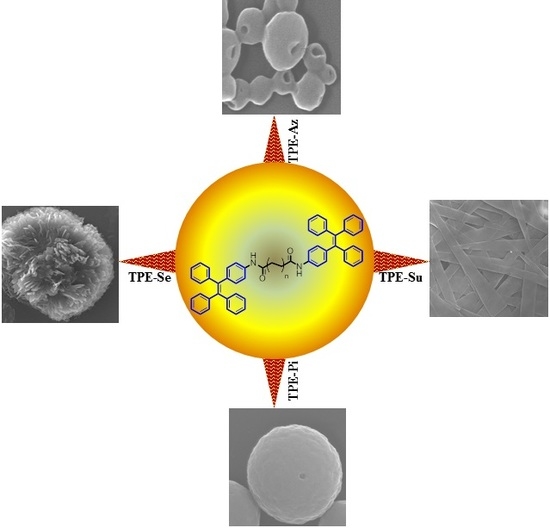
Influence of Odd and Even Alkyl Chains on Supramolecular Nanoarchitecture via Self-Assembly of Tetraphenylethylene-Based AIEgens
Abstract
:1. Introduction
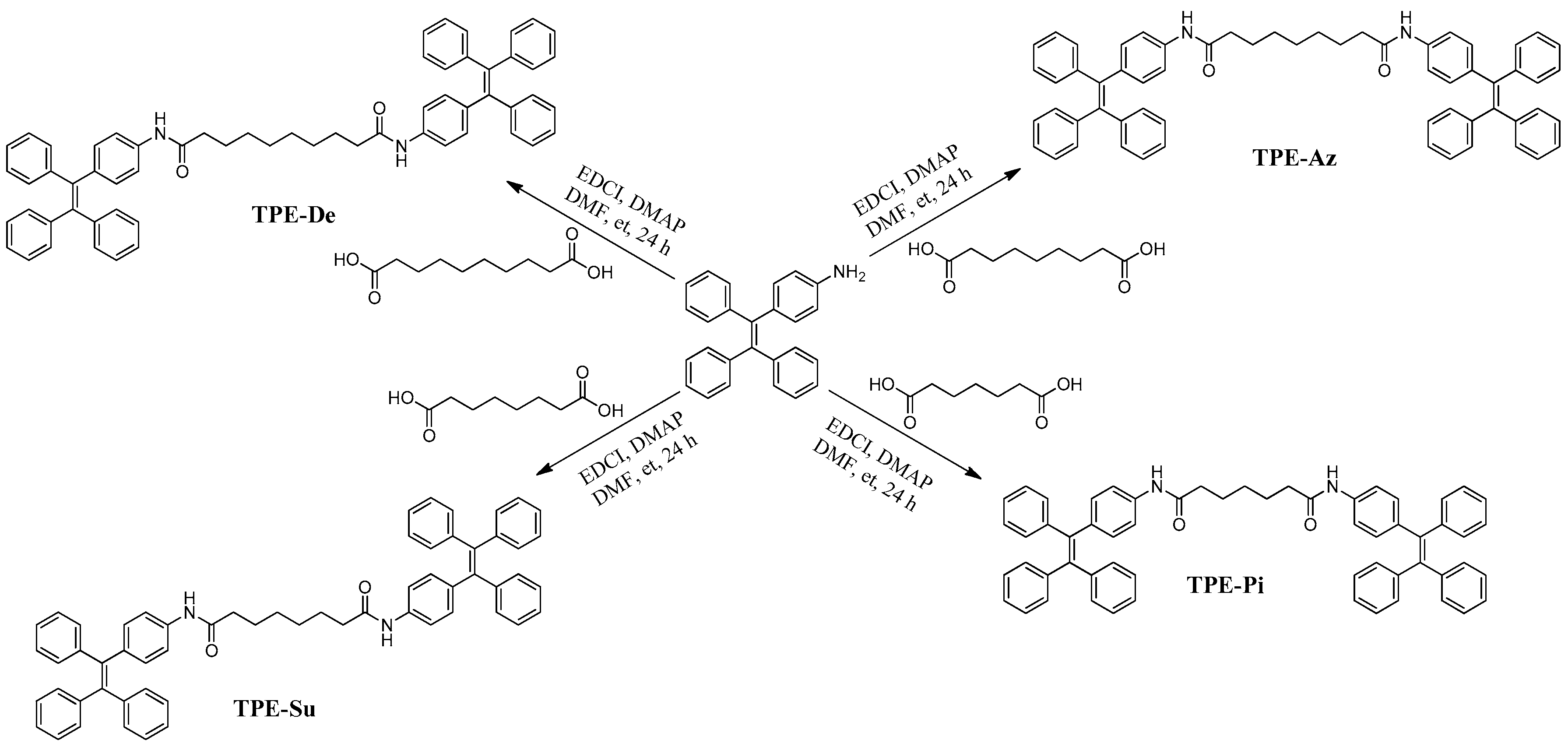
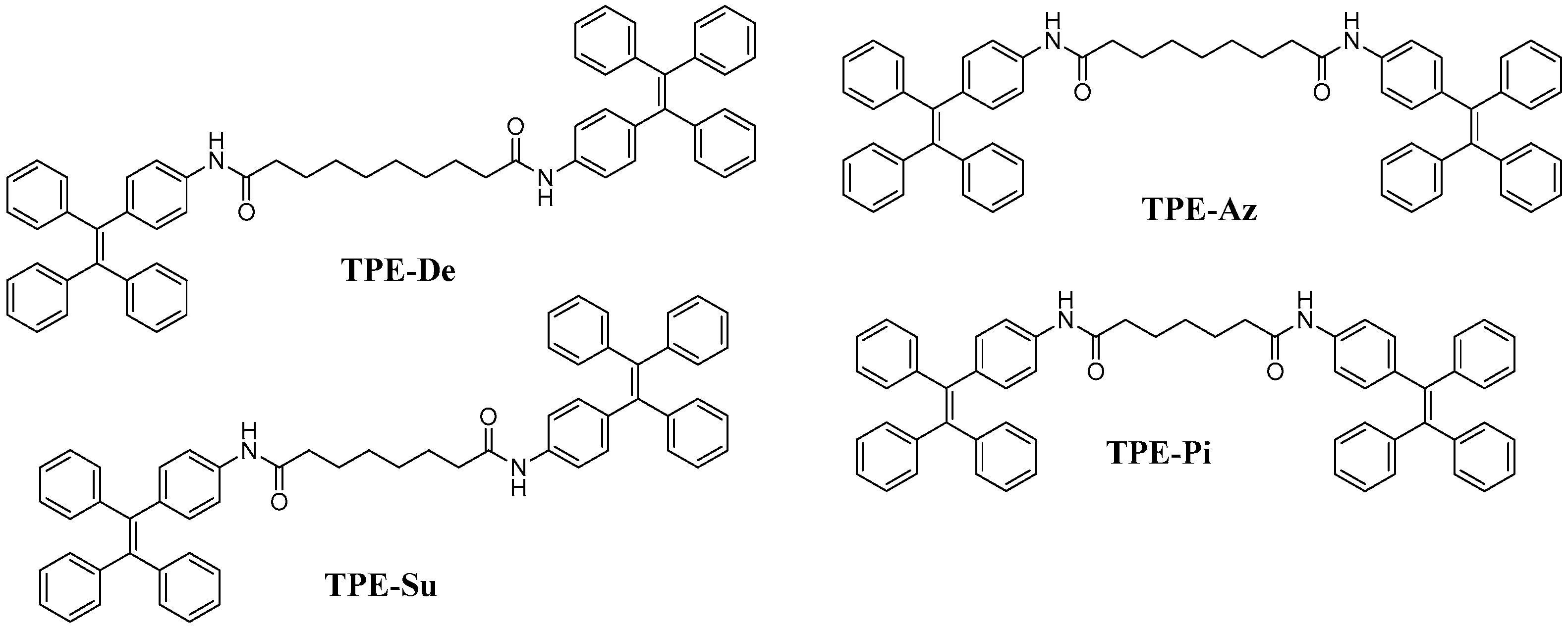
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Spectroscopic Measurements
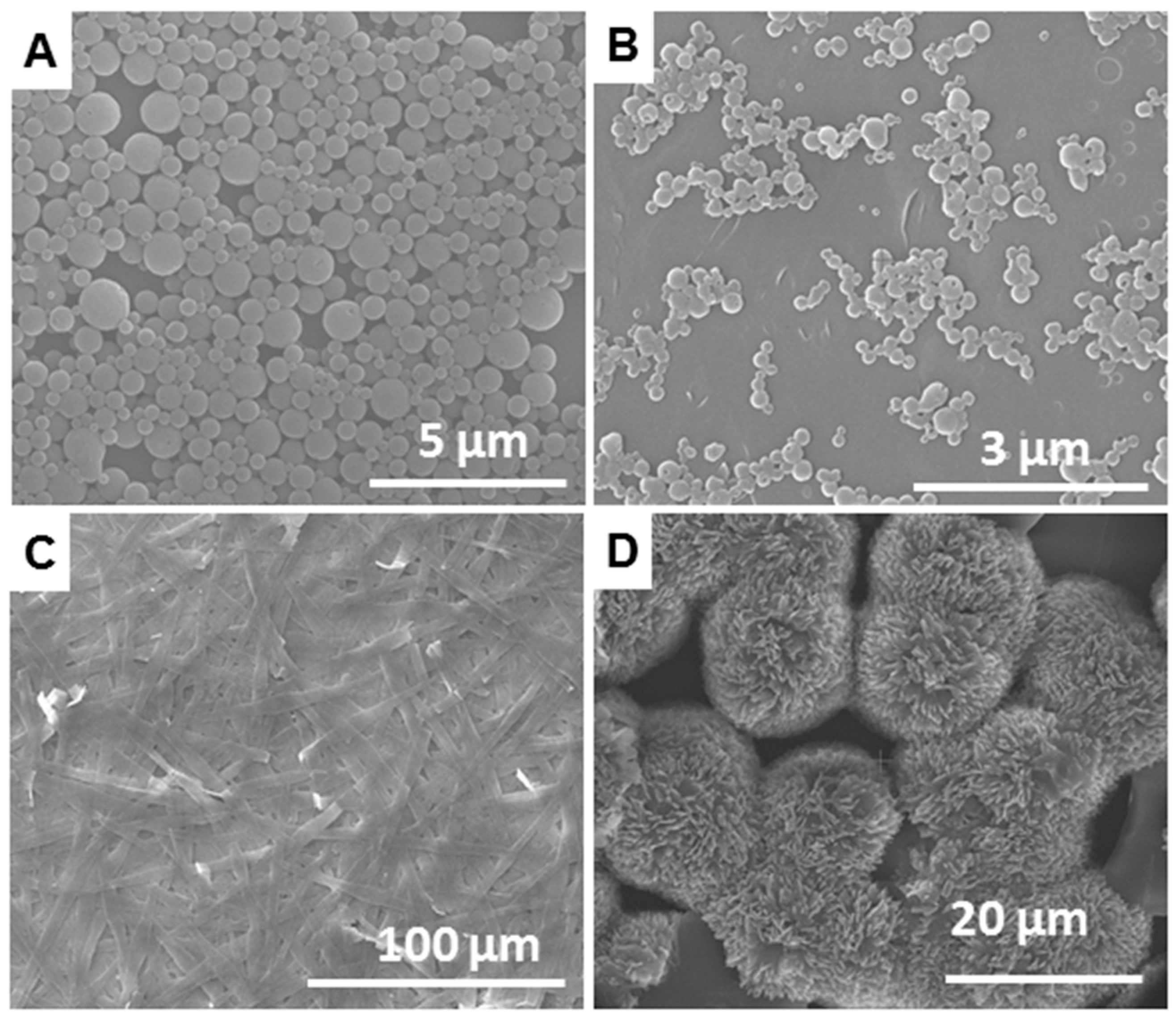
2.3. SEM Imaging
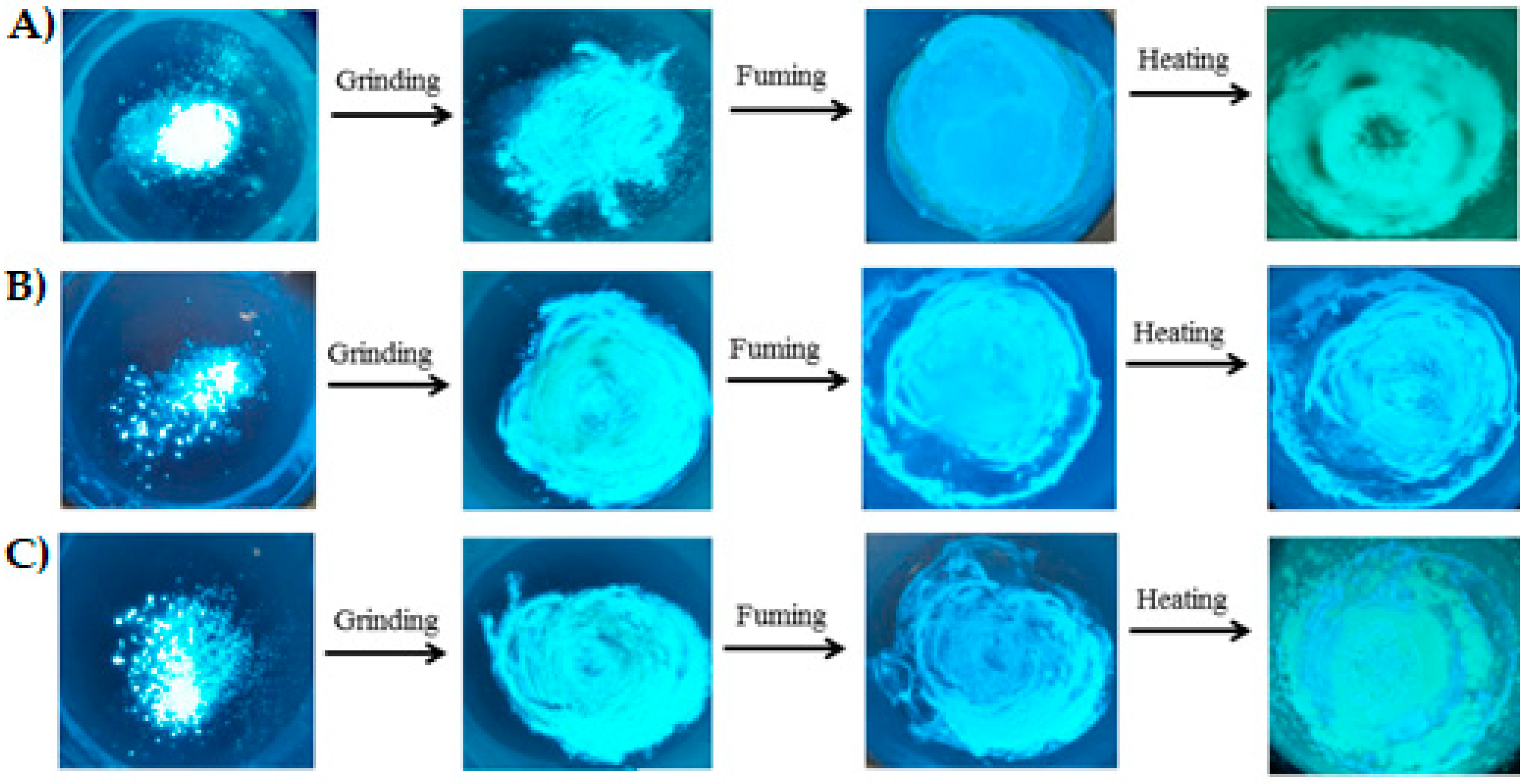
2.4. Mechanochromism Study
3. Results
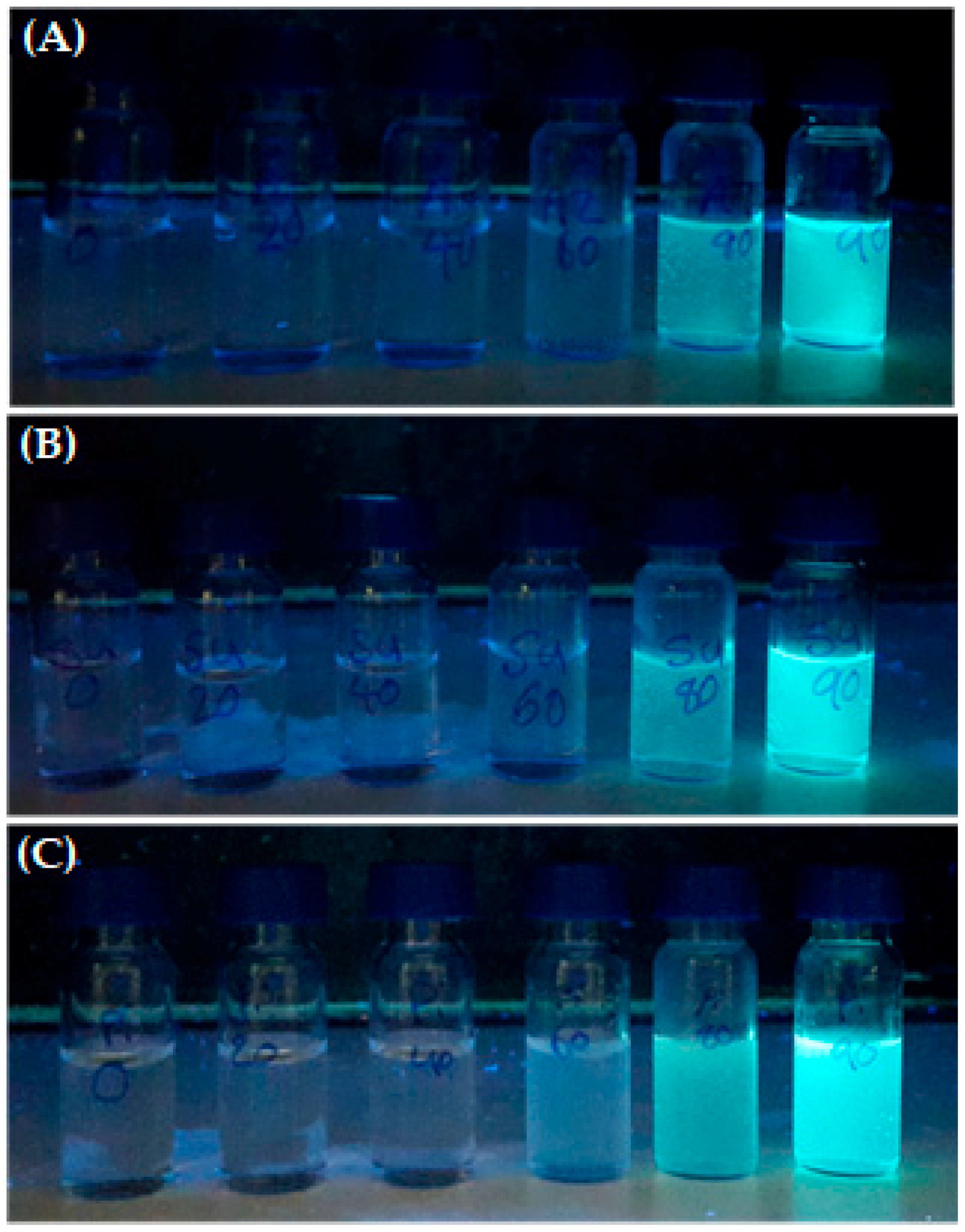
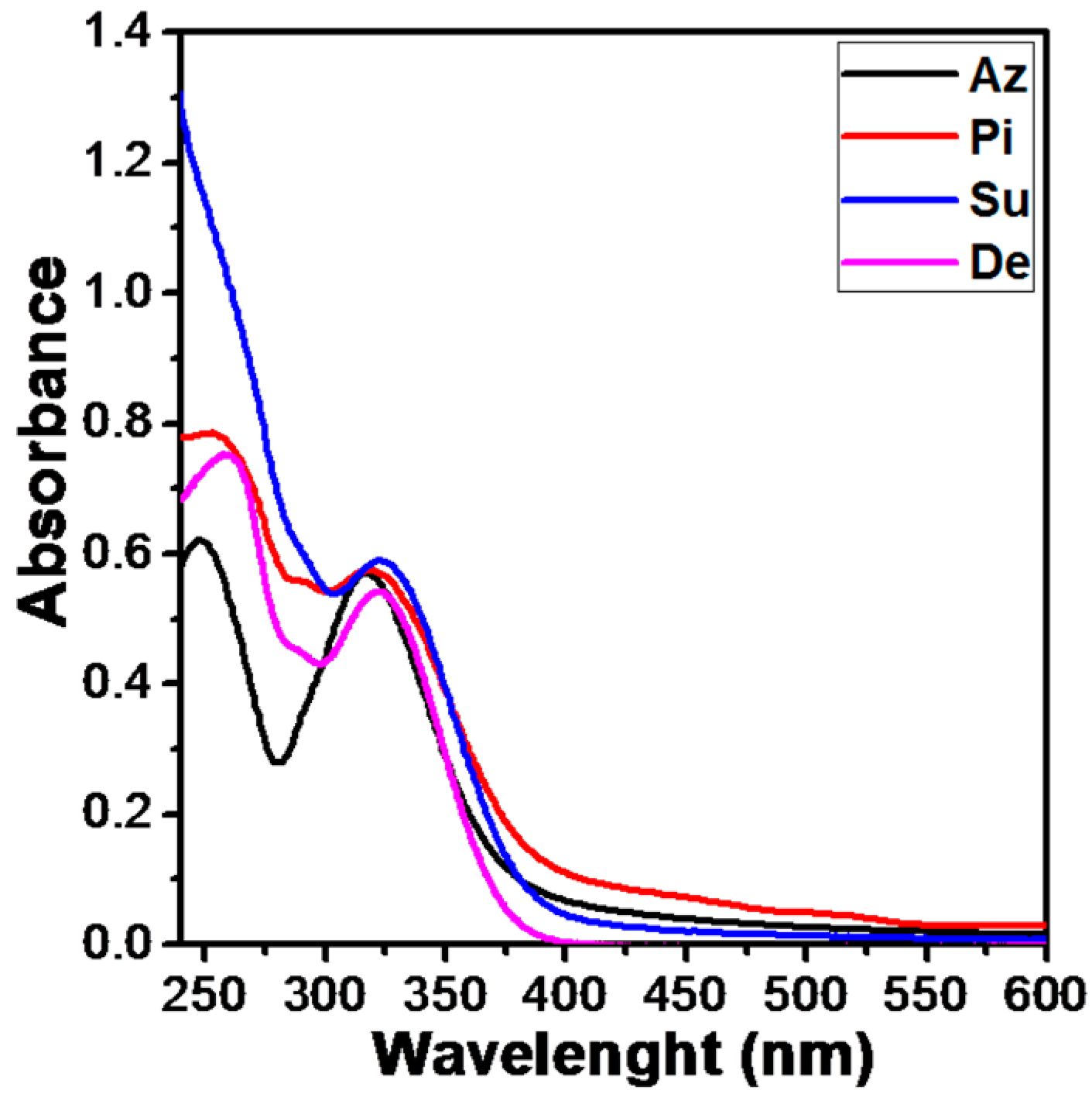
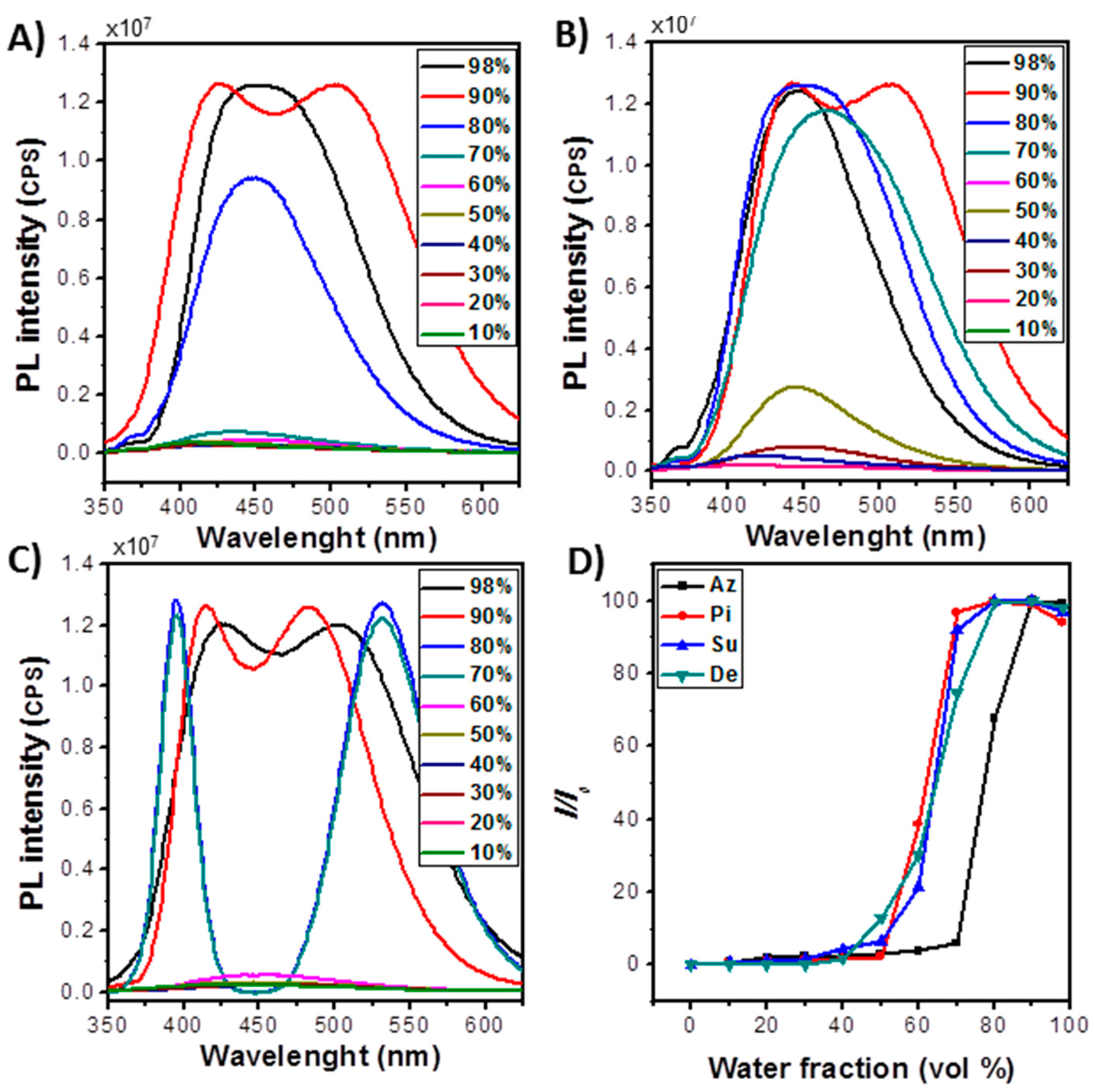
UV-Vis Absorption and Fluorescence Properties
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lehn, J.M. Supramolecular Chemistry: Concepts and Perspectives; VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Zang, L.; Che, Y.; Moore, J.S. One-dimensional self-assembly of planar π-conjugated molecules: Adaptable building blocks for organic nanodevices. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 1596–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaeser, A.; Schenning, A.P.H.J. Fluorescent nanoparticles based on self-assembled π-conjugated systems. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 2985–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.S.; Fu, H.; Peng, A.; Ma, Y.; Liao, Q.; Yao, J. Construction and optoelectronic properties of organic one-dimensional nanostructures. Acc. Chem. Res. 2010, 43, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakrabarty, R.; Mukherjee, P.S.; Stang, P.J. Supramolecular coordination: Self-assembly of finite two-and three-dimensional ensembles. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 6810–6918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magginia, L.; Bonifazi, D. Hierarchised luminescent organic architectures: Design, synthesis, self-assembly, self-organisation and functions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 211–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, C.; Zhang, J.; Chen, M.; Yang, Z. Self-assembling small molecules for the detection of important analytes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 7257–7266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, S.S.; Praveen, V.K.; Ajayaghosh, A. Functional π-gelators and their applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 1973–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birks, J.B. Photophysics of Aromatic Molecules; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, J.; Xie, Z.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Cheng, L.; Chen, H.; Qiu, C.; Kwok, H.S.; Zhan, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, D.; et al. Aggregation-induced emission of 1-methyl-1,2,3,4,5-pentaphenylsilole. Chem. Commun. 2001, 18, 1740–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, J.; Hong, Y.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Qin, A.; Tang, Y.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-induced emission: The whole is more brilliant than the parts. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5429–5479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-induced emission: Phenomenon, mechanism and applications. Chem. Commun. 2009, 29, 4332–4353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-induced emission. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 5361–5388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Mei, J.; Chen, S.; Lu, P.; Qin, A.; Ma, Y.; Sun, J.Z.; Tang, B.Z. Tetraphenylethenyl-modified perylenebisimide: Aggregation-induced red emission, electrochemical properties and ordered microstructures. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 7387–7394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.Y.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhao, E.; Yuan, W.Z.; Liu, Y.; Lu, P.; Qin, A.; Ma, Y.; Sun, J.Z.; Tang, B.Z. Effects of substitution with donor–acceptor groups on the properties of tetraphenylethene trimer: Aggregation-induced emission, solvatochromism, and mechanochromism. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 7334–7347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rananaware, A.; Bhosale, R.S.; Ohkubo, K.; Patil, H.; Jones, L.A.; Jackson, S.L.; Fukuzumi, S.; Bhosale, S.V.; Bhosale, S.V. Tetraphenylethene-Based Star Shaped Porphyrins: Synthesis, Self-assembly, and Optical and Photophysical Study. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 3832–3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, H.-T.; Song, S.; Chen, Y.-C.; Shen, C.-H.; Zheng, Y.-S. Self-assembled tetraphenylethylene macrocycle nanofibrous materials for the visual detection of copper(II) in water. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 2353–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, C.; Zhao, L.; Fang, T.; Deng, X.; Ma, H.; Zhang, J.; Na, N.; Han, J.; Ouyang, J. Color- and morphology-controlled self-assembly of new electron-donor-substituted aggregation-induced emission compounds. Langmuir 2014, 30, 2351–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.; Cho, S.J.; Norikane, Y.; Shimizu, M.; Kimura, A.; Tamagawa, T.; Seki, T. Multistimuli-responsive azobenzene nanofibers with aggregation-induced emission enhancement characteristics. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 15815–15818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Zheng, H.-F.; Feng, H.-T.; Zheng, Y.-S. Microtubes and hollow microspheres formed by winding of nanoribbons from self-assembly of tetraphenylethylene amide macrocycles. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 15212–15215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Su, H.; Meng, L.; Zhao, Y.; Deng, C.; Ng, J.C.Y.; Lu, P.; Faisal, M.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Huang, X.; et al. What makes efficient circularly polarised luminescence in the condensed phase: Aggregation-induced circular dichroism and light emission. Chem. Sci. 2012, 3, 2737–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La, D.D.; Bhosale, S.V.; Jones, L.A.; Bhosale, S.V. Tetraphenylethylene-based AIE-Active Probes for Sensing Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rananaware, A.; La, D.D.; Jackson, S.M.; Bhosale, S.V. Construction of a highly efficient near-IR solid emitter based on naphthalene diimide with AIE-active tetraphenylethene periphery. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 16250–16255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zheng, X.; Su, H.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Wong, K.S.; Xue, S.; Huang, X.; Huang, X.; Li, B.S.; Tang, B.Z. Synthesis, optical properties, and helical self-assembly of a bivaline-containing tetraphenylethene. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anuradha, A.; La, D.D.; Al Kobaisi, M.; Bhosale, S.V. Right handed chiral superstructures from achiral molecules: Self-assembly with a twist. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15652. [Google Scholar]
- Rananaware, A.; Bhosale, R.S.; Patil, H.; Al Kobaisi, M.; Abraham, A.; Shukla, R.; Bhosale, S.V.; Bhosale, S.V. Precise aggregation-induced emission enhancement via H+ sensing and its use in ratiometric detection of intracellular pH values. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 59078–59082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Qin, A.; Liu, J.; Li, Z.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-induced emissions of tetraphenylethene derivatives and their utilities as chemical vapour sensors and in organic light-emitting diodes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 011111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La, D.D.; Anuradha, A.; Kaur Hundal, A.; Jones, L.A.; Bhosale, S.V. pH-Dependent self-assembly of water-soluble sulphonate-tetraphenylethylene with aggregation-induced emission. Supramol. Chem. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, J.; Leung, N.L.; Kwok, R.T.; Lam, J.W.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-induced emission: Together we shine, united we soar. Chem. Rev. 2015, 21, 11718–11940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Qin, A.; Tang, B.Z. Axial chiral aggregation-induced emission luminogens with aggregation-annihilated circular dichroism effect. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 5162–5166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jiao, J.; Jiang, X.; Li, J.; Cheng, Y.; Zhu, C. A tetraphenylethene-based chiral polymer: An AIE luminogen with high and tunable CPL dissymmetry factor. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 4713–4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Lam, J.W.; Tang, B.Z. Tetraphenylethene: A versatile AIE building block for the construction of efficient luminescent materials for organic light-emitting diodes. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 23726–23740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rananaware, A.; Gupta, A.; Lo, J.; Bilic, A.; Jones, L.; Bhargava, S.; Bhosale, S.V. A four-directional non-fullerene acceptor based on tetraphenylethylene and diketopyrrolopyrrole functionalities for efficient photovoltaic devices with a high open-circuit voltage of 1.18 V. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 8522–8525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salimimarand, M.; La, D.D.; Al Kobaisi, M.; Bhosale, S.V. Flower-like superstructures of AIE-active tetraphenylethylene through solvophobic controlled self-assembly. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salimimarand, M.; La, D.D.; Bhosale, S.V.; Jones, L.A.; Bhosale, S.V. Influence of Odd and Even Alkyl Chains on Supramolecular Nanoarchitecture via Self-Assembly of Tetraphenylethylene-Based AIEgens. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1119. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7111119
Salimimarand M, La DD, Bhosale SV, Jones LA, Bhosale SV. Influence of Odd and Even Alkyl Chains on Supramolecular Nanoarchitecture via Self-Assembly of Tetraphenylethylene-Based AIEgens. Applied Sciences. 2017; 7(11):1119. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7111119
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalimimarand, Mina, Duong Duc La, Sidhanath V. Bhosale, Lathe A. Jones, and Sheshanath V. Bhosale. 2017. "Influence of Odd and Even Alkyl Chains on Supramolecular Nanoarchitecture via Self-Assembly of Tetraphenylethylene-Based AIEgens" Applied Sciences 7, no. 11: 1119. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7111119
APA StyleSalimimarand, M., La, D. D., Bhosale, S. V., Jones, L. A., & Bhosale, S. V. (2017). Influence of Odd and Even Alkyl Chains on Supramolecular Nanoarchitecture via Self-Assembly of Tetraphenylethylene-Based AIEgens. Applied Sciences, 7(11), 1119. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7111119