Abstract
The accuracy of noise estimation is important for the performance of a speech denoising system. Most noise estimators suffer from either overestimation or underestimation on the noise level. An overestimate on noise magnitude will cause serious speech distortion for speech denoising. Conversely, a great quantity of residual noise will occur when the noise magnitude is underestimated. Accurately estimating noise magnitude is important for speech denoising. This study proposes employing variable segment length for noise tracking and variable thresholds for the determination of speech presence probability, resulting in the performance improvement for a minima-controlled-recursive-averaging (MCRA) algorithm in noise estimation. Initially, the fundamental frequency was estimated to determine whether a frame is a vowel. In the case of a vowel frame, the increment of segment lengths and the decrement of threshold for speech presence were performed which resulted in underestimating the level of noise magnitude. Accordingly, the speech distortion is reduced in denoised speech. On the contrary, the segment length decreases rapidly in noise-dominant regions. This enables the noise estimate to update quickly and the noise variation to track well, yielding interference noise being removed effectively through the process of speech denoising. Experimental results show that the proposed approach has been effective in improving the performance of the MCRA algorithm by preserving the weak vowels and consonants. The denoising performance is therefore improved.
1. Introduction
Interference noise deteriorates speech quality and intelligibility. The process of speech denoising can remove the interference noise, so speech denoising is important for the applications of mobile speech communication and multimedia signal processing. The accuracy of noise estimation affects the performance of speech denoising significantly. How to derive an approach to detecting non-stationary noise accurately is important to speech denoising.
Many studies have been conducted to estimate noise [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11]. Kianyfar and Abutalebi [1] proposed a noise estimator, which employed speech presence probability to update noise variance. Krawczyk-Becker et al. [2] proposed incorporating spectro-temporal correlations to improve the performance for noise tracking. A minima-controlled-recursive-averaging (MCRA) algorithm is a successful noise estimation approach for speech denoising [3,4]. The MCRA algorithm estimates noise power by averaging the past spectral power values. The noise power updated according to the probability of speech presence for each sub-band. Many novel methods have been proposed to improve the performance of the MCRA methods [5,6,7,8]. Fan et al. [5] proposed a method to shorten time delay for the detection of abrupt changes in noise. Noise update criteria were also additionally controlled to reduce speech leakage for the MCRA algorithm. Kum and Chang [6] proposed conditional maximizing a posteriori criterion with a second order to improve the performance of the MCRA algorithm. Wu et al. [7] proposed a modified version of the time variant recursive averaging of the MCRA algorithm by utilizing both noise and speech segments. In addition, speech denoising residue was employed to approximate the noise signal and to update noise spectra in speech-activity regions.
Based on the above discussions, most of the noise estimation methods do not consider speech properties in noise estimation. In this study, we employed the harmonic properties of a vowel to determine the segment length for tracking minimum statistics in the MCRA algorithm. In the case of a vowel frame and its neighbors, we perform the increment of segment length and the decrement of threshold for speech presence. This enables the MCRA algorithm to pick up the lower magnitude as a noise level. The noise estimate tends to be underestimated. This yields speech distortion reduction in the denoised signal. The quality of denoised speech is then improved. Conversely, the segment length decreases during noise-dominant frames. This enables the MCRA algorithm to update the level of noise estimate quickly and track noise variation accurately. The process of speech denoising can remove interference noise more effectively. Accordingly, denoised speech by using the proposed noise estimator sounds more comfortable than that using the MCRA algorithm. The noise estimation performance of the MCRA algorithm is therefore improved. In [4], an improved MCRA algorithm was proposed. This method estimates noise by averaging past spectral power values. The smoothing factor is adapted by the speech-presence probability controlled by the minima values of a smoothed periodogram. This method comprises two iterations for smoothing and minimum tracking. In [11], the noise estimate is updated by averaging the noisy speech power spectrum using smoothing factors adapted by the speech-presence probability, which is determined by the ratio of the noisy speech power spectrum to its local minimum. The differences between the proposed method and the other two methods [4,12] are that the proposed method considers the harmonic properties to control the segment length, which is utilized for updating the minimum power. This minimum power is employed to determine the value of signal-presence probability. In addition, the threshold of speech-presence probability is also determined according to the class of noisy speech, including vowel frames, neighbor frames of a vowel, and noise-dominant frames.
2. Review of the MCRA Noise Estimator
A noise-interfered speech signal can be modeled as the sum of the speech signal and interference noise in the frame of the time domain, given as
where v is the sample index in a frame.
The noise-interfered signal is analyzed and transformed to the frequency domain, given as
where and h represent the frequency bin index and analysis window, respectively. N and M are the frame size and update step in time.
Let and indicate the hypotheses for speech-absence and speech-presence, respectively. They are presented as [3]
where and represent the spectrum of clean speech and additive noise, respectively.
Let denote the variance of the noise. The noise estimates for speech absence and presence can be obtained, given as
where denotes a smoothing parameter. and respectively represent the hypotheses of speech absence and presence.
The noise estimate given in (4) can be obtained by
where denotes the probability of speech presence, which can be obtained by
where is a smoothing factor for speech presence probability. is an indicator function for speech presence, given as
where represents a threshold for speech presence. represents the ratio between the local energy of the noise-interfered signal and its estimated minimum , given as
where
The smoothed version of the local energy is computed by a first order recursive average, given as
The minimum and a temporary variable are initialized by and . Hence, a sample-wise comparison of and yield the minimum value for the current frame, given as
Whenever L (L = 64) frames have been read, is initialized to the value of , given as
In addition, the value of is updated by
The minimum is employed to determine the value of the speech indicator given in (7) and (8) for the MCRA method [3].
3. Modification of MCRA Algorithm
Although the noise detection performance of the MCRA algorithm is acceptable, this algorithm can be improved. Here we employ harmonic properties of a vowel to determine the segment length L and the threshold for speech-presence of each sub-band. In the case of vowel regions, the segment length is increased. This enables the modified MCRA algorithm to select a smaller minimum value as a noise reference than that of the original MCRA algorithm. Meanwhile, the threshold of speech-presence is adjusted to be smaller in a vowel and its neighbor frames, enabling weak vowels and consonant components to be classified as speech. The weak vowels and consonants can be preserved through the process of speech denoising. Accordingly, the quality of denoised speech is improved.
3.1. Variable Segment Length Adapted by Harmonic Properties
Harmonic properties are utilized to determine the segment length L that controls the period for the update of noise estimate. Initially, the number of harmonic spectra is utilized to determine whether a frame is a vowel. If the frame is detected as a vowel, the segment length L increases. This increases the period for the search of spectral minimum as given in (14), yielding noise spectrum being underestimated. Conversely, the segment length L decreases when a noise-dominant frame is detected. The segment length is expressed by
where l is the segment index. and represent the length increment of segment for updating given in (13) in a vowel and the corresponding neighbor regions, respectively. They are empirically chosen to be 63 and 12, respectively. controls the neighbor frames to be included for the regions of onset, offset, and consonants. It is set to be 3. controls the decrement ratio of segment length for noise regions. It is empirically chosen to be 0.9. is a vowel flag, expressed by
In (15), the segment length significantly increases with L1 frames when a frame is detected as a vowel. Conversely, the segment length decreases with a ratio of 0.9 of the current segment length, i.e., 0.9·L, when a frame has been detected as speech absence. A consonant may appear in the precedence of a vowel for spoken Mandarin Chinese. We increased the segment length slightly with L2 frames, yielding noise magnitude being underestimated. This enables a consonant to be preserved by the process of speech denoising. In the regions of onset and offset during a vowel, the segment length also increases slightly with length L2.
Figure 1 shows the contour of detected minimum power, which is employed to determine the value of the speech indicator given in (7) and (8). The smaller the detected minimum of the magnitude is, the higher the speech presence probability is. In the case of speech-pause regions, the proposed method can improve the MCRA method by well tracking the variation of interference noise, in particular during frames 0 to 40 and frames 380 to 400. So the level of interference noise can be estimated well. This is attributed to the segment length, which has been shortened by the factor (0.9) as given in (15). The estimate of minimum power updates quickly. Accordingly, the quantity of background noise in denoised speech effectively reduces, yielding denoised speech sounding less annoying than that using the MCRA noise estimator. Conversely, the MCRA method is unable to track the variation of noise spectrum very well. Plenty of residual noise exists in denoised speech. In the case of weak vowels, the segment length increases during a vowel as well as its neighbor frames (during frames 255 to 300). This enables the minimum power to be underestimated. The corresponding value of speech presence probability increases, yielding the quantity of speech components with weak energy, such as weak vowels and consonants, which is then preserved when speech denoising is performed. The speech distortion in the denoised signal is reduced.
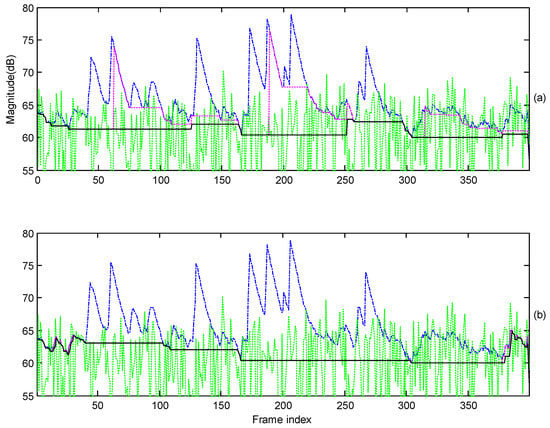
Figure 1.
Contour of estimated minimum power. (a) Minimum power estimated by the MCRA noise estimator for a sub-band (solid: minimum power, green dotted: true noise power, blue dotted: temporary power, dash dot: local power), spoken by a female speaker, interfered by white noise with an average SegSNR = 10 dB); (b) Minimum power estimated by the proposed noise estimator.
3.2. Speech Presence Probability Adapted by Harmonic Properties
In (7), the threshold of speech-presence is a constant in the MCRA algorithm [3]. If the value of is too high, a greater quantity of weak speech spectra, such as weak vowels and consonants, would be classified as noise. The value of the speech indicator function is set to zero. Although the quantity of the residual noise is reduced, speech distortion increases in denoised speech. The quality of denoised speech deteriorates. Conversely, if the value of is too small, a greater quantity of noise spectra would be classified as speech. The value of the speech indicator function is falsely set to unity. Although the speech distortion is reduced, the quantity of residual noise increases. Therefore, the denoised speech sounds annoying and uncomfortable.
The harmonic property of vowels is employed to adapt the threshold of speech presence , given as
where , , and represent the thresholds of speech presence for a vowel, the neighbor frames of a vowel, and noise-dominant regions, respectively. The values of the threshold are empirically chosen to be 1.5, 1, and 5, respectively.
In (17), the values , , and are determined in white noise corruption with various input SNRs at which the selected values can obtain the largest improvement of the average segmental SNR. In the cases of a vowel and the corresponding neighbor frames, the thresholds are small. This prevents weak vowels and consonants from being classified as noise, and then removed by the process of speech denoising. Accordingly, the quality of denoised speech is improved by using the harmonic properties of vowels to adapt the threshold of speech presence.
Figure 2 presents the comparisons of estimated probability of speech-presence. The values of the speech-presence probability in the proposed method (Figure 2c) are higher than that of the MCRA method shown in Figure 2b during the offset and onset of vowels. Moreover, the consonants of an utterance also can have the value of the speech-presence probability approaching unity. This is attributed to the thresholds of speech presence being reduced for a vowel and its neighbor frames as given in (17), enabling the speech spectra to be preserved by the process of speech denoising. The quality of denoised speech using the MCRA noise estimator improves. Conversely, the threshold is set to a high level during noise-dominant regions, enabling interference noise to be accurately classified as noise, i.e., the corresponding values of speech presence probability approaching zero, in particular at the beginning and ending of the utterance shown in Figure 2c.
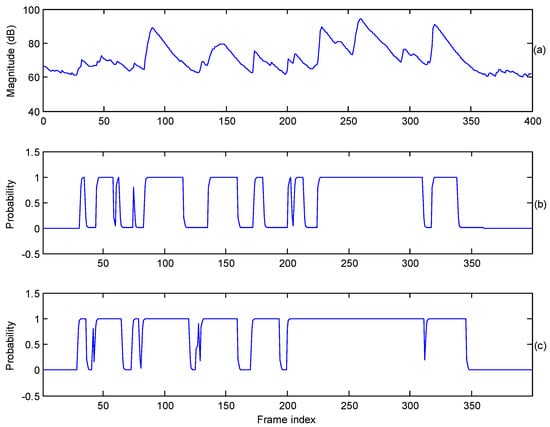
Figure 2.
Contours of estimated speech-presence probability. (a) Local power of a sub-band (spoken by a female speaker, interfered by white noise with an average SegSNR = 10 dB); (b) speech presence probability estimated by the MCRA estimator; (c) speech presence probability estimated by the proposed noise estimator.
Figure 3 shows an example of the magnitude contour of the estimated noise power spectrum. Noise estimates are updated during the speech presence and speech-absence periods for the MCRA and proposed methods. The noise magnitude is well estimated by these two noise estimators. By comparing the noise estimates during speech-activity regions, the magnitude of the noise estimate for the proposed approach is smaller than that detected by the MCRA algorithm. So the speech spectra including weak vowels and consonants are well preserved by the process of speech denoising. When observing the noise estimate during the speech-pause regions, both methods can well track the variation of noise spectra, in particular during the beginning and ending regions of the utterance. The noise estimates are updated quickly. Accordingly, the quantity of residual noise in denoised speech can be effectively removed, yielding denoised speech sounding not annoying.
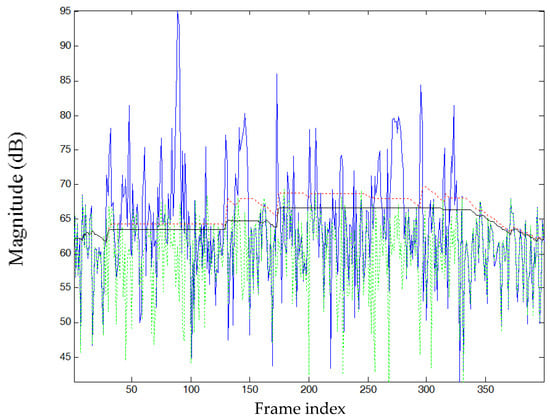
Figure 3.
Contour of the estimated noise power for a sub-band of speech (spoken by a female speaker, interfered by white noise with an average SegSNR = 10 dB). Blue line: Power of noisy speech; green dotted line: true noise; red dotted line: estimated by the MCRA method; black solid line: proposed method.
In the case of non-stationary noise interference, such as factory noise, the proposed method also performs well in noise estimation shown in Figure 4. By comparing the estimated magnitude of noise contours for the MCRA and proposed methods, the level of the proposed method is lower than that of the MCRA method during vowel regions. This ensures that the speech components with weak energy are preserved by the process of speech denoising. On the contrary, the levels of noise estimate for the proposed method are not less than that obtained by the MCRA method during noise-dominated regions. Accordingly, the proposed method still can well track noise magnitude at non-stationary noise interference environments.
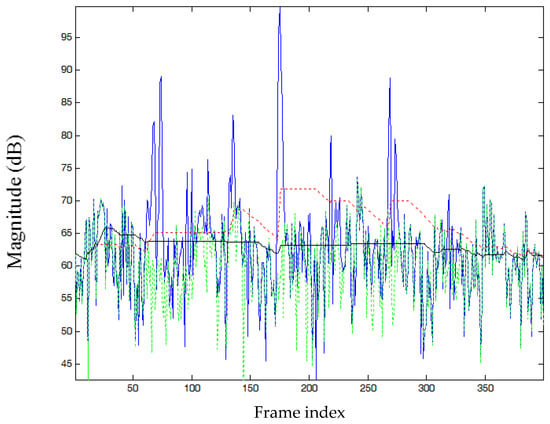
Figure 4.
Contour of the estimated noise power for a sub-band of speech (spoken by a female speaker, interfered by factory noise with an average SegSNR = 10 dB). Blue line: Power of noisy speech; green dotted line: true noise; red dotted line: estimated by MCRA method; black solid line: proposed method.
3.3. Detection of Vowel Frames
A harmonic spectrum distributes in the frequency ranging from 50 to 500 Hz for a vowel. Performing low-pass filtering on noisy speech with cut-off frequency of 500 Hz to obtain the low-pass signal can be applied to estimate a pitch period by reducing the inferring of high-frequency signals. In turn, we compute the auto-correlation function and the average magnitude difference function (AMDF) of the low-passed signal , given as
In the position of the pitch period, the value of the AMDF is small; meanwhile, the value of given in (18) is large. The ratio between and AMDF is enlarged, yielding the increasing of the discriminability. It is beneficial to improve the accuracy in estimating the pitch period. A weighted autocorrelation function (WAC) is then computed to improve the discriminability at the pitch position, given as [12]
where ( = 5) is a constant value to prevent the denominator being zero.
A modified pitch period is employed to improve the pitch estimation, given as [13]
where is the maximum allowed value for pitch variation in adjacent frames and empirically chosen to be 6.
A vowel continues for some successive frames. The detected pitch period can be further refined by rejecting the vowel candidates with a short period. The refined pitch can be expressed by [13]
where ( = 5) represents the minimum period for a vowel segment. and denote the ending and the starting frames of the lth vowel segment.
A harmonic spectral bin is estimated by the fundamental frequency obtained by
where and are represented in terms of spectral bin and sample indices in the experiments.
The fundamental frequency obtained by (23) is refined and shifted with an offset , given as
where can be computed by
where and represent the start and end frames for the lth segment, respectively. denotes the frequency near with the spectral peak.
In (25), the positions of and can be well defined by the estimation of onset and offset for a vowel in slight noise interference. These two positions are difficult to estimate accurately when the level of interference noise increases. Accordingly, we employ robust harmonics, which contain strong speech energy, to detect vowel frames in an utterance.
Robust harmonics appear at the neighbor sub-bands of the multiple fundamental frequencies, i.e., . The higher the frequency is, the weaker the harmonic is. Accordingly, we can search for robust harmonics from low to high frequencies. The number of robust harmonics is estimated by
where represents the frequency bin of the kth harmonic. is the variation threshold of adjacent harmonic frequencies for determining the robust harmonics.
In (26), if the bin frequency varies heavily between two adjacent harmonics ( and ), the harmonic structure in higher frequencies () becomes weaker than that in the lower frequencies (). The boundary frequency of robust harmonics () is marked; meanwhile the number of robust harmonics K* is determined. If a robust harmonic exits in a frame, this frame is classified as a vowel frame, i.e.,
where denotes the vowel flag of a frame.
In (27), the vowel flag is unity if a frame is classified as a vowel. On the contrary, is zero when a frame is not a vowel, i.e., the frame may be a consonant or noise. Many harmonic spectra are destroyed by background noise, in particular at heavy noise interference conditions. This enables most weak harmonics to disappear in noisy speech. Because the energy of harmonics at low frequencies is strong, they may still survive in heavy noise interference. Employing (26) to estimate the number of strong harmonics is robust to noise interference. Therefore, the vowel frame detected by (27) does not vary with respect to input SNR levels and the noise types in the experiments.
4. Experimental Results
Speech signals spoken by ten speakers (five male and five female speakers) in Mandarin Chinese were employed for testing the system performance. The speech signals were interfered by factory, F16 (recorded inside the cockpit of a F16 aircraft), white, car, babble (speech-like) and helicopter (recorded inside the cockpit of a helicopter) noise signals, which were all extracted from the Noisex-92 database. Three input average segmental SNR levels (0, 5 and 10 dBs) were utilized to evaluate the performance of denoising systems. The sampling frequency and the frame size are 8 kHz and 256 (with 50% overlap), respectively.
We performed the average of segmental SNR improvement (Avg_SegSNR_Imp) and perceptual evaluation of speech quality (PESQ) [14,15] to evaluate the system performance for speech denoising. In addition, waveform plots and spectrogram observation were also conducted for performance evaluation. The original MCRA noise estimator [3], the forward-backward MCRA (FB_MCRA) noise estimator [8] were conducted for performance comparison. A three-step-decision gain factor [16] was employed to perform speech denoising for various noise estimators. Some samples of denoised speech can be downloaded via the web links shown in Appendix A.
4.1. Speech Denoising Method
The spectral estimate of the speech signal is obtained by
where denotes a gain factor. It can be expressed by
where and represent the over-subtraction factor and spectral floor factor. They can be calculated by [17]
and
where the values of , and are empirically chosen as 1, 6 and 0.02, respectively [17]. is the noise masking threshold (NMT). and denote the maximum value and minimum value of the NMT in the frame, respectively.
In (29), this gain factor is one of the most flexible forms of subtractive-type algorithm. This factor allows for a variation of the tradeoff between noise reduction, residual noise and speech distortion by adequately controlling the values of the free parameters and . Moreover, the quantity of musical residual noise can be reduced significantly by the consideration of noise masking threshold as given in (30) and (31). Thus, the gain factor given in (29) is employed for speech denoising.
A two-step-decision-directed (TSDD) algorithm [18] is employed to estimate the spectra of speech , given as
where
where and respectively represent the a posteriori SNR and a decision-directed gain factor, given as
where = , is the estimated spectrum of noise. E is the expectation operator.
In (32), the estimated spectrum of speech is only utilized for the computation of the NMT. Detailed procedures for the computation of the NMT can be found in [19]. The denoised speech signal is obtained by
where denotes the operator of the inverse Fourier transform.
4.2. Segmental SNR Improvement
The average segmental SNR improvement (Avg_SegSNR_Imp) can evaluate the quantities of speech distortion, residual noise and noise reduction for denoised speech. The Avg_SegSNR_Imp can be computed by
where and represent the Avg_SegSNR of denoised speech and observed signals, respectively. The and can be computed by
where and M′ denote the set of speech-presence frames in an utterance and the number of speech-presence frames, respectively.
From (37), the quality of denoised speech becomes better if this denoised speech obtains a larger Avg_SegSNR_Imp value. Table 1 presents the performance comparisons for various noise estimation methods by the Avg_SegSNR_Imp. The proposed method is superior to the MCRA and FB_MCRA algorithms in most conditions. This is due to a quantity of consonants and weak vowels that are preserved by the underestimation of interference noise. These results are achieved by increasing the segment length to track the minimum spectral magnitude of noisy speech. In addition, the segment length reduces during speech-pause regions. This enables the spectral magnitude of noise to update quickly, yielding noise spectra being effectively removed by speech denoising. Accordingly, the proposed method can obtain higher scores of the average segmental-SNR improvement than the other approaches. In the cases of the babble (speech-like) noise interference, the proposed noise estimator also outperforms the other two methods for slight noise corruption (input SNR equaling 5 dB and 10 dB). The performances of the three methods are very comparable in heavy corruption of babble noise.

Table 1.
Comparison of SegSNR improvement for the denoised speech in various noise corruptions.
4.3. Perceptual Evaluation of Speech Quality
ITU-T P.862 [14] recommended the PESQ measure [15] as the standard for the speech quality evaluation of test speech signals. This measure better correlates with subjective listening tests than most objective measures. Table 2 presents the PESQ comparisons. The quality of denoised speech becomes better if this denoised speech obtains a larger value of the PESQ score.

Table 2.
Comparisons of perceptual evaluation of speech quality (PESQ) for the denoised speech in various noise corruptions.
The maximal PESQ score corresponds to the best speech quality. One can find that the proposed method outperforms the other two methods in most conditions. In the cases of heavy noise corruption for helicopter-cockpit and car noise, the FB_MCRA is superior to the MCRA and the proposed methods. This attributes to the selection of larger magnitude in forward and backward noise estimation for the FB_MCRA method, enabling a great quantity of interference noise to be removed by speech denoising. In the cases of babble (speech-like) noise corruption, the proposed method cannot outperform the other methods. The reason is that the background noise is wrongly regarded as weak vowels. The level of interference noise is underestimated, and therefore interference noise cannot be removed effectively by the process of speech denosing. Although the proposed method does not outperform the other methods in some cases, the performance of the proposed approach is very close to that of the FB_MCRA or MCRA approach. In the cases of middle and slight noise corruptions (5 dB and 10 dB), the proposed approach outperforms the other methods. This is due to that the harmonic structure of noisy speech does not been destroyed by interference noise. The harmonic structure is preserved by the underestimate of noise magnitude by which the segment length increases according to (15). The denoised speech using the proposed noise estimator results in less distortion. Therefore, the proposed method obtains higher scores of the PESQ than the other two methods in most noise corruptions.
4.4. Waveforms
Figure 5 and Figure 6 demonstrate two examples of waveform plots for performance comparisons. Speech signals uttered by a male and a female speaker were interfered by helicopter-cockpit and factory noise with Avg_SegSNR = 5 dB. In Figure 5c–e and Figure 6c–e, a clipped signal is absent at the output waveforms of the denoised speech. This is attributed to all noise estimators that do not over-estimate the level of noise power spectra for each sub-band, yielding denoised speech not suffering from serious speech distortion. By comparing Figure 5c–e, interference noise can be effectively removed by using the three noise estimators for speech denoising. The proposed method can preserve a greater quantity of speech components than the other two methods during speech presence regions, including weak vowels, the onset and offset of a vowel, and consonants marked by ellipses. This is due to the adaptation of harmonic properties for the determination of segment length and the thresholds for speech presence as given in (5) and (17).
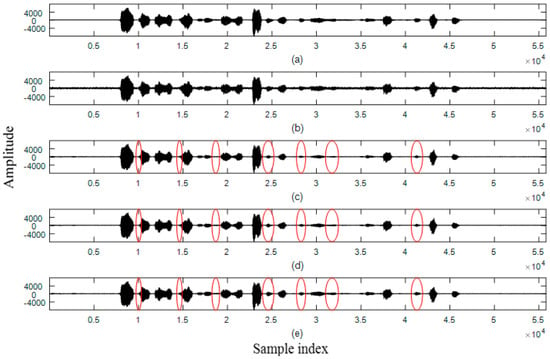
Figure 5.
Example of a speech signal spoken in Mandarin Chinese by a male speaker. (From top to bottom) (a) clean speech; (b) speech interfered by helicopter noise with an average SegSNR = 5 dB; (c) denoised speech using the MCRA noise estimator; (d) denoised speech using the forward-backward MCRA noise estimator; (e) denoised speech using the proposed noise estimator.
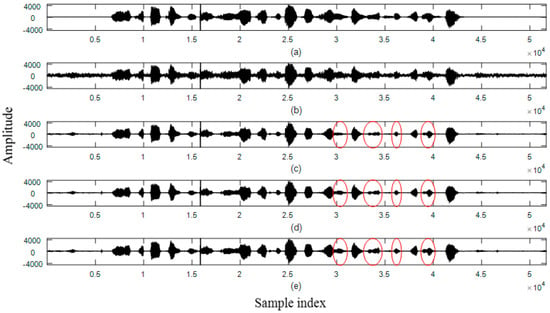
Figure 6.
Example of a speech signal spoken in Mandarin Chinese by a female speaker. (From top to bottom) (a) clean speech; (b) speech interfered by factory noise with an average SegSNR = 5 dB; (c) denoised speech using the MCRA noise estimator; (d) denoised speech using the forward-backward MCRA noise estimator; (e) denoised speech using the proposed noise estimator.
By observing Figure 6, a speech signal is corrupted by factory noise as shown in Figure 6b. Factory noise is non-stationary. It is a challenge to remove this noise interference noise in noisy speech. By comparing the denoised speech shown in Figure 6c–e, the proposed approach (Figure 6e) is better to preserve speech components for weak vowels and consonants marked by ellipses. Accordingly, the proposed method can improve the performance of the MCRA noise estimator by the preservation of weak speech components.
4.5. Spectrograms
The quantity of residual noise in denoised speech cannot be easily qualified by an objective measure. To analyze the time-frequency structures of denoised speech and residual noise is particularly important. Observing speech spectrograms can yield more information about the speech distortion and residual noise. Figure 7 and Figure 8 present spectrogram comparisons for denoised speech using various noise estimators.
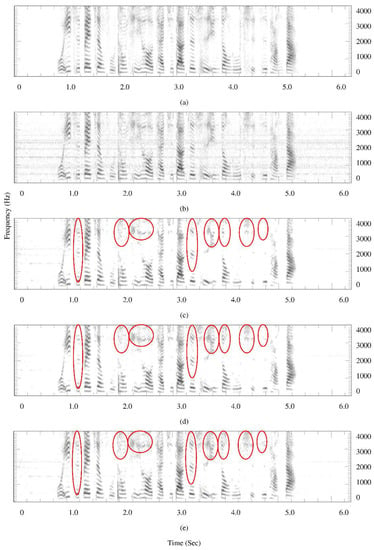
Figure 7.
Spectrograms of speech spoken by a female speaker, (a) clean speech; (b) speech interfered by helicopter-cockpit noise with average SegSNR = 10 dB; (c) denoised speech using the MCRA noise estimator; (d) denoised speech using the forward-backward MCRA noise estimator; (e) denoised speech using the proposed noise estimator.
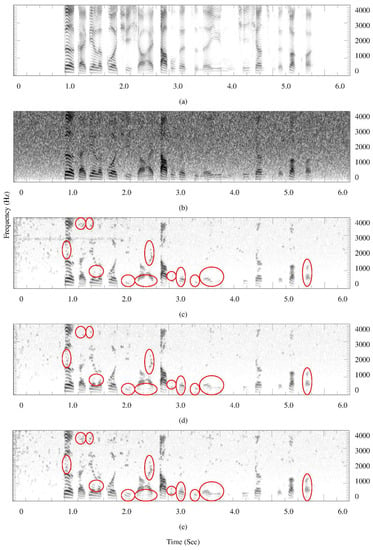
Figure 8.
Spectrograms of speech spoken by a male speaker, (a) clean speech; (b) noisy speech interfered by white noise with average SegSNR = 0 dB; (c) denoised speech using the MCRA noise estimator; (d) denoised speech using the forward-backward MCRA noise estimator; (e) denoised speech using the proposed noise estimator.
In Figure 7, a speech signal is corrupted by helicopter-cockpit noise signals with Avg_SegSNR = 10 dB (Figure 7b). By comparing Figure 7c–e, the level of interference noise is estimated well by the three noise estimators, enabling interference noise to be effectively removed by speech denoising. Employing the proposed approach is better able to preserve weak vowels and speech components in denoised speech during speech presence regions (marked in ellipse). So the harmonic structure of a vowel by using the proposed approach is better than the other two methods. The quality of denoised speech improves. This is attributed to the increase in the value of the speech presence probability for weak vowels and consonants, yielding the level of noise spectra being underestimated. The quantity of noisy speech that had been suppressed by speech denoising is decreased. Speech distortion is reduced, resulting in denoised speech sounding more comfortable than the other two approaches.
In Figure 8, a speech signal is heavily corrupted by white noise signals with Avg_SegSNR = 0 dB (Figure 8b). By comparing Figure 8c–e, interference noise can be effectively removed by speech denoising. This ensures that an MCRA-based method can be employed to cope with heavy noise corruptions. Although employing the FB_MCRA method can enable interference noise to be significantly removed by speech denoising, the harmonic structure is the worst among the three methods. It causes larger speech distortion than that using the MCRA and proposed noise estimators. The quality of denoised speech deteriorates. On the contrary, the proposed approach can well preserve weak vowels in denoised speech during speech presence regions (marked by ellipse). Therefore, the harmonic structure of a vowel by using the proposed method is better than the other two approaches. The quality of denoised speech is improved. These results confirm that the proposed approach can well estimate the level of noise spectra, even with environments of heavy noise corruption.
4.6. Log Spectral Distance
The log spectral distance (LSD) can be employed to measure the distortion between true noise and the estimated version. This measure is expressed by [20]
where and denote the power spectrum of true noise and the estimated version, respectively.
Table 3 presents the LSD comparisons for each noise estimator. The quality of denoised speech becomes better if this denoised speech obtains smaller value of the LSD score. One can find that the proposed method outperforms the other two methods in most conditions. Even in the cases of the babble noise interference, the proposed noise estimator also outperforms the other two methods. Accordingly, the proposed method can estimate the level of background noise accurately. In the conditions of heavy interference in stationary noise, such as helicopter and car noise interference with input SNR equaling 0 dB, the proposed method cannot outperform the other two methods. This may attribute to the underestimation of level of background noise, causing the larger values of the LSD.

Table 3.
Comparison of log spectral distance (LSD) for the denoised speech in various noise corruptions.
4.7. Speech Distortion Index
The speech distortion index (SDI) was defined to measure the deformed degree of a speech signal. It is given as [21]
where E denotes mathematical expectation. is the variance of speech.
The index in (41) is between zero and unity for a denoised speech. A denoised speech signal is highly distorted when the SDI is close to unity. Conversely, denoised speech is lowly distorted when the SDI is near zero. Table 4 presents the SDI comparisons for each noise estimator. In the condition of car noise corruption with input SNR equaling 0 dB, the performances of the MCRA-FB and proposed methods are comparable and are superior to the MCRA method. In the other noise corruptions, the proposed method outperforms the other two methods. Accordingly, the proposed noise estimator can improve the quality of denoised speech by more preservation on speech components.

Table 4.
Comparisons of speech distortion index (SDI) for the denoised speech in various noise corruptions.
4.8. Discussion
In general, by the underestimation of noise power spectral density (PSD), one would expect less reduction of noise and hence lower SegSNR improvement while more preservation of speech i.e., a better PESQ quality. The reason why the proposed method can obtain higher SegSNR improvement than the MCRA method 1 is discussed as follows.
The spectral estimate of speech can be obtained by multiplying a gain factor with the spectrum of noisy speech as given in (28). Decomposing (28) can obtain
By assuming that the speech and noise signals are uncorrelated and the noise is zero-mean, the distortion PSD between speech and noise can be expressed as
where and denote the PSD of residual noise and speech distortion, respectively.
In the case of a strong vowel, the PSD of speech () is much greater than that of background noise (), i.e., >> . An underestimate of background noise obtains small gain factor. Thus the gain factor using the proposed noise estimator () is smaller than that using the MCRA method (), i.e., < . This fact enables the PSD of speech distortion for the proposed method () to be much less than that of the MCRA method (), i.e., ; meanwhile the PSD of residual noise for the proposed method is greater than that of the MCRA method, i.e., . The total distortion PSD given in (43) () is less than that of the MCRA method (), i.e., . Accordingly, the Avg_SegSNR given in (38) of the proposed method is larger than that of the MCRA method. A better Avg_SegSNR improvement achieves in the proposed method.
In the case of a weak vowel, the PSD of speech () is slightly greater than that of residual noise (), i.e., > . An underestimate of background noise also obtains small gain factor. Thus the gain factor using the proposed noise estimator () is smaller than that using the MCRA method (), i.e., < . This fact enables the PSD of speech distortion for the proposed method () to be less than that using the MCRA method (), i.e., ; meanwhile the PSD of residual noise of the proposed method is greater than that of the MCRA method, i.e., . The total distortion () may be slightly greater or comparable to that of the MCRA method (). Therefore, the Avg_SegSNR of the proposed method may be slightly better than the MCRA method.
In the case of a noise-dominated region, the PSD of speech () is less than that of background noise (), i.e., < . Harmonics would be absent. The level of background noise is not underestimated in the proposed method. Thus the gain factor using the proposed noise estimator () is comparable to that using the MCRA method (), i.e., . The Avg_SegSNR of the proposed method is comparable to the MCRA method.
Recently, deep learning based speech enhancement has become popular [22,23,24]. In [22], a deep auto-encoder (DAE) was proposed for speech denoising. This method trains the DAE by the features of noisy and speech pairs, enabling the DAE to learn the statistical difference between speech and noise, which helps to separate speech and noise for speech denoising. In [23], a SNR-based convolutional neural network (CNN) was proposed for speech denoising. This CNN can well deal with the local temporal-spectral structures of speech signals. In addition, the CNN is adapted by the SNR to improve denoising performance. Xu et al. [24] proposed using deep neural networks (DNN) with a multiple-layer deep architecture for speech denoising. Large training features were utilized to train the DNN. The trained DNN plays the roles of nonlinear mapping from noisy speech features to clean speech features, enabling the acoustic context of denoised speech to be improved. By training the weighting and bias factors of the DNN using the feature pairs of noisy speech and clean speech, the DNN can capture the context information along the time axis by multiple frames expansion and along the frequency axis by log-spectral features with full frequency bins.
The proposed noise estimator also can be further developed to incorporate with the DNN to capture the variation contour of noise power spectra for each frequency bin as a future work. Initially, speech utterances are interfered by various kinds of background noise to produce noisy speech for training the DNN. The log power spectra of noisy speech are employed as features to train the DNN model. In addition, the log power spectra of interference noise are also employed to train a DNN simultaneously. In the noise estimation phase, the log power spectra of noisy speech are computed and fed into the DNN. The mapping between the log power spectra of noisy speech and noise is performed by the trained DNN. Hence, by concatenating the output features of the noise DNN can obtain the power spectra of noise. Because speech components are absent in noise regions in an observed signal, the power spectra of the observed signal are more suitable to be the noise estimate. Accordingly, the noise estimator has to be adapted by the SNR, enabling the accuracy of noise estimation to be further improved.
5. Conclusions
This paper proposed using variable segment length for updating noise magnitude and variable thresholds for the determination of speech presence probability to improve the performance of the minima-controlled-recursive-averaging (MCRA) algorithm. Since the harmonic properties of a vowel are considered in the determination of the segment length and speech presence probability, the performance of noise estimation can be improved. The segment length increases and the threshold for speech presence decreases in speech-dominant regions, enabling noise to be underestimated. Therefore, the speech distortion decreases in denoised speech. Conversely, the segment length decreases and the threshold for speech presence probability is maintained at a high level in noise-dominant regions, enabling noise estimates to be updated quickly. The interference noise can be estimated well and can be effectively removed by the process of speech denoising. Experimental results show that the proposed approach can effectively improve the performance of the MCRA algorithm. Consequently, the performance of speech denoising is improved.
Acknowledgments
This research was sponsored by the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan, under contract number MOST 104-2221-E-468-007. Our gratitude also goes to Michael Burton (Asia University) for his help in English proofreading.
Author Contributions
Ching-Ta Lu conceived and designed the algorithms, performed the experiments, and wrote the paper; Chung-Lin Lei performed the experiments and analyzed the data; Jun-Hong Shen, Ling-Ling Wang and Kun-Fu Tseng provided valuable discussions, analyzed the data, and revised the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Appendix A
The web links of speech files are as follows.
- Set 1: speech interfered by factory noise with average SegSNR = 5 dB
- Clean Speech: Spoken by a female speaker
- Noisy Speech
- MCRA
- MCRA_FB
- Proposed
- Set 2: Speech interfered by white noise with average SegSNR = 0 dB
- Clean Speech: Spoken by a male speaker
- Noisy Speech
- MCRA
- MCRA_FB
- Proposed
References
- Kianyfar, A.; Abutalebi, H.R. Improved speech enhancement method based on auditory filter bank and fast noise estimation. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Telecommunications, Tehran, Iran, 9–11 September 2014; pp. 441–445.
- Krawczyk-Becker, M.; Fischer, D.; Gerkmann, T. Utilizing spectro-temporal correlations for an improved speech presence probability based noise power estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Brisbane, Australia, 19–24 April 2015; pp. 365–369.
- Cohen, I.; Berdugo, B. Noise estimation by minima controlled recursive averaging for robust speech enhancement. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2002, 9, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, I. Noise spectrum estimation in adverse environments: Improved minima controlled recursive averaging. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 2003, 11, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, N.; Rosca, J.; Balan, R. Speech noise estimation using enhanced minima controlled recursive averaging. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Honolulu, HI, USA, 15–20 April 2007; pp. 581–584.
- Kum, J.M.; Chang, J.H. Speech enhancement based on minima controlled recursive averaging incorporating second-order conditional map criterion. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2009, 16, 624–627. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Zhu, W.P.; Swamy, M.N.S. Noise spectrum estimation with improved minimum controlled recursive averaging based on speech enhancement residue. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Boise, ID, USA, 5–8 August 2012; pp. 948–951.
- Chen, Y.J.; Wu, J.L. Forward-backward minima controlled recursive averaging to speech enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Computational Intelligence for Multimedia, Signal and Vision Processing, Singapore, 16–19 April 2013; pp. 49–52.
- Yong, P.C.; Nordoholm, S.; Dam, H.H. Noise estimation with low complexity for speech enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE Workshop on Applications of Signal Processing to Audio and Acoustics, New Paltz, NY, USA, 16–19 October 2011; pp. 109–112.
- Mai, V.K.; Pastor, D.; Aissa-EI-Bey, A.; Le-Bidan, R. Robust estimation of non-stationary noise power spectrum for speech enhancement. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2015, 23, 670–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangachari, S.; Loizou, P.C. A noise-estimation algorithm for highly non-stationary environments. Speech Commun. 2006, 48, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimanura, T.; Kobayashi, H. Weighted autocorrelation for pitch extraction of noisy speech. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 2001, 9, 727–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.-T. Reduction of musical residual noise using block-and-directional-median filter adapted by harmonic properties. Speech Commun. 2014, 58, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ITU-T, ITU-T P.862. Perceptual Evaluation of Speech Quality (PESQ), an Objective Method for End-to-End Speech Quality Assessment of Narrow-Band Telephone Networks and Speech Codecs; Int. Telecommun. Union: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Rix, A.W.; Beerends, J.G.; Hollier, M.P.; Hekstra, A.P. Perceptual evaluation of speech quality assessment of telephone networks and codecs. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 7–11 May 2001; pp. 749–752.
- Lu, C.-T. Noise reduction using three-step gain factor and iterative-directional-median filter. Appl. Acoust. 2014, 76, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virag, N. Single channel speech enhancement based on masking properties of the human auditory system. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 1999, 7, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plapous, C.; Marro, C.; Scalart, P. Improved singal-to-noise ratio estimation for speech enhancement. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2006, 14, 2098–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, M.R.; Atal, B.S.; Hall, J.L. Optimizing digital speech coders by exploiting masking properties of the human ear. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1979, 66, 1647–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loizou, P.C. Speech Enhancement Theory and Practice; CRC Presss Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; pp. 198–202. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Benesty, J.; Huang, Y.; Docle, S. New insights into the noise reduction Wiener filter. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2006, 14, 1218–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Tsao, Y.; Matsuda, S.; Hori, C. Speech enhancement based on deep denoising autoencoder. In Proceedings of the Interspeech, Lyon, France, 25–29 August 2013.
- Fu, S.-W.; Tsao, Y.; Lu, X. SNR-Aware Convolutional Neural Network Modeling for Speech Enhancement. In Proceedings of the Interspeech, San Francisco, CA, USA, 8–12 September 2016.
- Xu, Y.; Du, J.; Dai, L.-R.; Lee, C.-H. An experimental study on speech enhancement based on deep neural networks. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2014, 21, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).