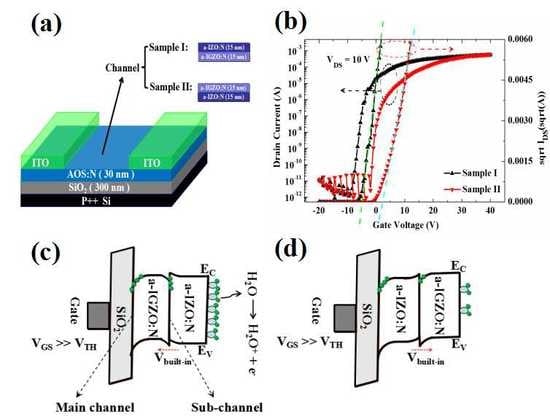
Amorphous Oxide Thin Film Transistors with Nitrogen-Doped Hetero-Structure Channel Layers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
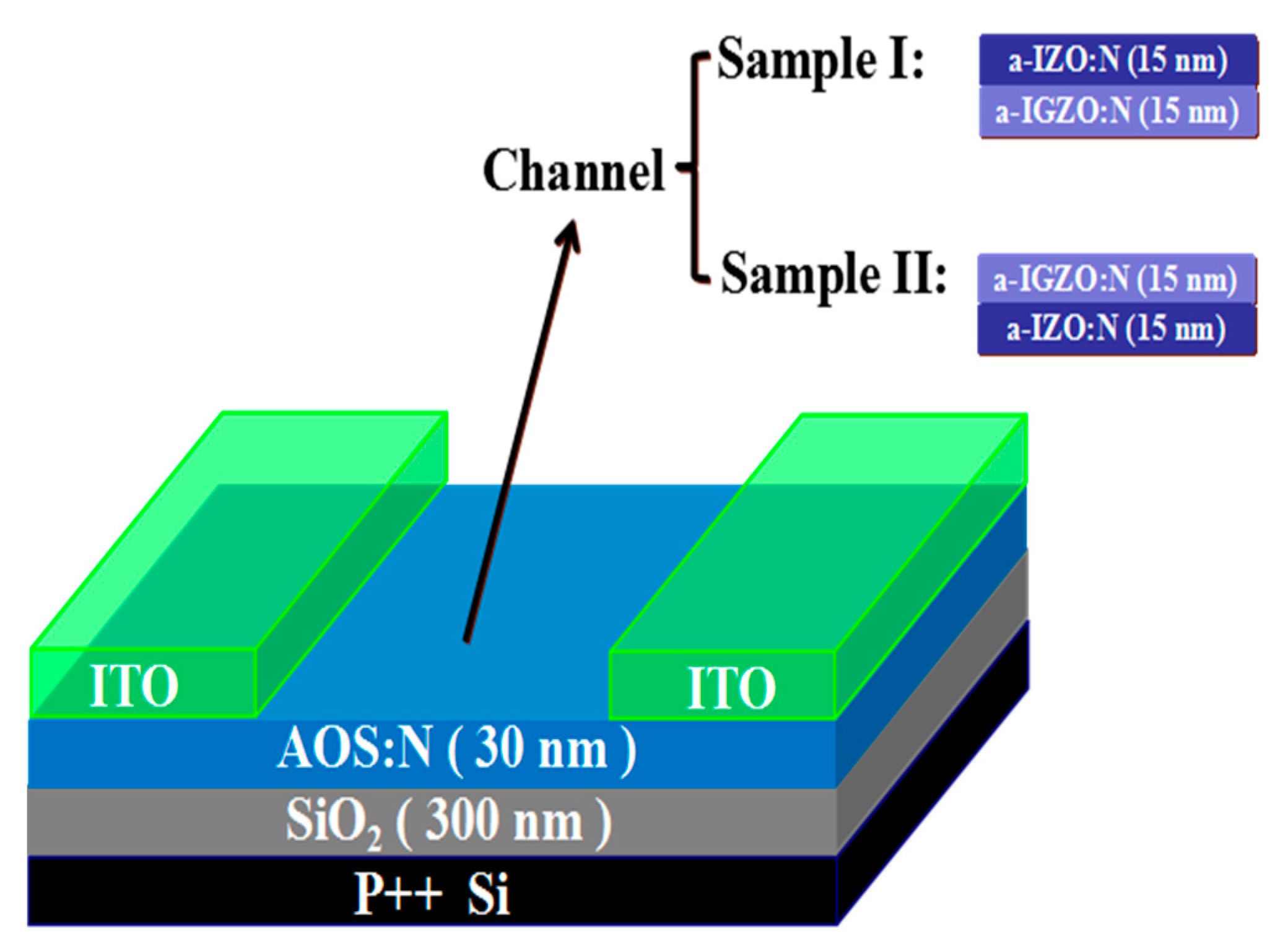
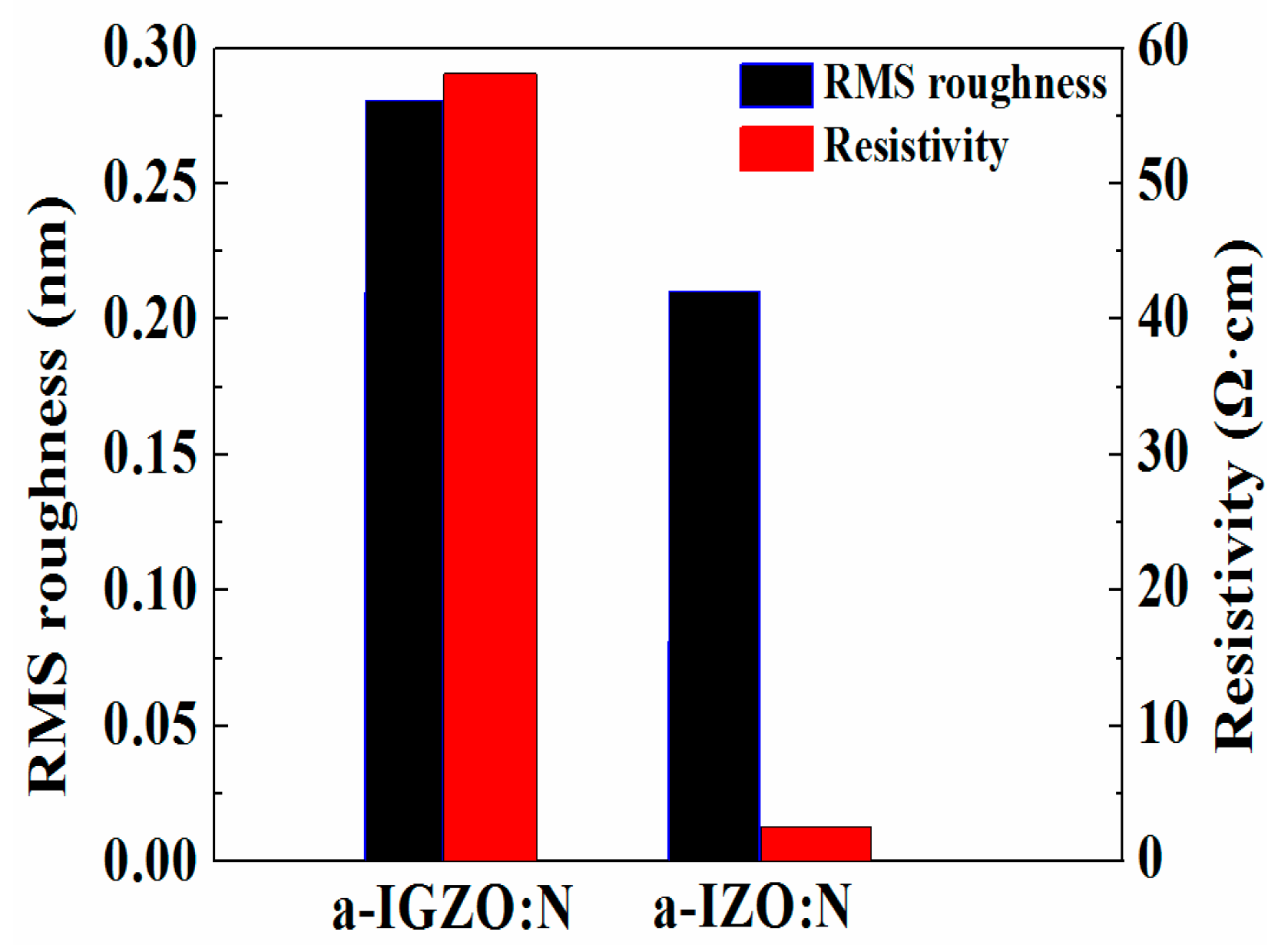
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nomura, K.; Ohta, H.; Takagi, A.; Kamiya, T.; Hirano, M.; Hosono, H. Room-temperature fabrication of transparent flexible thin-film transistors using amorphous oxide semiconductors. Nature 2004, 432, 488–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, K.; Kamiya, T.; Ikenaga, E.; Yanagi, H.; Kobayashi, K.; Hosono, H. Depth analysis of sub-gap electronic states in amorphous oxide semiconductor, a-In-Ga-Zn-O, studied by hard x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 109, 073726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Chang, S.; Koo, S.M.; Lee, S.Y. High-performance a-IGZO TFT with ZrO2 gate dielectric fabricated at room temperature. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2010, 31, 225–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.L.; Ren, F.; Lim, W.; Norton, D.P.; Pearton, S.J.; Kravchenko, I.I.; Zavada, J.M. Room temperature deposited indium zinc oxide thin film transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 90, 232103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunato, E.; Barquinha, P.; Goncalves, G.; Pereira, L.; Martins, R. High mobility and low threshold voltage transparent thin film transistors based on amorphous indium zinc oxide semiconductors. Solid-State Electron. 2008, 90, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, T.; Sasaoka, T. Emergent oxide TFT technologies for next-generation AM-OLED displays. SID Symp. Dig. Tech. Papers 2011, 42, 710–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.C.; Wu, C.H.; Ting, W.C. Stability improvement of amorphous InGaZnO TFTs by an asymmetric design. Electron. Lett. 2015, 51, 1534–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.H.; Lee, C.T. Stability of Indium Gallium Zinc Aluminum oxide thin-film transistors with treatment processes. J. Electron. Mater. 2017, 46, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mativenga, M.; Li, X.; Um, J.; Geng, D.; Jin, S.; Jang, J. Highly-stable and transparent oxide TFTs for rollable displays. Symp. Dig. Tech. Papers 2015, 46, 883–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.T.; Chou, Y.T.; Teng, L.F.; Li, F.H.; Shieh, H.P. Nitrogenated amorphous InGaZnO thin film transistor. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 052102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Yan, H.; Tsai, Y.C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Shieh, H.P.D. Influences of nitrogen doping on the electrical characteristics of Indium-Zinc-Oxide thin film transistors. IEEE Trans. Dev. Mater. Reliab. 2016, 16, 642–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, J.; Jang, K.; Balaji, N.; Choi, W.; Trinh, T.T.; Yi, J. Negative gate-bias temperature stability of N-doped InGaZnO active-layer thin-film transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 083505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Xu, J.; Liu, G.; Zhang, L.; Dong, C. Development and analysis of nitrogen-doped amorphous InGaZnO thin film transistors. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2017, 64, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, J.J.; Aguilar-Frutis, M.A.; Alarcón, G.; Falcony, C.; Méndez-Garcíab, V.H.; Araiza, J.J. Band gap engineering of indium zinc oxide by nitrogen incorporation. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2014, 187, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, A.S.J.; Kwon, S.J.; Kim, H.; Park, J.S. High performance thin film transistor with low temperature atomic layer deposition nitrogen-doped ZnO. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 183513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, B.; Noh, H.K.; Choi, E.A.; Chang, K.J. O-vacancy as the origin of negative bias illumination stress instability in amorphous In–Ga–Zn–O thin film transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 022108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, R.; Dong, C.; Yang, B.R.; Shieh, H.P.D. Modulation of interface and bulk states in amorphous InGaZnO thin-film transistors with double stacked channel layers. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 52, 090205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, R.; Dong, C.; Liu, P.T.; Shieh, H.P.D. Influence of channel layer and passivation layer on the stability of amorphous InGaZnO thin film transistors. Microelectron. Reliab. 2013, 53, 1879–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, E.; Lee, S.Y. Influence of a highly doped buried layer for HfInZnO thin-film transistors. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2011, 27, 012001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.; Ahn, S.E.; Song, I.; Jeon, Y.; Kim, Y.; Kim, S.; Choi, H.; Kim, H.; Lee, E.; Lee, S.; et al. Dual gate photo-thin film transistor with high photoconductive gain for high reliability, and low noise flat panel transparent imager. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), Washington, DC, USA, 5–7 December 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.C.; Lee, H.N. Improvement of the performance and stability of oxide semiconductor thin-film transistors using double-stacked active layers. IEEE Electron Dev. Lett. 2012, 33, 818–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Nathan, A.; Robertson, J. Challenges in visible wavelength detection using optically transparent oxide semiconductors. IEEE Sens. 2012, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Jeon, S.; Robertson, J.; Nathan, A. How to achieve ultra high photoconductive gain for transparent oxide semiconductor image sensors. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), San Francisco, CA, USA, 10–13 December 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Wu, Q.; Xu, L.; Xu, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, G.; Dong, C. Amorphous oxide thin film transistors with nitrogen-doped active layers. SID Symp. Dig. Tech. Papers 2016, 47, 1033–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Wu, Q.; Xu, L.; Zhang, L.; Liu, G.; Dong, C. Nitrogen-doped amorphous oxide semiconductor thin film transistors with double-stacked channel layers. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 387, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, B.; Ha, Y.G.; Moon, J.; Facchetti, A.; Marks, T.J. Role of gallium doping in dramatically lowering amorphous-oxide processing temperatures for solution-derived indium zinc oxide thin-film transistors. Adv. Mater. 2009, 22, 1346–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, H.B.; Li, Y.; Wee, A.T.S. An XPS investigation of the oxidation/corrosion of melt-spun Mg. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2000, 158, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frangini, S.; Giorgi, R.; Lascovich, J.; Mignone, A. XPS study of passive films formed ion an iron-aluminium intermetallic compound in acid solution. Surf. Interface Anal. 1994, 21, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Dong, C.; Zhou, D.; Chen, Y.; Wu, J.; Xie, H.; Chiang, C.L.; Chen, P.L.; Lai, T.C.; Lo, C.C.; et al. Thermal stability of amorphous InGaZnO thin-film transistors with different oxygen-contained active layers. IEEE J. Disp. Technol. 2015, 11, 610–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaglioglu, B.; Yeom, H.Y.; Beresford, R.; Paine, D.C. High-mobility amorphous In2O3–10 wt % ZnO thin film transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 062103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, A.; Abe, K.; Hayashi, R.; Kumomi, H.; Nomura, K.; Kamiya, T.; Hirano, M.; Hosono, H. Amorphous In–Ga–Zn–O coplanar homojunction thin-film transistor. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 133502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Jeong, J.K.; Chung, H.J.; Mo, Y.G.; Kim, H.D. Electronic transport properties of amorphous indium-gallium-zinc oxide semiconductor upon exposure to water. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 072104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.T.; Chou, Y.T.; Teng, L.F. Environment-dependent metastability of passivation-free indium zinc oxide thin film transistor after gate bias stress. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 95, 233504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, J.; Jang, K.; Balaji, N.; Yi, J. Suppression of temperature instability in InGaZnO thin-film transistors by in situ nitrogen doping. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2013, 28, 115010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

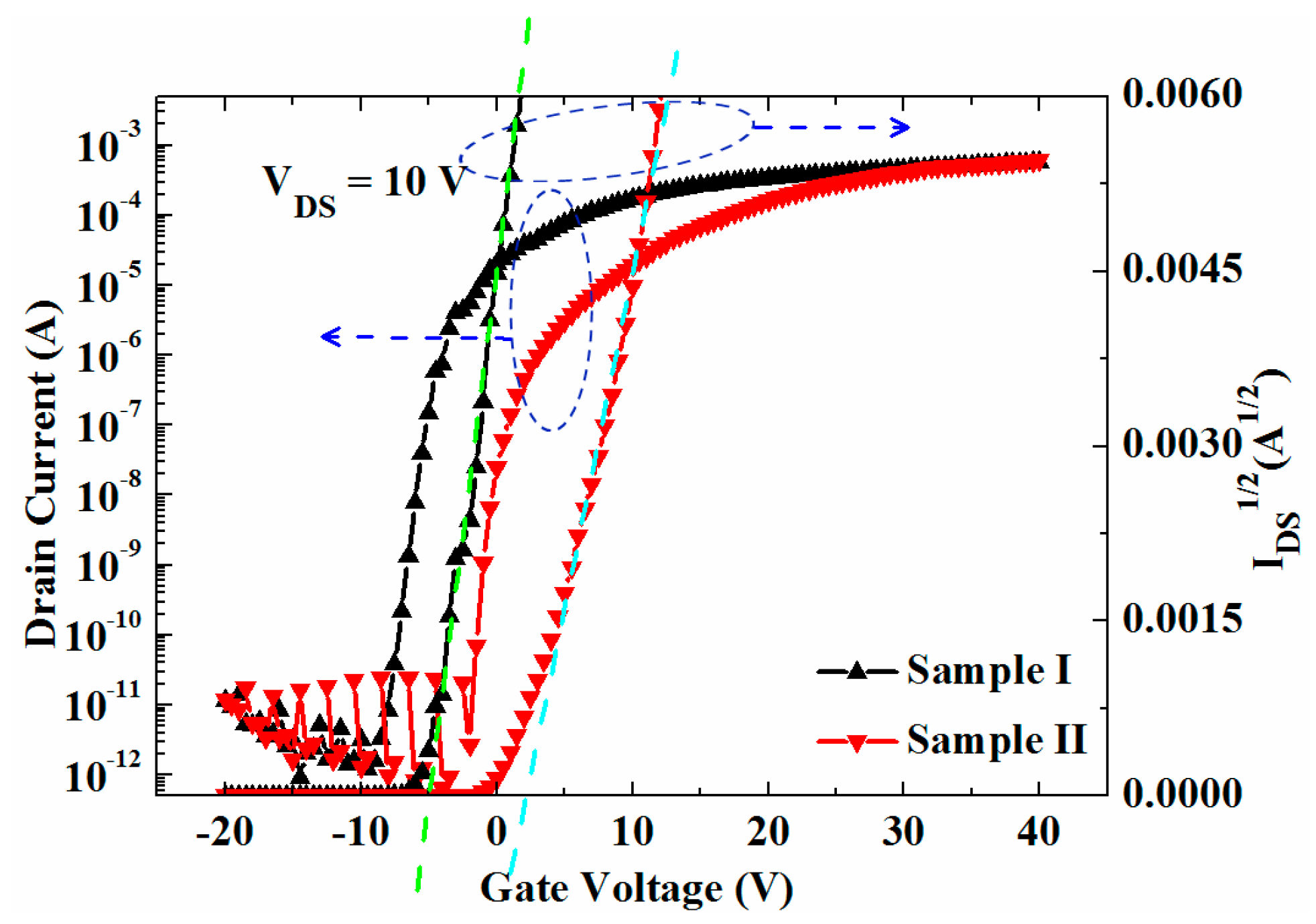
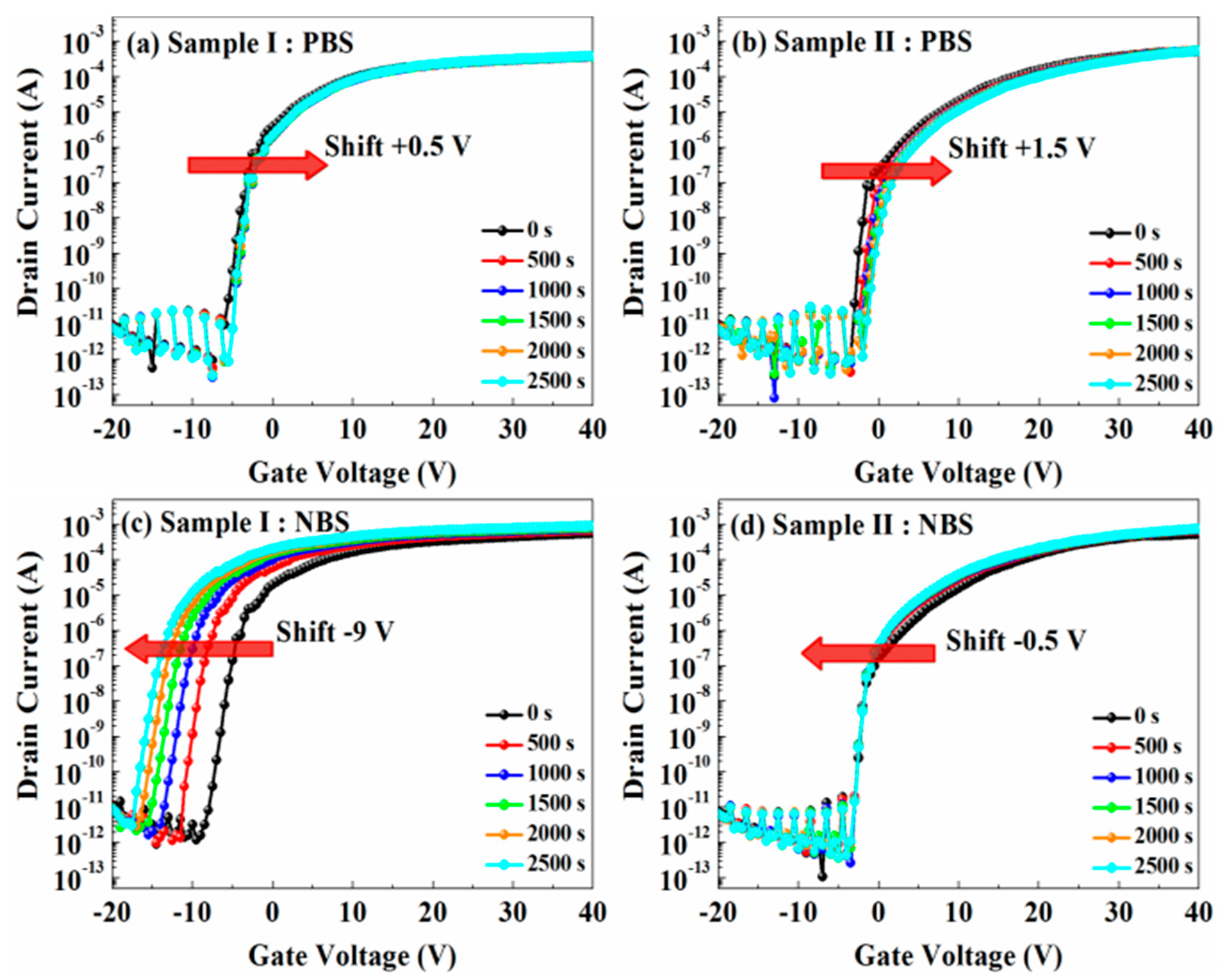
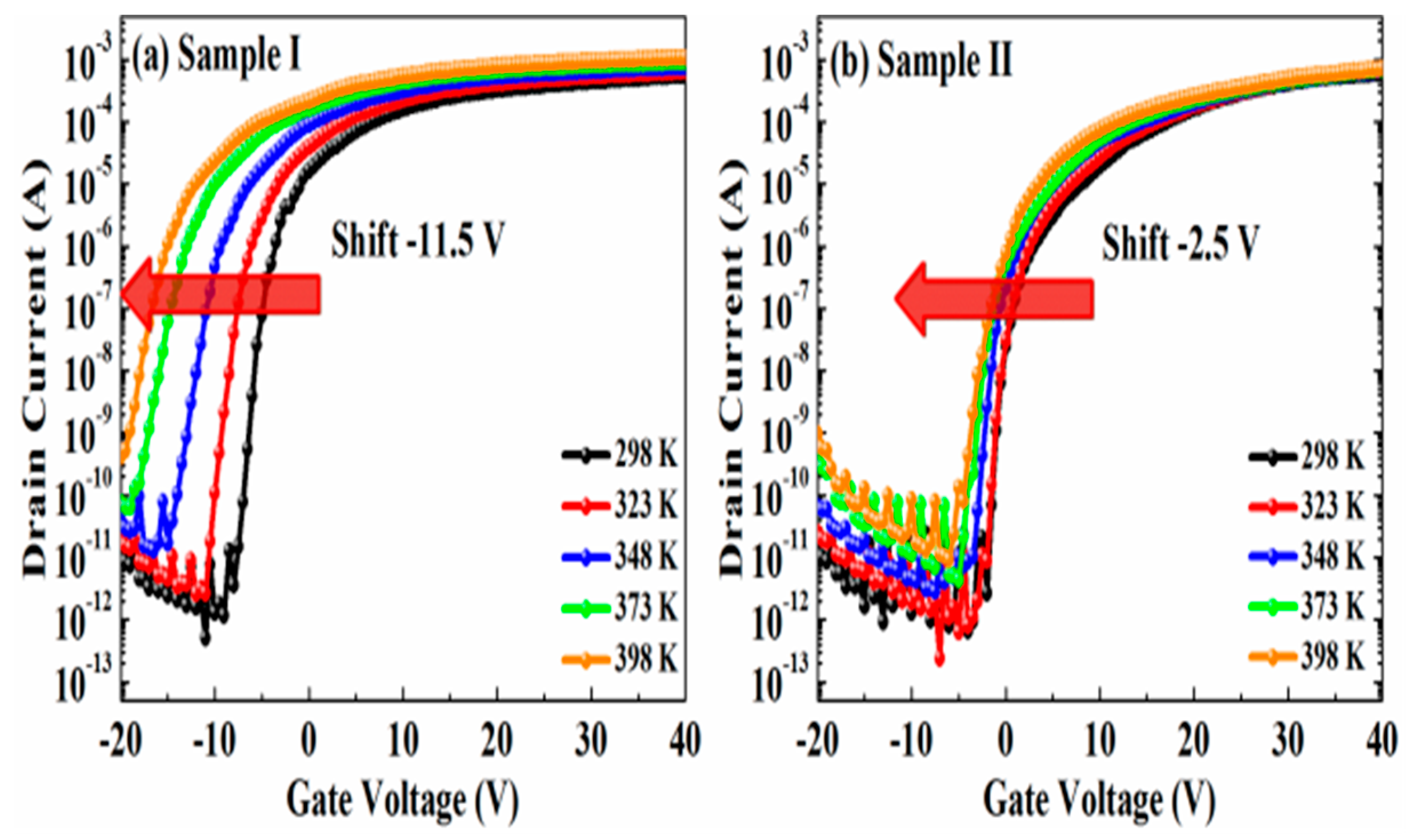
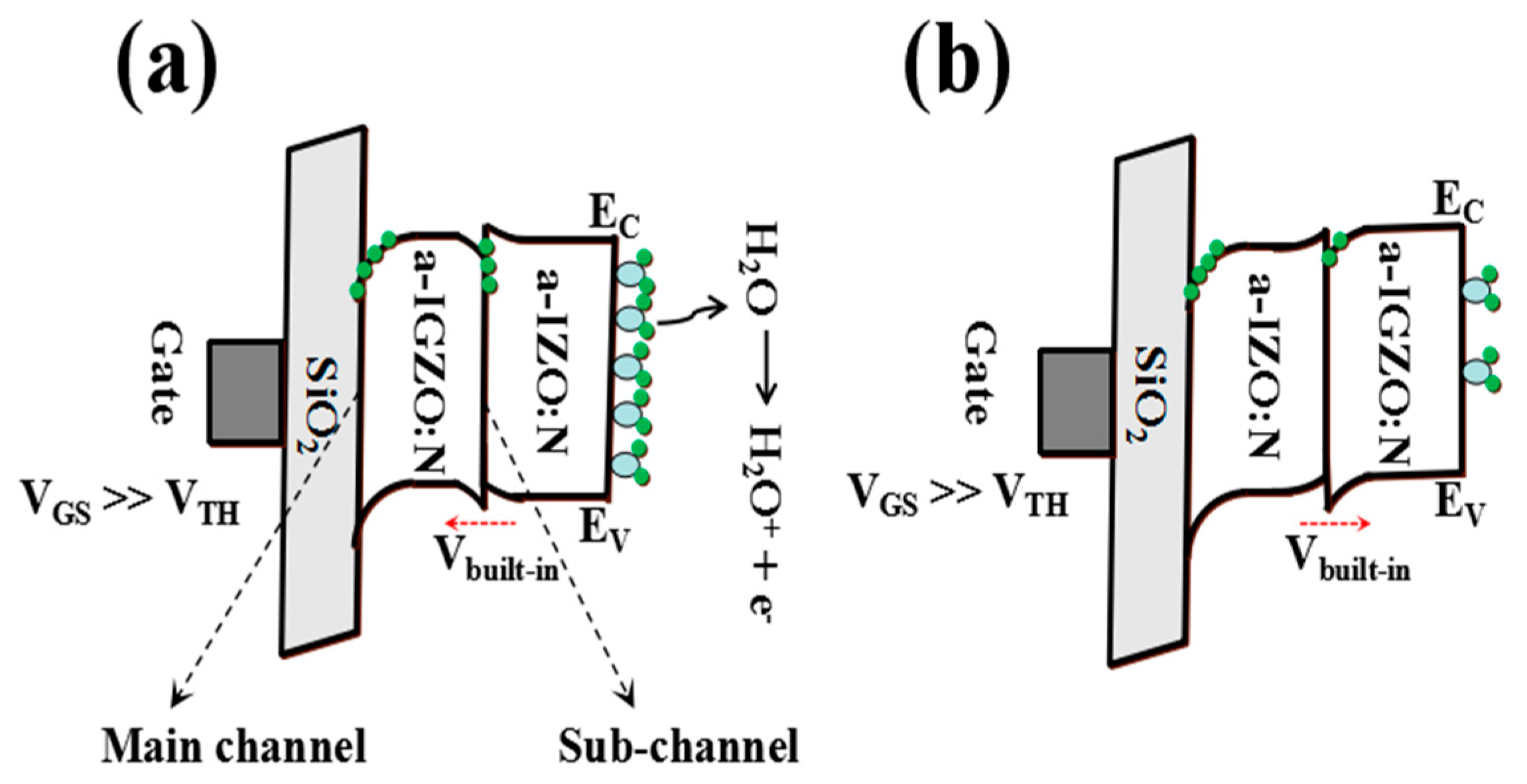
| Sample | µFE (cm2·V−1·s−1) | SS (V/dec) | VTH (V) | ION/IOFF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 31.9 | 0.8 | −5.0 | 1.2 × 108 |
| II | 15 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 1.1 × 108 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, H.; Liu, G.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Dong, C. Amorphous Oxide Thin Film Transistors with Nitrogen-Doped Hetero-Structure Channel Layers. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7101099
Xie H, Liu G, Zhang L, Zhou Y, Dong C. Amorphous Oxide Thin Film Transistors with Nitrogen-Doped Hetero-Structure Channel Layers. Applied Sciences. 2017; 7(10):1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7101099
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Haiting, Guochao Liu, Lei Zhang, Yan Zhou, and Chengyuan Dong. 2017. "Amorphous Oxide Thin Film Transistors with Nitrogen-Doped Hetero-Structure Channel Layers" Applied Sciences 7, no. 10: 1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7101099
APA StyleXie, H., Liu, G., Zhang, L., Zhou, Y., & Dong, C. (2017). Amorphous Oxide Thin Film Transistors with Nitrogen-Doped Hetero-Structure Channel Layers. Applied Sciences, 7(10), 1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7101099