Early Detection of Aspergillus parasiticus Infection in Maize Kernels Using Near-Infrared Hyperspectral Imaging and Multivariate Data Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Maize Kernel Preparation
2.2. Fungal Inoculation
2.3. NIR Hyperspectral System and Image Calibration
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Hyperspectral Image Analysis
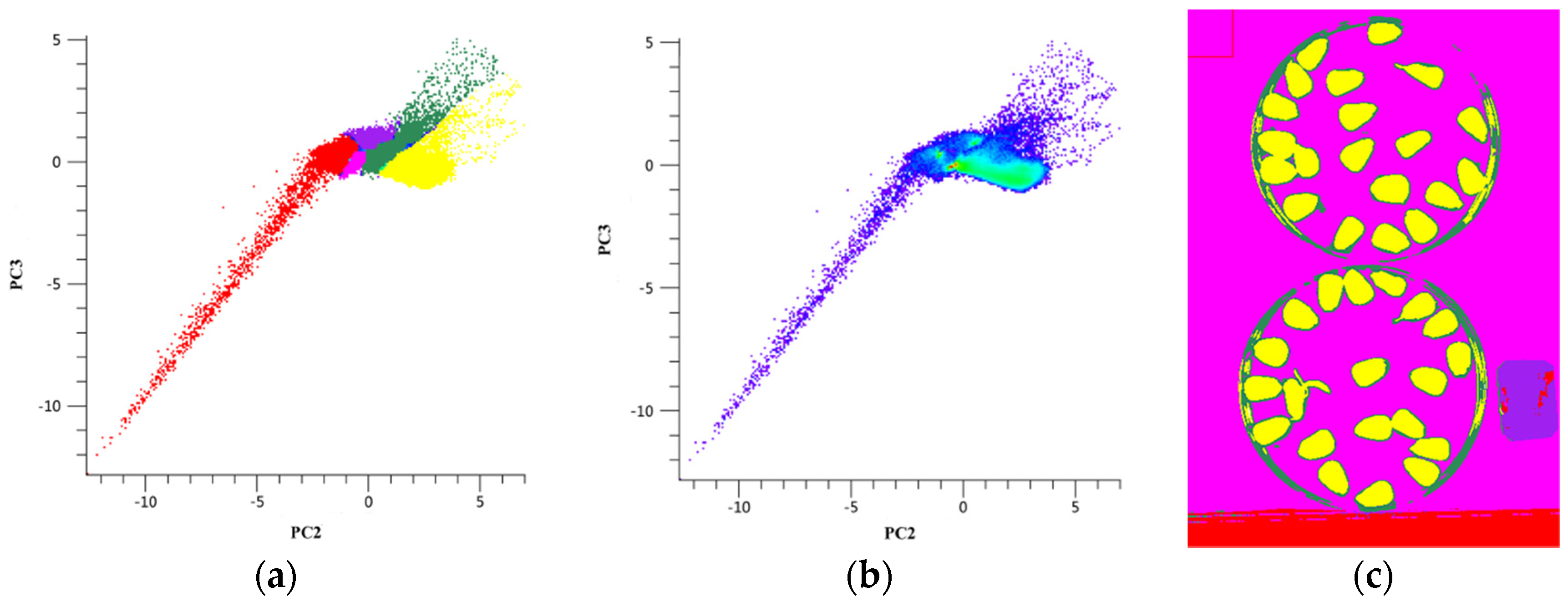
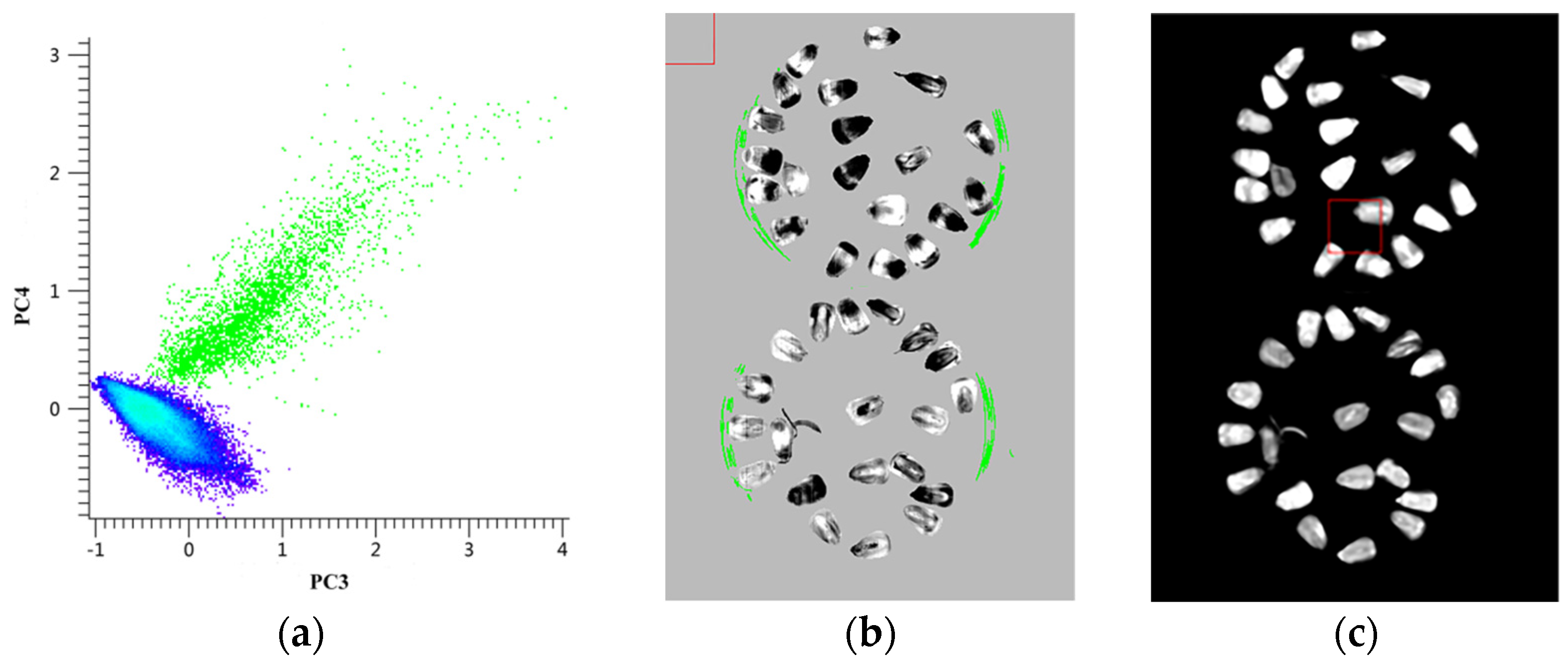
3.1.1. ROIs Extraction Based on PCA and Masking
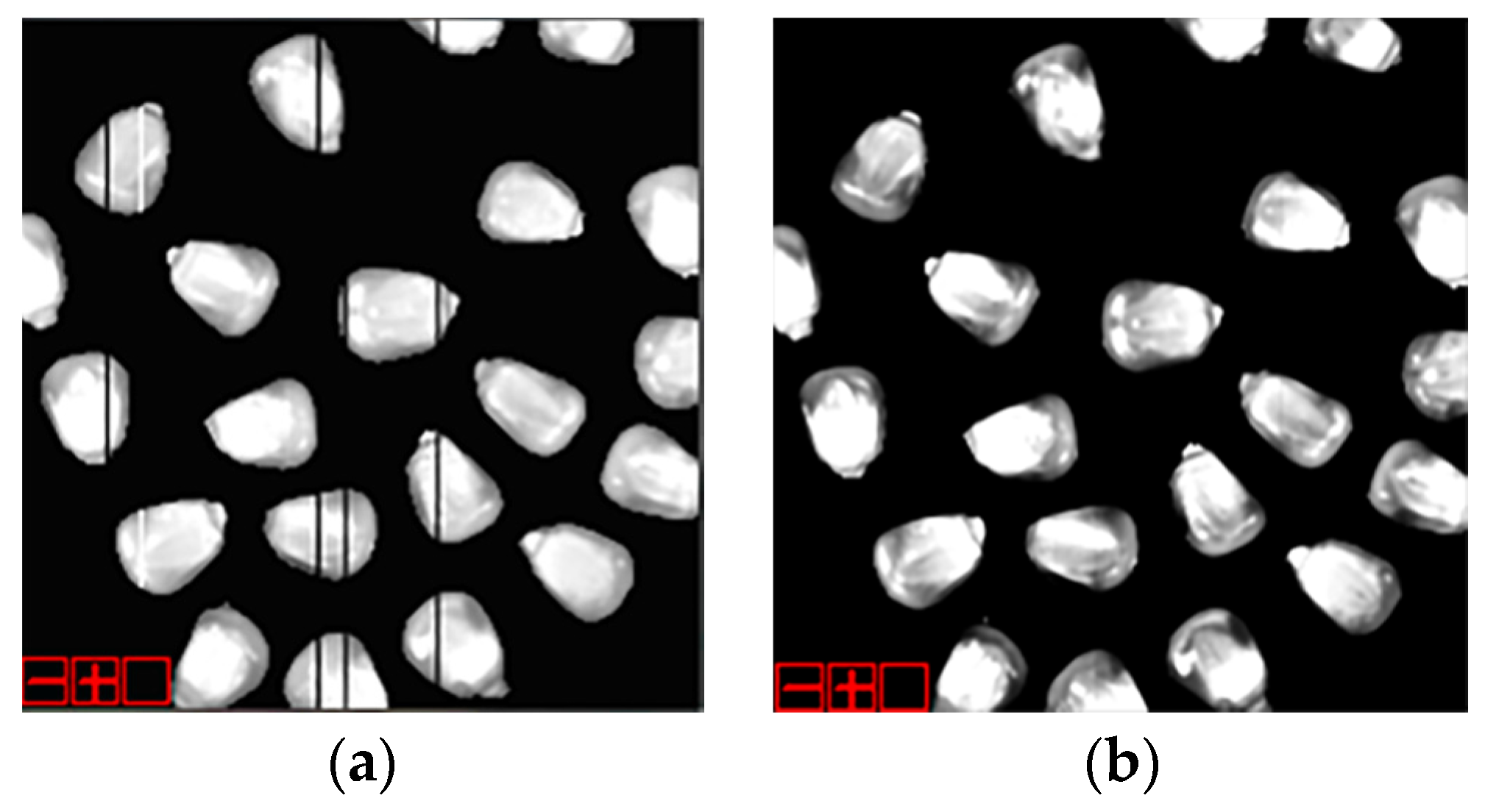
3.1.2. Further Processing of Bad Pixels and Separability Computation of Contamination Levels
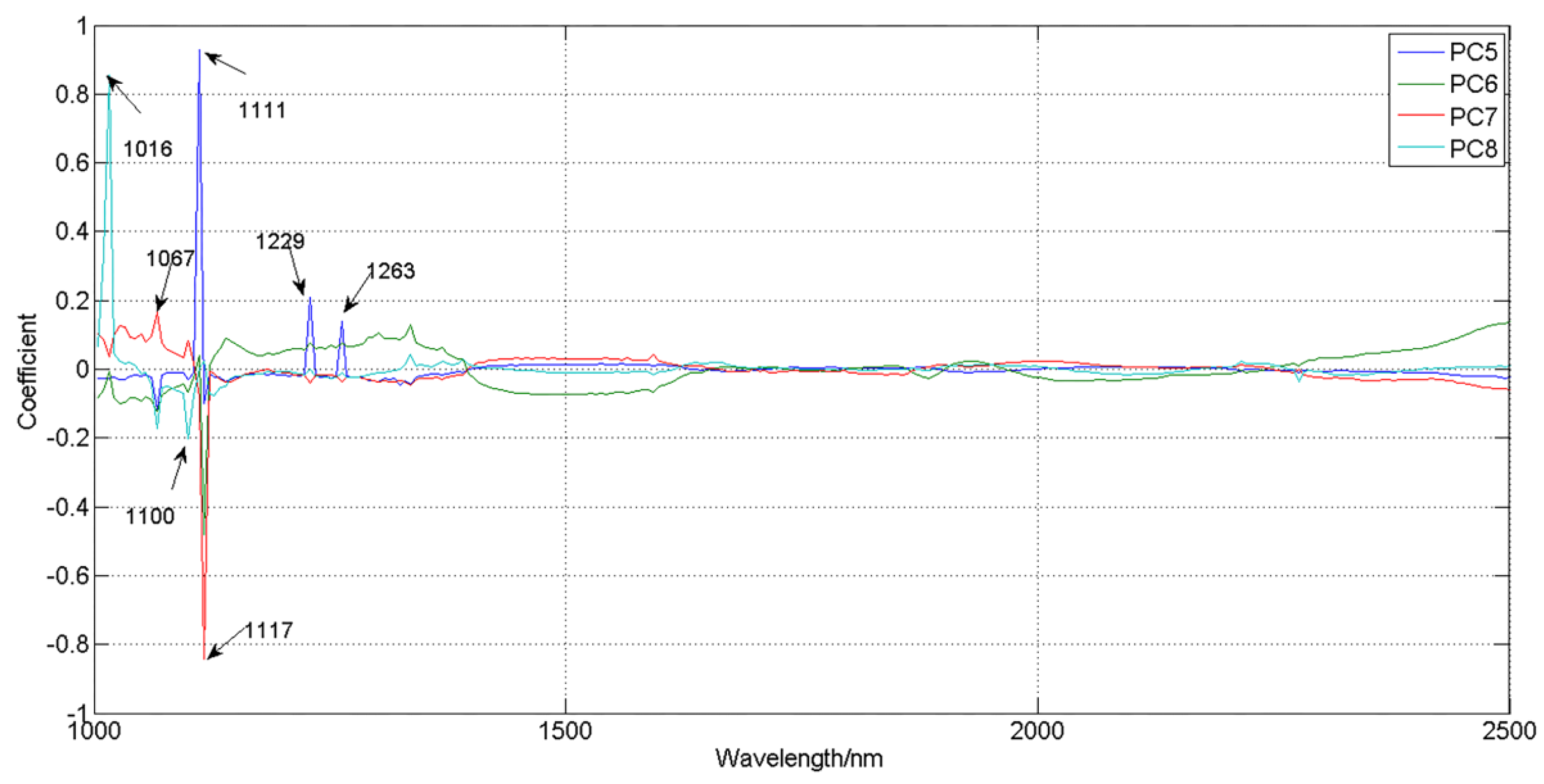
3.2. Spectral Analysis
3.2.1. Classification Based on Data of Maize Kernels with Germ Up
3.2.2. Classification Based on Data of the Mixture of Maize Kernels Orientated Germ Up and Down
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fanelli, C.; Ricelli, A.; Reverberi, M.; Fabbri, A.A.; Pandalai, S.G. Aflatoxins and ochratoxins in cereal grains: An open challenge. Recent Res. Dev. Crop Sci. 2004, 1, 295–317. [Google Scholar]
- Del Fiore, A.; Reverberi, M.; Ricelli, A.; Pinzari, F.; Serranti, S.; Fabbri, A.A.; Bonifazi, G.; Fanelli, C. Early detection of toxigenic fungi on maize by hyperspectral imaging analysis. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 144, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teye, E.; Huang, X.; Afoakwa, N. Review on the potential use of near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) for the measurement of chemical residues in food. Am. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, J.D.; Eaton, D.L.; Guengerich, F.P.; Coulombe, R.A. Alfatoxin B1 activation in human lung. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1997, 144, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthomi, J.W.; Ndung’u, J.K.; Gathumbi, J.K.; Mutitu, E.W.; Wagacha, J.M. The occurrence of Fusarium species and mycotoxins in Kenyan wheat. Crop Prot. 2008, 27, 1215–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Martínez, M.S.; Martínez, A.J. Mold occurrence and aflatoxin B1 and fumonisin B1 determination in corn samples in Venezuela. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 2833–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castells, M.; Marín, S.; Sanchis, V.; Ramos, A.J. Distribution of fumonisins and aflatoxins in corn fractions during industrial cornflake processing. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 123, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paepens, C.; De Saeger, S.; Sibanda, L.; Barna-Vetro, I.; Léglise, I.; Van Hove, F.; Van Peteghem, C. A flow-through enzyme immunoassay for the screening of fumonisins in maize. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 523, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Chen, Y.R.; Mehl, P.M. Hyperspectral reflectance and fluorescence imaging system for food quality and safety. Trans. ASAE 2001, 44, 721–729. [Google Scholar]
- Gowen, A.A.; O’Donnell, C.; Cullen, P.J.; Downey, G.; Frias, J.M. Hyperspectral imaging—An emerging process analytical tool for food quality and safety control. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 18, 590–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Chao, K.; Kim, M.S.; Lu, R.; Burks, T.F. Hyperspectral and multispectral imaging for evaluating food safety and quality. J. Food Eng. 2013, 118, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geladi, P.; Burger, J.; Lestander, T. Hyperspectral imaging: Calibration problems and solutions. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2004, 72, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geladi, P.; Grahn, H.; Burger, J. Multivariate images, hyperspectral imaging: Background and equipment. In Techniques and Applications of the Hyperspectral Image Analysis; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: West Sussex, UK, 2007; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, H.; Hruska, Z.; Brown, R.L.; Cleveland, T.E. Hyperspectral bright greenish-yellow fluorescence (BGYF) imaging of aflatoxin contaminated corn kernels. In Proceedings of the Optics for Natural Resources, Agriculture, and Foods, Boston, MA, USA, 1 October 2006.
- Firrao, G.; Torelli, E.; Gobbi, E.; Raranciuc, S.; Bianchi, G.; Locci, R. Prediction of milled maize fumonisin contamination by multispectral image analysis. J. Cereal Sci. 2010, 52, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Heitschmidt, G.W.; Ni, X.; Windham, W.R.; Hawkins, S.; Chu, X. Identification of aflatoxin B1 on maize kernel surfaces using hyperspectral imaging. Food Control 2014, 42, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Heitschmidt, G.W.; Windham, W.R.; Feldner, P.; Ni, X.; Chu, X. Feasibility of detecting aflatoxin B1 on inoculated maize kernels surface using Vis/NIR hyperspectral imaging. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, M116–M122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Lawrence, K.C.; Ni, X.; Yoon, S.C.; Heitschmidt, G.W.; Feldner, P. Near-infrared hyperspectral imaging for detecting Aflatoxin B1 of maize kernels. Food Control 2015, 51, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandpal, L.M.; Lee, S.; Kim, M.S.; Bae, H.; Cho, B.K. Short wave infrared (SWIR) hyperspectral imaging technique for examination of aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) on corn kernels. Food Control 2015, 51, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, T.C.; Wicklow, D.T.; Maghirang, E.B.; Xie, F.; Dowell, F.E. Detecting aflatoxin in single corn kernels by transmittance and reflectance spectroscopy. Trans. ASAE 2001, 44, 1247–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowell, F.E.; Pearson, T.C.; Maghirang, E.B.; Xie, F.; Wicklow, D.T. Reflectance and transmittance spectroscopy applied to detecting fumonisin in single corn kernels infected with Fusarium verticillioides. Cereal Chem. 2002, 79, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Ibañez, V.; Soldado, A.; Martínez-Fernández, A.; De la Roza-Delgado, B. Application of near infrared spectroscopy for rapid detection of aflatoxin B1 in maize and barley as analytical quality assessment. Food Chem. 2009, 113, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, C.B.; Jayas, D.S.; Paliwal, J.; White, N.D.G. Fungal detection in wheat using near-infrared hyperspectral imaging. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 2171–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Paliwal, J.; Jayas, D.S.; White, N.D.G. Classification of fungal infected wheat kernels using near-infrared reflectance hyperspectral imaging and support vector machine. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 1779–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauriegel, E.; Giebel, A.; Geyer, M.; Schmidt, U.; Herppich, W.B. Early detection of Fusarium infection in wheat using hyper-spectral imaging. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2011, 75, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.J.; Geladi, P.; Britz, T.J.; Manley, M. Investigation of fungal development in maize kernels using NIR hyperspectral imaging and multivariate data analysis. J. Cereal Sci. 2012, 55, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Hruska, Z.; Kincaid, R.; Brown, R.L.; Bhatnagar, D.; Cleveland, T.E. Detecting maize inoculated with toxigenic and atoxigenic fungal strains with fluorescence hyperspectral imagery. Biosyst. Eng. 2013, 115, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Song, L.; Sun, Y.; Hu, P.; Tu, K.; Pan, L.; Yang, H.; Huang, M. Black heart detection in white radish by hyperspectral transmittance imaging combined with chemometric analysis and a successive projections algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, D.A.; Ciurczak, E.W. Handbook of Near-Infrared Analysis, 3rd ed.; Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Guiñón, J.L.; Ortega, E.; García-Antón, J.; Pérez-Herranz, V. Moving average and Savitzki-Golay smoothing filters using Mathcad. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Engineering Education-ICEE, Coimbra, Portugal, 3–7 September 2007.
- Rinnan, Å.; van den Berg, F.; Engelsen, S.B. Review of the most common pre-processing techniques for near-infrared spectra. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2009, 28, 1201–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Song, Q.; Tang, G.; Feng, Q.; Lin, L. The combined optimization of Savitzky-Golay smoothing and multiplicative scatter correction for FT-NIR PLS models. ISRN Spectrosc. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candolfi, A.; De Maesschalck, R.; Jouan-Rimbaud, D.; Hailey, P.A.; Massart, D.L. The influence of data pre-processing in the pattern recognition of excipients near-infrared spectra. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1999, 21, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasaponara, R. On the use of principal component analysis (PCA) for evaluating interannual vegetation anomalies from SPOT/VEGETATION NDVI temporal series. Ecol. Model. 2006, 194, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, L.; Andersson, P.L.; Johansson, E.; Tysklind, M. Megavariate analysis of environmental QSAR data. Part I—A basic framework founded on principal component analysis (PCA), partial least squares (PLS), and statistical molecular design (SMD). Mol. Divers. 2006, 10, 169–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himberg, J.; Mantyjarvi, J.; Korpipaa, P. Using PCA and ICA for exploratory data analysis in situation awareness. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Multisensor Fusion and Integration for Intelligent Systems, Baden-Baden, Germany, 20–22 August 2001; pp. 127–131.
- Galvao, R.K.H.; Araujo, M.C.U.; Jose, G.E.; Pontes, M.J.C.; Silva, E.C.; Saldanha, T.C.B. A method for calibration and validation subset partitioning. Talanta 2005, 67, 736–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devos, O.; Ruckebusch, C.; Durand, A.; Duponchel, L.; Huvenne, J.P. Support vector machines (SVM) in near infrared (NIR) spectroscopy: Focus on parameters optimization and model interpretation. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2009, 96, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhao, J.; Fang, C.H.; Wang, D. Feasibility study on identification of green, black and Oolong teas using near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy based on support vector machine (SVM). Spectrochim. Acta A 2007, 66, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.C.; Yang, J.H.; Wu, C.G.; Wang, C.Y.; Liang, Y.C. A novel LS-SVMs hyper-parameter selection based on particle swarm optimization. Neurocomputing 2008, 71, 3211–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.L.; Dun, J.F. A distributed PSO–SVM hybrid system with feature selection and parameter optimization. Appl. Soft Comput. 2008, 8, 1381–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.L.; Chen, Z.Y.; Cleveland, T.E.; Russin, J.S. Advances in the development of host resistance in corn to aflatoxin contamination by Aspergillus flavus. Phytopathology 1999, 89, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, T.C.; Wicklow, D.T. Detection of corn kernels infected by fungi. Trans. ASABE 2006, 49, 1235–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manley, M.; McGoverin, C.M.; Engelbrecht, P.; Geladi, P. Influence of grain topography on near infrared hyperspectral images. Talanta 2012, 89, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
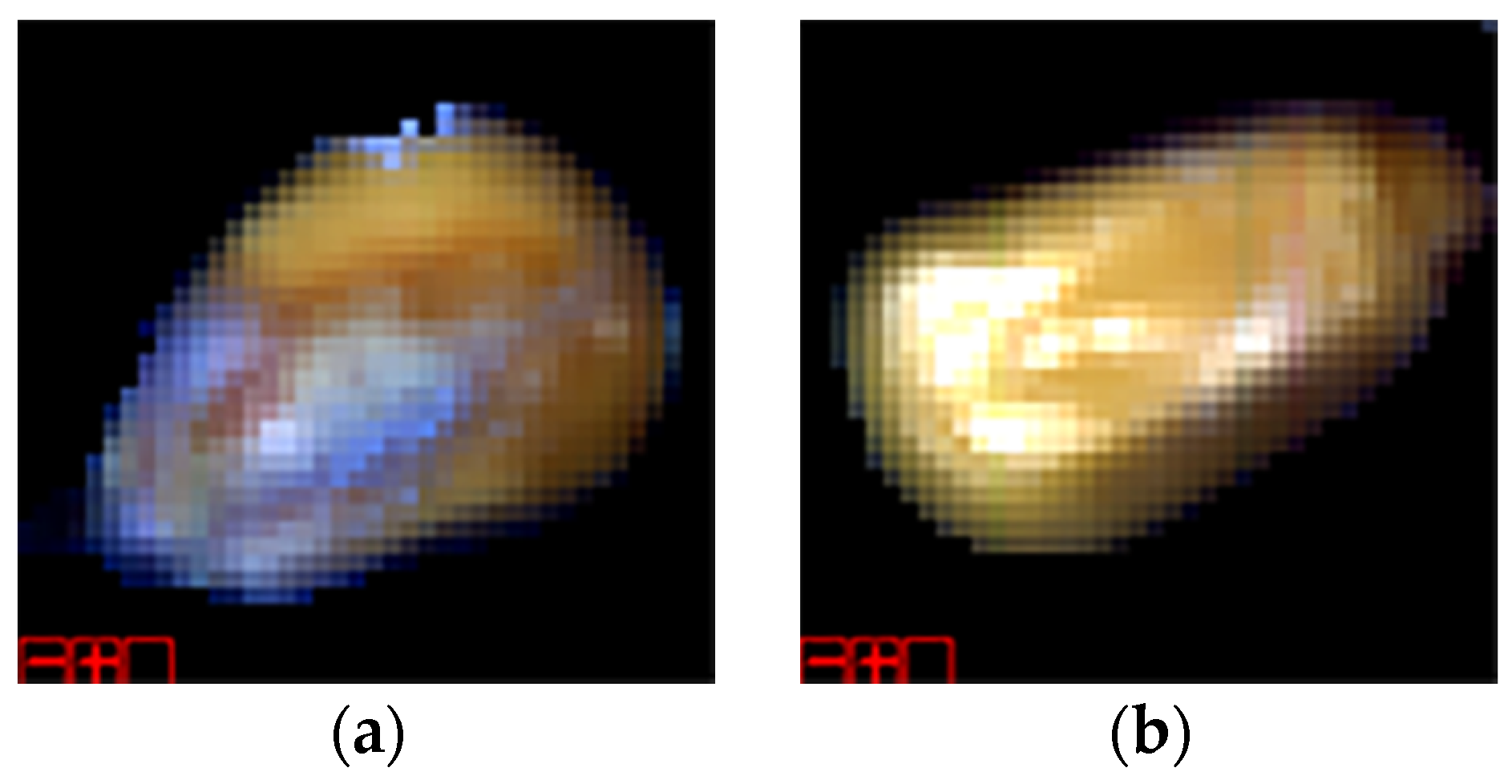


| Pretreatment Methods | MAS | SGS | MAS + NMZ | SGS + NMZ | MAS + SNV | SGS + SNV | MAS + MSC | SGS + MSC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCs | 8 | 7 | 9 | 9 | 11 | 9 | 6 | 6 |
| Calibration (%) | 89.58 | 88.54 | 100 | 100 | 97.92 | 97.92 | 82.29 | 84.38 |
| Validation (%) | 87.50 | 87.50 | 72.92 | 72.92 | 91.67 | 87.50 | 81.25 | 83.33 |
| Actual Result | Predicting Result | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calibration | Validation | |||||||
| DC | D1–2 | D3–4 | D5–7 | DC | D1–2 | D3–4 | D5–7 | |
| DC | 9 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 3 | 0 |
| D1–2 | 0 | 22 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 14 | 0 | 0 |
| D3–4 | 0 | 0 | 21 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 14 | 1 |
| D5–7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 42 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 12 |
| Precision (%) | 100.00 | 100.00 | 91.30 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 82.35 | 92.31 |
| Sensitivity (%) | 81.82 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 57.14 | 100.00 | 93.33 | 100.00 |
| Specificity (%) | 100.00 | 100.00 | 97.33 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 90.91 | 97.22 |
| Overall accuracy (%) | 97.92 | 91.67 | ||||||
| Pretreatment Methods | MAS | SGS | MAS + NMZ | SGS + NMZ | MAS + SNV | SGS + SNV | MAS + MSC | SGS + MSC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCs | 8 | 7 | 9 | 9 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 6 |
| Calibration (%) | 88.54 | 84.90 | 100 | 100 | 95.83 | 89.58 | 80.21 | 79.17 |
| Validation (%) | 79.17 | 75.00 | 67.71 | 70.83 | 84.38 | 81.25 | 77.08 | 76.04 |
| Actual Result | Predicting Result | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calibration | Validation | |||||||
| DC | D1–2 | D3–4 | D5–7 | DC | D1–2 | D3–4 | D5–7 | |
| DC | 18 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 7 | 0 | 7 | 1 |
| D1–2 | 1 | 43 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 28 | 0 | 0 |
| D3–4 | 0 | 0 | 39 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 26 | 2 |
| D5–7 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 84 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 20 |
| Precision (%) | 90.00 | 100.00 | 95.12 | 95.45 | 77.78 | 100.00 | 72.22 | 86.96 |
| Sensitivity (%) | 85.71 | 97.73 | 92.86 | 98.82 | 46.67 | 100.00 | 86.67 | 86.96 |
| Specificity (%) | 98.83 | 100.00 | 98.67 | 96.26 | 97.53 | 100.00 | 84.85 | 91.67 |
| Overall accuracy (%) | 95.83 | 84.38 | ||||||
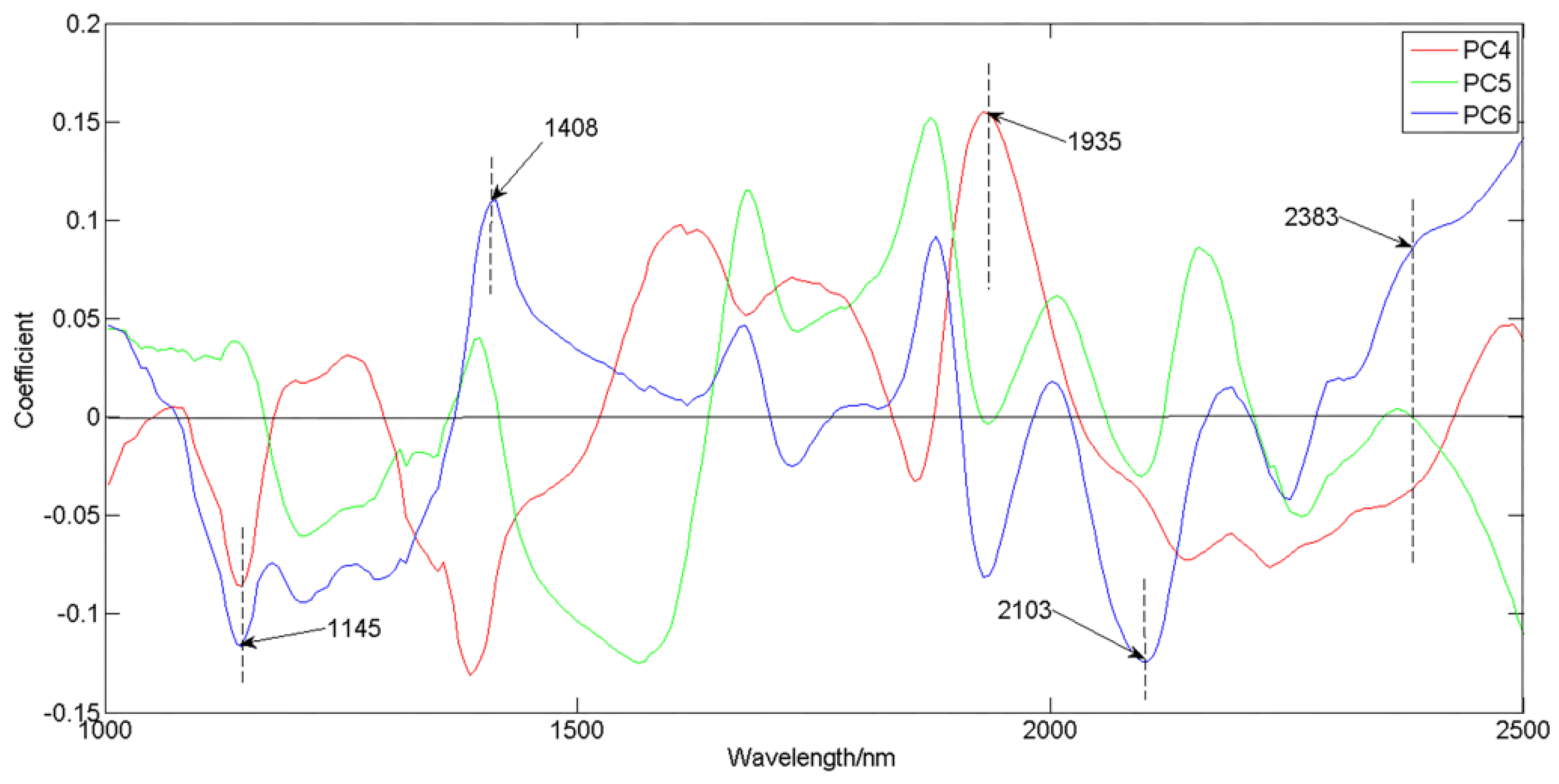
| PCs | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | PC5 | PC6 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variance percent (%) | 75.98 | 16.84 | 4.37 | 1.30 | 0.47 | 0.44 | 99.40 |
© 2017 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, X.; Wang, W.; Chu, X.; Li, C.; Kimuli, D. Early Detection of Aspergillus parasiticus Infection in Maize Kernels Using Near-Infrared Hyperspectral Imaging and Multivariate Data Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7010090
Zhao X, Wang W, Chu X, Li C, Kimuli D. Early Detection of Aspergillus parasiticus Infection in Maize Kernels Using Near-Infrared Hyperspectral Imaging and Multivariate Data Analysis. Applied Sciences. 2017; 7(1):90. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7010090
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Xin, Wei Wang, Xuan Chu, Chunyang Li, and Daniel Kimuli. 2017. "Early Detection of Aspergillus parasiticus Infection in Maize Kernels Using Near-Infrared Hyperspectral Imaging and Multivariate Data Analysis" Applied Sciences 7, no. 1: 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7010090
APA StyleZhao, X., Wang, W., Chu, X., Li, C., & Kimuli, D. (2017). Early Detection of Aspergillus parasiticus Infection in Maize Kernels Using Near-Infrared Hyperspectral Imaging and Multivariate Data Analysis. Applied Sciences, 7(1), 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7010090








