Assessment on Stationarity of EMG Signals with Different Windows Size During Isotonic Contractions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
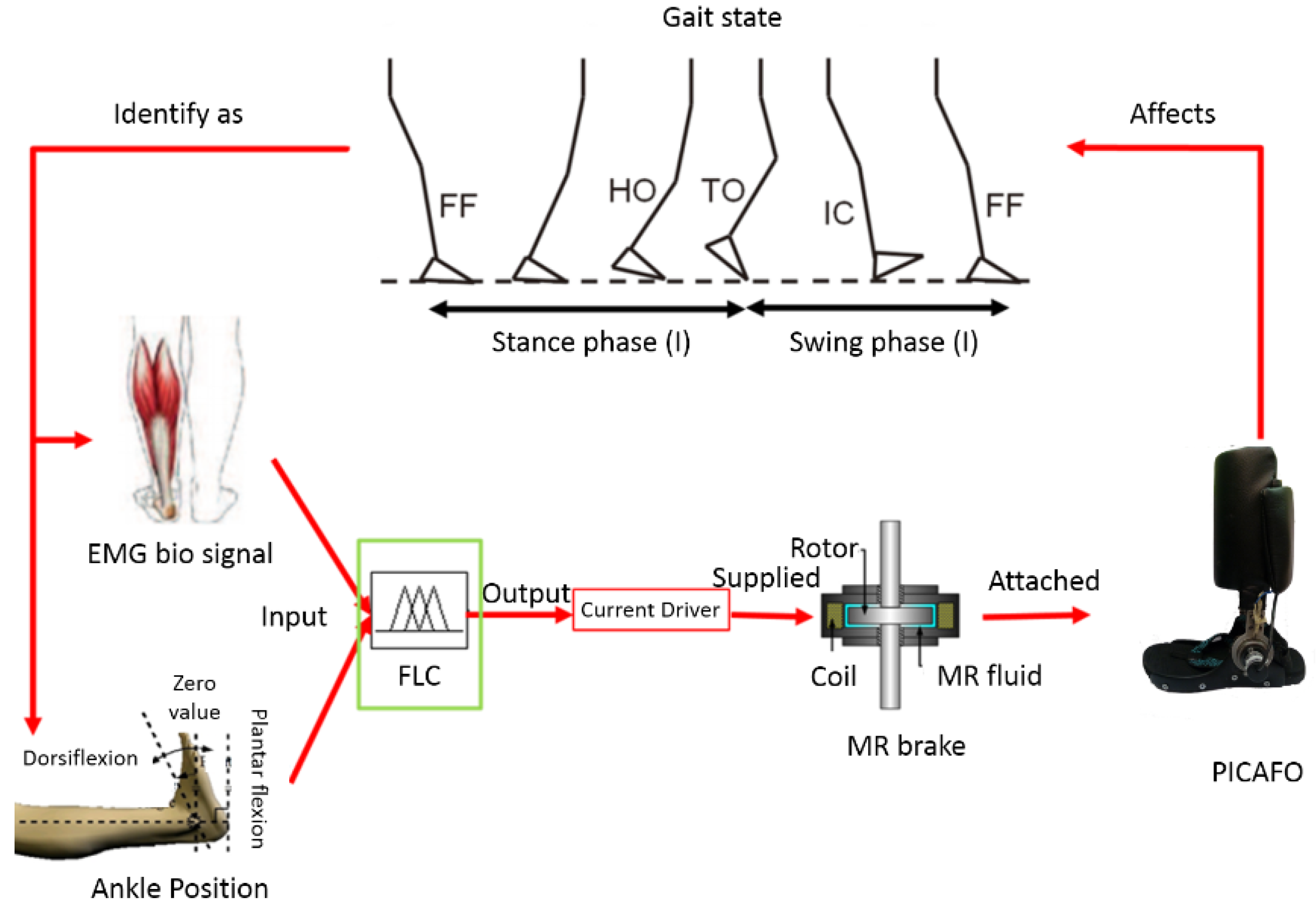
2. Materials and Methods
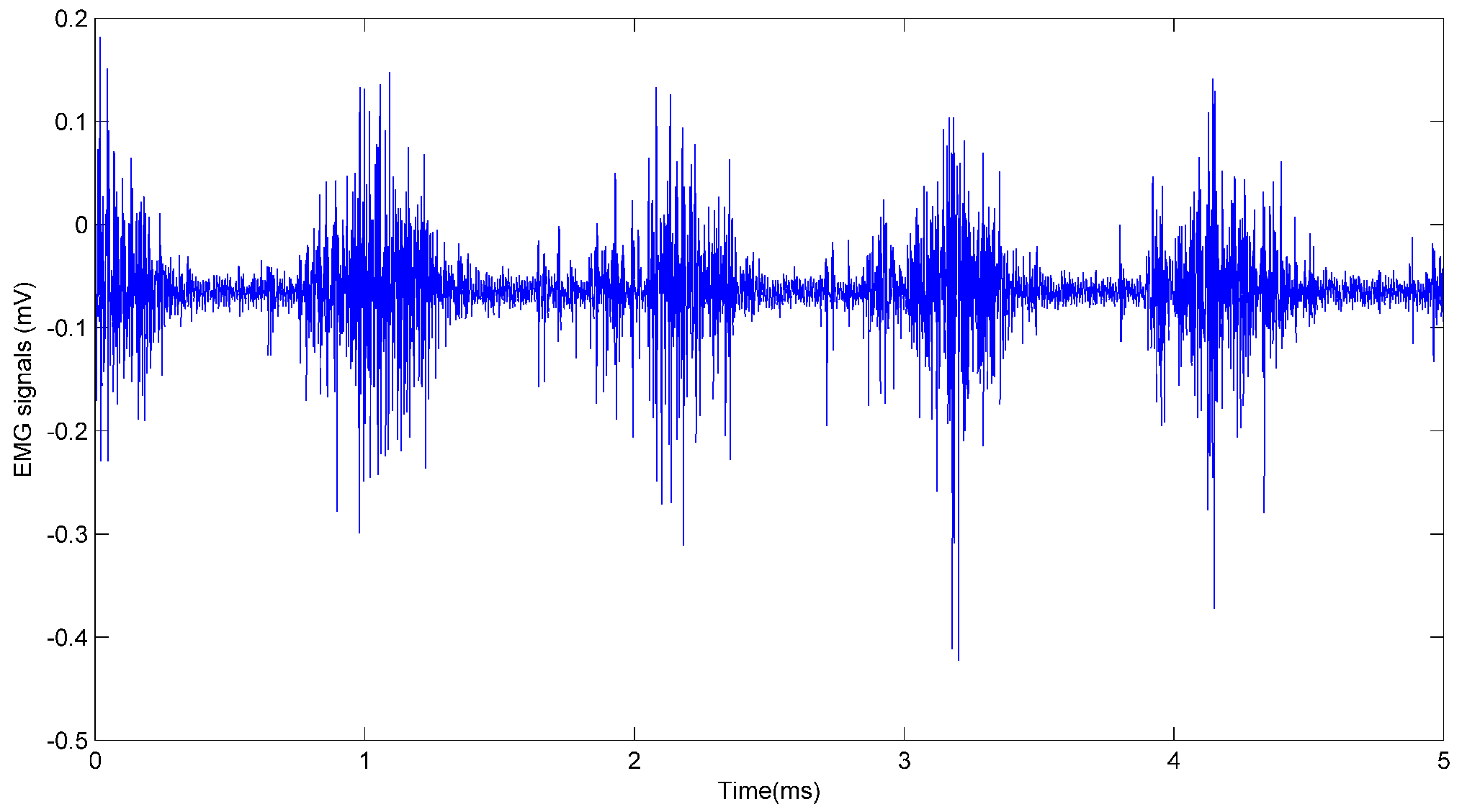
2.1. Data Acquisition and Processing
2.2. Stationary Tests
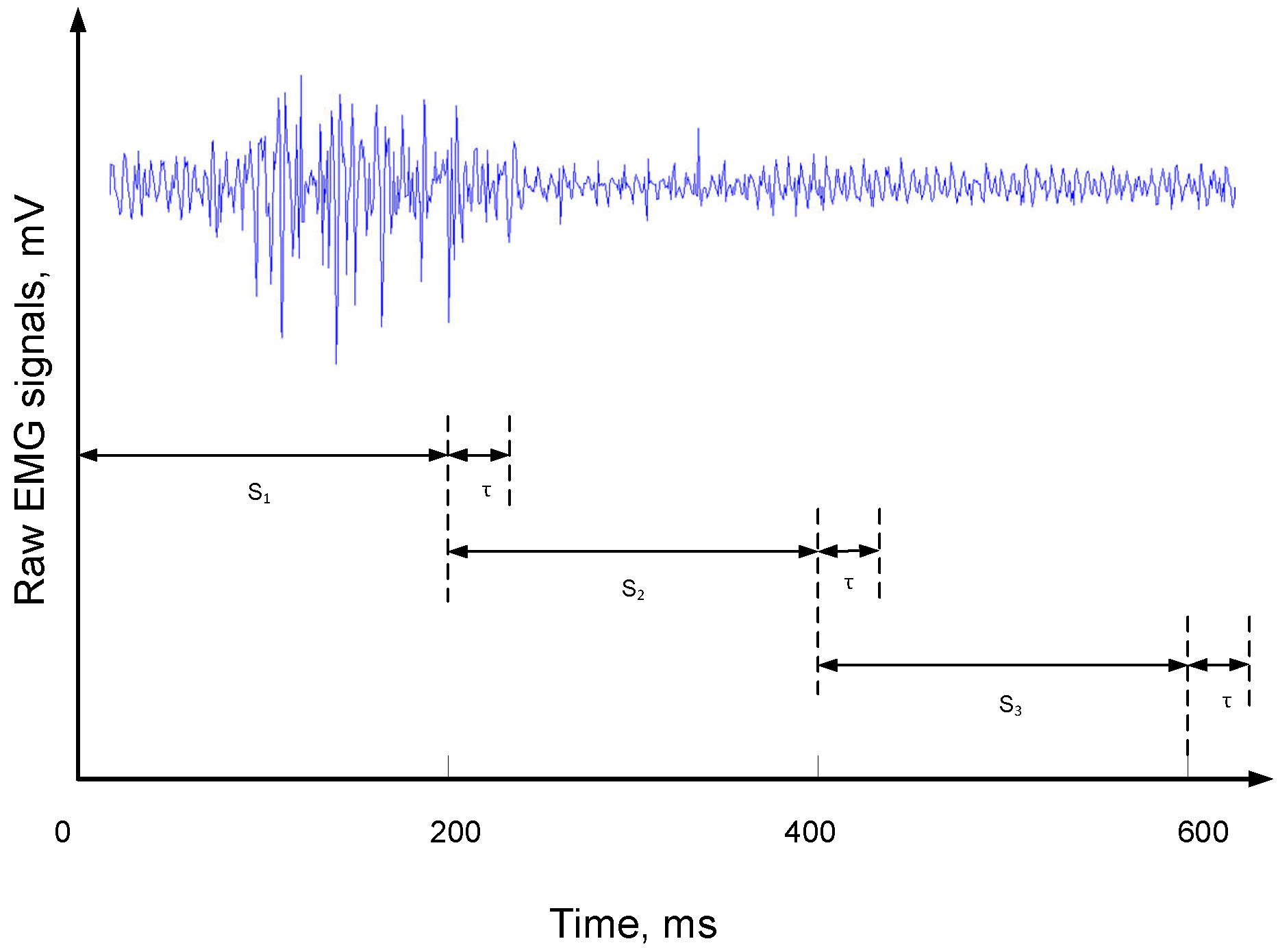
2.3. Reverse Arrangements Test
Modified Reverse Arrangements Test
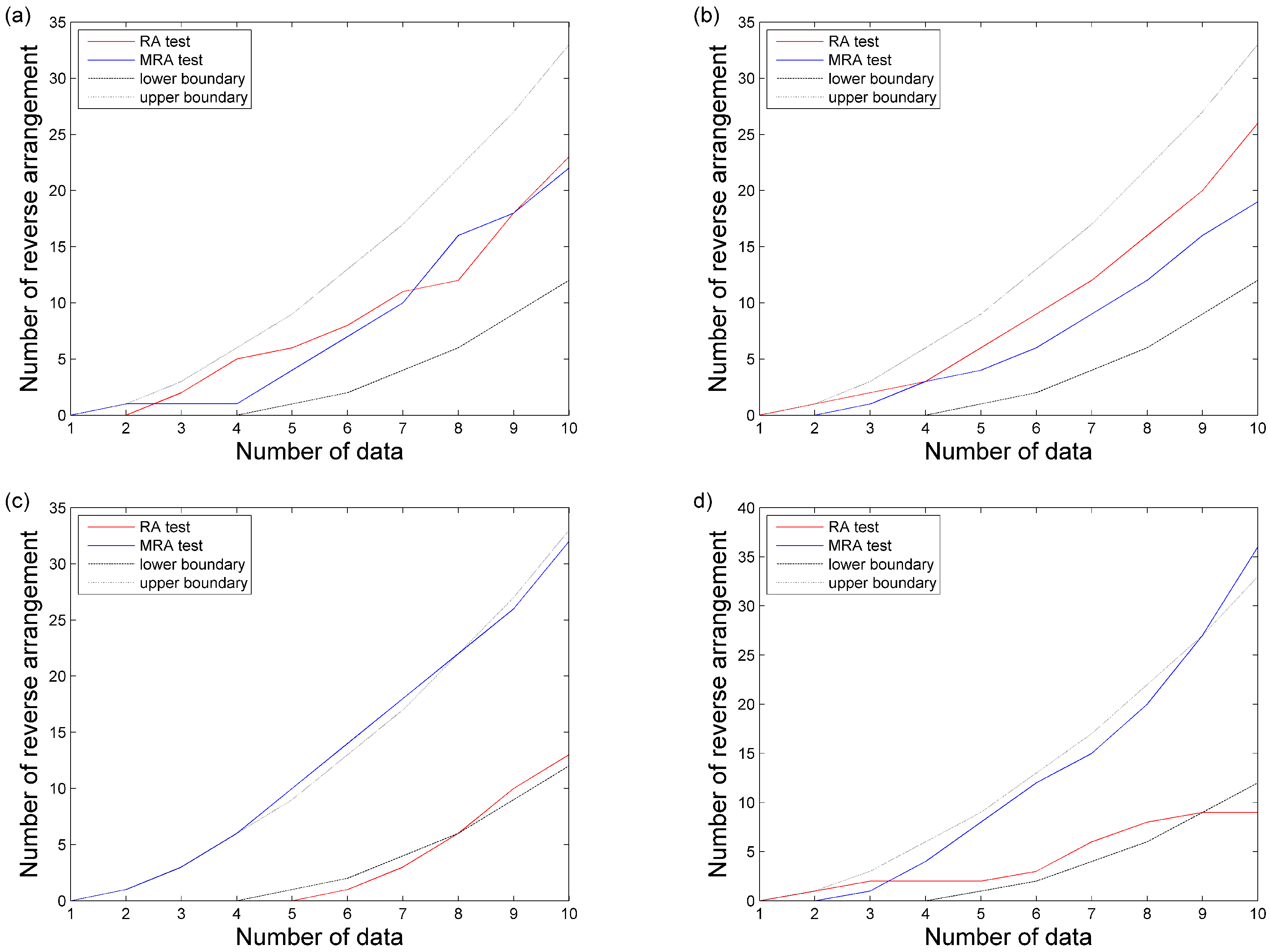
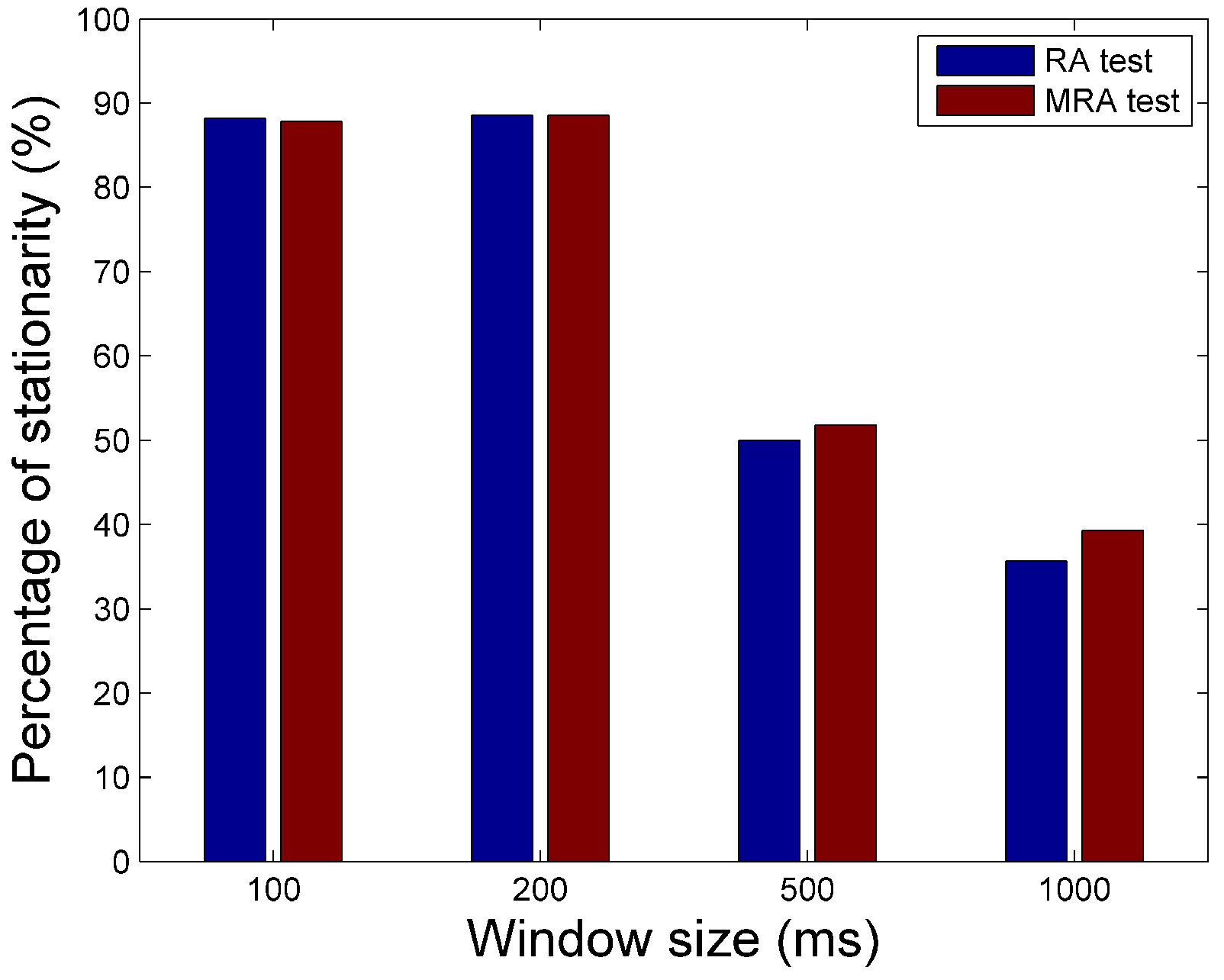
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chowdhury, R.H.; Reaz, M.B.I.; Ali, M.A.M. Surface Electromyography signal processing and classification techniques. Sensors 2013, 13, 12431–12466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elamvazuthi, I.; Duy, N.; Ali, Z.; Su, S.; Ahamed Khan, M.; Parasuraman, S. Electromyography (EMG) based classification of neuromuscular disorders using multi-layer perceptron. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 76, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subasi, A. Classification of EMG signals using PSO optimized SVM for diagnosis of neuromuscular disorders. Comput. Biol. Med. 2013, 43, 576–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, D.R.; MacIsaac, D.T. A comparison of EMG-based muscle fatigue assessments during dynamic contractions. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2013, 23, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batzianoulis, I.; El-Khoury, S.; Pirondini, E.; Coscia, M.; Micera, S.; Billard, A. EMG-based decoding of grasp gestures in reaching-to-grasping motions. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2017, 91, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artemiadis, P.K.; Kyriakopoulos, K.J. EMG-based control of a robot arm using low-dimensional embeddings. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2010, 26, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Lee, J.; Ko, H.; Kim, K. A preliminary analysis of analysis window size and voting size with a time delay for a robust real-time sEMG pattern recognition. In Proceedings of the 2014 11th International Conference on Ubiquitous Robots and Ambient Intelligence (URAI), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 12–15 November 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Richer, R.; Blank, P.; Schuldhaus, D.; Eskofier, B.M. Real-time ECG and EMG analysis for biking using android-based mobile devices. In Proceedings of the 2014 11th International Conference on Wearable and Implantable Body Sensor Networks, Zürich, Switzerland, 16–19 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Adiputra, D.; Ubaidillah; Mazlan, S.A.; Zamzuri, H.; Rahman, M.A.A. Fuzzy logic control for ankle foot orthoses equipped with magnetorheological brake. J. Teknol. 2016, 78, 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Naik, G.R.; Al-Timemy, A.H.; Nguyen, H.T. Transradial amputee gesture classification using an optimal number of sEMG sensors: An approach using ICA clustering. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2016, 24, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazmi, N.; Abdul Rahman, M.A.; Yamamoto, S.I.; Ahmad, S.A.; Zamzuri, H.; Mazlan, S.A. A review of classification techniques of EMG signals during isotonic and isometric contractions. Sensors 2016, 16, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, N.; Sheng, X.; Farina, D.; Zhu, X. User adaptation in long-term, open-loop myoelectric training: Implications for EMG pattern recognition in prosthesis control. J. Neural Eng. 2015, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, X.; Jelfs, B.; Chan, R.H.M.; Tin, C. Self-recalibrating surface EMG pattern recognition for neuroprosthesis control based on convolutional neural network. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakoty, N.M.; Hazarika, S.M.; Gan, J.Q. EMG feature set selection through linear relationship for grasp recognition. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 2016, 36, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazmi, N.; Mazlan, S.A.; Zamzuri, H.; Abdul Rahman, M.A. Fitting distribution for electromyography and electroencephalography signals based on goodness-of-fit tests. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 76, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudgins, B.; Parker, P.; Scott, R. A new strategy for multifunction myoelectric control. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1993, 1, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rechy-Ramirezn, E.J.; Huosheng, H. Bio-signal based control in assistive robots: A survey. Digit. Commun. Netw. 2015, 1, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phinyomark, A.; Phukpattaranont, P.; Limsakul, C. Feature reduction and selection for EMG signal classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 7420–7431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oskoei, M.A.; Hu, H. Support vector machine-based classification scheme for myoelectric control applied to upper limb. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 55, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ani, A.; Koprinska, I.; Naik, G.R.; Khushaba, R.N. A dynamic channel selection algorithm for the classification of EEG and EMG data. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bilodeau, M.; Cincera, M.; Arsenault, A.B.; Grave, D. Normality and stationarity of EMG Signals of elbow flexor muscles during ramp and step isometric contractions. J. Elecrromyogr. Kinesiol. 1997, 7, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessard, C.S. Signal Processing of Random Physiological Signals; Morgan & Clypool Publishers: San Rafael, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, T.W.; Housh, T.J.; Weir, J.P.; Cramer, J.T.; Vardaxis, V.; Johnson, G.O.; Coburn, J.W.; Malek, M.H.; Mielke, M. An examination of the Runs Test, Reverse Arrangements Test, and modified Reverse Arrangements Test for assessing surface EMG signal stationarity. J. Neurosci. Methods 2006, 156, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.J.; Kim, J.Y. Stationarity test of electromyographic signals during isokinetic trunk exertions. Work 2012, 41, 2545–2547. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Messaoudi, N.; Bekka, R.E.; Ravier, P.; Harba, R. Assessment of the non-Gaussianity and non-linearity levels of simulated sEMG signals on stationary segments. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2017, 32, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thongpanja, S.; Phinyomark, A.; Quaine, F.; Laurillau, Y.; Wongkittisuksa, B.; Limsakul, C.; Phukpattaranont, P. Effects of window size and contraction types on the stationarity of biceps brachii muscle EMG signals. In Proceedings of the 7th International Convention on Rehabilitation Engineering and Assistive Technology, Gyeonggi-do, Korea, 29–31 August 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Farina, D.; Merletti, R. Comparison of algorithms for estimation of EMG variables during voluntary isometric contractions. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2000, 10, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phinyomark, A.; Qu, F.; Chrbonnier, S.; Serviere, C.; Tarpin-Benard, F.; Laurillau, Y. EMG feature evaluation for improving myoelectric pattern recognition robustness. Expert Syst. Appl. 2013, 40, 4832–4840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englehart, K.; Hudgin, B.; Parker, P.A. A wavelet-based continuous classification scheme for multifunction myoelectric control. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2001, 48, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadzri, A.A.A.; Ahmad, S.A.; Marhaban, M.H.; Haslina, J. Characterization of surface electromyography using time domain features for determining hand motion and stages of contraction. Australas. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2014, 37, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazmi, N.; Yamamoto, S.I.; Abdul Rahman, M.A.; Ahmad, S.A.; Adiputra, D.; Zamzuri, H.; Mazlan, S.A. Fuzzy logic for walking patterns based on surface electromyography signals with different membership functions. In Proceedings of the 2016 6th International Workshop on Computer Science and Engineering, Tokyo, Japan, 17–19 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bendat, J.; Piersol, A. Random Data: Analysis and Measurement Procedures, 3rd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, Y.J.; Kim, J.Y. The effects of load, flexion, twisting and window size on the stationarit y of trunk muscle EMG signals. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2012, 42, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.A.; Chappell, P.H. Moving approximate entropy applied to surface electromyographic signals. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2008, 3, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AL-Quraishi, M.S.; Ishak, A.J.; Ahmad, S.A.; Hasan, M.K.; Al-Qurishi, M.; Ghapanchizadeh, H.; Alamri, A. Classifcation of ankle joint movements based on surface electromyography signals for rehabilitation robot applications. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2016, 55, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, R.; Caterina, G.D.; Lakany, H.; Petropoulakis, L.; Conway, B.; Soraghan, J. Study on interaction between temporal and spatial information in classification of EMG signals in myoelectric prostheses. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Author | Type of Contractions | Window Size (ms) | Stationarity Tests |
|---|---|---|---|
| [25] | Isometric | 250 | Run, RA, and MRA |
| [26] | Isotonic | 125 | MRA |
| [26] | Isometric | 372 | MRA |
| This study | Isotonic | 200 | RA and MRA |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nazmi, N.; Abdul Rahman, M.A.; Yamamoto, S.-i.; Ahmad, S.A.; Malarvili, M.; Mazlan, S.A.; Zamzuri, H. Assessment on Stationarity of EMG Signals with Different Windows Size During Isotonic Contractions. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7101050
Nazmi N, Abdul Rahman MA, Yamamoto S-i, Ahmad SA, Malarvili M, Mazlan SA, Zamzuri H. Assessment on Stationarity of EMG Signals with Different Windows Size During Isotonic Contractions. Applied Sciences. 2017; 7(10):1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7101050
Chicago/Turabian StyleNazmi, Nurhazimah, Mohd Azizi Abdul Rahman, Shin-ichiroh Yamamoto, Siti Anom Ahmad, MB Malarvili, Saiful Amri Mazlan, and Hairi Zamzuri. 2017. "Assessment on Stationarity of EMG Signals with Different Windows Size During Isotonic Contractions" Applied Sciences 7, no. 10: 1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7101050
APA StyleNazmi, N., Abdul Rahman, M. A., Yamamoto, S.-i., Ahmad, S. A., Malarvili, M., Mazlan, S. A., & Zamzuri, H. (2017). Assessment on Stationarity of EMG Signals with Different Windows Size During Isotonic Contractions. Applied Sciences, 7(10), 1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7101050







