| Red | 0.07 | 0.44 | 0.86 | |
| Formulae | Color | D5 Solvent-Assisted Dyeing | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 4 (0.3%) | Sample 5 (1.5%) | Sample 6 (3%) | ||
| Theoretical | Yellow | 0.10 | 0.50 | 1.00 |
| Blue | 0.10 | 0.50 | 1.00 | |
| Red | 0.10 | 0.50 | 1.00 | |
| CIEL*a*b* | Yellow | 0.15 | 0.60 | 1.33 |
| Blue | 0.13 | 0.46 | 1.11 | |
| Red | 0.11 | 0.49 | 1.24 | |
| CIEL*u*v* | Yellow | 0.15 | 0.60 | 1.15 |
| Blue | 0.13 | 0.46 | 0.86 | |
| Red | 0.11 | 0.49 | 1.07 | |
| ANLAB | Yellow | 0.15 | 0.60 | 1.33 |
| Blue | 0.13 | 0.46 | 1.11 | |
| Red | 0.11 | 0.49 | 1.24 | |
| Hunter lab | Yellow | 0.15 | 0.66 | 1.33 |
| Blue | 0.13 | 0.63 | 1.11 | |
| Red | 0.11 | 0.58 | 1.24 | |
| FMC2 | Yellow | 0.15 | 0.60 | 1.15 |
| Blue | 0.13 | 0.46 | 0.86 | |
| Red | 0.11 | 0.49 | 1.07 | |
| JPC79 | Yellow | 0.15 | 0.66 | 1.33 |
| Blue | 0.13 | 0.63 | 1.11 | |
| Red | 0.11 | 0.58 | 1.24 | |
| CMC 1.0 | Yellow | 0.15 | 0.60 | 1.33 |
| Blue | 0.13 | 0.46 | 1.11 | |
| Red | 0.11 | 0.49 | 1.24 | |
| BFD 1.0 | Yellow | 0.15 | 0.60 | 1.33 |
| Blue | 0.13 | 0.46 | 1.11 | |
| Red | 0.11 | 0.49 | 1.24 | |
| CIE94 1.0 | Yellow | 0.15 | 0.66 | 1.33 |
| Blue | 0.13 | 0.63 | 1.11 | |
| Red | 0.11 | 0.58 | 1.24 | |
| Formulae | Color | Water-Based Dyeing | D5 Solvent-Assisted Dyeing | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 (0.3%) | Sample 2 (1.5%) | Sample 3 (3%) | Sample 4 (0.3%) | Sample 5 (1.5%) | Sample 6 (3%) | ||
| CIEL*a*b* | Yellow | ↑0.02 | ↑0.12 | ↑0.10 | ↑0.05 | ↑0.10 | ↑0.33 |
| Blue | ↓0.02 | 0.00 | ↓0.04 | ↑0.03 | ↓0.04 | ↑0.11 | |
| Red | ↓0.03 | ↓0.06 | ↓0.14 | ↑0.01 | ↓0.01 | ↑0.24 | |
| CIEL*u*v* | Yellow | ↑0.02 | ↑0.12 | ↑0.10 | ↑0.05 | ↑0.10 | ↑0.15 |
| Blue | ↓0.02 | 0.00 | ↓0.04 | ↑0.03 | ↓0.04 | ↓0.14 | |
| Red | ↓0.03 | ↓0.06 | ↓0.14 | ↑0.01 | ↓0.01 | ↑0.07 | |
| ANLAB | Yellow | ↑0.02 | ↑0.12 | ↑0.10 | ↑0.05 | ↑0.10 | ↑0.33 |
| Blue | ↓0.02 | 0.00 | ↓0.04 | ↑0.03 | ↓0.04 | ↑0.11 | |
| Red | ↓0.03 | ↓0.06 | ↓0.14 | ↑0.01 | ↓0.01 | ↑0.24 | |
| Hunter lab | Yellow | ↑0.02 | ↑0.12 | ↑0.10 | ↑0.05 | ↑0.16 | ↑0.33 |
| Blue | ↓0.02 | 0.00 | ↓0.04 | ↑0.03 | ↑0.13 | ↑0.11 | |
| Red | ↓0.03 | ↓0.06 | ↓0.14 | ↑0.01 | ↑0.08 | ↑0.24 | |
| FMC2 | Yellow | ↑0.02 | ↑0.12 | ↑0.10 | ↑0.05 | ↑0.16 | ↑0.33 |
| Blue | ↓0.02 | 0.00 | ↓0.04 | ↑0.03 | ↑0.13 | ↑0.11 | |
| Red | ↓0.03 | ↓0.06 | ↓0.14 | ↑0.01 | ↑0.08 | ↑0.24 | |
| JPC79 | Yellow | ↑0.02 | ↑0.12 | ↓0.07 | ↑0.05 | ↑0.10 | ↑0.15 |
| Blue | ↓0.02 | 0.00 | ↓0.18 | ↑0.03 | ↓0.04 | ↓0.14 | |
| Red | ↓0.03 | ↓0.06 | ↓0.17 | ↑0.01 | ↓0.01 | ↑0.07 | |
| CMC 1.0 | Yellow | ↑0.02 | ↑0.12 | ↑0.10 | ↑0.05 | ↑0.16 | ↑0.33 |
| Blue | ↓0.02 | 0.00 | ↓0.04 | ↑0.03 | ↑0.13 | ↑0.11 | |
| Red | ↓0.03 | ↓0.06 | ↓0.14 | ↑0.01 | ↑0.08 | ↑0.24 | |
| BFD 1.0 | Yellow | ↑0.02 | ↑0.12 | ↑0.10 | ↑0.05 | ↑0.10 | ↑0.33 |
| Blue | ↓0.02 | 0.00 | ↓0.04 | ↑0.03 | ↓0.04 | ↑0.11 | |
| Red | ↓0.03 | ↓0.06 | ↓0.14 | ↑0.01 | ↓0.01 | ↑0.24 | |
| CIE94 1.0 | Yellow | ↑0.02 | ↑0.12 | ↑0.10 | ↑0.05 | ↑0.10 | ↑0.33 |
| Blue | ↓0.02 | 0.00 | ↓0.04 | ↑0.03 | ↓0.04 | ↑0.11 | |
| Red | ↓0.03 | ↓0.06 | ↓0.14 | ↑0.01 | ↓0.01 | ↑0.24 | |
| Formulae | Color | Water-Based Dyeing | Solvent-Assisted Dyeing | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 (0.3%) | Sample 2 (1.5%) | Sample 3 (3%) | Sample 4 (0.3%) | Sample 5 (1.5%) | Sample 6 (3%) | ||
| CIEL*a*b* | Yellow | ↑20.12 | ↑24.76 | ↑10.39 | ↑54.98 | ↑20.78 | ↑33.15 |
| Blue | ↓16.19 | ↑0.95 | ↓3.83 | ↑28.38 | ↓7.18 | ↑11.25 | |
| Red | ↓27.60 | ↓12.33 | ↓14.18 | ↑9.00 | ↓2.72 | ↑23.92 | |
| CIEL*u*v* | Yellow | ↑20.12 | ↑24.76 | ↑10.39 | ↑54.98 | ↑20.78 | ↑14.95 |
| Blue | ↓16.19 | ↑0.95 | ↓3.83 | ↑28.38 | ↓7.18 | ↓14.25 | |
| Red | ↓27.60 | ↓12.33 | ↓14.18 | ↑9.00 | ↓2.72 | ↑7.21 | |
| ANLAB | Yellow | ↑20.12 | ↑24.76 | ↑10.39 | ↑54.98 | ↑20.78 | ↑33.15 |
| Blue | ↓16.19 | ↑0.95 | ↓3.83 | ↑28.38 | ↓7.18 | ↑11.25 | |
| Red | ↓27.60 | ↓12.33 | ↓14.18 | ↑9.00 | ↓2.72 | ↑23.92 | |
| Hunter lab | Yellow | ↑20.12 | ↑24.76 | ↑10.39 | ↑54.98 | ↑32.30 | ↑33.15 |
| Blue | ↓16.19 | ↑0.95 | ↓3.83 | ↑28.38 | ↑26.37 | ↑11.25 | |
| Red | ↓27.60 | ↓12.33 | ↓14.18 | ↑9.00 | ↑15.71 | ↑23.92 | |
| FMC2 | Yellow | ↑20.12 | ↑24.76 | ↓6.92 | ↑54.98 | ↑20.78 | ↑14.95 |
| Blue | ↓16.19 | ↑0.95 | ↓18.11 | ↑28.38 | ↓7.18 | ↓14.25 | |
| Red | ↓27.60 | ↓12.33 | ↓16.95 | ↑9.00 | ↓2.72 | ↑7.21 | |
| JPC79 | Yellow | ↑20.12 | ↑5.66 | ↑10.39 | ↑54.98 | ↑32.30 | ↑33.15 |
| Blue | ↓16.19 | ↓9.34 | ↓3.83 | ↑28.38 | ↑26.37 | ↑11.25 | |
| Red | ↓27.60 | ↓10.52 | ↓14.18 | ↑9.00 | ↑15.71 | ↑23.92 | |
| CMC 1.0 | Yellow | ↑20.12 | ↑24.76 | ↑10.39 | ↑54.98 | ↑20.78 | ↑33.15 |
| Blue | ↓16.19 | ↑0.95 | ↓3.83 | ↑28.38 | ↓7.18 | ↑11.25 | |
| Red | ↓27.60 | ↓12.33 | ↓14.18 | ↑9.00 | ↓2.72 | ↑23.92 | |
| BFD 1.0 | Yellow | ↑20.12 | ↑24.76 | ↑10.39 | ↑54.98 | ↑20.78 | ↑33.15 |
| Blue | ↓16.19 | ↑0.95 | ↓3.83 | ↑28.38 | ↓7.18 | ↑11.25 | |
| Red | ↓27.60 | ↓12.33 | ↓14.18 | ↑9.00 | ↓2.72 | ↑23.92 | |
| CIE94 1.0 | Yellow | ↑20.12 | ↑24.76 | ↑10.39 | ↑54.98 | ↑32.30 | ↑33.15 |
| Blue | ↓16.19 | ↑0.95 | ↓3.83 | ↑28.38 | ↑26.37 | ↑11.25 | |
| Red | ↓27.60 | ↓12.33 | ↓14.18 | ↑9.00 | ↑15.71 | ↑23.92 | |
| Sample | Water | Solvent | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RUI | Visual Assessment | RUI | Visual Assessment | |
| Red 0.1% | 0.17 | Excellent | 0.19 | Excellent |
| Red 0.5% | 0.34 | Good | 0.10 | Excellent |
| Red 1.5% | 0.24 | Good | 0.23 | Good |
| Red 2.5% | 0.33 | Good | 0.13 | Excellent |
| Red 3.5% | 0.16 | Excellent | 0.18 | Excellent |
| Yellow 0.1% | 0.03 | Excellent | 0.30 | Good |
| Yellow 0.5% | 0.08 | Excellent | 0.22 | Good |
| Yellow 1.5% | 0.01 | Excellent | 0.37 | Good |
| Yellow 2.5% | 0.06 | Excellent | 0.31 | Good |
| Yellow 3.5% | 0.15 | Excellent | 0.11 | Excellent |
| Blue 0.1% | 0.14 | Excellent | 0.05 | Excellent |
| Blue 0.5% | 0.04 | Excellent | 0.30 | Good |
| Blue 1.5% | 0.03 | Excellent | 0.05 | Excellent |
| Blue 2.5% | 0.09 | Excellent | 0.30 | Good |
| Blue 3.5% | 0.17 | Excellent | 0.40 | Good |
| Mixture 0.3% | 0.02 | Excellent | 0.20 | Good |
| Mixture 1.5% | 0.08 | Excellent | 0.29 | Good |
| Mixture 3.0% | 0.09 | Excellent | 0.18 | Excellent |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, A.Y.L.; Wang, Y.M.; Lee, C.H.; Kan, C.-W. Computer Color Matching and Levelness of PEG-Based Reverse Micellar Decamethyl cyclopentasiloxane (D5) Solvent-Assisted Reactive Dyeing on Cotton Fiber. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7070682
Tang AYL, Wang YM, Lee CH, Kan C-W. Computer Color Matching and Levelness of PEG-Based Reverse Micellar Decamethyl cyclopentasiloxane (D5) Solvent-Assisted Reactive Dyeing on Cotton Fiber. Applied Sciences. 2017; 7(7):682. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7070682
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Alan Y. L., Yan Ming Wang, Chang Hao Lee, and Chi-Wai Kan. 2017. "Computer Color Matching and Levelness of PEG-Based Reverse Micellar Decamethyl cyclopentasiloxane (D5) Solvent-Assisted Reactive Dyeing on Cotton Fiber" Applied Sciences 7, no. 7: 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7070682
APA StyleTang, A. Y. L., Wang, Y. M., Lee, C. H., & Kan, C.-W. (2017). Computer Color Matching and Levelness of PEG-Based Reverse Micellar Decamethyl cyclopentasiloxane (D5) Solvent-Assisted Reactive Dyeing on Cotton Fiber. Applied Sciences, 7(7), 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7070682







